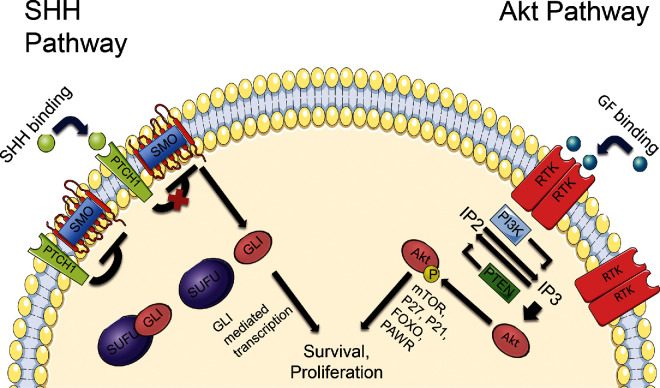
FIGURE 2.
Details of the SHH and Akt pathways. Without SHH binding, PTCH1 renders smoothened (SMO) inactive and inhibits it from signaling downstream targets. When SHH binds to PTCH1, SMO is released from this inhibition, allowing it to interact with SUFU. This results in the activation and nuclear translocation of glioma-associated oncogene homologue 1 (GLI1) and (GLI2), and the degradation of GLI3. In the Akt pathway, PTEN normally targets IP3 to inhibit the phosphorylation of Akt. When growth factor (GF) binding to receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) occurs, PI3K signaling is increased, leading to IP3 accumulation, phosphorylation of Akt and activation of downstream targets.