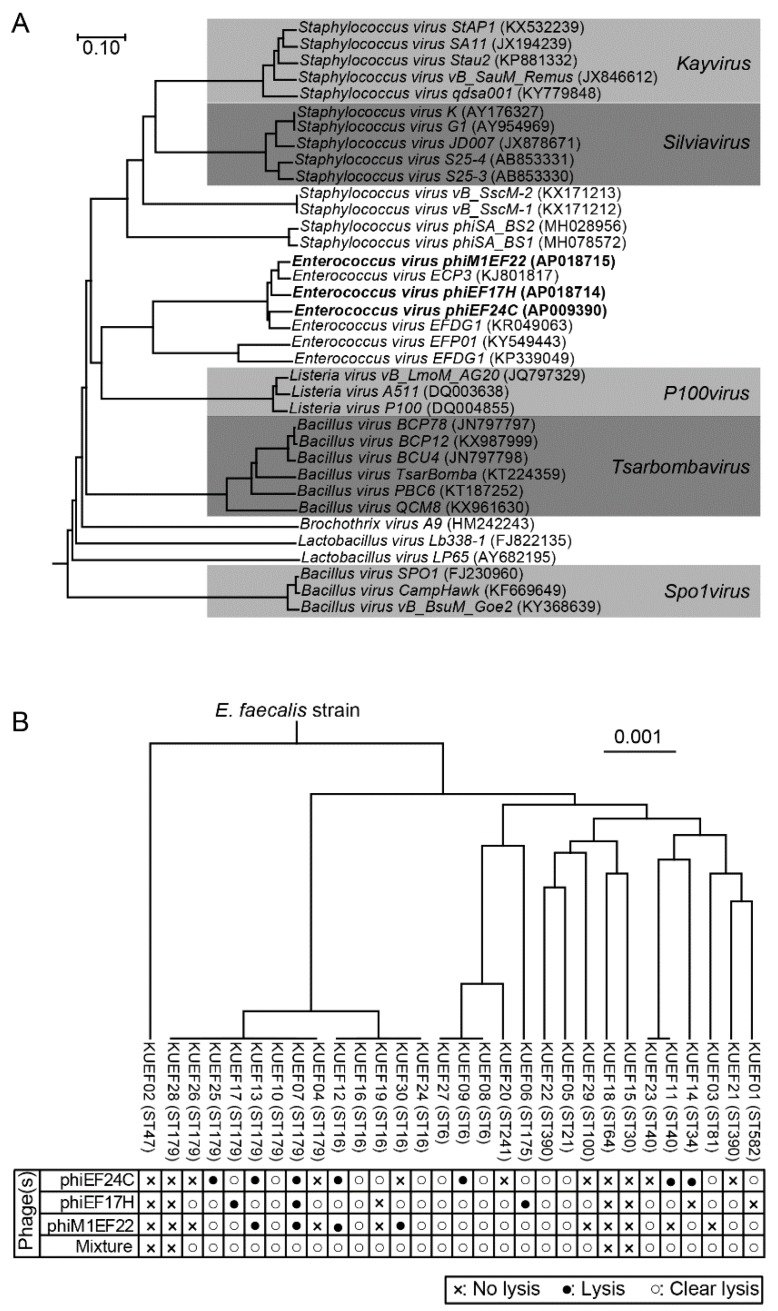
Figure 1.
Enterococcus phages phiEF24C, phiEF17H, and phiM1EF22 and their lytic activity to various E. faecalis strains. (A) Viral proteomic trees of Enterococcus phages phiEF24C, phiEF17H, and phiM1EF22 in the family Myoviridae subfamily Spounavirinae. Enterococcus phages phiEF24C, phiEF17H, and phiM1EF22 are shown in bold. Phage taxonomical names are shown followed by the GenBank accession number in parentheses. The phages belonging to a certain viral genus are shown in grey highlight, on which the viral genus names are indicated. (B) E. faecalis strains isolated from vaginal swabs and their sensitivity to phages. Phylogenetic tree of E. faecalis strains was constructed based on the concatenated multilocus sequence typing (MLST) alleles. In the phylogenetic tree, E. faecalis strain names are followed by sequence types (STs) in brackets. Phage sensitivities to each phage and phage mixture are shown below the phylogenetic tree.