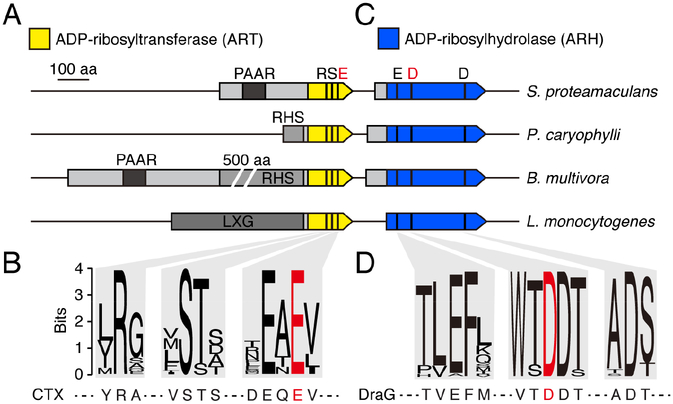
Figure 1.
Proteins sharing conserved motifs with ART and ARH proteins are associated with interbacterial toxin delivery pathways. (A) and (C) Scaled depiction of representative genomic loci from the indicated species (Serratia proteamaculans, Pseudomonas caryophylli, Burkholderia mutltivora, Listeria monocytogenes) encoding predicted ART (yellow) and ARH (blue) domain-containing proteins. Regions encoding N-terminal domains of T6SS (PAAR, RHS) and Esx system (LXG) substrates shaded in grey. Black bars designate location of bases encoding the noted residues conserved in ART and ARH proteins; residues targeted for mutagenesis in this study depicted in red. (B) and (D) Sequence logos generated from alignments of ART (B) and ARH (D) family proteins associated with bacterial contact dependent antagonism pathways (locus tag numbers for genes encoding sequences used provided in Table S1). Sequences from characterized ART (CTX toxin) and ARH (DraG) shown below for reference. See also Table S1.