Abstract
Marine natural products have become an increasingly important source of new drug leads during recent years. In an attempt to identify novel anti-microbial natural products by bioprospecting deep-sea Actinobacteria, three new angucyclines, nocardiopsistins A-C, were isolated from Nocardiopsis sp. strain HB-J378. Notably, the supplementation of the rare earth salt Lanthanum chloride (LaCl3) during fermentation of HB-J378 significantly increased the yield of these angucyclines. The structures of nocardiopsistins A-C were identified by 1D and 2D NMR and HR-MS data. Nocardiopsistins A-C have activity against MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) with MICs of 3.12–12.5 μg/mL; the potency of nocardiopsistin B is similar to that of the positive control, chloramphenicol. Bioinformatic analysis of the draft genome of HB-J378 identified a set of three core genes in a biosynthetic gene cluster that encode a typical aromatic or type II polyketide synthase (PKS) system, including ketoacyl:ACP synthase α-subunit (KSα), β-subunit (KSβ) and acyl carrier protein (ACP). The production of nocardiopsistins A-C was abolished when the three genes were knocked out, indicating their indispensable role in the production of nocardiopsistins.
Keywords: Nocardiopsis, Nocardiopsistins, Angucycline, Anti-MRSA, Actinobacteria, LaCl3
1. Introduction
Microbial natural products are one of the most important sources for clinical drugs and have been mined for many decades [1,2]. During the past two decades, many novel marine natural products (MNPs) have been discovered from marine life every year [3], forming a huge reservoir of new structures for drug discovery [[4], [5], [6]]. Of these, marine microorganisms are major producers of MNPs. Recently, researchers have exhibited a growing interest in the less-exploited deep-sea microorganisms derived from diverse geographical locations or from complex symbiotic systems, such as are found in marine sponges [7,8]. Advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have facilitated natural product discovery efforts to enter a new genomic era [9]. Genomic studies of microbial natural product producers have revealed that the secondary metabolic capability of microbes are largely underestimated [10]; although a single digit number of secondary metabolites are usually detected in culture, dozens of metabolic gene clusters are predicted in a genome. A large number of silent or cryptic gene clusters have been uncovered by bioinformatic analysis and the genome sequences deposited in databases [11]. Strategies that efficiently activate cryptic gene clusters, allowing for genome mining, play a critical role in the discovery of novel natural products in the genomic era [12].
The application of chemical elicitors such as LaCl3 is very simple and efficient and has been shown to be an effective strategy to stimulate or improve secondary metabolism in bacteria [13,14]. In a preliminary study using deep-sea Actinobacteria for anti-infective natural products, some strains acquired antimicrobial activity upon supplementation with LaCl3, while others showed an increased level of activity [15]. The strain HB-J378, formerly named J378, was selected for investigation because its anti-MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) activity was significantly enhanced by the addition of LaCl3 [15]. Here, we report the isolation and identification of nocardiopsistins A-C (1–3), a group of new angucyclines, which were activated by the elicitor and are responsible for the anti-MRSA activity. We also demonstrated unambiguously by gene knock-out that a set of three genes in gene cluster #11 is indispensable for the production of nocardiopsistins. These genes encode minimal core components of aromatic or type II polyketide synthases (PKSs), which are highly homologous to that of the urdamycin, oviedomycin and landomycin pathways.
1. Materials and methods
1.1. Chemicals and general experimental procedures
Lanthanum chloride (LaCl3) was obtained from ACROS Organics; premixed LB powder was obtained from BD Difco; the Sephadex LH-20 resin was purchased from GE Healthcare. All organic solvents were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific. As a step of the chemical purification process, crude extracts were fractionated by reversed-phase C-18 flash chromatography using an Isco Combiflash® RFx4 equipped with PeakTrak software (Teledyne Isco)on a RediSep Rf Gold C18 column (size 50 g). HPLC analyses of crude extracts and fractions were performed on an UltiMate 3000 system (Thermo Fisher) with an Apollo C18 column (250 mm × 4.5 mm) or a semi-preparative column (Apollo C18 column, 250 mm × 10 mm). HRESI-MS data were recorded on an LTQ Orbitrap VELOS (Thermo Fisher) or an Agilent Q-TOF high-resolution mass spectrometer. NMR data were collected on a JEOL ECA-600 spectrometer operating at 600.17 MHz for 1H and 150.9 MHz for 13C. The edited-g-HSQC spectrum was optimized for 140 Hz, and the g-HMBC spectrum was optimized for 8 Hz. Samples were dissolved in CDCl3 and chemical shifts were referenced to solvent, e.g. CDCl3 δH observed at 7.24 ppm and δC observed at 77.0 ppm.
1.2. Bacterium and phylogenetic analysis
The strain HB-J378 which was isolated from a specimen (5-VI-96-3-009) of the marine sponge Theonella sp. is held in the Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute (HBOI) Marine Microbial Culture Collection. For general growth, the strain was cultivated on GYM agar plates (glucose 4 g, malt extract 10 g, yeast extract 4 g, NZ-amine type A 1 g, sea salt 39.5 g, agar 20 g per liter) at 28 °C; liquid culture was carried out in SPY medium (soluble starch 20 g, glucose 10 g, peptone 5 g, yeast extract 5 g, K2HPO4 0.5 g, MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g, CaCO3 2 g, and sea salt 39.5 g, per liter) on a shaker (250 rpm) at 28 °C. For phylogenetic analysis, genomic DNA was extracted from fresh-grown mycelia using Chelex resin (Promega) according to the manufacturer's manual; the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using universal primers Eco9 and Loop27rc (Table 1). PCR products were observed on 1% agarose gels, purified, and sent for Sanger sequencing at Eurofins Genomics. Dual direction sequencing using both forward and reverse primers allowed an accurate editing of sequences. The consensus sequences were aligned for the closest relative in the GenBank database using BLAST [16]. The partial 16S rRNA sequences shared high homologies with various Nocardiopsis species, with N. dassonvillei subsp. albirubida NBRC 13392 as the top hit (accession no. NR_112743).
Table 1.
Primers used in this study.
| Name | Sequences (5′ → 3′) | Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| Eco9 | CAG TTT GAT CCT GGC TCAG | |
| Loop27rc | GAC TAC CAG GGT ATC TAA TC | |
| aac(3)IV-F | ATT CTT CGC ATC CCG CCT CT | |
| aac(3)IV-R | GCC CGT TAC ACC GGA CCT TG | |
| C11F-for | CATATG TCA GCA GCT TCA CCG ACT C | NdeI |
| C11F-rev | ACTAGT CTG TCG TCA TGT GTG GTC GT | SpeI |
| C11R-for | ACTAGT GGC ACG GCC TGT GAC CAC A | SpeI |
| C11R-rev | AAGCTT GGC GAT CAG CCG GTA CAC AT | HindIII |
| C11FR-for | GCT GTT CCA GCA GAT CAG C | |
| C11FR-rev | GCA GAG GAA CAC CTG CTT AC |
1.3. Fermentation and metabolic profile analysis
For small-scale fermentation, spores of Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378 were inoculated into 250-mL flasks each containing 100 mL of SPY media; LaCl3 was supplemented at 2 mM. For large-scale fermentation, spores were inoculated in 70 flasks each containing 100 mL SPY medium with 2 mM LaCl3. All flasks were cultured on a rotary shaker at 200 rpm and 28 °C for 7 days. The broth (7 L) was extracted four times with equal volume of ethyl acetate using three times of sonication for 20 min each. The combined EtOAc layers were concentrated under vacuum at 30 °C. Samples were dissolved in methanol and centrifuged to remove precipitates before HPLC. The mobile phases consisted of H2O+0.1% TFA (solvent A)/MeCN (solvent B), eluted by a gradient of 5 min equilibration, 5% B; 0 min, 5% B; 15 min, 100% B; 20 min, 100% B, and a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min.
1.4. Antimicrobial bioassay
The antimicrobial activity of purified compounds was tested against Candida albicans, MRSA, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa using a standard disk-diffusion method [17]. Strong inhibition against MRSA was observed. Microtiter broth dilution [18] was performed to determine minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of each purified compound. Chloramphenicol and DMSO were included as the positive and negative control, respectively.
1.5. Knock-out of PKS genes
The traditional double-crossover strategy was used to knock-out genes of interest. The left arm (L-arm, 1.1-kb) was amplified using primers C11F-for/C11F-rev, and the right arm (R-arm, 1.1-kb) with primers C11R-for/C11R-rev (Table 1). After sequencing confirmation of PCR products, the L-arm and R-arm fragments were digested by NdeI/SpeI, and SpeI/HindIII, respectively, and ligated into pYH7 (kindly gifted by Prof. Yuhui Sun [19]) digested by NdeI/HindIII, and recombinant plasmid pYH7-c11/PKS was transformed into Escherichia coli ET12567/pUZ8002. Conjugation of pYH7-c11/PKS into Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378 was performed as described previously [20]. Briefly, spores were collected from MS sea salt agar plates, subjected to heat shock at 55 °C for 10min, and then suspended in LB as recipients. For donors, an overnight culture of E. coli ET12567/pUZ8002 containing the plasmid pYH7-c11/PKS was inoculated into fresh 50 mL LB at a ratio of 1:100, and when OD600 reached 0.4–0.6, cells were collected by centrifugation and washed twice with LB, then suspended in LB. The donors and recipients were mixed and spun briefly, they were then plated on MS sea salt agar plates supplemented with 10 mM MgCl2. After 15 h incubation at 28 °C, apramycin (75 μg/mL) and nalidixic acid (50 μg/mL) were overlaid to select exconjugants. Exconjugants were then passaged on plates without any antibiotic for 3–4 generations, single clones with the deletion of PKS genes were confirmed by PCR using primers C11FR-for and C11FR-rev (Table 1). A knock-out mutant was randomly chosen for further fermentation and analytic experiments.
1.6. Accession number
The partial 16S rRNA sequence of Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378 has been submitted to GenBank with an accession number MH779065.
2. Results
2.1. Improved production and isolation of compounds from Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378
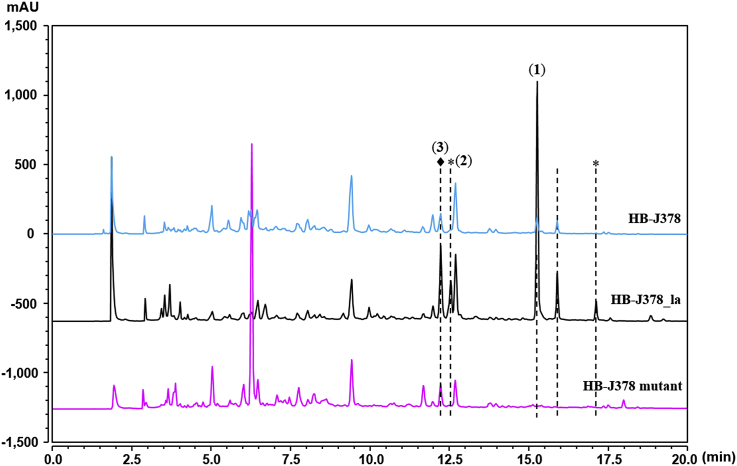
Fermentation in the presence of 2 mM LaCl3 led to a doubling of the inhibition zone in the anti-MRSA assay for the crude ethyl acetate extract, 25 mm (with LaCl3) vs 12 mm (without LaCl3) [15]. While the yield of nocardiopsistin A (1) was enhanced approximately 4-fold, nocardiopsistin B (2) was only produced when LaCl3 was present (Fig. 1). Fractions enriched in these compounds from flash chromatography were further separated by Sephadex LH20 (25 mm × 51 cm), eluted with MeOH/CH2Cl2 (1:1); tubes with targeted peaks as determined by HPLC analysis were combined for semi-preparative purification. Nocardiopsistin A (1) (6 mg, tR = 11.2 min) was obtained using 80% MeCN at a flow rate of 3 mL/min, whereas nocardiopsistin B (2) (3.5 mg, tR = 20.5 min) and nocardiopsistin C (3) (1.5 mg, tR = 18.1 min) were purified using 70% MeOH at a flow rate of 3 mL/min.
Fig. 1.
HPLC analysis of secondary metabolic profiles of the wild-type strain HB-J378 without or with (‘-la’) the supplementation of 2 mM LaCl3, and the in-frame deletion mutant of PKS genes. Peaks representing nocardiopsistin compounds were indicated by dashed lines. *, new peaks activated by LaCl3; ♦, nocardiopsistin C (3) is co-eluted at the same retention time with unknown compounds.
2.2. Structural characterization of nocardiopsistins A-C
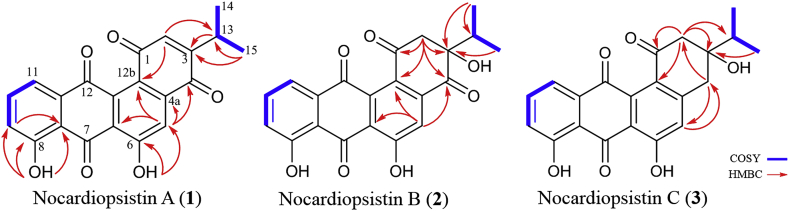
Nocardiopsistin A (1) was obtained as yellow powder. Its molecular formula was suggested to be C21H14O6 on the basis of HRESI-MS data observed at m/z 363.0838 [M+H]+ (calcd. for C21H15O6 363.0869). 1H and 13C NMR data are shown in Table 2. 1D NMR data suggested the angucyclinone skeleton which was very similar to the data reported for oviedomycin [21]. A primary difference was the observation of resonances attributable to two methyl groups [δH 1.23 and δH 1.21] each appearing as doublets. These were coupled to H-13 (δH 3.2) assigning an isopropyl group in 1. The isopropyl functionality was placed at C-3 based upon correlations in the HMBC spectrum between both H-13 and CH3-15 (δH 1.21) to C-3 (δC 155.6) and from H-2 (δH 6.90) to C-13. The resonance at δH 6.91 (s, H-2) was assigned by the HMBC correlation with C-12b (δC 127.4) and C-13. HO-8 was assigned by HMBC correlations with C-7a, C-8, and C-9, whereas the position of HO-6 was confirmed by HMBC correlations with C-6 and C-6a (Fig. 2, Table 2). HRESI-MS data, UV spectrum, chemical shifts and HMBC correlations, and full 1D/2D NMR data were shown in Supplementary Figs. S1–S6.
Table 2.
1H (600 MHz) and 13C NMR (150 MHz) spectroscopic data for compounds 1–3 in CDCl3.
| Position |
1 |
2 |
3 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (multi, J in Hz) | δC | HMBC | δH (multi, J in Hz) | δC | HMBC | δH (multi, J in Hz) | δC | HMBC | |
| 1 | 183.4 | 192.2 | 196.8 | ||||||
| 2 | 6.90 (s, 1H) | 135.7* | 3, 4, 12a, 12b, 13, 14 | 3.46 (d, 1H, 13.2) | 50.8 | 1, 3, 4, 12b, 13 | 3.05 (d, 1H, 15.1) | 49.9 | 1, 3, 13 |
| 3.34 (d, 1H, 13.2) | 1, 3, 4, 13 | 2.82 (dd, 1H, 15.1, 3.0) | 1, 3, 4, 12b | ||||||
| 3 | 155.6 | 81.2 | 76.6 | ||||||
| 4 | 182.7 | 199.9 | 3.08 (d, 1H, 16.5) | 39.8 | 2, 3, 4a, 5, 12b, 13 | ||||
| 2.97 (dd, 1H, 16.5, 3.0) | 2, 3 | ||||||||
| 4a | 140.0 | 140.4 | 151.0 | ||||||
| 5 | 7.87 (s, 1H) | 120.4** | 4, 6, 6a, 7, 12b | 7.78 (s, 1H) | 120.6 | 4, 6a, 12b | 7.01 (s, 1H) | 122.3 | 4, 6, 6a, 12b |
| 6 | 164.7 | 164.4 | 163.7 | ||||||
| 6-OH | 12.5 s | 4a, 6, 6a, 7 | 12.42 s | 4a, 6, 6a | 12.3 s | 5, 6, 6a | |||
| 6a | 120.4** | 121.2 | 116.6 | ||||||
| 7 | 192.6 | 192.5* | 192.6 | ||||||
| 7a | 115.2 | 115.1 | 115.0 | ||||||
| 8 | 162.5 | 162.7 | 162.0 | ||||||
| 8-OH | 11.55 s | 7, 7a, 8, 9, 10 | 11.54 s | 7a, 8, 9 | 11.86 s | 7a, 8, 9 | |||
| 9 | 7.31 (dd, 1H, 7.2, 3) | 124.3 | 7a, 8, 11 | 7.33 (dd, 1H, 8.4, 1.2) | 124.7 | 7a, 8, 11 | 7.25 (m, 1H) | 124.0 | 7a, 8, 11, 11a |
| 10 | 7.75 (overlapped, 1H) | 138.6 | 8, 11a, 12 | 7.75 (t, 1H, 7.8) | 138.8 | 8, 11a | 7.67 (m, 1H) | 137.7 | 8 |
| 11 | 7.74 (overlapped, 1H) | 120.3** | 7a, 9, 11a | 7.72 (dd, 1H, 7.8, 1.8) | 120.7 | 7a, 9, 12 | 7.67 (m, 1H) | 120.1 | 7a, 9, 10, 12 |
| 11a | 135.8* | 135.4 | 135.4 | ||||||
| 12 | 182.7 | 182.1 | 183.0 | ||||||
| 12a | 138.9 | 138.4* | 137.6 | ||||||
| 12b | 127.2 | 131.7 | 129.4 | ||||||
| 13 | 3.20 (m, 1H) | 27.3 | 2, 3, 4, 14 | 1.82 (m, 1H) | 33.6 | 15 | 1.87 (pentet, 1H, 6.9) | 38.2 | 2, 3, 4, 14, 15 |
| 14-CH3 | 1.23 (s, 3H) | 21.4 | 3, 13, 15 | 1.08 (d, 3H, 6.0) | 15.5 | 3, 13, 15 | 1.04 (d, 3H, 6.9) | 16.8 | 3, 13, 15 |
| 15-CH3 | 1.21 (s, 3H) | 21.4 | 3, 13, 14 | 0.77 (d, 3H, 6.0) | 16.5 | 3, 13, 14 | 1.04 (d, 3H, 6.9) | 16.8 | 3, 13, 14 |
*, ** chemical shifts can't be assigned.
Fig. 2.
Chemical structures and COSY, HMBC correlations of nocardiopsistins A (1), B (2), and C (3).
Nocardiopsistin B (2) was obtained as yellow powder. Its molecular formula was suggested to be C21H16O7 based upon the observation of a peak in the HRESI-MS spectrum at m/z 381.0948 [M+H]+ (calcd. for C21H17O7 381.0974). The UV and 1D NMR data were similar to that observed for 1 with key differences being the observation of a methylene group [δH 3.46 d (J = 13.2), 3.34 d (J = 13.2); δC 50.8] and a quaternary carbon [δC 81.2] and loss of two olefinic resonances. This suggested that there was a reduction of a double bond in 2. The mass spectrum suggested the presence of an additional —OH group which could be placed at either C-2 or C-3. The methylene proton observed at δH 3.46 (H-2a) showed correlations in the 2D HMBC spectrum to C-12b (δc 131.7) C-1 (δc 192.2), C-3 (δc 81.6), and C-4 (δc 199.9) and C-13 (δc 33.6). H-5 (δH 7.78) showed correlations in the HMBC spectrum to C-12b, C-4 and C-6a. All of these are consistent with assignment of the methylene group at C-2. The hydroxyl functionality was attached to C-3 (δc 81.2) on the basis of HMBC correlations between C-3 and both methyl resonances of the isopropyl unit (δH 1.08 and δH 0.77) and the chemical shift (Fig. 2, Table 2); conformational position of this —OH group could not be assigned solely based on NMR data. The remainder of the molecule are the same as in 1 and all NMR data is consistent with this assignment. HRESI-MS data, UV spectrum, chemical shifts and HMBC correlations, and full 1D/2D NMR data were shown in Supplementary Figs. S7–S12.
Nocardiopsistin C (3) was obtained as yellow powder. Its molecular formula was suggested to be C21H18O6 based upon the observation of a peak in the HRESI-MS spectrum at m/z 361.1154 [M+H]+ (calcd. for C21H19O6 367.1182). Inspection of the 1H and 13C NMR spectra suggested that it was closely related to compound 2 with a primary difference being the presence of an additional methylene group observed at δH 3.08 d (J = 16.5), 2.97 dd (J = 16.5, 3.0); δC 39.8 and the loss of the resonance attributable to the C-4 ketone in 2. The singlet proton observed at δH 7.01 (H-5) showed long range coupling in the HMBC spectrum to the carbon of the new methylene group supporting the replacement of the C-4 ketone with a methylene group. The protons of the new methylene group showed correlations in the HMBC spectrum to C-5 providing further support of the assignment. As with both 1 and 2 resonances attributable to an isopropyl functionality were observed and both H-13 and the methyl protons attached to C-13 showed correlations in the HMBC spectrum to a quaternary carbon observed at δC 76.8 similar to what was found for 2 suggesting the presence of hydroxyl functionality at C-3. The 2D-COSY spectrum indicated a long range coupling between H-2b [δH 2.82] and H-4b [δH 2.97] of the methylene groups and the magnitude of the coupling constant is consistent with w-coupling. The NMR data observed for the remaining atoms was similar to that of compounds 1 and 2 with all correlations observed in the COSY and HMBC spectrum being consistent with structure 3. HRESI-MS data, UV spectrum, chemical shifts and HMBC correlations, and full 1D/2D NMR data were shown in Supplementary Fig. S13–S18.
2.3. Anti-MRSA activity of nocardiopsistins A-C
Our preliminary study [15] reported only an anti-MRSA activity of the HB-J378 crude extract. After purification, nocardiopsistins A-C were tested again against three pathogens, MRSA together with C. albicans and P. aeruginosa. As expected, no inhibitory activity of purified compounds were observed against C. albicans and P. aeruginosa; all compounds inhibited the growth of MRSA. We further determined the MIC of each compound. As shown in Table 3, nocardiopsistin B, with a hydroxyl group (—OH) at C3 (Fig. 2), showed the best anti-MRSA activity with the same MIC (3.12 μg/mL) as that of chloramphenicol, whereas nocardiopsistins A and C have a moderate anti-MRSA activity (MIC = 12.5 μg/mL).
Table 3.
The activity of nocardiopsistins A-C (1–3) against MRSA.
| Compound | MIC (μg/ml) |
|---|---|
| Nocardiopsistin A (1) | 12.5 |
| B (2) | 3.12 |
| C (3) | 12.5 |
| Chloramphenicol | 3.12 |
2.4. Identification of PKS genes indispensable for the biosynthesis of nocardiopsistins
In an attempt to define the biosynthetic origin of nocardiopsistins, the draft genome of HB-J378 was determined by the Illumina sequencing platform and analyzed using antiSMASH [22] to predict metabolic gene clusters. Twenty-three (23) biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) were predicted using the latest version (4.1.0) of antiSMASH. Since nocardiopsistins A-C (1–3) are angucycline-type compounds, they are presumably synthesized by an aromatic or type II PKS system. The nocardiopsistins are structurally very similar to oviedomycin [23,24] with the primary difference being the incorporation of the unique isopropyl starter unit, which is likely derived from an isobutyryl-CoA.
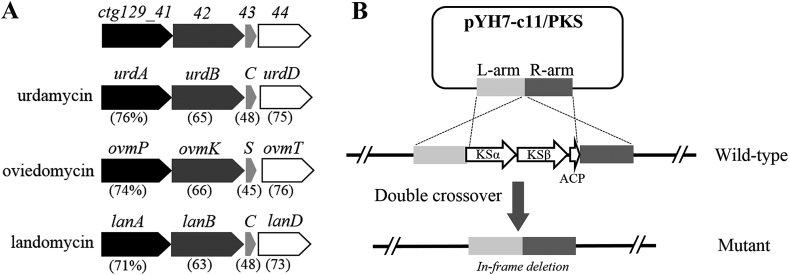
Interestingly, out of 4 BGCs that show the potential to produce polyketides, cluster #11 is a typical type II PKS gene cluster which contains three contiguous genes encoding KSα, KSβ (also named chain length factor, CLF) and ACP showing high homologies to the corresponding core PKS components of urdamycin, oviedomycin, and landomycin (Fig. 3A) [[24], [25], [26], [27]]. In order to confirm whether this gene cluster is responsible for the biosynthesis of nocardiopsistins, in-frame deletion of the three PKS genes was performed via double crossover homologous recombination (Fig. 3B). The absence of genes in HB-J378 mutants was confirmed by PCR using primers C11FR-for/CRFR-rev. Three mutants were obtained and fermented in 100-mL SPY medium each; HPLC analysis showed the production of nocardiopsistins was abolished in all mutants, with one representative shown in Fig. 1. Accordingly, the mutant extract did not show anti-MRSA activity in the same disk fusion assay (data not shown). These results demonstrated clearly that the PKS genes are indispensable for nocardiopsistin production, the gene cluster #11 is likely the BGC for nocardiopsistins, and that nocardiopsistins are responsible for the anti-MRSA activity in the strain HB-J378.
Fig. 3.
(A) Nocardiopsistin PKS genes are highly homologous to other angucyclines, such as landomycin pathway (lan, accession #AF080235), oviedomycin pathway (ovm, accession #AJ632203); and urdamycin pathway (urd, accession #X87093). The number in parentheses indicates sequence identity between nocardiopsistin genes with its corresponding homologous genes. The conserved gene (empty arrows) encoding a C9 reductase often present in angucycline pathways is also included. (B) Illustration of the in-frame deletion of nocardiopsistin PKS genes in HB-J378 using double crossover.
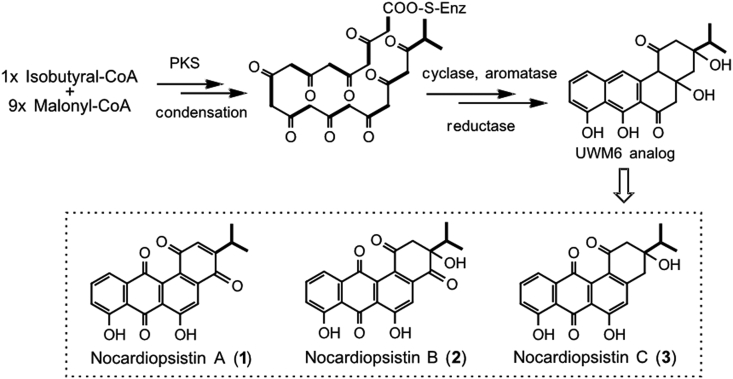
Angucyclines are a large group of well-known aromatic polyketide compounds; their biosynthetic pathways have been extensively characterized [23]. Based on the reported oviedomycin pathway [24], a simplified biosynthetic pathway of nocardiopsistins A-C was proposed, likely through an analogue of the key angucycline biosynthetic intermediate UWM6 [23], using a molecule of isobutyral-CoA and nine molecules of malonyl-CoA (Fig. 4). Notably, isobutyryl-CoA is rarely used as a starter unit in angucyclines.
Fig. 4.
Proposed biosynthesis of nocardiopsistins A-C (1–3).
3. Discussion
In our previous study, a chemical elicitor LaCl3 has been demonstrated to efficiently activate or enhance antimicrobial activities in more than half of the strains used in that study [15]. By using this method, we found that the anti-MRSA activity of a marine sponge-derived bacterium Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378 was doubled by simply supplying 2 mM LaCl3. Although the mechanism remains elusive, supplementation of LaCl3 can be a simple and efficient method to elicit the production of novel marine natural products from dee-sea actinomycetes, a group of largely un-tapped secondary metabolite-rich microorganisms, or to increase the yield of bioactive components.
In this work, we identified nocardiopsistins A-C as the metabolites enhanced by LaCl3 and that are responsible for the observed anti-MRSA activity in Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378. Chemical structures indicated that these bioactive compounds are a group of new angucyclines, using an unusual isobutyryl-CoA as the biosynthetic starter unit. Angucyclines are the largest group of aromatic or type II PKS-derived natural products, and are extremely rich in various biological activities [23,28]. The biosynthesis of these compounds often undergoes unusual chemistry reactions, such as post-PKS framework rearrangements or glycosylation [23]. Although the genus Norcardiopsis is relatively newly established [29,30], its members are a rich source of value-added natural products with structural diversity and with a wide range of biological activities such as cytotoxicity, antitumor, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory and protein kinase inhibitory [31,32], and they have been recognized as a group of biotechnologically and pharmaceutically important bacteria.
Analyzing the draft genome of HB-J378 suggested that the aromatic polyketide gene cluster #11 is probably involved in the production of nocardiopsistins A-C. We constructed in-frame deletion mutants of three core PKS genes in the cluster, which are highly homologous to genes from other angucycline pathways (Fig. 3); as expected, production of nocardiopsistins A-C were abolished (Fig. 1). Notably, the antiSMASH-predicted 46.6-kb gene cluster locates in a relatively large contig #129 (66.4-kb) of the genome assembly; forty-eight (48) predicted ORFs likely includes all enzymes needed for the biosynthesis of nocardiopsistins, as the BGCs of angucycline compounds are usually small, typically around 30-kb [23]. Interestingly, by expressing only 12 structural genes that spans nearly 14-kb DNA isolated from Streptomyces ansochromogenes under the control of PhrdB in a heterologous host S. coelicolor M1146, oviedomycin was produced [33]. In the gene cluster #11, two ORFs, Ctg129_49 and Ctg129_50, are probably responsible for the incorporation of the unusual starter unit. Unexpectedly, the gene cluster lacks genes related to sugar biosynthesis and transfer, as glycosylation is a very common post-PKS structural modification of angucyclines [23]. Rather, a gene ctg129_57 whose product is highly homologous to flavin-dependent halogenases is found in the gene cluster, suggesting that HB-J378 can produce halogenated nocardiopsistin analogues. Halogenation, bromination, chlorination, iodination, and in particular fluorination, is an important structural modification of natural products, which often leads to significantly enhanced bioactivity and thus is of strong interest to drug discovery [34]. However, halogenation of angucyclines has been rarely reported; only a very limited number of halogenated angucyclines have been discovered, such as the dichlorocyclopropane compound JBIR-88 isolated from a lichen-derived Streptomyces sp [35] and hyperchlorinated allocyclinones produced by Actinoallomurus sp [36]. Identification of halogenated compounds in HB-J378 is in process.
4. Conclusion
In summary, we have identified three new angucyclines with anti-MRSA activity, nocardiopsistins A-C, from the marine sponge-derived Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378. Their production can be activated by simply supplying the rare earth salt LaCl3. A unique isobutyryl-CoA is suggested to be the biosynthetic starter unit of nocardiopsistins. AntiSMASH analysis of secondary metabolic gene clusters identified an aromatic PKS gene cluster; knock-out of its core PKS genes indicated this cluster is likely involved in the production of nocardiopsistins.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Prof. Yuhui Sun from Wuhan University, China, for his kind gift of the vector pYH7. This work was supported in part by the NIH grant CA209189.
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2018.10.008.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Shen B. A new golden age of natural products drug discovery. Cell. 2015;163(6):1297–1300. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Katz L., Baltz R.H. Natural product discovery: past, present, and future. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;43(2–3):155–176. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1723-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blunt J.W., Carroll A.R., Copp B.R., Davis R.A., Keyzers R.A., Prinsep M.R. Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 2018;35(1):8–53. doi: 10.1039/c7np00052a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lindequist U. Marine-derived pharmaceuticals - challenges and opportunities. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2016;24(6):561–571. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Montaser R., Luesch H. Marine natural products: a new wave of drugs? Future Med Chem. 2011;3(12):1475–1489. doi: 10.4155/fmc.11.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Altmann K.H. Drugs from the oceans: marine natural products as leads for drug discovery. Chimia (Aarau) 2017;71(10):646–652. doi: 10.2533/chimia.2017.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Subramani R., Aalbersberg W. Marine actinomycetes: an ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol Res. 2012;167(10):571–580. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2012.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Manivasagan P., Kang K.H., Sivakumar K., Li-Chan E.C., Oh H.M., Kim S.K. Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014;38(1):172–188. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deane C.D., Mitchell D.A. Lessons learned from the transformation of natural product discovery to a genome-driven endeavor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;41(2):315–331. doi: 10.1007/s10295-013-1361-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Van Lanen S.G., Shen B. Microbial genomics for the improvement of natural product discovery. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006;9(3):252–260. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Medema M.H., Fischbach M.A. Computational approaches to natural product discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11(9):639–648. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rutledge P.J., Challis G.L. Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13(8):509–523. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tanaka Y., Hosaka T., Ochi K. Rare earth elements activate the secondary metabolite-biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2010;63(8):477–481. doi: 10.1038/ja.2010.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ochi K., Hosaka T. New strategies for drug discovery: activation of silent or weakly expressed microbial gene clusters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97(1):87–98. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4551-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xu D., Han L., Li C., Cao Q., Zhu D., Barrett N.H., Harmody D., Chen J., Zhu H., McCarthy P.J., Sun X., Wang G. Bioprospecting deep-sea actinobacteria for novel anti-infective natural products. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:787. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W., Lipman D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wright A.E., Botelho J.C., Guzman E., Harmody D., Linley P., McCarthy P.J., Pitts T.P., Pomponi S.A., Reed J.K. Neopeltolide, a macrolide from a lithistid sponge of the family Neopeltidae. J Nat Prod. 2007;70(3):412–416. doi: 10.1021/np060597h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Institute CaLS . seventh ed. vol. 27. 2007. (Methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria: approved standard M11-A7). 2. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sun Y., He X., Liang J., Zhou X., Deng Z. Analysis of functions in plasmid pHZ1358 influencing its genetic and structural stability in Streptomyces lividans 1326. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;82(2):303–310. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1793-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tobias Kieser M.J.B., Buttner Mark J., Chater Keith F., Hopwood David A. The John Innes Foundation; 2000. Practical Streptomyces genetics. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mendez C., Kunzel E., Lipata F., Lombo F., Cotham W., Walla M., Bearden D.W., Brana A.F., Salas J.A., Rohr J. Oviedomycin, an unusual angucyclinone encoded by genes of the oleandomycin-producer Streptomyces antibioticus ATCC11891. J Nat Prod. 2002;65(5):779–782. doi: 10.1021/np010555n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Weber T., Blin K., Duddela S., Krug D., Kim H.U., Bruccoleri R., Lee S.Y., Fischbach M.A., Muller R., Wohlleben W., Breitling R., Takano E., Medema M.H. antiSMASH 3.0-a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W237–W243. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kharel M.K., Pahari P., Shepherd M.D., Tibrewal N., Nybo S.E., Shaaban K.A., Rohr J. Angucyclines: biosynthesis, mode-of-action, new natural products, and synthesis. Nat Prod Rep. 2012;29(2):264–325. doi: 10.1039/c1np00068c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lombo F., Brana A.F., Salas J.A., Mendez C. Genetic organization of the biosynthetic gene cluster for the antitumor angucycline oviedomycin in Streptomyces antibioticus ATCC 11891. Chembiochem. 2004;5(9):1181–1187. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200400073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Westrich L., Domann S., Faust B., Bedford D., Hopwood D.A., Bechthold A. Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster from Streptomyces cyanogenus S136 probably involved in landomycin biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;170(2):381–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhu L., Ostash B., Rix U., Nur E.A.M., Mayers A., Luzhetskyy A., Mendez C., Salas J.A., Bechthold A., Fedorenko V., Rohr J. Identification of the function of gene lndM2 encoding a bifunctional oxygenase-reductase involved in the biosynthesis of the antitumor antibiotic landomycin E by Streptomyces globisporus 1912 supports the originally assigned structure for landomycinone. J Org Chem. 2005;70(2):631–638. doi: 10.1021/jo0483623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Decker H., Haag S. Cloning and characterization of a polyketide synthase gene from Streptomyces fradiae Tu2717, which carries the genes for biosynthesis of the angucycline antibiotic urdamycin A and a gene probably involved in its oxygenation. J Bacteriol. 1995;177(21):6126–6136. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.21.6126-6136.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Krohn K., Rohr J. Angucyclines: total syntheses, new structures, and biosynthetic studies of an emerging new class of antibiotics. Bioorg Chem Deoxysugars Polyketides Relat Classes Synth Biosynth Enzymes. 1997;188:127–195. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Meyer J. Nocardiopsis, a new genus of order actinomycetales. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 1976;26(4):487–493. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rainey F.A., Ward-Rainey N., Kroppenstedt R.M., Stackebrandt E. The genus Nocardiopsis represents a phylogenetically coherent taxon and a distinct actinomycete lineage: proposal of Nocardiopsaceae fam nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996;46:1088–1092. doi: 10.1099/00207713-46-4-1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bennur T., Ravi Kumar A., Zinjarde S.S., Javdekar V. Nocardiopsis species: a potential source of bioactive compounds. J Appl Microbiol. 2016;120(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/jam.12950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ibrahim A.H., Desoukey S.Y., Fouad M.A., Kamel M.S., Gulder T.A.M., Abdelmohsen U.R. Natural product potential of the genus Nocardiopsis. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(5) doi: 10.3390/md16050147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xu J., Zhang J., Zhuo J., Li Y., Tian Y., Tan H. Activation and mechanism of a cryptic oviedomycin gene cluster via the disruption of a global regulatory gene, adpA, in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(48):19708–19720. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.809145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Neumann C.S., Fujimori D.G., Walsh C.T. Halogenation strategies in natural product biosynthesis. Chem Biol. 2008;15(2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Motohashi K., Takagi M., Yamamura H., Hayakawa M., Shin-Ya K. A new angucycline and a new butenolide isolated from lichen-derived Streptomyces spp. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2010;63(9):545–548. doi: 10.1038/ja.2010.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cruz J.C., Maffioli S.I., Bernasconi A., Brunati C., Gaspari E., Sosio M., Wellington E., Donadio S. Allocyclinones, hyperchlorinated angucyclinones from Actinoallomurus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2017;70(1):73–78. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.