Abstract
Objective:
The purpose of this article is to review the imaging findings of necrotizing fasciitis as seen on radiograph, ultrasound, CT, and MRI, and to recognize the early findings in this potentially fatal disease.
Conclusion:
Although classically a clinical diagnosis, imaging is a powerful adjunct to facilitate early diagnosis in equivocal cases. Compared to plain radiography, ultrasound, CT and MR provide higher sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Cross-sectional imaging findings include asymmetric thickening of fascia, soft tissue air, blurring of fascial planes, inflammatory fat stranding, reactive lymphadenopathy, and nonenhancement of muscular fascia.
INTRODUCTION
Necrotizing fasciitis is a rapidly spreading soft tissue infection involving the deep fascial layers, which can cause secondary necrosis leading to significant morbidity and mortality.1–3 It most commonly affects the lower extremities accounting for approximately 50% of cases, and can affect different body parts including the perineum (as in Fournier’s gangrene), and submandibular region (as in Ludwig angina).
Although a very uncommon soft-tissue infection, it has significant mortality up to 70–80% and constitutes a life-threatening surgical emergency.1, 2 The most important predictor of mortality is a delay in diagnosis, thus it is essential to make a prompt diagnosis.2 Clinically, the findings of necrotizing fasciitis can overlap with other soft-tissue infections including cellulitis, abscess or even compartment syndrome, but pain out of proportion to the degree of skin involvement and signs of systemic shock should alert the clinician to the possibility of necrotizing fasciitis.4–6 Other red flag clinical findings are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical findings suggestive of necrotizing fasciitis vs cellulitis.7
| Clinical findings | Likelihood ratio |
| Skin necrosis | +30.0 |
| Hypotension | +8.0 |
| Hemorrhagic bullae | +8.0 |
| Recent surgery | +7.0 |
| Diarrhea | +6.0 |
| Fluctuance | +5.0 |
| Pain out of proportion | +4.5 |
| Altered mental status | +3.3 |
| Erythema progressing beyond margins | +3.1 |
There have been association with intravenous drug use as well as chronic conditions including diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression, obesity, and peripheral vascular disease.3, 8 A history of recent surgery (within the past 90 days) at the affected site has been shown to be a strong predictor for necrotizing fasciitis.7
Infection typically begins in the superficial fascial planes, then rapidly progress into the deep fascial layers, which causes necrosis secondary to microvascular occlusion.1 The rate of spread of infection is directly proportional to the thickness of the subcutaneous layers, with fastest spread seen in the lower extremities due to the lack of fibrous boundaries between subcutaneous tissue and fascia.2, 9
Necrotizing fasciitis is a clinical diagnosis since imaging findings can be nonspecific or unremarkable early in the course of the disease.1 The majority of cases are initially misdiagnosed, causing delay in diagnosis.10 Imaging appearances of necrotizing fasciitis can also overlap with other conditions, including nonnecrotizing fasciitis, dermatomyositis, graft vs host disease, or ischemic myonecrosis.1 The main utility of imaging is to determine the extent of the soft-tissue infection as well as to guide surgical planning.1, 8 If the patient is presenting with shock, imaging should not delay the initiation of treatment.1 Definitive diagnosis is based on surgical exploration and biopsy and aggressive surgical fasciotomy of necrotic tissue is required to prevent the spread of infection.7
RADIOGRAPHY
Early findings of necrotizing fasciitis on radiography can appear similar to cellulitis including soft-tissue opacity and thickening.11–13 The classical findings of dissecting gas along fascial planes in the absence of trauma is a specific sign, but is only seen in 24.8–55.0% of patients, and may not be seen until late in the disease (Figures 1 and 2).1, 10,12 Necrotizing fasciitis commonly affects the lower extremities, with involvement of the perineum or scrotum, classically known as Fournier’s gangrene (Figure 3).3, 14,15 Soft-tissue gas is typically caused by gas-forming anaerobic infections, although this may not be present in diabetic patients.16 As such, the absence of soft-tissue emphysema does not exclude a diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis.1
Figure 1.
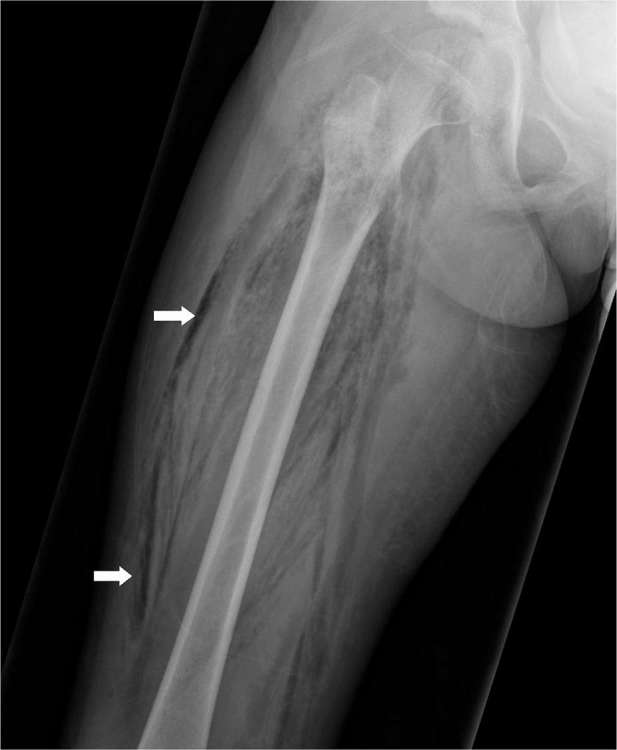
A 45-year-old male with necrotizing fasciitis of the right thigh. Extensive streaky soft-tissue gas is seen extending along the fascial planes of the right thigh on radiograph.
Figure 2.
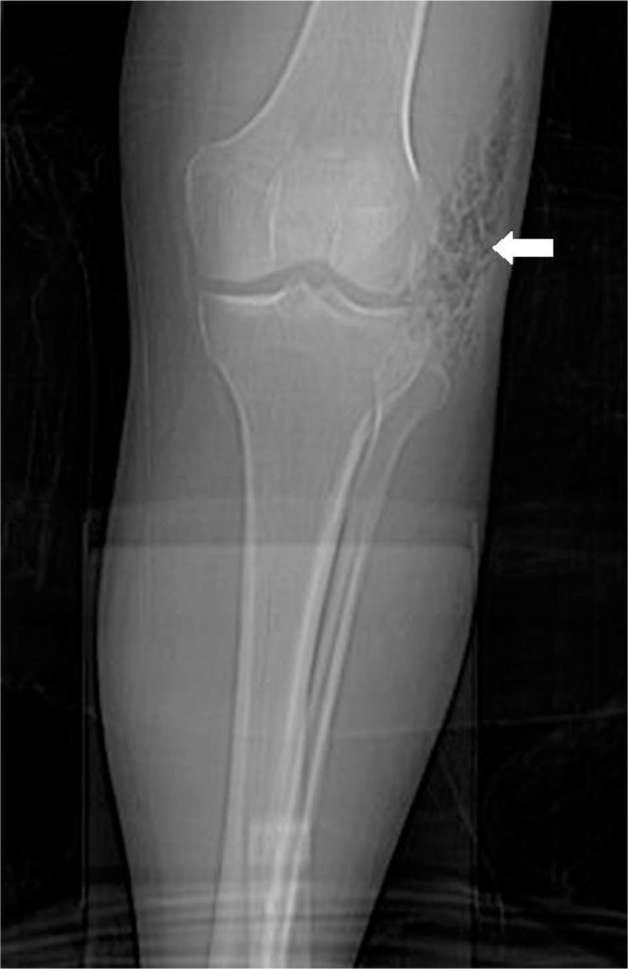
A 53-year-old male with necrotizing fasciitis of the left knee. Soft-tissue gas is seen at the lateral aspect of the left knee along the fascial planes on the radiograph.
Figure 3.
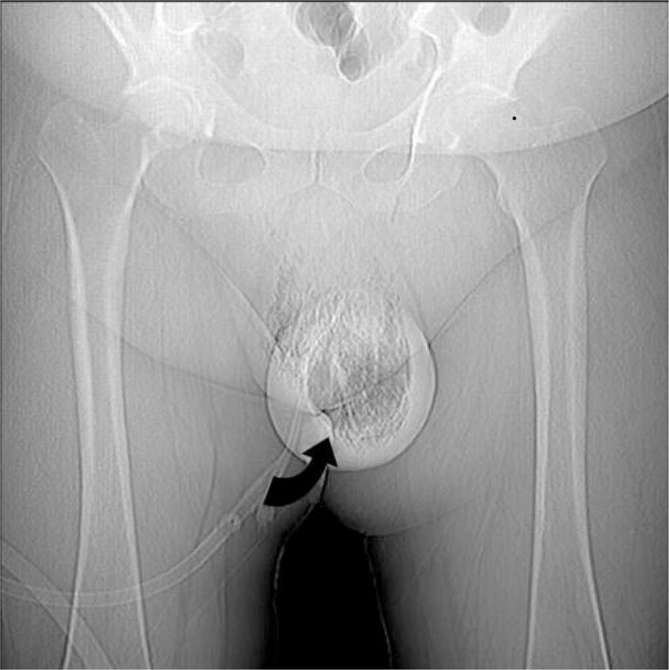
A 57-year-old diabetic male with pneumoscrotum. Large volume of gas seen within the scrotum wall and scrotum sac on the scout image (curved black arrow), consistent with Fournier’s gangrene.
Despite its limitations, radiographs can be more sensitive than physical exam for the detection of soft-tissue gas, with radiographic findings present before clinical crepitus is detected.17 Radiographs can also be helpful in identifying other causes of infection including the presence of a foreign body or underlying fracture.3, 13
ULTRASOUND
The role of ultrasound is limited in the work-up of necrotizing fasciitis given that the lack of resolution of deeper structures.8 The presence of soft-tissue gas can be more apparent on ultrasound compared to radiographs.17, 18 Findings include an echogenic layer of gas above the deep fascia with posterior dirty acoustic shadowing (Figure 4).19 Other nonspecific findings include hyperechogenicity of the overlying fat, with cobblestone appearance indicating subcutaneous edema, but these findings can also be seen in cellulitis or anasarca.8, 19 Color Doppler evaluation may not reveal hypervascularity.8 Specific signs that are helpful to differentiate necrotizing fasciitis from cellulitis include irregularity of the fascia, abnormal fluid collection along fascial planes, and diffuse fascia thickening when compared to the contralateral unaffected side.8
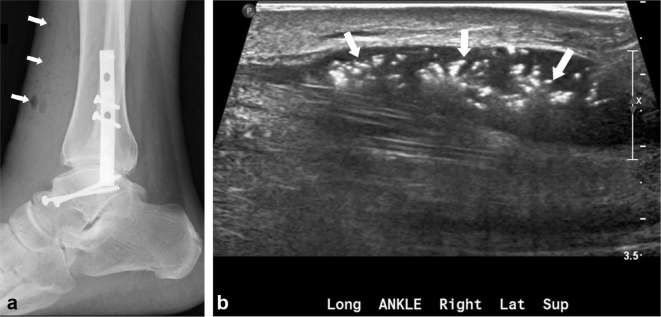
Figure 4.
A 39-year-old male with necrotizing fasciitis of the right ankle. There is subcutaneous emphysema (arrows) overlying the right ankle with plate and screw fixation seen (a). The soft-tissue air deep to the fascia is seen as multiple echogenic foci (arrows) on ultrasound study (b).
Ultrasound is helpful to rule out deep venous thrombosis, assess for possible foreign bodies, and guide potential diagnostic fluid aspiration.8, 13 Sensitivity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis is 88.2%, with a specificity of 93.3%.20
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
CT is the primary imaging modality in the work-up of necrotizing fasciitis given its wide availability and high spatial resolution compared to radiography or ultrasound.3 Soft-tissue gas is a pertinent CT finding, but absence of it should not exclude the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis if clinically suspected.1, 2,11,17 Gas within fluid collections along subfascial planes is the hallmark of necrotizing fasciitis (Figures 5 and 6).11, 21 The lack of soft-tissue gas on CT may be due to early disease, aerobic infections, or if the patient is diabetic.1, 16 The sensitivity of CT in diagnosing necrotizing fasciitis is 80%, but it lacks specificity as findings can also be seen in nonnecrotizing fasciitis.21, 22 Thickening and nonenhancement of the fascia on contrast-enhanced CT may be helpful to distinguish from nonnecrotizing fasciitis.2 Subfascial and intermuscular fluid accumulation can also be seen on CT, and may represent early findings of necrotizing fasciitis (Figure 7).21
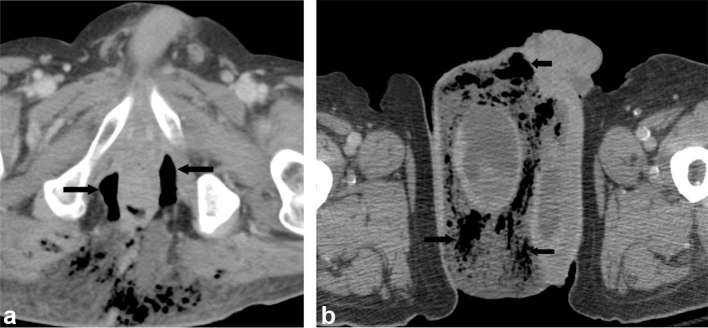
Figure 5.
A 64-year-old male with Fournier’s gangrene with perforated diverticulitis. Contrast-enhanced CT demonstrates air (arrows) and edema in the scrotum, surrounding the right testicle (a). Contrast-enhanced CT demonstrates a horse-shoe shaped perirectal air collection (arrows), extending into the subcutaneous tissues of the ischiorectal fossa and medial gluteal region (b).
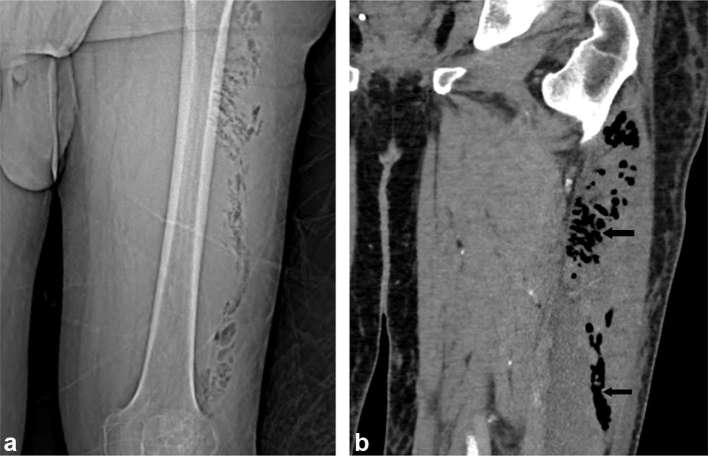
Figure 6.
A 55-year-old male with necrotizing Fasciitis of the left thigh. Scout film (a) and contrast-enhanced CT (b) shows intramuscular pockets of gas (arrows) in the left lateral thigh.
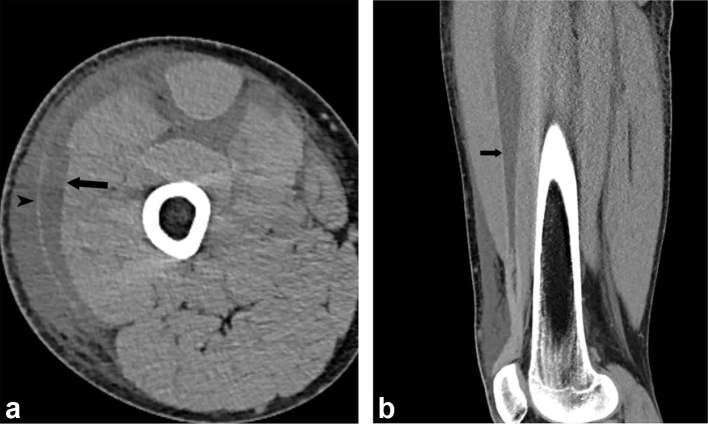
Figure 7.
A 39-year-old-male with necrotizing fasciitis of the right thigh. Contrast-enhanced CT demonstrates crescentic subfascial fluid (arrow) with fluid also seen superficial to the fascia (arrow head) and between muscle planes (a). Sagittal CT reformation demonstrates linear fluid collection (arrow) deep to the rectus femoris muscle (b).
Other CT findings include increase soft-tissue attenuation, subcutaneous edema and inflammatory fat stranding, which can also be seen in cellulitis.2,21–23 In a study by Wysoki et al. of 20 consecutive patients with necrotizing fasciitis, CT revealed fascial thickening and fat stranding in 80%, soft tissue gas in 55%, and abscesses in 35%.22
CT is helpful in guiding surgical debridement and drainage by evaluating the extent of soft tissue and osseous involvement, identifying the potential infectious source and identifying potential complications including vascular rupture or tissue necrosis.1, 2,13,22
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
MRI is the gold-standard for soft-tissue infections as it provides excellent soft-tissue contrast resolution with a sensitivity of 93% for the diagnosis for necrotizing fasciitis.1, 24 Essential sequences include T1 weighted imaging to assess anatomy, and T2 fat saturated or short tauinversion-recovery sequences to look for fascial thickening and edema.3, 25 Post gadolinium sequences are helpful to delineate the extent of infection, identify abscesses and areas of necrosis, but may not be feasible in patients with acute renal failure, which is common in this patient population.3, 26
Deep fascial thickening and subfascial fluid accumulation can be seen as high signal on fluid sensitive sequences (Figures 8 and 9).21 The deep intramuscular fascia is usually protected in the setting of cellulitis, but is involved in necrotizing fasciitis.1 Fascial thickening begins in the superficial fascia and extends along the deep intermuscular fascia, not just in areas contiguous to the deep peripheral fascia.1, 18 Hyperintensity and thickness of the fascia greater than or equal to 3 mm on fat saturated T2 weighted or short tauinversion-recovery images with involvement of three or more compartments is a sensitive finding to suggest necrotizing fasciitis.3, 8,13,25,27 The absence of T2 hyperintensity within the deep fascia can essentially exclude a diagnosis necrotizing fasciitis.3, 18,21
Figure 8.
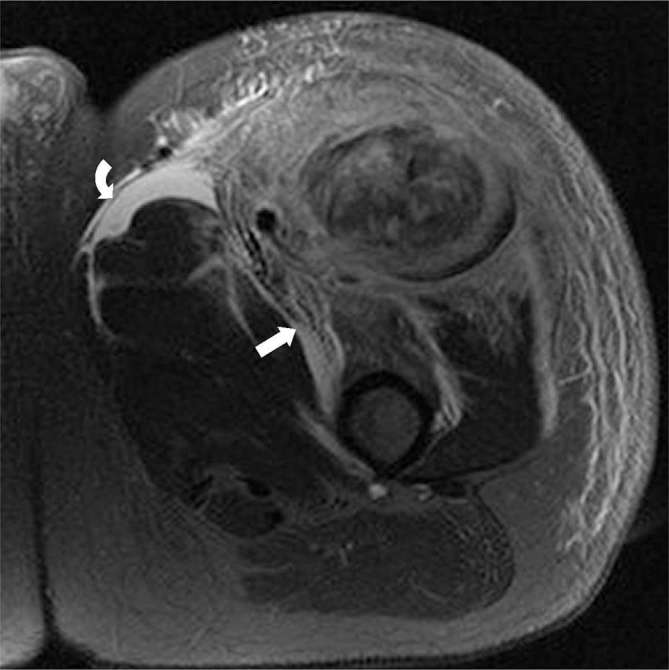
A 47-year-old male with necrotizing fasciitis of the left thigh. T2 weighted image with fat saturation of the left thigh demonstrates a large area of myonecrosis within the proximal rectus femoris muscle, with extensive muscular, fascial, and subcutaneous enhancement and edema, with crescentic fascial fluid collections, predominantly around the rectus femoris and sartorius, suggestive of necrotizing fasciitis.
Figure 9.
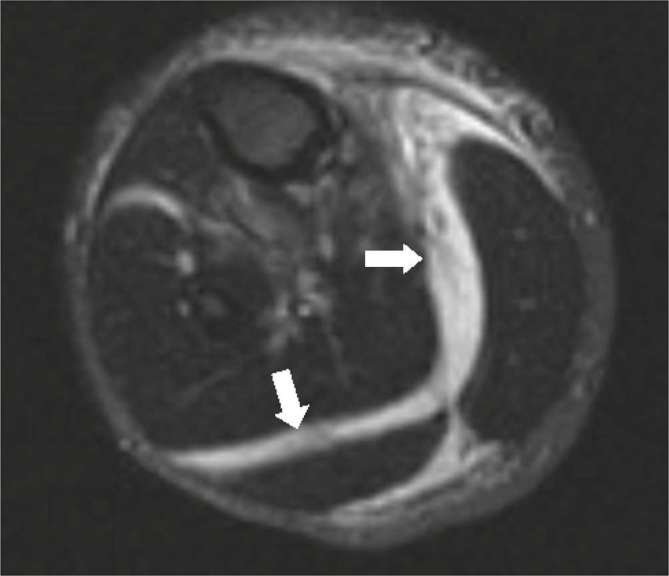
A 35-year-old male with necrotizing fasciitis of the right calf. T2 weighted images with fat saturation demonstrates extensive high signal within the intermuscular septa surrounding the gastrocnemius and soleus muscle bellies suggestive of subfascial fluid (white arrows).
Contrast enhancement of the fascia can be variable depending on the stage of necrosis.1, 13,25 Enhancement of the affected fascia is thought to represent extravasated contrast from increased capillary permeability. In later stages, nonenhancement of the fascia may be seen due to necrosis, which can be helpful to differentiate from nonnecrotizing fasciitis.3, 28,29
Although more apparent on CT, gas in the soft tissues is represented by punctate or curvilinear T1 and T2 low signal with corresponding blooming artifact on gradient echo sequences.1, 18,25,30 Although a highly specific finding, the absence of soft-tissue gas does not exclude the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis.3, 11
Diffuse high signal can also be seen in the muscle and subcutaneous fat.13 If subcutaneous edema is not the predominant feature, one should consider necrotizing fasciitis rather than cellulitis.1, 13 A summary of spectrum of findings for necrotizing fasciitis is summarized in Figure 10 and Table 2.
Figure 10.
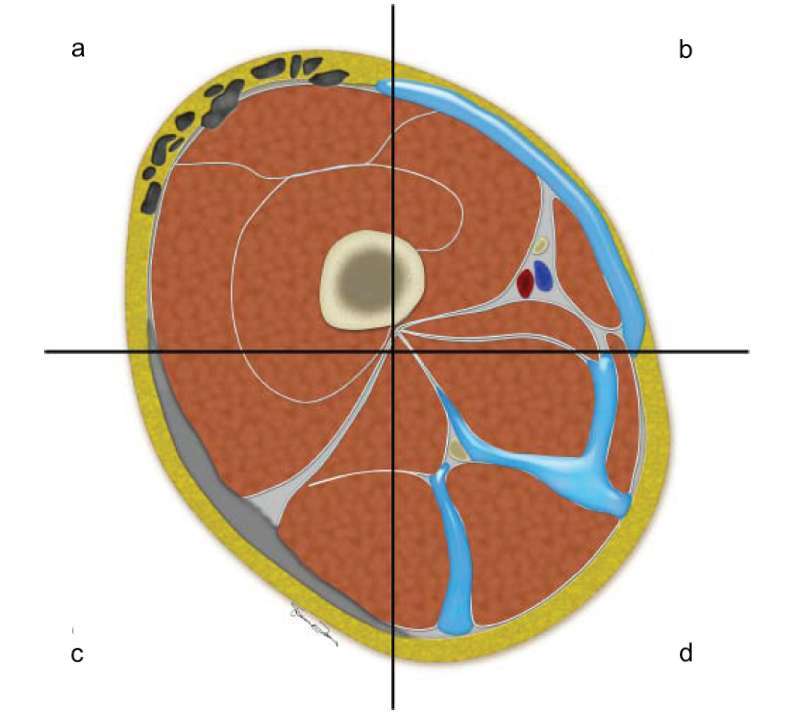
Cross-sectional schematic diagram through the right thigh demonstrating the various findings of necrotizing fasciitis. Subcutaneous and subfacial emphysema, which are classical finding of necrotizing fasciitis (a). Subfacial fluid along the superficial fascial layers, which can be seen in early necrotizing fasciitis (b). Diffuse thickening of the superficial fascia, which can be seen in the early phase of necrotizing fasciitis (c). Fluid tracking along deep and intermuscular fascia, which can be seen in advanced cases (d).
Table 2.
Summary of imaging findings of necrotizing fasciitis
| Modality | Key findings |
| Radiography | |
| Ultrasound | |
| CT | |
| MRI |
CONCLUSION
Skin findings, pain out of proportion, and signs of systemic shock should alert the clinician to the possibility of necrotizing fasciitis. Although it is a clinical diagnosis, imaging is a powerful adjunct to facilitate early diagnosis in equivocal cases. Compared to plain radiography, ultrasound, CT and MR provide higher sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Soft-tissue gas is a specific finding on all modalities, but is not present in all patients with necrotizing fasciitis. Cross-sectional imaging findings include asymmetric thickening of the fascia, soft-tissue air, blurring of fascial planes, inflammatory fat stranding, reactive lymphadenopathy, and nonenhancement of the muscular fascia. Fascial thickening and involvement of multiple compartments is a sensitive finding on MRI. Negative studies or nonspecific findings in the context of high clinical suspicion for necrotizing fasciitis, should be treated promptly as this is a clinical diagnosis.
Contributor Information
David K Tso, Email: dktso@mgh.harvard.edu.
Ajay K Singh, Email: ASINGH1@mgh.harvard.edu.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chaudhry AA, Baker KS, Gould ES, Gupta R. Necrotizing fasciitis and its mimics: what radiologists need to know. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015; 204: 128–39. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.12676 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fayad LM, Carrino JA, Fishman EK. Musculoskeletal infection: role of CT in the emergency department. Radiographics 2007; 27: 1723–36. doi: 10.1148/rg.276075033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hayeri MR, Ziai P, Shehata ML, Teytelboym OM, Huang BK. Soft-tissue infections and their imaging mimics: from cellulitis to necrotizing fasciitis. Radiographics 2016; 36: 1888–910. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016160068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Puvanendran R, Huey JC, Pasupathy S. Necrotizing fasciitis. Can Fam Physician 2009; 55: 981–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wong CH, Wang YS. The diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2005; 18: 101–6. doi: 10.1097/01.qco.0000160896.74492.ea [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anaya DA, Dellinger EP. Necrotizing soft-tissue infection: diagnosis and management. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 705–10. doi: 10.1086/511638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Alayed KA, Tan C, Daneman N. Red flags for necrotizing fasciitis: a case control study. Int J Infect Dis 2015; 36: 15–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.04.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clark ML, Fisher KL. Sonographic detection of necrotizing fasciitis. J Diagn Med Sonogr 2017; 33: 311–6. doi: 10.1177/8756479317701412 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Headley AJ. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: a primary care review. Am Fam Physician 2003; 68: 323–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goh T, Goh LG, Ang CH, Wong CH. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Surg 2014; 101: e119–e125. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fugitt JB, Puckett ML, Quigley MM, Kerr SM. Necrotizing fasciitis. Radiographics 2004; 24: 1472–6. doi: 10.1148/rg.245035169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bakleh M, Wold LE, Mandrekar JN, Harmsen WS, Dimashkieh HH, Baddour LM. Correlation of histopathologic findings with clinical outcome in necrotizing fasciitis. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: 410–4. doi: 10.1086/427286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gök MC, Turhan Y, Demiroğlu M, Kılıç B, Akkuş M, Özkan K. Radiological assessment in necrotizing fasciitis. Med J Islam World Acad Sci 2017; 25: 19–21. doi: 10.5505/ias.2017.11886 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med 2004; 32: 1535–41. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000129486.35458.7D [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wall DB, Klein SR, Black S, de Virgilio C. A simple model to help distinguish necrotizing fasciitis from nonnecrotizing soft tissue infection. J Am Coll Surg 2000; 191: 227–31. doi: 10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00318-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Green RJ, Dafoe DC, Rajfin TA. Necrotizing fasciitis. Chest 1996; 110: 219–229. doi: 10.1378/chest.110.1.219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Levenson RB, Singh AK, Novelline RA. Fournier gangrene: role of imaging. Radiographics 2008; 28: 519–28. doi: 10.1148/rg.282075048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kim KT, Kim YJ, Won Lee J, Kim YJ, Park SW, Lim MK, et al. Can necrotizing infectious fasciitis be differentiated from nonnecrotizing infectious fasciitis with MR imaging? Radiology 2011; 259: 816–24. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wronski M, Slodkowski M, Cebulski W, Karkocha D, Krasnodebski IW. Necrotizing fasciitis: early sonographic diagnosis. J Clin Ultrasound 2011; 39: 236–9. doi: 10.1002/jcu.20766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yen ZS, Wang HP, Ma HM, Chen SC, Chen WJ. Ultrasonographic screening of clinically-suspected necrotizing fasciitis. Acad Emerg Med 2002; 9: 1448–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2002.tb01619.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Malghem J, Lecouvet FE, Omoumi P, Maldague BE, Vande Berg BC. Necrotizing fasciitis: contribution and limitations of diagnostic imaging. Joint Bone Spine 2013; 80: 146–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.08.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wysoki MG, Santora TA, Shah RM, Friedman AC. Necrotizing fasciitis: CT characteristics. Radiology 1997; 203: 859–63. doi: 10.1148/radiology.203.3.9169717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zacharias N, Velmahos GC, Salama A, Alam HB, de Moya M, King DR, et al. Diagnosis of necrotizing soft tissue infections by computed tomography. Arch Surg 2010; 145: 452–5. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2010.50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gothner M, Dudda M, Kruppa C, Schildhauer TA, Swol J. Fulminant necrotizing fasciitis of the thigh, following an infection of the sacro-iliac joint in an immunosuppressed, young woman. Orthop Rev 2015; 7: 84–6. doi: 10.4081/or.2015.5825 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ali SZ, Srinivasan S, Peh WC. MRI in necrotizing fasciitis of the extremities. Br J Radiol 2014; 87: 20130560. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20130560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Miller TT, Randolph DA, Staron RB, Feldman F, Cushin S. Fat-suppressed MRI of musculoskeletal infection: fast T2-weighted techniques versus gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images. Skeletal Radiol 1997; 26: 654–8. doi: 10.1007/s002560050305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Arslan A, Pierre-Jerome C, Borthne A. Necrotizing fasciitis: unreliable MRI findings in the preoperative diagnosis. Eur J Radiol 2000; 36: 139–43. doi: 10.1016/S0720-048X(00)00164-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schmid MR, Kossmann T, Duewell S. Differentiation of necrotizing fasciitis and cellulitis using MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998; 170: 615–20. doi: 10.2214/ajr.170.3.9490940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brothers TE, Tagge DU, Stutley JE, Conway WF, Del Schutte H, Byrne TK. Magnetic resonance imaging differentiates between necrotizing and non-necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity. J Am Coll Surg 1998; 187: 416–21. doi: 10.1016/S1072-7515(98)00192-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Paz Maya S, Dualde Beltrán D, Lemercier P, Leiva-Salinas C. Necrotizing fasciitis: an urgent diagnosis. Skeletal Radiol 2014; 43: 577–89. doi: 10.1007/s00256-013-1813-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]