Abstract
Hepatitis C infection is universal and the most common indication of liver transplantation in the United States. The period of less effective interferon therapy with intolerable side effects has gone. Now we have stepped into the era of direct acting anti-viral agents (DAAs) against hepatitis C virus. Treatment of hepatitis C is now extremely effective, tolerable and requires a short duration of intake of oral agents. Less monitoring is required with the current therapy and drug-drug interactions are less than the previous regimen. The current treatment options of chronic hepatitis C with various DAAs are discussed in this article.
Keywords: Direct acting anti-viral agents, Hepatitis C virus infection, Post-liver transplant, Hepatitis C virus/human immunodeficiency virus co-infection
Core tip: Treatment of hepatitis C has now become much easy and simple with the advent of direct acting anti-viral agents (DAAs) against hepatitis C virus (HCV). Although the DAAs are highly effective in eradicating HCV infection, they have different mechanisms of action, side effects, resistance factors and drug-drug interactions. The treatment also varies in special situations like HCV/ human immunodeficiency virus co-infection and post-liver transplant patients. Physicians treating patients with HCV infection should have a clear knowledge about the DAAs as well as the current guidelines.
INTRODUCTION
Chronic hepatitis C infection is common in the United States and throughout the world. About 3 million people in the United States and 177.5 million people in the world suffer from chronic hepatitis C infection[1]. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) contains structural proteins - core or C protein, E1 and E2 envelope proteins, and nonstructural proteins - P7, NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A and NS5B[2]. HCV contains error prone RNA dependent RNA polymerase and mutation is present during each viral replication[3]. As a result, HCV exists as a quasispecies characterized by the presence of various genetically distinct variants which protect the HCV from host defenses as well as anti-HCV agents[4]. DAA are specific antiviral agents targeting the critical steps of HCV replication. With the development of direct acting anti-viral agent (DAA), the treatment of chronic hepatitis C has been completely revolutionized. In 1990’s when we had only Interferon therapy, the sustained virological response (SVR) was 17% with many side effects[5]. Then Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin came after few years but still the SVR was 40% to 50%[6]. In 2011, the first generation NS3/4A protease inhibitors (Telaprevir and Boceprevir) were launched to be used with pegylated interferon and ribavirin for the treatment of hepatitis C genotype 1 infection. The SVR improved to about 70% at the expense of many side effects, drug-drug interactions and complex regimen of administration of medications and cost[7]. Now we have 2nd generation NS3/4A protease inhibitors, NS5A inhibitors and NS5B inhibitors. They have markedly improved the efficacy of treatment of HCV infection. The different DAAs with their dose, efficacy, side effects, drug-drug interactions as well as specific treatment against different genotypes of HCV will be discussed in the following sections (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
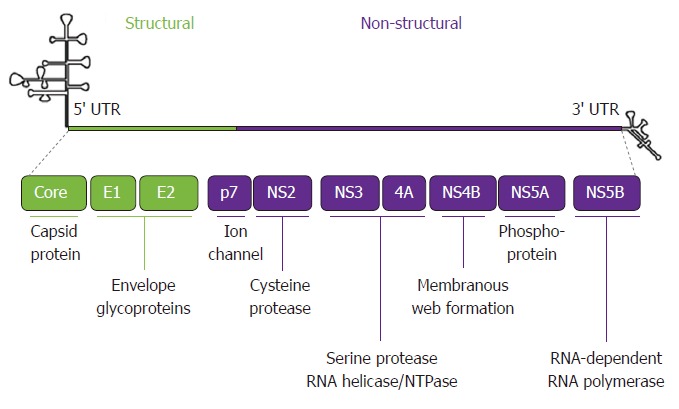
Hepatitis C virus RNA (genome).
NS3/4A protease inhibitors
HCV NS3/4A is a multifunctional protein composed of a membrane-targeted serine protease domain and a helicase domain. NS3/4A protease is responsible for maturation of a viral polyprotein that cleaves and generates NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A and NS5B. Thus NS3/4A protease is essential for viral replication[8]. NS3/4A protease inhibitors (PIs) are classified into first generation PIs and second generation PIs[9]. The first generation PIs include boceprevir and telaprevir. They are no longer used in clinical practice. The second generation PIs includes simeprevir, paritaprevir, grazoprevir, glecaprevir and voxilaprevir. They are highly potent DAAs but they have low barrier to resistance and limited genotypic coverage.
Simeprevir is a once daily macrocyclic 2nd - waive NS3/4A protease inhibitor approved to be used with pegylated interferon and ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 patients in 2013. In QUEST-1 and QUEST-2 trials (simeprevir + PEG + RBV vs PEG + RBV in treatment-naïve genotype 1 patients), 80% to 81% of treatment-naïve patients achieved SVR12, i.e., negative viral load 12 wk after completion of treatment[10,11]. Patients who had Q80K polymorphism had only 58% SVR12. In PROMISE trial, Simeprevir was given with pegylated interferon and ribavirin to treatment (Interferon)-experienced hepatitis C genotype 1 patients. The SVR12 was 79.2%. The SVR 12 also varied with the host IL28B genotype. Patient’s IL28B genotype is involved in the host immune response to HCV infection. There are 3 IL28B subtypes: CC, CT and TT. The IL28B CC genotypes had the highest response and the IL28B TT genotypes had the lowest response[12]. In COSMOS trial, combination of simeprevir and sofosbuvir (NS5B inhibitor) with or without ribavirin were given to HCV genotype 1 infected patients - both treatment-naïve patients and non-responders to pegylated interferon and ribavirin for 12 wk and 24 wk. Ninety-two percent to 94% of patients achieved SVR12[13]. In OPTIMIST-1 trial, combination of simeprevir and sofosbuvir was given to treatment-naïve non-cirrhotic HCV genotype 1 infected patients. Ninety-seven percent of patients who received this combination achieved SVR12 in the 12 wk arm whereas only 83% achieved SVR12 in the 8-wk arm[14]. In OPTIMIST-2 trial, cirrhotic patients due to HCV genotype 1 infection received combination of simeprevir and sofosbuvir for 12 wk. SVR12 was achieved in 83% of patients: 88% in treatment-naïve patients and 79% in treatment-experienced patients[15].
The main side effects of Simeprevir include headache, fatigue, nausea, photosensitivity and skin rash[16]. Latent HBV infection could be reactivated if patient is on simeprevir. Simprevir can also cause hepatic failure if used in decompensated cirrhosis of liver. Simeprevir has sulphur moiety which may cause sulphur allergy. Patients on simeprevir should not take moderate to high intensity enzyme-inducers or enzyme-inhibitors as they may decrease or increase the serum levels of simeprevir. Prior to the use of Simeprevir, it is recommended to do Q80K polymorphism screening (HCV GenoSure NS3/4A Assay) which has been found in 35% of patients infected with HCV genotype 1, and in more than 40% of patients infected with HCV genotype 1a[17]. In the Interferon free era, combination of simeprevir 150 mg/d and sofosbuvir 400 mg/d for 12 wk is recommended as an alternative regimen in the treatment of treatment-naïve genotype 1a or 1b patients without cirrhosis as per the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD).
Drug-drug interactions: Common medications which are not recommended to be co-administered with Simeprevir include systemic antibiotics like clarithromycin, erythromycin, systemic antifungals like fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole, antimycobacterials like rifampin, rifabutin, anti-hepatitis C medication ledipasvir, anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) medications like ritonavir, darunavir, efavirenz, nevirapine, etravirine, delavirdine, atazanavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir, indinavir, fosamprenavir, tipranavir, anti-arrhythmic drug like amiodarone, anticonvulsants like phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, dexamethasone, cyclosporine, milk thistle and St. John’s Wort[18].
Paritaprevir is a macrocyclic NS3/4A protease inhibitor used in combination with low dose ritonavir which is a strong CYP3A inhibitor, and thus increases peak and trough level of Paritaprevir[19]. Paritaprevir/ritonavir-ombitasvir (NS5A inhibitor) - a 3 drug fixed dose combination tablet co-packaged with dasabuvir (NS5B inhibitor) tablet in Viekira Pak, and dasabuvir, ombitasvir, paritaprevir and ritonavir - a 4 drug fixed dose combination tablet in Viekira XR with or without ribavirin are approved for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C genotype 1[20]. Paritaprevir/ritonavir-ombitasvir (in TECHNIVIE) with ribavirin is approved for the treatment hepatitis C genotype 4 without cirrhosis of liver. Viekira Pak and Viekira XR carry a higher pill burden than other regimen. They are also contraindicated in advanced cirrhosis of liver (Child-Pugh B and C). They are metabolized mainly in the liver. As a result, no dose adjustment is needed even in severe renal failure including those on dialysis[21]. If the patient has HBV/HCV co-infection and not receiving HBV antiviral therapy, HBV reactivation can occur leading to severe hepatitis, hepatic failure and death. In RUBY-1 trial, 90% of patients with HCV genotype 1 infection and end-stage renal disease (CKD 4 and CKD 5) had SVR12, i.e., negative serum HCV RNA after 12 wk of therapy with dasabuvir, ombitasvir, paritaprevir and ritonavir[22]. In case of HCV genotype 1a infection - Viekira should be continued for 12 wk in non-cirrhotics and 24 wk in cirrhotics. In case of HCV genotype 1b infection - Viekira should be given for 12 wk irrespective of cirrhosis or non-cirrhosis status[23]. In liver transplant recipients with normal liver function and mild hepatic fibrosis, Viekira pak or Viekira XR with weight-based ribavirin should be given for 24 wk. The common side effects of Viekira include nausea, insomnia, itching and asthenia.
Drug-drug interaction: Common medications which are contra-indicated with Viekira include lipid lowering agent gemfibrozil, HMG co-reductase inhibitors - simvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin, anti-arrhythmic drug dronedarone, α-1 adrenoreceptor blocker alfuzosin, anti-anginal medication ranolazine, phosphodiesterase inhibitor sildenafil, anticonvulsants like phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, sedative/hypnotics triazolam, midazolam, anti-gout medication colchicine, antimycobacterial medication rifampin, antipsychotic medication lurasidone and pimozide, ergot agents methylergonovine, ergotamine and dihydroergotamine, ethinyl estradiol containing medications, prokinetic agent cisapride, herbal agent St. John’s Wort, immunosuppressive agents tacrolimus, sirolimus and everolimus, and anti-HIV medication efavirenz[24].
Grazoprevir is a macrocyclic NS3/4A serine protease inhibitor against HCV genotype 1 and 4. It is used in combination with Elbasvir (NS5A inhibitor) for the treatment of HCV genotypes 1 and 4. In clinical trials, combination of elbasvir and grazoprevir (Zepatier) has been shown to achieve SVR in 94% to 97% of cases of genotype 1 infection and 97% to 100% of cases of genotype 4 infection. The overall SVR for non-cirrhotics was 97% and for cirrhotics 95.7%[25]. The regimen was effective in stage 4 to 5 chronic kidney disease[26]. In case of HCV genotype 1a infection, NS5A resistance testing should be done prior to initiation of elbasvir and grazoprevir therapy. In 10% to 15% of cases, NS5A polymorphism is positive and in that case weight-based ribavirin (less than 66 kg = 800 mg/d, 66 to 80 kg = 1000 mg/d, 81 to 105 kg = 1200 mg/d, greater than 105 kg = 1400 mg/d administered in two divided doses with food) should be added and the duration should be increased from 12 to 16 wk. Otherwise HCV genotype 1a or 1b infection requires only 12 wk of Zepatier therapy irrespective of exposure to pegylated interferon and ribavirin (PEG/RIBA), and presence of cirrhosis of liver. In case of HCV genotype 4 infection, the duration of Zepatier therapy is 12 wk for treatment-naïve patients, but it should be extended to 16 wk if PEG/RIBA experienced with prior on-treatment virologic failure[27]. In C-ISLE study, Elbasvir/Grazoprevir plus Sofosbuvir was given to patients with compensated cirrhosis due to HCV genotype 3 infection for 12 wk. The SVR12 was 96% in treatment-naïve patients and 100% in PEG-interferon/Ribavirin experienced patients[28]. HBV reactivation can occur on grazoprevir/elbasvir therapy if the patient is co-infected with HBV and not receiving anti-HBV therapy. HBV serology (HBsAg and anti-HBc) and HCV resistance associated polymorphisms as mentioned before should be tested prior to initiation of Zepatier therapy. Common side effects include headache, nausea and fatigue[29].
Common medications which are not recommended to be used with Zepatier include antibiotic Nafcillin, antifungal oral ketoconazole, anti-HIV medication etravirine, cobicistat containing medications like tenofovir, emtricitabine, cobicistat, HMG Co-A reductase inhibitors atorvastatin (dose should not exceed > 20 mg/d), rosuvastatin (dose should not exceed > 10 mg/d), simvastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin (should be closely monitored for myopathy), nacolepsy medication modafinil, immunosuppressant tacrolimus, and endothelin antagonist bosentan[29].
Drug-drug interaction: Glecaprevir is a NS3/4A protease inhibitor coformulated with NS5A inhibitor pibrentasvir (Mavyret). Glecaprevir-pibrentasvir combination has been shown to have pangenotypic anti-HCV activity. In EXPEDITION-1 study, glecaprevir (300 mg) - pibrentasvir (120 mg) coformulation when given daily for 12 wk to treatment-naïve or treatment experienced (pegylated interferon plus ribavirin or sofosbuvir plus ribavirin) patients with HCV genotypes, infection and compensated cirrhosis, 99% of patients achieved SVR at 12 wk[30]. Another study showed glecaprevir-pibrentasvir combination when given for 8 wk to patients with HCV genotype-1 and 3 infection had SVR 12 of 99.1% and 95% respectively[31]. Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have more chronic hepatitis C, particularly in patients on hemodialysis, 8.4% hemodialysis patients had chronic hepatitis C in the year of 2000. When patients with severe renal failure (stage 4 or 5 CKD or dialysis dependence) and HCV genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection with or without compensated cirrhosis, treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced (pegylated interferon, ribavirin, sofosbuvir or a combination of these medications), were treated with glecaprevir-pibrentasvir combination for 12 wk, they had sustained SVR12 of 98%[32]. No dose adjustment was required in patients with severe renal failure or in hemodialysis patients[33].
Three tablets of fixed dose Glecaprevir 100 mg/Pibrentasvir 40 mg (i.e., 300 mg/120 mg total dose) PO once daily is given with food.
In treatment-naïve patients[33], the recommended duration is 8 wk for genotypes 1 to 6 infection without cirrhosis. But the treatment duration is 12 wk for genotypes 1 to 6 infection with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A). In treatment-experienced patients. In non-cirrhotics: Genotype 1 and NS5A inhibitor prior treatment: 16 wk. Genotype 1 and NS3/4A protease inhibitor prior treatment: 12 wk. Genotypes 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 (prior treatment with boceprevir, or telaprevir or simeprevir with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, simeprevir and sofosbuvir): 8 wk. Genotype 3 (prior treatment with boceprevir, or telaprevir or simeprevir with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, simeprevir and sofosbuvir): 16 wk.
In treatment-experienced patients[33] with compensated cirrhotics (Child-Pugh A): Genotype 1 and NS5A inhibitor prior treatment: 16 wk. Genotype 1 and NS3/4A protease inhibitor prior treatment: 12 wk. Genotypes 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 (prior treatment with boceprevir, or telaprevir or simeprevir with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, simeprevir and sofosbuvir): 12 wk. Genotype 3 (prior treatment with, boceprevir, or telaprevir or simeprevir with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, simeprevir and sofosbuvir): 16 wk. Common side effects of Mavyret include headache, fatigue, nausea and diarrhea.
Commonly used medications which can cause drug interaction with Mavyret include HMG Co-A reductase inhibitors atorvastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, pravastatin, pitavastatin, fluvastatin, ethinyl estradiol containing medications, anticoagulant dabigatran, antiarrhythmic digoxin, anticonvulsant carbamazepine, antimycobacterial rifampin, anti-HIV medications efavirenz, ritonavir, lopinavir, darunavir, atazanavir, herbal medication St. John’s Wort, and immunosuppressant cyclosporine[34].
Voxilaprevir is a NS3/4A protease inhibitor. It is used in the fixed dose combination of sofosbuvir and velpatasvir (NS5A inhibitor), commercially available as Vosevi. In POLARIS-1, sofosbuvir (400 mg)/velpatasvir (100 mg)/voxilaprevir (100 mg) single pill was given daily for 12 wk to NS5A inhibitor-experienced patients with HCV genotype 1-6 infection. In POLARIS-4, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir was given daily for 12 wk to DAA experienced (but not NS5A experienced) patients with HCV genotype 1-3 infection, and also to patients with HCV genotype 4 infection. Forty-six percent of all these patients had compensated cirrhosis of liver. In POLARIS-1, the SVR was 96%, and in POLARIS-4, the SVR was 98%[35]. Currently, Vosevi is approved for retreatment of: (1) HCV genotype 1-6 infection in adults who were previously treated with an NS5A inhibitor-containing regimen; and (2) HCV genotype 1a or 3 infection in adults who were previously treated with sofosbuvir-containing regimen without an NS5A inhibitor[36]. Vosevi can be given to patients without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis, and no dose adjustment is required even in severe renal impairment with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) < 30 mL/min or end stage renal disease. If the patient is HBV coinfected and not receiving anti-HBV therapy, HBV reactivation can occur during or after completion of treatment with Vosevi. So, serological evidence of HBV infection (HBVsAg and anti-HBVc antibody) should be looked for before initiation of therapy with Vosevi. Common side effects of Vosevi include headache, nausea, diarrhea insomnia, asthenia and fatigue.
Drug-drug interaction: Certain medications are not recommended with Vosevi. These include anatacids like aluminum or magnesium hydroxide, H2 receptor antagonists like Famotidine, proton pump inhibitor like omeprazole, anticoagulant like dabigatran, anti-arrhythmic agents like digoxin, amiodarone, HMG Co-A reductase inhibitors atorvastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, pravastatin, pitavastatin, anticonvulsants like phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepin, anti-HIV medications efavirenz, tenofovir, lopinavir, atazanavir, tipranavir/ritonavir, antimycobactrial agents like rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentin, immunosuppressant cyclosporine, and herbal supplement St. John’s Wort[37].
NS5A inhibitors
Inhibit hyperphosphorylation of NS5A phosphoprotein which is necessary for HCV RNA replication, and they also cause transfer of NS5A from the endoplasmic reticulum to lipid droplets in HCV replicon-containing cells leading to significant reduction of HCV RNA in cell culture[38]. Ledipasvir, ombitasvir, daclatasvir, elbasvir, velpatasvir and pibrentasvir are NS5A inhibitors. They are highly potent DAA with multigenetic coverage and intermediate barrier to resistance.
Ledipasvir is a NS5A inhibitor used as part of combination therapy with Sofosbuvir (NS5B inhibitor) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. The fixed dose combination called Harvoni (90 mg of Ledipasvir and 400 mg Sofosbuvir) developed by Gilead Sciences was approved by the FDA in 2014.
Effectiveness, duration and need for addition of ribavirin with this medication depend on viral load, genotype, compensated or decompensated cirrhosis, treatment naïve or treatment-experienced status, and pre or post-transplant status.
In ION-1 phase 3 clinical trial, 99% of treatment naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 who received Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir combination for 12 wk achieved SVR[39]. In ION-2 phase 3 clinical trial, 99% of patients with previously treated genotype-1 HCV infection who received Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir combination for 24 wk had SVR[40]. Patients with HCV genotype-1 infection and compensated cirrhosis were studied with Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir combination for 12 and 24 wk in treatment naïve and treatment experienced patients with or without ribavirin[41]. The overall SVR was 96%: 98% in treatment-naïve group vs 95% in treatment-experienced group, 95% in 12 wk therapy group vs 98% in 24 wk therapy group, 95% without ribavirin vs 97% with ribavirin. The only group who did not do well was the treatment-experienced group who received Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir combination for only 12 wk and without ribavirin. Their SVR was 90%[41]. As a result, this combination is recommended to be continued for 24 wk in treatment-experienced HCV genotype-1 infection with compensated cirrhosis. Patients with HCV genotype-4 with or without compensated cirrhosis were treated with Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir combination with or without ribavirin. Overall SVR12 was 95.4% in non-cirrhotics and 93.2% in cirrhotics[42]. Patients with HCV genotype 5 with or without compensated cirrhosis were treated with Ledspavir-Sofosbuvir for 12 wk in a multi-center open-label study. The SVR12 was 95% in both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced groups; 89% of cirrhotics and 97% of non-cirrhotics achieved SVR12[43]. A small study showed when fixed dose combination of Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir was given to treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients with HCV genotype 6 infection for 12 wk, 96% of them achieved SVR12[44]. At the present time, Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir combination is indicated for the treatment of HCV genotype 1, 4, 5 and 6 infections with or without compensated cirrhosis. It is also used in HCV genotype 1 infection with decompensated cirrhosis in combination with ribavirin. Post liver transplant recipients who have HCV genotype 1 or 4 infection with or without compensated cirrhosis can be treated with Ledispavir-Sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for 12 wk. In one study, 96% of patients who had F-0 to F-3 fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis achieved SVR[45].
Common side effects of Harvoni include headache, fatigue, nausea and diarrhea. Harvoni like other DAAs can reactivate HBV if the patient is HBV/HCV co-infected and not receiving anti-HBV therapy. So prior to initiation of Harvoni, serological evidence of HBV infection should be tested and treated if positive.
Drug-drug interaction: Co-administration of amiodarone with Harvoni may cause serious symptomatic bradycardia. Dose adjustment or regimen change may be required for certain medications. These include antiarrhythmic drug digoxin, HMG Co-A reductase inhibitor rosuvastatin, anticoagulant warfarin, acid reducing agents proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor antagonists, antacids, anticonvulsants phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, antimycobacterials rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, anti-HCV medication simeprevir, anti-HIV medications tenofovir DF, emtricitabine, cobicistat, elvitegravir, tipranavir/ritonavir, regimen containing tenofovor DF and an HIV protease inhibitor/ritonavir or cobicistat: darunavir/ritonavir or cobicistat + emtricitabine/tenofovir DF, atazanavir/ritonavir or cobicistat + emtricitabine/tenofovir DF, lopinavir/ritonavir + emtricitabine/tenofovir DF, and herbal supplement St. John’s Wort[46].
Ombitasvir is a NS5A inhibitor. After absorption, it binds to NS5A and blocks the activity of NS5A to prevent HCV replication. It is used in combination with paritaprevir, retinovir and dasabuvir with or without ribavirin. In Viekira pak, paritaprevir, ritonavir and ombitasvir packaged in a single table, and dasabuvir is a different tablet. The daily dose of Viekira pak is 2 tablets of paritaprevir, ritonavir and ombitasvir in the morning, and one tablet of dasabuvir twice a day. In Viekira XR, each tablet contains partaprevir, ritonavir, ombitasvir and dasabuvir. 3 tablets have to be taken daily for 12 to 24 wk.
Daclatasvir is a highly selective pangenotypic NS5A inhibitor[47]. It has dual mode of action as it binds to the N-terminal of NS5A and thus prevents viral replication and viral assembly. It is the first oral medication used in combination with sofosbuvir for 12 wk for the treatment of hepatitis C genotype 3 infection. HCV genotype 3 is the most aggressive (having faster disease progression) and most treatment resistant genotype affecting 12% of all HCV genotypes in United States. In Ally-3 trial, a 12 wk therapy of daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir achieved SVR12 in 96% of non-cirrhotic patients infected with HCV genotype 3 irrespective of prior treatment experience[48]. In Ally 3+ trial, daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir plus ribavirin were given to treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients with advanced fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis for 12 or 16 wk. The SVR12 was 90% in the 12 wk and 92% in the 16 wk group[49]. In Ally-2 trial, 12 wk course of daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir achieved SVR12 of 97% in patients infected with HCV genotype 1 to 4 coinfected with HIV[50]. The efficacy of daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir in cirrhotic patients infected with HCV genotype 1 to 6 is being studied in Ally-1 trial[51].
Common side effects include headache, fatigue, nausea and diarrhea. Certain drugs are contraindicated to be used with daclatasvir. These include anticonvulsants phenytoin, carbamazepine, antimycobacterial agent rifampin and herbal supplement St. John’s Wort.
Drug-drug interactions: Medications which can cause significant drug interactions with daclatasvir include statins, digoxin, dabigatran, ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, nafcillin, dexamethasone, buprenorphine, modafinil, bosentan, anti-HIV medications - protease inhibitors: atazanavir with ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir; Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Efavirenz Etravirine Nevirapine; and cobicistat-containing antiretroviral: atazanavir/cobicistat, elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate[52].
Elbasvir is a potent NS5A inhibitor. It is used in combination with grazoprevir which is a NS3/4A protease inhibitor. The combination is effective against HCV genotypes 1 and 4. Elbasvir can be less effective when there are many resistance- associated variants or substitutions (RAVs or RASs) of NS5A[53]. Elbasvir-Grazoprevir can be taken in empty stomach or with food. In C-EDGE trial, treatment-naïve HCV infected patients had a good response (SVR12) rate to 12 wk therapy of Elbasvir-Grazoprevir: 92% with genotype 1a, 99% with genotype 1b, 100% with genotype 4 and 80% with genotype 6; 97% in cirrhotics and 94% in non-cirrhotics[54]. In C-EDGE TE trial, patients with prior exposure to pegylated interferon and ribavirin, Elbasvir/Grazoprevir with or without ribavirin was highly effective in inducing an SVR12 in patients with HCV genotype 1, 4 and 6 including patients with cirrhosis[55].
Velpatasvir is a pangenotypic second generation NS5A inhibitor and is much more potent with a higher barrier to resistance than the first generation NS5A inhibitors (ledispavir and Daclatasvir). It acts as a defective substrate for NS5A and prevents HCV replication. It is used as a fixed dose co-formulation with sofosbuvir (Epclusa). In a double blind placebo-controlled study, sofosbuvir-velpatasvir combination was given daily for 12 wk to untreated and previously treated patients with HCV infection genotypes 1-6 including those with compensated cirrhosis. The SVR was 99%[56]. Another study showed that when sofosbuvir-velpatasvir combination plus ribavirin were given daily for 12 wk to decompensated cirrhotics (Child - Pugh - Turcotte class B) due to HCV infection genotype 1-6, the SVR was 94%[57].
Common side effects of Epclusa include headache, fatigue, insomnia, nausea and diarrhea. If the patient is HBV/HCV coinfected and not receiving ant-HBV therapy, administration of Epclusa may cause reactivation of HBV and fulminant hepatitis during or after treatment with Epclusa.
Drug-drug interactions: Similar to Harvoni, co-administration of Amiodarone with Epclusa may lead serious symptomatic bradycardia. Dose alteration or regimen change may be recommended for certain medications. These include acid suppressant agents proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor blockers, antacids (aluminum and magnesium hydroxide), HMG Co-A reductase inhibitors atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, anti-arrhythmic drug digoxin, anticonvulsants phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, antimycobacterials rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, anti-HIV medications efavirenz, etravirine, nevirapine, tipranavir/ritonavir, Regimens containing tenofovir DF, anti-cancer medication topotecan, and herbal supplement St. John’s wort[58].
Pibrentasvir is a 2ed generation NS5A inhibitor coformulated with glecaprevir (Mavyret). As mentioned before glecaprevir/pibrentasvir combination is pangenotypic and can be used in severe renal failure, including hemodialysis patients.
NS5B inhibitors
They act on the catalytic site of NS5B polymerase. They cause HCV RNA chain termination after being incorporated into the RNA chain. Nucleotide NS5B inhibitors are already activated. They act on the active site of NS5B polymerase. Non-Nucleoside NS5B inhibitors need to be activated by cellular kinase 3 times to become the triphosphate which is the active form. They act on different allosteric sites (thumb, finger and palm domains) to downregulate NS5B polymerase[59]. Nucleotide NS5B inhibitors are moderately potent DAA with pangenotypic coverage and have high barrier to resistance. Non-nucleoside NS5B inhibitors are moderately potent DAA with limited genotypic coverage and low barrier to resistance.
Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide NS5B polymerase inhibitor[60]. It is coformulated with Ledipasvir for the treatment of hepatitis C genotype 1, 4, 5 and 6 infection. A meta-analysis showed no additional benefit when ribavirin was added to sofosbuvir/ledipasvir for the treatment genotype 1 infection[61]. As mentioned before, sofosbuvir/daclatasvir combination is effective for the treatment of hepatitis C genotypes 1 to 4[62]. Patients with HCV genotypes 2 and 3 infections were treated with sofosbuvir and ribavirin for 12 wk and 24 wk respectively: SVR 12 was 93% for genotype 2 infection, and 85% for genotype 3 infection. In non-cirrhoitc HCV genotype 3 infection, the SVR was 91% whereas in cirrhotic genotype 3 infection, the SVR was 68%[63]. Sofosbuvir has been coformulated with other NS5A inhibitor or NS3/4A protease inhibitor to make the combination more effective against HCV and also pangenotypic.
Common side effects of Sofosbuvir include headache, nausea, insomnia and fatigue. Reactivation of HBV with fulminant hepatitis can occur if the patient is HBV/HCV co-infected and not receiving anti-HBV therapy.
Drug-drug interactions: Dose alteration or change in regimen is recommended for certain medications. These include anticonvulsants phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, anti-HIV medications tipranavir/ritonavir, antimycobacterial agents rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, and herbal supplement St. John’s Wort[64].
Dasabuvir is a non-nucleoside NS5B polymerase inhibitor. It is used in combination with Paritaprevir/ritonavir-ombitasvir ((in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR) with or without ribavirin for the treatment of hepatitis C genotype 1 infection with or without compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A). It binds to the palm domain of NS5B, and thus prevents elongation of HCV RNA. The binding site is poorly conserved across other HCV genotypes. As a result, Dasabuvir is only effective against HCV genotype 1 infection. Every year new DAAs are being added in our clinical practice. Currently, the various DAAs available in formulation are as follows (Table 1).
Table 1.
Direct acting anti-viral agents with posology
| No. | Trade name | Generic name with doses |
| 1 | Sovaldi | Sofosbuvir 400 mg |
| 2 | Olysio | Simeprevir 150 mg |
| 3 | Daklinza | Daclatasvir 30 mg/60 mg/90 mg |
| 4 | Harvoni | Ledipasvir 90 mg/Sofosbuvir 400 mg |
| 5 | Viekira Pak | 1 d pack contains Paritaprevir 75 mg/Ombitasvir 12.5 mg/Ritonavir 50 mg tablet × 2 and Dasabuvir 250 mg tablet × 2 |
| 6 | Viekira XR | Extended release tablet contains Dasabuvir 200 mg/ombitasvir 8.33 mg/Paritaprevir 50 mg/Ritonavir 33.33 mg |
| 7 | Technivie | Ombitasvir 12.5 mg/Paritaprevir 75 mg/Ritonavir 50 mg |
| 8 | Epclusa | Sofosbuvir 400 mg/ Velpatasvir 100 mg |
| 9 | Zepatier | Elbasvir 50 mg/ Grazoprevir 100 mg |
| 10 | Mavyret | Glecaprevir 100 mg/ Pibrentasvir 40 mg |
| 11 | Vosevi | Sofosbuvir 400 mg/Velpatasvir 100 mg/Voxilaprevir 100 mg |
Individualized treatment options
In 2018, we treat hepatitis C with combination of at least two DAAs or one DAA with ribavirin. Several factors are to be considered before planning treatment for hepatitis C. These include HCV genotype, HCV viral load, treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced (PEG/RIBA, NS3/4A protease inhibitor, NS5A inhibitor, NS5B inhibitor) patient, cirrhotic or non-cirrhotic patient, absence or presence of baseline NS5A resistance-associated substitutions (RASs), patient’s current medications considering any drug-drug interactions (DDI), patient’s renal function, co-infection with HIV, post-liver transplant infection, and of course, patient’s insurance and financial status. Guidelines for the treatment of hepatitis C was updated by the European Association for the Study of Liver (EASL) in 2016 and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) in 2017[65,66]. Individualized treatments as per the AASLD guidelines[66] are listed in Tables 2 and 3.
Table 2.
Genotype 1a and 1b infection - treatment-naïve (with compensated cirrhosis) and non-cirrhotic
| No. | First line therapy | Alternative regimen |
| Genotype 1a infection - treatment-naïve and non-cirrhotic | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk | Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir (in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR) with weight-based ribavirin - 12 wk |
| 2 | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) for patients without baseline NS5A RAVs for Elbasvir - 12 wk | Simeprevir (Olysio) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| 3 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk < Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 8 wk in non-black, HIV-uninfected individuals with serum HCV RNA < 6 million units/mL | Daclatasvir(Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| 4 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) with weight-based ribavirin for patients with baseline NS5A RAVs for Elbasvir - 16 wk |
| Genotype 1a infection - treatment-naïve with compensated cirrhosis | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) with weight-based ribavirin for patients with baseline NS5A RASs for Elbasvir - 16 wk |
| 2 | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) for patients without baseline NS5A RAVs for Elbasvir - 12 wk | |
| 3 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk | |
| 4 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 1b infection - treatment-naïve and non-cirrhotic | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk | Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir (in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR) - 12 wk |
| 2 | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) - 12 wk | Simeprevir (Olysio) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| 3 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk < Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni - 8 wk in non-black, HIV-uninfected individuals with serum HCV RNA < 6 million units/mL | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| 4 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 1b infection - treatment-naïve with compensated cirrhosis | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir (in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR) - 12 wk |
| 2 | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier - 12 wk | |
| 3 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk | |
| 4 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa - 12 wk | |
RAVs: Resistance- associated variants; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
Table 3.
Genotype 1 infection-treatment-experienced
| Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret): Duration of treatment depends on previous regimen and presence or absence of compensated cirrhosis. | ||
| Previous regimen | No cirrhosis | Compensated cirrhosis |
| Pegylated IFN, ribavirin and/or Sofosbuvir but no prior exposure to NS3/4A PI or NS5A inhibitor | 8 wk | 12 wk |
| NS3/4A PI but no prior exposure to NS5A inhibitor | 12 wk | 12 wk |
| NS5A inhibitor but no prior exposure to NS3/4A PI | 16 wk | 16 wk |
| Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier): Duration depends on viral load irrespective of no cirrhosis or compensated cirrhosis as per EASL guideline. | ||
| Previous regimen | HCV RNA ≤ 800000 IU/mL | HCV RNA > 800000 IU/mL |
| Pegylated IFN and ribavirin | 12 wk without ribavirin | 16 wk with ribavirin |
| Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni): Applicable for both non-cirrhotics andcompensated cirrhotics. | ||
| Previous regimen | With ribavirin | Without ribavirin |
| PEG IFN and ribavirin | 12 wk | 24 wk |
| Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa): Treatment is same for both non-cirrhotics and compensated cirrhotics. | ||
| Previous regimen | No cirrhosis | Compensated cirrhosis |
| PEG IFN and ribavirin | 12 wk without ribavirin | 12 wk without ribavirin |
| Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi): Applicable for both non-cirrhotics and compensated cirrhotics. | ||
| Previous regimen | With ribavirin | Without ribavirin |
| PEG IFN and ribavirin | 12 wk | 24 wk |
| Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir (in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR) with weight-based ribavirin. | ||
| Previous regimen | No cirrhosis | Compensated cirrhosis |
| PEG IFN and ribavirin | 12 wk | 24 wk |
IFN: Interferon; PI; Protease inhibitors; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
Genotype 1 infection-treatment-experienced
Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret): Duration of treatment depends on previous regimen and presence or absence of compensated cirrhosis. Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier): duration depends on viral load irrespective of no cirrhosis or compensated cirrhosis as per EASL guideline. Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni): Applicable for both non-cirrhotics and compensated cirrhotics. Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa): treatment is same for both non-cirrhotics and compensated cirrhotics. Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi): applicable for both non-cirrhotics and compensated cirrhotics. Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir (in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR) with weight-based ribavirin (Tables 3-6).
Table 6.
Genotype 2-6 infection - treatment-experienced
| First line therapy | Alternative regimen | |
| Genotype 2 infection - treatment-experienced | ||
| Pegylated IFN/ribavirin-experienced without cirrhosis | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk or Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| Pegylated IFN/ribavirin-experienced with compensated cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk or Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 16 to 24 wk |
| Sofosbuvir plus ribavirin-experienced with or without compensated cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk or Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 3 infection - treatment-experienced | ||
| Pegylated IFN/ ribavirin-experienced without cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk or Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 16 wk or Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir - 12 wk |
| Pegylated IFN/ ribavirin-experienced with compensated cirrhosis | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) - 12 wk or Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir (Vosevi) -12 wk | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) plus weight-based ribavirin - 12 wk or Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 16 wk |
| DAA-experienced including NS5A inhibitors with or without compensated cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir (Vosevi) - 12 wk or in case of NS5A inhibitor failure and cirrhosis - Vosevi plus weight-based Ribavirin - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 4 infection - treatment-experienced | ||
| Pegylated IFN/ ribavirin-experienced without cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) -12 wk or Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk or Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) in virologic relapse - 12 wk or Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk | Ombitasvir 25 mg/Paritaprevir 150 mg/Ritonavir 100 mg plus weight based Ribavirin - 12 wk or Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) with weight-based Ribavirin (in case of prior on-treatment virologic failure) - 16 wk |
| Pegylated IFN/ ribavirin-experienced with compensated cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk or Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) in virologic relapse - 12 wk or Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | Ombitasvir 25 mg/Paritaprevir 150 mg/ Ritonavir 100 mg plus weight based Ribavirin - 12 wk or Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) with weight-based Ribavirin (in case of prior on-treatment virologic failure - 16 wk or Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) plus weight-based Ribavirin) - 12 wk |
| DAA-experienced including NS5A inhibitors with or without compensated cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir (Vosevi) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 5 or 6 infection - treatment-experienced (recommended regimen) | ||
| Pegylated IFN/ ribavirin-experienced with or without compensated cirrhosis | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk for patients without cirrhosis and 12 wk for patients with compensated cirrhosis or Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) plus weight-based Ribavirin - 12 wk or Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | |
| DAA-experienced including NS5A inhibitors with or without compensated cirrhosis | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/ Voxilaprevir (Vosevi) - 12 wk | |
IFN: Interferon; DAA: Direct acting anti-viral agent.
Table 4.
Genotype 2-4 infection - treatment-naïve (with compensated cirrhosis) and non-cirrhotic
| No. | First line therapy | Alternative regimen |
| Genotype 2 infection - treatment-naïve and non-cirrhotic | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk | Daclatasvir(Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| 2 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 2 infection - treatment-naïve with compensated cirrhosis | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | Daclatasvir(Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 16 to 24 wk |
| 2 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 3 infection - treatment-naïve and non- cirrhotic | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - 12 wk |
| 2 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 3 infection - treatment-naïve with compensated cirrhosis | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | Vosevi - Sofosbuvir 400 mg/ Velpatasvir 100 mg/ Voxilaprevir 100 mg when Y93 is present - 12 wk |
| 2 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with or without weight-based ribavirin - 24 wk |
| Genotype 4 infection - treatment-naïve and non-cirrhotic | ||
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 8 wk | Ombitasvir 25 mg/Paritaprevir 150 mg/ Ritonavir 100 mg (Technivie) with weight-based ribavirin - 12 wk |
| 2 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | |
| 3 | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) - 12 wk | |
| 4 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk | |
| Genotype 4 infection - treatment-naïve with compensated cirrhosis | ||
| 1 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) - 12 wk | Ombitasvir 25 mg/Paritaprevir 150 mg/ Ritonavir 100 mg (Technivie) with weight-based ribavirin - 12 wk |
| 2 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk | |
| 3 | Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier) - 12 wk | |
| 4 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) - 12 wk | |
Table 5.
Genotype 5 or 6 infection - treatment-naïve with and without compensated cirrhosis
| No. | DAA | No cirrhosis | Compensated cirrhosis |
| 1 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) | 8 wk | 12 wk |
| 2 | Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) | 12 wk | 12 wk |
| 3 | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) | 12 wk | 12 wk |
DAA: Direct acting anti-viral agent.
HCV/HIV Co-infection
Twenty percent to 30% of the 34 million HIV infected individuals in the world are co-infected with HCV[67]. HCV/HIV co-infection carries increased morbidity and mortality including advanced hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis[68]. HCV/HIV co-infected patients have higher HCV viral load, more chance of developing chronic HCV infection and rapid development of advanced liver disease than HCV mono-infected patients. The main challenge of treating these group of patients is drug-drug interactions, i.e., interactions between anti-HCV DAAs and anti-retroviral medications[69]. But the SVR and side effects are similar to those of HCV mono-infected patients[70]. Ideally, HCV/HIV co-infection should be managed by or in collaboration with a HIV practitioner. No change in antiretroviral therapy should be done without consultation of the HIV practitioner. Certain guidelines given by AASLD and IDSA are as follows[66]: (1) Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni): This combination has certain interactions with anti-retrovirals mentioned before. As it increases serum level of tenofovir disoproxil fumerate which may cause renal toxicity, renal function should be monitored and tenofovir disoproxil fumerare should be used with GFR > 60 mL/min. Tenofovir alafenamide could be an alternative option; (2) Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir (in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR): The anti-HIV medications which do not have substantial interaction with Vikira Pak and Viekira XR include atazanavir, dolutegravir, emtricitabine, enfuvirtide, lamivudine, raltegravir, and tenofovir; (3) Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa): Can have drug-drug interactions with anti-retrovirals mentioned before. As velpatasvir can increase the serum level of tenofovir disoproxil fumerate, renal function should be checked and tenofovir disoproxil fumerate should not be used with a GFR of less than 60 mL/min. Tenofovir alafenamide could be used instead; (4) Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier): Certain antiretrovirals do not have significant drug-drug interactions with elbasvir/grazoprevir combinations. These include tenofovir, lamivudine, emtricitabine, abacavir, dolutegravir, raltegravir, rilpivirine, and enfuvirtide; (5) Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret): The anti-retrovirals which do not have significant drug-drug interactions with Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir include lamivudine, tenofovir, emtricitabine, abacavir, dolutegravir, raltegravir, rilpivirine, and enfuvirtide; (6) Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir (Vosevi): Has some drug-drug interactions with certain anti-retrovirals mentioned before. But some of the anti-retrovirals do not have significant interactions with this combination (Vosevi). These include lamivudine, emtricitabine, dolutegravir, enfuvirtide, raltegravir and rilpivirine; (7) Simeprevir (used in combination with another DAA): Does not have significant drug-drug interactions with certain anti-retrovirals which include lamivudine, tenofovir, emtricitabine, abacavir, dolutegravir, raltegravir, rilpivirine, enfuvirtide and maraviroc; and (8) Daclatasvir (used in combination with another DAA): Has significant drug-drug interactions with certain anti-retrovirals mentioned before. Certain dose adjustment include: cobicistat/atazanavir (decrease dose to 30 mg/d), cobicistat/elvitegravir (decrease dose to 30 mg/d), ritonavir/atazanavir (decrease dose to 30 mg/d), and efavirenz or etravirine (increase dose to 90 mg/d).
HCV infection in post-liver transplant patients
Recurrence of hepatitis C infection following liver transplantation is universal in all patients with pre-transplantation viremia. The course varies from asymptomatic infection to fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis[71]. About one third of post-transplant HCV-infected patients develop allograft cirrhosis 5 to 7 years after transplantation[72]. As per AASLD and IDSA guidelines published on September 21, 2017 the various treatment options are list in Table 7[66].
Table 7.
Recommended and alternative therapy
| Genotype | Treatment-naïve and - experienced patients with HCV infection in the allograft without cirrhosis | Treatment-naïve and - experienced patients with HCV infection in the allograft with compensated cirrhosis | Treatment-naïve and - experienced patients with HCV infection in the allograft with decompensated cirrhosis |
| Recommended therapy | |||
| 1, 4, 5 or 6 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk or Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) for 12 wk | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) with weight-based ribavirin - 12 wk | Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) with initial low dose of ribavirin (600 mg), increase the dose as tolerated - 12 wk |
| 2 or 3 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) - 12 wk or Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with initial low dose of ribavirin (600 mg), increase the dose as tolerated for 12 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with initial low dose of ribavirin (600 mg), increase the dose as tolerated - 12 wk | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with initial low dose of ribavirin (600 mg), increase the dose as tolerated for 12 wk or Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) with weight-based ribavirin - 12 wk |
| Alternative therapy | |||
| 1, 4, 5 or 6 | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with initial low dose of ribavirin (600 mg), increase the dose as tolerated for 12 wk or HCV genotype 1 or 4 infection only: Simeprevir (Olysio) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with or without weight-based ribavirin | Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with initial low dose of ribavirin (600 mg), increase the dose as tolerated for 12 wk or HCV genotype 1 or 4 infection only: Simeprevir (Olysio) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) with or without weight-based ribavirin | |
| 2 or 3 | Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret) for 12 wk or Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) with weight-based ribavirin for 12 wk | ||
HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
There are drug-drug interactions between DAA and calcineurin inhibitors: cyclosporine A and Tacrolimus. When Sofosbuvir is used with cyclosporine A, serum level of sofosbuvir is increased by 4.5 fold but GS -331007 metabolite remains unchanged. So no dose adjustment is required[73]. Sofosbuvir has no drug interaction with Tacrolimus[74]. When Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir and dasabuvir- (PrOD) in Viekira Pak and Viekira XR are used with cyclosporine A, there is 5.8 fold increased serum level of cyclosporine A suggesting use of 1/5th of dose of cyclosporine A and requirement of monitoring of serum level of cyclosporine A. When PrOD are used with tacrolimus, there is 57 fold increase in tacrolimus level in the blood, suggesting use of 0.5 mg of tacrolimus once a week, and monitoring of tacrolimus level in the blood[75]. When elbasvir/grazoprevir combination is used with cyclosporine A, there is 15 fold increases in grazoprevir level in the blood. As a result, this combination is not recommended to be used. When elbasvir/grazoprevir are used with tacrolimus, there is 43% increase in tacrolimus level, and although no prior dose adjustment is required, frequent monitoring of tacrolimus level, tacrolimus-associated side effects and renal function should be done[76]. When glecaprevir/pibrentasvir is used with higher dose (400 mg) of cyclosporine A, there is 5 fold increase in glecaprevir level in the blood. This combination is not recommended in patients requiring more than 100 mg of cyclosporine A[77]. When glecaprevir/pibrentasvir combination is used with tacrolimus, there is 1.45 fold increase in tacrolimus level suggesting no prior dose adjustment but tacrolimus level should be monitored. When sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir combination is used with cyclosporine A, there is 9.4 fold increase in voxilaprevir. This combination is not recommended[78].
DAA and hepatocellular carcinoma
Concern emerged after the study done by Reig et al[79] in 2016 showing higher rate of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) recurrence after DAA treatment in patients with prior HCC. Subsequently few studies were done to evaluate this finding. Large VA cohort study did not find any increased risk of developing HCC after DAA therapy[80]. Fortunately, the concern has lost its importance. But all cirrhotic patients should be under surveillance for HCC after DAA therapy.
DAA failure
DAA failure or relapse has occurred in less than 10% of HCV infected patients in clinical trials. In a multicenter real life study, the overall failure rate was found to be 3.6%[81]. As mentioned before, HCV exists as a quasispecies with production of various genetically distinct variants due to replication errors. Due to this high mutation rate of HCV genome, changes in the critical coding regions may occur making the virus less susceptible to anti-HCV therapy. Viral variants containing polymorphisms or substitutions resistant to DAA are also called baseline resistant-associated substitutions (RASs) and they exist in a small percentage of patients with chronic HCV infection prior to anti-HCV therapy. Sometimes RASs develop after initiation of DAA therapy when they are called treatment-emergent or treatment-selected RASs. Subtherapeutic DAA level may predispose to the development of RASs. NS5A and NS3 RASs are frequently seen in cases of failure of DAA containing NS5A or NS3 inhibitor[82]. On the other hand, there is rare development of NS5B RASs even after exposure to a failed DAA therapy containing. NS5B inhibitor, possibly due to binding of NS5B inhibitor to the highly conserved catalytic site of the viral genome making generation of RASs extremely difficult[83].
AASLD and IDSA recommend testing for NS5A RASs if DAAs containing NS5A inhibitors fail[82]. Testing for baseline NS5A RASs is recommended in patients infected with HCV genotype 1a prior to initiation of elbasvir and grazoprevir therapy[84]. Baseline NS5A RASs testing should also be considered in patients with cirrhosis of liver due to HCV genotype 1a infection prior to sofosbuvir plus daclatasvir therapy[85]. NS5A RASs testing should be considered in certain situations: (1) treatment-naïve HCV genotype 3 infection with compensated cirrhosis of liver prior to treatment with either Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) for 12 wk or Daclatasvir (Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) for 24 wk; (2) treatment-experienced HCV genotype 3 infection without cirrhosis prior to treatment with Daclatasvir(Daklinza) plus Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) for 12 wk; and (3) treatment-experienced HCV genotype 3 infection with or without cirrhosis prior to treatment with Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Epclusa) for 12 wk. If Y93H is found, weight-based ribavirin should be added[82]. DAA failure has been associated with certain predisposing factors like presence of RASs, sofosbuvir/ribavirin treatment, HCV genotype 3, and cirrhosis of liver[81,86].
CONCLUSION
DAAs have changed the treatment plan and outcome of chronic hepatitis C infection in this pegylated interferion free era. There are various DAAs available in the market and these include second generation NS3/4A protease inhibitors, NS5A and NS5B inhibitors. AASLD, IDSA and EASL recommend combination of DAAs with or without ribavirin. As the success rate is high, side effects are low, drug-drug interactions are less, and duration of therapy is relatively short, more and more patients are getting treatment for the cure of hepatitis C infection. Some DAAs require preliminary testing to find out the effectiveness of that particular DAA, for example Q80K polymorphism in case of Simeprevir, and NS5A resistance testing in case of elabasvir. HBV co-infection testing should be done prior to initiation of any DAA therapy to prevent fulminant hepatitis and liver failure. Drug-drug interaction, and specific conditions like HCV/HIV co-infection and HCV infection in post-liver transplant patients should considered before initiating any treatment plan. Although DAA can eradicate HCV infection, it does not decrease the chance of developing HCC in cirrhotic patients. So they should be under regular HCC surveillance. The next challenge will be the development of HCV vaccine to reduce the incidence of HCV infection in the world.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Peer-review started: April 11, 2018
First decision: May 2, 2018
Article in press: May 24, 2018
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: United States
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): D
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Blackadar C, Santos-Lopez G S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Bian YN
References
- 1.Petruzziello A, Marigliano S, Loquercio G, Cozzolino A, Cacciapuoti C. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: An up-date of the distribution and circulation of hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:7824–7840. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pawlotsky JM. NS5A inhibitors in the treatment of hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2013;59:375–382. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ogata N, Alter HJ, Miller RH, Purcell RH. Nucleotide sequence and mutation rate of the H strain of hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:3392–3396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pawlotsky JM. Hepatitis C virus population dynamics during infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;299:261–284. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26397-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Myers RP, Regimbeau C, Thevenot T, Leroy V, Mathurin P, Opolon P, Zarski JP, Poynard T. Interferon for interferon naive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD000370. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Palumbo E. Pegylated interferon and ribavirin treatment for hepatitis C virus infection. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2011;2:39–45. doi: 10.1177/2040622310384308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Meyer S, Dierynck I, Ghys A, Beumont M, Daems B, Van Baelen B, Sullivan JC, Bartels DJ, Kieffer TL, Zeuzem S, et al. Characterization of telaprevir treatment outcomes and resistance in patients with prior treatment failure: results from the REALIZE trial. Hepatology. 2012;56:2106–2115. doi: 10.1002/hep.25962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chatel-Chaix L, Baril M, Lamarre D. Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease Inhibitors: A Light at the End of the Tunnel. Viruses. 2010;2:1752–1765. doi: 10.3390/v2081752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Salam KA, Akimitsu N. Hepatitis C virus NS3 inhibitors: current and future perspectives. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:467869. doi: 10.1155/2013/467869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jacobson IM, Dore GJ, Foster GR, Fried MW, Radu M, Rafalsky VV, Moroz L, Craxi A, Peeters M, Lenz O, et al. Simeprevir with pegylated interferon alfa 2a plus ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (QUEST-1): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;384:403–413. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Manns M, Marcellin P, Poordad F, de Araujo ES, Buti M, Horsmans Y, Janczewska E, Villamil F, Scott J, Peeters M, et al. Simeprevir with pegylated interferon alfa 2a or 2b plus ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (QUEST-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2014;384:414–426. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Forns X, Lawitz E, Zeuzem S, Gane E, Bronowicki JP, Andreone P, Horban A, Brown A, Peeters M, Lenz O, et al. Simeprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin leads to high rates of SVR in patients with HCV genotype 1 who relapsed after previous therapy: a phase 3 trial. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1669–79.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.02.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lawitz E, Sulkowski MS, Ghalib R, Rodriguez-Torres M, Younossi ZM, Corregidor A, DeJesus E, Pearlman B, Rabinovitz M, Gitlin N, et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir, with or without ribavirin, to treat chronic infection with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 in non-responders to pegylated interferon and ribavirin and treatment-naive patients: the COSMOS randomised study. Lancet. 2014;384:1756–1765. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kwo P, Gitlin N, Nahass R, Bernstein D, Etzkorn K, Rojter S, Schiff E, Davis M, Ruane P, Younes Z, et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir (12 and 8 weeks) in hepatitis C virus genotype 1-infected patients without cirrhosis: OPTIMIST-1, a phase 3, randomized study. Hepatology. 2016;64:370–380. doi: 10.1002/hep.28467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lawitz E, Matusow G, DeJesus E, Yoshida EM, Felizarta F, Ghalib R, Godofsky E, Herring RW, Poleynard G, Sheikh A, et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and cirrhosis: A phase 3 study (OPTIMIST-2) Hepatology. 2016;64:360–369. doi: 10.1002/hep.28422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cunha JP. 2017. Olysio Side Effects Center. Last reviewed on May 25. Available from: https://www.rxlist.com/olysio-side-effects-drug-center.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vidal LL, Soares MA, Santos AF. NS3 protease polymorphisms and genetic barrier to drug resistance of distinct hepatitis C virus genotypes from worldwide treatment-naïve subjects. J Viral Hepat. 2016;23:840–849. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.OLYSIO. Potentially significant drug interactions—drug-drug interactions (DDIs) [Internet] Available from: https://www.olysio.com/hcp/safety-profile/drug-interactions.
- 19.Hussaini T. Paritaprevir/ritonavir-ombitasvir and dasabuvir, the 3D regimen for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a concise review. Hepat Med. 2016;8:61–68. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S72429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Viekira XR. An individualized approach for patients like Michael—with renal impairment [Internet]. Available from: https://www.viekira.com/hcp/individualized-approaches/michael-renal-impairment.
- 21.Viekira Pak and Viekira XR [Internet]. Available from: http://hepatitiscmedications.hcvadvocate.org/viekira-pak/
- 22.Pockros PJ, Reddy KR, Mantry PS, Cohen E, Bennett M, Sulkowski MS, Bernstein DE, Cohen DE, Shulman NS, Wang D, et al. Efficacy of Direct-Acting Antiviral Combination for Patients With Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection and Severe Renal Impairment or End-Stage Renal Disease. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1590–1598. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Raedler LA. Viekira Pak (Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir Tablets; Dasabuvir Tablets): All-Oral Fixed Combination Approved for Genotype 1 Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2015;8:142–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Viekira PakTM and Drug Interaction Information for Patients. Available from: https://www.hepatitis.va.gov/pdf/viekira-drug-interactions.pdf.
- 25.Ahmed H, Abushouk AI, Menshawy A, Attia A, Mohamed A, Negida A, Abdel-Daim MM. Meta-Analysis of Grazoprevir plus Elbasvir for Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection. Ann Hepatol. 2018;17:18–32. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.7532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Roth D, Nelson DR, Bruchfeld A, Liapakis A, Silva M, Monsour H Jr, Martin P, Pol S, Londoño MC, Hassanein T, Zamor PJ, Zuckerman E, Wan S, Jackson B, Nguyen BY, Robertson M, Barr E, Wahl J, Greaves W. Grazoprevir plus elbasvir in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (the C-SURFER study): a combination phase 3 study. Lancet. 2015;386:1537–1545. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Al-Salama ZT, Deeks ED. Elbasvir/Grazoprevir: A Review in Chronic HCV Genotypes 1 and 4. Drugs. 2017;77:911–921. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0739-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Foster GR, Agarwal K, Cramp ME, Moreea S, Barclay S, Collier J, Brown AS, Ryder SD, Ustianowski A, Forton DM, et al. Elbasvir/grazoprevir and sofosbuvir for hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection with compensated cirrhosis: A randomized trial. Hepatology. 2018;67:2113–2126. doi: 10.1002/hep.29852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Drugs without clinically significant interactions with zepatier. Available from: https://www.merckconnect.com/zepatier/drug-interactions.html?hcpUser=yes.
- 30.Forns X, Lee SS, Valdes J, Lens S, Ghalib R, Aguilar H, Felizarta F, Hassanein T, Hinrichsen H, Rincon D, et al. Glecaprevir plus pibrentasvir for chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 infection in adults with compensated cirrhosis (EXPEDITION-1): a single-arm, open-label, multicentre phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:1062–1068. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30496-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zeuzem S, Foster GR, Wang S, Asatryan A, Gane E, Feld JJ, Asselah T, Bourlière M, Ruane PJ, Wedemeyer H, et al. Glecaprevir-Pibrentasvir for 8 or 12 Weeks in HCV Genotype 1 or 3 Infection. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:354–369. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1702417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gane E, Lawitz E, Pugatch D, Papatheodoridis G, Bräu N, Brown A, Pol S, Leroy V, Persico M, Moreno C, et al. Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir in Patients with HCV and Severe Renal Impairment. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1448–1455. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1704053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Warning: Risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients coinfected with HCV and HBV. Highlights of prescribing information. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209394s000lbl.pdf.
- 34.Mavyret (glecaprevir and pibrentasvir). Available from: https://www.rxlist.com/mavyret-drug.htm.
- 35.Bourlière M, Gordon SC, Flamm SL, Cooper CL, Ramji A, Tong M, Ravendhran N, Vierling JM, Tran TT, Pianko S, et al. Sofosbuvir, Velpatasvir, and Voxilaprevir for Previously Treated HCV Infection. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2134–2146. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1613512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chahine EB, Kelley D, Childs-Kean LM. Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir: A Pan-Genotypic Direct-Acting Antiviral Combination for Hepatitis C. Ann Pharmacother. 2018;52:352–363. doi: 10.1177/1060028017741508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.GILEAD. Available from: http://www.gilead.com/~/media/Files/pdfs/medicines/liver-disease/vosevi/vosevi_pi.pdf.
- 38.Targett-Adams P, Graham EJ, Middleton J, Palmer A, Shaw SM, Lavender H, Brain P, Tran TD, Jones LH, Wakenhut F, et al. Small molecules targeting hepatitis C virus-encoded NS5A cause subcellular redistribution of their target: insights into compound modes of action. J Virol. 2011;85:6353–6368. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00215-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P, Chojkier M, Gitlin N, Puoti M, Romero-Gomez M, Zarski JP, Agarwal K, Buggisch P, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1889–1898. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Afdhal N, Reddy KR, Nelson DR, Lawitz E, Gordon SC, Schiff E, Nahass R, Ghalib R, Gitlin N, Herring R, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for previously treated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1483–1493. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1316366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Reddy KR, Bourlière M, Sulkowski M, Omata M, Zeuzem S, Feld JJ, Lawitz E, Marcellin P, Welzel TM, Hyland R, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir in patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection and compensated cirrhosis: An integrated safety and efficacy analysis. Hepatology. 2015;62:79–86. doi: 10.1002/hep.27826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Crespo J, Calleja JL, Fernández I, Sacristan B, Ruiz-Antorán B, Ampuero J, Hernández-Conde M, García-Samaniego J, Gea F, Buti M, et al. Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Oral Combination Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 4 Infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:945–949.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Abergel A, Asselah T, Metivier S, Kersey K, Jiang D, Mo H, Pang PS, Samuel D, Loustaud-Ratti V. Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 5 infection: an open-label, multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:459–464. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gane EJ, Hyland RH, An D, Svarovskaia E, Pang PS, Brainard D, Stedman CA. Efficacy of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir, with or without ribavirin, for 12 weeks in patients with HCV genotype 3 or 6 infection. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1454–1461.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Charlton M, Everson GT, Flamm SL, Kumar P, Landis C, Brown RS Jr, Fried MW, Terrault NA, O’Leary JG, Vargas HE, Kuo A, Schiff E, Sulkowski MS, Gilroy R, Watt KD, Brown K, Kwo P, Pungpapong S, Korenblat KM, Muir AJ, Teperman L, Fontana RJ, Denning J, Arterburn S, Dvory-Sobol H, Brandt-Sarif T, Pang PS, McHutchison JG, Reddy KR, Afdhal N; SOLAR-1 Investigators. Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir Plus Ribavirin for Treatment of HCV Infection in Patients With Advanced Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:649–659. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.GILEAD. Available from: https://www.gilead.com/~/media/Files/pdfs/medicines/liver-disease/harvoni/harvoni_pi.pdf.
- 47.Gandhi Y, Eley T, Fura A, Li W, Bertz RJ, Garimella T. Daclatasvir: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018;57:911–928. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0624-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nelson DR, Cooper JN, Lalezari JP, Lawitz E, Pockros PJ, Gitlin N, Freilich BF, Younes ZH, Harlan W, Ghalib R, et al. All-oral 12-week treatment with daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection: ALLY-3 phase III study. Hepatology. 2015;61:1127–1135. doi: 10.1002/hep.27726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Leroy V, Angus P, Bronowicki JP, Dore GJ, Hezode C, Pianko S, Pol S, Stuart K, Tse E, McPhee F, et al. Daclatasvir, sofosbuvir, and ribavirin for hepatitis C virus genotype 3 and advanced liver disease: A randomized phase III study (ALLY-3+) Hepatology. 2016;63:1430–1441. doi: 10.1002/hep.28473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wyles DL, Ruane PJ, Sulkowski MS, Dieterich D, Luetkemeyer A, Morgan TR, Sherman KE, Dretler R, Fishbein D, Gathe JC Jr, Henn S, Hinestrosa F, Huynh C, McDonald C, Mills A, Overton ET, Ramgopal M, Rashbaum B, Ray G, Scarsella A, Yozviak J, McPhee F, Liu Z, Hughes E, Yin PD, Noviello S, Ackerman P; ALLY-2 Investigators. Daclatasvir plus Sofosbuvir for HCV in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:714–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1503153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pol S, Corouge M, Vallet-Pichard A. Daclatasvir-sofosbuvir combination therapy with or without ribavirin for hepatitis C virus infection: from the clinical trials to real life. Hepat Med. 2016;8:21–26. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S62014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Garimella T, You X, Wang R, Huang SP, Kandoussi H, Bifano M, Bertz R, Eley T. A Review of Daclatasvir Drug-Drug Interactions. Adv Ther. 2016;33:1867–1884. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0407-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cada DJ, Kim AP, Baker DE. Elbasvir/Grazoprevir. Hosp Pharm. 2016;51:665–686. doi: 10.1310/hpj5108-665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zeuzem S, Ghalib R, Reddy KR, Pockros PJ, Ben Ari Z, Zhao Y, Brown DD, Wan S, DiNubile MJ, Nguyen BY, et al. Grazoprevir-Elbasvir Combination Therapy for Treatment-Naive Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1, 4, or 6 Infection: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:1–13. doi: 10.7326/M15-0785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kwo P, Gane EJ, Peng CY, Pearlman B, Vierling JM, Serfaty L, Buti M, Shafran S, Stryszak P, Lin L, et al. Effectiveness of Elbasvir and Grazoprevir Combination, With or Without Ribavirin, for Treatment-Experienced Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:164–175.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Feld JJ, Jacobson IM, Hézode C, Asselah T, Ruane PJ, Gruener N, Abergel A, Mangia A, Lai CL, Chan HL, et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 Infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2599–2607. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1512610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Curry MP, O’Leary JG, Bzowej N, Muir AJ, Korenblat KM, Fenkel JM, Reddy KR, Lawitz E, Flamm SL, Schiano T, et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2618–2628. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1512614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.GILEAD. Available from: https://www.gilead.com/~/media/files/pdfs/medicines/liver-disease/epclusa/epclusa_pi.pdf.
- 59.Vachon ML, Dieterich DT. The era of direct-acting antivirals has begun: the beginning of the end for HCV? Semin Liver Dis. 2011;31:399–409. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1297928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bhatia HK, Singh H, Grewal N, Natt NK. Sofosbuvir: A novel treatment option for chronic hepatitis C infection. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2014;5:278–284. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.142464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ferreira VL, Assis Jarek NA, Tonin FS, Borba HH, Wiens A, Muzzillo DA, Pontarolo R. Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir with or without ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C genotype 1: A pairwise meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:749–755. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.El-Khayat H, Fouad Y, Mohamed HI, El-Amin H, Kamal EM, Maher M, Risk A. Sofosbuvir plus daclatasvir with or without ribavirin in 551 patients with hepatitis C-related cirrhosis, genotype 4. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47:674–679. doi: 10.1111/apt.14482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zeuzem S, Dusheiko GM, Salupere R, Mangia A, Flisiak R, Hyland RH, Illeperuma A, Svarovskaia E, Brainard DM, Symonds WT, et al. Sofosbuvir and ribavirin in HCV genotypes 2 and 3. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1993–2001. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1316145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sovaldi. Available from: https://www.rxlist.com/sovaldi-drug.htm#indications_dosage.
- 65.European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2016. J Hepatol. 2017;66:153–194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.AASLD-IDSA. 2017. Recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C. Available from: http://hcvguidelines.org/ [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hernandez MD, Sherman KE. HIV/hepatitis C coinfection natural history and disease progression. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2011;6:478–482. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32834bd365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Thein HH, Yi Q, Dore GJ, Krahn MD. Natural history of hepatitis C virus infection in HIV-infected individuals and the impact of HIV in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: a meta-analysis. AIDS. 2008;22:1979–1991. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32830e6d51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.AIDSinfo. Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents Living with HIV. Available from: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv/26/hcv-hiv.
- 70.Bhattacharya D, Belperio PS, Shahoumian TA, Loomis TP, Goetz MB, Mole LA, Backus LI. Effectiveness of All-Oral Antiviral Regimens in 996 Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1-Coinfected Patients Treated in Routine Practice. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64:1711–1720. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mitchell O, Gurakar A. Management of Hepatitis C Post-liver Transplantation: a Comprehensive Review. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2015;3:140–148. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2015.00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Vinaixa C, Rubín A, Aguilera V, Berenguer M. Recurrence of hepatitis C after liver transplantation. Ann Gastroenterol. 2013;26:304–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Talavera Pons S, Boyer A, Lamblin G, Chennell P, Châtenet FT, Nicolas C, Sautou V, Abergel A. Managing drug-drug interactions with new direct-acting antiviral agents in chronic hepatitis C. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83:269–293. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Drug interactions with Sofosbuvir. Available from: http://www.hcvdruginfo.ca/downloads/Hepatitis%20C-sofosbuvir%20int.pdf.
- 75.Drug interactions with ABBVIE’S 3D regimen. Available from: http://hcvdruginfo.ca/downloads/Hepatitis%20C-int_Abbvie%203D%20regimen.pdf.
- 76.Faragon JJ. Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (Zepatier™) Drug Interactions A Quick Guide for Clinicians. Available from: https://aidsetc.org/sites/default/files/resources_files/ELBGRZ%20HIV_and_HCV_Drug_Interaction_Quick_Guide%20February%202018.pdf.
- 77.Faragon JJ. Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (Mavyret™) Drug Interactions A Quick Guide for Clinicians. Available from: https://aidsetc.org/sites/default/files/resources_files/PBRGCPHIV_and_HCV_Drug_Interaction_Quick_Guide%20February%202018.pdf.
- 78.FDA. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209195s000lbl.pdf.
- 79.Reig M, Mariño Z, Perelló C, Iñarrairaegui M, Ribeiro A, Lens S, Díaz A, Vilana R, Darnell A, Varela M, et al. Unexpected high rate of early tumor recurrence in patients with HCV-related HCC undergoing interferon-free therapy. J Hepatol. 2016;65:719–726. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kanwal F, Kramer J, Asch SM, Chayanupatkul M, Cao Y, El-Serag HB. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in HCV Patients Treated With Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:996–1005.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kondili LA, Gaeta GB, Brunetto MR, Di Leo A, Iannone A, Santantonio TA, Giammario A, Raimondo G, Filomia R, Coppola C, et al. Incidence of DAA failure and the clinical impact of retreatment in real-life patients treated in the advanced stage of liver disease: Interim evaluations from the PITER network. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0185728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C. Available from: http://www.hcvguidelines.org/full-report-view.
- 83.Svarovskaia ES, Dvory-Sobol H, Parkin N, Hebner C, Gontcharova V, Martin R, Ouyang W, Han B, Xu S, Ku K, et al. Infrequent development of resistance in genotype 1-6 hepatitis C virus-infected subjects treated with sofosbuvir in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:1666–1674. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zepatier™ [package insert]. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck Co Inc, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Daklinza™ [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Co, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Boesecke C, Ingiliz P, Berger F, Lutz T, Schewe K, Schulze Zur Wiesch J, Baumgarten A, Christensen S, Rockstroh JK, Mauss S; GECCO Study Group. Liver Cirrhosis as a Risk Factor for Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy Failure in Real-Life Hepatitis C Virus/Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4:ofx158. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofx158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


