The title molecule is comprised of two non-coplanar benzene rings connected by an imino group in a trans-configuration. In the crystal, the molecules are linked via O—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [101].
Keywords: crystal structure; syringaldehyde; 4-methoxyaniline; 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde
Abstract
In the title compound, C16H17NO4, the dihedral angle between benzene rings is 72.7 (2)°. The methoxy groups are rotated by 2.4 (2) and −4.9 (2) (benzilidene moiety) and by 5.6 (3)° (aniline moiety) relative to the adjacent benzene ring. In the crystal, the molecules are linked into chains along [101] through C—H⋯O and O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds.
Chemical context
Syringaldehyde is a product of the catalytic decomposition of lignin (Crestini et al., 2010 ▸). Syringaldehyde is widely used as a molecular marker to monitor pollution sources and detect the extent of combustion (Robinson et al., 2006 ▸). It is also known to be an antioxidant (Ibrahim et al., 2012 ▸), anticancer, anti-inflammatory (Duke, 2003 ▸) and antifungal agent (Gurpilhares et al., 2006 ▸). In addition, its Schiff bases are known to exhibit a wide range of biological activities (Shi & Zhou, 2011 ▸; da Silva et al., 2011 ▸).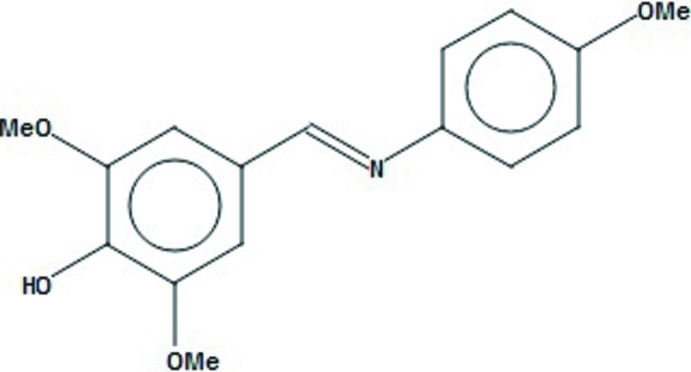
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title molecule is shown on Fig. 1 ▸. The compound has a trans-configuration of the C9=N1 double bond. The molecule has a non-planar conformation with the two benzene rings forming a dihedral angle of 72.7 (2)°. The methoxy groups are almost co-planar with the planes of the adjacent aromatic rings [the C1—O1—C4—C3, C2—O3—C6—C7 and C16—O4—C13—C12 torsion angles are −4.9 (2), 2.4 (2) and 5.6 (3)°, respectively].
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, the molecules are connected via C7—H7⋯O2ii and O2—H2⋯N1i hydrogen bonding (Table 1 ▸), forming chains along the [101] direction (Fig. 2 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯N1i | 0.82 | 2.21 | 2.9415 (18) | 149 |
| C7—H7⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.29 | 3.2043 (18) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 2.
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds (see Table 1 ▸).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD version 5.39, update of May 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) revealed the structures of five similar Schiff bases based on p-methoxyaniline and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde: 4-[(4-methoxyphenylimino)methyl]phenol, (I) (VUKDEK; Yeap et al., 1992 ▸), (E)-5-methoxy-2-[(4-methoxyphenylimino)methyl]phenol, (II) (NURNAQ; Sahin et al., 2010 ▸), 2-methoxy-4-{[(4-methoxyphenyl)imino]methyl}phenol, (III) (MOTLIR; Singh et al., 2008 ▸), 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-[(4-methoxyphenylimino)methyl]phenol, (IV) (WEFTEH; Xin et al., 2006 ▸) and 5-bromo-2-methoxy-4-{[(4-methoxyphenyl)imino]methyl}phenol monohydrate, (V) (GAPFEK; Mao et al., 2012 ▸). The dihedral angle between the benzene rings in the title compound [72.7 (2)°] is larger than those in compounds (I), (III) and (IV) (49.75–53.63°). Compounds (II) and (V) are almost planar. In all of the compounds, the methoxy groups deviate from the plane of aromatic system. There are no C—H⋯π or π–π interactions in the crystal structure of the title compound, in contrast to what is observed for compounds (I), (IV) and (V).
Synthesis
4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (syringaldehyde) (0.05 mol) was added to a mixture of 50 ml of methanol and p-methoxyaniline (PMA) (5 ml, 0.05 mol) and 50 ml of distilled water. The reaction mixture was taken in a clean 250 ml round-bottom flask and stirred well with a magnetic stirrer. It was then refluxed for 7 h. The dark-yellow product that formed was separated by filtration, dried under vacuum and recrystallized from methanol solution upon slow evaporation for two days (yield 65%, m.p. 353–357 K).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model: O—H = 0.82–0.96 Å and C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) or 1.5U eq(O, Cmethyl).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C16H17NO4 |
| M r | 287.30 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.4996 (15), 12.4896 (18), 11.8128 (17) |
| β (°) | 107.936 (5) |
| V (Å3) | 1473.8 (4) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.45 × 0.33 × 0.21 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 19289, 2887, 2306 |
| R int | 0.035 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.044, 0.116, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 2887 |
| No. of parameters | 194 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.17, −0.21 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013713/ld2146sup1.cif
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013713/ld2146Isup3.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013713/ld2146Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 1843910
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, Langat Singh College, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar Bihar University, Muzaffarpur, Bihar, India for the research lab and National Taras Shevchenko University, Department of Chemistry, Volodymyrska Str. 64, 01601 Kyiv, Ukraine, for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C16H17NO4 | F(000) = 608 |
| Mr = 287.30 | Dx = 1.295 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.4996 (15) Å | Cell parameters from 6353 reflections |
| b = 12.4896 (18) Å | θ = 2.3–28.3° |
| c = 11.8128 (17) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 107.936 (5)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1473.8 (4) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.45 × 0.33 × 0.21 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | Rint = 0.035 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.3° |
| 19289 measured reflections | h = −12→12 |
| 2887 independent reflections | k = −15→15 |
| 2306 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | l = −14→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0509P)2 + 0.4295P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2887 reflections | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 194 parameters | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O2 | 0.34000 (12) | 0.73324 (9) | 0.04196 (10) | 0.0465 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.347012 | 0.797633 | 0.056037 | 0.070* | |
| O3 | 0.52685 (12) | 0.84064 (9) | 0.20703 (10) | 0.0473 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.32775 (12) | 0.52385 (9) | 0.03728 (11) | 0.0530 (4) | |
| O4 | 1.04377 (13) | 0.24711 (10) | 0.85736 (10) | 0.0524 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.76944 (13) | 0.53851 (10) | 0.50837 (11) | 0.0388 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.83876 (15) | 0.46251 (12) | 0.59633 (13) | 0.0350 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.93325 (16) | 0.39274 (12) | 0.57930 (14) | 0.0369 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.951974 | 0.392859 | 0.507304 | 0.044* | |
| C8 | 0.61237 (15) | 0.56465 (13) | 0.31098 (13) | 0.0355 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.42672 (15) | 0.56804 (13) | 0.12973 (13) | 0.0371 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.53028 (15) | 0.73189 (12) | 0.21930 (13) | 0.0344 (4) | |
| C14 | 1.00014 (16) | 0.32282 (12) | 0.66827 (14) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| H14 | 1.064957 | 0.277361 | 0.656291 | 0.046* | |
| C7 | 0.61974 (15) | 0.67549 (13) | 0.30970 (13) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.684472 | 0.711472 | 0.369303 | 0.043* | |
| C9 | 0.69704 (15) | 0.50052 (13) | 0.40957 (14) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.697878 | 0.426753 | 0.399120 | 0.045* | |
| C5 | 0.43155 (15) | 0.67913 (13) | 0.13033 (13) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.51728 (16) | 0.51059 (13) | 0.21959 (14) | 0.0386 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.514739 | 0.436151 | 0.219040 | 0.046* | |
| C13 | 0.97179 (16) | 0.31969 (13) | 0.77481 (14) | 0.0380 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.81296 (18) | 0.46051 (15) | 0.70406 (15) | 0.0486 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.751385 | 0.508458 | 0.717490 | 0.058* | |
| C12 | 0.87678 (18) | 0.38867 (16) | 0.79243 (16) | 0.0505 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.855831 | 0.386815 | 0.863378 | 0.061* | |
| C2 | 0.6266 (2) | 0.90036 (14) | 0.29204 (16) | 0.0546 (5) | |
| H2B | 0.615906 | 0.975079 | 0.272312 | 0.082* | |
| H2C | 0.713615 | 0.877111 | 0.291596 | 0.082* | |
| H2D | 0.617836 | 0.889302 | 0.369713 | 0.082* | |
| C1 | 0.3232 (2) | 0.41090 (15) | 0.02729 (18) | 0.0603 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.255752 | 0.390654 | −0.044946 | 0.090* | |
| H1B | 0.302110 | 0.380713 | 0.094094 | 0.090* | |
| H1C | 0.408703 | 0.384713 | 0.025963 | 0.090* | |
| C16 | 1.0104 (2) | 0.2356 (2) | 0.96441 (19) | 0.0743 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.918409 | 0.214220 | 0.945995 | 0.111* | |
| H16B | 1.023357 | 0.302705 | 1.006081 | 0.111* | |
| H16C | 1.066751 | 0.182152 | 1.013549 | 0.111* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O2 | 0.0477 (7) | 0.0351 (6) | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0128 (5) | 0.0021 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0525 (7) | 0.0317 (6) | 0.0402 (6) | −0.0019 (5) | −0.0114 (5) | 0.0026 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0521 (7) | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0488 (7) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0152 (6) | −0.0056 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0602 (8) | 0.0525 (8) | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0195 (6) | 0.0174 (6) | 0.0221 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0403 (7) | 0.0353 (7) | 0.0342 (7) | 0.0050 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0049 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0353 (8) | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0324 (8) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0039 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0442 (9) | 0.0333 (8) | 0.0314 (8) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0091 (7) | 0.0009 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0371 (8) | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0025 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0341 (8) | 0.0375 (9) | 0.0337 (8) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | −0.0034 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0323 (8) | 0.0308 (8) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0418 (9) | 0.0317 (8) | 0.0413 (9) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0121 (7) | 0.0022 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0339 (8) | 0.0380 (9) | 0.0291 (8) | −0.0018 (7) | −0.0011 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0368 (8) | 0.0333 (8) | 0.0389 (9) | 0.0028 (7) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0049 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0319 (8) | 0.0373 (9) | 0.0285 (8) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0402 (9) | 0.0314 (8) | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0052 (7) | 0.0017 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0378 (9) | 0.0348 (9) | 0.0380 (9) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0066 (7) | 0.0080 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0460 (10) | 0.0548 (11) | 0.0458 (10) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0156 (8) | 0.0111 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0529 (11) | 0.0624 (12) | 0.0400 (9) | 0.0154 (9) | 0.0198 (8) | 0.0145 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0591 (12) | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0509 (11) | −0.0115 (8) | −0.0089 (9) | 0.0027 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0658 (13) | 0.0427 (11) | 0.0568 (11) | −0.0089 (9) | −0.0042 (10) | −0.0113 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0816 (16) | 0.0896 (17) | 0.0569 (13) | 0.0299 (13) | 0.0291 (11) | 0.0395 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2i | 3.159 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.379 (2) |
| O2—C5 | 1.3610 (17) | C6—C5 | 1.394 (2) |
| O2—H2 | 0.8200 | C14—C13 | 1.380 (2) |
| O3—C6 | 1.3652 (19) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C2 | 1.4193 (19) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C4 | 1.3704 (18) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C1 | 1.415 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C13 | 1.3748 (18) | C13—C12 | 1.382 (2) |
| O4—C16 | 1.420 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (2) |
| N1—C9 | 1.2722 (19) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C10 | 1.4299 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.380 (2) | C2—H2B | 0.9600 |
| C10—C15 | 1.381 (2) | C2—H2C | 0.9600 |
| C15—C14 | 1.381 (2) | C2—H2D | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9300 | C1—H1A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C7 | 1.387 (2) | C1—H1B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C3 | 1.398 (2) | C1—H1C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.466 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C3 | 1.387 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.388 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C5—O2—H2 | 109.5 | C4—C5—C6 | 119.60 (13) |
| C6—O3—C2 | 117.27 (12) | C4—C3—C8 | 119.96 (15) |
| C4—O1—C1 | 117.75 (13) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| C13—O4—C16 | 117.76 (14) | C8—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| C9—N1—C10 | 116.47 (13) | O4—C13—C14 | 116.08 (14) |
| C11—C10—C15 | 118.47 (14) | O4—C13—C12 | 124.69 (15) |
| C11—C10—N1 | 118.78 (14) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.22 (14) |
| C15—C10—N1 | 122.73 (14) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.36 (16) |
| C14—C15—C10 | 120.54 (15) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 119.7 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C10—C15—H15 | 119.7 | C13—C12—C11 | 119.69 (16) |
| C7—C8—C3 | 120.18 (14) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 122.12 (14) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| C3—C8—C9 | 117.62 (14) | O3—C2—H2B | 109.5 |
| O1—C4—C3 | 125.06 (15) | O3—C2—H2C | 109.5 |
| O1—C4—C5 | 115.09 (13) | H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.85 (14) | O3—C2—H2D | 109.5 |
| O3—C6—C7 | 125.44 (13) | H2B—C2—H2D | 109.5 |
| O3—C6—C5 | 113.65 (13) | H2C—C2—H2D | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.91 (14) | O1—C1—H1A | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.67 (15) | O1—C1—H1B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 | H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 | O1—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.44 (14) | H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 | H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.3 | O4—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| N1—C9—C8 | 124.73 (15) | O4—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| N1—C9—H9 | 117.6 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 117.6 | O4—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—C5—C4 | 118.44 (13) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—C5—C6 | 121.96 (14) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—N1—C10—C11 | −120.05 (18) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.1 (2) |
| C9—N1—C10—C15 | 61.7 (2) | O3—C6—C5—O2 | −1.2 (2) |
| C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.0 (2) | C7—C6—C5—O2 | 178.26 (15) |
| N1—C10—C15—C14 | 178.20 (15) | O3—C6—C5—C4 | 177.70 (14) |
| C1—O1—C4—C3 | −4.9 (3) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | −2.8 (2) |
| C1—O1—C4—C5 | 175.89 (16) | O1—C4—C3—C8 | −178.61 (15) |
| C2—O3—C6—C7 | 2.4 (2) | C5—C4—C3—C8 | 0.5 (2) |
| C2—O3—C6—C5 | −178.17 (15) | C7—C8—C3—C4 | −2.4 (2) |
| C10—C15—C14—C13 | 1.4 (2) | C9—C8—C3—C4 | 174.26 (15) |
| O3—C6—C7—C8 | −179.66 (15) | C16—O4—C13—C14 | −175.25 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.9 (2) | C16—O4—C13—C12 | 5.6 (3) |
| C3—C8—C7—C6 | 1.7 (2) | C15—C14—C13—O4 | 179.86 (15) |
| C9—C8—C7—C6 | −174.84 (15) | C15—C14—C13—C12 | −1.0 (3) |
| C10—N1—C9—C8 | 176.30 (14) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | −1.8 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—N1 | 10.4 (3) | N1—C10—C11—C12 | 179.89 (16) |
| C3—C8—C9—N1 | −166.23 (16) | O4—C13—C12—C11 | 178.25 (17) |
| O1—C4—C5—O2 | 0.2 (2) | C14—C13—C12—C11 | −0.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—O2 | −178.98 (14) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 2.2 (3) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.72 (14) |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···N1i | 0.82 | 2.21 | 2.9415 (18) | 149 |
| C7—H7···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.29 | 3.2043 (18) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) x+1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
References
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Crestini, C., Crucianelli, M., Orlandi, M. & Saladino, R. (2010). Catal. Today, 156, 8–22.
- Duke, J. A. (2003). CRC book of medicinal spices. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press LLC.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gurpilhares, D. B., Pessoa, A. Jr & Roberto, I. C. (2006). Process Biochem. 41, 631–637.
- Ibrahim, M. N., Sriprasanthi, R. B., Shamsudeen, S., Adam, F. & Bhawani, S. A. (2012). BioResources J. 7, 4377–4399.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mao, C.-G., Wang, S.-S., Su, D.-C. & Qian, S.-S. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A. L., Subramanian, R., Donahue, N. M., Bernardo-Bricker, A. & Rogge, W. F. (2006). Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 7811–7819. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sahin, O., Buyukgungor, O., Albayrak, C. & Odabasoglu, M. (2010). Chin. J. Struct. Chem.(Jiegou Huaxue), 29, 359–361.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Shi, Y. & Zhou, C. H. (2011). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21, 956–960.
- Silva, C. M. da, da Silva, D. L., Modolo, L. V., Alves, R. B., de Resende, M. A., Martins, C. V. B., de Fátima, A. & Ângelo, (2011). J. Adv. Res. 2, 1–8.
- Singh, N. B., Das, S. S., Gupta, P., Gupta, A. & Fröhlich, R. (2008). Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 490, 106–123.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Xin, C.-W., Zeng, T. & Li, J.-S. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o1560–o1561.
- Yeap, G.-Y., Fun, H.-K., Teoh, S.-G., Teo, S.-B., Chinnakali, K. & Yip, B.-C. (1992). Acta Cryst. C48, 2257–2258.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013713/ld2146sup1.cif
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013713/ld2146Isup3.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013713/ld2146Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 1843910
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




