Abstract
Palliative care (pc) is part of the recommended standard of care for patients with advanced cancer. Nevertheless, delivery of pc is inconsistent. Patients who could benefit from pc services are often referred late—or not at all. In planning for improvements to oncology pc practice in our health care system, we sought to identify barriers to the provision of earlier pc, as perceived by health care providers managing patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mcrc). We used the Michie Theoretical Domains Framework (tdf) and Behaviour Change Wheel (bcw), together with knowledge of previously identified barriers, to develop a 31-question survey. The survey was distributed by e-mail to mcrc health care providers, including physicians, nurses, and allied staff. Responses were obtained from 57 providers (40% response rate).
The most frequently cited barriers were opportunity-related—specifically, lack of time, of clinic space for consultations, and of access to specialist pc staff or services. Qualitative responses revealed that resource limitations varied by cancer centre location. In urban centres, time and space were key barriers. In rural areas, access to specialist pc was the main limiter. Self-perceived capability to manage pc needs was a barrier for 40% of physicians and 30% of nurses. Motivation was the greatest facilitator, with 89% of clinicians perceiving that patients benefit from pc. Based on the Michie tdf and bcw model, interventions that best address the identified barriers are enablement and environmental restructuring. Those findings are informing the development of an intervention plan to improve oncology pc practices in a publicly funded health care system.
Keywords: Palliative care, early referral, oncology care, perceptions, knowledge translation, Behaviour Change Wheel, colorectal cancer
INTRODUCTION
Palliative care (pc), which focuses on preventing and relieving the symptoms and physical and psychological distress of a serious illness, is part of the recommended standard of care for patients with advanced cancer in Canada1. Nevertheless, delivery of pc is inconsistent2, with some patients being referred late—or not at all3. The Palliative Care Early and Systematic project was conceived to address that problem at a system level, aiming to deliver early, systematic, and oncology-integrated pc for patients with advanced cancer (in whom cure or remission is unlikely) in a publicly funded health care system (Alberta), starting with patients having metastatic colorectal cancer (mcrc).
Using the knowledge-to-action cycle4 to implement change, we first sought to assess the barriers to pc use as perceived by oncology clinicians in Alberta. Previous studies5,6 have identified barriers such as communication within and between care teams7,8, accurate prognostication9–11, discomfort with engaging patients in difficult conversations7,12, patient acceptance of pc11,13, and insufficient resources3,9,11. However, few studies have used a validated method to assess those barriers in one group of clinicians across a large health system. We used the Michie Theoretical Domains Framework and COM Behaviour (com-b) Change Wheel14,15, together with knowledge of previously identified barriers, to develop a survey of barriers to pc use. Here, we report the results of the survey.
METHODS
The survey (provided in the supplemental file) had 5 sections and posed 31 questions. Part 1 collected demographic information. Parts 2–5 queried for potential barriers to referring patients to pc, to working with pc team members, to addressing the pc needs of patients in the cancer clinic, and to recommending a new routine pc pathway respectively. Questions in parts 2–5 used a 7-point ordinal scale and were informed by previously reported barriers and by the Michie Theoretical Domains Framework of factors influencing clinician uptake of a guideline. The questions were mapped to Michie com-b categories14,15 to better identify the sources of behaviour influencing the responses and to provide a starting point for devising a behaviour-change strategy. Four open-ended response questions queried for unanticipated barriers, and one queried for ideas for improvements. The study was approved by the Health Research Ethics Board of Alberta (hreba.cc-17-0073).
The survey was administered online using the REDCap Web application (Research Electronic Data Capture, version 7.2: REDCap Consortium, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, U.S.A.)16. Surveys were distributed by e-mail to oncology health care providers (defined here as physicians, nurses, and allied staff) treating mcrc at all provincial cancer centres (2 tertiary, 5 regional). Additionally, researchers attended tumour group meetings to engage potential respondents in person and to distribute paper-based surveys. Participation was voluntary and anonymous.
Data Analysis
For questions in Parts 2–4 (using an ordinal scale), all “agree” responses (entirely= 7; mostly= 6; somewhat= 5) were collapsed as barriers. All “disagree” responses (entirely = 1; mostly = 2; somewhat = 3) were collapsed as facilitators. “Neither agree nor disagree” responses (= 4) were labelled neutral. “Don’t know” responses were scored as 0. “Barrier strength” was calculated as the average response value for a question. Factors most frequently cited as barriers were identified by using the percentage of barrier responses to rank them. Open-ended response questions were analyzed using conventional content analysis17. Three researchers (MAE, JRA, SK) coded all responses before grouping them into themes. Final consensus on the codes and themes was achieved at a meeting of the three coders and a senior investigator (JES).
RESULTS
The survey response rate was 40% (60 respondents from an estimated 150 e-mail recipients). Three respondents were excluded for reporting that they never worked with mcrc patients. In keeping with the staff distribution in the province, most respondents were oncologists (31%) or cancer clinic nurses (33%) with medical oncology as their primary discipline (72%). Most respondents (76%) worked at a tertiary cancer centre, had 5 or more years’ experience in their professional role (79%), and cared for 10 or more mcrc patients monthly.
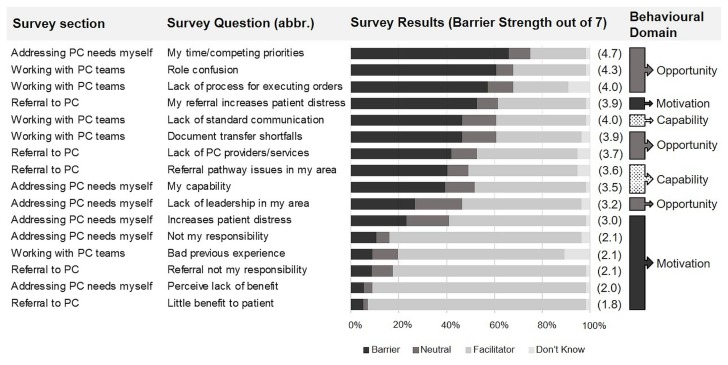
Figure 1 ranks the most frequently cited barriers to addressing the pc needs of mcrc patients. The three most frequently cited barriers were “my time/competing work priorities,” “role confusion,” and “lack of process for executing new orders for patients who are at home.” Those barriers map to the com-b “opportunity” category14. Respondents were divided on whether factors involving “capability”14 were barriers. “Motivation”-influenced behaviours were largely cited as facilitators, including the perceived benefit of pc to patients, the perception that managing pc needs is an oncology clinician’s responsibility, and positive prior experience working with pc teams. The exception was for “patient distress at the term palliative,” which was perceived as a barrier by 53% of respondents. Motivation to recommend a new pc pathway to patients was also high, with 89% of respondents reporting “likely to.”
FIGURE 1.
Factors most frequently identified as barriers to early, systematic, or oncology-integrated palliative care for patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Survey questions were posed using an ordinal scale (1–7) and framed as “A barrier I face is….” All “agree” responses (entirely = 7; mostly = 6; somewhat = 5) were collapsed as barriers. All “disagree” responses (entirely = 1; mostly = 2; somewhat = 3) were collapsed as facilitators. Responses that neither agreed nor disagreed (= 4) were labelled neutral. “Don’t know” responses were scored as 0. Survey questions were ranked by the percentage of observed barrier responses (largest to smallest). Barrier strength was calculated as the average response value. Questions are mapped to the Michie COM (Capability, Opportunity, Motivation) Behaviour Change Wheel. abbr. = abbreviated; PC = palliative care.
Responses to Open-Ended Survey Questions
Table i highlights 9 themes emerging from the open-ended responses in parts 2–4. Themes were categorized as barriers related to the pc service, to clinicians, and to patients. The qualitative findings largely complement what was found quantitatively. Here, the most frequently identified barrier was insufficient resources. Respondents from metropolitan tertiary centres emphasized clinician time and clinic space; rural community respondents emphasized access to specialist pc staff and services. Two respondents identified a barrier not explored by the quantitative questions: clinician discomfort starting conversations about end of life.
TABLE I.
Clinician-identified barriers to providing early, systematic, and oncology-integrated palliative care for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
| Category | Theme | Exemplar quote | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Name | Description | ||
| Palliative care service | |||
| Insufficient resources | Insufficient resources [staff, time, clinic space (rooms, beds), necessary component of palliative care service in the region] | Not enough nursing support for effective symptom control, management, and follow-up. Not enough clinic room or time to see, follow up patients in a timely fashion — Physician 1, Tertiary Centre 1 |
|
| Palliative care services perceived as suboptimal | Clinician is aware of the palliative care referral process and the services provided, but perceives the process or services to be too difficult to access (complexity), too slow to access (timeliness), inadequate (for example, no long-term follow-up), or too limited or insufficient to provide benefit to patients. | Currently, when I refer to palliative care, the patient is seen once or twice and then discharged from clinic once their symptoms are stable. There is no ongoing follow-up, and they need to be re-referred if new symptoms develop. In patients with uncomplicated symptom issues, it is simpler to treat them myself. — Physician 2, Tertiary Centre 2 |
|
|
| |||
| Clinician | |||
| Poor communication | Insufficient or poor-quality communication processes between clinicians or care teams | All teams are excellent. It is the fact that no one cooperates together. The [patient] and family have to retell their story and journey over and over. They need one point of contact! — Nurse 1, Regional Centre 1 |
|
| Professional role confusion | Inadequate clinician role definition when care teams integrate, leading to varied interpretations about who does what. | There seems to be no clear role division. — Nurse 2, Tertiary Centre 1 |
|
| Confusion concerning palliative care services | Clinicians are not clear who, how, or when to refer patients to palliative care services, or clinicians are not clear about the services that palliative care provides (or both). | I feel staff need to understand that the palliative care program is not only for patients who are going to pass in “a week.” It is for patients who may have months or years to live, but [who] need extra services. For example, pain control, home care, etc. — Nurse 3, Regional Centre 1 |
|
| Difficult conversation | Clinicians are uncomfortable having a conversation about palliative care with the patient. | The need for frank and open discussion, starting with the primary doctors involved. Very difficult discussion for many oncology doctors. — Nurse 1, Regional Centre 1 |
|
|
| |||
| Patient | |||
| Patient does not qualify for palliative care services | Patient deemed not “qualified” for palliative care services when requested. | They are sometimes refused, as we are told they are not yet a “suitable” client. — Nurse 4, Tertiary Centre 1 |
|
| Palliative care not needed | Lack of perceived (by clinician) need for palliative care services at this time | I usually refer patients with more complex symptoms and/or poor performance status (metastatic pancreas patients, etc.). Many metastatic colorectal cancer patients early in their disease course seem less likely to have complex symptoms, and many have good performance status. — Physician 3, Tertiary Centre 2 |
|
| Patient declines | Patient declines palliative care referral | Sometimes … I think that a patient would benefit, the patient agrees to the referral, and then when … contacted, the patient feels [that] they don’t need palliative care services. — Nurse 5, Tertiary Centre 2 |
|
Survey respondents were asked to provide their ideas for improving the integration of early pc within cancer care, with 17 responses being received. Table ii highlights 9 themes emerging from those comments, which were grouped into 3 foci: processes (referral, communication); education and awareness; and resources. Several comments pointed to the urgent need for an oncology pc clinical practice guideline. Further, to aid in delivering systematic pc, respondents suggested the use of process maps, chronologic communication sheets, and a single point of contact for patients. One tertiary cancer centre respondent said, “Having a pc team member physically present in a [cancer] clinic as a first point of contact” would improve oncology pc integration. Also related to processes, an oncologist commented, “The role of pc versus the treating oncologist in ongoing follow-up [has] to be clear.” Several respondents pointed to the need for better patient and clinician education about pc. Increased resources (space, time, staff) were also cited as ways to improve the integration of pc into cancer care. Finally, respondents indicated that early pc initiatives should focus on all advanced cancer patients and be dictated by greatest need.
TABLE II.
Ideas from oncology clinicians for improving the integration of early palliative care within cancer care for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
| Theme | Description | Exemplar quote |
|---|---|---|
| Processes | ||
| Need clinical practice guidelines in the management of palliative care patients in the province | Establish clinical practice guidelines in the management of palliative care patients in the province. None exists for informing Albertan physicians about standards of care or processes in Alberta. This extends beyond GI patients, and incorporates all cancer patients with symptomatic, incurable cancers. Guidelines are available for palliative radiotherapy and oncologic emergencies. Feedback suggests these are very useful to non-oncology physicians and care givers. —Physician 3, Tertiary Centre 1 |
|
| Need process map for delivering standardized palliative care | I think a process map for the [outpatient department] to start the process helps. And a chronological communication sheet that we can quickly refer to rather than trying to piece together all the steps that have been addressed. i.e., Looking through paper chart … then ARIAa [an oncology information system] notes … then talking to clinic nurse … or talking with doctor. A lot of time wasted trying to figure things out. —Nurse 6, Tertiary Centre 2 |
|
| Need standardized communication processes (chronological communication sheets) to easily find palliative care treatment plans and changes | ||
| Patients need one point of contact, a person who is well informed and knows the process and how care teams are integrated | One point of contact. Integrate home care and teams to give patient and family a primary contact and a family conference immediately. —Nurse 1, Regional Centre 1 |
|
|
| ||
| Education or awareness | ||
| Systematically educate patients/families about palliative care early in their disease trajectory | Standardized patient information to give to all metastatic patients about the role of palliative care and the services they offer. —Physician 4, Regional Centre 2 |
|
| Introducing [palliative care services] early and referring back to it during clinic appointments would help patients and family to know that resources are there when the time comes that they do need them. —Nurse 7, Tertiary Centre 2 |
||
| Systematically educate clinicians about palliative care: established practice guidelines, established process map | Education, communication, and review for all staff members (nurses). This would have everyone using the same message, and patients will not become confused or have different messages from staff. —Nurse 3, Regional Centre 2 |
|
|
| ||
| Resources | ||
| Increase palliative care resources so that more patients can be seen | Finding the time and space to conduct the referral. —Physician 5, Tertiary Centre 1 |
|
Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA, U.S.A.
GI = gastrointestinal.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
In our public health care system, oncology clinicians reported that lack of opportunity was the greatest impediment to delivering early, systematic, oncology-integrated pc to mcrc patients. They identified their own lack of time (attributable to high staff-to-patient ratios and competing work priorities), but also a lack of proper facilities and of access to specialist pc staff or services. In areas with large urban populations, time and space for pc consults were key barriers; in areas with largely rural populations, access to specialist pc was the main limiter.
Opportunity barriers have been identified in prior studies. In a study of pc referral practices among Canadian oncologists3, the availability of comprehensive specialist pc was one of two main barriers preventing timely referral. In other jurisdictions, oncology staff time and access to specialist pc services and staff3,9,11 were identified barriers, as were process barriers impeding communication within and between care teams7,8. Patient distress at the term “palliative” was the 4th most frequently identified barrier (Figure 1)—a commonality with earlier studies11,13. Although we did not seek to quantify the frequency with which clinicians experience discomfort engaging patients and families in difficult end-of-life conversations7,12, that discomfort can be a corollary of patient distress and was identified in the open-ended responses. Clinician discomfort as a barrier contrasted with the most frequently identified facilitator: a belief in the benefit of pc for patients. Interestingly, in one comprehensive study of pc referral practices among cancer specialists in Australia, resource-related barriers were rarely (<6%) reported as a reason for not referring patients to specialist pc11. Rather, the principal reason for non-referral was the cancer specialist’s own ability to manage a patient’s symptoms, which contrasts with reasons given by oncologists in the present study, who mentioned their own capability to manage a patient’s symptoms as a barrier 39% of the time.
Using the Michie Theoretical Domains Framework and com-b models14,15 to frame the survey was a study strength. It allowed for an exploration of the factors influencing clinician behaviour in our provincial context. A limitation was having to estimate the response rate, which, although higher than reported for other physician surveys18, might suffer from a potential non-responder bias19. Further, we note that the survey questions were framed to identify barriers, not facilitators. The latter term was assigned to facilitate analysis and interpretation; however, factors not being identified as barriers does not necessarily mean that those factors are facilitators.
To summarize, the 3 most frequently cited barriers were all opportunity-influenced14. The Michie Behaviour Wheel suggests that interventions to address opportunity-related barriers include “enablement” (for example, clearly defining roles and responsibilities), “environmental restructuring” (for example, electronic health record prompts for simplified pc referral), and “restriction” (for example, implementing practice guidelines to increase the desired behaviour by reducing the opportunity to engage in competing behaviours). Those findings have informed the Palliative Care Early and Systematic project and will aid in the development of an intervention plan to improve oncology pc clinical practice in our publicly funded health care system.
Supplemental Materials
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant: Partnerships for Health System Improvement for Cancer Control–LOI (HCR-150727).
Footnotes
Supplemental material available at http://www.current-oncology.com
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES
We have read and understood Current Oncology’s policy on disclosing conflicts of interest, and we declare that we have none.
REFERENCES
- 1.Mitera G, Earle C, Latosinsky S, et al. Choosing Wisely Canada cancer list: ten low-value or harmful practices that should be avoided in cancer care. J Oncol Pract. 2015;11:e296–303. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2015.004325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.United States, The National Academies, Institute of Medicine (iom), Committee on Improving the Quality of Cancer Care. Delivering High-Quality Cancer Care: Charting a New Course for a System in Crisis. Washington, DC: IOM; 2013. [Available online at: https://www.nap.edu/resource/18359/qualitycancercare_rb.pdf; cited 2 January 2017] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wentlandt K, Krzyzanowska MK, Swami N, Rodin GM, Le LW, Zimmermann C. Referral practices of oncologists to specialized palliative care. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:4380–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.0248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Graham ID, Logan J, Harrison MB, et al. Lost in knowledge translation: time for a map? J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2006;26:13–24. doi: 10.1002/chp.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhi WI, Smith TJ. Early integration of palliative care into oncology: evidence, challenges and barriers. Ann Palliat Med. 2015;4:122–31. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2015.07.03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fassbender K, Watanabe SM. Early palliative care and its translation into oncology practice in Canada: barriers and challenges. Ann Palliat Med. 2015;4:135–49. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2015.06.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Odeniyi F, Nathanson PG, Schall TE, Walter JK. Communication challenges of oncologists and intensivists caring for pediatric oncology patients: a qualitative study. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2017;54:909–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2017.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oosterink JJ, Oosterveld-Vlug MG, Glaudemans JJ, Pasman HR, Willems DL, Onwuteaka-Philipsen BD. Interprofessional communication between oncologic specialists and general practitioners on end-of-life issues needs improvement. Family Pract. 2016;33:727–32. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmw064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sommerbakk R, Haugen DF, Tjora A, Kaasa S, Hjermstad MJ. Barriers to and facilitators for implementing quality improvements in palliative care—results from a qualitative interview study in Norway. BMC Palliat Care. 2016;15:61. doi: 10.1186/s12904-016-0132-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Currow DC, Allingham S, Bird S, et al. Referral patterns and proximity to palliative care inpatient services by level of socioeconomic disadvantage. A national study using spatial analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12:424. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-12-424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johnson CE, Girgis A, Paul CL, Currow DC. Cancer specialists’ palliative care referral practices and perceptions: results of a national survey. Palliat Med. 2008;22:51–7. doi: 10.1177/0269216307085181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Buckley de Meritens A, Margolis B, Blinderman C, et al. Practice patterns, attitudes, and barriers to palliative care consultation by gynecologic oncologists. J Oncol Pract. 2017;13:e703–11. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2017.021048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boyd D, Merkh K, Rutledge DN, Randall V. Nurses’ perceptions and experiences with end-of-life communication and care. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2011;38:E229–39. doi: 10.1188/11.ONF.E229-E239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Michie S, van Stralen MM, West R. The Behaviour Change Wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci. 2011;6:42. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-6-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cane J, O’Connor D, Michie S. Validation of the Theoretical Domains Framework for use in behaviour change and implementation research. Implement Sci. 2012;7:37. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-7-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42:377–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsieh HF, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15:1277–88. doi: 10.1177/1049732305276687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.College of Family Physicians of Canada, Canadian Medical Association, and Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. National Physician Survey: 2014 Response Rates [Web page] Mississauga, ON: National Physician Survey; 2014. [Available at: http://nationalphysiciansurvey.ca/surveys/2014-survey/response-rates; cited 2 January 2018] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Statistics Canada. Response and nonresponse [Web page, archival] Ottawa, ON: Statistics Canada; 2015. [Available at: http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/12-539-x/2009001/response-reponse-eng.htm; cited 2 January 2018] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.