Abstract
Muscle dysmorphia (MD) is a condition that is characterized by body image disturbance, a drive for muscularity and excessive exercising. It leads to considerable functional impairment. Most previous studies focused on male samples. The study aimed to validate a German version of the Muscle Dysmorphic Disorder Inventory (MDDI) in order to make the instrument available in German speaking countries. We further aimed to explore for gender differences in the MDDI factors (measurement invariance) and to assess the relationship between MD and positive dimensions of body experience as well as exercise dependence. 394 participants (53% females, mean age 24.3 years) took part in an internet-based survey. The three-factor structure of the English version of the MDDI was replicated, independent of gender (multi group CFA; Base model TLI = .961; CFI = .970). Cronbach´s alpha was .81-.84 for the subscales and .75 for the MDDI total score. MD was associated with exercise dependence and negatively correlated with dimensions of positive body experience, which can be considered relevant for satisfying relationships and a positive sense of self: e.g. body contact and sexual fulfillment. Men and women showed differences in two subscales of the MDDI (appearance intolerance, drive for size). Testing for measurement invariance resulted in weak invariance: Equivalent factor structure for men and women, but significantly different loadings and coefficients. No statistically significant difference in the MDDI total score was found. The findings suggest good psychometric properties of the German version of the MDDI. Future studies should address the question of cut-off scores and norms for different samples as well as a possible overlap between MD and eating disorder psychopathology in women.
Introduction
Muscle dysmorphia (MD) is a condition that “is characterized by a fear of being too small, and by perceiving oneself as small and weak, even when one is actually large and muscular.” [1]. It is reported to be most prevalent in weightlifters and bodybuilders [2]. MD encompasses a psychological, behavioral and social dimension. On the psychological level, individuals with MD show a pathological pursuit of muscularity, including a preoccupation with their appearance and body image disturbance: Although they are usually leaner and more muscular than others, they feel small and try to hide their body [3]. Showing their body leads to intense shame and embarrassment [4]. On a behavioral level, MD is characterized by excessive hours of exercising, disordered eating practices and often steroid use [5,6]. Life time prevalence rates of mood disorders, anxiety disorders and eating disorders in individuals with MD are significantly higher compared to controls [2]. Overall, MD is a disabling condition that—on a social level—leads to considerable impairment in work functioning and a withdrawal from social contacts [7]. Nevertheless, MD often remains undetected [2].
Pope et al. [3] proposed diagnostic criteria for MD, which are still valid today. However, although MD was included in the DSM-5 as a subtype of body dysmorphic disorder [8], there is still no consensus on this decision. It remains a topic of debate, if MD should be categorized as a body dysmorphic disorder, an eating disorder, a behavioral addiction or an obsessive-compulsive disorder [6,9,10].
It is uncontroversial that exercise psychopathology is a key symptom in MD. Therefore, one could expect a close relationship between MD and exercise dependence, as excessive hours of exercising, an increase in negative affect when missing exercise sessions and an impact on social functioning will be overlapping features [11]. Most definitions of exercise dependence are oriented on criteria of addiction and include the following symptoms: Tolerance, withdrawal symptoms when stopping to exercise, continuance despite negative consequences, time (spending large amounts of time exercising), reduction in other activities, lack of control and intention effects (exercising longer than expected) [12]. Exercise dependence is not characterized by body image disturbance or appearance intolerance, which are key symptoms in MD.
Authors criticize the underrepresentation of males in studies on body image disturbance and disordered eating [6,13], because an over-evaluation of shape and weight is not limited to females and increasingly present in men [13,14]. The internalization of an ideal body figure as well as social body comparison were found to be associated with a drive for muscularity in men and may increase overall body dissatisfaction [15,16]. In contrast to women, men seem to be preoccupied with a drive for muscularity and body composition (leanness) rather than thinness [17].
Dos Santos Filho et al. [9] conducted a systematic review on studies in MD and identified 34 articles. The samples mainly consisted of male bodybuilders, weightlifters or college students. Prevalence rates of MD ranged from over 50% in studies assessing highly selective groups like competitive bodybuilders to about 6–7% in primarily male college students [18–20]. However, it is important to note that most studies used screening instruments (self-report) and not a clinical interview. Therefore, it can be assumed that clinically relevant MD is less common and probably a rare condition in the general population. Only six articles in this review reported on samples including females [9]. Furthermore, more than half of the studies were conducted in the U.S., and most of them included sample sizes of less than 100 participants.
A prerequisite for research in the field are validated instruments which are translated in several languages. Validated instruments are also useful for screening purposes in clinical practice. There are instruments for the measurement of a drive for muscularity like the DMS (Drive for Muscularity Scale; [17,21]) and instruments that aim to assess features of MD more specifically, based on Pope et al.´s criteria [3]. Instruments for the assessment of MD comprise the MDSQ (Muscle Dysmorphia Symptom Questionnaire), the MASS (Muscle Appearance Satisfaction Scale), the MDQ (Muscle Dysmorphia Questionnaire), the MDI (Muscle Dysmorphic Inventory) and the MDDI (Muscle Dysmorphic Disorder Inventory; [22]). The MDI and the MASS were found to be the most used instruments in a recent systematic review and meta-analysis, followed by the MDDI [23]. However, MASS and MDI do not address the functional impairment aspect, which is important to evaluate the pathological dimension of MD and one diagnostic criterion. Therefore, we chose the MDDI for translation, which improved the MDI by adding a scale that measures functional impairment. The MDDI was already validated in Italian language [24,25]. The Italian version revealed the same factor structure as the original version and showed good convergent and divergent validity. Cronbach´s alpha was between α = .80 and α = .85 for the total score and two subscales. However, one subscale (appearance intolerance) showed a low level of internal consistency (α = .45) [25].
Aims of the study
We aimed to validate the German version of the MDDI in order to make the instrument available for the assessment of muscular dysmorphia (MD) in German-speaking countries. Secondly, we aimed to evaluate the influence of gender (factor structure including measurement invariance, psychopathological features of MD in men and women). Finally, and as part of the validation process we intended to analyze the relationship between psychopathological features of MD and different dimensions of positive body experience (e.g. body acceptance, body contact, vitality, sexual fulfillment) as well as exercise dependence.
We expected features of MD and especially a drive for muscularity to be significantly more prevalent in males compared to females, although we assumed MD to be also present in women. In terms of convergent validity, we hypothesized that there will be a) a positive correlation between the MDDI total score and exercise dependence in both, men and women and b) a negative correlation between appearance intolerance and the acceptance of one´s own body. Finally, we assumed a negative correlation between MD (MDDI total score) and further dimensions of body experiences, which can be assumed to contribute to quality of life and satisfying relationships (body contact, sexual fulfillment, vitality), independent of gender.
Materials and methods
Translation of the MDDI
The translation was conducted according to the standards for the translation of instruments [26,27]. The items of the MDDI were translated into German by the first and third author (AZ, HA). Two words were difficult to translate in such a way that they capture the exact meaning in the context of body experience in German: “big” and “small”. Their translation was discussed in detail within the research group. In a next step, items were back-translated by a native speaker. In case of a deviance, the German translation was discussed and adapted. In a final step, the back-translation was presented to the developer of the MDDI (TH), who approved the final version (for items see Table 1).
Table 1. Items of the MDDI: English and German version.
| English (original version): Item | German: Item | Subscale |
|---|---|---|
| I01. I think my body is too skinny/slender. | 1. Ich finde meinen Körper zu schmächtig | DS |
| I02. I wear loose clothing so that people can't see my body. | 2. Ich trage weite Kleidung, sodass Menschen meinen Körper nicht sehen können | AI |
| I03. I hate my body. | 3. Ich hasse meinen Körper | AI |
| I04. I wish I could be heavier. | 4. Ich wünschte mir, ich könnte kräftiger werden | DS |
| I05. I find my chest to be too small. | 5. Ich finde meinen Oberkörper zu schmächtig | DS |
| I06. I think my legs are too thin. | 6. Ich finde meine Beine zu dünn | DS |
| I07. I feel like I have too much body fat. | 7. Ich fühle mich, als wenn ich zu viel Körperfett habe | AI |
| I08. I wish my arms were stronger. | 8. Ich wünschte mir, meine Arme wären kräftiger | DS |
| I09. I am embarrassed to let people see me without a shirt or t-shirt. | 9. Ich schäme mich, mich Menschen ohne Hemd / T-Shirt zu zeigen | AI |
| I10. I feel anxious when I miss one or more days of exercise. | 10. Ich fühle mich unruhig / ängstlich, wenn ich einen oder mehrere Trainingstage verpasse | FI |
| I11. I cancel social activities with friends (e.g. watching football, invitations to dinner, going to the movie theater, etc.) because of my workout/exercise schedule. | 11. Ich schlage soziale Aktivitäten (z.B. Fußballspiele schauen, Essenseinladungen, ins Kino gehen, etc.) mit Freunden aufgrund meines Trainingsplans aus | FI |
| I12. I feel depressed when I miss one or more days of exercise. | 12. Ich fühle mich niedergeschlagen, wenn ich einen oder mehrere Trainingstage verpasse | FI |
| I13. I miss opportunities to meet new people because of my workout schedule. | 13. Ich lasse mir aufgrund meines Trainingsplans Chancen entgehen, neue Menschen kennenzulernen | FI |
Note: DS = drive for size, AI = appearance intolerance, FI = functional impairment
Sample
Participants were recruited through interest groups (fitness, bodybuilding) in social media using Lime Survey (www.limesurvey.org). The survey could be processed on an online platform without entering personal data (anonymously). First, an information page on the aims of the study was presented, followed by questions on socio-demographic data and self-report questionnaires. Inclusion criteria were an age between 18 and 45 years and being physically active: Participants should train at least three times a week in a fitness gym. The study was approved by the local ethics committee (University of Freiburg; No 17/14).
Overall, 394 individuals took part in the survey (for sample description see Table 2).
Table 2. Sample description.
| Variable | Values / metric | M (SD) / % (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | years | 24.3 (5.2) |
| Gender | female | 53% (209) |
| male | 47% (184) | |
| unknown | <1% (1) | |
| Nationality | German | 88.8% (350) |
| Other | 11.2% (44) | |
| Partnership | Yes | 45.5% (180) |
| Education | University | 35.4% (140) |
| Student, in education | 27.8% (110) | |
| Other | 19.7% (78) | |
| Unknown | 17.1% (66) | |
| Occupation | Full time | 31.2% (123) |
| In education | 28.7% (113) | |
| Working part time or occasionally | 19.0% (75) | |
| Unemployed | 1.0% (4) | |
| Other (housewife, retired, disabled, etc.) | 20.1% (79) | |
Instruments
MDDI
The Muscle Dysmorphic Disorder Inventory [22] is a 13 item questionnaire, which showed good internal consistency (total score: α = .81) and good to excellent retest-reliability (r = .87). It was based on the muscle dysmorphia inventory MDI [28], improving this instrument by adding an additional dimension (functional impairment). The items form three subscales (drive for size (DS), appearance intolerance (AI), functional impairment (FI)). Cronbach´s alpha for the subscales was α = .85 for DS, it was α = .77 for AI and α = .80 for FI. Items (see Table 1) can be rated on a five-point Likert scale with responses ranging from 1 (never) to 5 (always). A total score can be derived by the sum of the subscales. A threshold value of > 39 points was proposed [29] and used in a previous study (e.g. [24]).
DKB-35
The Dresden Body Image Inventory [30] is a German questionnaire (self-rating) for the assessment of cognitive as well as affective components of body image. It comprises 35 items and five subscales: Vitality, body- acceptance, self-enhancement, body contact and sexual fulfillment. Construct validity and differential validity were demonstrated as well as retest reliability [31]. Internal consistency varied between Cronbach´s α = .76 and α = .91.
EDS-D
The Exercise Dependence Scale ([12]; German version: [32]) is a self-report instrument with 21 items, which was developed to measure exercise dependence. There are seven subscales, oriented on criteria for addiction (tolerance, withdrawal effects, continuance, lack of control, reduction in other activities, time, intention). The items are rated on a 6-point Likert scale. The EDS showed good validity and internal as well as test-retest reliability [33]. Criteria were defined to distinguish three groups: Individuals “at risk for exercise dependence”, which have a score of 15 or more on at least three subscales, individuals with some symptoms (“nondependent-symptomatic”: showing a score of 7 or more on at least three subscales and not being classified as “at risk”) and a “non-dependent-asymptomatic” group.
Questionnaire on sports behavior [34]
The quantity of exercise was assessed with the German ‘‘Fragebogen zum Sportverhalten” by asking for type of sports activity, frequency (per month) and duration (per episode). For analysis, the minutes of sports activity per week were calculated (physical exercise index).
Data analysis
Confirmatory factor analyses (CFAs, ML estimator) were computed with R (V3.1.4), the lavaan library (V0.5–23.1097), and its embedded procedures (esp. cfa, measurementInvariance). The fit of the factor structure was determined by the criteria of Hu and Bentler [35], where adequate fit is indicated by CFI and TLI > .95, RMSEA < .06 and SRMR < .08. To examine measurement invariance between men and women a multi group CFA was conducted. Measurement invariance between male and female samples was examined by Chi2 and CFI difference statistics. In order to estimate gender specific models, two separate CFAs were computed. The online survey required listwise complete data for all MDDI-Items. One subject did not indicate his/her gender, thus reducing the available N for subgroup analyses by one. Descriptive statistics and difference tests of subsamples were computed with SAS-JMP (V.10).
Results
MDDI scores: Descriptive statistics
There was no significant difference in the MDDI total score when comparing men and women. However, men had significantly higher scores on the scale “drive for size” (DS) compared to women, while women showed significantly higher scores for “appearance intolerance” (AI). See Table 3 for item and factor scores as well as comparisons.
Table 3. Descriptive statistics of items and scores.
| Item/Score | Factor | α ** | All; N = 394 | Male; N = 184 | Female; N = 209 | Wilcox* | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected item total correlation |
M | SD | Min | Max | M | SD | Min | Max | M | SD | Min | Max | P< | ||||
| I01 Body too skinny | DS | .80 | .79 | 2.14 | 1.07 | 1 | 5 | 2.56 | 1.02 | 1 | 5 | 1.78 | 0.98 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I02 Wear losse clothing | AI | .81 | .79 | 2.11 | 1.06 | 1 | 5 | 1.75 | 0.92 | 1 | 5 | 2.42 | 1.08 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I03 Hate my body | AI | .83 | .78 | 2.07 | 1.05 | 1 | 5 | 1.75 | 0.96 | 1 | 5 | 2.35 | 1.04 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I04 Wish to be havier | DS | .81 | .79 | 2.82 | 1.22 | 1 | 5 | 3.37 | 1.10 | 1 | 5 | 2.33 | 1.12 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I05 Chest too small | DS | .82 | .78 | 2.12 | 1.14 | 1 | 5 | 2.53 | 1.09 | 1 | 5 | 1.76 | 1.05 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I06 Legs too thin | DS | .70 | .83 | 1.78 | 1.06 | 1 | 5 | 2.31 | 1.15 | 1 | 5 | 1.31 | 0.72 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I07 Too much body fat | AI | .78 | .81 | 3.45 | 1.18 | 1 | 5 | 3.18 | 1.21 | 1 | 5 | 3.68 | 1.11 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I08 Arms should be stronger | DS | .75 | .81 | 2.73 | 1.20 | 1 | 5 | 3.18 | 1.14 | 1 | 5 | 2.34 | 1.11 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I09 Embarrassed letting people see me | AI | .84 | .76 | 2.23 | 1.24 | 1 | 5 | 1.83 | 1.11 | 1 | 5 | 2.59 | 1.24 | 1 | 5 | .001 | |
| I10 Anxious if not exercising | FI | .77 | .79 | 3.23 | 1.18 | 1 | 5 | 3.14 | 1.22 | 1 | 5 | 3.30 | 1.14 | 1 | 5 | .185 | |
| I11 Cancel social activities | FI | .83 | .77 | 2.56 | 1.05 | 1 | 5 | 2.48 | 1.07 | 1 | 5 | 2.62 | 1.03 | 1 | 5 | .150 | |
| I12 Depressed if not exercising | FI | .80 | .75 | 3.31 | 1.11 | 1 | 5 | 3.22 | 1.16 | 1 | 5 | 3.39 | 1.06 | 1 | 5 | .137 | |
| I13 Not meeting new people | FI | .81 | .76 | 2.33 | 1.09 | 1 | 5 | 2.26 | 1.06 | 1 | 5 | 2.39 | 1.10 | 1 | 5 | .238 | |
| DS Drive for Size | .84 | 11.58 | 4.43 | 5 | 25 | 13.95 | 4.11 | 5 | 25 | 9.53 | 3.58 | 5 | 23 | .001 | |||
| AI Appearance Intolerance | .83 | 9.86 | 3.69 | 4 | 20 | 8.50 | 3.31 | 4 | 20 | 11.03 | 3.61 | 4 | 20 | .001 | |||
| FI Functional Impairment | .81 | 11.39 | 3.54 | 4 | 20 | 11.08 | 3.61 | 4 | 20 | 11.68 | 3.46 | 4 | 20 | .068 | |||
| MDDI TOTAL Score | 32.83 | 7.37 | 14 | 54 | 33.53 | 7.71 | 14 | 54 | 32.25 | 7.01 | 17 | 54 | .062 | ||||
Note: Labels of items are abbreviations; gender: missing data for one case
* Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test for significant difference between genders, all distributions slightly but significantly different from normal distribution
** standardized alphas for items “if item removed”
Scoring keys: DS = I1+I4+I5+I6+I8;AI = I2+I3+I7+I9;FI = I10+I11+I12+I13;TOTAL = DS+AI+FI
Confirmatory factor analysis
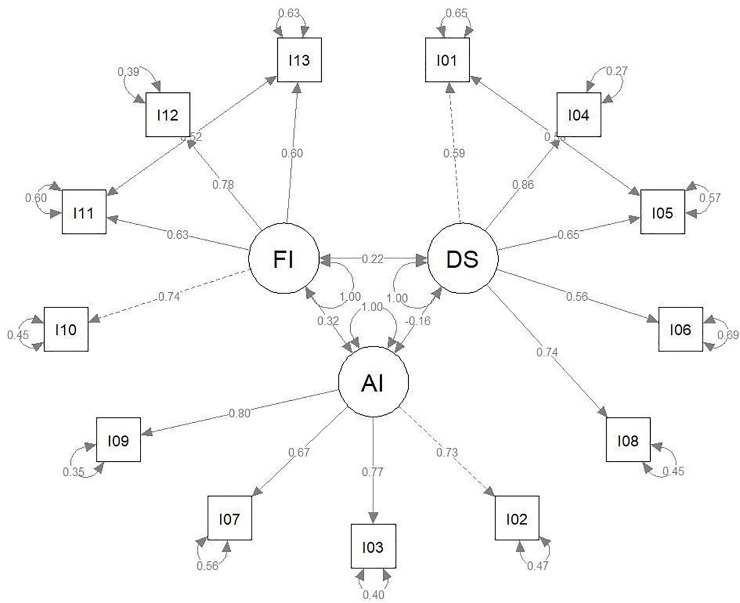
The factorial model for the CFA (ML estimator) relied on the factorization of Hildebrandt et al. [22], which suggests three independent factors (DS, AI, FI). This model yielded insufficient fit indices, where modification indices indicated correlated errors of the Item pairs (I01 = “I think my body is too skinny / slender, I05 = “I find my chest to be too small”; I11 = “I cancel social activities with friends because of my exercise schedule, I13 = “I miss opportunities to meet new people because of my workout schedule”). The final model took care of the error covariance. In both cases the correlated errors occur within one factor. There are no multiple factor loadings or correlated errors between factors. Therefore we evaluated the correlated errors as a minor disturbance of the theoretical model fit (see Fig 1).
Fig 1. R-Code of MDDI factor model.
model.MDDI <—'.+ DS = ~ I01 + I04 + I05 + I06 + I08.+ AI = ~ I02 + I03 + I07 + I09.+ FI = ~ I10 + I11 + I12 + I13.+ DS ~~ AI.+ DS ~~ FI.+ AI ~~ FI.+ I01~~I05.+ I11 ~~ I13'.
The model fitted the data sufficiently well (estimator = ML). The same model was applied to the subsamples of male and female subjects. The model was very similar in both subsamples and the total sample (see Table 3). The Chi2-test was always significant, while CFI, TLI, RMSEA and SRMR indicated good or sufficient fit (CFI, TLI > .95; RMSEA < .06; SRMR < .08). The fit indices of all three models are listed in Table 4. The parameters of the base model including all available cases are shown in Fig 1 and Table 5.
Table 4. Fit indices of the CFA models.
| Sample | Chi2; df; p< | TLI | CFI | RMSEA (CI90) p< | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total sample | 121.8; 60; .001 | .961 | .970 | .051 (.038 | .064) .428 | .048 |
| Male sample | 87.7; 60; .011 | .957 | .967 | .072 (.025 | .072) .478 | .065 |
| Female sample | 89.6; 60; .008 | .960 | .969 | .048 (.25 | .068); .528 | .055 |
Note: criteria of good fit = TLI, CFI > 0.95; RMSEA < 0.06; SRMR < 0.08, Chi2 = n.s.
Table 5. Parameters of the fitted model (whole sample).
| Relation | Est | SE | CI.lower | CI.upper | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | = ~ | I01 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| DS | = ~ | I04 | 1.657 | 0.150 | 1.364 | 1.951 |
| DS | = ~ | I05 | 1.179 | 0.077 | 1.028 | 1.329 |
| DS | = ~ | I06 | 0.939 | 0.107 | 0.729 | 1.148 |
| DS | = ~ | I08 | 1.408 | 0.132 | 1.149 | 1.667 |
| AI | = ~ | I02 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| AI | = ~ | I03 | 1.049 | 0.077 | 0.898 | 1.200 |
| AI | = ~ | I07 | 1.020 | 0.085 | 0.853 | 1.187 |
| AI | = ~ | I09 | 1.289 | 0.092 | 1.108 | 1.469 |
| FI | = ~ | I10 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| FI | = ~ | I11 | 0.764 | 0.073 | 0.621 | 0.907 |
| FI | = ~ | I12 | 0.999 | 0.086 | 0.830 | 1.168 |
| FI | = ~ | I13 | 0.755 | 0.075 | 0.607 | 0.902 |
| DS | ~~ | AI | -0.079 | 0.030 | -0.138 | -0.020 |
| DS | ~~ | FI | 0.120 | 0.036 | 0.049 | 0.191 |
| AI | ~~ | FI | 0.213 | 0.046 | 0.124 | 0.302 |
| I01 | ~~ | I05 | 0.432 | 0.051 | 0.332 | 0.533 |
| I11 | ~~ | I13 | 0.363 | 0.051 | 0.263 | 0.463 |
| I01 | ~~ | I01 | 0.748 | 0.060 | 0.630 | 0.866 |
| I04 | ~~ | I04 | 0.400 | 0.063 | 0.277 | 0.524 |
| I05 | ~~ | I05 | 0.734 | 0.062 | 0.613 | 0.856 |
| I06 | ~~ | I06 | 0.780 | 0.061 | 0.660 | 0.899 |
| I08 | ~~ | I08 | 0.645 | 0.063 | 0.522 | 0.768 |
| I02 | ~~ | I02 | 0.531 | 0.048 | 0.436 | 0.625 |
Note: DS = drive for size, AI = appearance intolerance, FI = functional impairment; NA = not available; CI = confidence interval; p = .95 for CI.lower and CI.upper p = .95; I01 –I13 = item numbers of the MDDI; Est = estimate, SE = standard error
Measurement invariance between male and female samples
Testing the measurement invariance of the three models in a multi group CFA showed a weak invariance, as the loadings were not significantly different (see Table 6, tests of ΔChi2) between the subsamples of male and female subjects. Significant differences were found for intercepts and means.
Table 6. Measurement invariance.
| Fit | Df | AIC | Chi2 | ΔChi2 | Df diff | P< | CFI | ΔCFI | RMSEA | ΔRMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| configural | 122 | 13677 | 235.5 | - | - | - | .937 | - | .069 | - |
| loadings | 132 | 13671 | 249.6 | 14.0 | 10 | .172 | .935 | .002 | .067 | .001 |
| intercepts | 142 | 13683 | 281.7 | 32.1 | 10 | .001 | .923 | .012 | .071 | .003 |
| means | 145 | 13837 | 441.6 | 159.9 | 3 | .001 | .836 | .087 | .102 | .031 |
Note: fit.configural = base model; fit.loadings = testing for differences in factor structure (n.s.); fit.intercepts = testing for differences in item means (sign. gender differences); fit.means = testing for differences in latent variable means.
The incremental change of Chi-Square values and its significance test (see Table 4) show that the loadings are not significantly different for men and women. In other words, the factor structure is invariant. However, the intercepts and means differ significantly. This corresponds to the significant difference found in the factor scores. As already shown above with the item statistics (Table 3), the main differences between male and female subjects were found in the factors appearance intolerance (AI; females > males) and drive for size (DS; males > females).
Reliability
Cronbach´s alpha for the DS subscale was α = .84, Cronbach´s alpha for the AI subscale was α = .83, for the FI subscale it was α = .81 and for the total score Cronbach´s alpha was α = .75.
Individuals “at risk” for muscle dysmorphia
Using a cut-off of > 39, 20.3% of individuals (80/394) were classified as “at risk” for muscle dysmorphia. In the “at risk” group were more men than women (46 vs. 34; Chi2 = 4.602; df = 2; p < .032).
Correlations with body experience (DKB-35) and exercise pathology (EDS)
Results for correlations with the EDS-D total score are shown in Table 7, correlations with DKB-35 scales in Table 8. The EDS-D total score showed significant correlations with all MDDI scales (small correlations according to Cohen r < .3 for associations with drive for size (DS) and appearance intolerance (AI), large correlations (r > .5) with functional impairment (FI) and the total score).
Table 7. Correlations of MDDI factors with the EDS-D total score.
| ID | Variable | N | M | SD | [1] | [2] | [3] | [4] | [5] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | MDDI_DriveForSize | 394 | 11.58 | 4.43 | 1 | - .14 | .20 | .63 | .13 |
| [2] | MDDI_AppearanceIntolerance | 394 | 9.86 | 3.69 | 1 | .26 | .54 | .27 | |
| [3] | MDDI_FunctonalImpairment | 394 | 11.39 | 3.54 | 1 | .73 | .63 | ||
| [4] | MDDI_Total | 394 | 32.83 | 7.37 | 1 | .52 | |||
| [5] | EDS_Total | 352 | 3.08 | 0.80 | 1 |
Note: All correlations sign., p < .05; Pearson Corr. Coefficients.
Table 8. Correlations of MDDI factors with the DKB-35 scales.
| Variable | M | SD | MDDI DS | MDDI AI | MDDI FI | MDDI Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DKB35_1Vitality | 3.88 | 0.53 | -.05 | -.48 | -.02 | -.28 |
| DKB35_2BodyAcceptance | 2.23 | 0.59 | .08 | -.83 | -.24 | -.49 |
| DKB35_3SexualFulfillment | 2.70 | 0.86 | -.02 | -.36 | -.21 | -.29 |
| DKB35_4SelfEnhancement | 2.24 | 0.58 | .05 | -.34 | .03 | -.13 |
| DKB35_5BodyContact | 3.78 | 0.72 | -.03 | -.35 | -.21 | -.29 |
Note: All correlations with p < .05 in bold letters; N = 370
The appearance intolerance (AI) subscale and all scales of the DKB-35 correlated negatively and significantly (medium to large r). Functional impairment (FI) correlated negatively with body acceptance, body contact and sexual fulfillment (small r). There was no association between the drive for size (DS) subscale and the DKB-35 scales.
MDDI scores and risk for exercise dependence
32 individuals were classified “at risk for exercise dependence”, 189 as “non-dependent-asymptomatic” and 131 as “non-dependent symptomatic”. The “at risk for exercise dependence” group showed significantly higher values for appearance intolerance (AI) (F = 6.387; df = 2; p < .002), functional impairment (FI) (F = 44.727; df = 2; p < .001) as well as the MDDI total score (F = 24.565; df = 2; p < .001). However, there was no significant difference in drive for size (DS) scores between groups.
Discussion
We were able to replicate the factor structure of the MDDI in the German version, independent of gender. The model fit is slightly impaired by unexplained correlations of the errors of two pairs of items and a significant Chi2-Test, but overall, the limitations are minor and acceptable for a translation and application of the test in another country. However, the invariance of the MDDI factors between genders is only given for the configuration and loadings of the items, not for item means and factor means. This is consistent with the expectation to find different patterns of symptomatology between men and women: According to our hypothesis, men showed a stronger wish for muscularity, while women had more difficulties with tolerating their appearance (hating their body, feeling to have too much body fat and wanting to hide their body). Both aspects were also differentially associated with functional impairment: Appearance intolerance was more relevant for functional impairment in women, while a drive for muscularity was in men. The result is in line with previous findings that men show a stronger drive for muscularity, while women are more preoccupied with thinness [17,36].
Internal consistency was comparable to the original version (Cronbach´s alpha between α = .80 and α = .85), with only a slightly lower level for the appearance intolerance subscale (AI; α = .77). A lower level of internal consistency for the AI subscale was also found in the Italian version.
In our study women and men did not differ in functional impairment and showed a similar total score of the MDDI. However, when using the cut-off of > 39 points, more men (25% vs. 16%) were classified “at risk” than females. Longobardi et al. [24] found a comparable percentage of 25% to be “at risk” for MD in an online survey for validating the MDDI in Italy (male sample). Although the higher prevalence of MD in males is in line with previous research, it seems more important to mention the relatively high percentage of women that were classified “at risk” for MD in our study, although we cannot rule out that this finding is due to an overlap with features of an eating disorder and general body dissatisfaction.
Overall, we think there is the need for further studies on prevalence rates of MD in different samples (athletes, females, community samples), combining screening instruments and clinical interviews. Furthermore, more research is necessary to clarify the relevance of this disturbance for women. This is also important before the background of a change in body ideals: A more athletic and muscular ideal seem to play an increasing role in media-transported ideals for women [37].
We found that the MDDI total score was significantly correlated with the total score of the EDS (exercise dependence). Additionally, the subgroup that was classified “at risk for exercise dependence” showed the highest MDDI total scores, which can be considered an indicator for convergent validity. The correlation between the MDDI and the EDS total score was mainly due to high correlations with the subscale functional impairment. The items of the functional impairment subscale address aspects that coincide with central criteria for exercise dependence: Feeling depressed or anxious when missing exercise sessions, canceling social activities or missing opportunities to meet new people because of exercising. This replicates previous findings that exercise pathology is a key symptom of MD. However, small (although significant) correlations with the two other MDDI-Scores (appearance intolerance, drive for size) also point to differences between both conditions.
In terms of the relationship with dimensions of body experience, appearance intolerance showed a large correlation with low body acceptance. Furthermore, appearance intolerance was associated with difficulties in body contact, less sexual fulfillment and less vitality. These dimensions were also associated with functional impairment. Overall, the findings show that MD is associated with impairments in body experience that can be considered highly relevant for satisfying relationships and a positive sense of self, replicating a previous finding [7]. However, it is unclear if MD leads to difficulties with body contact and sexuality, or if the attempt to attain a powerful body is an attempt to compensate for feelings of inadequacy, vulnerability and a negative self-concept. The latter would be supported by a study of Fabris et al. [38], who found an association between a risk for MD and more insecure (especially avoidant) attachment styles. Insecure attachment styles are characterized by more negative models of self and others, caused by early developmental experiences [39].
One result did not correspond to our assumptions. For the drive for size scale (DS) we found only a small correlation with exercise dependence (EDS total score) and no significant correlations with different dimensions of body experience (DKB-35 scales: vitality, body acceptance, sexual fulfillment, self-enhancement and body contact). This finding is difficult to explain and seems not due to overall low scores on this scale (in our study it was M (mean) = 14.0 for men; in a study including male competing body-builders it was M = 15.4, while the score was M = 10.0 for not competing males [25]; in another study the score was M = 20.6 in males with MD and 10.6 in males with anorexia nervosa [40]). One possible explanation could be that an urge for muscularity alone is not necessarily a sign of psychopathology. This might only be the case if it is accompanied by a body image disturbance and excessive training.
In summary, the strength of this study on MD is to include both genders and a larger sample. A further strength is to address the relationship between MD symptoms and positive dimensions of body experience as well as the relationship to exercise dependence. A main limitation is that we did not include a measure of eating pathology (however, instruments had to be restricted to assure compliance with an online-survey). Since it was a self-report online-survey, we cannot reliably estimate the percentage of individuals with a clinically relevant MD (structured interviews would have been necessary to address this question). Furthermore, there the risk for a selection bias in a self-selected internet survey.
Overall, the German version of the MDDI can be considered an instrument that can be used in male as well as female samples to assess symptoms of muscle dysmorphia in German speaking countries. However, as the MDDI is a self-report tool, no diagnosis can be derived. For such a purpose, it has to be combined with a clinical interview.
Future studies should address test-retest-reliability to analyze temporal stability of the tool as well as the question of cut-off scores and norms for different samples (males, females, community samples and risk groups), which are relevant to identify individuals in need for further clinical assessment and treatment.
Acknowledgments
The article processing charge was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the University of Freiburg in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Data Availability
All our data are contained within the paper.
Funding Statement
The article processing charge was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the University of Freiburg in the funding program Open Access Publishing (see Acknowledgments). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Pope HG, Katz DL, Hudson JI. Anorexia nervosa and “reverse anorexia” among 108 male bodybuilders. Compr Psychiatry. 1993;34: 406–409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cunningham M, Griffiths S, Mitchison D, M Mond J, Castle D, Murray S. Muscle Dysmorphia: An Overview of Clinical Features and Treatment Options. J Cogn Psychother. 2017;31 10.1891/0889-8391.31.3.158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pope HG, Gruber AJ, Choi P, Olivardia R, Phillips KA. Muscle Dysmorphia: An Underrecognized Form of Body Dysmorphic Disorder. Psychosomatics. 1997;38: 548–557. 10.1016/S0033-3182(97)71400-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Olivardia R, Pope HG, Hudson JI. Muscle dysmorphia in male weightlifters: a case-control study. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157: 1291–1296. 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.8.1291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hildebrandt T, Schlundt D, Langenbucher J, Chung T. Presence of muscle dysmorphia symptomology among male weightlifters. Compr Psychiatry. 2006;47: 127–135. 10.1016/j.comppsych.2005.06.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Murray SB, Nagata JM, Griffiths S, Calzo JP, Brown TA, Mitchison D, et al. The enigma of male eating disorders: A critical review and synthesis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2017;57: 1–11. 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Olivardia R, Pope HG, Hudson JI. Muscle dysmorphia in male weightlifters: a case-control study. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157: 1291–1296. 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.8.1291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.American Psychiatric Association [APA]. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition: DSM 5. Arlington, VA, US: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 9.dos Santos Filho CA, Tirico PP, Stefano SC, Touyz SW, Claudino AM. Systematic review of the diagnostic category muscle dysmorphia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016;50: 322–333. 10.1177/0004867415614106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Foster AC, Shorter GW, Griffiths MD. Muscle dysmorphia: could it be classified as an addiction to body image? J Behav Addict. 2015;4: 1–5. 10.1556/JBA.3.2014.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hildebrandt T, Alfano L, Langenbucher JW. Body image disturbance in 1000 male appearance and performance enhancing drug users. J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44: 841–846. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.01.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hausenblas H, Symons Downs D. How much is too much? The development and validation of the exercise dependence scale. Psychology & Health. 2002;17: 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mitchison D, Mond J. Epidemiology of eating disorders, eating disordered behaviour, and body image disturbance in males: a narrative review. J Eat Disord. 2015;3 10.1186/s40337-015-0058-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bentley C, Gratwick-Sarll K, Harrison C, Mond J. Sex differences in psychosocial impairment associated with eating disorder features in adolescents: A school-based study: Adolescent Sex Differences in ED Impairment. Int J Eat Disord. 2015;48: 633–640. 10.1002/eat.22396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Karazsia BT, Crowther JH. Social body comparison and internalization: mediators of social influences on men’s muscularity-oriented body dissatisfaction. Body Image. 2009;6: 105–112. 10.1016/j.bodyim.2008.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schneider C, Rollitz L, Voracek M, Hennig-Fast K. Biological, Psychological, and Sociocultural Factors Contributing to the Drive for Muscularity in Weight-Training Men. Front Psychol. 2016;7 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McCreary DR, Sasse DK. An Exploration of the Drive for Muscularity in Adolescent Boys and Girls. J Am Coll Health. 2000;48: 297–304. 10.1080/07448480009596271 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bo S, Zoccali R, Ponzo V, Soldati L, De Carli L, Benso A, et al. University courses, eating problems and muscle dysmorphia: are there any associations? J Transl Med. 2014;12 10.1186/1479-5876-12-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Compte EJ, Sepulveda AR, Torrente F. A two-stage epidemiological study of eating disorders and muscle dysmorphia in male university students in Buenos Aires. Int J Eat Disord. 2015;48: 1092–1101. 10.1002/eat.22448 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hitzeroth V, Wessels C, Zungu-Dirwayi N, Oosthuizen P, Stein DJ. Muscle dysmorphia: a South African sample. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;55: 521–523. 10.1046/j.1440-1819.2001.00899.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chaba L, d’Arripe-Longueville F, Lentillon-Kaestner V, Scoffier-Mériaux S. Adaptation and validation of a short French version of the Drive for Muscularity Scale in male athletes (DMS-FR). PLoS ONE. 2018;13: e0196608 10.1371/journal.pone.0196608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hildebrandt T, Langenbucher J, Schlundt DG. Muscularity concerns among men: development of attitudinal and perceptual measures. Body Image. 2004;1: 169–181. 10.1016/j.bodyim.2004.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mitchell L, Murray SB, Cobley S, Hackett D, Gifford J, Capling L, et al. Muscle Dysmorphia Symptomatology and Associated Psychological Features in Bodybuilders and Non-Bodybuilder Resistance Trainers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017;47: 233–259. 10.1007/s40279-016-0564-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Longobardi C, Prino LE, Fabris MA, Settanni M. Muscle dysmorphia and psychopathology: Findings from an Italian sample of male bodybuilders. Psychiatry Res. 2017;256: 231–236. 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.06.065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Santarnecchi E, Dèttore D. Muscle dysmorphia in different degrees of bodybuilding activities: Validation of the Italian version of Muscle Dysmorphia Disorder Inventory and Bodybuilder Image Grid. Body Image. 2012;9: 396–403. 10.1016/j.bodyim.2012.03.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hambleton R, de Jong J. Advances in translating and adapting educational ans psychological tests. Language Testing, Advances in translating and adapting educational and psychological tests. 2003; 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schmitt M, Eid M. Richtlinien für die Übersetzung fremdsprachiger Messinstrumente. Diagnostica. 2007; 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schlundt DG, Woodford H, Brownlee A. Muscle dysmorphia in male weightlifters: Psychological characteristics and practices. Unpublished manuscript; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Varangis E, Folberth W, Hildebrandt T, Langenbucher J. Confirmatory factor analysis for the Muscle Dysmorphic Disorder Inventory among male appearance and performance enhancing drug users. International Conference on Eatig Disorders, Austin (poster ID 3793); 2007.
- 30.Pöhlmann K, Roth M, Brähler E, Joraschky P. Der Dresdner Körperbildfragebogen (DKB-35): Validierung auf der Basis einer klinischen Stichprobe. Psychother Med Psychol. 2013;64: 93–100. 10.1055/s-0033-1351276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Matthes J, Franke GH, Jäger S. Psychometric analysis of the “Dresdner Körperbildfragebogen” (DKB-35) in a non-clinical sample. Z Med Psychol. 2012;21: 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zeeck A, Leonhart R, Mosebach N, Schlegel S, Linster H-W, Hartmann A. Psychopathologische Aspekte von Sport: Eine deutsche Adaptation der “Exercise Dependence Scale” (EDS-R). Zeitschrift für Sportpsychologie. 2013;20: 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Symons Downs D, Hausenblas H, Nigg CR. Factorial validity and psychometric examination of the Exercise Dependence Scale—Revised. Measurement in Physical Education and Exercise Sciences. 2004;8: 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fuchs R. Fragebogen zur Erfassung der sportlichen Aktivität [questionnaire on sports behavior] Unpublished project report. Institute of sport and sport sciences, University of Freiburg, Germany; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hu L, Bentler P. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal. 1999;6: 1–55. 10.1080/10705519909540118 [Google Scholar]
- 36.McCreary DR, Sasse D, Saucier D, Dorsch KD. Measuring the drive for muscularity: Factorial validity of the Drive for Muscularity Scale in Men and Women. Psychology of Men & Masculinity. 2004;5: 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Boepple L, Ata RN, Rum R, Thompson JK. Strong is the new skinny: A content analysis of fitspiration websites. Body Image. 2016;17: 132–135. 10.1016/j.bodyim.2016.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fabris M, Longobardi C, Prino L, Settani M. Attachment style and risk of muscle dysmorphia in a sample of male body builders. Psychology of Men & Masculinity. 2018;19: 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mikulincer M, Shaver PR. An attachment perspective on psychopathology. World Psychiatry. 2012;11: 11–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Murray SB, Rieger E, Hildebrandt T, Karlov L, Russell J, Boon E, et al. A comparison of eating, exercise, shape, and weight related symptomatology in males with muscle dysmorphia and anorexia nervosa. Body Image. 2012;9: 193–200. 10.1016/j.bodyim.2012.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All our data are contained within the paper.