Abstract
Aim:
In our study, two different methods were used to determine the size and size distribution of the sliver and selenium nanoparticles via dynamic light scattering (DLS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Background:
Nanotechnology dealing with metal and metalloid nanoparticles has been usually applied in nearly each field of science, engineering, and technology including biology and medicine etc due to presence of size and shape dependent unusual physical and chemical properties. In the most recent decade, numerous groups including appreciably developed metal and metalloid nanoparticles based theranostic approaches for the treatment of almost human diseases. Amongst many nanoparticles, recently silver and selenium nanoparticles have been broadly used in the antimicrobial coatings, textiles, paints, keyboards, engineering, food industry, electronics, cosmetics, bio-sensing, wound dressings, and even in biomedical devices.
Methods:
In our study, silver nanoparticles were prepared by using the chemical reduction method. Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) were synthesized by the chemical reduction of sodium selenite by glutathione (reduced form) and stabilized by bovine serum albumin (BSA). Characterization of silver and selenium nanoparticles samples were analyzed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM).
Conclusions:
Due to characterization by DLS technique, nanoparticles size was found the range of 79.22 nm and 178 nm for Sliver and Selenium Nanoparticles respectively. Sliver nanoparticles shown morphological average size and shape with SEM reveals spherical shape particles with the size of 80.32 nm whereas Selenium nanoparticles shown rod shape particles with the size of 74.29 nm.
Keywords: Biomedical devices, dynamic light scattering, microbial infections, nanotechnology, scanning electron microscopy, selenium nanoparticles
INTRODUCTION
Nanosized materials possess desirable novel and superior properties to macrosized materials, and homogeneous nanoparticle suspensions play an important role in many scientific and industrial applications, for example, in colloidal science,[1] nanotoxicological studies,[2] high thermal conductivity fluids,[3] and nanofluidics.[4] In these applications, the recent experience has identified the need for a well-defined and accurate method of characterizing nanoparticles in suspension. Among the available experimental methods (e.g., photocentrifuges, X-ray disc centrifuges, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and scanning mobility particle sizer), dynamic light scattering can provide information about particles with sizes in the range from a few nanometers to several micrometers. Even though the application of DLS to particle sizing in dilute solutions has become increasingly common because the diffusion of particles in a solution is influenced by the kinetic and hydrodynamic conditions, the repeatability and the uncertainty of DLS measurements are often insufficient to accurately evaluate the real size of nanoparticles.
Silver and its compounds are known to have antimicrobial properties. Early in the 19th century, 0.5% AgNO3 was used for the treatment and prevention of microbial infections such as ophthalmia neonatorum (by German obstetrician Carl Crede). When the era of antibiotics began with the discovery of penicillin, the use of silver slowly diminished;[5] however, currently, due to the lack of effectiveness of conventional drugs, the use of silver for treating infections has regained importance. However, the use of ionic silver has one major flaw: it is easily inactivated by complexation and precipitation. As a result, the use of silver ions has been limited.[6] Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), which are zerovalent, can be a valuable alternative to ionic silver (Sintubin et al.,).[7] AgNPs are a nontoxic and safe antibacterial agent[8,9] for the human body. In addition, nano-Ags are also reported to possess antifungal activity,[10] anti-inflammatory properties,[11] antiviral activity,[12] and antiangiogenic activity.[13] Nano-Ags can be applied safely in therapy when the effective concentrations against various types of organisms have been determined.
Selenium (Se) is an essential element in human and animal body in low concentration. It is a necessary dietary constituent of at least 25 human selenoproteins and enzymes-containing selenocysteine.[14] In the environment, it exists in many oxidation states (−2, 0, +4, and +6) and forms such as ionic selenite (Na2SeO3) and selenate (Na2SeO4), solid-state Se (0), and selenomethionine (SeMet)/selenocysteine.[15,16] Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) can be synthesized through physical methods such as laser ablation, UV radiation, and hydrothermal techniques.[17,18] Chemical synthesis is mediated by precipitation, acid decomposition, and catalytic reduction using ascorbic acid, glucose, sulfur dioxide, and sodium dodecyl sulfate.[19,20]
Metal and metalloid nanoparticles have been frequently useful in almost every field of science, and technology including biomedical, due to the presence of small size-dependent and shape-dependent curious physical and chemical properties. In last decades, applications of Ag-based and Se-based nanoparticles were discussed in the field of infectious diseases treatment such as biofilms on medical devices[21,22] and as an antimicrobial.[8,9] In other aspect, other researchers Haris and Khan[23] studied that novel SeNPs-enhanced photodynamic therapy of toluidine blue O against biofilm forming Streptococcus mutans bacterial isolates. Haris and Ahmad[24] were studied the impact of metal oxide (ZnO and TiO2) nanoparticles on beneficial soil microorganisms and their secondary metabolites. The antibacterial potential of nanoparticles was determined by growth kinetics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Soni[25] was discussed the biodegradable nanoparticles for delivering drugs and silencing multiple genes or gene activation in diabetic nephropathy. Chauhan et al.[26] were also discussed the applications of nanotechnology in forensic investigation that reveals the hidden evidence, which can prove to be helpful for the forensic scientists to give an outcome to their investigation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals
All chemicals of silver and selenium nanoparticles used in this experiment were highest purified and purchased from Central Drug House (P) Ltd, Delhi, India. Distilled water was also used for the preparation of reagents. Further study was done at Department of Biotechnology, IFTM University Moradabad, India.
Preparation of nanoparticles using the chemical reduction method
Preparation of silver nanoparticles
In this study, silver colloid was prepared by using the chemical reduction method. All solutions of reacting materials were prepared in distilled water.
Solution 1: 0.0849 g of silver nitrate (AgNO3) was dissolved in 500 ml of distilled water, and then the solution was heated to boiling
Solution 2: Then, 1 g of trisodium citrate (C6H5O7Na3) was dissolved in 100 ml of distilled water
Working solution: Five ml of trisodium citrate was added to 500 ml of AgNO3 after boiling (drop by drop). During the process, the solution was forcefully mixed. The solution was left on hot plate for 2 h at 90°C for heated (uncontinuous manner) then it was cooled at room temperature, the color was reddish-green[27] appeared. Prepared AgNPs were collected in 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube and kept at room temperature for further experiment.
Preparation of selenium nanoparticles
SeNPs were synthesized by the chemical reduction of sodium selenite by glutathione (reduced form) and stabilized by bovine serum albumin (BSA). Specifically, 3 ml of 25 mM Na2SeO3, 3 mL of 100 mM GSH, and 0.15 g BSA were added to 9 ml of double-distilled water (dH2O) in a sterile cabinet. All solutions were made in a sterile environment using a sterile cabinet and double-distilled water. After mixing the reactant solution, 1M NaOH was added to bring the pH of the solution to the alkaline media. SeNPs were formed immediately following the addition of NaOH as visualized by a color change of the reactant solution from clear white to clear red color. Then, SeNPs were collected by centrifuging (Cooling centrifuge C-24 BL) the solution at 13,000 rpm at −4°C temperature with 30-min duration sterilized by ultraviolet light exposure, before use in bacteria experiment.[28] Prepared SeNPs were collected in 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube and were kept at room temperature for further experiment.
Characterization of silver and selenium nanoparticles
Particle size analyzer (dynamic light scattering)
DLS was used to measure the hydrodynamic diameter. The particle size of the AgNPs sample was analyzed by DLS using the Litesizer™ 500 under the following conditions (at wavelength 658 nm, particle absorption coefficient 0.01, diffusion coefficient 6.2 μm2/s, water refractive index 1.33, and intensity 79.67 nm). To measure the particle size, a volume of 0.1 ml of the AgNPs solution in 2 ml of deionized water (DI H2O) was placed in a polystyrene cuvette and measured at 25°C.[29]
SeNP sample was analyzed by DLS using the Microtrac, Bluewave model, Germany, under the following conditions (at water refractive index 1.33 and wavelength 780 nm). To measure the particle size, a volume of 0.1 mL of the SeNPs solution in 2 mL of deionized water (DI H2O) was placed in a polystyrene cuvette and calculated at 25°C temperature.[29]
Scanning electron microscopy
SEM is a type of electron microscope that takes the image to the sample by scanning with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern. The electrons interact with atoms that can make up the sample producing signals that hold information about the sample's surface topography, composition, and other properties such as electrical conductivity. Nanoparticles of the silver colloid were prepared using chemical reduction method whereas SeNPs were synthesized by the reduction of sodium selenite by glutathione (reduced form) and stabilized by BSA. Nanoparticles (Ag and Se) were sterilized by ultraviolet light in laminar air flow. The sterilized nanoparticles were carefully mounted on SEM stubs by using adhesive tape and uniformly coated with Gold. Both nanoparticles samples were placed in a sample chamber of SEM (JEOL JSM-6490 LV, Japan) and scanning was performed under different magnifications ranging from ×15,000 to ×35,000 and voltage 20–30 kV.[27,28,29,30]
RESULTS
Preparation of silver and selenium nanoparticles
AgNPs synthesis adopting chemical reduction process was primarily confirmed by the color change in the reaction mixture from pale yellow to reddish-green clearly indicating to the synthesis of AgNPs.[27] The reddish-green color's formation was observed within 10 min after the dropwise addition of trisodium citrate to the silver nitrate solution. The antibacterial activity of AgNPs (consisting of silver nitrate) and nanoparticle-coated face masks to protect against biofilm forming infectious agent Staphylococcus aureus. AgNPs are now extensively used as antimicrobial agents and utilized in the development of antimicrobial dressings and anti-microbial medical devices.
SeNPs were synthesized by the reduction of sodium selenite by glutathione (reduced form) and formed immediately following the addition of NaOH (make alkaline medium) as visualized by a color change of the reactant solution from clear white to clear red.[28] SeNPs were then collected by centrifuging (Cooling centrifuge C-24) at 13,000 rpm at −4°C for 30 min sterilized by ultraviolet light exposure.
Characterization of silver and selenium nanoparticles
Particle size analyzer (dynamic light scattering)
Particle size was determined using DLS measurement. The hydrodynamic diameters of AgNPs and SeNPs in aqueous solution were determined using DLS.
The particle size of the AgNPs sample was analyzed using DLS using the Litesizer™ 500 found 79.22 nm [Table 1] size under the following conditions: diffusion coefficient 6.2 μm2/s, water refractive index 1.33, intensity 79.67 nm, and temperature 25°C[31] under the 658-nm laser wavelength with an angle detection of 175° (backscatter). DLS method has several pitfalls, in particular, with respect to the influence of dust particles or small amounts of large aggregates in addition to a main component of distinctly smaller size.[32] In many chemical companies, sedimentation velocity analysis in the analytical ultracentrifuge has been a standard technique for studying size of the colloidal particles, frequently using noncommercial apparatus.[33] Figure 1 shows the size distribution by the intensity of AgNPs in solution and correlation function of AgNPs shows in Figure 2.
Table 1.
Measurement of the nanoparticles (Ag and Se) shape and size under different microscope
| Characteristics | DLS | SEM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | SeNPs | AgNPs | SeNPs | |
| Size (nm) | 79.22 | 178 | 80.32 | 74.29 |
| Shape | - | - | Spherical | Rod |
DLS: Dynamic light scattering, SEM: Scanning electron microscope, AgNPs: Silver nanoparticles, SeNPs: Selenium nanoparticles
Figure 1.
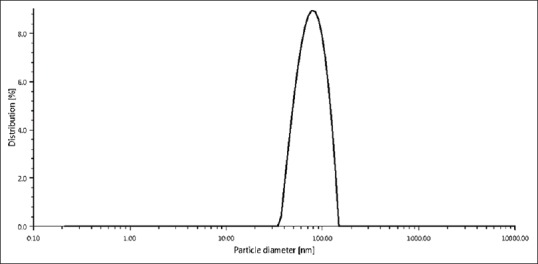
Dynamic light-scattering image of silver nanoparticles size distribution by the intensity in solution
Figure 2.
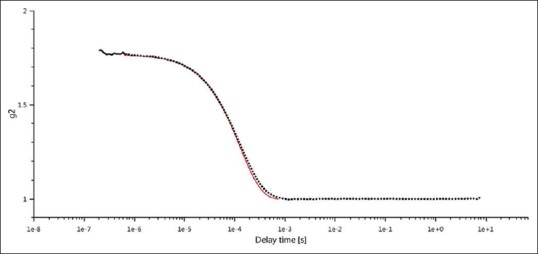
Dynamic light-scattering image of silver nanoparticles of correlation function
SeNP size sample was analyzed using DLS using the Microtrac, Bluewave model, Germany, in the range of 178 nm [Table 1], under the following conditions: laser wavelength 780 nm, water refractive index 1.33 at room temperature (25°C).[31] Figure 3 shows the size distribution by particles number of SeNPs in solution and size distribution by volume particles of SeNPs shows in Figure 4.
Figure 3.
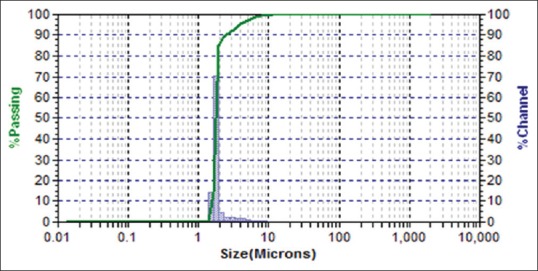
Dynamic light-scattering image of selenium nanoparticles size distribution by number of particles
Figure 4.
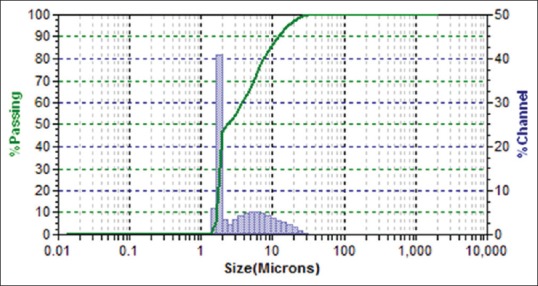
Dynamic light-scattering image of selenium nanoparticles size distribution by volume of particles
Scanning electron microscopy
The shape and size of the silver and SeNPs were measured using SEM. Particle morphology shape and size with SEM reveal that spherical shape with the size of the particle was in the range 80.32 nm for AgNPs [Figure 5, Table 1] whereas rods shape particles with the size of the particle were in the range 74.29 nm [Table 1] for SeNPs [Figure 6]. Smaller-sized Ag and Se nanoparticles have many positive attributes, such as good conductivity, chemical stability, and catalytic and antibacterial activities, which would make them suitable for many practical applications.
Figure 5.
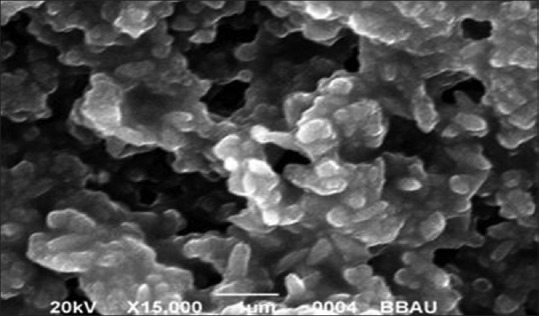
Scanning electron microscopy image of silver nanoparticles
Figure 6.
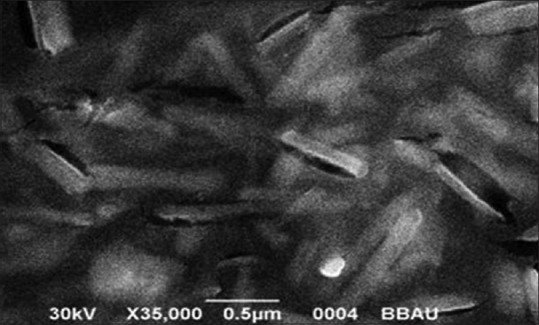
Scanning electron microscopy image of selenium nanoparticles
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces the sample images due to scanning the surface of the object with the focused beam of electrons and widely considered the gold standard for nanoparticle characterization.
DISCUSSION
Characterization of silver and selenium nanoparticles
Silver nanoparticles and selenium nanoparticles characterization by particle size analyzer (dynamic light scattering)
Two main types of particle size analyzers, i.e., DLS and laser particle analyzers. DLS, one of the most popular light-scattering modalities can probe the size distribution of small particles at the scale from submicron down to one nanometer in solution or suspension using a monochromatic light source.[34] DLS was used to measure the hydrodynamic diameter. DLS analyzers measure the particles in solutions in the 0.6 nm–6000 nm range of any nanoparticle. The main advantage of DLS is the short time required to perform the measurement and the relatively low cost of the apparatus, therefore, DLS become the preferred method for nanoparticle sizing.[32]
The DLS technique measures the diffusion coefficient of suspended nanoparticles undergoing Brownian motion in a solution by analyzing the fluctuating scattered intensity from the nanoparticles in the solution. The scattered light from the suspension of nanoparticles fluctuates in a characteristic time scale, i.e., inversely proportional to the particle diffusion coefficient. This can provide information about particles with sizes in the range from a few nanometers to several micrometers. Even though the application of DLS to particle sizing in dilute solutions has become increasingly common because the diffusion of particles in a solution is influenced by the kinetic and hydrodynamic conditions, the repeatability and the uncertainty of DLS measurements are often insufficient to accurately evaluate the real size of nanoparticles. In the case of a concentrated solution, these effects become more significant, and therefore, a process, extrapolating the concentration and scattering angle to extremely low values, is used to obtain the real size of nanoparticles in solutions.[35,36]
Figures 1 and 3 show the DLS pictures of AgNPs size distribution by the intensity in solution and SeNP size distribution by particle number, respectively, as well as Figures 2 and 4 show the DLS pictures of AgNPs of the correlation function and DLS image of SeNPs size distribution by particles volume, respectively. The particle size determined by DLS detector was slightly larger than the nominal size, probably because both methods measure a hydrodynamic size, rather than physical size.
In our result, we noticed that the synthesized AgNPs were polydispersed and polydispersity index was found in 18.9%, and AgNPs size 79.22 nm was analyzed. With respect to the observations made in the present study most literature report a similar particle size ranging of AgNPs from 55 to 85 nm by DLS[37] whereas for SeNP size found 178 nm was analyzed. Certain reports have, however, documented a very less particle size range 3–18 nm[38] and closely similar size range (30–150 nm) was found by Sarkar et al.[31]
Silver nanoparticles and selenium nanoparticles characterization by scanning electron microscopy
Nowadays, numerous microscopic techniques are commercially available, whenever transmission electron microscopy and SEM are the most popular microscopes for the analysis of the nanoparticles.
The shape and size of the silver and SeNPs were measured using SEM. The particle morphology shape and size with SEM reveal that spherical shape with the size of the particles was in the range 80.32 nm for AgNPs [Figure 5] showed close similarity with our result ranging from 60 to 80 nm[39,40,41,42] whereas rods-shape particles with the size of the particles was in the range 74.29 nm for SeNPs [Figure 6], showed similarity with our result ranging from 50 to 150 nm.[43]
CONCLUSION
Silver and SeNPs were successfully prepared by using the chemical reduction method. Both nanoparticles preparation confirmation was done by qualitative analysis, i.e., AgNPs appeared as a reddish-green color and SeNPs appeared as a clear white to clear red color, and characterization of NPs was shown by particle size analyzer (DLS) as well as SEM. By DLS, nanoparticles size was found the range of 79.22 nm and 178 nm for AgNPs and SeNPs, respectively, and through SEM, nanoparticles size was found the range of 80.32 nm with spherical as well as 74.29 nm with rods shape of AgNPs and SeNPs, respectively. These nanoparticles can be used as a therapeutic drug for various diseases such as antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, biofilm eradication, and cancer treatment. Smaller sizes of nanoparticles have great capacity to eradicate any disease due to the high surface area.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Brambilla G, Masri D E, Pierno M, Berthier L, Cipelletti L, Petekidis G, Schofield AB. Probing the equilibrium dynamics of colloidal hard spheres above the mode-coupling glass transition Phys.Rev. Lett. 2009;102:1–4. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.085703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Iker MB, Dorota W, Patrick H, Jonathan S, Iseult L, Kenneth D. Characterisation of nanoparticle size and state prior to nanotoxicological studies J.Nanopart. Res. 2010;12:47–53. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Madrid AP, Lapas LC, Rubi JM. Heat exchange between two interacting nanoparticles beyond the fluctuation-dissipation regime Phys.Rev. Lett. 2009;103:1–4. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.048301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schoch RB, Han J, Renaud P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics Rev.Mod. Phys. 2008;80:839–883. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Klasen HJ. Historical review of the use of silver in the treatment of burns. I. Early uses. Burns. 2000;26:117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0305-4179(99)00108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Atiyeh BS, Costagliola M, Hayek SN, Dibo SA. Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: review of the literature. Burns. 2007;33:139–148. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2006.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sintubin L, De Windt W, Dick J, Mast J, Van Der Ha D, Verstraete W, et al. Lactic acid bacteria as reducing and capping agent for the fast and efficient production of silver nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;84:741–9. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Verma P. A Review on synthesis and their antibacterial activity of Silver and Selenium nanoparticles against biofilm forming Staphylococcus aureus. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2015;4:652–77. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Verma P, Maheshwari SK. Minimum Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) assay of Silver and Selenium Nanoparticles against Biofilm forming Staphylococcus aureus. JMSCR. 2017;5:20213–22. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim KJ, Sung WS, Suh BK, Moon SK, Choi JS, Kim JG, et al. Antifungal activity and mode of action of silver nano-particles on Candida albicans. Biometals. 2009;22:235–42. doi: 10.1007/s10534-008-9159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nadworny PL, Wang J, Tredget EE, Burrell RE. Antiinflammatory activity of nanocrystalline silver in a porcine contact dermatitis model. Nanomedicine. 2008;4:241–51. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2008.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rogers JV, Parkinson CV, Choi YW, Speshock JL, Hussain SM. A preliminary assessment of silver nanoparticle inhibition of monkeypox virus plaque formation. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2008;3:129–33. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gurunathan S, Lee KJ, Kalishwaralal K, Sheikpranbabu S, Vaidyanathan R, Eom SH. Antiangiogenic properties of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2009;30:6341–50. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang J, Spallholz J. Toxicity of selenium compounds and nanoselenium particles. In: Casciano D, Sahu SC, editors. Handbook of Systems Toxicology. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley and Sons; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Biswas K, Barton L, Tsui W, Shuman K, Gillespie J, Eze C. A novel method for the measurement of elemental selenium produced by bacterial reduction of selenite. J Microbiol Methods. 2011;86:140–4. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2011.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bo Li D, Cheng Y, Wu C, Li W, Li N, Yang Z, et al. Selenite reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is mediated by fumarate reductase in periplasm. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3735. doi: 10.1038/srep03735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Iranifam M, Fathinia M, Sadeghi T, Hanifehpour Y, Khataee A, Joo S. A novel selenium nanoparticles-enhanced chemiluminescence system for determination of dinitrobutylphenol. Talanta. 2013;107:263–9. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.12.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Overschelde O, Guisbiers G, Snyders R. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by excimer pulsed laser ablation in water. Appl Mater. 2013;1:042114. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhang L. Creation of highly stable selenium nanoparticles capped with hyperbranched polysaccharide in water. Langmuir. 2010;26:17617–23. doi: 10.1021/la1033959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dwivedi C, Shah C, Singh K, Kumar M, Bajaj P. An organic acidinduced synthesis and characterization of selenium. Nanopart J Nanotechnol. 2011:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Verma P, Maheshwari SK, Mathur A. A review on Bacterial Biofilm Formation and Disassembly.Int. J Pharm Sci Res. 2013;4:2900–6. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Verma P, Singh S. Clinical distribution of Biofilm forming Staphylococcus aureus and its sensitivity against some antibiotics. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2015;4:942–52. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Haris Z, Khan AU. Selenium Nanoparticle Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy against Biofilm forming Streptococcus mutans. Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res. 2017;3:1287–94. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Haris Z, Ahmad I. Impact of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Beneficial Soil Microorganisms and their Secondary Metabolites. Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res. 2017;3:1020–30. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Soni NO. Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Delivering Drugs and Silencing Multiple Genes or Gene activation in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res. 2017;3:1329–38. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chauhan V, Singh V, Tiwari A. Applications of Nanotechnology in Forensic Investigation. Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res. 2017;3:1047–51. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sileikaite A, Puiso J, Prosycevas I, Tamulevicius S. Investigation of Silver Nanoparticles Formation Kinetics during Reduction of Silver Nitrate with Sodium Citrate. Materials Science. 2009;15:21–7. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tran PA, Webster TJ. Selenium nanoparticles inhibit Staphylococcus aureus growth. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:1553–8. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S21729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bootz A, Vogel V, Schubert D, Kreuter J. Comparison of scanning electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering and analytical ultracentrifugation for the sizing of poly (butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2004;57:369–75. doi: 10.1016/S0939-6411(03)00193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Razi MK, Maamoury RS, Banihashemi S. Preparation of nanoselenium particles by water solution phase method from industrial dust. dust. Int. J. Nano. Dim. 2011;1:261–7. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sarkar J, Dey P, Saha S, Acharya K. Mycosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles. Micro & Nano Letters. 2011;6:599–602. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Berne B, Pecora R. Dynamic Light Scattering with Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics, Dover Publications, Mineola, NY. 2000 [Google Scholar]
- 33.Machtle W. High-resolution, submicron particle size distribution analysis using gravitational-sweep sedimentation, Biophys. J. 1999;76:1080–91. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77273-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sapsford KE, Tyner KM, Dair BJ, Deschamps JR, Medintz IL. Analyzing nanomaterial bioconjugates: a review of current and emerging purification and characterization techniques. Anal Chem. 2011;83:4453–88. doi: 10.1021/ac200853a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Johnson CS, Gabriel DA. Laser Light Scattering. New York: Dover; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Takahashi K, Kato H, Saito T, Matsuyama S, Kinugasa S. Precise measurement of the size of nanoparticles by dynamic light scattering with uncertainty analysis Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2008;25:31–8. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mukherjee S, Chowdhury D, Kotcherlakota R, Patra S, Vinothkumar B, Bhadra MP, Sreedhar B, Patra CR. Potential Theranostics Application of Bio-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (4-in-1 System. Theranostics. 2014;4:316–35. doi: 10.7150/thno.7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sharma G, Sharma AR, Bhavesh R, Park J, ET, et al. Biomolecule-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles using Dried Vitis vinifera (Raisin) Extract. Molecules. 2014;19:2761–70. doi: 10.3390/molecules19032761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Namasivayam SKR, Preethi M, and Arvind Bharani RS. Biofilm Inhibitory effect of Silver nanoparticles coated Catheter against Staphylococcus aureus and Evaluation of its Synergistic effect with Antibiotics. International Journal of Biological & Pharmaceutical Research. 2012;3:259–65. [Google Scholar]
- 40.El-Kheshen AA, El-Rab SFG. Effect of reducing and protecting agents on size of silver nanoparticles and their anti-bacterial activity. Der Pharma Chemica. 2012;4:53–65. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dimitrijevic R, Cvetkovic O, Miodragovic Z, Simic M, Manojlovic D, and Jovic V. SEM/EDX and XRD characterization of silver nanocrystalline Thin film prepared from organometallic solution precursor. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2013;49B:91–5. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Devaraj P, Kumari P, Aarti C, Renganathan A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Cannonball Leaves and Their Cytotoxic Activity against MCF-7 Cell Line. Journal of Nanotechnology. 2013;2013:1–5. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ramamurthy CH, Sampath KS, Arunkumar P, Kumar MS, Sujatha V, Prem Kumar K, Thirunavukkarasu C. Green synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles and its augmented cytotoxicity with doxorubicin on cancer cells. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2013;36:1131–9. doi: 10.1007/s00449-012-0867-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


