Abstract
Tauopathies are neurodegenerative diseases characterized by tau protein pathology in the nervous system. EIF2AK3 (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 3), also known as PERK (protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase), was identified by genome-wide association study as a genetic risk factor in several tauopathies. PERK is a key regulator of the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR), an intracellular signal transduction mechanism that protects cells from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. PERK variants had previously been identified in Wolcott–Rallison Syndrome, a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder, and these variants completely abrogated the function of PERK’s kinase domain or prevented PERK expression. In contrast, the PERK tauopathy risk variants were distinct from the Wolcott–Rallison variants and introduced missense alterations throughout the PERK protein. The function of PERK tauopathy variants and their effects on neurodegeneration are unknown. Here, we discovered that tauopathy-associated PERK alleles showed reduced signaling activity and increased PERK protein turnover compared to protective PERK alleles. We found that iPSC-derived neurons carrying PERK risk alleles were highly vulnerable to ER stress-induced injury with increased tau pathology. We found that chemical inhibition of PERK in human iPSC-derived neurons also increased neuronal cell death in response to ER stress. Our results indicate that tauopathy-associated PERK alleles are functional hypomorphs during the UPR. We propose that reduced PERK function leads to neurodegeneration by increasing neuronal vulnerability to ER stress-associated damage. In this view, therapies to enhance PERK signaling would benefit at-risk carriers of hypomorphic alleles.
Introduction
Tauopathies are neurodegenerative diseases defined by misfolded hyperphosphorylated tau deposits in the brain (1). Tauopathies include Alzheimer’s disease (AD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration, frontotemporal lobar dementia (FTLD), chronic traumatic encephalopathy and primary age-related tauopathy (1–3). The vast majority of tauopathies arise sporadically. Retrospective epidemiologic studies have identified environmental factors, such as repetitive head trauma, low education levels or exposure to neurotoxins, more commonly encountered by those who developed tauopathies (4,5). Genomic sequencing studies have also identified genetic polymorphisms over-represented in patients with tauopathies. However, the mechanisms by which environmental and genetic risk factors cause neurodegeneration remain largely unknown.
PSP is a rare tauopathy with prevalence ranging from 3.1 to 6.5 per 100000 people in retrospective studies (6,7). Clinically, patients develop progressively debilitating parkinsonism-like symptoms typically during the sixth decade of life (8–10). Supportive treatments can ameliorate PSP symptoms such as balance/gait problems or motor speech defects, but there is no cure. The average survival time after onset of PSP symptoms is 7 years (11). The postmortem gross neuropathology of PSP reveals pathognomonic neurodegeneration preferentially affecting the basal ganglia, brainstem, diencephalon and cerebellum (11). Microscopically, abnormal tau protein deposits are evident in neurons as neurofibrillary tangles and in glia as tufted astrocytes (11).
Numerous missense and splice-site mutations in microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) cause rare autosomal dominant forms of FTLD but are not found in sporadic tauopathies (12). However, investigation of the MAPT locus in case-control studies of sporadic tauopathies revealed that the H1 haplotype, bearing an inversion of the genomic region on chromosome 17 containing MAPT, was a significant risk factor for PSP (13). More recently, a genome-wide association study (GWAS) identified polymorphisms in three novel genes that significantly increased risk for PSP: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 3 (EIF2AK3), myelin-associated oligodendrocyte basic protein (MOBP) and syntaxin 6 (STX6) (14). The EIF2AK3 polymorphism was also associated with increased risk for late-onset AD in patients carrying APOE ε4 in a case-control study (15). The mechanism by which genetic polymorphisms in EIF2AK3 confer increased tauopathy risk is unknown.
EIF2AK3 is also known as PERK (protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase). PERK is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident transmembrane serine/threonine kinase that is a key regulator of the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) (16). The UPR is a conserved intracellular signal transduction mechanism that maintains ER homeostasis in all eukaryotic cells (16). In response to ER stress, PERK dimerizes to activate its serine/threonine kinase function (16). PERK’s kinase targets eIF2α, an essential factor required for translation initiation (17). Phosphorylation of eIF2α by PERK inhibits ternary complex formation resulting in translational attenuation (17,18). By dampening new protein synthesis, PERK signaling reduces the protein folding demands on the ER and thereby reduces ER stress and restores ER homeostasis. PERK activation also initiates transcriptional programs through the generation of the ATF4, ATF5 and CHOP bZIP transcription factors (19). The messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts encoding these genes share unusual 5ʹ regulatory elements that enable them to escape phospho-eIF2α-mediated translational attenuation and/or employ non-canonical modes of translational initiation, such that these transcription factors are up-regulated when PERK is activated, thereby activating their downstream transcriptional programs (20–23).
PERK is essential for cellular homeostasis. Perk-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) are highly sensitive to ER stress-induced cell death, and Perk-/- mice rapidly develop secretory cell defects best characterized in the exocrine and endocrine pancreas shortly after birth, and these mice fail to thrive (24,25). In Wolcott–Rallison syndrome, over 50 mutations in PERK have been identified that introduce premature stop codons, frameshifts or directly damage the kinase domain in affected individuals (26). In this rare autosomal recessive disease, children develop early onset non-autoimmune diabetes, hepatic dysfunction, skeletal abnormalities, growth retardation and rarely survive to adulthood (26). The similar phenotypes of Perk-/- mice and Wolcott–Rallison syndrome patients demonstrate the essential function of the PERK protein. Overactivation of PERK also disrupts cellular homeostasis and causes cell death through proapoptotic transcriptional programs induced by the ATF4 and CHOP transcription factors (27,28). Consistent with this, ablation of Atf4 or Chop reduces ER stress-induced damage and improves function in some animal models of disease arising from excessive ER stress (29–34). These findings emphasize that PERK signaling must be precisely balanced, as too little PERK signaling or too much PERK signaling leads to pathology.
Increased immunostaining of activated PERK protein was detected directly in human post-mortem brain sections from AD, Parkinson’s disease and PSP patients (35,36). In mice, small molecule inhibition of PERK kinase activity (GSK2606414) or phospho-eIF2α-mediated translational attenuation (ISRIB) prevented neurodegeneration and neuropathology in prion encephalopathy models (37,38). Wild-type mice-administered ISRIB also showed significant cognitive and memory improvement in physiological and behavioral paradigms (39). Conversely, enhancement of PERK activity and translational attenuation, by genetic modification or small molecule therapy (Sephin1), also prevented neurodegeneration and neuropathology in mouse models of myelination disease and misfolded SOD1-induced amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (40–43). In transgenic mouse tauopathy models, both PERK activation and inhibition resulted in protective effects. Pharmacologic activation of PERK reduced tau pathology, prevented dendritic spine and motor neuron loss and improved memory and locomotor function in P301S tau mice (44); conversely, pharmacological inhibition of PERK in transgenic mice expressing P301L tau also prevented neurodegeneration, reduced tau pathology and delayed clinical signs (45). These studies suggest that activating or inhibiting the PERK pathway can provide therapeutic benefit for tauopathies in mouse models, but it is unclear if these studies are relevant to human tauopathies, because the PERK polymorphisms identified as risk factors for tauopathy in people are not conserved in the homologous mouse Perk gene.
The functional consequences of human tauopathy-associated PERK polymorphisms and mechanism by which these polymorphisms confer neurodegeneration risk are unknown. Furthermore, these tauopathy-associated PERK polymorphisms are completely distinct from all of the previously identified genetic PERK alterations found in Wolcott–Rallison syndrome. In this study, we generated biochemical and patient stem cell resources to define the functional consequences of tauopathy PERK polymorphisms and to investigate the effects of these PERK alleles on neuronal survival during ER stress.
Results
Reduced activity of tauopathy-associated PERK variants
The tauopathy risk single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs7571971 originally identified by GWAS was in linkage disequilibrium with three additional SNPs (rs867529, rs13045 and rs1805165) that introduced amino acid substitutions into the PERK protein at position 136 (serine to cysteine), 166 (arginine to glutamine) and 704 (serine to alanine) (14,15,45–47). These SNPs can be grouped as non-risk Haplotype A or risk Haplotype B (S136C, R166Q and S704A) (Fig. 1A). To determine the functional consequences of these tauopathy-associated coding variants on PERK activity, we first expressed human PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B in Perk-/- MEFs) (24,25). PERK mRNA and protein levels were equivalent in Perk-/- MEFs expressing Haplotype A or Haplotype B (Fig. 1B and C). However, we found that PERK Haplotype B-expressing cells had significantly diminished phospho-eIF2α levels compared to Haplotype A (Fig. 1B). To further examine this, we generated Perk-/- MEFs stably expressing human PERK Haplotype A or B and performed a dose-response study with the ER stress-inducing agent, thapsigargin (Tg). We again observed diminished phospho-eIF2α generation in Haplotype B-expressing cells compared to Haplotype A-expressing cells treated with the same dose of ER stress-inducing drug (Fig. 1D). These findings revealed that risk Haplotype B PERK had reduced kinase activity compared to the non-risk Haplotype A in response to ER stress.
Figure 1.
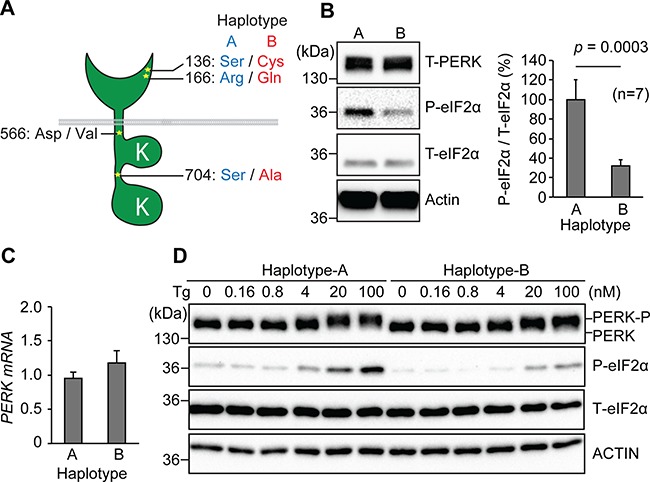
Tauopathy-associated EIF2AK3/PERK variants show reduced activity. (A) Amino acid variations between PERK Haplotype A (low risk), Haplotype B (high risk) and at residue 566 are shown. (B)Perk-/- MEFs were transfected with full-length human PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B, and cell lysates were immunoblotted for total PERK (T-PERK), phosphorylated eIF2α (P-eIF2α), total eIF2α (T-eIF2α) and actin (loading control). Area intensity of P-eIF2α and T-eIF2α immunoblotting data was quantified by Image J. Representative immunoblots are shown and quantified (n = 7). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. (C) Relative expression of human Perk mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR. PERK mRNA levels are shown and quantified (n = 5). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. (D) Stable Perk-/- MEFs reconstituted with human PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B were treated with Tg at the indicated concentrations for 1 h, and protein lysates were immunoblotted for PERK, P-eIF2α,T-eIF2α and actin. The position of phosphorylated PERK (P-PERK) is indicated. Representative immunoblots are shown (n = 5).
We next investigated the mechanisms underlying Haplotype B’s reduced activity. Numerous serines and threonines are present in PERK, and sustained trans-autophosphorylation of some of these residues is necessary for activation of the PERK kinase. The S704A coding variant lies within PERK’s cytosolic serine/threonine kinase domain (Fig. 1A) (17,48). We investigated whether this serine to alanine substitution affected PERK’s kinase activity by fusing PERK’s kinase domain (PERK-KD) to FK506-binding protein (Fv2E) to enable artificial kinase activation of the Fv2E-PERK-KD fusion molecule by dimerizing chemical, AP20187 (21,27). We generated stable HEK293 cell lines expressing Fv2E-PERK-KD with serine or alanine at residue 704 using Flp-In/frt as previously described (27). After AP20187 addition, we found that Fv2E-PERK-KD bearing alanine at 704 was less efficient at phosphorylating eIF2α at lower dimerizer concentrations compared to Fv2E-PERK with an intact serine at residue 704 (Fig. 2A). These studies identified impaired kinase activity by the S704A amino acid conversion as a cause for decreased Haplotype B signaling, compared to Haplotype A.
Figure 2.
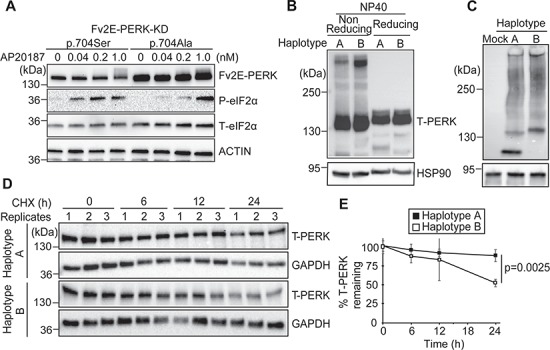
Tauopathy-associated EIF2AK3/PERK variants show impaired kinase activity, increased redox-dependent protein aggregation and increased protein turnover. (A) HEK293 cells stably expressing Fv2E-PERK-KD(704S) or Fv2E-PERK-KD(704A) were treated with increasing concentrations of AP20187 for 1 h. Protein lysates were immunoblotted for Fv2E-PERK (anti-FK506), P-eIF2α, T-eIF2α and actin (loading control). Representative immunoblots are shown (n = 5). (B) Lysates from Perk-/- MEFs expressing human PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B were prepared in NP40 lysis buffer with or without reducing agent (100 mm DTT). Proteins were resolved by 5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel in Tris-Glycine SDS buffer, and PERK was detected by immunoblotting. HSP90 was used as a loading control. Representative immunoblots are shown (n = 5). (C) Lysates from (B) were prepared in 0.2% NP40 lysis buffer, resolved by 4% polyacrylamide gel in Tris-Glycine buffer and transferred onto PVDF membrane in Tris-Glycine methanol buffer. HSP90 was used as a loading control. Cell lysates from mock-treated Perk-/- MEFs were included as a control for PERK antibody specificity. Representative immunoblots are shown (n = 5). (D) CHX (100 μm) was added to medium of Perk-/- MEFs expressing PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B. Lysates were collected at 0, 6, 12, 24 h after CHX exposure. PERK was detected by immunoblotting. Representative immunoblots are shown (n = 3). (E) Quantification of (D). PERK protein levels were normalized to respective loading control protein levels. The graph represents the PERK band intensity relative to time point 0 h (n = 3 for each time point; error bars = standard deviation). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis.
The luminal domain of the PERK Haplotype A protein has four cysteines that can generate two intramolecular disulfide bridges in the oxidative environment within the ER lumen. In contrast, the S136C coding variant introduced a 5th luminal cysteine into the luminal domain of the Haplotype B PERK molecule (Fig. 1A). The odd number of luminal cysteines in the Haplotype B PERK protein can cause abnormal intra- or inter-molecular disulfide bridges and protein aggregation in the Haplotype B PERK protein compared to Haplotype A. In support of this, we observed that the PERK Haplotype B protein formed more redox-dependent, higher molecular weight complexes (Fig. 2B), and more slowly migrating composites on semi-native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) compared to PERK Haplotype A protein (Fig. 2C). These findings revealed that Haplotype B adopted a different protein conformation than Haplotype A in a redox-dependent manner likely arising from the odd number of luminal cysteines.
Figure 3.
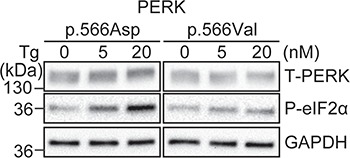
V566 has less kinase activity than D566. (A)Perk-/- MEFs were transfected with PERK(p566Asp) or PERK(p566Val) and treated with Tg at the indicated concentration for 1 h. Protein lysates were immunoblotted for PERK, phosphorylated PERK (P-PERK), P-eIF2α and GAPDH (loading control). Representative immunoblots are shown (n = 5).
Last, we investigated if the signaling and protein folding differences identified between PERK Haplotype A and PERK Haplotype B proteins lead to any differences in protein stability. Using cycloheximide (CHX) chase to measure protein half-life, we saw increased turnover of Haplotype B compared to the PERK Haplotype A protein (Fig. 2D and E). In sum, we identified three mechanisms to explain the decreased signaling seen with the risk PERK Haplotype B protein compared to Haplotype A: decreased kinase activity caused by the S704A change, altered redox-dependent protein conformation caused by the S136C change and increased turnover of the Haplotype B protein.
An additional PERK SNP, rs55791823, was also found to be enriched 16-fold in the PSP population (46). This SNP was not linked to those associated with PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B. This SNP introduced an amino acid substitution that converted PERK residue 566 from aspartate to valine (D566V) (Fig. 1A) (46). We examined how the D566V risk polymorphism affected PERK activity. We found that Perk-/- MEFs expressing PERK with 566V generated less phospho-eIF2α in response to Tg compared to MEFs expressing PERK bearing the non-risk 566D (Fig. 3). Based on our studies, we conclude that all known tauopathy-associated PERK coding variants are functional hypomorphs with reduced PERK signaling compared to non-risk PERK alleles.
Patient iPSC-derived neurons with tauopathy PERK alleles are more vulnerable to ER stress
Next, we investigated how human neurons carrying tauopathy PERK alleles behaved in response to ER stress. To study human neurons with tauopathy PERK alleles, we collected fibroblasts from PSP patients that were homozygous for the risk Haplotype B, and in one case, was also heterozygous for the 566V polymorphism (Table 1). For comparison, we identified fibroblasts from non-demented control (NDC) patients that were homozygous carriers of protective PERK alleles (Haplotype A and 566D) (Table 1). We reprogrammed all fibroblasts into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by non-integrating Sendai virus and confirmed pluripotency by embryoid body formation and gene expression (Fig. 4A and B). We confirmed that iPSCs had normal chromosomal karyotypes (Fig. 4C). We generated and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)-purified homogenous populations of neural stem cells from these iPSCs and differentiated them into neural cultures as previously described (Fig. 4D) (49–51). Immunofluorescent staining with neuronal and astrocytic markers confirmed robust differentiation of NDC and PSP iPSCs (Fig. 4E). The differentiated neuronal cultures showed voltage-dependent action potential and spontaneous synaptic activities reversibly blocked by a GABAA receptor antagonist and stably expressed tau protein (49,50).
Table 1.
Cell lines clinical information and Perk genotype of human subjects and experimental iPSC lines
| Clinical diagnosis | Gender | Age of onset | Age of biopsy | Rs7571971 (C/T) (intronic) | Rs867529 (C/G) TCC->TGC Ser136Cys | Rs13045 (G/A) CGA->CAA Arg166Gln | Rs55791823 (A/T) GAT->GTT Asp566Val | Rs1805165 (T/G) TCT->GCT Ser704Ala | iPSC lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | male | n/a | 86 | C/C | C/C | G/G | A/A | T/T | NDC1.1 NDC1.2 |
| control | male | n/a | 85 | C/C | C/C | G/G | A/A | T/T | NDC2.1 |
| control | male | n/a | 84 | C/C | C/C | G/G | A/A | T/T | NDC4 |
| PSP | male | 62 | 67 | T/T | G/G | A/A | A/T | G/G | PSP1.1 PSP1.2 |
| PSP | male | 74 | 78 | T/T | G/G | A/A | A/A | G/G | PSP2.1 PSP2.2 |
Figure 4.
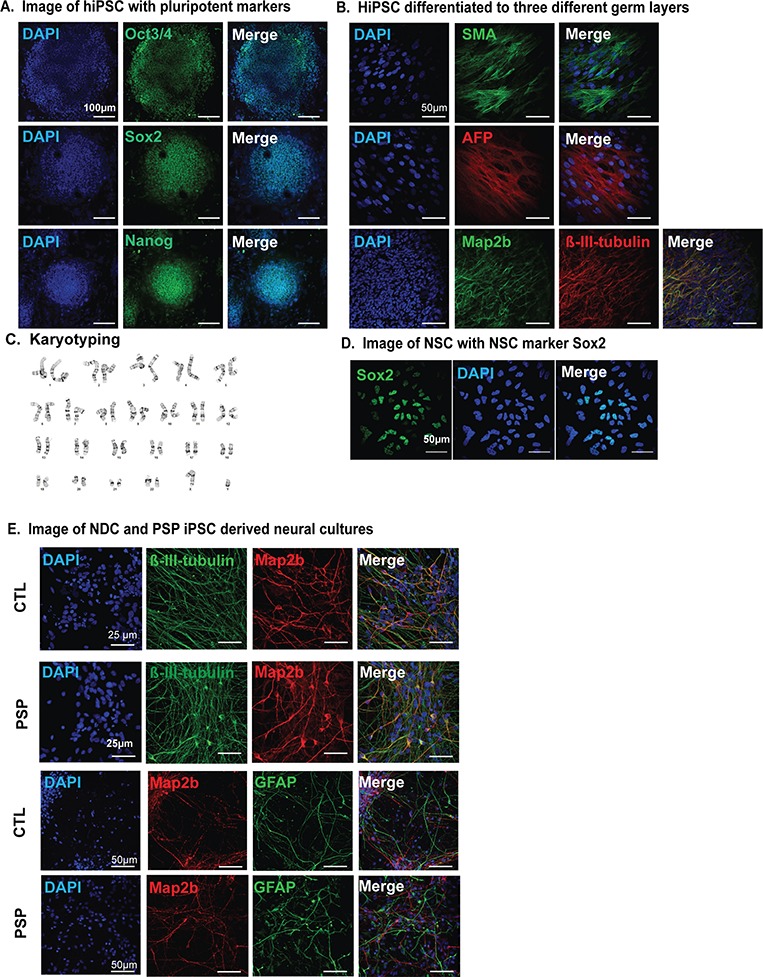
Generation of iPSC-derived neuronal cultures from PSP patients. (A) Images of representative iPSCs expressing pluripotency markers, Oct3/4, Sox2 and Nanog. Scale bar is 100 μm. (B) EB cultures derived from iPSC were stained with endodermal marker, α-fetoprotein (AFP), mesodermal marker, smooth muscle actin and neuroectodermal markers, Map2b or β-III-tubulin. Scale bar is 50 μm. (C) Representative G-banded normal karyotype from an iPSC line. (D) Representative images of FACS-purified iPSC-derived neural stem cells expressing NSC marker Sox2. Scale bar is 50 μm. (E) Representative images of 4 week differentiated neural cultures immunofluorescently stained with neuronal markers Map2b, β-III-tubulin or astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acid protein. Scale bar is 50 or 25 μm as shown.
We found that neuronal cultures derived from patient iPSCs carrying the tauopathy PERK alleles had diminished PERK and phospho-eIF2α protein levels compared to neuronal cultures with non-risk PERK alleles at baseline (Fig. 5A and B). Consistent with reduced PERK function in neurons carrying the PERK risk variants, we saw significantly reduced induction of CHOP after Tg treatment in neuronal cultures carrying tauopathy PERK alleles compared to controls at two progressive dosages of Tg (Fig. 5C). Together, these results indicate that iPSC-derived neurons carrying tauopathy-associated PERK variants show reduced PERK activity similar to the results we obtained when we expressed the tauopathy-associated PERK variants in Perk-/- MEFs (Fig. 1). PERK signaling is required for cell viability during ER stress, and Perk-/- MEFs are exquisitely sensitive to ER stress-induced cell death (25). Therefore, we tested if hypomorphic PERK alleles compromised neuronal survival in response to ER stress. Under basal maintenance conditions, we observed no cell death morphologically or biochemically (Fig. 5D). However, when we treated iPSC-derived neuronal cultures with tunicamycin, an agent that causes ER stress by inhibiting protein glycosylation, we found that neurons carrying hypomorphic PERK alleles were much more vulnerable to ER stress and underwent apoptosis as determined by pronounced induction of cleaved caspase 3 and PARP proteins (Fig. 5E). They also displayed increased number of condensed and fragmented nuclei, features of dying cells (Supplementary Material, Fig. 1A and B) (52,53). Unexpectedly, we also saw increased levels of total tau (K9JA) and pathological phosphorylated tau (AT8 and PHF1) during ER stress in neuronal cultures carrying hypomorphic PERK alleles (Fig. 5E) without any changes in MAPT expression (Fig. 5F). These findings revealed that neurons carrying tauopathy-associated PERK alleles showed hypomorphic signaling activity, similar to our biochemical studies and showed increased vulnerability to ER stress-induced damage compared to neurons carrying non-risk PERK alleles.
Figure 5.
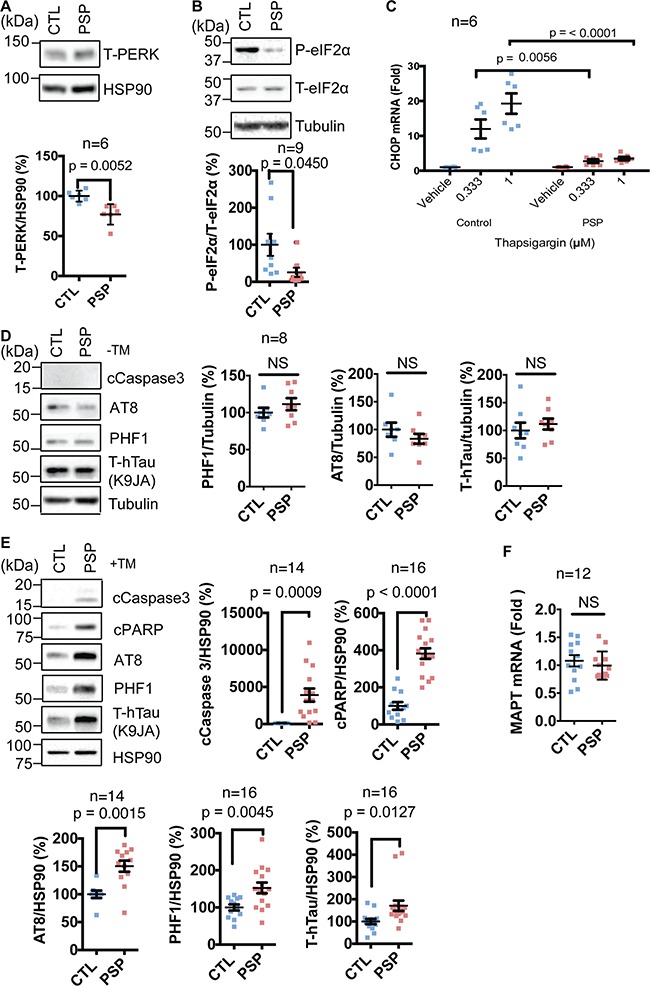
iPSC-derived neurons carrying hypomorphic Perk risk alleles are susceptible to ER stress and tau protein pathology. (A) Protein lysates from 4-week-old PSP and NDC iPSC-derived neuronal cultures under basal conditions were collected. Representative immunoblots for PERK and HSP90 (loading control) are shown and quantified (n = 6 biological replicates). At least three independent PSP or NDC iPSCs were analyzed for all studies. Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. (B) P-eIF2α, T-eIF2α and tubulin (loading control) were immunoblotted from human iPSC-derived neuronal cultures under basal conditions. Representative immunoblots are shown and quantified (n = 9). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. (C)Chop mRNA levels were quantified by qRT-PCR from iPSC-derived human neuronal cultures after Tg exposure for 5 h at the indicated dosage and are shown relative to vehicle-treated cultures (n = 6). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey was performed for statistical analysis. (D) Cleaved caspase 3, phosphorylated tau (AT8, PHF1) and total human tau (K9JA) were immunoblotted from human iPSC-derived neuronal cultures under basal non-ER stressed conditions. Representative blots are shown and quantified (n = 8). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. (E) Cleaved caspase 3, cleaved PARP, phosphorylated tau, total tau and HSP90 (loading control) were immunoblotted from iPSC-derived neuronal cultures treated with tunicamycin (12 h, 2 μg/ml). Representative blots are shown and quantified (n = 14–16 as indicated). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. (F)MAPT mRNA levels were quantified by qRT-PCR from iPSC-derived human neuronal cultures after TM exposure for 12 h and are shown relative to vehicle-treated cultures (n = 12). Unpaired student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis.
Pharmacologic inhibition of PERK increases neuronal cell death
To further test if impaired PERK signaling compromised survival and disrupted tau protein homeostasis, we pharmacologically inhibited PERK by treating neuronal cultures carrying non-risk PERK alleles with a chemical PERK inhibitor (PERKi), GSK2656157 (54). We confirmed that PERKi drug treatment was effective in our neuronal cultures through decreased levels of phospho-eIF2α and CHOP mRNA in PERKi-treated cultures compared to tunicamycin alone (Fig. 6A and B). We found that PERKi treatment with tunicamycin significantly increased neuronal cell death (Fig. 6C, Supplementary Material, Fig. 1C and D) similar to the increased neuronal cell death we saw with neurons expressing hypomorphic PERK alleles (Fig. 5, Supplementary Material, Fig. 1A and B). We also saw significantly increased tau protein levels with combined PERKi and tunicamycin treatment (Fig. 6C) occurring independent of changes in MAPT expression (Fig. 6D). Our studies demonstrated that pharmacologic inhibition of PERK increased neuronal cell death in response to ER stress and also disrupted tau protein homeostasis. Taken together with our analysis of neuronal cultures expressing hypomorphic PERK variants, our findings showed that impairment of PERK signaling, either by expression of functional PERK hypomorphs or by pharmacologic PERK inhibition, increased neuronal vulnerability to ER stress-induced cell death and abnormally increased tau protein levels.
Figure 6.
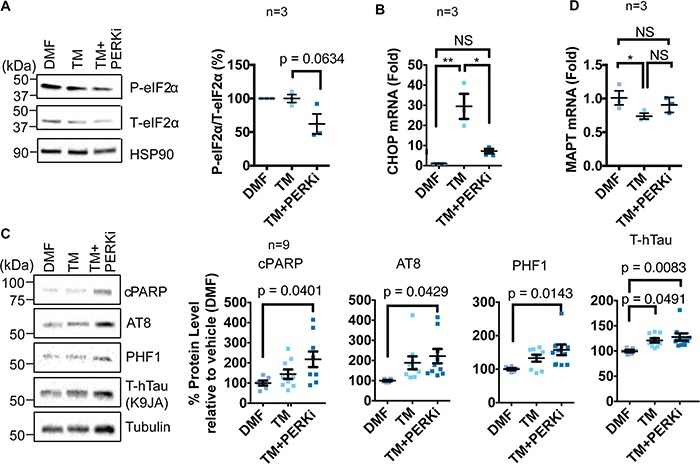
iPSC-derived neurons carrying normal PERK alleles are susceptible to ER stress and tau protein pathology when treated with PERK inhibitor. (A) NDC iPSC-derived neuronal cultures were treated with vehicle, tunicamycin (2 μg/ml) and GSK2656157 (PERKi) (200 nM) for 5 h. Representative blots for p-eIF2α, total eIF2α and HSP90 (loading control) are shown and quantified by densitometry (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test was performed for statistical analysis. (B)Chop mRNA levels were quantified by qRT-PCR from NDC iPSC-derived neuronal cultures treated (5 h) with the indicated agents and are graphed relative to vehicle treated control. (n =3 ), *P-value<0.05, **P-value<0.005. One-way ANOVA with Tukey test was performed for statistical analysis. (C) Cleaved PARP, phosphorylated pathologic tau (AT8, PHF1), total tau (K9JA) and tubulin (loading control) were immunoblotted from NDC iPSC-derived neuronal cell lysates treated with DMF, TM or TM+PERKi for 12 h. Representative blots are shown, and protein levels were quantified by densitometry and shown relative to DMF-treated samples (n = 9). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test was performed for statistical analysis. (D)MAPT mRNA levels were quantified by qRT-PCR from iPSC-derived human neuronal cultures treated with DMF, TM or TM+PERKi for 5 h and are shown relative to DMF-treated cultures (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test was performed for statistical analysis.
Discussion
Several GWAS identified PERK alleles as risk factors for PSP and subtypes of AD (14,15,46). These tauopathy-associated PERK alleles are not conserved in other species and are distinct from previously identified human PERK disease variants associated with Wolcott–Rallison syndrome. In our study, we found that tauopathy-associated PERK alleles negatively impacted PERK’s ability to activate its signal transduction pathway in response to ER stress. In PSP patient iPSC-derived neurons, we found that a physiological consequence of impaired PERK signaling was increased neuronal cell death when exposed to ER stress agents. Unexpectedly, we also found disruption of tau protein homeostasis when PERK signaling was reduced genetically or pharmacologically. We conclude that tauopathy-associated PERK alleles are functional hypomorphs with impaired signaling, and impaired PERK activity heightens neuronal damage in response to ER stress.
Our studies show that the risk PERK Haplotype B protein is less effective at phosphorylating eIF2α and less stable, and these molecular defects contribute to its hypomorphic function (Figs 1 and 2). PERK Haplotype B is widespread with 30% frequency in populations of Northern European descent (47). How does PERK Haplotype B with its reduced signaling during ER stress increase tauopathy risk in people carrying this allele? One model is that people with reduced PERK activity are more susceptible to environmental risk factors for tauopathies. In Northern France, a geographic cluster of patients with PSP was found in an area with extensive industrial waste and arsenic contamination of soil and drinking water (55). Another cluster of patients with PSP-like symptoms was identified in Guam and linked to cycad neurotoxin ingestion and exposure (56). A third cluster of PSP-like patients was identified on the Caribbean island of Guadeloupe and linked to consumption of tropical plants containing annonacin (5,57). Arsenic and neurotoxins cause ER stress, and annonacin targets mitochondrial ATP generation that could subsequently impair ER function to cause ER stress (58–61). As PERK is essential for cells to survive ER stress, reduced PERK signaling, arising in Haplotype B carriers, likely increases damage upon exposure to these environmental agents linked to tauopathy.
We found that genetic or chemical inhibition of PERK signaling in iPSC-derived neurons undergoing tunicamycin-induced ER stress led to an unexpected increase in neuronal tau protein levels, involving both total tau levels and hyperphosphorylated tau, independent of changes in MAPT expression (Figs 5 and 6). How could impaired PERK signaling lead to increased tau protein independent of increased MAPT expression? Under ER stress conditions, PERK decreases the rate of cellular protein synthesis by phosphorylating the translation initiating factor eIF2α, which diminishes mRNA translation as phospho-eIF2α cannot initiate ternary complex formation. In our studies, tauopathy-associated PERK alleles consistently showed reduced phosphorylation of eIF2α. One consequence of reduced PERK signaling during ER stress may therefore be increased or sustained translation of the MAPT mRNA, leading to increased tau protein levels. This potential mechanism could underlie the increase in tau protein levels seen in neurons carrying hypomorphic disease-associated PERK alleles. In this model, increased tau protein synthesis arises through the inability of disease PERK alleles to attenuate translation. Increased tau protein then leads to accumulation of tau tangles and other tau neuropathology that defines tauopathies.
Figure 7.
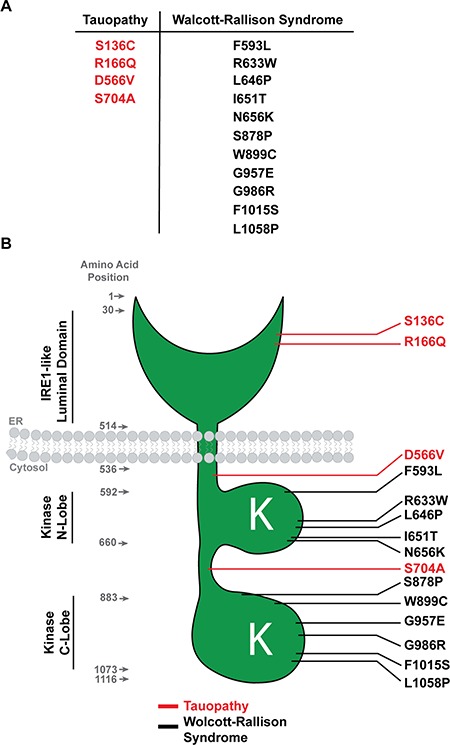
Summary model schematic comparing PERK tauopathy variants versus PERK Wolcott–Rallison variants. (A) Table summarizing missense mutations in tauopathy versus Wolcott–Rallison Syndrome. (B) Diagram showing the positions of the PERK variants in tauopathy (red) and Wolcott–Rallison Syndrome (black).
Our study defines a new set of functional variants in the human PERK gene. The Wolcott–Rallison PERK variants introduce nonsense and splice-site mutations that trigger nonsense-mediated mRNA decay with no PERK protein synthesis, or they directly mutate the kinase lobes and nullify its enzymatic activities (Fig. 7). The absence of PERK protein and abrogation of kinase function by the Wolcott–Rallison PERK mutations cause clinical phenotypes that closely align with those seen in the Perk-/- mouse (e.g. pancreatic insufficiency). The Perk-/- mice and Wolcott–Rallison patients typically do not survive to an advanced age when PSP symptoms emerge. However, a recent post-mortem brain autopsy of a 4-year-old Wolcott–Rallison patient showed neurodegeneration with tau pathology (62). In contrast, the tauopathy-associated PERK coding variants alter amino acids in the PERK luminal domain involved in ER stress sensing (S136C, R166Q) and in regions of the cytosolic domain proposed to include a ‘disordered linker’ (S704A, D566V) that joins essential lobes of the PERK kinase in crystallographic studies of the PERK cytosolic domain (Fig. 7B). The PERK kinase lobes are intact in these tauopathy PERK alleles, and phosphorylation of eIF2α still emerged after ER stress in our studies, albeit with slower kinetics. In contrast, no phosphorylation of eIF2α was found in Perk-/- MEFs after ER stress. Our studies reveal that tauopathy-associated PERK variants are a novel class of hypomorphic human PERK alleles arising from impaired stress sensing by the luminal domain and slower activation kinetics of the cytosolic kinase, while the Wolcott–Rallison PERK variants are effectively null PERK alleles. Interestingly, the residues altered in tauopathy risk PERK alleles are not conserved in the mouse PERK protein. The human PERK gene is organized into additional haplotypes besides the A and B Haplotypes, and additional SNPs are also present in non-coding regions of the gene (46,47). Future studies will define the functional consequence of these genetic variations and relation to tauopathies.
Pharmacologic PERK activation or PERK inhibition prevented neuropathology, neurodegeneration and improved survival in transgenic mouse tauopathy models developed through MAPT P301L or MAPT P301S overexpression (44,45). The mouse Perk gene does not have the tauopathy-linked genetic variants found in the human PERK gene, so it is unclear how these transgenic tauopathy mouse studies apply to the human condition. Nevertheless, these animal studies highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting PERK to treat neurodegeneration. In particular, small molecule compounds have been identified that directly inhibit the PERK pathway and include molecules that directly inhibit the PERK kinase or ISRIB, a molecule that abrogates the downstream effects of phospho-eIF2α (39,54). Small molecules have also been found that enhance the PERK pathway by increasing phospho-eIF2α levels (40). Our findings have implications on the use of these PERK pathway activators and inhibitors for trials in tauopathy patients. Specifically, PERK pathway activators would benefit individuals carrying hypomorphic alleles by enhancing and/or restoring PERK signaling. However, treating patients carrying the PERK risk alleles with PERK inhibitors would further lower PERK function and potentially exacerbate pathology. Indeed, in our iPSC-derived neuronal models, we found increased tau levels with GSK2656157 treatment (Fig. 6C). Genotyping patient PERK risk allele status prior to clinical trials investigating PERK modulation would be essential to assign the optimal small molecule PERK strategy (activator or inhibitor) to improve clinical trial success. Identifying the genetic status of PERK in patients may also be useful in lifestyle modifications to avoid environmental conditions and agents linked to ER stress in carriers of hypomorphic PERK alleles.
PERK operates in parallel with the IRE1 and ATF6 signaling effectors of the UPR (16). IRE1 and ATF6 initiate distinct signaling pathways and transcriptional programs to help prevent ER stress and protein misfolding. The roles of IRE1 and ATF6 in the pathogenesis of tauopathies are unclear, but they have been implicated in other neurodegenerative diseases (63). Small molecule activators and inhibitors of the IRE1 and ATF6 pathways have also been identified (64–67). Another pharmacologic approach to treat tauopathies may be modulating these alternative UPR pathways when PERK is compromised.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
Perk-/- MEFs were derived from the Eif2ak3tm1Dron mice generated by Dr David Ron (24,25) and provided by Dr Randy Kaufman. Flp-In 293 cells used for establishment of Fv2E-PERK isogenic cell lines were purchased from Invitrogen (R75007 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Corning) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Corning), 1% non-essential amino acids (Gibco, Waltham, MA) and 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin solution (Gibco) at 37°C in humidified 5% CO2 incubator.
Plasmid construction
Construction of pcDNA-full-length human PERK was performed by Gibson assembly strategy (New England Biolabs; NEB, Ipswich, MA) using pcDNA3.1 vector linearized with HindIII and XhoI and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fragment amplified with human PERK specific primers (forward: ggctagcgtttaaacttaagcttgccaccATGGAGCGCGCCATCAGC and reverse: acgggccctctagactcgagCTAATTGCTTGGCAAAGGGCATG). Human PERK HaplotypeA and Haplotype B were created by PCR mutagenesis strategy with PrimeSTAR Max master mix (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). pLPC-PGK-full-length PERK was used for retrovirus packaging in Phoenix-ampho cells as previously described (68). Human PERK-KD was amplified from pcDNA-full-length human PERK Haplotype A or Haplotype B using primers (forward: actggaaactaggggtCGCAGGCTTTTC ATCCT and reverse: agatcagcttctgctcATTGCTTGGCAAAGGGC AT), and PCR fragments were inserted into pEF5/FRT/Fv2E vector by Gibson assembly reaction. pEF5/FRT/Fv2E-humanPERK-KD plasmid was used for establishment of isogenic HEK293 cell line expressing each Fv2E-PERK-KD-p.704Ser or -p.704Ala and by Flp-In system (Invitrogen/Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Immunoblotting
Protein extraction was performed in SDS lysis buffer (62.5 mm Tris-HCl pH 6.8, 2% w/v SDS and 10% Glycerol) supplemented with 1% protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). NP-40 lysis buffer (1% or 0.2% NP-40, 150 mm NaCl, 50 mm Tris-HCl pH8.0 and 10% Glycerol) supplemented with 1% protease inhibitor cocktail was used for the non-reducing experiment and semi-native PAGE experiment. Sample viscosity in cell lysate prepared with SDS lysis buffer was disposed by sonication. Cell lysate prepared with NP-40 buffer was incubated on ice for 15 min followed by centrifugation to remove insoluble residue. For regular immunoblotting, protein concentration was measured by BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 10–20 μg protein sample was prepared in 1X NuPAGE LDS sample buffer (Invitrogen) followed by heat incubation at 70°C for 10 min in the presence of 100 mm DTT. Protein lysate for semi-native PAGE was mixed with bromophenol blue. Protein samples were resolved in 4–15% gradient precast gel (BioRad, Hercules, CA), 5% Tris-Glycine SDS poly acryl amide gel, 4% Tris-Glycine poly acryl amide gel and electrically transferred onto PVDF membrane in Tris-Glycine Methanol buffer at 250 mA for 1 h. Membranes were preincubated with blocking buffer (5% blocking milk in TBS pH7.6 containing 0.1% Tween-20) for 1 h at room temperature, and subsequently incubated with primary antibody diluted in 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) solution in tris buffered saline with Tween (TBST) at 4°C overnight. Primary antibodies were used as follows: rabbit monoclonal anti-PERK (C33E10; Cell Signaling Technology, dilution at 1:1000), rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-eIF2α (Ser51) (119A11; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, dilution at 1:1000), mouse monoclonal anti-eIF2α (G-12; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, dilution at 1:1000), mouse monoclonal anti-actin (C-4; Millipore, Burlington, MA, dilution at 1:20 000), rabbit polyclonal anti-Hsp90 (GeneTex, Irvine, CA, dilution at 1:1000), rabbit monoclonal phosphor-PERK(T982) (provided from Eli Lilly, Indianapolis, IN, dilution at 1:1000), rabbit polyclonal anti-Atf4 (CREB-2) (C-20: Santa Cruz Biotechnology, dilution at 1:1000), mouse monoclonal CHOP (GADD153) (B-3: Santa Cruz Biotechnology, dilution at 1:1000), rabbit polyclonal anti-FKBP-12 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, dilution at 1:1000), eIF2α (Abcam, dilution at 1:2000), phospho-eIF2α (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom, dilution at 1:2000), β-actin (Sigma, dilution at 1:8000), tubulin (Sigma, dilution at 1:8000), HSP90 (1:1000 Abcam). PHF1 (Gift of Dr Peter Davies; Albert Einstein, San Antonio, TX , dilution at 1:1000), AT-8 (1:200 Pierce, Appleton, WI), Activated-Caspase 3 (Cell Signaling, dilution at 1:1000), PARP (Cell Signaling, dilution at 1:1000). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit secondary antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology and diluted at 1:3000 in blocking buffer. Secondary antibody was reacted for 1 h at room temperature on a gentle bench-top shaker. SuperSignal West Pico or Femto chemiluminescent substrates (Thermo Fisher Scientific) were used as a HRP substrate, and signal was detected by ChemiDoc XRS Imager (BioRad).
Real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted with RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to manufacturer’s instruction, and 1 μg RNA was subsequently used for reverse transcriptase reaction with iScript cDNA synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad). Real-time PCR was performed with iQ SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad) on CFX96 thermal cycler (BioRad). Primers for human specific PERK were forward: GAGAAGTGGCAAGAAAAGATGG and reverse: CTGCGTATTTTAACTGATGGTGC. Primers specific for mouse Rpl19 were forward: ATGCCAACTCCCGTCAGCAG and reverse: TCATCCTTCTCATCCAGGTCACC. Rpl19 expression was used as internal control for normalization of relative expression of PERK.
PERK protein turnover
Perk-/- MEFs were transiently transfected with PGK-PERK Haplotype A and Haplotype B plasmid with polyethylenimine-MAX (Polysciences Inc., Warrington, PA), and then incubated for 18 h. Cells were treated with 100 μM CHX (Sigma) for 0, 6, 12 or 24 h. Following treatment, the cells were collected and lysed in NP-40 buffer. Immunoblot analyses were performed to determine total PERK protein levels as described above. Relative band density values were measured using ImageJ software. Protein levels were normalized with respect to the HSP90 loading control, and then expressed as a percentage of the protein levels at 0 h time point.
Collection of skin biopsy from patients and generation of fibroblasts
Patient dermal biopsies were collected from patients who were diagnosed with PSP with guideline Litvan et al. (8). Consents approved by the institutional review board were obtained. The skin biopsies were enzymatically treated and cut up into small pieces. Fibroblasts were grown out from the skin biopsies (50).
Genotyping of SNP
Genomic DNA was used to determine the SNP (rs7571971) and was extracted from fibroblast cell pellets using the Quick-gDNA MiniPrep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA). Total RNA was extracted from cell pellets by RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). The iScript™ cDNA Synthesis Kit (BioRad) was used to reverse transcribe total RNA into cDNA. DNA was amplified by PCR using high fidelity polymerase Phusion (NEB) or PicoMaxx (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA). The SNPs were determined by Sanger sequencing from both forward and reverse directions.
Generation and culture of hiPSC
Adult human dermal fibroblasts were transduced with non-integrating Sendai Virus vectors carrying hc-Myc, hKlf4 and KOS (CytoTune-iPS 2.0 Sendai Reprogramming Kit, Invitrogen), following the manufacturer’s instructions, or episomally with plasmids (69). The colonies were picked at 3–4 weeks when visible. They were initially passaged by mechanical dissociation and subsequently adapted to Accutase (Sigma). HiPSC lines were characterized for their ability to differentiate into cells of the three germ layers and for the expression of biomarkers for pluripotency.
Neural differentiation and isolation of NSC
Protocol was previously described (51). Briefly, PA6 cells were plated in a 10 cm dish and seeded with 100 000 cells iPSC next day. To enhance neural induction, cultures were treated with 5 μm Dorsomorphin (Sigma) for the first 6 days of differentiation. On day 12, neural stem cells (NSCs) were sorted using cell surface signature CD24+/CD184+/CD44-/CD271-. NSCs were expanded in NSC growth medium, containing DMEM:F12+Glutamax, 1X B27, 1X N2, 1X P/S (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) and 20 ng/ml basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF, R&D, Biopioneer, San Diego, CA). When the culture was 80% confluent, medium was changed to neuron differentiation medium: DMEM:F12+Glutamax, 1X B27, 1X N2, 1X P/S, for 4 weeks.
Generation of neuronal cultures
The protocol was previously described (51). Briefly, NSCs were seeded at 150 K/cm2 on a plastic dish coated with matrigel (83 μg/ml) or on glass coverslips coated with polyornithine 20 μg/ml and matrigel (83 μg/ml) prior to plating. NSCs were grown to about 80% confluency before initiating differentiation achieved by withdrawing the growth factor bFGF from the NSC media (DMEM-F12, 1% N2, 2% B27, Pen/strep and 20 ng/ml bFGF).
CHOP qRT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). cDNA was synthesized from total RNA using random primers with iScript cDNA synthesis kit (BioRad). RT-PCR reactions were conducted using CFX96 thermocycler (BioRad), with the cDNA as template, and primers (forward, 5ʹ-ACCAAGGGAGAACCAGGAAACG-3, and reverse, 5ʹ- TCACCATTCGGTCAATCAGAGC-3ʹ) specific to human CHOP mRNA. qRT-PCR program was 95°C, 10 min, and 40 cycles of 95°C, 20 s and 58°C for 1 min.
Tunicamycin, Tg, GSK2656157 treatment
Human neuronal cultures were treated with 2 μg/ml tunicamycin (EMD Millipore), 3 μm Tg (Sigma), or 200 nM GSK2656157 (Selleckchem) as final concentrations. The drugs were dissolved in either DMSO or DMF. DMSO or DMF was added to the vehicle control, at the concentration used in the drug treatment as controls.
Embryoid bodies generation
HiPSC colonies were treated with dispase (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) for 30 min at 37°C then dissociated by pipetting. Clusters of the dissociated cells were placed in low-adhesion plates (Corning) with iPSC media without FGF. Media was changed every 3 days. After 7 days, the clusters of cells grew to Embryoid bodies (EBs) and were seeded on cover glass coated with Matrigel (BD Biosciences). Cultures were maintained in either neuron differentiation media or fibroblast media for another 7 days.
Immunofluorescence studies
Cultures were fixed at room temperature with 4% paraformaldehyde. Fixed cultures were blocked for 45 min at room temperature in blocking solution (3% BSA, 0.3% Triton-x100, 1X PBS) stained for 2 h at room temperature or overnight at 4°C followed by 2× 5-minute washes with PBS. Primary antibodies used were anti-smooth muscle actin clone 1A4 (Biolegend) at 1:100, rabbit α-fetal protein (Dako, Santa Clara, CA) at 1:200. All secondary antibodies were applied in blocking solution at 1:1000 dilution for 45 min at room temperature. Antifade solution (ProLong Gold, Thermo, Waltham, MA) was applied to preserve the immunofluorescent signal before mounting coverslips to glass slides. Samples were imaged with a Leica confocal microscope while data collection and measurements were performed on ImageJ.
Statistical analysis
Student’s t-tests or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post-hoc analysis were performed to calculate statistical significance.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank David Ron and Randy Kaufman for Perk-/- MEFs and Kelsey Baron, Brenda Hug, Yuqi Kang and Kaitlyn Quach for technical support. S.H.Y., N.H., A.K. and J.H.L. conceived the project. S.H.Y., N.H., Q.L., X.V.S., D.L. and P.C. performed the experiments. A.K. and I.S.L. provided the patient biopsies. S.H.Y., N.H. and J.H.L. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest statement. None declared.
Funding
This work was supported in part by NIH (P50AG005131, R01NS088485, R01EY027355, U54OD020351), VA Merits (I01RX002340, I01BX002284) and Academic Senate (UCSD RN192H-YUAN).
References
- 1. Lee V.M., Goedert M. and Trojanowski J.Q. (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 24, 1121–1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ballatore C., Lee V.M. and Trojanowski J.Q. (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 8, 663–672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Crary J.F., Trojanowski J.Q., Schneider J.A., Abisambra J.F., Abner E.L., Alafuzoff I., Arnold S.E., Attems J., Beach T.G., Bigio E.H. et al. (2014) Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): a common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol., 128, 755–766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Escobar-Khondiker M., Hollerhage M., Muriel M.P., Champy P., Bach A., Depienne C., Respondek G., Yamada E.S., Lannuzel A., Yagi T. et al. (2007) Annonacin, a natural mitochondrial complex I inhibitor, causes tau pathology in cultured neurons. J. Neurosci., 27, 7827–7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Lannuzel A., Hoglinger G.U., Verhaeghe S., Gire L., Belson S., Escobar-Khondiker M., Poullain P., Oertel W.H., Hirsch E.C., Dubois B. et al. (2007) Atypical parkinsonism in Guadeloupe: a common risk factor for two closely related phenotypes? Brain, 130, 816–827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Nath U., Ben-Shlomo Y., Thomson R.G., Morris H.R., Wood N.W., Lees A.J. and Burn D.J. (2001) The prevalence of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome) in the UK. Brain, 124, 1438–1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Schrag A., Ben-Shlomo Y. and Quinn N.P. (1999) Prevalence of progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy: a cross-sectional study. Lancet, 354, 1771–1775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Litvan I., Agid Y., Calne D., Campbell G., Dubois B., Duvoisin R.C., Goetz C.G., Golbe L.I., Grafman J., Growdon J.H. et al. (1996) Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology, 47, 1–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Steele J.C., Richardson J.C. and Olszewski J. (1964) Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. A heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch. Neurol., 10, 333–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Hoglinger G.U., Respondek G., Stamelou M., Kurz C., Josephs K.A., Lang A.E., Mollenhauer B., Muller U., Nilsson C., Whitwell J.L. et al. (2017) Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: the movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord., 32, 853–864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Dickson D.W., Rademakers R. and Hutton M.L. (2007) Progressive supranuclear palsy: pathology and genetics. Brain Pathol., 17, 74–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Wang Y. and Mandelkow E. (2016) Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 17, 5–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Caffrey T.M. and Wade-Martins R. (2007) Functional MAPT haplotypes: bridging the gap between genotype and neuropathology. Neurobiol. Dis., 27, 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hoglinger G.U., Melhem N.M., Dickson D.W., Sleiman P.M., Wang L.S., Klei L., Rademakers R., Silva R., Litvan I., Riley D.E. et al. (2011) Identification of common variants influencing risk of the tauopathy progressive supranuclear palsy. Nat. Genet., 43, 699–705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Liu Q.Y., Yu J.T., Miao D., Ma X.Y., Wang H.F., Wang W. and Tan L. (2013) An exploratory study on STX6, MOBP, MAPT, and EIF2AK3 and late-onset alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging, 34 (1519), e1513–e1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Walter P. and Ron D. (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science, 334, 1081–1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Harding H.P., Zhang Y. and Ron D. (1999) Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature, 397, 271–274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Wek R.C., Jiang H.Y. and Anthony T.G. (2006) Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control. Biochem. Soc. Trans., 34, 7–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Harding H.P., Novoa I., Zhang Y., Zeng H., Wek R., Schapira M. and Ron D. (2000) Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell, 6, 1099–1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Starck S.R., Tsai J.C., Chen K., Shodiya M., Wang L., Yahiro K., Martins-Green M., Shastri N. and Walter P. (2016) Translation from the 5’ untranslated region shapes the integrated stress response. Science, 351, 465–475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Lu P.D., Harding H.P. and Ron D. (2004) Translation reinitiation at alternative open reading frames regulates gene expression in an integrated stress response. J. Cell Biol., 167, 27–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Vattem K.M. and Wek R.C. (2004) Reinitiation involving upstream ORFs regulates ATF4 mRNA translation in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 11269–11274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Palam L.R., Baird T.D. and Wek R.C. (2011) Phosphorylation of eIF2 facilitates ribosomal bypass of an inhibitory upstream ORF to enhance CHOP translation. J. Biol. Chem., 286, 10939–10949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Harding H.P., Zeng H., Zhang Y., Jungries R., Chung P., Plesken H., Sabatini D.D. and Ron D. (2001) Diabetes mellitus and exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in perk-/- mice reveals a role for translational control in secretory cell survival. Mol. Cell, 7, 1153–1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Harding H.P., Zhang Y., Bertolotti A., Zeng H. and Ron D. (2000) Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell, 5, 897–904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Julier C. and Nicolino M. (2010) Wolcott–Rallison syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis., 5, 29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Lin J.H., Li H., Zhang Y., Ron D. and Walter P. (2009) Divergent effects of PERK and IRE1 signaling on cell viability. PLoS One, 4, e4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Han J., Back S.H., Hur J., Lin Y.H., Gildersleeve R., Shan J., Yuan C.L., Krokowski D., Wang S., Hatzoglou M. et al. (2013) ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat. Cell Biol., 15, 481–490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Oyadomari S., Koizumi A., Takeda K., Gotoh T., Akira S., Araki E. and Mori M. (2002) Targeted disruption of the Chop gene delays endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated diabetes. J. Clin. Invest., 109, 525–532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Pennuto M., Tinelli E., Malaguti M., Del Carro U., D'Antonio M., Ron D., Quattrini A., Feltri M.L. and Wrabetz L. (2008) Ablation of the UPR-mediator CHOP restores motor function and reduces demyelination in Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1B mice. Neuron, 57, 393–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hu Y. (2012) Differential effects of unfolded protein response pathways on axon injury-induced death of retinal ganglion cells. Neuron, 73, 445–452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Bhootada Y., Kotla P., Zolotukhin S., Gorbatyuk O., Bebok Z., Athar M. and Gorbatyuk M. (2016) Limited ATF4 expression in degenerating retinas with ongoing ER stress promotes photoreceptor survival in a mouse model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. PLoS One, 11, e0154779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Baleriola J., Walker C.A., Jean Y.Y., Crary J.F., Troy C.M., Nagy P.L. and Hengst U. (2014) Axonally synthesized ATF4 transmits a neurodegenerative signal across brain regions. Cell, 158, 1159–1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Matus S., Lopez E., Valenzuela V., Nassif M. and Hetz C. (2013) Functional contribution of the transcription factor ATF4 to the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One, 8, e66672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Stutzbach L.D., Xie S.X., Naj A.C., Albin R., Gilman S., Lee V.M., Trojanowski J.Q., Devlin B. and Schellenberg G.D. (2013) The unfolded protein response is activated in disease-affected brain regions in progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun., 1, 31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Hoozemans J.J.M., Veerhuis R., Haastert E.S., Rozemuller J.M., Baas F., Eikelenboom P. and Scheper W. (2005) The unfolded protein response is activated in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol., 110, 165–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Moreno J.A., Halliday M., Molloy C., Radford H., Verity N., Axten J.M., Ortori C.A., Willis A.E., Fischer P.M., Barrett D.A. et al. (2013) Oral treatment targeting the unfolded protein response prevents neurodegeneration and clinical disease in prion-infected mice. Sci. Transl. Med., 5, 206ra138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Halliday M., Radford H., Sekine Y., Moreno J., Verity N., Quesne J., Ortori C.A., Barrett D.A., Fromont C., Fischer P.M. et al. (2015) Partial restoration of protein synthesis rates by the small molecule ISRIB prevents neurodegeneration without pancreatic toxicity. Cell Death Dis., 6, e1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Sidrauski C., Acosta-Alvear D., Khoutorsky A., Vedantham P., Hearn B.R., Li H., Gamache K., Gallagher C.M., Ang K.K., Wilson C. et al. (2013) Pharmacological brake-release of mRNA translation enhances cognitive memory. Elife, 2, e00498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Das I., Krzyzosiak A., Schneider K., Wrabetz L., D'Antonio M., Barry N., Sigurdardottir A. and Bertolotti A. (2015) Preventing proteostasis diseases by selective inhibition of a phosphatase regulatory subunit. Science, 348, 239–242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wang L., Popko B., Tixier E. and Roos R.P. (2014) Guanabenz, which enhances the unfolded protein response, ameliorates mutant SOD1-induced amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis., 71, 317–324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Wang L., Popko B. and Roos R.P. (2014) An enhanced integrated stress response ameliorates mutant SOD1-induced ALS. Hum. Mol. Genet., 23, 2629–2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. D'Antonio M., Musner N., Scapin C., Ungaro D., Del Carro U., Ron D., Feltri M.L. and Wrabetz L. (2013) Resetting translational homeostasis restores myelination in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1B mice. J. Exp. Med., 210, 821–838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Bruch J., Xu H., Rosler T.W., De Andrade A., Kuhn P.H., Lichtenthaler S.F., Arzberger T., Winklhofer K.F., Muller U. and Hoglinger G.U. (2017) PERK activation mitigates tau pathology in vitro and in vivo. EMBO Mol. Med., 9, 371–384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Radford H., Moreno J.A., Verity N., Halliday M. and Mallucci G.R. (2015) PERK inhibition prevents tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia. Acta Neuropathol., 130, 633–642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Ferrari R., Ryten M., Simone R., Trabzuni D., Nicolaou N., Hondhamuni G., Ramasamy A., Vandrovcova J., Consortium U.K.B.E., Weale M.E. et al. (2014) Assessment of common variability and expression quantitative trait loci for genome-wide associations for progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurobiol. Aging, 35 (1514), e1511–e1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Liu J., Hoppman N., O'Connell J.R., Wang H., Streeten E.A., McLenithan J.C., Mitchell B.D. and Shuldiner A.R. (2012) A functional haplotype in EIF2AK3, an ER stress sensor, is associated with lower bone mineral density. J. Bone Miner. Res., 27, 331–341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Cui W., Li J., Ron D. and Sha B. (2011) The structure of the PERK kinase domain suggests the mechanism for its activation. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr., 67, 423–428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Reilly P., Winston C.N., Baron K.R., Trejo M., Rockenstein E.M., Akers J.C., Kfoury N., Diamond M., Masliah E., Rissman R.A. et al. (2017) Novel human neuronal tau model exhibiting neurofibrillary tangles and transcellular propagation. Neurobiol. Dis., 106, 222–234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Israel M.A., Yuan S.H., Bardy C., Reyna S.M., Mu Y., Herrera C., Hefferan M.P., Van Gorp S., Nazor K.L., Boscolo F.S. et al. (2012) Probing sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease using induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature, 482, 216–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Yuan S.H., Martin J., Elia J., Flippin J., Paramban R.I., Hefferan M.P., Vidal J.G., Mu Y., Killian R.L., Israel M.A. et al. (2011) Cell-surface marker signatures for the isolation of neural stem cells, glia and neurons derived from human pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One, 6, e17540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Baarine M., Thandapilly S.J., Louis X.L., Mazue F., Yu L., Delmas D., Netticadan T., Lizard G. and Latruffe N. (2011) Pro-apoptotic versus anti-apoptotic properties of dietary resveratrol on tumoral and normal cardiac cells. Genes Nutr., 6, 161–169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Salim L.Z., Othman R., Abdulla M.A., Al-Jashamy K., Ali H.M., Hassandarvish P., Dehghan F., Ibrahim M.Y., Omer F.A. and Mohan S. (2014) Thymoquinone inhibits murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One, 9, e115340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Axten J.M., Medina J.R., Feng Y., Shu A., Romeril S.P., Grant S.W., Li W.H., Heerding D.A., Minthorn E., Mencken T. et al. (2012) Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)-7H-p yrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). J. Med. Chem., 55, 7193–7207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Caparros-Lefebvre D., Golbe L.I., Deramecourt V., Maurage C.A., Huin V., Buee-Scherrer V., Obriot H., Sablonniere B., Caparros F., Buee L. et al. (2015) A geographical cluster of progressive supranuclear palsy in northern France. Neurology, 85, 1293–1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Cox P.A. and Sacks O.W. (2002) Cycad neurotoxins, consumption of flying foxes, and ALS-PDC disease in Guam. Neurology, 58, 956–959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Champy P., Melot A., Guerineau Eng V., Gleye C., Fall D., Hoglinger G.U., Ruberg M., Lannuzel A., Laprevote O., Laurens A. et al. (2005) Quantification of acetogenins in Annona muricata linked to atypical parkinsonism in guadeloupe. Mov. Disord., 20, 1629–1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Foufelle F. and Fromenty B. (2016) Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug-induced toxicity. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect., 4, e00211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Okle O., Stemmer K., Deschl U. and Dietrich D.R. (2013) L-BMAA induced ER stress and enhanced caspase 12 cleavage in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells at low nonexcitotoxic concentrations. Toxicol. Sci., 131, 217–224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Shen H., Kim K., Oh Y., Yoon K.S., Baik H.H., Kim S.S., Ha J., Kang I. and Choe W. (2016) Neurotoxin betaNmethylaminoLalanine induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep., 14, 4873–4880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Schapira A.H. (2010) Complex I: inhibitors, inhibition and neurodegeneration. Exp. Neurol., 224, 331–335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Bruch J., Kurz C., Vasiljevic A., Nicolino M., Arzberger T. and Hoglinger G.U. (2015) Early neurodegeneration in the brain of a child without functional PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 74, 850–857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Hetz C. and Mollereau B. (2014) Disturbance of endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 15, 233–249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Gallagher C.M., Garri C., Cain E.L., Ang K.K., Wilson C.G., Chen S., Hearn B.R., Jaishankar P., Aranda-Diaz A., Arkin M.R. et al. (2016) Ceapins are a new class of unfolded protein response inhibitors, selectively targeting the ATF6alpha branch. Elife, 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Plate L., Cooley C.B., Chen J.J., Paxman R.J., Gallagher C.M., Madoux F., Genereux J.C., Dobbs W., Garza D., Spicer T.P. et al. (2016) Small molecule proteostasis regulators that reprogram the ER to reduce extracellular protein aggregation. Elife, 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Volkmann K., Lucas J.L., Vuga D., Wang X., Brumm D., Stiles C., Kriebel D., Der-Sarkissian A., Krishnan K., Schweitzer C. et al. (2011) Potent and selective inhibitors of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 endoribonuclease. J. Biol. Chem., 286, 12743–12755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Mendez A.S., Alfaro J., Morales-Soto M.A., Dar A.C., McCullagh E., Gotthardt K., Li H., Acosta-Alvear D., Sidrauski C., Korennykh A.V. et al. (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-independent activation of unfolded protein response kinases by a small molecule ATP-mimic. Elife, 4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Hiramatsu N., Messah C., Han J., Lavail M.M., Kaufman R.J. and Lin J.H. (2014) Translational and post-translational regulation of XIAP by eIF2alpha and ATF4 promotes ER stress-induced cell death during the unfolded protein response. Mol. Biol. Cell, 2014 May; 25 (9), 1411–1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Okita K., Matsumura Y., Sato Y., Okada A., Morizane A., Okamoto S., Hong H., Nakagawa M., Tanabe K., Tezuka K. et al. (2011) A more efficient method to generate integration-free human iPS cells. Nat. Methods, 8, 409–412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


