Figure 7. Spinal inhibition of 12/15-LOX attenuates formalin Phase II acute flinching and persistent allodynia.
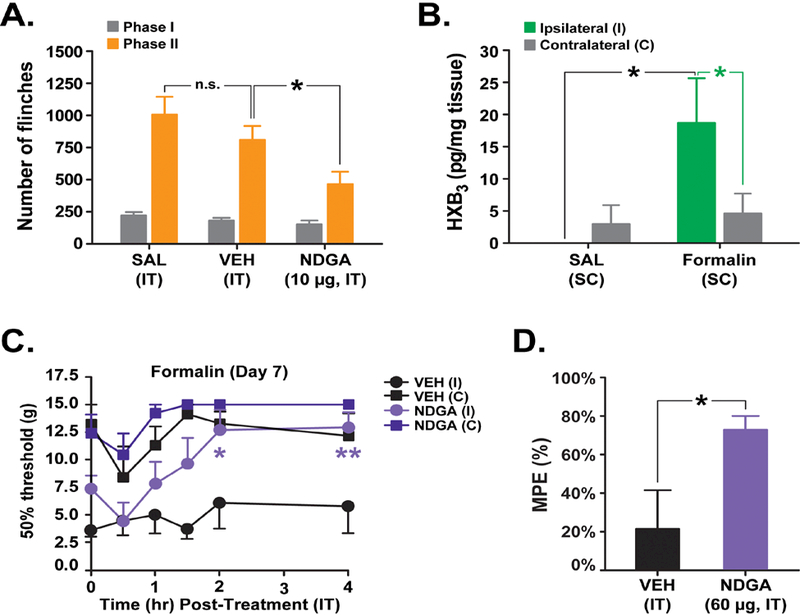
(A) Pretreatment with the general 12/15-LOX inhibitor NDGA (10 μg IT) significantly reduces Phase II acute flinching following SC formalin (2.5%, 50 μl) into the dorsal surface of the hindpaw. (B) HXB3 levels are increased significantly in ipsilateral (I) but not contralateral (C) lumbar spinal cord on day 7 following SC formalin (5%, 50 μl), concurrent with allodynia. Post-treatment with NDGA (60 μg IT) reverses established IPLT formalin-induced allodynia on day 7 as depicted by (C) timecourse and (D) %MPE values. n = 6 rats/treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, v. VEH; n.s. not significantly different from SAL. SAL = saline; VEH = vehicle; SC = subcutaneous; MPE = maximum possible effect.
