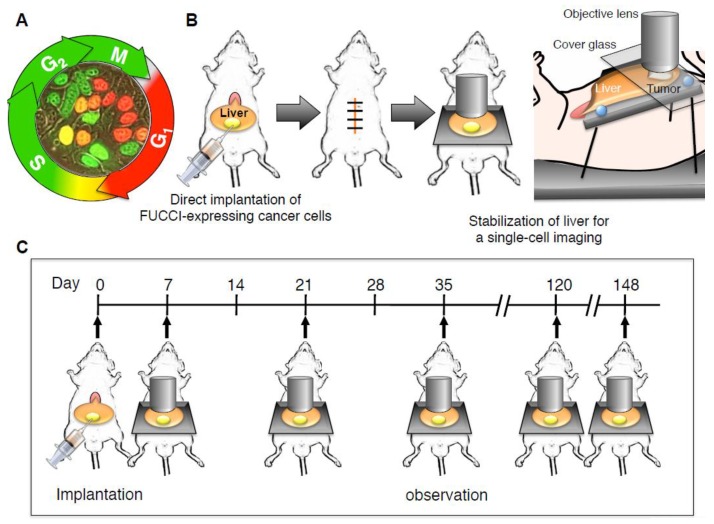
Figure 1.
An abdominal skin-flap window for longitudinal intravital imaging of fluorescence ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator (FUCCI)-expressing cancer cells in the liver of a live mouse. (A) FUCCI-expressing MKN45 gastric cancer cells in G0/G1, S, or G2/M phases are red, yellow, or green, respectively. (B) The schematic diagram shows the method of longitudinal intravital confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) imaging of FUCCI-expressing gastric-cancer cells growing in the liver using a skin-flap window. All animal procedures were performed under anesthesia using s.c. administration of a ketamine mixture (10 μl ketamine HCl, 7.6 μl xylazine, 2.4 μL acepromazine maleate, and 10 μL PBS). FUCCI-expressing MKN45 cells were harvested by brief trypsinization. Single-cell suspensions were prepared at a final concentration of 2 × 105 cells/5 μl Matrigel (BD). After laparotomy, FUCCI-expressing cancer cells were subserosally injected directly into the left lobe of the liver using a 31 gauge needle. After cancer-cell implantation, the abdominal wall of the mice was closed with 6-0 sutures. Mice were anesthetized as described above and placed on a custom-designed imaging box. The liver was exteriorized and placed on a Styrofoam box, and a cover glass was gently placed on the liver, which inhibited vibration caused by heartbeat and respiratory movement. CLSM imaging was performed using the FV1000 confocal laser microscope (Olympus Corp, Tokyo, Japan) with two-laser diodes (473 nm and 559 nm). A 4 × (0.20 numerical aperture immersion) objective lens and 20 × (0.95 numerical aperture immersion) objective lens (Olympus) were used. 800 × 800 pixels and 1.0 μm z steps were scanned, which took 1–2 s per section. Scanning and image acquisition were controlled by Fluoview software (Olympus). (C) The schematic diagram shows the method of longitudinal intravital CLSM imaging of FUCCI-expressing gastric cancer cells growing in the liver using an abdominal skin-flap window. The abdominal skin-flap window method enables ten laparotomies during 150 days.