Key Points
Question
Do oral contraceptives have an effect on drug-induced corrected QT prolongation, a surrogate for the risk of drug-induced torsade de pointes?
Findings
In a cohort of 498 healthy, nonmenopausal women, sotalol-induced QT interval prolongation was amplified by oral contraceptive pills with antiandrogenic properties; the strongest effect was observed in women taking drospirenone (as opposed to levonorgestrel). This finding was confirmed using the European pharmacovigilance database, which showed a higher reporting rate of suspected contraceptive pill-induced ventricular arrhythmias on drospirenone vs levonorgestrel.
Meaning
Drospirenone, an antiandrogenic contraceptive pill, as compared with levonorgestrel, was associated with increased drug-induced corrected QT prolongation and increased reporting for suspected contraceptive pill-induced ventricular arrhythmias in the European pharmacovigilance database.
This cohort study assesses the extent of sotalol-induced QT prolongation and specific T-wave changes after sotalol exposure in healthy nonmenopausal women according to the androgenic activity of the oral contraceptives they take.
Abstract
Importance
Women are at higher risk of drug-induced torsade de pointes (TdP) than men. Androgens are protective. Influence of oral contraception on drug-induced TdP and QT prolongation is controversial.
Objective
To determine if the extent of sotalol-induced corrected QT (QTc) prolongation and specific T-wave morphological changes, which are biomarkers for the risk of drug-induced TdP, differ in patients according to the androgenic activity of the type of oral contraceptive (OCs) they take compared with patients who took no pills.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A cohort of 498 healthy, nonmenopausal women received 80 mg of oral sotalol, a drug with known risk of drug-induced TdP, during this study in a clinical investigation center. The participants also took either no oral contraception or received OCs with different types of progestin: levonorgestrel (which has high androgenic potency), desogestrel or gestodene (which has intermediate androgenic potency), or drospirenone (which has antiandrogenic properties). Women were enrolled from February 2008 to February 2012, and data analysis took place from September 2014 to May 2018.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Electrocardiographic changes 3 hours after sotalol administration.
Results
A total of 137 women received levonorgestrel, 41 received desogestrel, 51 received gestodene, and 62 received drospirenone; another 207 received no OCs. Baseline QTc duration, plasma sotalol levels, and potassium levels did not significantly differ among groups. However, 3 hours after sotalol exposure, QTc prolongation was greater in women taking drospirenone (mean [SD] increase, 31.2 [12.6] milliseconds from baseline) than in women taking no OCs (mean [SD] increase, 24.6 [12.5] milliseconds; P = .005) or those taking levonorgestrel (mean [SD] increase, 24.2 [13.7] milliseconds; P = .005). The frequency of sotalol-induced T-wave alteration was higher in women taking drospirenone (n = 13 of 61 [21.0%]) than those taking levonorgestrel (n = 20 of 137 [14.6%]) or women taking no OCs (n = 24 of 207 [11.6%]; P = .01). Disproportionality analysis using the European pharmacovigilance database showed a higher reporting rate of OC-induced prolonged QT and ventricular arrhythmias in women taking drospirenone than levonorgestrel (drug-induced long QT syndrome: reporting odds ratio [ROR], 6.2 [95% CI, 1.3-30.8]; P = .01; ventricular arrhythmia: ROR, 3.3 [95% CI, 1.7-6.3]; P < .001).
Conclusions and Relevance
Contraceptive pills are associated with variable drug-induced alterations of ventricular repolarization in healthy nonmenopausal women. Drospirenone, an antiandrogenic pill, was associated with increased sotalol-induced QTc prolongation, although absolute QTc prolongation was modest. This finding was supported by the European pharmacovigilance database, which showed a higher reporting rate of suspected OC-induced ventricular arrhythmias on drospirenone compared with levonorgestrel. More data are required on whether antiandrogenic OCs lead to clinically significant adverse events in patients taking QTc-prolonging drugs.
Introduction
A prolonged heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) on electrocardiogram (ECG) is a marker of an increased risk of Torsades de Pointes (TdP).1 Sex hormones modulate QTc and contribute to the longer QTc observed in the general population of women vs men and androgenized women.1,2,3 Conversely, it has been proposed that QTc might be influenced by the androgenicity of oral contraceptive (OC) agents in women.4
A major cause of drug-induced long QT syndrome (diLQTS) is inhibition of the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr.5,6 The present work is an addition to a prospective genetic study7 in which healthy participants were challenged with a single low dose of sotalol (an IKr blocker); this study searched for genetic polymorphisms associated with excessive diLQTS. Oral contraceptive pills were the only treatment allowed before inclusion in that study.7 The objective of this study is to assess the association between the extent of sotalol-induced QTc lengthening and appearance of ECG signs indicating IKr inhibition per the varying androgenic activity of OC pills taken by healthy women.
Methods
Study Design
From February 2008 to February 2012, 615 healthy women were enrolled in the Genome Wide Analysis of Sotalol-Induced IKr Inhibition During Ventricular Repolarization (GENEREPOL) study (NCT00773201). The study protocol received institutional review board approval from the Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects of Paris Ile de France V in Paris, France, and written informed consent was obtained from the participants.
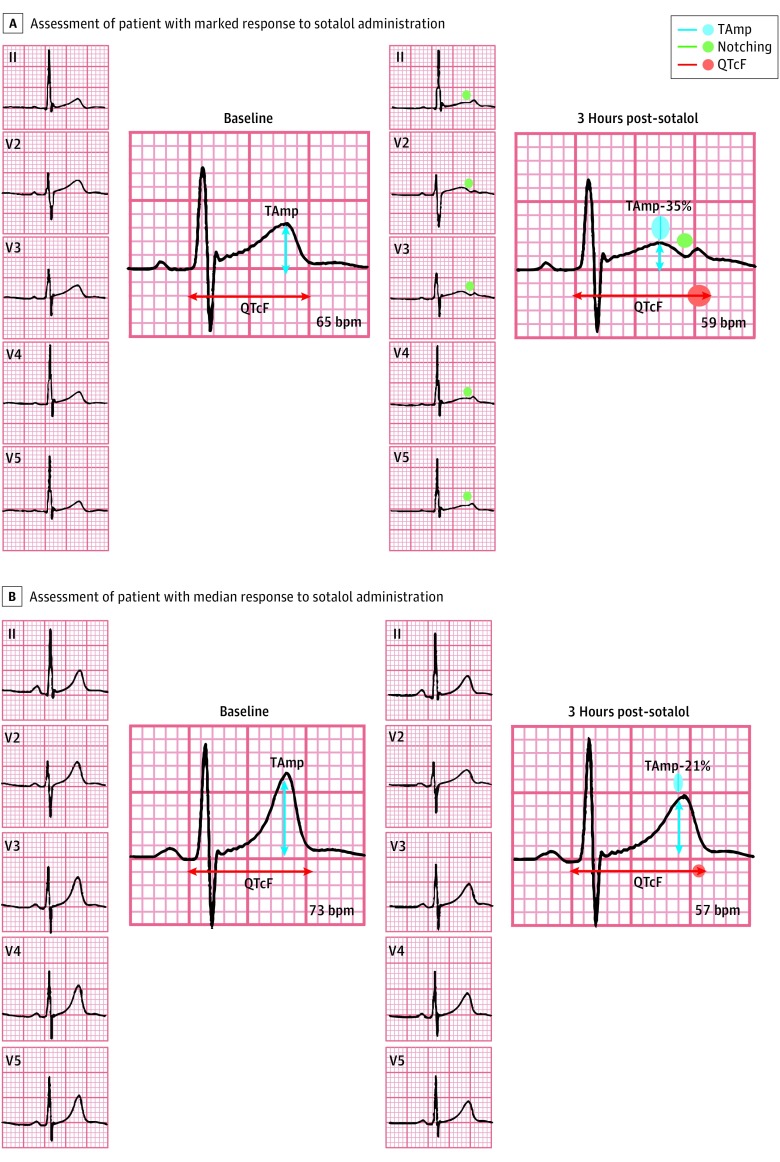
After enrollment, each participant received a single 80-mg oral dose of sotalol.7 Because sotalol-induced LQTS represents the equivalent of an acquired form of congenital LQT2 syndrome (which involves a defect in IKr),8 we evaluated ECG duration and morphology at baseline and the changes 3 hours after sotalol intake.7 The inhibition of IKr is associated with QTc prolongation and the appearance of notches (Figure 1).7 We used the Fridericia correction9,10 (QT/3√RR, in which QT is the time from the start of the Q wave to the end of the T wave and RR is defined as the time from the onset of 1 QRS complex to the start of the next). Further details of the parent protocol are provided in the eAppendix in the Supplement.7
Figure 1. Electrocardiogram Analyses.
Assessment of QT intervals and notching in a woman with a marked response to sotalol administration (A) and a woman with a median response to sotalol administration (B). The T-wave notches correspond to an additional deflection with inverse polarity during the repolarization phase, which is associated with a further increased risk of ventricular arrhythmia in patients with long QT syndrome. In the participant with marked response, the QT interval corrected by the Fridericia method (QTcF) increased by 8.9%, while T-wave maximal amplitude (TAmp) decreased by 35%; in the participant with median response, QTcF increased by 4.8% and TAmp decreased by 21%.
Long-term contraception was the only treatment allowed. The type of contraceptive modality was left at the discretion of the treating physician.
Nonmenopausal women were considered for this analysis if they were taking no oral contraception or if they had received any of the following OCs: levonorgestrel (a second-generation progestin with high androgenic potency), desogestrel or gestodene (a third-generation progestins with intermediate androgenic potency), or drospirenone (an antiandrogenic agent).
Statistics
Demographic and ECG data are presented by descriptive statistics as number (percentage), mean values with SDs, or medians with interquartile range (IQR). Comparisons of quantitative variables were performed by Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn post hoc test if nonnormally distributed or by analysis of variance and Tukey post hoc tests if normally distributed. Comparisons of qualitative variables were performed by χ2 test. Multivariable analyses were performed by analysis of covariance (for changes in QTc duration) or logistic regression (for changes in notching 3 hours after sotalol exposure). Only covariates with significant univariate association with changes in QTc duration or notching at 3 hours after exposure (ie, age, kalemia, plasma levels of sotalol 3 hours after exposure, and type of OC) were further integrated for multivariable analyses. For analysis of covariance, β coefficients were calculated to allow for direct comparison of the relative influence of the explanatory variables on the dependent variable and their significance. We used XLSTAT software version 17.05 (Addinsoft), and P ≤ .05 was considered significant. Data analysis took place from September 2014 to May 2018.
Disproportionality Analysis
The European database of suspected adverse drug reaction (ADR) reports11 is a publicly accessible portal designed for searches of data on suspected ADR for authorized medicinal products in the European Economic Area. Disproportionality analyses (also known as case/noncase analyses) were performed for drospirenone vs levonorgestrel.3,12 This method compared the proportion of selected specific ADR reported for a single drug (drospirenone) with the proportion of the same ADR for a control drug (levonorgestrel). The denominators in these analyses were the overall ADRs reported for each drug.3,12 Reactions are based on the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities classification. Disproportionality was estimated by calculating the reporting odds ratio (ROR).3,12,13 We searched for ADRs arising from suspected OC-induced ventricular arrhythmias, cardiac deaths, and LQTS from inception until May 9, 2018.12,13
Results
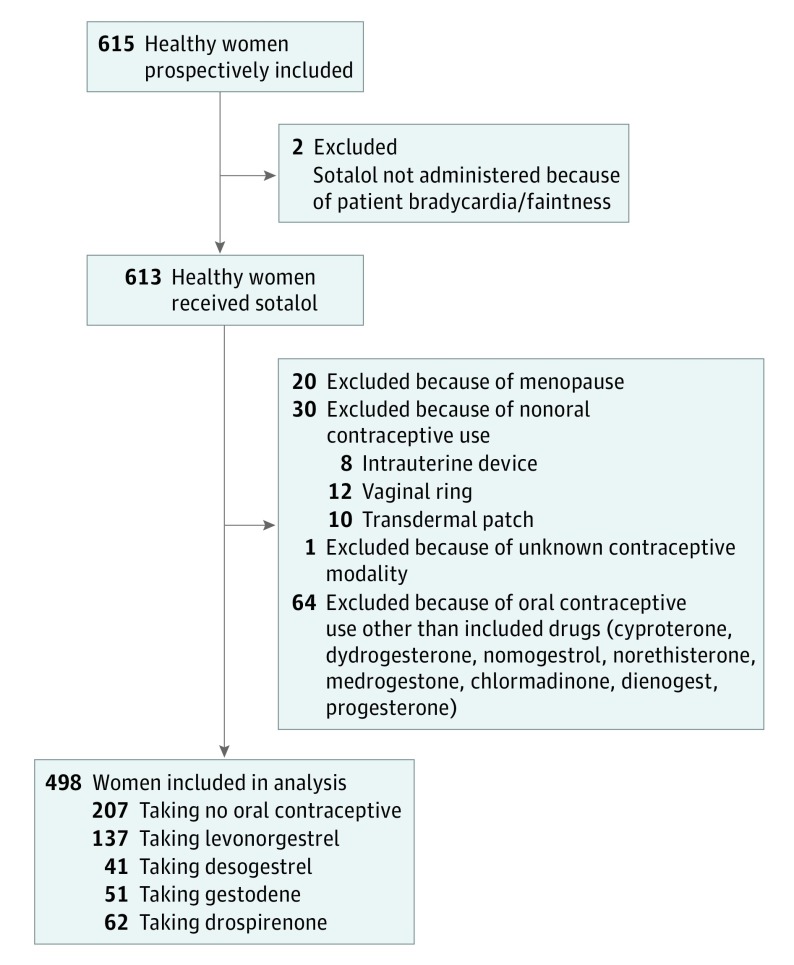
Of the 615 women initially recruited to this study, 498 were included (81.0%; Figure 2). Of these, 207 women were taking no oral contraception (41.6%), and 291 were categorized as taking levonorgestrel (n = 137 of 291 [47.1%]), desogestrel (n = 41 [14.1%]), gestodene (n = 51 [17.5%]), or drospirenone (n = 62 [21.3%]); in most cases, these were combined with ethynil-estradiol (eTable 1 in the Supplement). Women receiving no OCs were slightly older (median [IQR] age, 25.7 [21.0-41.7] years) than those receiving levonorgestrel (median [IQR] age, 23.0 [21.0-26.5] years; P < .001) or drospirenone (median [IQR] age, 22.3 [20.7-24.7] years; P < .001). Kalemia was within normal range and not significantly different among groups, as was the mean level of plasma sotalol 3 hours after drug exposure (Table).
Figure 2. Flowchart of Included Participants.
Among the oral contraceptives included in the analysis, levonorgestrel was considered a second-generation progestin, desogestrel and gestodene third-generation progestins, and drospirenone a fourth-generation progestin.
Table. Demographic and Electrocardiogram Characteristics of Women Who Received Sotalol, by Oral Contraceptive.
| Characteristic | Mean (SD) | P Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Oral Contraceptives (n = 207) | Levonorgestrel (n = 137) | Desogestrel (n = 41) | Gestodene (n = 51) | Drospirenone (n = 62) | ||
| Age, median (IQR), y | 25.7 (20.9-41.7)a | 23 (21-26.5)b | 22.8 (20.7-25.2) | 23 (21-24.6) | 22.3 (20.7-24.7)c | <.001 |
| Kalemia, mmol/L | 4.05 (0.27) | 3.99 (0.28) | 4.00 (0.28) | 3.94 (0.25) | 4.02 (0.28) | .07 |
| Plasma levels of sotalol 3 h after exposure, median (IQR), ng/mL | 422 (340-564) | 384 (287-491) | 441 (282-565) | 414 (299-538) | 413 (341-515) | .06 |
| Weight, kg | 62 (8.8) | 60.8 (7.1) | 60.4 (6.5) | 59.9 (7.4) | 59.3 (7.3) | .11 |
| Creatinine clearance, mL/min/1.73 m2d | 111.9 (26.3) | 105.5 (15.9) | 107.4 (13.6) | 106.6 (18) | 106.4 (17.4) | .43 |
| Baseline QTc, ms | 393.8 (16.9) | 392 (14.2) | 390 (12.1) | 393.7 (14.3) | 394.7 (15.2) | .46 |
| Baseline notching, No. (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Change in QTc duration, ms | 24.6 (12.5)e | 24.2 (13.7)e | 27 (12.7) | 28.1 (13.2) | 31.2 (12.6)f | .003 |
| Change in QTc duration, % | 6.2 (3.2)e | 6.2 (3.5)e | 6.9 (3.2) | 7.1 (3.4) | 7.9 (3.1)g | .003 |
| Notching 3 h after exposure, No. (%) | 24 (11.6)h | 20 (14.6) | 3 (7.3) | 10 (19.6)i | 13 (21.0)j | .01 |
Abbreviations: IQR, interquartile range, NA, not applicable; QTc, corrected QT interval.
P < .001 compared with drospirenone; P = .01-.05 compared with levonorgestrel, after post hoc test adjusted for multiple comparisons.
P = .01 to .05 compared with no oral contraceptives, after post hoc test adjusted for multiple comparisons.
P < .001 compared with no oral contraceptives.
Evaluated by Cockcroft-Gault Equation; data were available for patients taking no oral contraceptives (n = 95), levonorgestrel (n = 48), desogestrel (n = 27), gestodene (n = 19), and drospirenone (n = 29).
P = .01 to .001 compared with drospirenone after post hoc tests adjusted for multiple comparisons.
P = .01 to .001 compared with no oral contraceptives, after post hoc test adjusted for multiple comparisons; P = .01 to .001 compared with levonorgestrel, after post hoc test adjusted for multiple comparisons.
P = .01 to .001 compared with no oral contraceptives, after post hoc test adjusted for multiple comparisons; P = .01 to .001 compared with levonorgestrel, after post hoc test adjusted for multiple comparisons.
P = .03 compared with drospirenone; P = .05 compared with gestodene.
P = .05 compared with no oral contraceptives.
P = .03 compared with no oral contraceptives.
Baseline QTc duration was not significantly different among the groups taking OCs (Table), and no notch was found in any participant. Three hours after sotalol administration (Table), mean (SD) QTc prolongation differed among the groups taking OCs, ranging from 24.2 (13.7) milliseconds in the levonorgestrel group to 31.2 (12.6) milliseconds in the drospirenone group (P < .001). Compared with participants taking no OCs or levonorgestrel, participants receiving drospirenone had greater sotalol-induced QTc prolongation (a mean [SD] increase of 6.6 [2.6] milliseconds; P = .005 compared with those on no OCs, and 7.0 [2.7] milliseconds; P = .005 compared with those taking levonorgestrel). The T-wave notches observed 3 hours after sotalol administration were more frequent in women receiving drospirenone (n = 13 of 62 [21.0%]) or gestodene (n = 10 of 51 [19.6%]) than in women receiving desogestrel (n = 3 of 41 [7.3%]), levonorgestrel (n = 20 of 137 [14.6%]) or no OCs (n = 24 of 207 [11.6%]; P = .01 across all). Three hours after sotalol administration, QTc prolongation greater than or equal to 50 milliseconds was more frequent in women receiving drospirenone (n = 5 of 62 [8.1%]) or gestodene (n = 3 of 51 [5.9%]) than in women receiving desogestrel (n = 0 of 41 [0%]), levonorgestrel (n = 6 of 137 [4.4%]), or no OC (n = 3 of 207 [1.4%]; P = .003).
Changes in QTc duration were associated with plasma levels of sotalol 3 hours after drug exposure (r = 0.44; P < .001), kalemia (r = 0.1; P = .05) but not with age or baseline QTc duration. Appearance of notching at 3 hours after exposure was associated with plasma levels of sotalol at 3 hours (r = 0.2; P < .001) but not with kalemia or age.
Multivariable analysis included plasma levels of sotalol at 3 hours, kalemia, and the type of OC used. The type of OC, plasma levels of sotalol at 3 hours after exposure (β = 0.44; SD, 0.04; P < .001) and kalemia (β = 0.08; SD, 0.04; P = .05) remained significant variables explaining change in QTc duration (r = 0.47; P < .001) in multivariable analysis. Compared with drospirenone, taking no OC and taking levonorgestrel were associated with less sotalol-induced QTc prolongation (taking no OC: β = –0.28; SD, 0.06; P < .001; and taking levonorgestrel: β = –0.19; SD, 0.06; P < .001).
Using multivariable logistic regression, the type of OC and plasma levels 3 hours after sotalol exposure (OR, 1.003 [95% CI, 1.002-1.005]; P < .001) remained significantly associated with notching at 3 hours after exposure. Sotalol-induced notches occurred more frequently in patients taking drospirenone than in the group taking no OC (OR, 2.32 [95% CI, 1.08-5.00]; P = .003).
The total number of individual case safety reports (ICSRs) in women, recorded by molecule and by Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities search terms (Preferred Terms level) from inception until May 2018 in the European pharmacovigilance database, are detailed in eTable 2 in the Supplement. The total number of ICSRs in women receiving drospirenone was 34 784; the total number for women taking levonorgestrel was 72 073. Disproportionality analysis comparing reported suspected diLQTS, ventricular arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest showed higher reporting rates for drospirenone vs levonorgestrel (diLQTS: 0.02% vs 0.002%; ROR, 6.2 [95% CI, 1.3-30.8]; P = .01; ventricular arrhythmias: 0.07% vs 0.02%; ROR, 3.3 [95% CI, 1.7-6.3]; P < .001; cardiac arrest: 0.42% vs 0.06%; ROR, 8.0 [95% CI, 5.6-11.4]; P < .001).
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study comparing the association between type of OC used and the magnitude of QTc prolongation as a result of an IKr blocker in healthy volunteers. We showed that QTc prolongation and T-wave morphological changes are associated with the androgenic potency of the progestin taken, although absolute QTc prolongation was modest. Drospirenone, an OC with antiandrogenic properties, was associated with greater drug-induced QTc prolongation and appearance of T-wave notches, while levonorgestrel, a second-generation OC with high androgenic activity, was not. The upper limit of the IQR for the difference in QTc increase between drospirenone vs levonorgestrel was longer than 10 milliseconds, a threshold considered as associated with a potential increase of proarrhythmia risk.9 However, this threshold is of unclear clinical significance, considering the nonrandomized nature of this relatively small study. Two to 5 times more women who were taking drosperinone developed a QTc prolongation of 50 milliseconds or longer compared with women taking either no OC or levonorgestrel. These results generate the hypothesis that drospirenone may be a risk factor for drug-induced TdP and sudden death in women receiving this OC. This hypothesis is also in line with the higher ROR for suspected OC-induced ventricular arrhythmias and cardiac death in women receiving drospirenone compared with levonorgestrel, as determined through analysis of the European pharmacovigilance database. More data are required on whether antiandrogenic OC use will lead to clinically significant adverse events in patients taking QTc-prolonging drugs, such as class III antiarrhythmic medications.
Sotalol is a potent IKr blocker with a dose-dependent risk of drug-induced TdP.14 Sotalol was chosen because it has small pharmacokinetic variability, with a maximal concentration expected approximately 3 hours after oral intake.15 We used a low single dose of sotalol (80 mg) for a standardized, short-acting, and safe IKr-blocking outcome. Therefore, the results of this study cannot provide a precise estimate of maximal drospirenone potential incremental association with sotalol-induced QTc prolongation and TdP risk in a real-life setting in which steady state is reached (160 to 320 mg per day, administered over the long term). Besides progesterone, which is the natural form of progestin, several parent compounds in the progestin family are used in OCs. These act on the progesterone receptor with variable bindings to other steroid hormone receptors.16 Levonorgestrel has a high androgenic potency, while gestodene and desogestrel are less androgenic with better clinical acceptance.16 Drospirenone has antiandrogenic properties.16
Limitations
Plasma endogenous or synthetic progestin levels (which vary between participants as a function of their weight, absorption, volume of distribution, and the timing of their last active OC intakes) were not assayed in this study. As a consequence, we were not able to take into consideration any potential higher sensitivity to diLQTS during the menstrual cycle in women taking no OCs or to evaluate the influence of progestin plasma levels at the time of ECG evaluations in women taking OCs.17 Administration of OCs was not randomized in this study, but the main factors influencing QTc (kalemia and plasma sotalol levels) did not significantly differ among groups. Small but statistically significant differences of age existed between groups, but age was not associated with changes in QTc duration or notching at 3 hours in this cohort of women exclusively of child-bearing age.
We acknowledge that pharmacovigilance epidemiological studies have mandatory limitations inherent to the lack of information on doses, associated drugs, and concomitant predisposing conditions, as well as imprecision in the exact number of individuals experiencing these events (vs ICSRs). They nevertheless remain a relevant method to detect signals in drug safety research and postmarketing surveillance, particularly for very rare ADRs, such as drug-induced TdP.12,13 The number of reports for a particular medicinal product may be influenced by the extent of use of the product, publicity, the nature of the reactions, and other factors, such as competition bias. Therefore, there is still a risk that comparisons of disproportionality between medicinal products in pharmacovigilance databases may be misleading.18
Conclusions
The findings of this study call for careful history-taking of OC use, and the type of OC taken could be useful in shared decision making in women with preexisting risk factors for drug-induced TdP.5 In 2015, a Guttmacher Institute fact sheet reported that 16% of approximately 60 million US women aged 15 to 44 years were taking OCs, with drospirenone having been the most advertised agent from 2005 to 2014.19
eAppendix. Methods
eTable 1. Characteristics of the different hormonal oral contraceptive pills.
eTable 2. Data from the EudraVigilance database (through 05/09/2018) concerning number and type (MedDRA classification) of declared individual case safety reports in women receiving drospirenone and levonorgestrel.
eReferences. Bibliography
References
- 1.Salem JE, Alexandre J, Bachelot A, Funck-Brentano C. Influence of steroid hormones on ventricular repolarization. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;167:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abehsira G, Bachelot A, Badilini F, et al. Complex influence of gonadotropins and sex steroid hormones on QT interval duration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(7):2776-2784. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1877 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Salem J-E, Waintraub X, Courtillot C, et al. Hypogonadism as a reversible cause of torsades de pointes in men [published online July 3, 2018]. Cir Cir. 2018;138. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sedlak T, Shufelt C, Iribarren C, Lyon LL, Bairey Merz CN. Oral contraceptive use and the ECG: evidence of an adverse QT effect on corrected QT interval. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2013;18(4):389-398. doi: 10.1111/anec.12050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Roden DM. Drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(10):1013-1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra032426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Li M, Ramos LG. Drug-induced QT prolongation and torsades de pointes. P T. 2017;42(7):473-477. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Salem JE, Germain M, Hulot JS, et al. Genome wide analysis of sotalol-induced Ikr inhibition during ventricular Repolarization, “GENEREPOL study”: lack of common variants with large effect sizes. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0181875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Graff C, Andersen MP, Xue JQ, et al. Identifying drug-induced repolarization abnormalities from distinct ECG patterns in congenital long QT syndrome: a study of sotalol effects on T-wave morphology. Drug Saf. 2009;32(7):599-611. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200932070-00006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.US Food and Drug Administration; US Department of Health and Human Services . International conference on harmonisation; guidance on E14 Clinical Evaluation of QT/QTc interval prolongation and proarrhythmic potential for non-antiarrhythmic drugs; availability. notice. Fed Regist. 2005;70(202):61134-61135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Saqué V, Vaglio M, Funck-Brentano C, et al. Fast, accurate and easy-to-teach QT interval assessment: The triplicate concatenation method. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;110(8-9):475-481. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2016.12.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.European Medicines Agency Eudravigilance: European database of suspected adverse drug reaction reports: online access to suspected side-effect reports. http://www.adrreports.eu/en/index.html. Accessed June 20, 2018.
- 12.Grouthier V, Lebrun-Vignes B, Glazer AM, et al. Increased long QT and torsade de pointes reporting on tamoxifen compared with aromatase inhibitors. Heart. 2018;pii:heartjnl-2017-312934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.De Bruin ML, Pettersson M, Meyboom RH, Hoes AW, Leufkens HG. Anti-HERG activity and the risk of drug-induced arrhythmias and sudden death. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(6):590-597. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kpaeyeh JA Jr, Wharton JM. Sotalol. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2016;8(2):437-452. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2016.02.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Funck-Brentano C. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of d-sotalol and d,l-sotalol. Eur Heart J. 1993;14(suppl H):30-35. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/14.suppl_H.30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sitruk-Ware R. Pharmacological profile of progestins. Maturitas. 2008;61(1-2):151-157. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2008.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rodriguez I, Kilborn MJ, Liu XK, Pezzullo JC, Woosley RL. Drug-induced QT prolongation in women during the menstrual cycle. JAMA. 2001;285(10):1322-1326. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.10.1322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Böhm R. OpenVigil Cave-at document; Version 2.0.2. http://openvigil.sourceforge.net/doc/openvigil-cave-at-v2.html. Published September 14, 2015. Accessed June 20, 2018.
- 19.Wu MH, Bartz D, Avorn J, Seeger JD. Trends in direct-to-consumer advertising of prescription contraceptives. Contraception. 2016;93(5):398-405. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2016.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eAppendix. Methods
eTable 1. Characteristics of the different hormonal oral contraceptive pills.
eTable 2. Data from the EudraVigilance database (through 05/09/2018) concerning number and type (MedDRA classification) of declared individual case safety reports in women receiving drospirenone and levonorgestrel.
eReferences. Bibliography