ABSTRACT
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a major component of the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and has been recognized as a contributing factor for inflammation-related cancers. We previously showed that embelin has potent anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects in a colitis-associated cancer (CAC) model. Here, by using this model, we assessed the effect of embelin on the accumulation and suppressive function of MDSCs. We have demonstrated that embelin substantially reduced accumulation of MDSCs in the peripheral lymphoid organ and tumor tissue of CAC-bearing mice. Embelin impaired immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs by reducing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and arginase 1 level, leading to restored T cell responses. In tumor milieu, embelin increased the infiltration of CD8+ T cells, NK cells and mature dendritic cells whilst depleted the regulatory T cells. Moreover, embelin could directly interfere with the generation and function of MDSCs in vitro. These effects of embelin on MDSCs were mediated largely via limiting C/EBPβ and STAT3 signaling. Our findings support the hypothesis that embelin may be a promising pharmacologic agent in regulating MDSC-mediated immune tolerance in colorectal cancer.
KEYWORDS: Embelin, colitis-associated cancer, microenvironment, MDSCs, STAT3
Introduction
Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that chronic inflammation is an important risk factor for developing cancer.1,2 Persistent inflammation promotes tumor initiation, growth, and metastasis.3 Clinically, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease is associated with an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC).4,5 Colitis-associated cancer (CAC) often shows rapid progression, with poor response to treatment and high mortality.6 Chronic colitis is often caused by a heightened immune response following initial injury or exposure to gut flora, and persistent inflammation can trigger mutagenic processes that serve as a cancer-initiating event. The common pathological changes of CAC involve recruitment and dysregulation of various types of immune cells and stromal cells, establishing a tumor microenvironment (TME).7,8 Continuous presence of immune cells and cytokines might transform an inflamed milieu into a highly tolerogenic microenvironment, which will affect host immune surveillance and protective immunity, thereby promoting tumor progression.2
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a major component of the immunosuppressive TME. Accumulation of MDSCs has been identified as a significant factor linking inflammation and cancer.9–11 MDSCs potently inhibit the anti-tumor immunity, and these effects are mediated by suppressing T cell response,12,13 blocking natural killer (NK) cell activation,14 limiting dendritic cell (DC) maturation12,15 and inducing the generation of regulatory T (Treg) cells.16 MDSCs express high level of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX), resulting in increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS).17 In addition, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and arginase 1 are overexpressed in MDSCs, leading to increased production of nitric oxide (NO) and arginine starvation, respectively.18,19 ROS, NO and arginase 1 are directly involved in MDSC-mediated immune suppression. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a crucial transcription factor controlling MDSC expansion and function,15,20 and the suppressive activity of arginase 1 and ROS reflects a downstream effect of STAT3 signaling.21 Moreover, in tumor-bearing host, the generation and the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs are dependent on CAAT-enhancer binding proteins β (C/EBPβ),22,23 which is often expressed at an enhanced level in MDSCs.
MDSC accumulation correlates with cancer stage, tumor burden, and survival in cancer patients including those with CRC.24,25 Thus, targeting MDSCs is thought to be a highly promising strategy of cancer immunotherapy. Approaches to reduce MDSC expansion, promote MDSC differentiation, and suppress MDSC function have been explored,26-28 but they are only partially effective. More effective therapeutic strategies that can inhibit MDSCs may hold a potential for successful cancer therapy.
Embelin (2,5-dihydroxy-3-undecyl-1,4-benzoquinone) is a non-peptidic small molecule inhibitor of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), and its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties have been reported earlier.29,30 Our previous studies have shown that embelin has potent anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects in a CAC model.31–33 Embelin can not only inhibit cancer cell proliferation but also modulate the TME. It decreases the expression and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and impairs the infiltration and function of tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) in the tumor milieu.33 Our finding suggests that myeloid cells may be a critical target of embelin to achieve its therapeutic benefits in CAC.
In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of embelin on MDSCs in a CAC-bearing model. We focused on whether embelin exerts its anti-tumor effects through interfering with MDSCs generation, accumulation, or activation.
Results
Embelin decreases MDSC accumulation in spleen and tumor in CAC-bearing mice
We have previously reported that embelin not only resolved the colonic inflammation but also dramatically inhibited the colitis-associated tumor initiation and progression in an azoxymethane (AOM)/dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced CAC model.32,33 Moreover, embelin treated mice exhibited a lower mortality rate than untreated controls during CAC challenge (Figure 1A), suggesting that embelin significantly improves the long-term survival rate of tumor-bearing mice. In addition, the spleen size of embelin-treated CAC-bearing mice was smaller than that of untreated group (Figure 1B). Macroscopically, the spleens of mice treated with embelin alone had no remarkable pathological changes. The spleens of CAC-bearing mice displayed pronounced infiltration of inflammatory cells, dilatation of splenic sinus and obscure structure of red and white pulps. Following treatment with embelin, partial remission of the pathological damage in spleen was observed as reflected by decreased the inflammatory cell infiltration and clear structure of red and white pulp (Figure 1C). These findings implied that embelin affects the immune system during CAC development.
Figure 1.
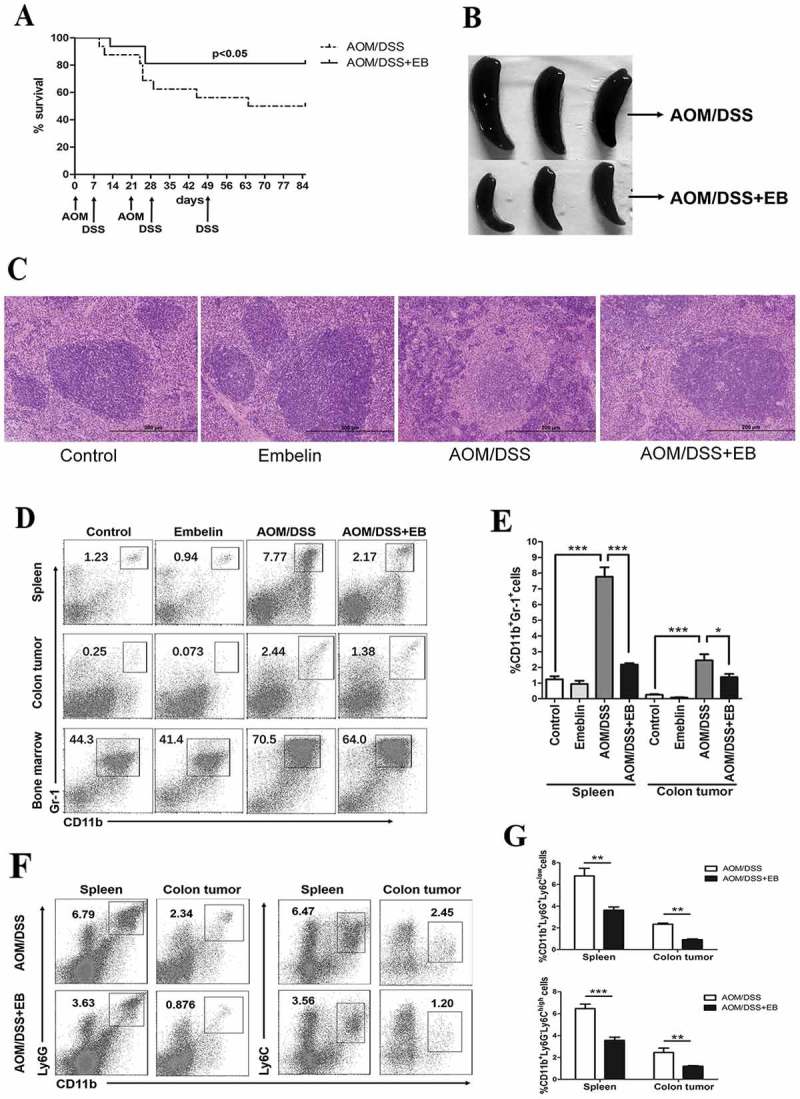
Embelin (EB) decreases accumulation of MDSCs in CAC-bearing mice.
CAC model was established by using AOM/DSS. A. Kaplan-Meier plot of survival of mice treated with or without embelin during CAC development (n = 16 per group). B. Representative images of spleens harvested from mice. C. Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of spleens from indicated group of mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. D. The immunocytes isolated from indicated organs were subjected to flow cytometry at day 85 of CAC establishment. The dot plots shown were gated on the viable cells, CD11b and Gr-1 flow plots were used to identify MDSCs. E. Data represents the percentage of MDSCs (CD11b+Gr-1+) in total viable cells from spleen and colon tumor. F. The subpopulation of PMN-MDSCs (CD11b+Ly6G+Ly6Clow) and M-MDSCs (CD11b+Ly6G−Ly6Chigh) in spleen and colon tumor of embelin-treated or untreated CAC mice. G. Data represents the percentage of PMN-MDSCs and M-MDSCs in total viable cells. All quantitative data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
As accumulation of MDSCs is a significant factor linking inflammation and cancer, we explored the effects of embelin on the quantity and function of MDSCs in CAC model. MDSCs are characterized by the expression of CD11b and myeloid lineage differentiation antigen Gr-1 in mice.34 By flow cytometry analysis, it was validated that CAC challenge resulted in a significant increase of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells in the spleen, colon tumor, and bone marrow (Figure 1D, E). The accumulation of these cells in both spleen and colon tumor after treatment with embelin was markedly reduced compared with untreated controls (Figure 1D, E). A decline trend of the population of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells in bone marrow following embelin treatment was also observed although this was not statistically significant (Figure 1D).
MDSCs are phenotypically divided into two major groups: polymorphonuclear (PMN-MDSCs, defined as CD11b +Ly6G+ Ly6Clow) and mononuclear (M-MDSCs, defined as CD11b+Ly6G−Ly6Chigh) subsets.34 We found that embelin dramatically reduced accumulation of both subsets of MDSCs in spleen and colon tumor (Figure 1F, G). Thus, embelin targets PNN-MDSCs and M-MDSCs that were elevated in peripheral lymphoid organ and tumor tissue of CAC-bearing mice. These effects may be responsible for the anti-tumor activities of embelin.
Embelin improves anti-tumor immune response in CAC mice
We further examined whether reduction of MDSCs after embelin treatment was associated with improved anti-tumor immune response in CAC mice. As expected, a significant increase in the population of CD3+CD8+ T cells in colon tumor was observed in embelin-treated mice (Figure 2A). Embelin also led to a substantial increase in the frequency of NK cell (CD3−NK1.1+) in tumors (Figure 2B). Moreover, embelin administration resulted in a trend toward maturation of DCs in the tumor milieu, as evidenced by an increased expression of MHCII in DCs (CD11c+CD11b+) (Figure 2C). MDSCs have been shown to exert their immunosuppressive effects by inducing Treg cells in tumor-bearing host.16 As shown in Figure 2D, there was a decreased population of Treg cells (CD4+CD25+Foxp3+) in tumors of mice treated with embelin. These data suggested that embelin improves the TME of CAC-bearing mice, thereby delaying tumor progression.
Figure 2.
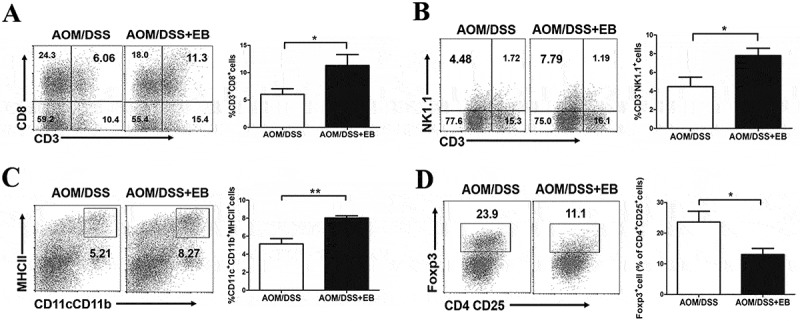
Embelin improves anti-tumor immune response in CAC mice.
Immunocytes were isolated from the colonic tumor of the CAC mice. The percentages of CD3+CD8+ cells (A), CD3−NK1.1+ cells (B), and CD11b+CD11c+MHCII+ cells (C) in total viable cells, and the percentage of Foxp3+ cells in CD4+CD25+ cells (D) from tumors of indicated mice were determined by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Embelin attenuates the immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs
To determine whether embelin could affect the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs, we examined the inhibitory effects of MDSCs on T cell proliferation in vitro. To assess antigen-specific T cell responses, we used OT-II transgenic T cells expressing TCR specific recognizing chicken ovalbumin (OVA)323–339. The antigen-nonspecific T cell response was evaluated after stimulation with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies. We found that although the tumor MDSCs from emeblin treated CAC mice showed a slightly weaker suppressive effect on antigen-specific and -nonspecific T cell responses, the difference was not statistically significant (data not shown). Notably, MDSCs obtained from spleens of embelin-treated mice had attenuated immunosuppressive effects on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation than MDSCs from control CAC mice upon anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation (Figure 3A). In addition, a significant lower level of antigen-specific CD4+ T cell suppression was observed in the splenic MDSCs from embelin-treated mice (Figure 3B). Thus, embelin not only limits the quantity of MDSCs but also alters their suppressive activity, leading to restored T cell response in CAC-bearing mice.
Figure 3.
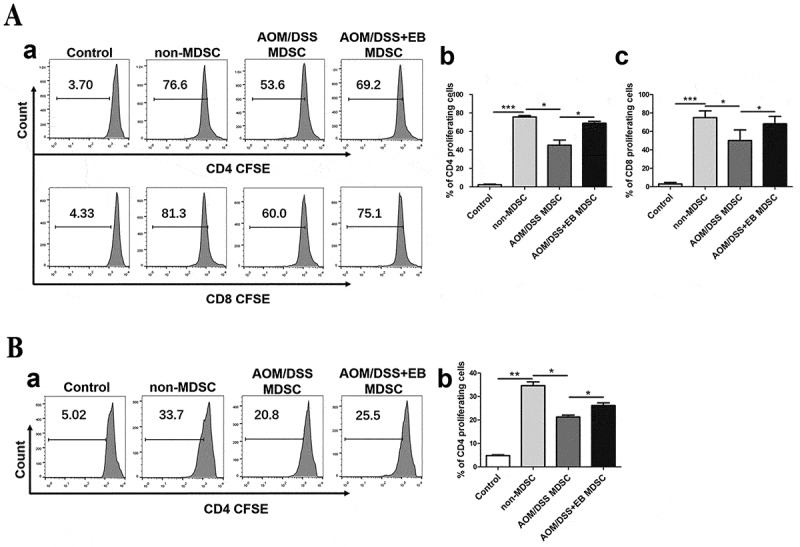
Embelin attenuates the immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs.
A. MDSCs isolated from the spleens of embelin-treated or untreated CAC mice were co-cultured with CFSE-labeled T cells from naïve mice and stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies for 4 days. Representative flow cytometric analysis of gated CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation is shown (a). The percentages of CD4+ (b) and CD8+ (c) proliferating T cells were quantified. B. MDSCs isolated from the spleens of embelin-treated or untreated CAC mice were co-cultured for 4 days with CFSE-labeled splenocytes from OT-II transgenic mice and stimulated with OVA323–339. Representative flow cytometric analysis of gated CD4+ T cell proliferation is shown (a). The percentage of CD4+ proliferating T cells were quantified (b). Bar graphs show mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Embelin down-regulates the MDSC-mediated immunosuppressive pathways
Several factors are involved in regulating the MDSC-mediated suppressive activity, among these ROS, arginase, iNOS and NO are most important.12,17,18 To evaluate the mechanism by which emeblin controls the MDSC-mediated immunosuppressive activity, we measured the level of ROS in splenic MDSCs. As shown in Figure 4A, embelin led to a significantly reduced level of ROS in MDSCs. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was decreased from 478.30 ± 40.33 in the untreated CAC mice to 83.83 ± 6.17 in the embelin-treated group. Expression of two subunits of NOX complex gp91hox and p47hox, which have been shown to be responsible for ROS production17, was also significantly reduced in MDSCs from embelin-treated mice than in the MDSCs from control CAC mice (Figure 4B). S100 calcium-binding proteins A9 (S100A9) has been implicated in the regulation of ROS generation by promoting NOX activity.35,36 As shown in Figure 4C, splenic MDSCs from embelin-treated CAC-bearing mice exhibited a significant reduction of S100A9 expression. In addition, arginase 1 expression and its enzymatic activity were diminished in the MDSCs from embelin-treated CAC mice as compared with untreated control (Figure 4D). In contrast, embelin did not alter the level of iNOS expression in MDSCs from CAC mice (data not shown). These results indicate that embelin could impair MDSC immunosuppressive activity by reducing ROS production and arginase 1 level.
Figure 4.
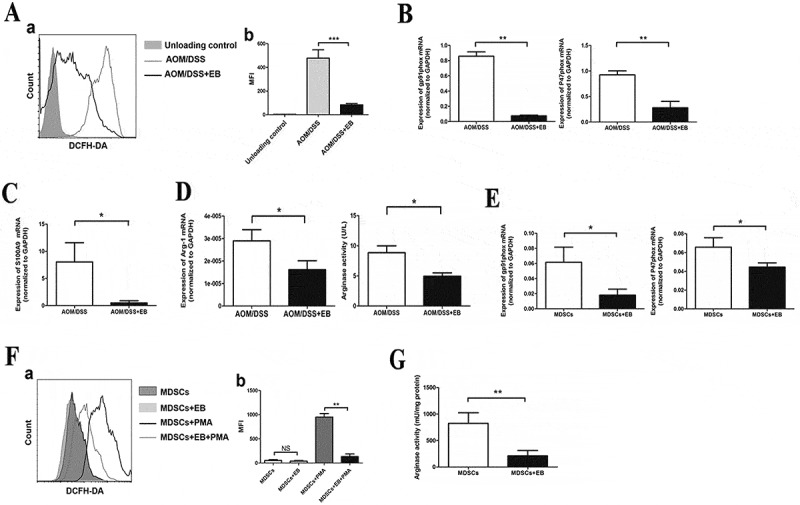
Embelin down-regulates the immunosuppressive pathways in MDSCs.
MDSCs were isolated from the spleens of embelin-treated or untreated CAC mice. A. Cells were loaded with DCFDA and ROS level within the population of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells was detected. A typical result of three independent experiments is shown (a) and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) value is presented (b). Expression of gp91phox and p47phox (B), and S100A9 (C) was measured by qRT-PCR. Arginase 1 mRNA expression and enzymatic activity (D) were evaluated. E. MDSCs were sorted from spleens of CAC mice and treated with embelin in vitro. Expression of gp91phox and p47phox was evaluated after treatment with embelin for 24 h. F. MDSCs were incubated with embelin for 1 h before being stimulated with PMA. ROS level in MDSCs was determined with DCFDA. A typical result (a) and the MFI value (b) are presented. G. MDSCs were treated with embtlin for 24 h, and arginase activity was determined. All results were obtained from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
We further used a complementary approach to validate that embelin regulates immunosuppressive pathways in MDSCs. Splenic MDSCs were sorted from CAC-bearing mice and treated with embelin in vitro. Consistent with the above in vivo data, embelin led to a pronounced decrease in the expression of gp91phox and p47phox (Figure 4E). Moreover, embelin significantly inhibited PMA-induced ROS production by MDSCs (Figure 4F). The arginase activity of MDSCs was also diminished upon embelin treatment in vitro (Figure 4G). Collectively, our data suggested that embelin could directly down-regulate MDSC-mediated immunosuppressive pathways in CAC-bearing mice.
Embelin impairs cytokine-induced MDSC generation and function in vitro
MDSC precursors mainly reside in normal bone marrow. Several inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) have been shown to be responsible for the induction and the expansion of MDSCs.22,37 These cytokines are produced by tumor cells or immune cells, and in the CAC model, we have demonstrated that tumor milieu are abound with these cytokines.32,33 Here, we examined whether embelin could affect the generation of MDSCs by bone marrow precursor cells exposed to these cytokines. As shown in Figure 5A, culture of whole bone marrow cells for 4 days in the presence of IL-6, G-CSF, M-CSF, or GM-CSF led to generation of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells. These cytokines also significantly enhanced the expression of IL-4Rα (CD124) (Figure 5B), a key factor for the MDSC suppressive activity.22,38 Upon treatment with embelin, the cytokine-induced generation of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells was significantly reduced together with a reduction in the population of CD124+ cells (Figure 5A, B). C/EBPβ was reported to play a critical role in cytokine-induced MDSC generation and suppressive activity.22 We found embelin markedly decreased the expression of C/EBPβ by CD11b+Gr-1+ cells that were generated by G-CSF, M-CSF, or GM-CSF (Figure 5C). These data suggest that embelin directly interferes with MDSC generation by inhibiting C/EBPβ signaling, thereby reducing MDSC infiltration in peripheral lymphoid organs and tumor tissue.
Figure 5.
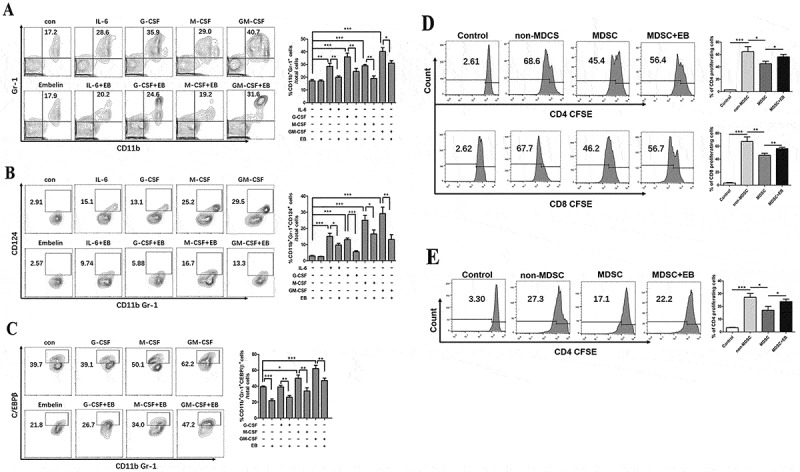
Embelin impairs cytokine-induced MDSC generation and function in vitro.
Bone marrow (BM) cells were cultured in the presence of different cytokines for 4 days with or without embelin treatment. A. Accumulation of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells in BM cells is shown in contour plots and quantified. The percentage of CD124+ cells (B) or C/EBPβ+ cells (C) in CD11b+Gr-1+ cells was determined by flow cytometry. Contour plots are from one of four independent experiments, and data are expressed as mean ± SD. BM cells were cultured for 4 days with GM-CSF and G-CSF in the presence or absence of embelin, CD11b+ BM-derived MDSCs were enriched, and their immunosuppressive activity was determined. D. BM-derived MDSCs were co-cultured with CFSE-labeled T cells from naïve mice and stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies. After 4 days, the percentage of CD4+ and CD8+ proliferating T cells is shown. E. BM-derived MDSCs were co-cultured for 4 days with CFSE-labeled splenocytes from OT-II transgenic mice and stimulated with OVA323–339. The percentage of CD4+ proliferating T cells is shown. All results were obtained from three independent experiments *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
We then assessed the impact of embelin on the immunosuppressive activity of bone marrow-derived MDSCs. Bone marrow cells were co-cultured with GM-CSF and G-CSF in the presence or absence of embelin, MDSCs were enriched, and their immunosuppressive activity was determined. Similar to the MDSCs from CAC-bearing mice, embelin significantly abrogated inhibitory effects of bone marrow-derived MDSCs on antigen-nonspecific and -specific T cell proliferation (Figure 5D, E). Thus, embelin could regulate the immunosuppressive function of both tumor-induced and bone marrow-derived MDSCs.
Embelin inhibits STAT3 activation in MDSCs
In our previous study, embelin was found to down-regulate the expression of phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) in the tumor stromal compartment of CAC-bearing mice.32 We therefore hypothesized that embelin could modulate the activation of STAT3 signaling in MDSCs. Intracellular pSTAT3 was determined in the CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs by flow cytometry analysis. As shown in Figure 6A, embelin treatment dramatically decreased the percentage of pSTAT3+ cells among MDSCs population in spleen (6.76% vs. 12.10%, P < 0.001) and colon tumor (3.41% vs. 5.81%, P < 0.01) from CAC-bearing mice. Moreover, Western blot analysis revealed a high level of pSTAT3 expression in MDSCs isolated from spleen and colon tumor of CAC-bearing mice. In comparison, embelin resulted in a significant reduction in the expression of pSTAT3 in MDSCs of both spleen and colon tumor (Figure 6B). To further elucidate the direct effects of embelin on STAT3 signaling, we measured the expression of pSTAT3 in bone marrow-derived MDSCs in response to IL-6 stimulation. As shown in Figure 6C, pretreatment with embelin abolished IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation in bone marrow-derived MDSCs, as evidenced by a significant decrease of the percentage of pSTAT3+ cells. These data demonstrate that embelin inhibits the STAT3 signaling in MDSCs, consequently leading to reduced immunosuppressive activity both in vivo and in vitro.
Figure 6.
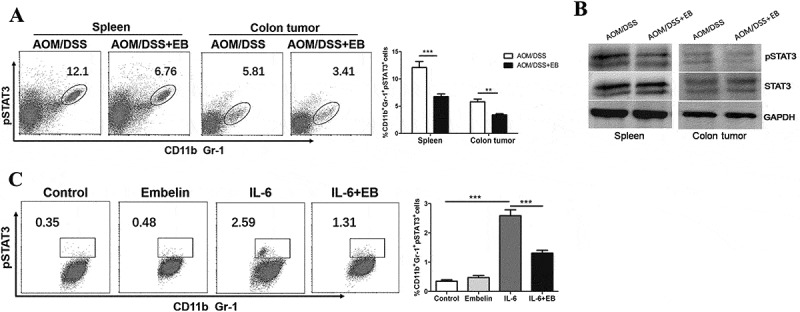
Embelin inhibites STAT3 activation in MDSCs.
A. Expression of pSTAT3 in CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs from spleens and colon tumors of embelin-treated or untreated CAC mice was determined by flow cytometry. B. MDSCs were isolated from spleens and colon tumors of CAC mice and pSTAT3 was evaluated by Western blot. C. BM-derived MDSCs were incubated with embelin for 1 h before treatment with IL-6 for 30 min. Expression of pSTAT3 was assessed by flow cytometry. A typical result of three independent experiments is shown. The percentage of pSTAT3+ cells in CD11b+Gr-1+ cells is calculated. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Discussions
Accumulation and pathological activation of MDSCs is common in tumors, including inflammation-associated cancers.9–11 In this study, we have demonstrated that embelin substantially reduced MDSC accumulation in the peripheral lymphoid organ and tumor tissue of CAC-bearing mice. Moreover, embelin impaired immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs by reducing ROS and arginase 1 level, leading to restored T cell response. In the TME of CAC mice, embelin increased the infiltration of CD8+ T cells, NK cells and mature DCs but decreased the population of Treg cells. Furthermore, embelin could directly interfere with MDSC generation and function in vitro. These effects of embelin on MDSCs were mediated largely via limiting C/EBPβ and STAT3 signaling.
MDSCs are a heterogeneous population of cells composed of myeloid progenitor cells and immature myeloid cells.12,13 Under physiological conditions, these cells differentiate in peripheral organs into mature DCs, macrophages, or granulocytes. In tumor-bearing individuals, impaired differentiation of MDSCs into mature myeloid cells may occur, resulting in expansion of MDSCs.12,13,15 Multiple inflammatory cytokines produced by the malignant cells and tumor stroma, including IL-6, IL-1β, CCL2, GM-CSF, M-CSF and G-CSF have been shown to be responsible for expansion and recruitment of MDSCs to tumor sites.13,22,37 Our data showed that embelin significantly reduced accumulation of MDSCs in the tumor tissue of CAC-bearing mice, and this is consistent with our previous finding that embelin decreased the level of IL-6, IL-1β, CCL2 and GM-CSF in tumor environment.32,33 Moreover, embelin diminished MDSC accumulation in non-tumoral peripheral lymphoid organ. Thus, embelin not only blocks MDSC migration to the tumor sites but also decreases the systemic level of MDSC to achieve an anti-tumor effect in CAC model.
By using a well-established in vitro culture system,22 we revealed that embelin reduced the population of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells induced by M-CSF, GM-CSF, G-CSF or IL-6, and this was accompanied with decreased IL-4Rα expression, suggesting that embelin could impair the generation and function of MDSCs. Importantly, we found that embelin down-regulated the expression of C/EBPβ during MDSC generation in response to various cytokines. C/EBPβ belongs to the family of leucine zipper transcription factors involved in the regulation of inflammatory- and tumor-derived myelopoiesis.23 Moreover, C/EBPβ is a critical regulator of the immunosuppressive environment created by tumors. Cytokines (e.g. GM-CSF and G-CSF) present in the TME can induce MDSC generation through C/EBPβ pathway. In tumor-bearing mice, both the abundance and suppressive activity of MDSCs were severely impaired in the absence of C/EBPβ.22,23 Thus, our results indicated that embelin attenuates MDCS expansion and function by inhibiting C/EBPβ expression.
It is widely accepted that MDSCs have suppressive effects on innate and adaptive immune responses via blocking the activation of NK and T cells.12–14 Moreover, MDSCs have been shown to induce Treg cells in tumor-bearing host.16 In our CAC model, we identified that embelin not only increased the intra-tumoral infiltration of CD8+ T cell and NK cells but also decreased the population of Treg cells. These effects coincided with the decreased MDSC accumulation in the tumor milieu, suggesting embelin could attenuate MDSC-mediated immunetolerance, permitting the anti-tumor responses. In the tumor milieu, differentiation of M-MDSCs to mature DCs is inhibited, whereas M-MDSCs could rapidly differentiate to immune suppressive TAM.39 These processes are closely associated with the up-regulation of S100A9 in MDSCs.36 We reported here that embelin could promote DC maturation and down-regulate S100A9 expression in vivo. In addition, we have previously demonstrated that embelin depleted TAM infiltration in the TME of CAC mice.33 Thus, embelin could favorably alter MDSC differentiation and restore the protective immune response, thereby improving TME and inhibiting CAC development.
The suppressive activity of MDSCs is associated with the high levels of ROS production and increased arginase activity.17,18 Here, we found that embelin can overcome the immunosuppressive activity of both CAC-induced and bone marrow-derived MDSCs, leading to restored T cell response. These effects of embelin were attributed to the decreased ROS production as well as reduced arginase activity. As ROS was also shown to be a major factor blocking MDSC differentiation into mature myeloid cells in cancer,40 we propose that embelin exerts its positive effects on MDSC differentiation partially through inhibition of ROS production.
Previous findings indicate that MDSCs in different site might use different mechanisms to suppress the function of T cells. In peripheral lymphoid organs, MDSCs retain a high level of NOX and increase ROS production. In contrast, within tumor milieu, MDSCs have low level of ROS, but dramatically up-regulate expression of iNOS and arginase.12,13 Our data revealed that in CAC-bearing mice, embelin significantly abrogated the immunesuppressive effects of splenic MDSCs, whereas it only had minor effect on the MDSCs of tumor tissues. Although embelin significantly inhibited ROS production and arginase activity, it only marginally inhibited iNOS expression and NO production. Thus, we speculate that the different effect of embelin on splenic or tumoral MDSCs may reflect its effect on different immunosuppressive molecules. Another possible explanation could be that tumor microenvironment contains a large number of different factors (such as hypoxia) that are not present in spleen, and this might influence MDSC function. As a result, embelin has a more pronounced inhibitory effect on splenic MDSCs than on the tumoral MDSCs. To what extent the different factors between spleen and TME are involved in the anti-tumor effect of embelin in CAC model remains to be elucidated in our future studies.
Activated STAT3 is not only involved in tumor cell survival but has also been proposed to be the main regulator of MDSC expansion and function.15,20,41 Previous study has demonstrated that the suppressive function of arginase 1 in MDSCs is a downstream target of activated STAT3.21 In addition, STAT3 up-regulates S100A9 expression at the transcriptional level.36 S100A9 promotes NOX activity and subsequently ROS generation.35 We previously showed that embelin diminished both the constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 activation in colon cancer cells.32 Here, embelin abrogated pSTAT3 expression in MDSCs from CAC-bearing mice and inhibited IL-6 induced STAT3 phosphorylation in vitro. Accordingly, arginase 1 and S100A9 expression as well as ROS production in MDSCs was decreased by embelin, leading to the impaired suppressive function in MDSCs. Thus, the anti-tumor action of embelin is, to some extent, mediated by limiting STAT3 signaling, and this effect is evident in both tumor cells and MDSCs. Moreover, C/EBPβ was reported to be a downstream target of the STAT3 signaling pathway, and STAT3 can promote myeloid progenitor cell expansion by inducing C/EBPβ.42,43 We could not rule out the possibility that embelin-mediated down-regulation of C/EBPβ in MDSCs might rely on its inhibitory effect on STAT3. Thus the mechanism by which embelin regulates C/EBPβ expression and function still need to be further investigated.
In conclusion, embelin effectively inhibits MDSC expansion and accumulation in CAC-bearing mice. Embelin impairs suppressive activity of MDSCs and improves the tumor microenvironment, leading to restoration of the anti-tumor immune response. Our findings support the hypothesis that embelin may be a novel agent to regulate MDSC-mediated immunosuppressive pathways in CAC. Further studies in improving the more efficient delivery of embelin into tumors may be warranted in clinically relevant colorectal cancer model.
Materials and methods
Mice and CAC model
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Studies Committee of Peking University First Hospital. CAC was induced in male C57BL/6 mice (8–10 weeks old) as we previously described.32,33 Mice were randomly divided into 4 groups: control, embelin alone (embelin), CAC challenge (AOM/DSS), and CAC challenge plus embelin treatment (AOM/DSS + embelin). AOM (10 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich) was intraperitoneally injected on day 0. Seven days later, mice were given 2% DSS (Affymetrix) in the drinking water for 7 days. Mice were then maintained on regular water for 7 days before receiving a second intraperitoneal injection of AOM (5 mg/kg). Seven days after the second AOM injection, mice were subjected to 2 more cycles of 2% DSS treatment (7 days/cycle), each separated by 14 days of regular water. Embelin (50 mg/d/kg, Advance Scientific & Chemical, Inc.) was mixed in the chow and provided to mice at the beginning of CAC challenge and was maintained throughout the entire experiment. OT-II TCR-transgenic mice recognizing chicken OVA323-339 in the context of I-Ab were bred in the Peking University First Hospital Animal Facility.
Cell isolation and flow cytometry analysis
Single cell suspensions derived from spleens were prepared by mechanical disruption and passed through a 40-µm cell strainer. Bone marrow cells were collected from mouse femurs and tibias. ACK Lysing Buffer (Invitrogen) was used to lyse red blood cells. The lamina propria immunocytes were isolated from colonic tissue as described previously.44 Briefly, colonic tissues were predigested in Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) containing 5 mmol/L EDTA and 1 mmol/L DTT for 20 min at 37°C. After washing, the remaining tissues were digested with collagenase IV (0.5 mg/ml, Sigma-Aldrich), DNase I (0.5 mg/ml, Sigma-Aldrich) and dispase II (3 mg/ml, Roche) for 20 min at 37°C. The process was repeated two times to ensure all visible small pieces were fully digested. The cell mixture was filtered through a 70-µm strainer, washed with PBS, and the immunocytes were separated by percoll density gradient centrifugation.
For cell surface antigens staining, single cell suspensions were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies for 30 min at 4°C. Intracellular Foxp3 staining was performed using Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (eBioscience). For pSTAT3 staining, cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at 37°C and permeabilized in ice-cold 90% methanol for 30 min at 4°C. The cells were stained with PE-conjugated pSTAT3 antibody for 1 h at room temperature. The following monoclonal anti-mouse antibodies were used: anti-CD3-PE, anti-CD4-APC, anti-CD4-PE-Cy7, anti-CD8-APC, anti-CD11b-FITC, anti-CD11b-PECy7, anti-Ly6C-APC, anti-Ly6G-PECy7, anti-CD11c-APC, anti-CD11c-Alexa Fluor 700, anti-MHCII-FITC, Anti-F4/80-PE, Anti-CD25-PE, Anti-Foxp3-PeCy5.5, anti-IL-17A-PE (all from eBioscience); and anti- IL4Rα-PE, anti-Gr-1-APC, anti-pSTAT3(Tyr705)-PE (BD Pharmingen). For C/EBPβ staining, the C/EBPβ antibody (Santa Cruz) and goat anti-rabbit lgG-Alexa Fluor 488 (Abcam) were used. Isotype-matched antibodies were used as controls. Samples were analyzed on a BD InfluxTM (BD Biosciences), and the data were analyzed using Flowjo software (TreeStar Inc.).
Cell purification
CD3+ T cells were selected from the spleen of C57BL/6 naïve mice using a T cell negative isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec). MDSCs were isolated from spleens of tumor-bearing mice using the Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Cell purity was assessed by flow cytometry and was consistently above 95%.
Mouse bone marrow-derived MDSCs
Tibias and femurs from C57BL/6 mice were removed and bone marrow was flushed. Bone marrow cells were collected and cultured in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin-streptomycin, 50 µmol/L 2-mercaptoethanol, 2 mmol/L L-glutamine, 100 ng/mL granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and 40 ng/mL granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (all from PeproTech) for 4 days. For functional assays, MDSCs were positively selected from bone marrow cultures using CD11b microbeads followed by magnetic separation (Miltenyi Biotec). As assessed by flow cytometry, more than 95% of the purified cells were CD11b+Gr-1+.
T cell proliferation assay
T cell proliferation was measured using the intracellular dye Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) (eBioscience). For antigen-specific responses, splenocytes from OT-II transgenic mice were labeled with 2 µmol/L CFSE and stimulated with OVA323–339 (Sigma-Aldrich). For anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-induced T cell proliferation, CFSE-labeled T cells were cultured in a 96-well plate coated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibody (2 μg/ml each) (eBioscience). Bone marrow-derived MDSCs or MDSCs isolated from spleens of CAC-bearing mice were added to the culture at different ratios. After four days, cells were stained for CD4 or CD8 and analyzed for CFSE dilution by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as the percentage of T cells proliferating compared with non-activated control.
ROS detection and arginase assay
ROS production by MDSCs was measured using the oxidation-sensitive dye 2ʹ,7ʹ-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA) (Invitrogen). Cells were incubated with 4 μmol/L DCFDA for 30 min at 37°C. For PMA-induced activation, cells were simultaneously cultured with DCFDA and 200 ng/ml PMA (Sigma-Aldrich). After washing, cells were labeled with anti-Gr-1 and anti-CD11b antibodies and detected by flow cytometry. Arginase activity was determined using Arginase Activity Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Western blot analysis and quantitative RT-PCR
Western blot analysis was performed as we described,32 and the following primary antibodies were used: anti-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase (GAPDH, Abcam), anti-pSTAT3, anti-STAT3 (Cell Signaling Technology). All secondary antibodies were purchased from Dako. Total RNA was extracted from cells with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). cDNA was synthesized using the High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kits, and quantitative real time PCR was performed using Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems). Gene expression was calculated relative to that of GAPDH. The sequences of primers are as follows: Arginase 1 forward: 5ʹ-CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACATC-3ʹ; GAPDH forward: 5ʹ-AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA-3ʹ; gp91phox forward: 5ʹ-AGTGCGTGTTGCTCGACAA-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-GCGGTGTGCAGTGCTATCAT-3ʹ; p47phox forward: 5ʹ- ACACCTTCATTCGCCATATTGC-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-TCGGTGAATTTTCTGTAGACCAC-3ʹ; S100A9 forward: 5ʹ-ATACTCTAGGAAGGAAGGACACC-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-TCCATGATGTCATTTATGAGGGC-3ʹ.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SD. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 5 software. Difference was analyzed by parametric (Student’s t test) or nonparametric (Mann-Whitney U or Wilcoxon test) test. Survival curves were compared using a log-rank Mantel-Cox test. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant #81472267, #81072019 and #81172271.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
References
- 1.Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A.. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:211–217. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.02.013 PMID: 15766659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M.. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883–899. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025 PMID: 20303878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature07205 PMID: 18650914 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eaden JA, Abrams KR, Mayberry JF. The risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Gut. 2001;48:526–535. PMID: 11247898 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Canavan C, Abrams KR, Mayberry J. Meta-analysis: colorectal and small bowel cancer risk in patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:1097–1104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02854.x PMID: 16611269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Feagins LA, Souza RF, Spechler SJ. Carcinogenesis in IBD: potential targets for the prevention of colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:297–305. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.44 PMID: 19404270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Strober W, Fuss I, Mannon P. The fundamental basis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:514–521. doi: 10.1172/JCI30587 PMID: 17332878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wu T, Dai Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017;387:61–68. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.043 PMID: 26845449 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ortiz ML, Kumar V, Martner A, Mony S, Donthireddy L, Condamine T, Seykora J, Knight SC, Malietzis G, Lee GH, et al. Immature myeloid cells directly contribute to skin tumor development by recruiting IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 2015;212:351–367. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140835 PMID: 25667306 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Katoh H, Wang D, Daikoku T, Sun H, Dey SK, Dubois RN. CXCR2-expressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells are essential to promote colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:631–644. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.10.009 PMID: 24229710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Sinha P. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: linking inflammation and cancer. J Immunol. 2009;182:4499–4506. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802740 PMID: 19342621 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:162–174. doi: 10.1038/nri2506 PMID: 19197294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kumar V, Patel S, Tcyganov E, Gabrilovich DI. The nature of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:208–220. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.01.004 PMID: 26858199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu C, Yu S, Kappes J, Wang J, Grizzle WE, Zinn KR, Zhang HG. Expansion of spleen myeloid suppressor cells represses NK cell cytotoxicity in tumor-bearing host. Blood. 2007;109:4336–4342. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-09-046201 PMID: 17244679 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Bronte V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:253–268. doi: 10.1038/nri3175 PMID: 22437938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Serafini P, Mgebroff S, Noonan K, Borrello I. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote cross-tolerance in B-cell lymphoma by expanding regulatory T cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:5439–5449. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6621 PMID: 18593947 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Corzo CA, Cotter MJ, Cheng P, Cheng F, Kusmartsev S, Sotomayor E, Padhya T, McCaffrey TV, McCaffrey JC, Gabrilovich DI. Mechanism regulating reactive oxygen species in tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 2009;182:5693–5701. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900092 PMID: 19380816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Raber P, Ochoa AC, Rodriguez PC. Metabolism of L-arginine by myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer: mechanisms of T cell suppression and therapeutic perspectives. Immunol Invest. 2012;41:614–634. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2012.680634 PMID: 23017138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Arina A, Bronte V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell impact on endogenous and adoptively transferred T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015;33:120–125. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.02.006 PMID: 25728992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dufait I, Van Valckenborgh E, Menu E, Escors D, De Ridder M, Breckpot K. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in myeloid-derived suppressor cells: an opportunity for cancer therapy. Oncotarget. 2016;7:42698–42715. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8311 PMID: 27029037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vasquez-Dunddel D, Pan F, Zeng Q, Gorbounov M, Albesiano E, Fu J, Blosser RL, Tam AJ, Bruno T, Zhang H, et al. STAT3 regulates arginase-I in myeloid-derived suppressor cells from cancer patients. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1580–1589. doi: 10.1172/JCI60083 PMID: 23454751 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Marigo I, Bosio E, Solito S, Mesa C, Fernandez A, Dolcetti L, Ugel S, Sonda N, Bicciato S, Falisi E. Tumor-induced tolerance and immune suppression depend on the C/EBPbeta transcription factor. Immunity. 2010;32:790–802. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.010 PMID: 20605485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hirai H, Zhang P, Dayaram T, Hetherington CJ, Mizuno S, Imanishi J, Akashi K, Tenen DG. C/EBPbeta is required for ‘emergency’ granulopoiesis. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:732–739. doi: 10.1038/ni1354 PMID: 16751774 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang B, Wang Z, Wu L, Zhang M, Li W, Ding J, Zhu J, Wei H, Zhao K. Circulating and tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma. PloS one. 2013;8:e57114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057114 PMID: 23437326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Condamine T, Ramachandran I, Youn JI, Gabrilovich DI. Regulation of tumor metastasis by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:97–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-051013-052304 PMID: 25341012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stiff A, Trikha P, Wesolowski R, Kendra K, Hsu V, Uppati S, McMichael E, Duggan M, Campbell A, Keller K, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells express bruton’s tyrosine kinase and can be depleted in tumor-bearing hosts by ibrutinib treatment. Cancer Res. 2016;76:2125–2136. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1490 PMID: 26880800 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vincent J, Mignot G, Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Bruchard M, Chevriaux A, Martin F, Apetoh L, Rebe C, Ghiringhelli F. 5-Fluorouracil selectively kills tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells resulting in enhanced T cell-dependent antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3052–3061. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3690 PMID: 20388795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ko JS, Zea AH, Rini BI, Ireland JL, Elson P, Cohen P, Golshayan A, Rayman PA, Wood L, Garcia J, et al. Sunitinib mediates reversal of myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:2148–2157. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1332 PMID: 19276286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Joshi R, Kamat JP, Mukherjee T. Free radical scavenging reactions and antioxidant activity of embelin: biochemical and pulse radiolytic studies. Chem Biol Interact. 2007;167:125–134. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2007.02.004 PMID: 17379198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kumar GK, Dhamotharan R, Kulkarni NM, Honnegowda S, Murugesan S. Embelin ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11:724–731. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.01.022 PMID: 21296695 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dai Y, Qiao L, Chan KW, Yang M, Ye J, Ma J, Zou B, Gu Q, Wang J, Pang R, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma contributes to the inhibitory effects of Embelin on colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4776–4783. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4754 PMID: 19458067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dai Y, Jiao H, Teng G, Wang W, Zhang R, Wang Y, Hebbard L, George J, Qiao L. Embelin reduces colitis-associated tumorigenesis through limiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:1206–1216. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0378 PMID: 24651526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wu T, Dai Y, Wang W, Teng G, Jiao H, Shuai X, Zhang R, Zhao P, Qiao L. Macrophage targeting contributes to the inhibitory effects of embelin on colitis-associated cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:19548–19558. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6969 PMID: 26799669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Movahedi K, Guilliams M, Van den Bossche J, Van den Bergh R, Gysemans C, Beschin A, De Baetselier P, Van Ginderachter JA. Identification of discrete tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell subpopulations with distinct T cell-suppressive activity. Blood. 2008;111:4233–4244. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-07-099226 PMID: 18272812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Benedyk M, Sopalla C, Nacken W, Bode G, Melkonyan H, Banfi B, Kerkhoff C. HaCaT keratinocytes overexpressing the S100 proteins S100A8 and S100A9 show increased NADPH oxidase and NF-kappaB activities. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:2001–2011. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700820 PMID: 17429438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cheng P, Corzo CA, Luetteke N, Yu B, Nagaraj S, Bui MM, Ortiz M, Nacken W, Sorg C, Vogl T, et al. Inhibition of dendritic cell differentiation and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer is regulated by S100A9 protein. J Exp Med. 2008;205:2235–2249. doi: 10.1084/jem.20080132 PMID: 18809714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gallina G, Dolcetti L, Serafini P, De Santo C, Marigo I, Colombo MP, Basso G, Brombacher F, Borrello I, Zanovello P, et al. Tumors induce a subset of inflammatory monocytes with immunosuppressive activity on CD8+ T cells. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:2777–2790. doi: 10.1172/JCI28828 PMID: 17016559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mandruzzato S, Solito S, Falisi E, Francescato S, Chiarion-Sileni V, Mocellin S, Zanon A, Rossi CR, Nitti D, Bronte V, et al. IL4Ralpha+ myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion in cancer patients. J Immunol. 2009;182:6562–6568. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803831 PMID: 19414811 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Corzo CA, Condamine T, Lu L, Cotter MJ, Youn JI, Cheng P, Cho HI, Celis E, Quiceno DG, Padhya T, et al. HIF-1alpha regulates function and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. J Exp Med. 2010;207:2439–2453. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100587 PMID: 20876310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kusmartsev S, Gabrilovich DI. Inhibition of myeloid cell differentiation in cancer: the role of reactive oxygen species. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;74:186–196. PMID: 12885935 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Mignot G, Vincent J, Bruchard M, Remy-Martin JP, Boireau W, Rouleau A, Simon B, Lanneau D, et al. Membrane-associated Hsp72 from tumor-derived exosomes mediates STAT3-dependent immunosuppressive function of mouse and human myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:457–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI40483 PMID: 20093776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Niehof M, Streetz K, Rakemann T, Bischoff SC, Manns MP, Horn F, Trautwein C. Interleukin-6-induced tethering of STAT3 to the LAP/C/EBPbeta promoter suggests a new mechanism of transcriptional regulation by STAT3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:9016–9027. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009284200 PMID: 11114305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang H, Nguyen-Jackson H, Panopoulos AD, Li HS, Murray PJ, Watowich SS. STAT3 controls myeloid progenitor growth during emergency granulopoiesis. Blood. 2010;116:2462–2471. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-259630 PMID: 20581311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Weigmann B, Tubbe I, Seidel D, Nicolaev A, Becker C, Neurath MF. Isolation and subsequent analysis of murine lamina propria mononuclear cells from colonic tissue. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2307–2311. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.315 PMID: 17947970 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


