Abstract
Metabolic reprogramming is a feature of cancer cells and crucial for tumor growth and metastasis. Interferon-γ (IFNγ) is a cytokine that plays a pivotal role in host antitumor immunity. However, little is known about the roles of metabolic reprogramming in immune responses. Here, we show that colon cancer cells reprogram metabolism to coordinate proper cellular responses to IFNγ by downregulating mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC)1 and 2 via STAT3 signaling. Forced overexpression of MPC promote the production of reactive oxygen species and enhance the apoptosis induced by IFNγ in colon cancer cells. Moreover, inhibiting STAT3 sensitize the antitumor efficacy of IFN-γ against colon cancer cells. Our findings present a previously unrecognized mechanism that colon cancer manipulate to resist IFNγ mediated antitumor immunity that have implications for targeting a unique aspect of this disease.
Abbreviations: IFN-γ, Interferon-γ; MPC1/2, Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1 and 2; TCA cycle, Tricarboxylic acid; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; STAT, Signal transducer and activator of transcription; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; γH2AX, Histone H2A.X; NAC, N-acetylcysteine NAC; GSSG, Oxidized glutathione; GSH, Reduced glutathione; NADP, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Keywords: Interferon-γ, Mitochondrial pyruvate carriers, Redox, Colon cancer, Glycolysis
Graphical abstract
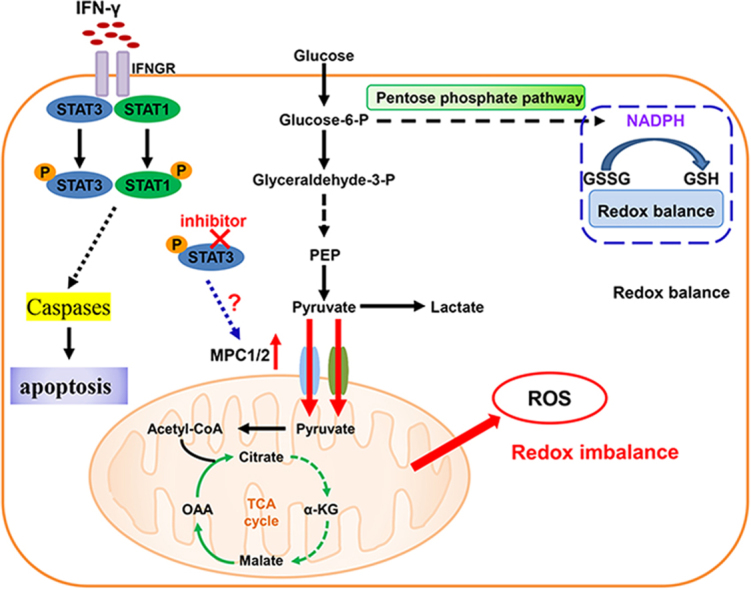
Highlights
-
•
IFNγ induces MPC downregulation via stat3 activation.
-
•
MPC promote the production of ROS and enhance the apoptosis.
-
•
STAT3 inhibition sensitize the antitumor efficacy of IFN-γ.
1. Introduction
IFNγ is considered to be a main effector of cancer immunosurveillance that suppresses tumor cell growth and induces tumor cell apoptosis [1], [2], [3]. However, clinical use of IFNγ to treat tumors has failed due to severe side effects and its relative inefficacy [4], [5]. Prior studies on tumor cell escape from IFNγ-mediated immune-surveillance focused on mutations in the IFNγ receptor IFNGR or the transcription factor STAT1 [6], [7], [8], [9]. Few studies have elucidated the mechanism by which IFNγ mediates changes in the epigenetic or transcriptomic landscape in tumor cells [8], [10]. Metabolic reprogramming is a feature of cancer cells that facilitates tumor growth and metastasis [11], [12], [13]. However, an oncogene-centric explanation of metabolic reprogram-ming does not fully consider the requirements of different cancer cells to adapt their metabolic requirements to respond to diverse environments. However, little is known about how IFNγ induces metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells and regulates key aspects of metabolism in cells, such as glycolysis. Previous work has reported that key enzymes or transporters regulate and catalyze glycolysis [14]. Mitochondrial pyruvate carriers, composed of two members (MPC1/2) are identified transporters that regulate glycolysis and the TCA cycle by controlling the entry of pyruvate into mitochondria [15], [16]. Previous studies have shown that mitochondrial pyruvate carriers (MPCs) are associated with cancer progression, and dysregulation may lead to a poor prognosis in many cancers [17], [18]. However, the mechanism of MPCs dysregulation and interaction with other factors in the tumor microenvironment has not yet been investigated.
In this study, we discovered a novel mechanism through which downregulation of MPCs in cancer cells blunts the adverse effects of IFNγ and reduces ROS production and apoptosis. STAT3-dependent inhibition of this downregulation improves IFNγ antitumor activity.
2. Methods and materials
2.1. Animals and Cell lines
Female C57BL/6 mice (4–6 weeks old) were purchased from HFK Bio-Technology. Co., LTD (Beijing, China). All procedures involving mice and experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Wuhan, China). For all animal work, experimental groups were randomized and included at least six mice per group. Animal studies were blinded during data analysis. Mouse colon cancer cell lines MC38, C26 and human tumor cell lines SW480 (colon cancer), CaCO-2 (colon cancer), MCF-7 (breast cancer) and A375 (melanoma) were purchased from the China Center for Type Culture Collection (Beijing, China) and cultured in RPMI1640 medium (Gibco, USA) with 10% FBS.
2.2. Plasmids and Reagents
Murine mpc1 and mpc2 and human MPC1 and MPC2 cDNAs were purchased from Sino-Biological (Beijing, China). The cDNAs were amplified and cloned into the viral vector pLVX-IRES-ZsGreen and pLVX-IRES-mcherry(Clontech) to produce pLVX-MPC1-Zsgreen and Plvx-MPC2-IRES-mcherry. The SoNar plasmids was a gift from Prof. Yi Yang(East China University of Science and Technology) [19]. Pspax2, pVSV-G were purchased from Addgene. STAT1 inhibitor Fludarabine and STAT3 inhibitor Stattic were purchased from Selleck Chemicals. Puromycin and lipo2000 were purchased from Invitrogen. Murine and human IFNγ were purchased from Peprotech. Polybrene,collagenase IV, lactate, sodium pyruvate and hyaluronidase were purchased from Sigma. MPC1 (D2L9I) and MPC2 (D4I7G) Rabbit mAb were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Boston, USA).
Additional reagents information, methods and data are available in the supplementary materials.
2.3. Statistics analysis
All experiments were performed at least three times. The results are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m and were analyzed by Student's t-test. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All data met the assumptions of the tests. Analyses were conducted using the Graphpad Prism 6 software.
3. Results
3.1. IFNγ induces downregulation of MPC1 and MPC2 in colon cancer
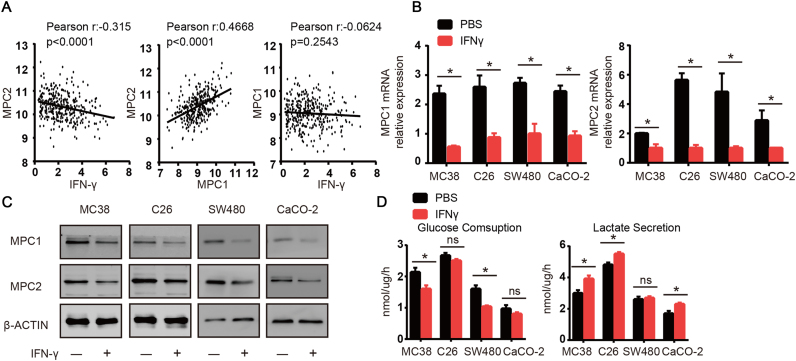
We analyzed mRNA expression in colorectal cancer samples (N = 333) from the TCGA database and found that the expression of MPC2 was inversely correlated with the mRNA levels of IFNγ (Fig. 1A). As we known, MPC1 and MPC2 worked as a heterodimer to import pyruvate into mitochondria [15], [17]. So, we also analyzed the correlation between MPC1 and MPC2 and found that the expression of MPC1 and MPC2 was highly positively correlated (Fig. 1A). Although we did not find statistically significant correlation between the expression of IFNγ and MPC1, the overall trend between IFNγ and MPC1 was inversely correlated (Fig. 1A). We then treated the murine colon cell lines MC38 and C26 and human colon cell lines SW480 and CaCO-2 with IFNγ for 48 h. Consistent with our TCGA analysis, we found that the mRNA and protein levels of both MPC1 and MPC2 were downregulated in the four colon cancer cell lines (Fig. 1B and C). Downregulation of MPC1/2 might influence glycolysis and showed changed glucose uptake and lactate secretion. After we tested the glucose and lactate levels in the medium of the murine and human colon cancer cell lines, we found that glucose uptake in the MC38 and SW480 lines was significantly reduced after the IFNγ treatment (Fig. 1D). However, lactate secretion was significantly increased in MC38, but not in SW480, which might be attributed to a significant decrease in glucose uptake in SW480 tumor cells. In the C26 and CaCO-2 cell lines, IFNγ treatment did not induce a significant decrease in glucose uptake, but the levels of lactate were significantly increased (Fig. 1D). Based on previous results, we sought to clarify the in vivo relationship between the MPC1/2 and IFNγ. We found that the IFNγ treatment significantly reduced the mRNA and protein levels of MPC1/2 in tumors tissues (Supplementary Fig. 1A and B). We tested the effects of IFNγ on other types of tumors and found that IFNγ downregulated MPC1/2 in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7 and human melanoma cell line A375 (Supplementary Fig. 1C). Together, these data suggested that IFNγ played an important role in regulating MPC1/2 expression in tumor cells.
Fig. 1.
IFNγ induces downregulation of MPC1 and MPC2 in colon cancer. (A) Coexpression analysis for MPC2 in colon cancer versus IFNγ, MPC1, and coexpression analysis for MPC1 in colon cancer versus IFNγ. Plotted data are log2 mRNA expression from RNA Seq RPKM (Data fromTCGA Research Network, IFNγ null patients were excluded). (B) MPC1 and MPC2 expression after treatment with IFNγ (10 ng/ml) for 48 h in four colon cancer cell lines (murine colon cancer cell lines, mc38 and C26, human colon cancer cell lines SW480 and CaCO-2) were analyzed by real-time PCR, PBS treated samples were used as control. (C) MPC1 and MPC2 expression after treatment with IFNγ were detected with western-blot, PBS treated samples were used as control. (D) Different colon cancer cells were pretreated with IFNγ (10 ng/ml) for 48 h, then 1.5 × 104 cells were seeded in 96-well plate in 100ul medium.24 h later the supernants were collected and glucose concentration and lactate concentration were detected. PBS treated samples were used as control. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m., N.S., no significant difference; *p < 0.05, (Student's t-test).
3.2. Downregulation of MPC1/2 attenuates IFNγ-induced apoptosis
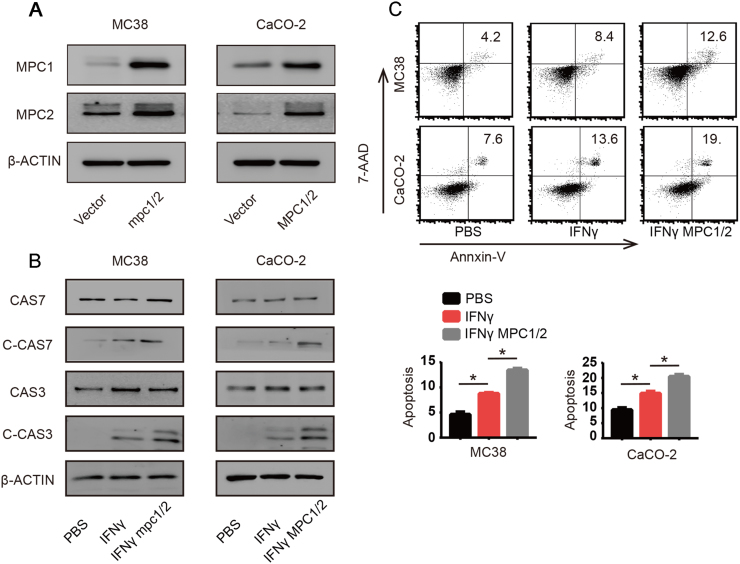
To elucidate the biological significance of MPC1/2 downregulation after IFNγ treatment, we constructed stable cell lines that over-expressed both MPC1 and MPC2 simultaneously (MPC1/2) (Fig. 2A). Metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells not only facilitates proliferation and determines the epigenetic landscape but also helps control apoptosis [13], [14]. We hypothesized that the downregulation of MPC1/2 might influence the apoptosis of cancer cells upon IFNγ treatment. It has been reported that IFNγ mainly induces tumor cell death via activating Caspases, which mainly include Caspase3 and Caspase7 [20], [21]. Therefore, we examined the effects of IFNγ on the activation of Caspase 3 and 7 in MPC1/2-overexpressing MC38 or CaCO-2 colon cancer cells. We found that IFNγ activated Caspase 3 and 7 in vector-infected MC38 or CaCO-2 colon cells, while the activation was largely increased in cancer cells overexpressing MPC1/2 (Fig. 2B). We then used flow cytometry-based methods to determine the effect of IFNγ and MPC1/2 on apoptosis. As expected, we found that IFNγ induced more apoptosis in MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells than in their vector-infected counterparts (Fig. 2C). Taken together, these data suggested that MPC1/2 downregulation reduce apoptosis induced by IFNγ.
Fig. 2.
Downregulation of MPC1/2 attenuates IFNγ-induced apoptosis. (A) Co-Overexpression of murine and human MPC1 and MPC2 in MC38 and CaCO-2 cancer cells. The overexpression was detected by western-blot. (B) After treated vector and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with PBS or IFNγ (50 ng/ml) for 48 h, the cell lysates were extracted and the levels of full lenghth Caspase 7 (CAS7) and Caspase 3 (CAS3) and cleaved Caspase 7 (C-CAS7) and cleaved Caspase 3 (C-CAS3) were detected by western-blot and β-actin was used as internal control. (C) Vector and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells were treated with PBS or IFNγ (50 ng/ml) for 48 h, then these cells were trypsinized and stained with Annexin-V and 7-AAD. The overall apoptosis was detected with flow cytometry. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m.; *p < 0.05, (Student's t-test).
3.3. Downregulation of MPC1/2 ameliorates apoptosis via inhibition of the production of reactive oxygen species
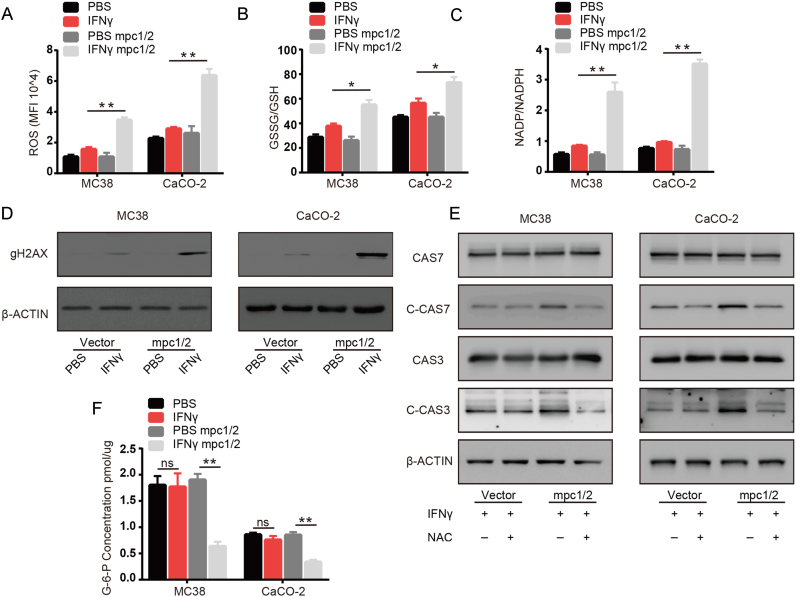
MPC1/2 is involved in regulating the rate of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, which helps maintain the redox balance [17], [18]. Excess ROS can damage cellular components or result in cell death [22], [23]. Therefore, we sought to clarify the biological significance of MPC1/2 downregulation in ROS production in tumor cells treated with IFNγ. We examined the effects of IFNγ on the total ROS production, GSSG/GSH ratio, NADP/NADPH ratio, γH2AX and effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on apoptosis in normal and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 colon cancer cells. We found that IFNγ only moderately increased total ROS production in normal MC38 and CaCO-2 colon cells, while IFNγ treatment increased ROS production in cancer cells overexpressing MPC1/2 (Fig. 3A). We also found that the GSSG/GSH and NADP/NADPH ratios were largely increased in MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cancer cells compared with normal cancer cells after IFNγ treatment (Fig. 3B and C). Consistent with the previous results, we also found that IFNγ treatment moderately increased the γH2AX level and overexpression of MPC1/2 largely enhanced the level of γH2AX (Fig. 3D). Then, we used the antioxidant NAC to determine the effects of ROS on apoptosis in IFNγ treated MC38 or CaCO-2 cells overexpressing MPC1/2. As expected, treatment with NAC protected cells from apoptosis (Supplementary Fig. 2A). The addition of NAC similarly suppressed Caspase 3 and 7 activation in cells overexpressing MPC1/2 treated with IFNγ (Fig. 3E). Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is critical for redox balance by generating cellular NADPH [24]. We hypothesized that downregulation of MPC1/2 promote the shuttling of glycolytic substrates through PPP to maintain redox balance. We therefore examined the level of Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), intermediates required for PPP, in IFNγ treated cells and found that cells overexpressing MPC1/2 showed decreased G6P levels compared with those of normal cells (Fig. 3F). Meanwhile, MPCs might directly influence the metabolic state between pyruvate and lactate, resulting in the changes of intracellular NAD+/NADH ratio and redox status. In addition, the NAD+/NADH ratio could also been used to reflect the ratio between lactate and pyruvate [25]. We next used SoNar, a genetic sensor to detect the intracellular NAD+/NADH ratio [19]. We found that IFNγ treatment largely decreased the NAD+/NADH ratio in MPCs overexpressing cells whereas a slight rise in vector control cells (Supplementary Fig. 2B), suggesting that IFNγ treatment alone did not induce drastic change in the ratio between lactate and pyruvate. Interestingly, lactate and pyruvate could inversely affect the NAD+/NADH ratio. To further confirm the effect of lactate and pyruvate in IFNγ treatment, we added lactate and pyruvate to the culture medium and treated with IFNγ. As expected, pyruvate could attenuate the apoptosis in IFNγ treated MPCs overexpressing cells while lactate could enhance apoptosis in both vector control cells and MPCs overexpressing cells under IFNγ treatment(Supplementary Fig. 2C). Decreased NAD+/NADH ratio would affect the electron transport chain and more importation of pyruvate into the mitochondria would lead to enhanced oxidative phosphorylation, both processes would arrive in mitochondria ROS production, and we also found that IFNγ could induce more ROS production in mitochondria in MPCs overexpressing cells(Supplementary Fig. 2D). Together, These findings suggested that downregulation of MPC1/2 reduce ROS production to facilitate the resistance of tumor cells to apoptosis induced by IFNγ.
Fig. 3.
Downregulation of MPC1/2 ameliorates apoptosis via inhibition of the production of reactive oxygen species. (A) After treated vector and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with IFNγ (50 ng/ml) for 48 h, the cells were trypsinized and stained with CellROX™ and detected the overall ROS level with flow cytometry. (B-D) After treated vector and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with PBS or IFNγ (50 ng/ml) for 48 h, the cell lysates were extracted, (B) the levels of GSH, GSSG were detected with kit and ratio of GSSG and GSH was calculated. (C) the Levels of NADP, NAPDH were detected with kit and ratio of NADP and NADPH was calculated. (D) γH2AX level was detected with western-blot and β-actin was used as internal control. (E) After treated vector and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with IFNγ (50 ng/ml) or IFNγ (50 ng/ml) combined with N-acetylcysteine (NAC,10 mM) for 48 h. The cell lysates were extracted and the levels of full lenghth Caspase 7 (CAS7) and Caspase 3 (CAS3) and cleaved Caspase 7 (C-CAS7) and cleaved Caspase 3 (C-CAS3) were detected by western-blot and β-actin was used as internal control. (F) After treated vector and MPC1/2 overexpressing MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with PBS or IFNγ (50 ng/ml) for 48 h, the cell lysates were extracted and the level of G6P was detected with kit. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m., N.S., no significant difference; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01(Student's t-test).
3.4. IFNγ induces MPC1/2 downregulation via stat3 activation
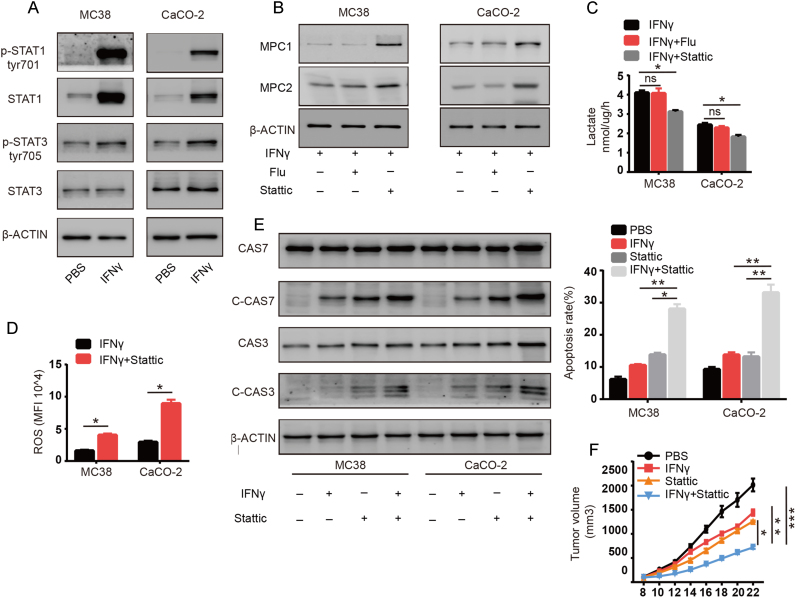
Next, we explored the molecular mechanisms underlying the downregulation of MPC1/2 induced by IFNγ. IFNγ mainly functions through activation of the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activation of transcription that depends on the transcription factors STAT1 and STAT3 [26], [27]. Both transcription factors activate a myriad of downstream genes that include key metabolic enzymes. We therefore examined the effects of IFNγ on MC38 and CaCO-2 cells and found that both STAT1 and STAT3 were activated, as indicated by increased phosphorylation (Fig. 4A). To confirm their role in MPC1/2 regulation, we treated cells with the STAT1 inhibitor Fludarabine or STAT3 inhibitor Stattic. We found that inhibiting STAT1 had little effect on MPC1/2 mRNA and protein expression in MC38 and CaCO-2 cells treated with both IFNγ and the inhibitors. However, inhibiting STAT3 partially reversed MPC1/2 expression, indicating that STAT3 plays an important role in downregulating MPC1/2 (Fig. 4B and Supplementary Fig. 3A–B). We also found that IFNγ treatment combined with inhibiting STAT3 largely impaired lactate production in MC38 and CaCO-2 cells, while inhibiting STAT1 did not have the same effect (Fig. 4C). We further tested STAT3 inhibition on ROS and apoptosis. As expected, inhibiting STAT3 boosted ROS production and apoptosis induced by IFNγ in both MC38 or CaCO-2 cells (Fig. 4D and E). Meanwhile, we found that combination treatment led to a decreased NAD+ /NADH ratio and more ROS production in mitochondria which was consistent with former results (Supplementary Fig. 3C–D). Moreover, we also found that combined treatment of the STAT3 inhibitor Stattic and IFNγ was more effective at reducing tumor growth in vivo than treatment with either alone (Fig. 4F). Taken together, these data suggested that IFNγ downregulated MPC1/2 via stat3 activation in colon cancer cells and STAT3 inhibitor enhanced the therapeutic effects of IFNγ against cancer cells.
Fig. 4.
IFNγ induces MPC1/2 downregulation via stat3 activation. (A) After treated MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with PBS or IFNγ (50 ng/ml) for 48 h, the cell lysates were extracted and the levels of phosphorylation STAT1, phosphorylation STAT3 STAT1 and STAT3 were detected with western-blot, β-actin was used as internal control. (B-C) After treated MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with IFNγ (50 ng/ml) or IFNγ combined with Fludarabine (1 uM) or IFNγ combined with Stattic (5 uM) for 48 h. (B) The cell lysates were extracted and the levels of MPC1 and MPC2 were detected with western-blot. (C) 1.5 × 104 of treated cells were seeded in 96-well plate in 100ul medium. 24 h later the supernants were collected and the level of lactate was detected. (D) After treated MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with IFNγ (50 ng/ml) or IFNγ combined with Stattic (5uM) for 48 h. the cells were trypsinized and stained with CellROX™ and detected the overall ROS level with flow cytometry. (E) After treated MC38 and CaCO-2 cells with IFNγ (50 ng/ml) or IFNγ combined with Stattic (10 uM) for 48 h. The cell lysates were extracted and the levels of full lenghth Caspase 7 and Caspase 3 and cleaved Caspase 7 and cleaved Caspase 3 were detected by western-blot and β-actin was used as internal control. In the same time, the cells were trypsinized and stained with Annexin-V and 7-AAD. The overall apoptosis was detected with flow cytometry. (F) Mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 MC38 cells. When tumor size was 5 × 5 mm, mice were treated with PBS, IFNγ (10 μg/mouse), Stattic (10 mg/kg) or IFN-γ combined with Stattic intratumorally for 10 days. Tumor growth was measured (n = 6). Data shown are representative of three independent experiments and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m., N.S., no significant difference; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Student's t-test).
4. Discussion
Although great progress has been made to elucidate the adverse effects of IFNγ on tumor cells. Little work has been done to illustrate the intracellular signaling feedback mechanisms employed by cancer cells to counteract the adverse effects induced by IFNγ. IFNγ treatment induces drastic changes in metabolic profiles. In this regard, our work elucidated that limiting ROS production by modulating glycolysis is a mechanism that is used by tumor cells to resist IFNγ. The regulatory mechanisms of MPC1/2 in tumor cells were not clearly identified and were predicted to be regulated either in an autonomous mechanism or by aberrant activation of oncogenes or loss of function of tumor suppressor genes. In our study, we identified that the downregulation of MPC1/2 was not autonomous but was instead induced by IFNγ secreted into the tumor microenvironment. Although the expression of MPCs varies among different individuals, it is significant negative correlation with the overall survival in different cancers, including lung cancer, colon cancer, esophageal cancer, and prostate cancer [17], [28]. Furthermore, downregulation of MPCs is related to stemness and tumor progression. Due to the heterogeneity of the tumor, the same tumor mass contains different subpopulations, which possesses different mold of metabolism, thereby facilitating another method to survive and progress. Therefore, MPC is one of the most promising targets for the treatment of cancer. Our work also revealed an unrecognized mechanism through which STAT3 promotes cancer cell survival. In line with this result, we formulated a new combinational therapy that includes IFNγ and the STAT3 inhibitor Stattic, which showed a strong therapeutic effect against cancer cells.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we presented a previously unrecognized mechanism that colon cancer manipulate to resist IFNγ mediated antitumor immunity and enhanced mitochondrial pyruvate transport by upregulating MPC1/2 could elicit a redox imbalance to sensitize the antitumor efficacy of IFN-γ in colon cancer. Our findings may have implications for targeting a unique aspect of this disease.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Prof. Yi Yang (East China University of Science and Technology) for the gift of SoNar plasmids.
Acknowledgments
Declarations of interest
None.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures involving mice and experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Wuhan, China).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81702767, 81502697), Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017CFB246, 2016CFB374, 2018CFC874), Hubei Province Health and Family Planning Scientific Research Project (WJ2017Q035, WJ2017Z023), the Union Hospital Key Laboratory Foundation of Biological Target Therapy (02.03.2013-80), the Young Scientist Innovation Team Project of Hubei Colleges (T201510), Beijing Medical and Health Foundation (YWJKJJHKYJJ-B17241-Q1) and the Scientific Research Foundation for Doctors of Shiyan Renmin Hospital (03328 to L.Y).
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.10.024.
Appendix A. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
References
- 1.Dunn G.P., Old L.J., Schreiber R.D. The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity. 2004;21(2):137–148. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schreiber R.D., Old L.J., Smyth M.J. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331(6024):1565–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1203486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takeda K., Nakayama M., Hayakawa Y., Kojima Y., Ikeda H., Imai N., Ogasawara K., Okumura K., Thomas D.M., Smyth M.J. IFN-gamma is required for cytotoxic T cell-dependent cancer genome immunoediting. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:14607. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bansal R., Tomar T., Ostman A., Poelstra K., Prakash J. Selective targeting of interferon gamma to stromal fibroblasts and pericytes as a novel therapeutic approach to inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012;11(11):2419–2428. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zaidi M.R., Merlino G. The two faces of interferon-gamma in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17(19):6118–6124. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ni Cheallaigh C., Sheedy F.J., Harris J., Munoz-Wolf N., Lee J., West K., McDermott E.P., Smyth A., Gleeson L.E., Coleman M., Martinez N., Hearnden C.H., Tynan G.A., Carroll E.C., Jones S.A., Corr S.C., Bernard N.J., Hughes M.M., Corcoran S.E., O'Sullivan M., Fallon C.M., Kornfeld H., Golenbock D., Gordon S.V., O'Neill L.A., Lavelle E.C., Keane J. A common variant in the adaptor mal regulates interferon gamma signaling. Immunity. 2016;44(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Qing Y., Stark G.R. Alternative activation of STAT1 and STAT3 in response to interferon-gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279(40):41679–41685. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406413200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marabelle A., Aspeslagh S., Postel-Vinay S., Soria J.C. JAK mutations as escape mechanisms to Anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(2):128–130. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Swann J.B., Smyth M.J. Immune surveillance of tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2007;117(5):1137–1146. doi: 10.1172/JCI31405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hallermalm K., Seki K., De Geer A., Motyka B., Bleackley R.C., Jager M.J., Froelich C.J., Kiessling R., Levitsky V., Levitskaya J. Modulation of the tumor cell phenotype by IFN-gamma results in resistance of uveal melanoma cells to granule-mediated lysis by cytotoxic lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2008;180(6):3766–3774. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.3766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kareva I., Hahnfeldt P. The emerging "hallmarks" of metabolic reprogramming and immune evasion: distinct or linked? Cancer Res. 2013;73(9):2737–2742. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yoshida G.J. Metabolic reprogramming: the emerging concept and associated therapeutic strategies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015;34:111. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0221-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vander Heiden M.G., Cantley L.C., Thompson C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324(5930):1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.1160809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Eboli M.L., Paradies G., Galeotti T., Papa S. Pyruvate transport in tumour-cell mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1977;460(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Paradies G., Capuano F., Palombini G., Galeotti T., Papa S. Transport of pyruvate in mitochondria from different tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1983;43(11):5068–5071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schell J.C., Olson K.A., Jiang L., Hawkins A.J., Van Vranken J.G., Xie J., Egnatchik R.A., Earl E.G., DeBerardinis R.J., Rutter J. A role for the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier as a repressor of the Warburg effect and colon cancer cell growth. Mol. Cell. 2014;56(3):400–413. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang C., Ko B., Hensley C.T., Jiang L., Wasti A.T., Kim J., Sudderth J., Calvaruso M.A., Lumata L., Mitsche M., Rutter J., Merritt M.E., DeBerardinis R.J. Glutamine oxidation maintains the TCA cycle and cell survival during impaired mitochondrial pyruvate transport. Mol. Cell. 2014;56(3):414–424. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhao Y., Wang A., Zou Y., Su N., Loscalzo J., Yang Y. In vivo monitoring of cellular energy metabolism using SoNar, a highly responsive sensor for NAD(+)/NADH redox state. Nat. Protoc. 2016;11(8):1345–1359. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sironi J.J., Ouchi T. STAT1-induced apoptosis is mediated by caspases 2, 3, and 7. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279(6):4066–4074. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307774200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ning Y., Riggins R.B., Mulla J.E., Chung H., Zwart A., Clarke R. IFNgamma restores breast cancer sensitivity to fulvestrant by regulating STAT1, IFN regulatory factor 1, NF-kappaB, BCL2 family members, and signaling to caspase-dependent apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010;9(5):1274–1285. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ray P.D., Huang B.W., Tsuji Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 2012;24(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schumacker P.T. Reactive oxygen species in cancer cells: live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell. 2006;10(3):175–176. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hamanaka R.B., Chandel N.S. Cell biology. Warburg effect and redox balance. Science. 2011;334(6060):1219–1220. doi: 10.1126/science.1215637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Titov D.V., Cracan V., Goodman R.P., Peng J., Grabarek Z., Mootha V.K. Complementation of mitochondrial electron transport chain by manipulation of the NAD+/NADH ratio. Science. 2016;352(6282):231–235. doi: 10.1126/science.aad4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aaronson D.S., Horvath C.M. A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 2002;296(5573):1653–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.1071545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Buchert M., Burns C.J., Ernst M., Targeting JAK kinase in solid tumors: emerging opportunities and challenges. Oncogene. 2016;35(8):939–951. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li X., Ji Y., Han G., Li X., Fan Z., Li Y., Zhong Y., Cao J., Zhao J., Zhang M., Wen J., Goscinski M.A., Nesland J.M., Suo Z. MPC1 and MPC2 expressions are associated with favorable clinical outcomes in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16(1):894. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2941-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.