In the molecular structure of the title compound, two dihydrofuran and two tetrahydrofuran rings as well as one piperidine ring are fused together. In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network.
Keywords: crystal structure, dihydrofuran ring, tetrahydrofuran ring, fused hexacyclic system, piperidine ring, Hiershfeld surface analysis
Abstract
The title molecule, C18H16F3NO7, comprises a fused cyclic system containing four five-membered (two dihydrofuran and two tetrahydrofuran) rings and one six-membered (piperidine) ring. The five-membered dihydrofuran and tetrahydrofuran rings adopt envelope conformations, and the six-membered piperidine ring adopts a distorted chair conformation. Intramolecular O⋯F interactions help to stabilize the conformational arrangement. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked by weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network. The Hirshfeld surface analysis confirms the dominant role of H⋯H contacts in establishing the packing.
Chemical context
Non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen, aerogen, halogen, chalcogen, pnicogen, tetrel and icosagen bonds, as well as n–π*, π–π stacking, π–cation, π–anion and hydrophobic interactions, have an impact on the synthesis, catalysis and design of materials and on biological processes (Shikhaliyev et al., 2018 ▸; Hazra et al., 2018 ▸). These weak forces can also control or organize the aggregation, conformation, tertiary and quaternary structure of a molecule, and its stabilization or other particular properties (Legon, 2017 ▸; Mahmudov et al., 2017a ▸,b ▸). In comparison with well-established hydrogen and halogen bonds (Cavallo et al., 2016 ▸; Mahmoudi et al., 2018 ▸; Vandyshev et al., 2017 ▸), chalcogen, pnicogen, tetrel and icosagen bonds are much less explored (Mahmudov et al., 2017a ▸; Scheiner, 2013 ▸; Mikherdov et al., 2016 ▸).
The title compound, C18H16F3NO7, has a 7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptene scaffold, thus making it a potential tool for the design and synthesis of new organic materials with various useful properties such as electronic materials, molecular tweezers, etc (Borisova et al., 2018a
▸,b
▸). During the structure determination, we noted rather unusual intramolecular O⋯F interactions. Here we report the synthesis, molecular and crystal structure of this compound as well as a Hirshfeld surface analysis.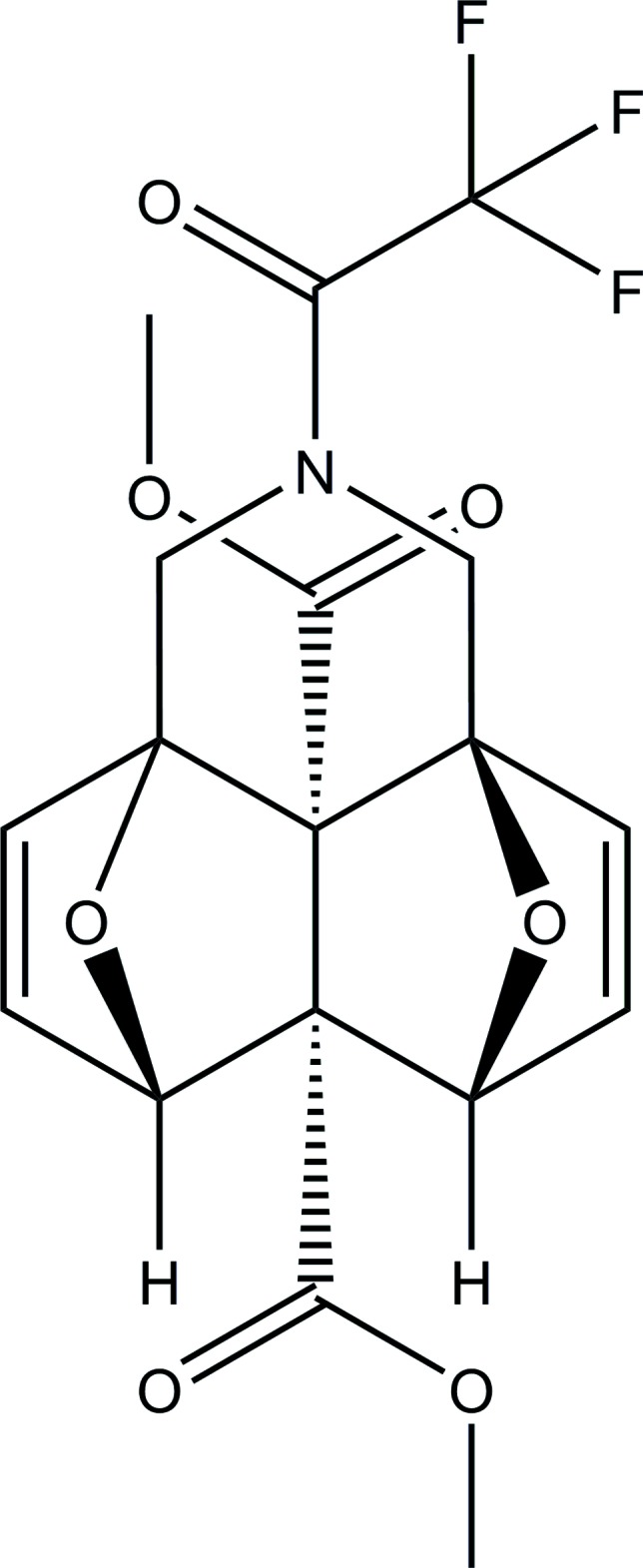
Structural commentary
The molecule of the title compound (Fig. 1 ▸) is made up from a fused cyclic system containing four five-membered rings (two dihydrofuran and two tetrahydrofuran) in the usual envelope conformations and a six-membered piperidine ring in a chair conformation. The latter is distorted because the environment of the N1 atom is intermediate between trigonal–planar and trigonal–pyramidal. The puckering parameters of the five-membered dihydrofuran [A (O1/C1/C2/C5/C6), B (O2/C1/C6/C7/C10)] and tetrahydrofuran [C (O1/C2–C5), D (O2/C7–C10)] rings are A: Q(2) = 0.5780 (15) Å, φ(2) = 359.75 (17)°; B: Q(2) = 0.5737 (16) Å, φ(2) = 4.53 (17)°; C: Q(2) = 0.5173 (15) Å, φ(2) = 179.60 (19)°; D: Q(2) = 0.5154 (16) Å, φ(2) = 178.2 (2)°. The puckering parameters of the six-membered piperidine ring (N1/C1/C2/C10–C12) are Q T = 0.5312 (17) Å, θ = 9.58 (18)°, φ = 329.1 (11)°.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. Hydrogen atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radius.
The molecular conformations are stabilized by weak intramolecular C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F interactions (Table 1 ▸) between methylene groups (C11; C12) and a methoxy group and the –CF3 group, respectively. A rather unusual intramolecular O⋯F interaction between one of the oxygen bridgehead atoms (O1) and one of the F atoms of the –CF3 group [C5—O1⋯F2 = 2.9336 (16) Å; C5—O1⋯F2 = 153.60 (9)°] might help to consolidate the conformational arrangement.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O3i | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.116 (2) | 128 |
| C5—H5⋯O2ii | 1.00 | 2.60 | 3.1960 (19) | 118 |
| C7—H7⋯O1ii | 1.00 | 2.54 | 3.2091 (19) | 124 |
| C11—H11B⋯O4 | 0.99 | 2.57 | 3.093 (2) | 113 |
| C12—H12A⋯O7iii | 0.99 | 2.52 | 3.328 (2) | 138 |
| C12—H12B⋯O5iii | 0.99 | 2.34 | 3.030 (2) | 127 |
| C12—H12B⋯F1 | 0.99 | 2.40 | 3.043 (2) | 122 |
| C12—H12B⋯F2 | 0.99 | 2.33 | 2.962 (2) | 121 |
| C16—H16A⋯F3iv | 0.98 | 2.62 | 3.475 (2) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv) 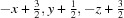 .
.
Supramolecular features
Intermolecular C—H⋯O interactions involving the O atoms of carbonyl groups, the oxygen bridgehead atoms and methoxy O atoms, as well as C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds define the crystal packing, which is shown in Fig. 2 ▸. These packing features lead to the formation of a three-dimensional network structure. C—H⋯π and π–π interactions are not observed, but H⋯H interactions dominate in the packing as detailed in the next section.
Figure 2.
The crystal structure of the title compound in a view along [100], emphasizing the intermolecular C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
Hirshfeld surface analysis
Hirshfeld surface and fingerprint plots were generated using CrystalExplorer (McKinnon et al., 2007 ▸). Hirshfeld surfaces enable the visualization of intermolecular interactions by different colors and color intensity, representing short or long contacts and indicating the relative strength of the interactions. Fig. 3 ▸ shows the Hirshfeld surface of the title compound mapped over d norm where it is evident from the bright-red spots appearing near the oxygen atoms that these atoms play a significant role in the molecular packing. The red spots represent closer contacts and negative d norm values on the surface, corresponding to the C—H⋯O interactions. The percentage contributions of various contacts to the total Hirshfeld surface are given in Table 2 ▸ and are also shown as two-dimensional fingerprint plots in Fig. 4 ▸. The H⋯H interactions appear in the middle of the scattered points in the two-dimensional fingerprint plots with an overall contribution to the Hirshfeld surface of 35.6% (Fig. 4 ▸ b). The contribution from the O⋯H/H⋯O contacts, corresponding to C—H⋯O interactions, is represented by a pair of sharp spikes characteristic of a strong hydrogen-bonding interaction (28.5%; Fig. 4 ▸ c). The contribution of the F⋯H/H⋯F intermolecular contacts to the Hirshfeld surfaces is 23.8% (Fig. 4 ▸ d). The small percentage contributions from the remaining interatomic contacts are summarized in Table 2 ▸ and indicated by their fingerprint plots for C⋯H/H⋯C (Fig. 4 ▸ e), F⋯F (Fig. 4 ▸ f), F⋯O/O⋯F (Fig. 4 ▸ g), O⋯O (Fig. 4 ▸ h), N⋯H/H⋯N (Fig. 4 ▸ i) and C⋯O/O⋯C (Fig. 4 ▸ j). The large number of H⋯H, O⋯H/H⋯O and F⋯H/H⋯F interactions suggest that van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonding play the major roles in the crystal packing (Hathwar et al., 2015 ▸).
Figure 3.
Hirshfeld surface of the title compound mapped over d norm.
Table 2. Percentage contributions of interatomic contacts to the Hirshfeld surface for the title compound.
| Contact | Percentage contribution |
|---|---|
| H⋯H | 35.6 |
| O⋯H/H⋯O | 28.5 |
| F⋯H/H⋯F | 23.8 |
| C⋯H/H⋯C | 5.5 |
| F⋯F | 2.7 |
| F⋯O/O⋯F | 1.6 |
| N⋯H/H⋯N | 1.1 |
| O⋯O | 1.1 |
| C⋯O/O⋯C | 0.2 |
Figure 4.
The two-dimensional fingerprint plots of the title compound, showing (a) all interactions, and delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) O⋯H/ H⋯O, (d) F⋯H/H⋯F, (e) C⋯H/H⋯C, (f) F⋯F, (g) F⋯O/O⋯F, (h) O⋯O, (i) N⋯H/H⋯N and (j) C⋯O/O⋯C interactions [d e and d i represent the distances from a point on the Hirshfeld surface to the nearest atoms outside (external) and inside (internal) the surface, respectively].
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.39; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for similar structures showed the two closest are those of 2-benzyl-6a,9b-bis(trifluoromethyl)-2,3,6a,9b-tetrahydro-1H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isoquinoline (CSD refcode HENLAQ; Borisova et al., 2018c ▸) and 2-benzyl-4,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-2,3,6a,9b-tetrahydro-1H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isoquinoline (HENLEU; Borisova et al., 2018d ▸). In the crystal of HENLAQ, inversion-related pairs of molecules are linked into dimers by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. These dimers form sheets lying parallel to (100). C—H⋯π interactions are also observed in the crystal structure of HENLAQ, together with intramolecular F⋯F contacts. The asymmetric unit of HENLEU contains two molecules. In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds, forming columns along [010]. Likewise, C—H⋯π interactions and F⋯F intramolecular contacts are also present.
Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the title compound and its characterization by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR and HRMS spectroscopy have previously been reported (Borisova et al., 2018a ▸). Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (DMAD, 1.84 ml, 0.015 mol) was added to a solution of 2,2,2-trifluoro-N,N-bis(furan-2-ylmethyl)acetamide (0.01 mol) in benzene (30 ml). The mixture was heated at reflux for 15.5–40 h at 353 K (GC–MS monitoring until disappearance of the starting material). The reaction mixture was cooled and left overnight at room temperature. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue (brown oil) was triturated with diethyl ether. The obtained crystals were filtered off and recrystallized from hexane/EtOAc (v:v = 2:1) to give the pure compound as a white powder (2.57 g, 6.2 mmol, yield 62%). R f = 0.56 (EtOAc/hexane, 2:1, Sorbfil). M.p. 467.2–467.9 K (from hexane/EtOAc). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.74–6.71 (2H, m, H-4 and H-9), 6.46 (2H, dd, J = 2.3 and J = 5.5 Hz, H-5 and H-8), 5.14 (2H, br s, H-6 and H-7), 5.10 (1H, d, J = 14.9 Hz, H-1A), 4.43 (1H, br d, J = 14.9 Hz, H-3A), 4.08 (1H, d, J = 14.9 Hz, H-3B), 3.64 (6H, s, 2 × CO2Me), 3.59 (1H, d, J = 14.9, H-1B). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.1 (2 × CO2Me), 157.2 (q, J = 35.5 Hz, F3C—C), 141.2 (C-5 and C-8), 137.5 (C-4 and C-9), 116.4 (q, J = 288.1 Hz, CF3), 87.1 (C-3a and C-9a), 83.8 (C-6 and C-7), 71.4 and 68.8 (C-9 and C-6a), 52.4 (2 × CO2Me), 44.8 (q, J = 3.8 Hz, C-1), 42.4 (C-3). 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3): δ −67.7 (s, CF3). IR νmax/cm−1 (KBr): 3109, 3055, 2956, 1713, 1688, 1197. HRMS (ESI–TOF): calculated for C18H16F3NO7 [M + H]+, 415.0879; found, 415.0889.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms were fixed and allowed to ride on the parent atoms, with C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å, and with U
iso(H) = 1.5U
eq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2U
eq(C) for all other H atoms. Eight outliers [(101), (011), ( 01), (002), (110), (363), (
01), (002), (110), (363), ( 03), (111)] were omitted in the final cycles of refinement.
03), (111)] were omitted in the final cycles of refinement.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C18H16F3NO7 |
| M r | 415.32 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 150 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.7661 (2), 11.2908 (3), 17.5089 (4) |
| β (°) | 96.021 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1723.41 (7) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.14 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.32 × 0.30 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.942, 0.946 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 11170, 3496, 2739 |
| R int | 0.028 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.626 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.036, 0.091, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 3496 |
| No. of parameters | 264 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.30, −0.25 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014305/wm5463sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014305/wm5463Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1872524
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C18H16F3NO7 | F(000) = 856 |
| Mr = 415.32 | Dx = 1.601 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.7661 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 3572 reflections |
| b = 11.2908 (3) Å | θ = 3.0–25.9° |
| c = 17.5089 (4) Å | µ = 0.14 mm−1 |
| β = 96.021 (1)° | T = 150 K |
| V = 1723.41 (7) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.35 × 0.32 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2739 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.028 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Tmin = 0.942, Tmax = 0.946 | h = −10→10 |
| 11170 measured reflections | k = −14→11 |
| 3496 independent reflections | l = −21→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.091 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0391P)2 + 0.8462P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3496 reflections | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 264 parameters | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.39473 (17) | 0.49611 (14) | 0.67777 (9) | 0.0151 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.34636 (17) | 0.36454 (14) | 0.65512 (9) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.17517 (18) | 0.35392 (15) | 0.66061 (10) | 0.0188 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.125910 | 0.313775 | 0.698918 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.10926 (18) | 0.41275 (15) | 0.60044 (9) | 0.0190 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.002414 | 0.423058 | 0.586488 | 0.023* | |
| C5 | 0.23948 (17) | 0.46040 (14) | 0.55824 (9) | 0.0166 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.211134 | 0.478143 | 0.502604 | 0.020* | |
| C6 | 0.31682 (17) | 0.56580 (14) | 0.60653 (9) | 0.0156 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.46580 (18) | 0.61837 (14) | 0.57545 (9) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.450625 | 0.648514 | 0.521478 | 0.022* | |
| C8 | 0.53785 (19) | 0.70697 (16) | 0.63430 (10) | 0.0223 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.534938 | 0.790901 | 0.630565 | 0.027* | |
| C9 | 0.60537 (19) | 0.64310 (16) | 0.69172 (10) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.663054 | 0.671359 | 0.737022 | 0.026* | |
| C10 | 0.57077 (18) | 0.51491 (15) | 0.66959 (9) | 0.0173 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.67413 (18) | 0.41488 (15) | 0.70014 (9) | 0.0196 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.777907 | 0.426465 | 0.683886 | 0.023* | |
| H11B | 0.683028 | 0.415179 | 0.756980 | 0.023* | |
| C12 | 0.45739 (18) | 0.27365 (15) | 0.69121 (9) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.456518 | 0.274715 | 0.747704 | 0.022* | |
| H12B | 0.426248 | 0.193647 | 0.672394 | 0.022* | |
| C13 | 0.68211 (18) | 0.24366 (16) | 0.61696 (10) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.61562 (19) | 0.12361 (17) | 0.58786 (11) | 0.0268 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.34324 (19) | 0.52840 (15) | 0.75488 (9) | 0.0187 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.4132 (2) | 0.54441 (18) | 0.88782 (9) | 0.0294 (4) | |
| H16A | 0.502378 | 0.535376 | 0.926090 | 0.044* | |
| H16B | 0.332265 | 0.489567 | 0.899623 | 0.044* | |
| H16C | 0.375106 | 0.625921 | 0.888922 | 0.044* | |
| C17 | 0.20610 (18) | 0.66654 (15) | 0.61749 (9) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| C18 | −0.0373 (2) | 0.74427 (17) | 0.57152 (12) | 0.0332 (5) | |
| H18A | −0.136339 | 0.716249 | 0.547019 | 0.050* | |
| H18B | −0.001422 | 0.810491 | 0.541928 | 0.050* | |
| H18C | −0.048909 | 0.770680 | 0.623910 | 0.050* | |
| N1 | 0.61226 (15) | 0.30034 (12) | 0.67137 (8) | 0.0174 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.35051 (12) | 0.36756 (10) | 0.57348 (6) | 0.0157 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.57083 (12) | 0.52159 (10) | 0.58756 (6) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.79898 (15) | 0.27623 (13) | 0.59189 (8) | 0.0386 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.45760 (13) | 0.51821 (11) | 0.81186 (6) | 0.0234 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.21495 (14) | 0.55547 (12) | 0.76498 (7) | 0.0274 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.07292 (13) | 0.64922 (10) | 0.57403 (7) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| O7 | 0.23490 (14) | 0.75410 (11) | 0.65517 (7) | 0.0263 (3) | |
| F1 | 0.60895 (14) | 0.04589 (10) | 0.64497 (7) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| F2 | 0.47566 (12) | 0.13074 (10) | 0.55061 (6) | 0.0350 (3) | |
| F3 | 0.70476 (14) | 0.07621 (12) | 0.53923 (8) | 0.0509 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0130 (8) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0139 (8) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0051 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0149 (8) | 0.0254 (9) | −0.0042 (6) | 0.0082 (7) | −0.0020 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0167 (9) | 0.0244 (9) | −0.0025 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | −0.0048 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0002 (6) | −0.0011 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0185 (8) | 0.0150 (8) | 0.0134 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0168 (9) | 0.0179 (8) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0039 (6) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0226 (9) | 0.0184 (9) | 0.0268 (9) | −0.0068 (7) | 0.0060 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0222 (9) | 0.0205 (9) | −0.0071 (7) | −0.0002 (7) | −0.0038 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0191 (8) | 0.0184 (9) | 0.0144 (8) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0230 (9) | 0.0180 (8) | −0.0029 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0193 (8) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0241 (10) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0007 (7) | 0.0020 (7) | −0.0008 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0226 (9) | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0315 (10) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0048 (7) | −0.0048 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0254 (9) | 0.0149 (8) | 0.0161 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0470 (11) | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0114 (8) | 0.0037 (9) | 0.0057 (8) | −0.0025 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0172 (9) | 0.0131 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0016 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0299 (10) | 0.0263 (11) | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0115 (8) | −0.0074 (8) | −0.0080 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0180 (7) | 0.0184 (7) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0014 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0176 (5) | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0141 (6) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0034 (4) | −0.0016 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0148 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0005 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0424 (9) | 0.0509 (9) | −0.0105 (6) | 0.0205 (6) | −0.0156 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0116 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0020 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0215 (6) | 0.0095 (6) | 0.0086 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0212 (6) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0261 (6) | 0.0044 (5) | −0.0023 (5) | −0.0039 (5) |
| O7 | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0272 (7) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0020 (5) | −0.0069 (5) |
| F1 | 0.0515 (7) | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0523 (8) | 0.0029 (5) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0056 (5) |
| F2 | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0320 (6) | 0.0427 (7) | −0.0024 (5) | −0.0073 (5) | −0.0102 (5) |
| F3 | 0.0405 (7) | 0.0496 (8) | 0.0662 (9) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0225 (6) | −0.0341 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C15 | 1.512 (2) | C11—N1 | 1.471 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.569 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C10 | 1.579 (2) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.584 (2) | C12—N1 | 1.467 (2) |
| C2—O1 | 1.4341 (19) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C12 | 1.507 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.519 (2) | C13—O3 | 1.213 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.326 (2) | C13—N1 | 1.347 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C13—C14 | 1.541 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.522 (2) | C14—F3 | 1.327 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C14—F2 | 1.330 (2) |
| C5—O1 | 1.4363 (19) | C14—F1 | 1.336 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.572 (2) | C15—O5 | 1.196 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 1.0000 | C15—O4 | 1.343 (2) |
| C6—C17 | 1.520 (2) | C16—O4 | 1.455 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.582 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| C7—O2 | 1.4303 (19) | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.525 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7 | 1.0000 | C17—O7 | 1.2006 (19) |
| C8—C9 | 1.325 (2) | C17—O6 | 1.3393 (19) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C18—O6 | 1.441 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.521 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C10—O2 | 1.4382 (19) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C10—C11 | 1.510 (2) | ||
| C15—C1—C6 | 116.28 (13) | C9—C10—C1 | 106.00 (13) |
| C15—C1—C10 | 115.76 (13) | N1—C11—C10 | 110.50 (12) |
| C6—C1—C10 | 102.03 (12) | N1—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C15—C1—C2 | 110.64 (13) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 100.86 (12) | N1—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C10—C1—C2 | 109.99 (12) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C12 | 110.57 (12) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 101.16 (12) | N1—C12—C2 | 109.50 (13) |
| C12—C2—C3 | 121.25 (13) | N1—C12—H12A | 109.8 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 101.14 (11) | C2—C12—H12A | 109.8 |
| C12—C2—C1 | 112.92 (13) | N1—C12—H12B | 109.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 107.37 (13) | C2—C12—H12B | 109.8 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 105.15 (14) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.2 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 127.4 | O3—C13—N1 | 125.15 (16) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 127.4 | O3—C13—C14 | 116.83 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 106.05 (14) | N1—C13—C14 | 117.88 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 127.0 | F3—C14—F2 | 106.54 (15) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 127.0 | F3—C14—F1 | 106.87 (16) |
| O1—C5—C4 | 100.37 (12) | F2—C14—F1 | 107.23 (14) |
| O1—C5—C6 | 101.94 (12) | F3—C14—C13 | 109.82 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 108.05 (13) | F2—C14—C13 | 113.97 (15) |
| O1—C5—H5 | 114.9 | F1—C14—C13 | 112.02 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 114.9 | O5—C15—O4 | 123.51 (15) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 114.9 | O5—C15—C1 | 124.53 (15) |
| C17—C6—C1 | 120.34 (13) | O4—C15—C1 | 111.90 (14) |
| C17—C6—C5 | 112.90 (13) | O4—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 100.09 (12) | O4—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C17—C6—C7 | 108.88 (13) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 98.94 (12) | O4—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 115.09 (13) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C8 | 100.74 (12) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C6 | 101.77 (12) | O7—C17—O6 | 123.57 (15) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 108.18 (13) | O7—C17—C6 | 125.81 (15) |
| O2—C7—H7 | 114.8 | O6—C17—C6 | 110.43 (13) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 114.8 | O6—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 114.8 | O6—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 106.02 (15) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 127.0 | O6—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 127.0 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 105.27 (14) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 127.4 | C13—N1—C12 | 124.77 (14) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 127.4 | C13—N1—C11 | 118.78 (13) |
| O2—C10—C11 | 109.26 (13) | C12—N1—C11 | 114.62 (13) |
| O2—C10—C9 | 100.58 (13) | C2—O1—C5 | 96.60 (11) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 121.69 (14) | C7—O2—C10 | 96.93 (11) |
| O2—C10—C1 | 101.56 (11) | C15—O4—C16 | 114.29 (13) |
| C11—C10—C1 | 115.03 (13) | C17—O6—C18 | 116.74 (13) |
| C15—C1—C2—O1 | 158.98 (12) | C6—C1—C10—C9 | 73.08 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 35.33 (13) | C2—C1—C10—C9 | 179.49 (12) |
| C10—C1—C2—O1 | −71.87 (14) | O2—C10—C11—N1 | −65.07 (16) |
| C15—C1—C2—C12 | −82.85 (16) | C9—C10—C11—N1 | 178.56 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—C12 | 153.50 (12) | C1—C10—C11—N1 | 48.35 (17) |
| C10—C1—C2—C12 | 46.30 (16) | O1—C2—C12—N1 | 57.13 (17) |
| C15—C1—C2—C3 | 53.42 (16) | C3—C2—C12—N1 | 175.15 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −70.24 (14) | C1—C2—C12—N1 | −55.37 (17) |
| C10—C1—C2—C3 | −177.43 (13) | O3—C13—C14—F3 | 0.8 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −32.33 (16) | N1—C13—C14—F3 | −175.17 (15) |
| C12—C2—C3—C4 | −154.93 (15) | O3—C13—C14—F2 | −118.68 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 73.22 (16) | N1—C13—C14—F2 | 65.4 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.44 (17) | O3—C13—C14—F1 | 119.35 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | 32.93 (16) | N1—C13—C14—F1 | −56.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −73.38 (16) | C6—C1—C15—O5 | 35.8 (2) |
| C15—C1—C6—C17 | 4.8 (2) | C10—C1—C15—O5 | 155.57 (16) |
| C10—C1—C6—C17 | −122.10 (14) | C2—C1—C15—O5 | −78.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C17 | 124.52 (14) | C6—C1—C15—O4 | −146.90 (14) |
| C15—C1—C6—C5 | −119.37 (14) | C10—C1—C15—O4 | −27.14 (19) |
| C10—C1—C6—C5 | 113.70 (12) | C2—C1—C15—O4 | 98.85 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.31 (13) | C1—C6—C17—O7 | 58.2 (2) |
| C15—C1—C6—C7 | 122.99 (14) | C5—C6—C17—O7 | 176.13 (15) |
| C10—C1—C6—C7 | −3.95 (14) | C7—C6—C17—O7 | −54.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −117.33 (12) | C1—C6—C17—O6 | −126.65 (15) |
| O1—C5—C6—C17 | −165.16 (12) | C5—C6—C17—O6 | −8.77 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C17 | −59.95 (17) | C7—C6—C17—O6 | 120.36 (14) |
| O1—C5—C6—C1 | −35.94 (13) | O3—C13—N1—C12 | 167.96 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 69.27 (14) | C14—C13—N1—C12 | −16.5 (2) |
| O1—C5—C6—C7 | 68.99 (15) | O3—C13—N1—C11 | 4.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 174.20 (13) | C14—C13—N1—C11 | 179.81 (14) |
| C17—C6—C7—O2 | 165.38 (12) | C2—C12—N1—C13 | −101.78 (18) |
| C1—C6—C7—O2 | 38.92 (14) | C2—C12—N1—C11 | 62.52 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | −66.71 (16) | C10—C11—N1—C13 | 106.74 (16) |
| C17—C6—C7—C8 | 59.79 (16) | C10—C11—N1—C12 | −58.57 (17) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −66.68 (15) | C12—C2—O1—C5 | −178.88 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −172.31 (13) | C3—C2—O1—C5 | 51.41 (13) |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | −31.04 (16) | C1—C2—O1—C5 | −59.02 (12) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 75.27 (16) | C4—C5—O1—C2 | −51.23 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −1.76 (17) | C6—C5—O1—C2 | 59.90 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10—O2 | 33.85 (16) | C8—C7—O2—C10 | 50.57 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 154.49 (15) | C6—C7—O2—C10 | −60.77 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10—C1 | −71.55 (16) | C11—C10—O2—C7 | 179.05 (12) |
| C15—C1—C10—O2 | −158.88 (13) | C9—C10—O2—C7 | −51.80 (13) |
| C6—C1—C10—O2 | −31.61 (14) | C1—C10—O2—C7 | 57.12 (13) |
| C2—C1—C10—O2 | 74.81 (14) | O5—C15—O4—C16 | −0.7 (2) |
| C15—C1—C10—C11 | 83.27 (17) | C1—C15—O4—C16 | −178.05 (14) |
| C6—C1—C10—C11 | −149.45 (13) | O7—C17—O6—C18 | 2.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C10—C11 | −43.04 (17) | C6—C17—O6—C18 | −173.02 (14) |
| C15—C1—C10—C9 | −54.19 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O3i | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.116 (2) | 128 |
| C5—H5···O2ii | 1.00 | 2.60 | 3.1960 (19) | 118 |
| C7—H7···O1ii | 1.00 | 2.54 | 3.2091 (19) | 124 |
| C11—H11B···O4 | 0.99 | 2.57 | 3.093 (2) | 113 |
| C12—H12A···O7iii | 0.99 | 2.52 | 3.328 (2) | 138 |
| C12—H12B···O5iii | 0.99 | 2.34 | 3.030 (2) | 127 |
| C12—H12B···F1 | 0.99 | 2.40 | 3.043 (2) | 122 |
| C12—H12B···F2 | 0.99 | 2.33 | 2.962 (2) | 121 |
| C16—H16A···F3iv | 0.98 | 2.62 | 3.475 (2) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Baku State University grant . Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation grant RFMEFI61917X0007.
References
- Borisova, K. K., Kvyatkovskaya, E. A., Nikitina, E. V., Aysin, R. R., Novikov, R. A. & Zubkov, F. I. (2018a). J. Org. Chem. 83, 4840–4850. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Borisova, K. K., Nikitina, E. V., Novikov, R. A., Khrustalev, V. N., Dorovatovskii, P. V., Zubavichus, Y. V., Kuznetsov, M. L., Zaytsev, V. P., Varlamov, A. V. & Zubkov, F. I. (2018b). Chem. Commun. 54, 2850–2853. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Borisova, K. K., Nikitina, E. V., Novikov, R. A., Khrustalev, V. N., Dorovatovskii, P. V., Zubavichus, Y. V., Kuznetsov, M. L., Zaytsev, V. P., Varlamov, A. V. & Zubkov, F. I. (2018c). Private communication (refcode 1570123). CCDC, Cambridge, England. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Borisova, K. K., Nikitina, E. V., Novikov, R. A., Khrustalev, V. N., Dorovatovskii, P. V., Zubavichus, Y. V., Kuznetsov, M. L., Zaytsev, V. P., Varlamov, A. V. & Zubkov, F. I. (2018d). Private communication (refcode 1570124). CCDC, Cambridge, England. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cavallo, G., Metrangolo, P., Milani, R., Pilati, T., Priimagi, A., Resnati, G. & Terraneo, G. (2016). Chem. Rev. 116, 2478–2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hathwar, V. R., Sist, M., Jørgensen, M. R. V., Mamakhel, A. H., Wang, X., Hoffmann, C. M., Sugimoto, K., Overgaard, J. & Iversen, B. B. (2015). IUCrJ, 2, 563–574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hazra, S., Martins, N. M. R., Mahmudov, K. T., Zubkov, F. I., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2018). J. Organomet. Chem. 867, 193–200.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Legon, A. C. (2017). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 14884–14896. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, G., Zangrando, E., Mitoraj, M. P., Gurbanov, A. V., Zubkov, F. I., Moosavifar, M., Konyaeva, I. A., Kirillov, A. M. & Safin, D. A. (2018). New J. Chem. 42, 4959–4971.
- Mahmudov, K. T., Kopylovich, M. N., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2017a). Dalton Trans. 46, 10121–10138. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mahmudov, K. T., Kopylovich, M. N., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2017b). Coord. Chem. Rev. 345, 54–72.
- McKinnon, J. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3814–3816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mikherdov, A. S., Kinzhalov, M. A., Novikov, A. S., Boyarskiy, V. P., Boyarskaya, I. A., Dar’in, D. V., Starova, G. L. & Kukushkin, V. Yu. (2016). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14129–14137. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Scheiner, S. (2013). Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 280–288. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Ahmadova, N. E., Gurbanov, A. V., Maharramov, A. M., Mammadova, G. Z., Nenajdenko, V. G., Zubkov, F. I., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2018). Dyes Pigments, 150, 377–381.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vandyshev, D. Yu., Shikhaliev, K. S., Potapov, A. Yu., Krysin, M. Yu., Zubkov, F. I. & Sapronova, L. V. (2017). Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 13, 2561–2568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014305/wm5463sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018014305/wm5463Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1872524
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






