The crystal structures of four (E) -methoxybenzaldehyde oxime derivatives, namely (2-methoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 1, 2,3-dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 2, 4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 3, and 2,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 4, are discussed. The arrangements of the 2-methoxy group and the H atom of the oxime unit are s-cis in compounds 1–3, but in both independent molecules of compound 4, the arrangements are s-trans. The primary intermolecular O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds generate C(3) chains in 1 and 2. In contrast, in compound 3, the O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds generate symmetric  (6) dimers. A more complex dimer is generated in 4 from the O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) and C—H(2-methoxy)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds.
(6) dimers. A more complex dimer is generated in 4 from the O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) and C—H(2-methoxy)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, oxime derivative, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The crystal structures of four (E)-methoxybenzaldehyde oxime derivatives, namely (2-methoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 1, 2,3-dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 2, 4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 3, and 2,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime, 4, are discussed. The arrangements of the 2-methoxy group and the H atom of the oxime unit are s-cis in compounds 1–3, but in both independent molecules of compound 4, the arrangements are s-trans. There is also a difference in the conformation of the two molecules in 4, involving the orientations of the 2- and 5-methoxy groups. The primary intermolecular O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds generate C(3) chains in 1 and 2. In contrast, in compound 3, the O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds generate symmetric R 2 2(6) dimers. A more complex dimer is generated in 4 from the O—H(oxime)⋯O(hydroxy) and C—H(2-methoxy)⋯O(hydroxy) hydrogen bonds. In all cases, further interactions, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π or π–π, generate three-dimensional arrays. Hirshfeld surface and fingerprint analyses are discussed.
Chemical context
In the plant kingdom, oximes play a vital role in metabolism (Sørensen et al., 2018 ▸). Aldoximes, RCH=NOH, are found in many biologically active compounds (Abele et al., 2008 ▸; Nikitjuka & Jirgensons, 2014 ▸), having a diverse range of uses including as anti-tumour agents (Martínez-Pascual et al., 2017 ▸; Qin et al., 2017 ▸; Canario et al., 2018 ▸; Huang et al., 2018 ▸), acaricidal and insecticidal agents (Dai et al., 2017 ▸), thymidine phosphorylase inhibitors (Zhao et al., 2018 ▸), anti-microbial agents (Yadav et al., 2017 ▸), bacteriocides (Kozlowska et al., 2017 ▸), anti-inflammatory agents (Mohassab et al. 2017 ▸), and in the treatment of nerve-gas poisoning (Lorke et al., 2008 ▸; Voicu et al., 2010 ▸; Katalinić et al., 2017 ▸; Radić et al., 2013 ▸).
Benzaldehyde oximes, ArCH=NOH, with their –CH=N—OH functional group are ideally arranged for classical O—H⋯O and/or O—H⋯N hydrogen bonding. The last survey of the classical hydrogen-bonding patterns in benzaldehyde oximes reported in 2010 (Low et al., 2010 ▸) confirmed that the most frequently found arrangements, with the exception of salicylaldoxines, are  (6) dimers and C(3) chains, Fig. 1 ▸. Aakeröy et al. (2013 ▸) reported the percentages of
(6) dimers and C(3) chains, Fig. 1 ▸. Aakeröy et al. (2013 ▸) reported the percentages of  (6) dimers and C(3) chains found in non-salicylaldoxine to be ca 72 and 24%, respectively – similar percentages can be derived from a recent survey of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.39, August 2018 update; Groom et al., 2016 ▸). Hydrogen bonds are considered to be the strongest and most directional of intermolecular interactions in molecules (Etter, 1990 ▸) and thus play the major roles in determining the overall supramolecular structures. However, the involvement of weaker intermolecular interactions, such as C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, π–π interactions and interactions involving the substituents, can have a significant influence on the supramolecular arrays generated. In a continuation of recent studies on aldoximes (Low et al. 2018 ▸; Gomes et al., 2018 ▸), we have determined the crystal structures of four methoxybenzaldehyde derivatives, namely 2-MeO-X-C6H3CH=NOH where X = H in 1, X = 3-MeO in 2, X = 4-MeO in 3 and X = 5-MeO in 4. The aim of the study was to further investigate the occurrence of
(6) dimers and C(3) chains found in non-salicylaldoxine to be ca 72 and 24%, respectively – similar percentages can be derived from a recent survey of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.39, August 2018 update; Groom et al., 2016 ▸). Hydrogen bonds are considered to be the strongest and most directional of intermolecular interactions in molecules (Etter, 1990 ▸) and thus play the major roles in determining the overall supramolecular structures. However, the involvement of weaker intermolecular interactions, such as C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, π–π interactions and interactions involving the substituents, can have a significant influence on the supramolecular arrays generated. In a continuation of recent studies on aldoximes (Low et al. 2018 ▸; Gomes et al., 2018 ▸), we have determined the crystal structures of four methoxybenzaldehyde derivatives, namely 2-MeO-X-C6H3CH=NOH where X = H in 1, X = 3-MeO in 2, X = 4-MeO in 3 and X = 5-MeO in 4. The aim of the study was to further investigate the occurrence of  (6) dimers and C(3) chains in a series of related compounds.
(6) dimers and C(3) chains in a series of related compounds.
Figure 1.
Illustrations of the C(3) chains and  (6) dimers formed by oximes
(6) dimers formed by oximes
Structural commentary
There are no unusual features in the molecular structures. Compound 1 crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pna21 with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 2 ▸), compound 2 crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group P212121 with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 3 ▸), compound 3 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P
 with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 4 ▸), and compound 4 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group, P21/c with two independent molecules, Mol A and Mol B, in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 5 ▸). The geometry about the oxime moiety in all molecules is (E). In compounds 1–3, the 2-methoxy group and the hydrogen of the oxime moiety have an s-cis arrangement. In contrast, in both molecules of compound 4, the 2-methoxy group and the hydrogen atom of the oxime moiety have an s-trans arrangement. The s-trans arrangement of the 2-alkoxy group and hydrogen atom of the oxime units in compound 4 is very much rarer than the s-cis arrangement found in compounds 1–3 and other non-salicylaldoximes. A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.39, August 2018 update; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) revealed that only salicylaldoximes and 2-alkoxybenzaldehyde oxime (E)-2-({2-[(E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl]phenoxy}methyl)-3-p-tolylacrylonitrile (LAQRIG; Suresh et al. 2012 ▸) had this s-trans arrangement. In contrast, the isomer 2-({2-[(hydroxyimino)methyl]phenoxy}methyl)-3-(2-methylphenyl)acrylonitrile (GARNEU; Govindan et al., 2012a
▸) and some similar compounds such as (E)-2-({2-[(E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl]phenoxy}methyl)-3-phenylacrylonitrile (LAQRUS; Govindan et al., 2012b
▸) had the s-cis arrangement.
with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 4 ▸), and compound 4 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group, P21/c with two independent molecules, Mol A and Mol B, in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 5 ▸). The geometry about the oxime moiety in all molecules is (E). In compounds 1–3, the 2-methoxy group and the hydrogen of the oxime moiety have an s-cis arrangement. In contrast, in both molecules of compound 4, the 2-methoxy group and the hydrogen atom of the oxime moiety have an s-trans arrangement. The s-trans arrangement of the 2-alkoxy group and hydrogen atom of the oxime units in compound 4 is very much rarer than the s-cis arrangement found in compounds 1–3 and other non-salicylaldoximes. A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.39, August 2018 update; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) revealed that only salicylaldoximes and 2-alkoxybenzaldehyde oxime (E)-2-({2-[(E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl]phenoxy}methyl)-3-p-tolylacrylonitrile (LAQRIG; Suresh et al. 2012 ▸) had this s-trans arrangement. In contrast, the isomer 2-({2-[(hydroxyimino)methyl]phenoxy}methyl)-3-(2-methylphenyl)acrylonitrile (GARNEU; Govindan et al., 2012a
▸) and some similar compounds such as (E)-2-({2-[(E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl]phenoxy}methyl)-3-phenylacrylonitrile (LAQRUS; Govindan et al., 2012b
▸) had the s-cis arrangement.
Figure 2.
Atom arrangements and numbering scheme for compound 1. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 3.
Atom arrangements and numbering system for compound 2. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 4.
Atom arrangements and numbering system for compound 3. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 5.
Atom arrangements and numbering system for the two independent molecules, Mol A and Mol B, of compound 4. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
There is a conformational difference between the two independent molecules Mol A and Mol B of compound 4. This difference is in the orientation of the two methoxy groups, see Fig. 5 ▸: in Mol A the orientation is s-trans and in Mol B, it is s-cis. As expected for a 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzene derivative, compound 4 is the least planar of the four oxime derivatives, with the 2-methoxy substituent furthest out of the plane of the attached phenyl group, see Table 1 ▸.
Table 1. Distances (Å) of OMe C atoms and oxime N and O atoms from benzene ring mean plane in compounds 1–4 .
| Atom | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 Mol A | 4 Mol B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C21 | 0.086 (3) | −1.140 (4) | 0.195 (1) | 0.121 (1) | 0.059 (1) |
| C31 | – | −0.011 (4) | – | – | – |
| C41 | – | – | 0.081 (1) | – | – |
| C51 | – | – | – | 0.033 (1) | 0.061 (1) |
| N12 | 0.061 (2) | 0.259 (3) | −0.177 (1) | 0.264 (1) | −0.020 (1) |
| O13 | −0.009 (2) | −0.027 (3) | 0.051 (1) | 0.242 (1) | 0.010 (1) |
Supramolecular features
Hydrogen bonding
In the crystal of 1, molecules are primarily linked by strong O13—H13⋯N12i hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸), forming C(3) chains, illustrated in Fig. 6 ▸. Also present in compound 1 are two weaker hydrogen bonds, namely, C3—H3⋯O13ii and C21—H21C⋯O13iii, as well as a weak π–π stacking interaction [Cg⋯Cg
iv = 4.025 (2) Å: slippage 2.105 Å: symmetry code; x, y, z − 1]. These three interactions generate the molecular arrangement shown in Fig. 7 ▸. The C3—H3⋯O13ii hydrogen bonds generate C7 chains in the c-axis direction, while the C21—H21C⋯O13iii hydrogen bonds form C(8) spiral chains along the a-axis direction: together these hydrogen bonds form  (22) rings. The tilted π–π stacks propagate in the c-axis direction. The involvement of the weaker C3—H3⋯O13ii, C21—H21C⋯O13iii and π–π interactions, along with the stronger O13—H13 ⋯N12i hydrogen bonds, creates the three-dimensional structure for 1.
(22) rings. The tilted π–π stacks propagate in the c-axis direction. The involvement of the weaker C3—H3⋯O13ii, C21—H21C⋯O13iii and π–π interactions, along with the stronger O13—H13 ⋯N12i hydrogen bonds, creates the three-dimensional structure for 1.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 1 .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O13—H13⋯N12i | 0.84 | 1.93 | 2.764 (2) | 170 |
| C3—H3⋯O13ii | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.442 (2) | 174 |
| C21—H21C⋯O13iii | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.506 (3) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 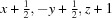 ; (iii)
; (iii) 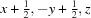 .
.
Figure 6.
Compound 1. Part of a C(3) chain formed by O13—H13⋯·N12 hydrogen bonds (dashed lines; see Table 2 ▸).
Figure 7.
Compound 1. Part of the arrangement generated from the combination of hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions (dashed lines; see Table 2 ▸).
As in 1, molecules of 2 are primarily linked by strong O13—H13 ⋯N12i hydrogen bonds (Table 3 ▸), forming C(3) chains: as such chains are very similar to those in compound 1, see Fig. 6 ▸, an illustration has not been provided for the C(3) chain in compound 2. Other intermolecular interactions in 2 are the weaker C21—H21B⋯O31iii and C31—H31B⋯O13iv hydrogen bonds and a C31—H31C⋯Cg1v interaction involving the C1–C6 ring. These three interactions combine to form the arrangement illustrated in Fig. 8 ▸. The C21—H21B⋯O31iii hydrogen bonds on their own generate C(6) chains, which propagate in the a-axis direction while the C31—H31B⋯O13iv hydrogen bonds generate spiral C(9) chains in the b-axis direction. Together these hydrogen bonds generate a network of  (26) rings. The C31—H31C⋯Cg1v interactions lead to chains along the a-axis direction. The involvement of the weaker C21—H21B⋯O31iii, C31—H31B⋯O13iv C and C—H⋯π interactions, along with the stronger O13—H13 ⋯N12i hydrogen bonds, creates a three-dimensional structure for 2. C4—H4⋯O12ii hydrogen bonds also occur.
(26) rings. The C31—H31C⋯Cg1v interactions lead to chains along the a-axis direction. The involvement of the weaker C21—H21B⋯O31iii, C31—H31B⋯O13iv C and C—H⋯π interactions, along with the stronger O13—H13 ⋯N12i hydrogen bonds, creates a three-dimensional structure for 2. C4—H4⋯O12ii hydrogen bonds also occur.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 2 .
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O13—H13⋯N12i | 0.97 (4) | 1.87 (5) | 2.805 (4) | 161 (4) |
| C4—H4⋯O21ii | 0.95 | 2.63 | 3.284 (4) | 126 |
| C21—H21B⋯O31iii | 0.98 | 2.54 | 3.323 (5) | 136 |
| C31—H31B⋯O13iv | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.448 (5) | 161 |
| C31—H31C⋯Cg1v | 0.98 | 2.73 | 3.599 (5) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Figure 8.
Compound 2. Part of the arrangement generated form C21—H21B⋯O31, C31—H31B⋯O13 and π–π interactions (dashed lines; see Table 3 ▸).
In compound 3,  (6) dimers are generated from strong O13—H13⋯N12i hydrogen bonds (Table 4 ▸), as illustrated in Fig. 9 ▸. Linkages of these
(6) dimers are generated from strong O13—H13⋯N12i hydrogen bonds (Table 4 ▸), as illustrated in Fig. 9 ▸. Linkages of these  (6) dimers by weaker C41—H41A(methoxy)⋯O13ii hydrogen bonds provide a two-molecule-wide ribbon. Within the ribbons are
(6) dimers by weaker C41—H41A(methoxy)⋯O13ii hydrogen bonds provide a two-molecule-wide ribbon. Within the ribbons are  (22) rings as well as the
(22) rings as well as the  (6) rings. An additional interaction in 3 is the C41—H41C⋯Cg1iii interaction, which generates a tilted ladder assembly, propagating in the a-axis direction, with the
(6) rings. An additional interaction in 3 is the C41—H41C⋯Cg1iii interaction, which generates a tilted ladder assembly, propagating in the a-axis direction, with the  (6) rings acting as the rungs and the C41—H41C⋯Cg1iii interactions as the supports.
(6) rings acting as the rungs and the C41—H41C⋯Cg1iii interactions as the supports.
Table 4. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 3 .
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O13—H13⋯N12i | 0.893 (18) | 1.995 (19) | 2.8124 (13) | 151.5 (15) |
| C41—H41A⋯O13ii | 0.98 | 2.63 | 3.0680 (15) | 107 |
| C41—H41C⋯Cg1iii | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.4479 (13) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Figure 9.
Compound 3. A two-molecule-wide ribbon generated from linking the  (6) dimers, formed by pairs of strong O13—H13—N12 hydrogen bonds and by weaker C41—H41A⋯O13 hydrogen bonds (dashed lines; see Table 4 ▸).
(6) dimers, formed by pairs of strong O13—H13—N12 hydrogen bonds and by weaker C41—H41A⋯O13 hydrogen bonds (dashed lines; see Table 4 ▸).
In compound 4, each of the two independent molecules forms symmetric dimers, see Fig. 10 ▸. These are generated from combinations of O113—H113⋯N112i and O113—H113⋯O121i hydrogen bonds (Table 5 ▸) for Mol A and O213—H213⋯N212ii and O213—H213⋯O221ii hydrogen bonds for Mol B. In each case, the dimers contain three rings, two  (6) and one
(6) and one  (6). There are short N⋯N distances across the
(6). There are short N⋯N distances across the  (6) dimer rings, 2.8595 (12) Å for MolA and 2.8956 (12) Å for Mol B, each being less than the sum of the van der Waals radius (3.10 Å) for two N atoms.
(6) dimer rings, 2.8595 (12) Å for MolA and 2.8956 (12) Å for Mol B, each being less than the sum of the van der Waals radius (3.10 Å) for two N atoms.
Figure 10.
Compound 4. Symmetric dimers of (a) Mol A and (b) Mol B. Hydrogen bonds (see Table 5 ▸) are shown as dashed lines.
Table 5. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 4 .
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C11–C16 and C21–C26 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O113—H113⋯O121i | 0.875 (16) | 2.247 (15) | 2.8944 (9) | 130.7 (12) |
| O113—H113⋯N112i | 0.875 (16) | 1.965 (16) | 2.7567 (10) | 149.9 (13) |
| O213—H213⋯O221ii | 0.877 (15) | 2.204 (15) | 2.8758 (9) | 133.1 (12) |
| O213—H213⋯N212ii | 0.877 (15) | 2.034 (15) | 2.8160 (10) | 147.9 (13) |
| C111—H111⋯O251 | 0.95 | 2.46 | 3.2458 (11) | 140 |
| C121—H12C⋯N212iii | 0.98 | 2.53 | 3.4400 (13) | 155 |
| C151—H15A⋯O113iv | 0.98 | 2.50 | 3.3947 (11) | 152 |
| C14—H14⋯Cg2iii | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.6656 (9) | 130 |
| C151—H15B⋯Cg2 | 0.98 | 2.72 | 3.5973 (10) | 149 |
| C24—H24⋯Cg1v | 0.95 | 2.67 | 3.4281 (10) | 137 |
| C211—H211⋯Cg1vi | 0.95 | 2.78 | 3.6272 (9) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  ; (vi)
; (vi)  .
.
The links between the two different dimers of 4 are provided by a number of C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions, listed in Table 5 ▸. Fig. 11 ▸ restricts the contacts to just the C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, namely C121—H12C⋯N212iii, C111—H111⋯O251 and C151—H15A⋯O113iv. To facilitate the viewing of the connection in Fig. 11 ▸, the two different dimers are drawn in different colours.
Figure 11.
Compound 4. Symmetric dimers of Mol A (green) and Mol B (blue). Intermolecular interactions (see Table 5 ▸) are shown as dashed lines.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
Hirshfeld surfaces (Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸) and two-dimensional fingerprint (FP) plots (Spackman & McKinnon, 2002 ▸), provide complementary information concerning the intermolecular interactions discussed above. The analyses were generated using Crystal Explorer3.1 (Wolff et al., 2012 ▸). The Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over d norm for 1–4 are illustrated in Fig. 12 ▸. The red areas on the surfaces correspond to close contacts. The fingerprint plots are shown in Fig. 13 ▸. In all of the FP plots, the pair of spikes pointing south-west relate to the N—H contacts, which in compounds 1 and 2 are involved in the C(3) chains, while in compounds 3 and 4, they are responsible for the creation of the dimers. In compound 3, the fins ending at d e, d i = 1.9,1.1 Å are due to C(π)⋯H/C(π)⋯H contacts. The FP plots for Mol A and Mol B of compound 4 are asymmetric because of the different interactions of each molecule. The double wings in the FP plot for Mol A in the second quadrant are complementary to those displayed in the fourth quadrant by MolB and relate to C⋯H close contacts connecting the two molecules. The spike ending at d i, d e = 1.1 Å in Mol A is due to H⋯H contacts.
Figure 12.
Hirshfeld surfaces for compounds 1–4. In each case, the interactions related to the red areas are designated.
Figure 13.
Fingerprint plots for compounds 1–4.
The percentages of the various atom–atom contacts, derived from the fingerprint plots, for the four compounds are shown in Table 6 ▸. The fact that compound 1 has only one methoxy group while the isomers, 2–4, have two is reflected in the greater percentages of contacts involving the oxygen close contacts. The C(3)-chain-forming compounds 1 and 2 show higher percentages of H⋯H and C⋯C contacts, but a lower percentage of H⋯C/C⋯H contacts, than the dimer-forming compounds 3 and 4.
Table 6. Percentages of atom–atom contacts for compounds 1, 2, 3 and 4 (Mol A and Mol B).
| Compound | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 Mol A | 4 Mol B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H⋯H | 52.7 | 49.1 | 43.7 | 41.5 | 38.6 |
| H⋯O/O⋯H | 16.2 | 22.5 | 23.4 | 24.9 | 26.3 |
| H⋯C/C⋯H | 11.3 | 14.5 | 20.4 | 22.7 | 25.9 |
| H⋯N/N⋯H | 8.1 | 6.6 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 8.1 |
| C⋯C | 7.9 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| O⋯C/C⋯O | 2.1 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| N⋯O/O⋯N | – | – | – | – | – |
| N⋯C/C⋯N | 1.6 | 1.8 | – | – | – |
| O⋯O | – | – | – | 0.4 | 0.2 |
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database survey (CSD Version 5.39, August 2018 update; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) revealed compounds similar to 2 and 3. The classical hydrogen bonds in 3,5-dimethoxybenzene oxime generate C(3) chains (VUZJAC; Dong et al., 2010 ▸). No benzene oxime derivative with only methoxy substituents has been reported in the database to form an  (6) or related dimer. The structure has been reported of 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzene oxime (MEQDAO; Chang, 2006 ▸) in which classical hydrogen bonds, formed between the oxime unit and the 4- and 5-methoxy moieties, but not the 2-methoxy group, result in the formation of a tetramer. The water molecule in 3,4.5-trimethoxybenzene monohydrate (HESWUY; Priya et al., 2006 ▸) is strongly involved in the hydrogen-bonding arrangements.
(6) or related dimer. The structure has been reported of 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzene oxime (MEQDAO; Chang, 2006 ▸) in which classical hydrogen bonds, formed between the oxime unit and the 4- and 5-methoxy moieties, but not the 2-methoxy group, result in the formation of a tetramer. The water molecule in 3,4.5-trimethoxybenzene monohydrate (HESWUY; Priya et al., 2006 ▸) is strongly involved in the hydrogen-bonding arrangements.
There are 376 structures, (411 fragments) in the CSD database with oxime  (6) dimers in which the N⋯N distance across the ring is less than or equal to 3.10 Å, the sum of two N-atom van der Waals radii. The H⋯O hydrogen-bond distance range was restricted to 1.739–2.285 Å to exclude improbable O⋯H distances based on a statistical analysis in Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▸). The N⋯N distances range from 2.727 to 3.097 Å with a mean value of 2.987 Å. There are 27 structures within the range 2.838 to 2.909 Å in which our values of 2.8595 (12) Å for MolA and 2.8956 (12) Å for MolB of compound4 lie. Only single-crystal organic compounds were searched for with no limit on the R factor.
(6) dimers in which the N⋯N distance across the ring is less than or equal to 3.10 Å, the sum of two N-atom van der Waals radii. The H⋯O hydrogen-bond distance range was restricted to 1.739–2.285 Å to exclude improbable O⋯H distances based on a statistical analysis in Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▸). The N⋯N distances range from 2.727 to 3.097 Å with a mean value of 2.987 Å. There are 27 structures within the range 2.838 to 2.909 Å in which our values of 2.8595 (12) Å for MolA and 2.8956 (12) Å for MolB of compound4 lie. Only single-crystal organic compounds were searched for with no limit on the R factor.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compounds were prepared from hydroxyamine and the corresponding benzaldehyde in methanol in the presence of potassium carbonate and were recrystallized from methanol solutions, m.p. = 364–365 K for compound 1, 371–373 K for 2, 378–380 K for 3 and 370–371 K for 4.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 7 ▸. All hydroxy hydrogen atoms were refined isotropically. C-bound H atoms were refined as riding with C—H = 0.95–0.98Å and U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C).
Table 7. Experimental details.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | C8H9NO2 | C9H11NO3 | C9H11NO3 | C9H11NO3 |
| M r | 151.16 | 181.19 | 181.19 | 181.19 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P n a21 | Orthorhombic, P212121 | Triclinic, P

|
Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 11.1719 (2), 16.4260 (3), 4.0249 (1) | 4.6775 (2), 13.0996 (5), 14.1984 (5) | 4.9441 (2), 8.2188 (4), 12.1308 (3) | 7.6480 (1), 21.3380 (4), 10.9421 (2) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 108.849 (3), 92.288 (3), 106.273 (4) | 90, 90.555 (2), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 738.61 (3) | 869.98 (6) | 443.17 (3) | 1785.59 (5) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 2 | 8 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα | Cu Kα | Cu Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.05 × 0.05 × 0.03 | 0.30 × 0.05 × 0.02 | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.05 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.13 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku 007HF equipped with Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC11 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector | Rigaku 007HF equipped with Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC11 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector | Rigaku 007HF equipped with Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC11 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector | Rigaku FRE+ equipped with VHF Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC12 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.848, 1.000 | 0.507, 1.000 | 0.802, 1.000 | 0.935, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 12857, 1345, 1325 | 7835, 1596, 1371 | 7618, 1594, 1462 | 38753, 4082, 3761 |
| R int | 0.038 | 0.095 | 0.033 | 0.020 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.649 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.033, 0.088, 1.08 | 0.058, 0.151, 1.04 | 0.035, 0.101, 0.88 | 0.031, 0.086, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 1345 | 1596 | 1594 | 4082 |
| No. of parameters | 102 | 124 | 124 | 247 |
| No. of restraints | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.17, −0.16 | 0.35, −0.20 | 0.20, −0.19 | 0.32, −0.19 |
| Absolute structure | Refined as a perfect inversion twin. | Flack x determined using 474 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | – | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.5 | 0.2 (3) | – | – |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 1, 2, 3, 4, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm2129sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21291sup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21292sup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21293sup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 4. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21294sup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21291sup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21292sup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21293sup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21294sup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff at the National Crystallographic Service, University of Southampton, for the data collection, help and advice (Coles & Gale, 2012 ▸).
supplementary crystallographic information
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Crystal data
| C8H9NO2 | Dx = 1.359 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 151.16 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Cell parameters from 7376 reflections |
| a = 11.1719 (2) Å | θ = 2.7–70.0° |
| b = 16.4260 (3) Å | µ = 0.82 mm−1 |
| c = 4.0249 (1) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 738.61 (3) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.05 × 0.05 × 0.03 mm |
| F(000) = 320 |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Data collection
| Rigaku 007HF equipped with Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC11 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector diffractometer | 1345 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating anode, Rigaku 007 HF | 1325 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.038 |
| profile data from ω–scans | θmax = 68.2°, θmin = 4.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.848, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −19→19 |
| 12857 measured reflections | l = −4→4 |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0559P)2 + 0.1277P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.088 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.08 | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 1345 reflections | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| 102 parameters | Absolute structure: Refined as a perfect inversion twin. |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.5 |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component perfect inversion twin. |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O13 | 0.45979 (12) | 0.42019 (8) | −0.4095 (4) | 0.0311 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.443792 | 0.464123 | −0.506595 | 0.047* | |
| O21 | 0.69333 (12) | 0.21322 (8) | 0.0350 (4) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| N12 | 0.56325 (15) | 0.43011 (9) | −0.2166 (5) | 0.0265 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.72029 (18) | 0.35490 (12) | 0.0488 (5) | 0.0260 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.76289 (18) | 0.27720 (11) | 0.1386 (6) | 0.0266 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.86797 (18) | 0.26830 (12) | 0.3172 (6) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.895987 | 0.215571 | 0.375132 | 0.036* | |
| C4 | 0.93229 (19) | 0.33707 (13) | 0.4113 (6) | 0.0316 (5) | |
| H4 | 1.004194 | 0.331184 | 0.535045 | 0.038* | |
| C5 | 0.89200 (18) | 0.41434 (12) | 0.3255 (6) | 0.0310 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.936169 | 0.461141 | 0.390355 | 0.037* | |
| C6 | 0.78780 (18) | 0.42272 (12) | 0.1462 (6) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.761062 | 0.475674 | 0.087081 | 0.035* | |
| C11 | 0.61087 (18) | 0.36135 (11) | −0.1461 (6) | 0.0275 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.573609 | 0.312951 | −0.223553 | 0.033* | |
| C21 | 0.7290 (2) | 0.13337 (11) | 0.1388 (7) | 0.0319 (5) | |
| H21A | 0.668356 | 0.093725 | 0.069500 | 0.048* | |
| H21B | 0.736939 | 0.132217 | 0.381231 | 0.048* | |
| H21C | 0.805963 | 0.119570 | 0.036670 | 0.048* |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O13 | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0199 (6) | 0.0389 (9) | −0.0001 (6) | −0.0067 (6) | 0.0040 (6) |
| O21 | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0172 (7) | 0.0391 (9) | 0.0000 (5) | −0.0025 (7) | 0.0018 (6) |
| N12 | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0215 (8) | 0.0279 (9) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0017 (7) | −0.0006 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0310 (10) | 0.0206 (9) | 0.0264 (11) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0041 (9) | −0.0005 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0194 (9) | 0.0281 (11) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0048 (9) | −0.0007 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0348 (10) | 0.0230 (9) | 0.0310 (11) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0316 (10) | 0.0307 (11) | 0.0324 (12) | 0.0001 (8) | 0.0009 (9) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0350 (11) | 0.0243 (10) | 0.0337 (12) | −0.0043 (7) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0025 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0362 (11) | 0.0203 (9) | 0.0322 (11) | 0.0003 (8) | 0.0023 (9) | −0.0007 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0352 (11) | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0292 (11) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0030 (9) | −0.0011 (8) |
| C21 | 0.0390 (11) | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0408 (12) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0028 (9) |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O13—N12 | 1.402 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| O13—H13 | 0.8400 | C4—C5 | 1.390 (3) |
| O21—C2 | 1.372 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O21—C21 | 1.433 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.377 (3) |
| N12—C11 | 1.280 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.401 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.409 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C11 | 1.456 (3) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (3) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.391 (3) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| N12—O13—H13 | 109.5 | C6—C5—C4 | 119.69 (18) |
| C2—O21—C21 | 117.07 (16) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 |
| C11—N12—O13 | 111.27 (15) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.80 (19) | C5—C6—C1 | 121.50 (18) |
| C6—C1—C11 | 123.00 (17) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 |
| C2—C1—C11 | 119.18 (17) | C1—C6—H6 | 119.3 |
| O21—C2—C3 | 123.87 (17) | N12—C11—C1 | 122.16 (18) |
| O21—C2—C1 | 115.11 (18) | N12—C11—H11 | 118.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.01 (17) | C1—C11—H11 | 118.9 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.58 (18) | O21—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | O21—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.4 (2) | O21—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C21—O21—C2—C3 | 4.2 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.4 (3) |
| C21—O21—C2—C1 | −176.10 (18) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—O21 | −179.70 (18) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.4 (3) |
| C11—C1—C2—O21 | −1.2 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.4 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (3) | C11—C1—C6—C5 | −178.8 (2) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | 178.5 (2) | O13—N12—C11—C1 | 179.25 (17) |
| O21—C2—C3—C4 | −179.9 (2) | C6—C1—C11—N12 | −6.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.4 (3) | C2—C1—C11—N12 | 175.2 (2) |
2-Methoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (1). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O13—H13···N12i | 0.84 | 1.93 | 2.764 (2) | 170 |
| C3—H3···O13ii | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.442 (2) | 174 |
| C21—H21C···O13iii | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.506 (3) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, z−1/2; (ii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z+1; (iii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z.
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Crystal data
| C9H11NO3 | Dx = 1.383 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 181.19 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 2093 reflections |
| a = 4.6775 (2) Å | θ = 4.6–67.5° |
| b = 13.0996 (5) Å | µ = 0.87 mm−1 |
| c = 14.1984 (5) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 869.98 (6) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.05 × 0.02 mm |
| F(000) = 384 |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Data collection
| Rigaku 007HF equipped with Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC11 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector diffractometer | 1596 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating anode, Rigaku 007 HF | 1371 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.095 |
| profile data from ω–scans | θmax = 68.2°, θmin = 4.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017) | h = −5→5 |
| Tmin = 0.507, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −15→15 |
| 7835 measured reflections | l = −17→16 |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.058 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1064P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.03 | Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3 |
| 1596 reflections | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| 124 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 474 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: 0.2 (3) |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O13 | −0.3161 (6) | 0.81289 (19) | 0.42174 (19) | 0.0376 (7) | |
| H13 | −0.382 (10) | 0.799 (3) | 0.485 (3) | 0.045 (12)* | |
| O21 | 0.3629 (5) | 0.73710 (18) | 0.18056 (18) | 0.0331 (6) | |
| O31 | 0.6683 (6) | 0.57595 (18) | 0.1198 (2) | 0.0370 (7) | |
| N12 | −0.1250 (7) | 0.7305 (2) | 0.4137 (2) | 0.0328 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.1671 (8) | 0.6379 (3) | 0.3072 (3) | 0.0311 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.3440 (8) | 0.6450 (2) | 0.2283 (3) | 0.0309 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.5135 (8) | 0.5622 (2) | 0.1997 (3) | 0.0315 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.5069 (9) | 0.4725 (3) | 0.2525 (2) | 0.0331 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.620619 | 0.415756 | 0.234431 | 0.040* | |
| C5 | 0.3334 (9) | 0.4664 (3) | 0.3318 (3) | 0.0344 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.332576 | 0.405472 | 0.368039 | 0.041* | |
| C6 | 0.1631 (9) | 0.5468 (3) | 0.3588 (3) | 0.0338 (9) | |
| H6 | 0.042859 | 0.540487 | 0.412457 | 0.041* | |
| C11 | −0.0229 (8) | 0.7232 (2) | 0.3309 (3) | 0.0332 (8) | |
| H11 | −0.069638 | 0.772807 | 0.284541 | 0.040* | |
| C21 | 0.2048 (9) | 0.7399 (3) | 0.0942 (3) | 0.0374 (9) | |
| H21A | 0.230310 | 0.806598 | 0.064099 | 0.056* | |
| H21B | 0.001542 | 0.728827 | 0.107410 | 0.056* | |
| H21C | 0.274481 | 0.686165 | 0.052004 | 0.056* | |
| C31 | 0.8511 (10) | 0.4933 (3) | 0.0919 (3) | 0.0390 (10) | |
| H31A | 0.952242 | 0.511808 | 0.033893 | 0.059* | |
| H31B | 0.735578 | 0.432080 | 0.080781 | 0.059* | |
| H31C | 0.990297 | 0.479650 | 0.141905 | 0.059* |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O13 | 0.0411 (16) | 0.0292 (13) | 0.0423 (16) | 0.0088 (12) | 0.0053 (13) | 0.0027 (11) |
| O21 | 0.0339 (14) | 0.0250 (12) | 0.0405 (14) | −0.0027 (11) | 0.0009 (12) | 0.0020 (10) |
| O31 | 0.0340 (14) | 0.0291 (12) | 0.0478 (15) | 0.0042 (11) | 0.0072 (13) | −0.0015 (11) |
| N12 | 0.0294 (16) | 0.0244 (14) | 0.0446 (18) | 0.0025 (13) | −0.0001 (15) | −0.0001 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0277 (18) | 0.0277 (17) | 0.038 (2) | −0.0008 (15) | −0.0021 (17) | −0.0004 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0297 (17) | 0.0244 (17) | 0.0387 (19) | −0.0018 (15) | −0.0012 (17) | 0.0017 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0285 (18) | 0.0262 (16) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0016 (15) | 0.0002 (16) | −0.0029 (15) |
| C4 | 0.0315 (18) | 0.0236 (17) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0017 (16) | −0.0025 (17) | −0.0036 (14) |
| C5 | 0.036 (2) | 0.0286 (17) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0000 (16) | −0.0054 (18) | 0.0019 (15) |
| C6 | 0.034 (2) | 0.0298 (18) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0001 (17) | −0.0004 (17) | 0.0019 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0353 (19) | 0.0238 (16) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0010 (17) | 0.0001 (18) | 0.0007 (15) |
| C21 | 0.040 (2) | 0.0324 (18) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0016 (17) | 0.0010 (17) | 0.0037 (15) |
| C31 | 0.035 (2) | 0.0296 (18) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0034 (16) | 0.009 (2) | −0.0068 (16) |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O13—N12 | 1.405 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.389 (5) |
| O13—H13 | 0.97 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O21—C2 | 1.386 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.375 (5) |
| O21—C21 | 1.432 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O31—C3 | 1.357 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| O31—C31 | 1.435 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N12—C11 | 1.273 (5) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.396 (5) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C6 | 1.401 (5) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C1—C11 | 1.467 (5) | C31—H31A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.404 (5) | C31—H31B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.394 (5) | C31—H31C | 0.9800 |
| N12—O13—H13 | 97 (3) | C5—C6—C1 | 119.9 (4) |
| C2—O21—C21 | 114.1 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| C3—O31—C31 | 116.6 (3) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| C11—N12—O13 | 111.8 (3) | N12—C11—C1 | 119.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.0 (3) | N12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—C11 | 119.5 (3) | C1—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C6—C1—C11 | 121.4 (3) | O21—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O21—C2—C1 | 119.2 (3) | O21—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| O21—C2—C3 | 119.7 (3) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.0 (3) | O21—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| O31—C3—C4 | 125.0 (3) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| O31—C3—C2 | 116.1 (3) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.9 (3) | O31—C31—H31A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.8 (3) | O31—C31—H31B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | H31A—C31—H31B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | O31—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.4 (3) | H31A—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | H31B—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.3 | ||
| C21—O21—C2—C1 | −103.3 (4) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.2 (5) |
| C21—O21—C2—C3 | 80.0 (4) | O31—C3—C4—C5 | −178.1 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—O21 | −175.9 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (5) |
| C11—C1—C2—O21 | 7.9 (5) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.1 (6) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.8 (5) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.4 (6) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | −175.4 (4) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.5 (6) |
| C31—O31—C3—C4 | −4.0 (5) | C11—C1—C6—C5 | 176.6 (3) |
| C31—O31—C3—C2 | 177.6 (4) | O13—N12—C11—C1 | −176.2 (3) |
| O21—C2—C3—O31 | −6.0 (5) | C2—C1—C11—N12 | −161.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—O31 | 177.3 (3) | C6—C1—C11—N12 | 22.8 (6) |
| O21—C2—C3—C4 | 175.5 (3) |
2,3-Dimethoxy-benzaldehyde oxime (2). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O13—H13···N12i | 0.97 (4) | 1.87 (5) | 2.805 (4) | 161 (4) |
| C4—H4···O21ii | 0.95 | 2.63 | 3.284 (4) | 126 |
| C21—H21B···O31iii | 0.98 | 2.54 | 3.323 (5) | 136 |
| C31—H31B···O13iv | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.448 (5) | 161 |
| C31—H31C···Cg1v | 0.98 | 2.73 | 3.599 (5) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x−1, y, z; (iv) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (v) x+1, y, z.
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Crystal data
| C9H11NO3 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 181.19 | F(000) = 192 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.358 Mg m−3 |
| a = 4.9441 (2) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 8.2188 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3758 reflections |
| c = 12.1308 (3) Å | θ = 3.9–69.9° |
| α = 108.849 (3)° | µ = 0.86 mm−1 |
| β = 92.288 (3)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 106.273 (4)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 443.17 (3) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Data collection
| Rigaku 007HF equipped with Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC11 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector diffractometer | 1594 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating anode, Rigaku 007 HF | 1462 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.033 |
| profile data from ω–scans | θmax = 68.2°, θmin = 3.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017) | h = −5→5 |
| Tmin = 0.802, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −9→9 |
| 7618 measured reflections | l = −14→13 |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.101 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0775P)2 + 0.1273P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.88 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1594 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 124 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O13 | −0.22417 (16) | 0.06653 (12) | 0.08642 (7) | 0.0311 (2) | |
| O21 | 0.29524 (16) | 0.56560 (10) | 0.41358 (7) | 0.0261 (2) | |
| O41 | 1.14895 (16) | 0.88605 (11) | 0.31075 (7) | 0.0273 (2) | |
| N12 | 0.05891 (19) | 0.17759 (13) | 0.09919 (8) | 0.0255 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.3951 (2) | 0.45758 (15) | 0.22073 (10) | 0.0231 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.4791 (2) | 0.58860 (15) | 0.33490 (9) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.7331 (2) | 0.72870 (15) | 0.36234 (9) | 0.0237 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.789071 | 0.815115 | 0.439846 | 0.028* | |
| C4 | 0.9063 (2) | 0.74213 (15) | 0.27541 (10) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.8276 (2) | 0.61490 (15) | 0.16177 (10) | 0.0247 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.945380 | 0.624026 | 0.102665 | 0.030* | |
| C6 | 0.5741 (2) | 0.47475 (15) | 0.13657 (10) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.520758 | 0.387495 | 0.059294 | 0.029* | |
| C11 | 0.1194 (2) | 0.31641 (15) | 0.19252 (10) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| H11 | −0.017316 | 0.328624 | 0.244952 | 0.029* | |
| C21 | 0.3513 (2) | 0.70704 (15) | 0.52560 (9) | 0.0281 (3) | |
| H21A | 0.196509 | 0.679099 | 0.571095 | 0.042* | |
| H21B | 0.364539 | 0.821605 | 0.514202 | 0.042* | |
| H21C | 0.531398 | 0.717369 | 0.568289 | 0.042* | |
| C41 | 1.3260 (2) | 0.90933 (16) | 0.22272 (10) | 0.0278 (3) | |
| H41A | 1.490351 | 1.018155 | 0.257704 | 0.042* | |
| H41B | 1.216391 | 0.922054 | 0.158580 | 0.042* | |
| H41C | 1.392155 | 0.803696 | 0.191690 | 0.042* | |
| H13 | −0.235 (4) | −0.031 (2) | 0.0244 (16) | 0.049 (5)* |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O13 | 0.0234 (4) | 0.0320 (5) | 0.0287 (5) | −0.0008 (3) | 0.0076 (3) | 0.0062 (4) |
| O21 | 0.0251 (4) | 0.0298 (4) | 0.0202 (4) | 0.0037 (3) | 0.0072 (3) | 0.0081 (3) |
| O41 | 0.0227 (4) | 0.0309 (5) | 0.0241 (4) | 0.0022 (3) | 0.0068 (3) | 0.0089 (3) |
| N12 | 0.0212 (5) | 0.0278 (5) | 0.0252 (5) | 0.0032 (4) | 0.0044 (4) | 0.0100 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0248 (6) | 0.0230 (6) | 0.0079 (4) | 0.0033 (4) | 0.0099 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0285 (6) | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0092 (4) | 0.0060 (4) | 0.0123 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0196 (5) | 0.0072 (5) | 0.0034 (4) | 0.0086 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0198 (6) | 0.0269 (6) | 0.0257 (6) | 0.0063 (4) | 0.0029 (4) | 0.0114 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0306 (6) | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0100 (5) | 0.0077 (4) | 0.0113 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0252 (6) | 0.0271 (6) | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0083 (5) | 0.0036 (4) | 0.0077 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0242 (6) | 0.0288 (6) | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0080 (5) | 0.0058 (4) | 0.0118 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0324 (6) | 0.0195 (6) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0077 (4) | 0.0075 (5) |
| C41 | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0333 (6) | 0.0258 (6) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0085 (4) | 0.0131 (5) |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O13—N12 | 1.4112 (12) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| O13—H13 | 0.893 (18) | C4—C5 | 1.3939 (16) |
| O21—C2 | 1.3648 (13) | C5—C6 | 1.3869 (16) |
| O21—C21 | 1.4294 (13) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O41—C4 | 1.3632 (13) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| O41—C41 | 1.4339 (13) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N12—C11 | 1.2728 (15) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3931 (16) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4107 (15) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C1—C11 | 1.4634 (15) | C41—H41A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3864 (16) | C41—H41B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3971 (16) | C41—H41C | 0.9800 |
| N12—O13—H13 | 103.5 (11) | C1—C6—C5 | 122.23 (10) |
| C2—O21—C21 | 117.44 (8) | C1—C6—H6 | 118.9 |
| C4—O41—C41 | 116.82 (9) | C5—C6—H6 | 118.9 |
| C11—N12—O13 | 111.40 (9) | N12—C11—C1 | 121.37 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.84 (10) | N12—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C6—C1—C11 | 122.31 (10) | C1—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C2—C1—C11 | 119.74 (10) | O21—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O21—C2—C3 | 123.79 (10) | O21—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| O21—C2—C1 | 115.34 (10) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.88 (10) | O21—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.64 (10) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | O41—C41—H41A | 109.5 |
| O41—C4—C3 | 115.11 (10) | O41—C41—H41B | 109.5 |
| O41—C4—C5 | 124.27 (10) | H41A—C41—H41B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.62 (10) | O41—C41—H41C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.78 (10) | H41A—C41—H41C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.6 | H41B—C41—H41C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.6 | ||
| C21—O21—C2—C3 | 8.36 (15) | C2—C3—C4—O41 | 179.03 (9) |
| C21—O21—C2—C1 | −171.96 (9) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.70 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—O21 | 179.72 (9) | O41—C4—C5—C6 | −179.69 (9) |
| C11—C1—C2—O21 | 3.38 (15) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.01 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.59 (16) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.11 (17) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | −176.93 (9) | C11—C1—C6—C5 | 176.12 (9) |
| O21—C2—C3—C4 | −179.34 (9) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.40 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.00 (16) | O13—N12—C11—C1 | −175.95 (9) |
| C41—O41—C4—C3 | −177.21 (9) | C6—C1—C11—N12 | 17.32 (17) |
| C41—O41—C4—C5 | 2.51 (16) | C2—C1—C11—N12 | −166.51 (10) |
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (3). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O13—H13···N12i | 0.893 (18) | 1.995 (19) | 2.8124 (13) | 151.5 (15) |
| C41—H41A···O13ii | 0.98 | 2.63 | 3.0680 (15) | 107 |
| C41—H41C···Cg1iii | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.4479 (13) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z; (ii) x+2, y+1, z; (iii) x+1, y, z.
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Crystal data
| C9H11NO3 | F(000) = 768 |
| Mr = 181.19 | Dx = 1.348 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 7.6480 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 21005 reflections |
| b = 21.3380 (4) Å | θ = 2.1–32.1° |
| c = 10.9421 (2) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 90.555 (2)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1785.59 (5) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.13 mm |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Data collection
| Rigaku FRE+ equipped with VHF Varimax confocal mirrors and an AFC12 goniometer and HyPix 6000 detector diffractometer | 4082 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode, Rigaku FRE+ | 3761 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Confocal mirrors, VHF Varimax monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| Detector resolution: 10 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.9° |
| profile data from ω–scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2017) | k = −27→27 |
| Tmin = 0.935, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −14→14 |
| 38753 measured reflections |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.086 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0477P)2 + 0.5056P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4082 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 247 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O121 | 1.05737 (9) | 0.46081 (3) | 0.23188 (6) | 0.01640 (15) | |
| O221 | 0.33772 (9) | 0.09728 (3) | 0.32374 (6) | 0.01705 (15) | |
| O151 | 0.88735 (9) | 0.21358 (3) | 0.13343 (6) | 0.01629 (14) | |
| O213 | 0.63115 (9) | 0.03239 (3) | 0.60782 (6) | 0.01852 (15) | |
| H213 | 0.6028 (19) | −0.0064 (7) | 0.5898 (13) | 0.036 (4)* | |
| O251 | 0.47197 (9) | 0.34248 (3) | 0.46029 (6) | 0.01810 (15) | |
| O113 | 0.84907 (9) | 0.45697 (3) | 0.56752 (6) | 0.01890 (15) | |
| H113 | 0.905 (2) | 0.4914 (7) | 0.5868 (13) | 0.036 (4)* | |
| N112 | 0.92134 (10) | 0.44408 (4) | 0.45300 (7) | 0.01543 (16) | |
| N212 | 0.53640 (10) | 0.06589 (4) | 0.51894 (7) | 0.01507 (16) | |
| C11 | 0.92057 (11) | 0.36690 (4) | 0.29191 (8) | 0.01265 (17) | |
| C12 | 1.01564 (11) | 0.40037 (4) | 0.20387 (8) | 0.01345 (17) | |
| C13 | 1.06269 (12) | 0.37068 (4) | 0.09534 (8) | 0.01520 (18) | |
| H13 | 1.125790 | 0.393201 | 0.035247 | 0.018* | |
| C14 | 1.01792 (11) | 0.30839 (4) | 0.07452 (8) | 0.01529 (18) | |
| H14 | 1.051935 | 0.288508 | 0.000789 | 0.018* | |
| C15 | 0.92359 (11) | 0.27498 (4) | 0.16103 (8) | 0.01354 (17) | |
| C16 | 0.87441 (11) | 0.30442 (4) | 0.26854 (8) | 0.01321 (17) | |
| H16 | 0.808499 | 0.281887 | 0.327125 | 0.016* | |
| C21 | 0.47308 (11) | 0.17198 (4) | 0.45403 (8) | 0.01312 (17) | |
| C22 | 0.36691 (11) | 0.15892 (4) | 0.35049 (8) | 0.01327 (17) | |
| C23 | 0.29914 (11) | 0.20820 (4) | 0.28236 (8) | 0.01541 (18) | |
| H23 | 0.229476 | 0.199464 | 0.212053 | 0.018* | |
| C24 | 0.33136 (12) | 0.27053 (4) | 0.31516 (8) | 0.01597 (18) | |
| H24 | 0.284202 | 0.303707 | 0.267240 | 0.019* | |
| C25 | 0.43233 (11) | 0.28369 (4) | 0.41782 (8) | 0.01448 (18) | |
| C26 | 0.50301 (11) | 0.23437 (4) | 0.48551 (8) | 0.01430 (17) | |
| H26 | 0.573634 | 0.243537 | 0.555138 | 0.017* | |
| C111 | 0.86582 (11) | 0.39220 (4) | 0.40987 (8) | 0.01383 (17) | |
| H111 | 0.784786 | 0.368751 | 0.456649 | 0.017* | |
| C121 | 1.16522 (14) | 0.49466 (5) | 0.14906 (9) | 0.0233 (2) | |
| H12A | 1.188699 | 0.536566 | 0.181970 | 0.035* | |
| H12B | 1.105118 | 0.498388 | 0.069891 | 0.035* | |
| H12C | 1.275896 | 0.472247 | 0.138464 | 0.035* | |
| C151 | 0.79088 (13) | 0.17920 (4) | 0.22231 (9) | 0.01864 (19) | |
| H15A | 0.769266 | 0.136629 | 0.192162 | 0.028* | |
| H15B | 0.679003 | 0.200181 | 0.236846 | 0.028* | |
| H15C | 0.858216 | 0.177225 | 0.298868 | 0.028* | |
| C211 | 0.55768 (11) | 0.12487 (4) | 0.53198 (8) | 0.01470 (18) | |
| H211 | 0.632715 | 0.139016 | 0.595943 | 0.018* | |
| C221 | 0.24158 (15) | 0.08339 (5) | 0.21389 (9) | 0.0238 (2) | |
| H22A | 0.233090 | 0.037865 | 0.203679 | 0.036* | |
| H22B | 0.302042 | 0.101530 | 0.143698 | 0.036* | |
| H22C | 0.123897 | 0.101296 | 0.219223 | 0.036* | |
| C251 | 0.41248 (14) | 0.39453 (4) | 0.38939 (9) | 0.0225 (2) | |
| H25A | 0.453866 | 0.433561 | 0.426991 | 0.034* | |
| H25B | 0.284384 | 0.394557 | 0.386171 | 0.034* | |
| H25C | 0.458345 | 0.391238 | 0.306319 | 0.034* |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O121 | 0.0203 (3) | 0.0116 (3) | 0.0174 (3) | −0.0029 (2) | 0.0052 (2) | −0.0001 (2) |
| O221 | 0.0220 (3) | 0.0133 (3) | 0.0157 (3) | −0.0018 (2) | −0.0063 (2) | −0.0012 (2) |
| O151 | 0.0188 (3) | 0.0128 (3) | 0.0173 (3) | −0.0015 (2) | 0.0015 (2) | −0.0033 (2) |
| O213 | 0.0230 (3) | 0.0136 (3) | 0.0189 (3) | 0.0017 (3) | −0.0077 (3) | 0.0021 (2) |
| O251 | 0.0208 (3) | 0.0111 (3) | 0.0223 (3) | −0.0006 (2) | −0.0048 (3) | 0.0004 (2) |
| O113 | 0.0263 (4) | 0.0160 (3) | 0.0145 (3) | −0.0053 (3) | 0.0077 (3) | −0.0043 (2) |
| N112 | 0.0186 (4) | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0129 (3) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0039 (3) | −0.0015 (3) |
| N212 | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0020 (3) | −0.0027 (3) | 0.0020 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0114 (4) | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0010 (3) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0004 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0122 (4) | 0.0158 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | −0.0006 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0142 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0019 (3) |
| C14 | 0.0152 (4) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0003 (3) | −0.0024 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0116 (4) | 0.0126 (4) | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0013 (3) | −0.0030 (3) | −0.0015 (3) |
| C16 | 0.0117 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | −0.0004 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C21 | 0.0125 (4) | 0.0141 (4) | 0.0128 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0007 (3) |
| C22 | 0.0126 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | −0.0012 (3) | 0.0012 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C23 | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | −0.0017 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C24 | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0153 (4) | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0020 (3) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0026 (3) |
| C25 | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0127 (4) | 0.0179 (4) | −0.0009 (3) | 0.0017 (3) | −0.0003 (3) |
| C26 | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0159 (4) | 0.0137 (4) | −0.0010 (3) | −0.0008 (3) | −0.0002 (3) |
| C111 | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0141 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | 0.0016 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C121 | 0.0312 (5) | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0228 (5) | −0.0063 (4) | 0.0096 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| C151 | 0.0245 (5) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0183 (4) | −0.0024 (3) | 0.0002 (4) | −0.0005 (3) |
| C211 | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0135 (4) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0018 (3) | −0.0005 (3) |
| C221 | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0188 (4) | 0.0204 (5) | −0.0043 (4) | −0.0119 (4) | −0.0020 (4) |
| C251 | 0.0280 (5) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0263 (5) | 0.0018 (4) | −0.0035 (4) | 0.0027 (4) |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O121—C12 | 1.3628 (10) | C21—C26 | 1.3935 (12) |
| O121—C121 | 1.4275 (11) | C21—C22 | 1.4151 (12) |
| O221—C22 | 1.3653 (10) | C21—C211 | 1.4651 (12) |
| O221—C221 | 1.4339 (11) | C22—C23 | 1.3866 (12) |
| O151—C15 | 1.3721 (10) | C23—C24 | 1.3988 (12) |
| O151—C151 | 1.4291 (11) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| O213—N212 | 1.4029 (9) | C24—C25 | 1.3858 (12) |
| O213—H213 | 0.877 (15) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| O251—C25 | 1.3706 (10) | C25—C26 | 1.3929 (12) |
| O251—C251 | 1.4268 (11) | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| O113—N112 | 1.4017 (9) | C111—H111 | 0.9500 |
| O113—H113 | 0.875 (16) | C121—H12A | 0.9800 |
| N112—C111 | 1.2747 (11) | C121—H12B | 0.9800 |
| N212—C211 | 1.2767 (12) | C121—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C11—C16 | 1.4020 (12) | C151—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.4072 (12) | C151—H15B | 0.9800 |
| C11—C111 | 1.4639 (12) | C151—H15C | 0.9800 |
| C12—C13 | 1.3962 (12) | C211—H211 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C14 | 1.3908 (12) | C221—H22A | 0.9800 |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C221—H22B | 0.9800 |
| C14—C15 | 1.3921 (12) | C221—H22C | 0.9800 |
| C14—H14 | 0.9500 | C251—H25A | 0.9800 |
| C15—C16 | 1.3887 (12) | C251—H25B | 0.9800 |
| C16—H16 | 0.9500 | C251—H25C | 0.9800 |
| C12—O121—C121 | 118.13 (7) | C23—C24—H24 | 120.1 |
| C22—O221—C221 | 117.40 (7) | O251—C25—C24 | 125.45 (8) |
| C15—O151—C151 | 116.42 (7) | O251—C25—C26 | 115.32 (8) |
| N212—O213—H213 | 101.5 (10) | C24—C25—C26 | 119.23 (8) |
| C25—O251—C251 | 117.38 (7) | C25—C26—C21 | 121.89 (8) |
| N112—O113—H113 | 100.6 (10) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.1 |
| C111—N112—O113 | 111.63 (7) | C21—C26—H26 | 119.1 |
| C211—N212—O213 | 111.12 (7) | N112—C111—C11 | 123.34 (8) |
| C16—C11—C12 | 119.24 (8) | N112—C111—H111 | 118.3 |
| C16—C11—C111 | 115.96 (8) | C11—C111—H111 | 118.3 |
| C12—C11—C111 | 124.79 (8) | O121—C121—H12A | 109.5 |
| O121—C12—C13 | 123.99 (8) | O121—C121—H12B | 109.5 |
| O121—C12—C11 | 116.60 (8) | H12A—C121—H12B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.41 (8) | O121—C121—H12C | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.53 (8) | H12A—C121—H12C | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 | H12B—C121—H12C | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 | O151—C151—H15A | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.42 (8) | O151—C151—H15B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 | H15A—C151—H15B | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.8 | O151—C151—H15C | 109.5 |
| O151—C15—C16 | 124.23 (8) | H15A—C151—H15C | 109.5 |
| O151—C15—C14 | 116.36 (8) | H15B—C151—H15C | 109.5 |
| C16—C15—C14 | 119.40 (8) | N212—C211—C21 | 123.80 (8) |
| C15—C16—C11 | 120.99 (8) | N212—C211—H211 | 118.1 |
| C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 | C21—C211—H211 | 118.1 |
| C11—C16—H16 | 119.5 | O221—C221—H22A | 109.5 |
| C26—C21—C22 | 118.53 (8) | O221—C221—H22B | 109.5 |
| C26—C21—C211 | 116.18 (8) | H22A—C221—H22B | 109.5 |
| C22—C21—C211 | 125.29 (8) | O221—C221—H22C | 109.5 |
| O221—C22—C23 | 123.76 (8) | H22A—C221—H22C | 109.5 |
| O221—C22—C21 | 116.92 (8) | H22B—C221—H22C | 109.5 |
| C23—C22—C21 | 119.32 (8) | O251—C251—H25A | 109.5 |
| C22—C23—C24 | 121.27 (8) | O251—C251—H25B | 109.5 |
| C22—C23—H23 | 119.4 | H25A—C251—H25B | 109.5 |
| C24—C23—H23 | 119.4 | O251—C251—H25C | 109.5 |
| C25—C24—C23 | 119.74 (8) | H25A—C251—H25C | 109.5 |
| C25—C24—H24 | 120.1 | H25B—C251—H25C | 109.5 |
| C121—O121—C12—C13 | −4.21 (13) | C211—C21—C22—O221 | 1.91 (13) |
| C121—O121—C12—C11 | 175.24 (8) | C26—C21—C22—C23 | 1.31 (12) |
| C16—C11—C12—O121 | −179.74 (7) | C211—C21—C22—C23 | −177.99 (8) |
| C111—C11—C12—O121 | −0.50 (13) | O221—C22—C23—C24 | 179.06 (8) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.26 (13) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −1.05 (13) |
| C111—C11—C12—C13 | 178.98 (8) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | −0.22 (13) |
| O121—C12—C13—C14 | 178.77 (8) | C251—O251—C25—C24 | −3.63 (13) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.67 (13) | C251—O251—C25—C26 | 175.86 (8) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.80 (13) | C23—C24—C25—O251 | −179.32 (8) |
| C151—O151—C15—C16 | 0.74 (12) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 1.21 (13) |
| C151—O151—C15—C14 | 179.85 (8) | O251—C25—C26—C21 | 179.53 (8) |
| C13—C14—C15—O151 | −179.15 (8) | C24—C25—C26—C21 | −0.94 (13) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.01 (13) | C22—C21—C26—C25 | −0.32 (13) |
| O151—C15—C16—C11 | 178.13 (8) | C211—C21—C26—C25 | 179.03 (8) |
| C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.95 (13) | O113—N112—C111—C11 | −179.60 (8) |
| C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.08 (13) | C16—C11—C111—N112 | 168.18 (8) |
| C111—C11—C16—C15 | −178.23 (8) | C12—C11—C111—N112 | −11.08 (14) |
| C221—O221—C22—C23 | 4.54 (13) | O213—N212—C211—C21 | −178.99 (8) |
| C221—O221—C22—C21 | −175.35 (8) | C26—C21—C211—N212 | 176.46 (8) |
| C26—C21—C22—O221 | −178.79 (8) | C22—C21—C211—N212 | −4.24 (14) |
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde oxime (4). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C11–C16 and C21–C26 rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O113—H113···O121i | 0.875 (16) | 2.247 (15) | 2.8944 (9) | 130.7 (12) |
| O113—H113···N112i | 0.875 (16) | 1.965 (16) | 2.7567 (10) | 149.9 (13) |
| O213—H213···O221ii | 0.877 (15) | 2.204 (15) | 2.8758 (9) | 133.1 (12) |
| O213—H213···N212ii | 0.877 (15) | 2.034 (15) | 2.8160 (10) | 147.9 (13) |
| C111—H111···O251 | 0.95 | 2.46 | 3.2458 (11) | 140 |
| C121—H12C···N212iii | 0.98 | 2.53 | 3.4400 (13) | 155 |
| C151—H15A···O113iv | 0.98 | 2.50 | 3.3947 (11) | 152 |
| C14—H14···Cg2iii | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.6656 (9) | 130 |
| C151—H15B···Cg2 | 0.98 | 2.72 | 3.5973 (10) | 149 |
| C24—H24···Cg1v | 0.95 | 2.67 | 3.4281 (10) | 137 |
| C211—H211···Cg1vi | 0.95 | 2.78 | 3.6272 (9) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) x+1, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (v) x−1, y, z; (vi) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
References
- Aakeröy, C. B., Sinha, A. S., Epa, K. N., Chopade, P. D., Smith, M. M. & Desper, J. (2013). Cryst. Growth Des. 13, 2687–2695.
- Abele, E., Abele, R. & Lukevics, E. (2008). Chem. Heterocycl. Cmpds, 44, 769–792.
- Canario, C., Silvestre, S., Falcao, A. & Alves, G. (2018). Curr. Med. Chem. 25, 660–686. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.-H. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o5699–o5700.
- Coles, S. J. & Gale, P. A. (2012). Chem. Sci. 3, 683–689.
- Dai, H., Chen, J., Li, G., Ge, S. S., Shi, Y. J., Fang, Y. & Ling, Y. (2017). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 27, 950–953. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dong, B., Zhang, Y. & Chen, J.-Z. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Gomes, L. R., de Souza, M. V. N., Da Costa, C. F., Wardell, J. L. & Low, J. N. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 1480–1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Govindan, E., Srinivasan, J., Bakthadoss, M. & SubbiahPandi, A. (2012a). Acta Cryst. E68, o484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Govindan, S., Vijayakumar, S., Jayakumar, S., Mannickam, B. & Sanmargam, A. (2012b). Acta Cryst. E68, o596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Huang, G., Zhao, H. R., Meng, Q. Q., Zhang, Q. J., Dong, J. Y., Zhu, B. Q. & Li, S. S. (2018). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 143, 166–181. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M. & Dittrich, B. (2011). J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 1281–1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Katalinić, M., Zandona, A., Ramić, A., Zorbaz, T., Primožic, I. & Kovarik, Z. (2017). Molecules, 22, 1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kozłowska, J., Potaniec, B., Żarowska, B. & Anioł, M. (2017). Molecules, 22, 1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lorke, D. E., Kalasz, H., Petroianu, G. A. & Tekes, K. (2008). Curr. Med. Chem. 15, 743–753. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Low, J. N., Santos, L. M. N. B. F., Lima, C. F. R. A. C., Brandão, P. & Gomes, L. R. (2010). Eur. J. Chem. 1, 61–66.
- Low, J. N., Wardell, J. L., Da Costa, C. F., Souza, M. V. N. & Gomes, L. R. (2018). Eur. J. Chem. 9, 151–160.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Martínez-Pascual, R., Meza-Reyes, S., Vega-Baez, J. L., Merino-Montiel, P., Padrón, J. M., Mendoza, Á. & Montiel-Smith, S. (2017). Steroids, 122, 24–33. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McArdle, P., Gilligan, K., Cunningham, D., Dark, R. & Mahon, M. (2004). CrystEngComm, 6, 303–309.
- Mohassab, M., Hassan, H. A., Abdelhamid, D., Abdel-Aziz, M., Dalby, K. N. & Kaoud, T. S. (2017). Bioorg. Chem. 75, 242–259. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nikitjuka, A. & Jirgensons, A. (2014). Chem. Heterocycl. Cmpd, 49, 1544–1559.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Priya, B. S., Basappa, S. N., Anandalwar, S. M., Prasad, J. S. & Rangappa, K. S. (2006). Anal. Sci.:X-Ray Structures Online, 22, x161–x162.
- Qin, H. L., Leng, J., Youssif, B. G. M., Amjad, M. W., Raja, M. A. G., Hussain, M. A., Hussain, Z., Kazmi, S. N. & Bukhari, S. N. A. (2017). Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 90, 443–449. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Radić, Z., Dale, T., Kovarik, Z., Berend, S., Garcia, E., Zhang, L., Amitai, G., Green, C., Radić, B., Duggan, B. M., Ajami, D., Rebek, J. Jr & Taylor, P. (2013). Biochem. J. 450, 231–242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2017). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Sørensen, M., Neilson, E. H. J. & Møller, B. L. (2018). Mol. Plant. 11, 95–117. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Spackman, M. A. & McKinnon, J. J. (2002). CrystEngComm, 4, 378–392.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suresh, G., Sabari, V., Srinivasan, J., Mannickam, B. & Aravindhan, S. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Voicu, V. A., Thiermann, H., Rădulescu, F. Ş., Mircioiu, C. & Miron, D. S. (2010). Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 106, 73–85. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. I., McKinnon, J. J., Turner, M. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2012). Crystal Explorer. The University of Western Australia.
- Yadav, P., Lal, K., Rani, P., Mor, S., Kumar, A. & Kumar, A. (2017). Med. Chem. Res. 26, 1469–1480.
- Zhao, S. Y., Li, K., Jin, Y. & Lin, J. (2018). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 144, 41–51. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 1, 2, 3, 4, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm2129sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21291sup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21292sup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21293sup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 4. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21294sup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21291sup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21292sup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21293sup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014020/qm21294sup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report















