Abstract
Depression is currently treated by pharmacotherapies that can elicit debilitating side effects for patients. Novel treatment options with limited side effects are currently being researched. Resveratrol is a polyphenol and phytoalexin found in the skins of grapes, red wine, Japanese knotweed, and peanuts. It has been studied extensively for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Resveratrol has also gained attention for its neuroprotective properties. The aim of the review was to examine the mechanisms by which resveratrol reduces depressive behaviors in animal models. In total, 22 studies met the established criteria for final review. Behavioral aspects of depression were investigated using validated measures such as the forced swimming test, tail suspension test, sucrose preference test, and open field test. While many physical measures were taken, three main biological mechanisms were explored: Regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis; decreased inflammation; and increased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and neurogenesis. Based on these findings, resveratrol may be deemed an effective treatment for depression in animal models at doses between 10–80 mg/kg/day, although higher doses had the most significant effects. Future studies should examine the effects of resveratrol on depression in humans to determine the eligibility of resveratrol as a natural antidepressant with less severe side effects.
Keywords: resveratrol, depression, anxiety, stress, neurogenesis, BDNF, inflammation
1. Introduction
Depression, the most common mental disorder, affects over 300 million individuals worldwide [1]. Mental, neurological, and substance-use disorders make up 13% of the global burden of disease, and depression is recognized as the third leading contributor. Depression has negative implications for individuals and their families and is associated with increased risk of mortality, lower income, higher unemployment, chronic disease, and other mental health disorders [2]. Furthermore, depression often leads to suicide, with 800,000 individuals dying due to suicide per year [1]. Depression also creates a major economic burden, which was estimated at $210.5 billion in 2010 [3]. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 11 percent of Americans over the age of 12 take antidepressant medication; from 2005 to 2008, antidepressant use increased 400% across all age groups [3,4].
While the pathogenesis of depression is known to include genetic, environmental, and psychosocial factors, the exact biological mechanisms remain to be elucidated [5]. Research on classical antidepressants reveals that multiple factors are involved and several brain regions are affected, helping to establish the mechanisms at play. These include dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, decreased neurogenesis, oxidative stress, and changes in serotonergic and adrenergic pathways [6].
Several antidepressant classes exist, including monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) [7]. TCAs effectively inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, but also affect other receptor systems and therefore have substantial adverse side effects. SSRIs reduce the reuptake of serotonin, and SNRIs reduce the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. SSRIs are now the most commonly prescribed antidepressants, as they have similar effectiveness as other medications while posing fewer severe side effects. Still, about half of patients experience a full remission, and the side effects of SSRIs, which include gastrointestinal issues, weight gain, sleep disturbances, and sexual dysfunction, can significantly impact quality of life [8]. Therefore, it is imperative to examine novel therapeutic agents with limited side effects for the treatment of depression.
There is growing evidence for the value of botanical compounds and other natural substances in the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In addition to resveratrol, plant components with possible antidepressant effects include anthocyanidins, catechins, and cocoa [9]. Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxystilbene) is a phytoalexin and polyphenol found predominantly in the skins of red grapes, red wine, Japanese knotweed, and some nuts [10]. It has been studied extensively for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticarcinogenic properties [11,12]. Resveratrol has also been implicated as a neuroprotective agent with the ability to increase neurogenesis, most notably in reducing Alzheimer’s disease progression [13]. More recently, resveratrol has been examined as a potential aid to improve sleep quality [14], reduce fatigue [15], and ameliorate anxiety and depression [16]. While resveratrol has been shown to decrease depressive behaviors and biochemical markers associated with depression in animal models, few human studies exist to replicate these findings. The objective of the present review was to examine the effects of resveratrol on depressive behaviors in animal models through mechanisms that include regulation of the HPA axis, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, increased neurogenesis, and increased monoamine production.
2. Methods
Articles were searched for using the databases PubMed Central and PsycInfo with the latest search date of August 2018. The phrases “resveratrol” and “depression” were entered into the search engine with the limitations of the years 2010 to 2018. This yielded 1859 articles from PubMed Central and 23 articles from PsycInfo. The titles of the articles were reviewed to determine if the study involved resveratrol and depression using an animal model. Based on this, 340 articles were chosen, and their abstracts were reviewed to inquire if they included resveratrol related to behavioral symptoms of depression or physical parameters of depression. Sixteen articles were read in depth to determine if they (a) included an animal model of depression treated with resveratrol and compared to a control and/or pharmaceutical antidepressant; (b) examined depressive behaviors using standardized protocols; and (c) explored the physiological mechanisms. Ten articles were established as eligible based on these methods, while 12 articles were chosen from the references of others, yielding a total of 22 articles for final review (Figure 1). The results of each study were reported based on mean differences with an alpha level of 0.01 or 0.05 based on the parameters set by each study author. Some studies had a broader focus that did not fit within the context of this review, and thus only those results that corresponded to our specific objectives were cited (Table 1).
Figure 1.
Process of article selection for final review.
Table 1.
Effects of Resveratrol on Behavioral and Clinical Outcomes of Depression.
| Author, Year | Animal Model | Intervention | Dosage/Route | Behavioral Outcomes w/RSV Txt | Clinical Outcomes w/RSV Txt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed and colleagues, 2014 [17] | reserpine-injected adult male Wistar rats | vehicle (saline + DMSO) reserpine reserpine + reserpine + RSV reserpine + resperpine + FLX × 3 days | RSV: 15, 30, 60 FLX: 24 | ↑ ambulation in OFT a,a (30/60) ↓ latency in OOFT a,a,a (15/30/60) FST ↓ immobility time in FST a,a,a (15/30/60) | ↑ NT levels: brain 5-HT a,a,a (15/30/60), dopamine a,a,a (15/30/60), and Norepinephrine a (60) |
| Ali and colleagues, 2015 [18] | CORT-injected male Swiss albino mice | CORT (con) CORT + RSV CORT + FLX Vehicle (con) 21 days | CORT: 40, s.c. RSV: 80, oral FLX: 15, oral Vehicle, 0, oral | ↑ sucrose preference c ↓ immobility time in FST b ↓ immobility time in TST a | ↓ serum CORT b ↑ hippocampal BDNF a |
| Chen and colleagues, 2017 [19] | LPS-injected male ICR mice | vehicle (saline) LPS LPS + RSV tests after 24 h | RSV: 0.3, i.c.v. | ↑ sucrose preference a ↓ immobility time in FST a | ↓ hippocampal superoxide a ↓ hippocampal apoptosis a ↑ hippocampal ATP production a ↑ hippocampal mitochondrial membrane potential a |
| Finnel and colleagues, 2017 [20] | social stress-exposed male Sprague-Dawley rats & Long-Evans retired breeders | RSV + social stress Vehicle + social stress 5 days social stress, Txt 7 days pre-social stress & during | RSV: 10, 30, i.p. Vehicle: 0, i.p. | ↑ sucrose preference c (30) | ↓ TNF-α c (10/30) ↓ IL-1β a,b (10/30) ↓ IL-6 c (10/30) ↓ IL-2 c (30)↓ IL-4 c (30) |
| Ge and colleagues, 2013 [21] | CUMS-exposed male Sprague-Dawley rats | CUMS + Vehicle CUMS + RSV CUMS + FLX CUMS 21 days, Txt days 14–21 | RSV: 15, i.p. FLX: 2, i.p. | ↑ sucrose preference a ↓ immobility time in FST c ↓ immobility time in TST c | ↓ serum CORT c ↓ serum MDA c ~ serum CRH d |
| Ge and colleagues, 2015 [22] | LPS-injected adult male Kunming mice | Vehicle (saline) Vehicle + LPS RSV + Vehicle RSV + LPS | RSV: 80, i.p. LPS: 0.83, i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST b ↑ swimming time in FST b ↓ immobility time in TST a ↑ sucrose preference a ~ locomotor activity d | ↓ hippocampal & PFC IL-1β a ↓ hippocampal TNF-α a ↓ PFC TNF-α b ↓ hippocampal & PFC pNF-κB p65 a ↑ PFC pCREB a ↑ hippocampal BDNF a |
| Ge and colleagues, 2016 [16] | SCH male Sprague-Dawley rats | SCH + Vehicle SCH + RSV SCH + LT4 Txt post SCH for 16 days | RSV: 15, i.g. LT4: 60 *, i.g. | ↑ sucrose preference b ↑ locomotor activity a ↓ immobility time in FST b ↓ immobility time in TST b | ↓ adrenal gland wt to body wt ratio b ↓ plasma CORT b ↓ CRH mRNA expresión b ↓ GSK-3β b ↑ pGSK-3β b ↑ pGSK-3β/ GSK-3β ratio b ↑ β-catenin b ↓ p β-catenin b ↓ p β-catenin/ β-catenin ratio b ↑ cyclin D1 & c-myc b ↓ TSH a ↓ TRH mRNA expression b |
| Huang and colleagues, 2013 [23] | male ICR mice | RSV FLX RSV + piperine | RSV: 1.25, 2.5, 10, 20, 40, 160, oral FLX: 10 i.p. piperine: 2.5 i.p. |
↓ immobility time in FST a,a,a,a(2.5/10/40/160) ↓ immobility time in TST a,a,a,a(2.5/10/40/160) ~ locomotor activityd ↓ reserpine-induced hypothermia a,a,a,a,a(1.25/2.5/5/10/20) and ptosis a (20) | ↑ 5-HT a,b (10/20), norepinephrine a (20), dopamine a (20) in FC ↓ 5-HIAA/5-HT in FC b (20) ↓ MAO-A in FC a,b,b (5/10/20) and hippocampus a,b (10/20) ↓ MAO-B in FC a (20) |
| Hurley and colleagues, 2014 [6] | Adult male Wistar kyoto rats | RSV v Vehicle Txt 20 min post-injection (acute) & 18–20 h post-injection (chronic) × 7 days | RSV: 0 (saline), 10, 40, i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST a,c (acute, 10/40) ↓ immobility time in FST a,c (chronic, 10/40) ~ sucrose preference d (acute) ↑ sucrose preference a,c (chronic, 10/40) ~ locomotor activity d (acute/chronic, 10/40) | ↑ hippocampal BDNF b (10/40) ~PFC BDNF d (acute/chronic, 10/40) |
| Kodali and colleagues, 2015 [24] | Late/middle-age male Fischer 344 rats | RSV v Vehicle 4 weeks txt, 4 weeks waiting period, behavioral tests | RSV: 40, i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST a | ↑ BrdU+ cells a ↑ hippocampal neurogenesis b ↑ DCX newly born neurons c ↑ hippocampal microvasculature b and CA1 subfield microvasculature a ↓ astrocyte hypertrophy c ↑ hippocampal resting microglia a |
| Li and colleagues, 2016 [25] | CORT-injected male ICR mice | CORT RSV FLX Pioglitazone × 3 weeks |
CORT: 40 s.c. RSV: 50, 100, oral FLX: 20, oral pioglitazone: 10, oral | ↑ sucrose preference b,c (50/100) ↓ immobility time in FST b,c (50/100) ~ locomotor activity d | ↓ serum CORT b,b (50/100) |
| Liu and colleagues, 2014 [26] | CUMS-exposed male Wistar rats | Vehicle RSV (80) DES (10) CUMS + vehicle CUMS + RSV (20, 40, 80) CUMS + DES × 5 weeks | RSV: 20, 40, 80, i.p. DES: 10, i.p. Vehicle: 1% ethanol, i.p. |
↑ sucrose preference a,a,b (20/40/80) ↓ immobility time in FST a,a (40/80) ↑ locomotor activity a (80) | ↓ serum CORT a (80) ↑ hippocampal BDNF b (80) ↑ amygdala BDNF b,b (40/80) ↑ hippocampal and amygdala pCREB/CREB ratio b,a (80) ↑ hippocampal pERK a,b (40/80) ↑ amygdala pERK a,a (40/80) |
| iu and colleagues, 2014 [27] | CUMS-exposed male Wistar rats | Vehicle RSV CUMS + vehicle CUMS + RSV × 5 weeks | vehicle (1% ethanol) RSV: 80 i.p. | ↓ escape latency in Morris water maze b ↑ exploration time in novel object recognition test a | ↓ serum CORT a ↑ PFC BDNF a ↑ hippocampal BDNF a ↓ hippocampal and PFC p CREB/CREB ratio a ↑ p ERK/ERK ratio a |
| Liu and colleagues, 2016 [5] | LPS-injected adult male C57/BL6 mice | Saline + DMSO Saline + RSV LPS + DMSO LPS + RSV × 14 days | RSV: 20, i.p. LPS: 1, i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST b ↓ immobility time in TST a | ↓ microglia w/ activated morphologies ↓ Ib-A1 immunoreactivity b ↑ BrdU+ cells b ↑ DCX+ neurons b ↑ type-1 RGL cells a ↑ symmetric division of RGL cells b ↓ hippocampal NF-κB expression b |
| Liu and colleagues, 2016 [28] | CUMS-exposed male Wistar rats | Vehicle RSV CUMS + vehicle CUMS + RSV CUMS + ketamine × 4 weeks | RSV: 80, i.p. Ketamine: 20, i.p. Vehicle: 1% ethanol, i.p. | ↑ sucrose preference a ↓ immobility time in FST b ↑ locomotor activity a | ↓ MDA in hippocampus & PFC c ↑ SOD in hippocampus c & PFC b ↑ phosphorylated mTOR in hippocampus a & PFC a ↑ p-Akt in hippocampus a & PFC a |
| López and colleagues, 2014 [29] | male CD1 mice | vehicle (saline) DMSO 1% DMSO 10% RSV OXO 4 buproprion citalopram DES imipramine moclobemide nisoxetine nomifensine | RSV: 2.5, 5, 10, i.p. OXO 4: 1, i.p. buproprion: 10 i.p. citalopram: 20 i.p. DES: 35 i.p. imipramine: 35 i.p. moclobemide: 35 i.p. nisoxetine: 2.5 i.p. nomifensine: 2.5 i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST a(10) | N/A |
| Pang and colleagues, 2015 [30] | middle cerebral artery occluded male Sprague-Dawley rats | sham/vehicle MCAO MCAO + RES MCAO + imipramine × 7 days pre-surgery; tested either day 8 or days 20–21 | RSV: 10, 20, 40, oral imipramine: 10 i.p. | ↑ sucrose preference a,b (20/40) ↓ immobility time in FST a,c (20/40) ~ locomotor activity d | ↑ hippocampal BDNF a ↑ hippocampal β-actin a ↓ adrenal gland index b (40) ↓ CRF expression in FC, hippocampus, and hypothalamus b,c (20/40) ↓ glucocorticoid receptor expression in FC b,c (20/40), hippocampus b,c (20/40), and hypothalamus a (40) ↑ BDNF expression in FC a,a (20/40), hippocampus b,b (20/40), and hypothalamus b,b (20/40) |
| Sakr and colleagues, 2015 [31] | CUMS- exposed male Sprague-Dawley rats | CUMS + watercontrol CUMS + FLX water CUMS + RSV CUMS + FLX/RSV × 4 weeks ctrl + water ctrl + FLX ctrl + RSV ctrl + FLX/RSV | FLX: 10, oral RSV: 20, oral | ↑ sucrose preference a ↑ immobility time in FST a | ↓ serum CORT a ↓ 5-HT in cerebral cortex and hippocampus a ↑ serum testosterone a ↑ testicular SOD a ↑ testicular CAT a ↑ testicular GSH a ↓ testicular MDA a |
| Wang and colleagues, 2013 [32] | male Kunming mice | Vehicle RSV FLX × 21 days; tests followed | RSV: 20, 40, 80, i.p. FLX: 10, i.p. Vehicle: 1% ethanol, i.p., 0.9% NaCl, i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST a,b,c (20/40/80) ↓ immobility time in TST a,c,c (20/40/80) ~ locomotor activity d | ↓ serum CORT b(80) ↑ PFC BDNF c,c,c (20/40/80) ↑ hippocampal BDNF c,c (40/80) ↑ pERK 1/2 in PFC a,a,c & hippocampus a,b,c (20/40/80) |
| Wang and colleagues, 2016 [33] | CRS-exposed male Wistar rats | RSV FLX CRS exposed 30 min after injection × 21 days | RSV: 80, i.p. FLX: 10, i.p. | ↑ sucrose preference a ↓ immobility time in FST a ~ locomotor activity d |
↑ hippocampal BDNF a ↑ PFC BDNF a ↑ BDNF/GFAP immunoreaction in hippocampus c ↑ pERK/ERK ratio in hippocampus b and PFC b ↑ bcl-2 hippocampal & PFC mRNA a ↓ hippocampal BAX mRNA b |
| Wang and colleagues, 2018 [34] | ouabain- exposed female J20 mice | ouabain + PBS (control) ouabain + RSV × 10 weeks | RSV: 10, oral | ↑ distance moved a ↑ path efficiency a ↓ time to recognize novel object a ↓ Rankin score a | ↓ plasma IL-1β, IL-17A, IL-8 and TNF-α a ↓ serum H3R a ↓ hippocampal plasma IL-1β, IL-17A, IL-8 and TNF-α a ↓ hippocampal CAT, SOD, GSH and NEG a ↓ hippocampal COX-2 expression a ↓ hippocampal neuron apoptosis a ↑ hippocampal neuron P53 and Bcl-2 a ↑ hippocampal neuron NETRIN1 and NRG3 a ↓ hippocampal neuron cAMP a |
| Xu and colleagues, 2010 [7] | male ICR mice | RSV Moclobemide (MAOI) Imipramine (TCA) Fluoxetine (SSRI) Treated w/PCPA or vehicle prior to FST & TST; treated w/apomorphine or vehicle after RSV Txt; behavioral tests 30 min post-RSV | RSV: 20, 40, 80, i.g. Moclobemide: 20, i.p. Imipramine: 20, i.p. Fluoxetine: 10, i.p. PCPA: 300, i.p. Apomorphine: 16, s.c. Vehicle |
↓ immobility time in FST a,b,c (20/40/80) ↓ immobility time in TST a,a,a (20/40/80) ~ locomotor activity d | ↑ 5-HT b (80), norepinephrine a (80) & dopamine a (80) in FC ↓ 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio in FC b (80) ↑ hippocampal 5-HT a,b (40/80) & norepinephrine a (80) ↓ hippocampal 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio a (80) ↓ MAO-A activity a,b,c (20,40,80) ↓ MAO-B activity b (80) |
ap < 0.05, b p < 0.01, c p < 0.001, d p > 0.05 ~ No change, * ug/kg/d (All others mg/kg/day). 5-HIAA, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; 5-HT, serotonin; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; bcl-2,ind B-cell lymphoma 2; BAX, bcl-2-like protein 4; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; CORT, corticosterone; CRH, corticotrophin-releasing hormone; CRS, chronic restraint stress; CUMS, chronic unpredictable mild stress; DES, desipramine; DCX, doublecortin; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; FC, frontal cortex; FLX, fluoxetine; FST, forced swimming test; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; GSH, glutathione; GSK, glycogen synthase kinase; i.c.v., intracerebroventricular; i.g., intragastric; i.p., intraperitoneal; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LT4, levothyroxine; MAO-A, monoamine oxidase A; MAO-B, monoamine oxidase B; MAOI, monoamine oxidase inhibitor; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; MDA, malondialdehyde; NEG, neuroglobin; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; OXO 4, 5-methoxyoxoisoaporphine; pβ-catenin, phosphorylated β-catenin; PCPA, parachlorophenylalanine; pCREB, phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein; PFC, prefrontal cortex; pGSK, phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase; pNF-κB, phosphorylated NF-κB; RGL, radial-glia-like cell; RSV, resveratrol; s.c., subcutaneous; SCH, subclinical hypothyroidism; SOD, superoxide dismutase; SSR, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TCA, tricyclic antidepressant; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; TST, tail suspension test; Txt, treatment.
3. Results
3.1. Resveratrol′s Effect on Depressive Behaviors
Several different tests were utilized to investigate the effects of resveratrol on depressive behaviors, including the forced swimming test (FST), tail suspension test (TST), sucrose preference test, and open field test (OFT). The FST and TST assess helplessness or behavioral despair, with higher immobility time indicating greater depressive behaviors [35]. Decreased sucrose preference indicates anhedonia, a common symptom of depression defined as the loss of the ability to feel pleasure [18]. The OFT measures locomotor activity, with reduced locomotor activity indicating anxiety-like behaviors associated with depression [28]. Other studies used the OFT as a measure of resveratrol’s specificity, as psychostimulants similarly decrease immobility time in the FST and TST, but cause an increase in locomotor activity [7,35,36].
In animal models of depression, resveratrol increases sucrose consumption in a dose-dependent manner, demonstrating resveratrol’s ability to counteract the reduction in reward-seeking behavior that tends to occur with depression [16,18,21,22,26,28]. Animals also exhibit decreased immobility time in the FST and TST, with resveratrol treatment ranging from 15–80 mg/kg/day [5,6,16,18,21,22,24,26,28,32]. Moreover, resveratrol has been shown to reduce depressive behaviors in rodents to a similar degree as the antidepressants fluoxetine, desipramine, and ketamine [7,16,18,21,26,28,32]. Several studies reveal that resveratrol has no effect on locomotor activity in the OFT, indicating its specificity [6,7,22,32,33], while others show a reversal of decreased locomotor activity, demonstrating resveratrol’s ability to reduce anxiety-like behaviors associated with depression [16,28].
3.2. HPA Axis Regulation
The HPA axis is a major endocrine system in the body that regulates how individuals adapt and behave in the face of stress. When a stressor presents, the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which stimulates the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary. ACTH enters the bloodstream and causes the release of glucocorticoids (cortisol in humans and corticosterone in animals) from the adrenal glands [37].
Studies show that serum and plasma cortisol is higher in individuals suffering from major depression [38,39,40]. Resveratrol attenuates this increase in serum and plasma corticosterone in several animal models of depression [16,18,21,26,32]. In one study, mice receiving corticosterone had significantly higher serum corticosterone levels than control animals, but resveratrol (80 mg/kg/day) reversed this effect similarly to fluoxetine [18]. Wang and colleagues also found that mice induced with stress via the FST and TST had lower serum corticosterone after 21 days of either resveratrol or fluoxetine treatment than vehicle mice [32].
In a rat model of subclinical hypothyroidism-induced depression, resveratrol not only reduced plasma corticosterone levels and depressive behaviors, but also hypothalamic CRH mRNA expression and levels of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) [16]. These results support the direct effect of resveratrol on hypothalamic activity. In contrast, others have recognized a decrease in serum corticosterone but no change in CRH mRNA expression with resveratrol treatment [21]. Together, these results illustrate the beneficial effects of resveratrol on regulating the HPA axis in animal models of depression.
3.3. Decreased Inflammation
Chronic inflammation has been associated with both psychological stress and the pathology of depression [40]. Medically ill patients with increased inflammatory cytokines have higher rates of depression, and even in the absence of medical illness, individuals with depression exhibit increased pro-inflammatory cytokines [41]. Pathogens or stress trigger a signaling cascade which activates transcription factors such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), which in turn increase the expression of pro-inflammatory genes [40].
Pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), play a key role in the immune and inflammatory response. While pro-inflammatory cytokines work to mitigate infection in the short term, continuous inflammation resulting from prolonged activation can lead to poor health outcomes and depression. In fact, one way that pro-inflammatory factors attempt to protect the organism is by promoting social withdrawal, a behavior displayed by depressed patients [40]. Resveratrol is able to downregulate NF-κB expression in the hippocampus [5,21] and prefrontal cortex [22] in mice treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). In addition, resveratrol supplementation reduces levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α) in animal models of depression [20,22].
Resveratrol is able to reduce microglial activation and Iba1 labeling of microglia in the hippocampus, establishing its anti-inflammatory effect [5,24]. Microglia are immune cells that reside in the brain. Overactivation of microglia occurs when neurons are damaged and is associated with several neurodegenerative disorders including depression [42].
3.4. Decreased Oxidative Stress
Depression is characterized by increased oxidative stress, as indicated by higher levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG). Some studies have also shown decreased antioxidant status, although these results are less consistent [43]. Although resveratrol’s direct antioxidant effects are modest, this polyphenol significantly reduces oxidative stress through its effects on gene expression, which include upregulation of antioxidant enzyme production and downregulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [44]. Two studies in male rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) showed reductions in oxidative stress following resveratrol treatment, which also reduced depression-like symptoms. Serum MDA was significantly reduced by 15 mg/kg/day of resveratrol, while a higher dosage (80 mg/kg/day) reduced MDA and increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus [21,28].
3.5. Decreased Amyloid Beta Cytotoxicity
Amyloid beta (Aβ), the primary component of plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients, may also promote depression by impairing function of the serotonin neurotransmitter system [45]. In rat and human cell cultures, resveratrol has demonstrated the ability to reduce Aβ levels and to attenuate Aβ-induced cytotoxicity and cell death [46,47,48,49]. Cells exposed to Aβ exhibited increased NF-κB activity, but pretreatment with resveratrol inhibited this effect [48]. These results suggest that resveratrol’s antidepressant effects may occur partly through a reduction in neural Aβ levels.
3.6. Increased Neurogenesis
3.6.1. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is imperative for neuroprotection due to its roles in neuronal plasticity and survival, synaptic transmission, and neurotransmitter synthesis [50]. Chronic stress and glucocorticoids decrease BDNF [51,52], while it is believed that antidepressants exert their effects in part by increasing BDNF levels [53]. In rodents, resveratrol increases BDNF levels in various brain regions, including the hippocampus [6,18,22,26,32], prefrontal cortex [6,26,32], and amygdala [26]. Notably, when corticosterone was administered to mice, levels of BDNF decreased in the hippocampus, but resveratrol attenuated this effect similarly to fluoxetine [18]. Hurley and colleagues showed that BDNF was increased in the hippocampus by both acute resveratrol treatment, and chronic administration over a seven-day period [6].
3.6.2. cAMP Response Element Binding Protein
Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) is a transcription factor associated with depression [54]. Low levels of CREB activity are implicated in depression [54], while chronic administration of antidepressants increases CREB mRNA expression in various brain regions of rodents [55,56]. Phosphorylated CREB (pCREB) binds to a receptor on the promoter region of the BDNF gene, enhancing its transcription [22,57]. Resveratrol increased pCREB and BDNF in the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala of mice exposed to LPS [22] and rats exposed to CUMS [26]. Thus, resveratrol may act similarly to classical antidepressants by upregulating CREB activity, thereby increasing BDNF expression.
3.6.3. Extracellular Regulated Kinase Pathway
Extracellular regulated kinase (ERK) signaling is involved in the survival and resilience of neurons [24]. In both humans and rodents, studies show that defects in the ERK signaling cascade are associated with depression [58,59]. In rats exposed to CUMS, antidepressants increase phosphorylation of ERK (pERK) [60] and hippocampal BDNF expression [61]. Resveratrol has also been shown to increase pERK in both the hippocampus [26,32,33] and prefrontal cortex [32,33] of rodents. Studies demonstrate that BDNF exerts antidepressant activity by upregulating the ERK pathway. Therefore, resveratrol may alleviate depressive symptoms both by increasing BDNF and by upregulating the ERK signaling cascade [26,32,33].
3.6.4. Neural Stem Cells
Neural stem cells reside in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus. Radial glia-like (RGL) cells have a bipolar structure and function as the main progenitor cells for adult hippocampal neurogenesis [5]. In mice administered LPS, resveratrol increased the number of RGL cells by increasing symmetric division [5]. Not only did resveratrol treatment increase the number of newly born cells and neurons in the hippocampus, these neurons lasted for at least two weeks, demonstrating the long-term effects of resveratrol treatment [5,24].
3.6.5. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathway
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a serine/threonine protein kinase involved in cell proliferation, survival, and protein synthesis [62]. It has been elucidated that phosphorylation of the mTOR signaling pathway is severely decreased in patients with major depression, while ketamine, an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist, has been shown to increase mTOR activity and relieve depression [63]. Following phosphorylation, Akt/protein kinase B (Akt) activates the mTOR signaling pathway [28]. Resveratrol is comparable to ketamine in reducing depressive symptoms and increasing Akt and mTOR levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of rats [28]. Therefore, resveratrol may ameliorate depressive symptoms via phosphorylation of Akt and subsequent activation of the mTOR pathway.
3.6.6. Canonical Pathway of Wnt-β-Catenin
Wnt-β-Catenin signaling plays a significant role in regulating hippocampal neurogenesis [64,65]. Dysregulation of this pathway is associated with several neuropsychiatric disorders including depression [65,66]. In addition, GSK-3β, a kinase involved in Wnt signaling, is used as a marker in neuropsychiatric disorders and is targeted by mood-stabilizing drugs such as lithium for bipolar disorder [65,67].
Rats with subclinical hypothyroidism-associated depression exhibited increased levels of GSK-3β and phosphorylated β-catenin, while c-myc and cyclin D1 were decreased. Resveratrol attenuated these effects by decreasing GSK-3β and phosphorylated β-catenin while increasing expression of the Wnt target genes c-myc and cyclin D1. These effects were accompanied by increased sucrose preference and decreased immobility time in the FST, indicating a reduction in behavioral symptoms of depression [16].
3.7. Serotonin, Norepinephrine, & Dopamine
Current pharmacotherapies for depression act on monoamine neurotransmitters, including serotonin and norepinephrine. SSRIs and SNRIs prevent reuptake of serotonin or norepinephrine, while MAOIs inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO), the enzyme responsible for degrading serotonin and norepinephrine [68]. Dopamine, which is responsible for reward and motivation, has also been implicated in depression, as modulating dopamine-producing neurons can either induce or mitigate depressive behaviors such as anhedonia [69]. In rodents, resveratrol has been shown to increase serotonin in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and striatum; norepinephrine in the frontal cortex and hippocampus; and dopamine in the frontal cortex and striatum [7,70]. In mice, resveratrol also decreased levels of the enzymes MAO A and B, which reduce neurotransmitter levels through oxidative deamination [7,23]. Treatment with resveratrol decreased depressive behaviors—however, the effects of resveratrol diminished in the absence of serotonin. Taken together, these results demonstrate that resveratrol may reduce depressive behaviors in mice via the serotonergic and noradrenergic systems [7].
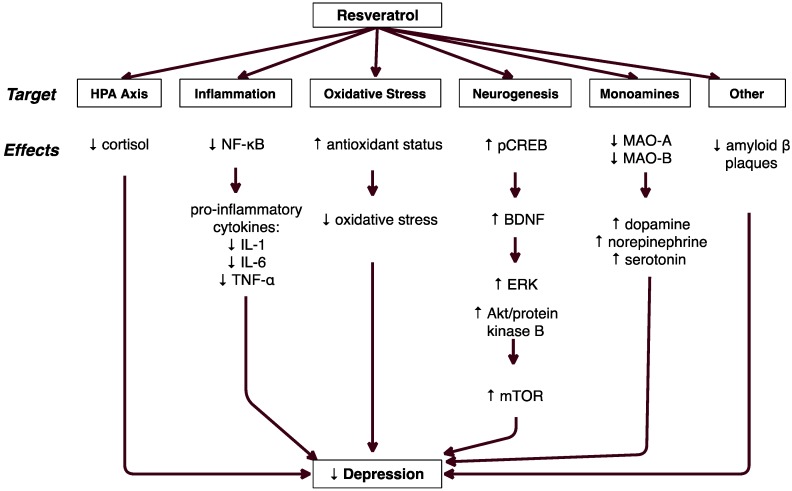
Figure 2 shows the major proposed mechanisms by which resveratrol exerts antidepressant effects. These mechanisms include modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, reduction of inflammation and oxidative stress, increased neurogenesis, altered monoamine levels, and reduction in amyloid beta plaques.
Figure 2.
Proposed Mechanisms of Antidepressant Effects of Resveratrol.
4. Discussion
Based on the current literature, resveratrol is a promising novel therapy for the treatment of depression. This natural polyphenol decreases behavioral symptoms of depression and improves biological parameters associated with depression in animal models [5,6,7,16,18,20,21,22,24,26,28,32,33]. The effects of resveratrol treatment are similar to those of classical antidepressants [7,16,18,19,21,26,32], validating its potential use as a therapeutic agent. For many, the side effects of antidepressants are deleterious [8]. This has created an urgent need for new treatments that can improve the symptoms of depression without compromising wellbeing.
Importantly, resveratrol reduced depressive symptoms in all studies reviewed regardless of the type of stress induced. Models used in the studies included corticosterone injection [18], social stress exposure [20], CUMS [21,26,28], LPS injection [5,22], subclinical hypothyroidism [16], chronic restraint stress (CRS) [33], and stress induced by tests of behavioral despair [6,7,24,32]. The causes of depression are multifactorial, and it is evident that many brain regions and neural pathways are involved [6]. Resveratrol was found to decrease depressive symptoms in rodents by regulating the HPA axis, decreasing inflammation, and increasing neurogenesis.
The HPA axis is a hormonal stress response system. In the healthy individual, the HPA axis is regulated by negative feedback mechanisms that prevent cortisol overproduction [28]. In depressed individuals, the HPA axis is dysregulated, causing either chronically high cortisol levels or a flattened cortisol curve referred to as the diurnal slope [38,39,40,71]. Cortisol must effectively bind to its glucocorticoid receptor on the PVN and the anterior pituitary for inhibition to occur. It is speculated that improper binding of cortisol to its receptor during negative feedback causes excessive production of cortisol or an abnormal cortisol curve [37,72,73].
In one study, healthy premenopausal women or those diagnosed with major depression were administered dexamethasone, which binds to the glucocorticoid receptor and suppresses cortisol production. Although cortisol production was reduced in all participants, those diagnosed with major depression showed less suppression than non-depressed controls. In addition, depressed subjects had flatter diurnal cortisol curves than non-depressed subjects [72]. These results illustrate that HPA axis dysfunction is a strong indicator of depression.
As demonstrated by the present review, resveratrol effectively reduced corticosterone in several animal models of depression [16,18,21,26,32]. These results coincide with studies of classical antidepressants that exhibit decreased stress response and corticosterone levels in aquatic animals exposed to fluoxetine and diazepam [74]. Resveratrol decreased corticosterone levels similarly to SSRIs and simultaneously improved depressive behaviors. Thus, resveratrol may be considered a regulator of the HPA axis in its ability to reduce corticosterone in animal models of depression.
Much research has focused upon the association between inflammation and depression, and results show that regardless of a comorbid medical illness, inflammation is often present in depressed patients 41]. While it is unclear whether inflammation causes depression or the reverse, it is well known that pro-inflammatory cytokines have effects that could contribute to depressive symptoms [75]. For example, research shows that pro-inflammatory cytokines activate the HPA axis by stimulating CRH release by the hypothalamus and ACTH release by the pituitary, thereby increasing cortisol production [76]. Pro-inflammatory cytokines can also decrease serotonin synthesis in the brain and play a role in neuronal development and plasticity. Chronic stress activates microglia, which secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines that create inflammation and inhibit neurogenesis [75]. Depressed individuals exhibit upregulation of NF-κB, which is also involved in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In vitro, resveratrol inhibited the activation of NF-κB by IL-1β [5,77]. The fact that resveratrol reduced both NF-κB expression and pro-inflammatory cytokines in animal models of depression suggests that resveratrol may attenuate the effects of inflammation on depression by downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Growing evidence suggests that oxidative stress is involved in the pathogenesis of depression. A recent meta-analysis of 23 observational studies found a significant association between depression and oxidative stress, and post-mortem studies have found indications of oxidative stress in the prefrontal cortex of patients with major depression [78,79]. MDA levels are positively associated with depression, particularly in patients who experience recurring episodes [34]. Another oxidative stress biomarker, 8-OHdG, is typically increased in depressed patients compared to healthy controls and correlates with the severity of depression [43]. Some studies show decreased levels of the SOD and glutathione, a finding consistent with the hypothesis that excessive ROS have overwhelmed the body’s antioxidant defenses. However, other studies have shown a positive relationship between antioxidant levels and depressive symptoms, and more research is needed to elucidate this relationship.
In addition to damaging cells, ROS can activate stress-responsive kinases including ERK, Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38, which in turn increase inflammation by activating NF-κB [80]. Resveratrol exerts antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals, and through its effects on redox-related gene expression [44]. Although few of the studies in this review examined oxidative stress and antioxidant markers, two studies in CUMS-exposed male rats did show reductions in MDA following resveratrol treatment. In a study by Ge et al., 15 mg/kg/day of resveratrol significantly decreased MDA in serum [21]. Subsequently, Liu et al. found that 80 mg/kg/day of resveratrol reduced MDA and increased SOD in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus [28]. Both studies also showed that resveratrol reduced depression-like symptoms, as indicated by sucrose preference, FST, and TST.
Depression affects up to 90% of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients and is considered a major risk factor for the disease [81]. Depression frequently precedes cognitive impairment in AD, possibly pointing to a common pathology underlying these psychiatric disorders [45]. One of the characteristic features of AD is the accumulation of plaques, which are composed primarily of the peptide amyloid beta (Aβ). Rather than simply being a marker of disease activity, Aβ appears to contribute directly to disease progression. For example, injected Aβ has been shown to impair memory and induce depressive-like behavior in mice [82]. Aβ appears to affect several of the mechanisms explored in this review. Like depression, AD is characterized by chronic inflammation and increased blood levels of proinflammatory cytokines [41,83]. In mice, intracerebroventricular infusion of Aβ was shown to increase mRNA expression and hippocampal levels of TNF-α [81]. Higher levels of TNF-α are associated with increased depressive-like behavior, as indicated by FST and SPT. However, when the mice were administered infliximab, an anti-TNF-α antibody, depression symptoms were reduced [81].
Increased production of proinflammatory cytokines is associated with altered serotonin (5-HT) metabolism. In mice, Aβ significantly decreased brain 5-HT levels, but pretreatment with 5-HT prevented Aβ-induced microglial activation and TNF-α production [81]. However, mice deficient in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4−/−) did not exhibit reduced 5-HT levels or increased depressive-like behavior. TLR4 levels were also elevated in AD patients and transgenic mouse models of AD. These results indicate that TLR4 may play a key role in modulating the depression-promoting effects of Aβ in mice, possibly by upregulating NF-κB, which increases production of inflammatory cytokines.
Another link between AD and depression is increased oxidative stress caused by elevated levels of ROS [48]. Aβ increases oxidative stress, and has been shown to induce apoptosis by generating hydrogen peroxide [48]. Aβ has also been reported to modulate the HPA axis. In a rat model of AD, Aβ increased norepinephrine in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus while decreasing production in the amygdala [84]. Interestingly, corticosterone is typically elevated in animal models of depression; however, plasma corticosterone was decreased in Aβ-treated rats [84]. Resveratrol has been shown to significantly reduce secreted and intracellular levels of amyloid beta [46,47,48,49]. In addition, resveratrol attenuated Aβ-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis [46,47,48]. These findings suggest that resveratrol may reduce the neurotoxicity of Aβ through several mechanisms, thus contributing to the antidepressant effects of this polyphenol.
As reported, resveratrol increased BDNF expression and decreased behavioral symptoms in several animal models of depression [6,18,22,32,33]. Previous research contends that levels of BDNF are lower in depressed individuals and that antidepressants raise levels of BDNF. There is strong evidence supporting the existence of a relationship between depression and BDNF expression, but exactly how antidepressant medications and resveratrol are able to manipulate this relationship is still being researched. It has been postulated that low levels of BDNF are partly caused by high glucocorticoid production. It is worth noting that some studies demonstrated a decrease in serum corticosterone alongside increased BDNF following resveratrol treatment [18,26,32].
Additionally, it is speculated that BDNF is regulated by both CREB expression and the ERK signaling pathway [85]. Based on the evidence that low levels of phosphorylated CREB (pCREB) are implicated in depression, and that this protein enhances BDNF transcription, it is reasonable to consider that increasing pCREB would decrease depressive symptoms. As discussed, resveratrol upregulated pCREB and BDNF while decreasing depressive behaviors, so it is conceivable that resveratrol exerts its effects via this mechanism [22,57]. However, another study found that resveratrol lowered pCREB and BDNF and subsequently reduced the proliferation of neural progenitor cells in the hippocampus of healthy mice, so this mechanism remains unclear [86]. Likewise, deficiencies in ERK signaling are associated with depression, while antidepressants have been shown to upregulate both pERK and BDNF [58,60]. Since resveratrol had comparable effects to standard antidepressants in regulating ERK signaling, increasing BDNF, and decreasing depressive behaviors, we can conceptualize that this may be another method through which resveratrol alleviates depressive behaviors in animal models.
While the majority of studies focused upon resveratrol’s effects on the HPA axis, inflammation, and BDNF expression, a few studies explored different methods by which resveratrol may reduce depressive symptoms in animals. These included resveratrol’s effects on neural stem cells [5,24], the Wnt-β-catenin pathway [16], mTOR signaling [28], and monoamine synthesis [7].
Studies show that reduced neurogenesis is associated with mental illness and stress, and that inflammation inhibits neurogenesis. Antidepressants increase the proliferation, maturation, and survival of neurons in the hippocampus [87]. In congruence with these findings, resveratrol increased the symmetric division of RGLs, which contributes to neuronal proliferation [5]. Additionally, depression is associated with abnormalities in Wnt signaling, an essential pathway for neurogenesis [65]. Resveratrol increased neurogenesis by upregulating the Wnt signaling pathway. Resveratrol also increased mTOR signaling, which similarly promotes increased neurogenesis [62].
Resveratrol increased levels of 5-HT, norepinephrine, and dopamine in various brain regions associated with depression, which coincides with the monoamine hypothesis [88]. Depression is associated with low levels of dopamine, and irregularities in dopaminergic neurons that play a large role in reward and motivation may be responsible for the anhedonia exhibited by depressed patients [89]. Based on the large body of research that has implicated these monoamines in depression, resveratrol may decrease depressive behaviors in animals by increasing neurotransmitter levels.
In 12 animal studies, resveratrol was compared to an antidepressant drug as an active control (Table 2). Nine studies compared resveratrol or a combination of resveratrol and piperine to the SSRI fluoxetine. The TCA imipramine was employed in four studies [7,23,29,30] and desipramine in two studies [26,29]. Other drugs administered included the citalopram (SSRI) [29], moclobemide (MAOI) [7,82], nisoxetine (norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor) [29], buproprion and nomifensine (norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor) [29], and ketamine (NMDA receptor antagonist) [28]. All studies administered only a single dosage of the pharmaceutical agent, but several dosages of resveratrol were typically given in order to evaluate dose-ranging effects. In general, resveratrol and the drugs were similarly effective with regard to depression-like behavior as indicated by sucrose preference test, FST, and TST. Resveratrol also had similar biochemical effects as the antidepressants, such as lower corticosterone [7,18,21,25,31,32] and higher 5-HT levels [17,23]. The majority of studies showed that resveratrol was most effective at 80 mg/kg/day. The Human Equivalent Dose (HED) of 80 mg/kg/day in rats is 12.9 mg/kg/day. Therefore, a 60 kg individual would require 775 mg of resveratrol per day to achieve similar results [90]. Based on these calculations, an effective dose of resveratrol would be more plausibly obtained through supplementation than through food or beverages.
Table 2.
Comparison of resveratrol with antidepressant drugs.
| Author, Year | Animal Model | Txt Duration | Dosages (mg/kg/Day) | Comparative Effectiveness of RSV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed and colleagues, 2014 [17] | reserpine-injected adult male Wistar rats | 3 day | RSV: 15, 30, 60, oral FLX: 24, oral | >FLX: Liver GSH (60), liver MDA (30/60) =FLX: FST (60), 5-HT (15/30/60), norepinephrine (60), dopamine (15/30/60), brain MDA (60) < FLX: OFT |
| Ali and colleagues, 2015 [18] | CORT-injected male Swiss albino mice | 21 days | RSV: 80, oral FLX: 15, oral | =FLX: Sucrose preference, immobility time in FST, immobility time in TST, serum CORT, hippocampal BDNF |
| Ge and colleagues, 2013 [21] | CUMS-exposed male Sprague-Dawley rats | 21 days | RSV: 15, i.p. FLX: 2, i.p. | =FLX: Sucrose preference, immobility time in FST, immobility time in TST, serum MDA, serum CORT <FLX: CRH mRNA expression |
| Huang and colleagues, 2013 [23] | male ICR mice | 4 days | RSV: 1.25, 2.5, 10, 20, 40, 80, oral + piperine: 2.5 i.p. FLX: 10 i.p. Imipramine: 10 i.p. | =FLX: Immobility time in FST (10/20), immobility time in TST (10/20) =Imipramine: locomotor activity; reserpine-induced hypothermia (10,20) and ptosis (20); FC 5-HT (10,20), norepinephrine (20), dopamine (20), and 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio (20) |
| Li and colleagues, 2016 [25] | CORT-injected male ICR mice | 21 days | RSV: 50,100, oral FLX: 20, oral | =FLX: Sucrose preference (50/100), immobility time in FST (50/100), CORT (50/100) |
| Liu and colleagues, 2014 [26] | CUMS-exposed male Wistar rats | 5 weeks | RSV: 20, 40, 80, i.p. DES: 10, i.p. | =sucrose preference (20/40/80), immobility time in FST (40/80), crossing and grooming in OFT (80), serum CORT (80) BDNF in hippocampus (80) and amygdala (40/80), p-CREB in hippocampus (80) and amygdala (80), p-ERK in hippocampus (40/80) and amygdala (40/80) |
| Liu and colleagues, 2016 [28] | CUMS-exposed male Wistar rats | 4 weeks | RSV: 80, i.p. Ketamine: 20, i.p | =Ketamine: Sucrose preference; immobility time in FST; OFT; PFC and hippocampal MDA and SOD; phosphoylated mTOR and Akt |
| López and colleagues, 2014 [29] | male CD1 mice | <1 day | RSV: 2.5, 5, 10, i.p. buproprion: 10 i.p. citalopram: 20 i.p. desipramine: 35 i.p. imipramine: 35 i.p. moclobemide: 35 i.p. nisoxetine: 2.5 i.p. nomifensine: 2.5 i.p. | ↓ immobility time in FST (10) |
| Pang and colleagues, 2015 [30] | middle cerebral artery occluded male Sprague-Dawley rats | 14 days | RSV: 10, 20, 40, oral Imipramine: 10 i.p. | =Imipramine: Sucrose preference (20/40); FST (20/40); CRF expression in hypothalamus (20/40), hippocampus (20/40) and FC (20/40); GR expression in hypothalamus (40), hippocampus (20/40), and FC (20/40); BDNF expression in hypothalamus (40), hippocampus (20/40) and FC (40) <Imipramine: adrenal gland index |
| Sakr and colleagues, 2015 [31] | CUMS-exposed male Sprague-Dawley rats | 28 days | RSV: 20, oral FLX: 10, oral | >FLX: MDA, SOD, CAT, GSH <FLX: Sucrose preference, immobility time in FST, serum testosterone, serum CORT, hippocampal 5-HT |
| Wang and colleagues, 2013 [32] | male Kunming mice | 21 days | RSV: 20, 40, 80, i.p. FLX: 10, i.p. | =FLX: Immobility time in FST (20/40/80), immobility time in TST (20/40/80), serum CORT (80), BDNF mRNA in hippocampus (40/80) and PFC (20/40/80), BDNF protein expression in hippocampus (20/40/80) and PFC (20/40/80) |
| Wang and colleagues, 2016 [33] | CRS-exposed male Wistar rats | 21 days | RSV: 80, i.p. FLX: 10, i.p. | =FLX: Sucrose preference; immobility time in FST; OFT; hippocampal and PFC BDNF mRNA and protein expression; hippocampal and PFC phosphorylated ERK mRNA and protein expression |
| Xu and colleagues, 2010 [7] | male ICR mice | 4 days | RSV: 20, 40, 80, i.g. FLX: 10, i.p. Moclobemide: 20, i.p. Imipramine: 20, i.p. |
>FLX: Dopamine in FC (80); 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio in FC (80), hippocampus (80) and hypothalamus (80); noradrenaline in FC (80) and hippocampus (80); MAO-A (20/40/80); MAO-B (80) =FLX: FST (20/40/80); TST (40/80); 5-HT in FC (80), hippocampus (40/80) and hypothalamus (80) >Imipramine: Dopamine in FC (80); 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio in FC (80), hippocampus (80) and hypothalamus (80); MAO-A (20/40/80); MAO-B (80) =Imipramine: FST (20/40/80); TST (40/80); apomorphine-induced hypothermia (20/40/80); 5-HT in FC (80), hippocampus (40/80) and hypothalamus (80); noradrenaline in FC (80) and hippocampus (80) =Moclobemide: MAO-A (20/40/80) >Moclobemide: MAO-B (80) |
5-HIAA, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; 5-HT, serotonin; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CAT, catalase; CORT, corticosterone; CRF, corticotropin-releasing factor; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; CRS, chronic restraint stress; CUMS, chronic unpredictable mild stress; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FC, frontal cortex; FLX, fluoxetine; FST, forced swimming test; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; GSH, glutathione; i.g., intragastric; i.p., intraparitoneal ; MAO-A, monoamine oxidase A; MAO-B, monoamine oxidase B; MDA, malondialdehyde; Mtor, mammalian target of rapamycin; OFT, open field test; PFC, prefrontal cortex; RSV, resveratrol; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TST, tail suspension test.
There are limitations of this review that make it difficult to accurately compare results. Firstly, the different methods used to induce depression or stress in animal models may affect the outcomes. Secondly, some studies took physical measurements directly after injection of resveratrol, while others waited for a longer period. Thirdly, some studies examined the acute effects of resveratrol, while others looked at chronic effects. However, most studies did conduct the trials over a period of at least three weeks. Fourthly, the dose of resveratrol ranged from 10 mg/kg/day to 80 mg/kg/day. Although this variation in dosage permitted researchers to evaluate dose-dependent effects, it made direct comparison of the results more difficult. Fifth, there are not yet enough published studies on the subject to determine the overlying mechanisms with a high degree of certainty. Sixth, there is a lack of studies in female subjects. Although Wang et al. found that resveratrol reduced depression-like symptoms in female mice [34], all other animal studies that met our inclusion criteria were conducted in male subjects. The reliance on male subjects reflects a broader tendency within psychiatric research, as most animal models of depression were developed using male rodents, and only later applied to females. The absence of female subjects is a cause for concern, as sex differences exist regarding both depression and the response to antidepressant treatment. These differences occur not only in humans, where they may largely be explained by social and cultural factors, but also in animal models, where they suggest the role of innate neurobiological factors [91]. Male and female rats respond differently to widely-used animal models of depression, including chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS), forced swim test, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure [91]. Because of sex-linked differences, the results of the published studies may not be applicable to females. Future studies of resveratrol and depression should attempt to determine whether existing results can be replicated in female animals.
Animal models of depression are at best imperfect analogues of clinical depression, and therefore caution must be exercised when extrapolating the results of animal studies to humans. Wine shows more positive effects on mood than other alcoholic beverages—however, the large number of components in wine makes it difficult to determine whether resveratrol was responsible for the beneficial effects [92]. Few studies have specifically examined the effects of resveratrol on depression in humans, although several studies have measured mood following resveratrol treatment [93,94,95,96,97]. Two of those studies found no significant differences in any measure of mood [17,96,97], and one found reduced anxiety following resveratrol treatment, but no changes in depression or other mood components [94]. The lack of significance in the latter study may have resulted from the resveratrol dosage, which was lower in proportion to body weight than the dosages used in most animal studies. Unfortunately, these studies have limited relevance to this review because at baseline the subjects were healthy adults who were not experiencing depressive symptoms. The trial by Davinelli et al. was conducted in postmenopausal women [93]. At baseline, depression was reported by many subjects, but not all, as depression was only one of several symptoms used as inclusion criteria. Compared with the placebo, resveratrol significantly reduced depressive symptoms as measured by the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D). In patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy (MHE), resveratrol treatment was also associated with decreased depression as measured by the Beck Depression Inventory [93]. In light of this limited evidence, more controlled clinical studies are needed to elucidate resveratrol’s antidepressant effects in humans.
In conclusion, resveratrol exhibited positive effects in animal models of depression comparable to the effects of several pharmaceutical antidepressants. Although these findings cannot be generalized to humans, results in animal models delineate the potential for resveratrol to serve as a natural antidepressant. Resveratrol’s excellent safety profile and limited side effects make it an appealing option for depression patients, either as an alternative or adjuvant to conventional therapies. The studies discussed in this review focused on various biological mechanisms, but it is likely that these mechanisms work in concert with one another. Because resveratrol affected many brain regions and neural pathways, this polyphenol may be beneficial in many cases of depression, even if the underlying causes are heterogeneous. Based on the present review, resveratrol merits further investigation as a possible therapeutic agent for the treatment of depression.
Author Contributions
Writing—Original Draft Preparation: A.M.; Writing—Review & Editing: M.Y.H.; Writing—Review & Editing: J.B.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Depression Fact Sheet. [(accessed on 15 August 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/
- 2.Collins P.Y., Patel V., Joestl S.S., March D., Insel T.R., Daar A.S., Bordin I.A., Costello E.J., Durkin M., Fairburn C., et al. Grand challenges in global mental health. Nature. 2011;475:27–30. doi: 10.1038/475027a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pratt L.A., Brody D.J., Gu Q. Antidepressant Use in Persons Aged 12 and over: United States, 2005–2008. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control, NCHS Data Brief; Hyattsville, MD, USA: 2011. pp. 1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.National Center for Health Statistics . Health, United States, 2010: With Special Feature on Death and Dying. U.S. Government Printing Office; Washington, DC, USA: 2011. [(accessed on 15 August 2018)]. p. 107. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus10.pdf#074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu L., Zhang Q., Cai Y., Sun D., He X., Wang L., Yu D., Li X., Xiong X., Xu H., et al. Resveratrol counteracts lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviors via enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:56045–56059. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hurley L.L., Akinfiresoye L., Kalejaiye O., Tizabi Y. Antidepressant effects of resveratrol in an animal model of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2014;268:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.03.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xu Y., Wang Z., You W., Zhang X., Li S., Barish P.A., Vernon M.M., Du X., Li G., Pan J., et al. Antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol: Involvement of serotonin and noradrenaline system. Eur. Neuropsychopharm. 2010;20:405–413. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ferguson J.M. Ssri antidepressant medications: Adverse effects and tolerability. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001;3:22–27. doi: 10.4088/PCC.v03n0105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nabavi S.M., Daglia M., Braidy N., Nabavi S.F. Natural products, micronutrients, and nutraceuticals for the treatment of depression: A short review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017;20:180–194. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2015.1103461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gambini J., Ingles M., Olaso G., Lopez-Grueso R., Bonet-Costa V., Gimeno-Mallench L., Mas-Bargues C., Abdelaziz K.M., Gomez-Cabrera M.C., Vina J., et al. Properties of resveratrol: In vitro and in vivo studies about metabolism, bioavailability, and biological effects in animal models and humans. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015;2015:837042. doi: 10.1155/2015/837042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Quincozes-Santos A., Bobermin L.D., Latini A., Wajner M., Souza D.O., Goncalves C.A., Gottfried C. Resveratrol protects c6 astrocyte cell line against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through heme oxygenase 1. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e64372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Malhotra A., Bath S., Elbarbry F. An organ system approach to explore the antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and cytoprotective actions of resveratrol. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015;2015:803971. doi: 10.1155/2015/803971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rege S.D., Geetha T., Griffin G.D., Broderick T.L., Babu J.R. Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol in alzheimer disease pathology. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:218. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wightman E.L., Haskell-Ramsay C.F., Reay J.L., Williamson G., Dew T., Zhang W., Kennedy D.O. The effects of chronic trans-resveratrol supplementation on aspects of cognitive function, mood, sleep, health and cerebral blood flow in healthy, young humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2015;114:1427–1437. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515003037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wu R.E., Huang W.C., Liao C.C., Chang Y.K., Kan N.W., Huang C.C. Resveratrol protects against physical fatigue and improves exercise performance in mice. Molecules. 2013;18:4689–4702. doi: 10.3390/molecules18044689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ge J.F., Xu Y.Y., Qin G., Cheng J.Q., Chen F.H. Resveratrol ameliorates the anxiety- and depression-like behavior of subclinical hypothyroidism rat: Possible involvement of the hpt axis, hpa axis, and wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016;7:44. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ahmed R.F., Abdel-Rahman R.F., Farid O.A.H.A., El-Marasy S.A., Hessin A.F. Combined hepatoprotective and antidepressant effects of resveratrol in an acute model of depression. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2014;52:191–197. doi: 10.1016/j.bfopcu.2014.06.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ali S.H., Madhana R.M., Athira K.V., Kasala E.R., Bodduluru L.N., Pitta S., Mahareddy J.R., Lahkar M. Resveratrol ameliorates depressive-like behavior in repeated corticosterone-induced depression in mice. Steroids. 2015;101:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2015.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen W.J., Du J.K., Hu X., Yu Q., Li D.X., Wang C.N., Zhu X.Y., Liu Y.J. Protective effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function in the hippocampus improves inflammation-induced depressive-like behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2017;182:54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Finnell J.E., Lombard C.M., Melson M.N., Singh N.P., Nagarkatti M., Nagarkatti P., Fadel J.R., Wood C.S., Wood S.K. The protective effects of resveratrol on social stress-induced cytokine release and depressive-like behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017;59:147–157. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.08.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ge J.F., Peng L., Cheng J.Q., Pan C.X., Tang J., Chen F.H., Li J. Antidepressant-like effect of resveratrol: Involvement of antioxidant effect and peripheral regulation on hpa axis. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013;114–115:64–69. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2013.10.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ge L., Liu L., Liu H., Liu S., Xue H., Wang X., Yuan L., Wang Z., Liu D. Resveratrol abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior, neuroinflammatory response, and creb/bdnf signaling in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015;768:49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.10.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huang W., Chen Z., Wang Q., Lin M., Wu S., Yan Q., Wu F., Yu X., Xie X., Li G., et al. Piperine potentiates the antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol: Involvement of monoaminergic system. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013;28:585–595. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9426-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kodali M., Parihar V.K., Hattiangady B., Mishra V., Shuai B., Shetty A.K. Resveratrol prevents age-related memory and mood dysfunction with increased hippocampal neurogenesis and microvasculature, and reduced glial activation. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:8075. doi: 10.1038/srep08075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li Y.-C., Liu Y.-M., Shen J.-D., Chen J.-J., Pei Y.-Y., Fang X.-Y. Resveratrol ameliorates the depressive-like behaviors and metabolic abnormalities induced by chronic corticosterone injection. Molecules. 2016;21:1341. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liu D., Xie K., Yang X., Gu J., Ge L., Wang X., Wang Z. Resveratrol reverses the effects of chronic unpredictable mild stress on behavior, serum corticosterone levels and bdnf expression in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2014;264:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu D., Zhang Q., Gu J., Wang X., Xie K., Xian X., Wang J., Jiang H., Wang Z. Resveratrol prevents impaired cognition induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2014;49:21–29. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu S., Li T., Liu H., Wang X., Bo S., Xie Y., Bai X., Wu L., Wang Z., Liu D. Resveratrol exerts antidepressant properties in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model through the regulation of oxidative stress and mtor pathway in the rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 2016;302:191–199. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.López M.C., Fontenla J.A., Uriarte E., Santana L., Sobarzo-Sánchez E. Comparison of the antidepressive effects of trans-resveratrol and 5-methoxy-7h-dibenzo[de,h]quinolin-7-one. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014;14:234–238. doi: 10.2174/1568026613666131213162753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pang C., Cao L., Wu F., Wang L., Wang G., Yu Y., Zhang M., Chen L., Wang W., Lv W., et al. The effect of trans-resveratrol on post-stroke depression via regulation of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neuropharmacology. 2015;97:447–456. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sakr H.F., Abbas A.M., Elsamanoudy A.Z., Ghoneim F.M. Effect of fluoxetine and resveratrol on testicular functions and oxidative stress in a rat model of chronic mild stress-induced depression. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015;66:515–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang Z., Gu J., Wang X., Xie K., Luan Q., Wan N., Zhang Q., Jiang H., Liu D. Antidepressant-like activity of resveratrol treatment in the forced swim test and tail suspension test in mice: The hpa axis, bdnf expression and phosphorylation of erk. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013;112:104–110. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2013.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang X., Xie Y., Zhang T., Bo S., Bai X., Liu H., Li T., Liu S., Zhou Y., Cong X., et al. Resveratrol reverses chronic restraint stress-induced depression-like behaviour: Involvement of bdnf level, erk phosphorylation and expression of bcl-2 and bax in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2016;125:134–143. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang F., Wang J., An J., Yuan G., Hao X., Zhang Y. Resveratrol ameliorates depressive disorder through the netrin1-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/camp signal transduction pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018;17:4611–4618. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Steru L., Chermat R., Thierry B., Simon P. The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1985;85:367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00428203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yin X., Guven N., Dietis N. Stress-based animal models of depression: Do we actually know what we are doing? Brain Res. 2016;1652:30–42. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.09.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Du X., Pang T.Y. Is dysregulation of the hpa-axis a core pathophysiology mediating co-morbid depression in neurodegenerative diseases? Front. Psychiatry. 2015;6:32. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lok A., Mocking R.J., Ruhe H.G., Visser I., Koeter M.W., Assies J., Bockting C.L., Olff M., Schene A.H. Longitudinal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis trait and state effects in recurrent depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012;37:892–902. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2011.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vythilingam M., Vermetten E., Anderson G.M., Luckenbaugh D., Anderson E.R., Snow J., Staib L.H., Charney D.S., Bremner J.D. Hippocampal volume, memory, and cortisol status in major depressive disorder: Effects of treatment. Biol. Psychiatry. 2004;56:101–112. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Slavich G.M., Irwin M.R. From stress to inflammation and major depressive disorder: A social signal transduction theory of depression. Psychol. Bull. 2014;140:774–815. doi: 10.1037/a0035302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Felger J.C., Lotrich F.E. Inflammatory cytokines in depression: Neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuroscience. 2013;246:199–229. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.04.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lull M.E., Block M.L. Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics. 2010;7:354–365. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2010.05.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lopresti A.L., Maker G.L., Hood S.D., Drummond P.D. A review of peripheral biomarkers in major depression: The potential of inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2014;48:102–111. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xia N., Daiber A., Forstermann U., Li H. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in the cardiovascular system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017;174:1633–1646. doi: 10.1111/bph.13492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Colaianna M., Tucci P., Zotti M., Morgese M.G., Schiavone S., Govoni S., Cuomo V., Trabace L. Soluble beta amyloid(1-42): A critical player in producing behavioural and biochemical changes evoking depressive-related state? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010;159:1704–1715. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Feng Y., Wang X.P., Yang S.G., Wang Y.J., Zhang X., Du X.T., Sun X.X., Zhao M., Huang L., Liu R.T. Resveratrol inhibits beta-amyloid oligomeric cytotoxicity but does not prevent oligomer formation. Neurotoxicology. 2009;30:986–995. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2009.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Han Y.S., Zheng W.H., Bastianetto S., Chabot J.G., Quirion R. Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons: Involvement of protein kinase c. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004;141:997–1005. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jang J. Protective effect of resveratrol on β-amyloid-induced oxidative pc12 cell death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003;34:1100–1110. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Marambaud P., Zhao H., Davies P. Resveratrol promotes clearance of alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:37377–37382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508246200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dwivedi Y. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in late-life depression. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 2013;21:433–449. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2012.10.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Smith M.A., Makino S., Kvetnansky R., Post R.M. Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mrnas in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1995;15:1768–1777. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-03-01768.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schaaf M.J., De Kloet E.R., Vreugdenhil E. Corticosterone effects on bdnf expression in the hippocampus. Implications for memory formation. Stress. 2000;3:201–208. doi: 10.3109/10253890009001124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dwivedi Y., Rizavi H.S., Pandey G.N. Antidepressants reverse corticosterone-mediated decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression: Differential regulation of specific exons by antidepressants and corticosterone. Neuroscience. 2006;139:1017–1029. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.12.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Xue W., Wang W., Gong T., Zhang H., Tao W., Xue L., Sun Y., Wang F., Chen G. Pka-creb-bdnf signaling regulated long lasting antidepressant activities of yueju but not ketamine. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:26331. doi: 10.1038/srep26331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nibuya M., Nestler E.J., Duman R.S. Chronic antidepressant administration increases the expression of camp response element binding protein (creb) in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1996;16:2365–2372. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-07-02365.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pinnock S.B., Blake A.M., Platt N.J., Herbert J. The roles of bdnf, pcreb and wnt3a in the latent period preceding activation of progenitor cell mitosis in the adult dentate gyrus by fluoxetine. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e13652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Conti A.C., Cryan J.F., Dalvi A., Lucki I., Blendy J.A. Camp response element-binding protein is essential for the upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcription, but not the behavioral or endocrine responses to antidepressant drugs. J. Neurosci. 2002;22:3262–3268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-08-03262.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Dwivedi Y., Zhang H. Altered erk1/2 signaling in the brain of learned helpless rats: Relevance in vulnerability to developing stress-induced depression. Neural Plast. 2016;2016:7383724. doi: 10.1155/2016/7383724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dwivedi Y., Rizavi H.S., Roberts R.C., Conley R.C., Tamminga C.A., Pandey G.N. Reduced activation and expression of erk1/2 map kinase in the post-mortem brain of depressed suicide subjects. J. Neurochem. 2001;77:916–928. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.First M., Gil-Ad I., Taler M., Tarasenko I., Novak N., Weizman A. The effects of fluoxetine treatment in a chronic mild stress rat model on depression-related behavior, brain neurotrophins and erk expression. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011;45:246–255. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.First M., Gil-Ad I., Taler M., Tarasenko I., Novak N., Weizman A. The effects of reboxetine treatment on depression-like behavior, brain neurotrophins, and erk expression in rats exposed to chronic mild stress. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013;50:88–97. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9872-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Abelaira H.M., Reus G.Z., Neotti M.V., Quevedo J. The role of mtor in depression and antidepressant responses. Life Sci. 2014;101:10–14. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chandran A., Iyo A.H., Jernigan C.S., Legutko B., Austin M.C., Karolewicz B. Reduced phosphorylation of the mtor signaling pathway components in the amygdala of rats exposed to chronic stress. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2013;40:240–245. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lie D.C., Colamarino S.A., Song H.J., Desire L., Mira H., Consiglio A., Lein E.S., Jessberger S., Lansford H., Dearie A.R., et al. Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature. 2005;437:1370–1375. doi: 10.1038/nature04108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hussaini S.M., Choi C.I., Cho C.H., Kim H.J., Jun H., Jang M.H. Wnt signaling in neuropsychiatric disorders: Ties with adult hippocampal neurogenesis and behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014;47:369–383. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Okerlund N.D., Cheyette B.N. Synaptic wnt signaling-a contributor to major psychiatric disorders? J. Neurodev. Disord. 2011;3:162–174. doi: 10.1007/s11689-011-9083-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Brand S.J., Moller M., Harvey B.H. A review of biomarkers in mood and psychotic disorders: A dissection of clinical vs. Preclinical correlates. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015;13:324–368. doi: 10.2174/1570159X13666150307004545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Berton O., Nestler E.J. New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: Beyond monoamines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006;7:137–151. doi: 10.1038/nrn1846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tye K.M., Mirzabekov J.J., Warden M.R., Ferenczi E.A., Tsai H.C., Finkelstein J., Kim S.Y., Adhikari A., Thompson K.R., Andalman A.S., et al. Dopamine neurons modulate neural encoding and expression of depression-related behaviour. Nature. 2013;493:537–541. doi: 10.1038/nature11740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sarubbo F., Ramis M.R., Aparicio S., Ruiz L., Esteban S., Miralles A., Moranta D. Improving effect of chronic resveratrol treatment on central monoamine synthesis and cognition in aged rats. Age (Dordr.) 2015;37:9777. doi: 10.1007/s11357-015-9777-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gartside S.E., Leitch M.M., McQuade R., Swarbrick D.J. Flattening the glucocorticoid rhythm causes changes in hippocampal expression of messenger rnas coding structural and functional proteins: Implications for aging and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:821–829. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jarcho M.R., Slavich G.M., Tylova-Stein H., Wolkowitz O.M., Burke H.M. Dysregulated diurnal cortisol pattern is associated with glucocorticoid resistance in women with major depressive disorder. Biol. Psychol. 2013;93:150–158. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2013.01.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zhu L.J., Liu M.Y., Li H., Liu X., Chen C., Han Z., Wu H.Y., Jing X., Zhou H.H., Suh H., et al. The different roles of glucocorticoids in the hippocampus and hypothalamus in chronic stress-induced hpa axis hyperactivity. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e97689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Abreu M.S., Koakoski G., Ferreira D., Oliveira T.A., Rosa J.G., Gusso D., Giacomini A.C., Piato A.L., Barcellos L.J. Diazepam and fluoxetine decrease the stress response in zebrafish. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e103232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Jeon S.W., Kim Y.K. Neuroinflammation and cytokine abnormality in major depression: Cause or consequence in that illness? World J. Psychiatry. 2016;6:283–293. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Besedovsky H.O., del Rey A. The cytokine-hpa axis feed-back circuit. Z. Rheumatol. 2000;59(Suppl. 2):II/26–II/30. doi: 10.1007/s003930070014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Busch F., Mobasheri A., Shayan P., Lueders C., Stahlmann R., Shakibaei M. Resveratrol modulates interleukin-1beta-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor kappab signaling pathways in human tenocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:38050–38063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.377028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Palta P., Samuel L.J., Miller E.R., Szanton S.L. Depression and oxidative stress: Results from a meta-analysis of observational studies. Psychosom. Med. 2014;76:12–19. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Shelton R.C., Claiborne J., Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M., Reddy R., Aschner M., Lewis D.A., Mirnics K. Altered expression of genes involved in inflammation and apoptosis in frontal cortex in major depression. Mol. Psychiatry. 2011;16:751–762. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bakunina N., Pariante C.M., Zunszain P.A. Immune mechanisms linked to depression via oxidative stress and neuroprogression. Immunology. 2015;144:365–373. doi: 10.1111/imm.12443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ledo J.H., Azevedo E.P., Beckman D., Ribeiro F.C., Santos L.E., Razolli D.S., Kincheski G.C., Melo H.M., Bellio M., Teixeira A.L., et al. Cross talk between brain innate immunity and serotonin signaling underlies depressive-like behavior induced by alzheimer’s amyloid-beta oligomers in mice. J. Neurosci. 2016;36:12106–12116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1269-16.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ledo J.H., Azevedo E.P., Clarke J.R., Ribeiro F.C., Figueiredo C.P., Foguel D., De Felice F.G., Ferreira S.T. Amyloid-beta oligomers link depressive-like behavior and cognitive deficits in mice. Mol. Psychiatry. 2013;18:1053–1054. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Swardfager W., Lanctot K., Rothenburg L., Wong A., Cappell J., Herrmann N. A meta-analysis of cytokines in alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry. 2010;68:930–941. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Morgese M.G., Tucci P., Colaianna M., Zotti M., Cuomo V., Schiavone S., Trabace L. Modulatory activity of soluble beta amyloid on hpa axis function in rats. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014;20:2539–2546. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Duman R.S. Role of neurotrophic factors in the etiology and treatment of mood disorders. Neuromol. Med. 2004;5:11–25. doi: 10.1385/NMM:5:1:011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Park H.R., Kong K.H., Yu B.P., Mattson M.P., Lee J. Resveratrol inhibits the proliferation of neural progenitor cells and hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:42588–42600. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.406413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Schoenfeld T.J., Cameron H.A. Adult neurogenesis and mental illness. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:113–128. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Neto F.L., Borges G., Torres-Sanchez S., Mico J.A., Berrocoso E. Neurotrophins role in depression neurobiology: A review of basic and clinical evidence. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011;9:530–552. doi: 10.2174/157015911798376262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Young C.B., Chen T., Nusslock R., Keller J., Schatzberg A.F., Menon V. Anhedonia and general distress show dissociable ventromedial prefrontal cortex connectivity in major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry. 2016;6:e810. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Nair A.B., Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016;7:27–31. doi: 10.4103/0976-0105.177703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Dalla C., Pitychoutis P.M., Kokras N., Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z. Sex differences in animal models of depression and antidepressant response. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010;106:226–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2009.00516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gea A., Beunza J.J., Estruch R., Sanchez-Villegas A., Salas-Salvado J., Buil-Cosiales P., Gomez-Gracia E., Covas M.I., Corella D., Fiol M., et al. Alcohol intake, wine consumption and the development of depression: The predimed study. BMC Med. 2013;11:192. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Davinelli S., Scapagnini G., Marzatico F., Nobile V., Ferrara N., Corbi G. Influence of equol and resveratrol supplementation on health-related quality of life in menopausal women: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Maturitas. 2017;96:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Evans H.M., Howe P.R., Wong R.H. Effects of resveratrol on cognitive performance, mood and cerebrovascular function in post-menopausal women; a 14-week randomised placebo-controlled intervention trial. Nutrients. 2017;9:27. doi: 10.3390/nu9010027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Malaguarnera G., Pennisi M., Bertino G., Motta M., Borzi A.M., Vicari E., Bella R., Drago F., Malaguarnera M. Resveratrol in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Nutrients. 2018;10:329. doi: 10.3390/nu10030329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Wightman E.L., Reay J.L., Haskell C.F., Williamson G., Dew T.P., Kennedy D.O. Effects of resveratrol alone or in combination with piperine on cerebral blood flow parameters and cognitive performance in human subjects: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over investigation. Br. J. Nutr. 2014;112:203–213. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514000737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Witte A.V., Kerti L., Margulies D.S., Floel A. Effects of resveratrol on memory performance, hippocampal functional connectivity, and glucose metabolism in healthy older adults. J. Neurosci. 2014;34:7862–7870. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0385-14.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]