FIGURE 1.
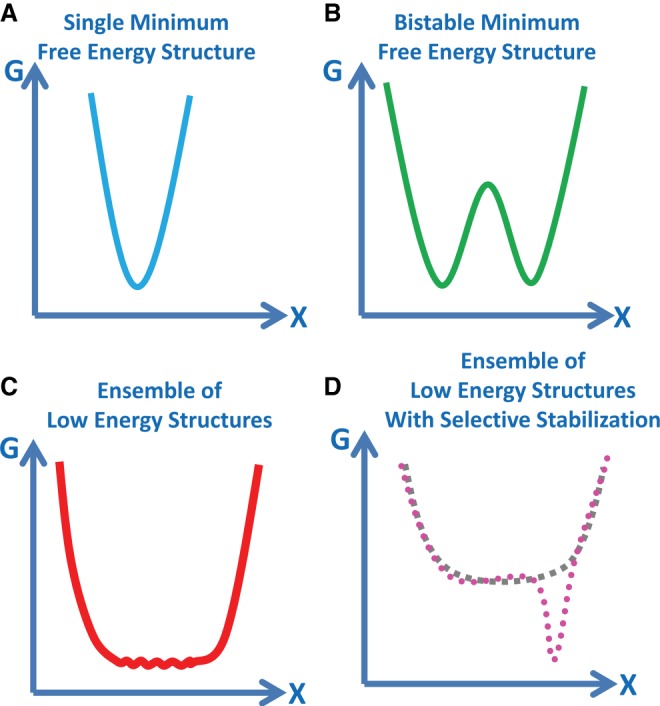
Models of the RNA folding problem. (A) A single minimum free energy structure is predicted for a single sequence in a traditional folding funnel. The conceptual graph plots free energy (G) versus conformational space (X). (B) A bi-stable free energy structure model has the two lowest energy structures with a high-energy barrier between the two folds. This model extends the single minimum free energy (MFE) model to riboswitches binding a ligand, for example. (C) An ensemble of low-energy structures resembles a low basin of possible structures rather than a folding funnel that converges to a single conformation. There are low or no energy barriers between different conformations. The bottom curve may be bumpy rather than smooth, although free energies may not distinguish very different structures. (D) An ensemble of low-energy structures (gray dashed line) may be selectively stabilized (magenta circles) by RNA binding a ligand or protein that recognizes motifs within the low-energy ensemble of structures.
