Abstract
Background and Purpose
3′‐Sialyllactose (3′‐SL) is a safe compound that is present in high levels in human milk. Although it has anti‐inflammatory properties and supports immune homeostasis, its effect on collagen‐induced arthritis (CIA) is unknown. In this study, we investigated the prophylactic and therapeutic effect of 3′‐SL on the progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in in vitro and in vivo models.
Experimental Approach
The anti‐arthritic effect of 3′‐SL was analysed with fibroblast‐like synoviocytes in vitro and an in vivo mouse model of CIA. RT‐PCR, Western blotting and ELISA were performed to evaluate its effects in vitro. Histological analysis of ankle and knee joints of mice with CIA was performed using immunohistochemistry, as well as safranin‐O and haematoxylin staining.
Key Results
3′‐SL markedly alleviated the severity of CIA in the mice by reducing paw swelling, clinical scores, incidence rate, serum levels of inflammatory cytokines and autoantibody production. Moreover, 3′‐SL reduced synovitis and pannus formation and suppressed cartilage destruction by blocking secretion of chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix_metalloproteinases and osteoclastogenesis via NF‐κB signalling. Notably, phosphorylation of p65, which is a key protein in the NF‐κB signalling pathway, was totally blocked by 3′‐SL in the RA models.
Conclusions and Implications
3′‐SL ameliorated pathogenesis of CIA by suppressing catabolic factor expression, proliferation of inflammatory immune cells and osteoclastogenesis. These effects were mediated via blockade of the NF‐κB signalling pathway. Therefore, 3′‐SL exerted prophylactic and therapeutic effects and could be a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment of RA.
Abbreviations
- 3′‐SL
3′‐sialyllactose
- CCL
chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand
- CIA
collagen‐induced arthritis
- CII
type II collagen
- CXCL
chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand
- FLS
fibroblast‐like synoviocytes
- MMP
- pp65
phosphorylated p65
- qRT‐PCR
quantitative RT‐PCR
- RA
rheumatoid arthritis
- WST‐1
2‐(4‐iodophenyl)‐3‐(4‐nitrophenyl)‐5‐(2,4‐disulfophenyl)‐2H‐tetrazolium
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disease. Although RA pathogenesis is not fully elucidated, synovial hyperplasia, pannus formation, inflammation, infiltration of various inflammatory cells and cartilage destruction are known to be involved because of dysfunction of fibroblast‐like synoviocytes (FLS), T lymphocytes and other immune cells such as B cells, monocytes and neutrophils (Noss and Brenner, 2008; Shi and Pamer, 2014; Roberts et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2017). Especially, FLS from the intimal lining are considered major effectors of cartilage destruction in RA based on their ability to produce large amounts of degradative enzymes (Bartok and Firestein, 2010). Among heterogeneous FLS, PDPN+CD34−THY1+ fibroblasts contribute to initiation, propagation and maintenance of chronic inflammation through the promotion of osteogenesis and secretion of pro‐inflammatory cytokines, for example (Mizoguchi et al., 2018).
Chemokines secreted by FLS are involved in immune cell recruitment to inflammatory sites and induction of inflammation in synovial tissues (Smith et al., 2008; McGettrick et al., 2009; Bartok and Firestein, 2010) and the CC and CXC chemokine families are the most studied (Shadidi et al., 2003; Szekanecz et al., 2010). In addition, excessive production of inflammatory cytokines (e.g. http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4974, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4998, IL‐17 and TNF‐α) plays a key role in joint damage through cartilage matrix degradation and inflammation during RA pathogenesis (Choy, 2012). Exposure to IL‐1β and TNF‐α rapidly induces expression of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix_metalloproteinase (MMP) and http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=1376 for cartilage degradation and inflammation through an NF‐κB‐dependent pathway in cultured FLS and collagen‐induced arthritis models (Lee et al., 2013; Calabrese and Rose‐John, 2014; Ryu et al., 2014). Cartilage destruction involves not only inflammatory cytokine‐induced MMP and COX2 expression but also autoantibody production and osteoclastogenic regulation (Tanaka, 2013). Interestingly, overall autoantibody production that involves B cell activation and differentiation is also controlled by the NF‐κB pathway (Gerondakis and Siebenlist, 2010). Furthermore, NF‐κB signalling regulates cytokine‐mediated osteoclast formation and activation during RA development (Boyce et al., 2015).
Previous reports collectively suggested that NF‐κB is mainly involved in RA pathogenesis and directly regulates the expression of various chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, autoantibody production and regulation of osteoclastogenesis in RA pathogenesis (Simmonds and Foxwell, 2008). Although currently developed anti‐arthritic drugs that target NF‐κB have serious gastrointestinal side effects (Quan et al., 2008), NF‐κB is still a good target in the development of new therapeutic agents against RA because disease progression can be slowed and joint damage can be prevented (Roman‐Blas and Jimenez, 2006). The ideal therapeutic agent should inhibit NF‐κB activation, while avoiding the gastrointestinal problems.
The oligosaccharide, 3′‐sialyllactose (3′‐SL), consists of N‐acetylneuraminic acid linked to the galactosyl subunit of lactose (Luo et al., 2014) and is found abundantly in human milk. This compound exhibits anti‐inflammatory properties and supports immune homeostasis (Donovan and Comstock, 2016). Although RA is an inflammatory disease, the effect of 3′‐SL on RA is unknown. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess the anti‐arthritic effects of 3′‐SL and the underlying mechanism(s). We also investigated whether 3′‐SL has prophylactic and therapeutic potential as a novel treatment for RA, due to its inhibitory effect on NF‐κB.
Methods
Animals
All animal care and experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Ajou (protocol number 2016‐0041) and complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, which was published by the US National Institutes of Health. Animal studies are reported in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines (Kilkenny et al., 2010; McGrath and Lilley, 2015). DBA/1 (Shizuoka, Japan) and C57BL/6 (DBL Co., Ltd., Chungbuk, Korea) male mice (8 weeks old) weighing 18–20 g were housed (4 per cage) under controlled temperatures (23°C) and were exposed to a 12 h light/dark cycle. Food and water were provided ad libitum.
Culture of FLS and immune cells
Human RA‐FLS were purchased from Cell Applications, Inc. and cultured with synoviocyte growth medium (Cell Applications, Inc.). The individual bones of 8‐week‐old male C57BL/6 (DBL Co., Ltd.) knee joints were isolated by dissection to expose the joint synovial tissue. Dissected bones, including synovial tissue, were chopped and incubated with 1 mg·kg−1 of collagenase Type I in DMEM for 4 h at 37°C. The mixture was filtered through a 70 mm mesh strainer and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U·mL−1 penicillin, and 100 μg·mL−1 streptomycin overnight. Non‐adherent cells were removed, and adherent cells were trypsinized for 2 min and split at a ratio of 1:3 after reaching 80% confluence. Cell passaging was continued in the same way. CD90.2+ FLS were cultured at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2. The medium was replaced with fresh medium every 3 days. CD90.2+ FLS were used from passage eight in these experiments. Jurkat T cells (ATCC‐TIB‐152) and THP‐1 cells (ATCC‐TIB‐202) were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat‐inactivated FBS, penicillin G (100 IU·mL−1), streptomycin (100 μg·mL−1) and l‐glutamine (2 mM) and were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 and 95% air.
FACS analysis
To identify pure CD90.2+ FLS, flow cytometry was performed using anti‐CD90.2 (140 303; BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA), and anti‐CD14 (123 309; BioLegend) antibodies, after eight passages (>95% CD90.2 and <1% CD14). Proliferation of B cell populations in spleens was analysed with FITC‐conjugated anti‐B220 (103 211; BioLegend) and phycoerythrin (PE)‐conjugated anti‐CD19 (115 507, BioLegend) antibodies. To identify the proliferation of FLS, macrophages and neutrophils, collagen‐induced arthritis mice were given BrdU (10 mg·kg−1; i.p.) 2 days before analysis. Isolated cells from knees and ankles were stained with anti‐CD90.2, anti‐CD68 (137 014; BioLegend), PE‐anti CD11b (101 208; BioLegend), anti‐Ly6G (127 606; BioLegend) and APC‐anti‐BrdU (339 080; BioLegend). Apoptosis of FLS, macrophages and neutrophils was analysed using an FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection kit (640 922; Biolegend) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
In vitro osteoclastogenesis
Total bone marrow cells were isolated from femurs and tibias of 7‐week‐old Balb/c male mice (DBL Co., Ltd.) by flushing the bone marrow cavity with α‐MEM containing 100 U·mL−1 penicillin, and 100 μg·mL−1 streptomycin. Red blood cells were removed using ACK lysing buffer (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) at room temperature for 1 min. The cells were cultured in α‐MEM supplemented with penicillin/streptomycin and 10% FBS and were stimulated with http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4905 (100 ng·mL−1) (Sigma‐Aldrich) for 3 days. Adherent cells were collected and seeded in 24‐well plates at 2 × 105 cells per well. These macrophage‐like osteoclast precursor cells were stimulated with receptor activator of NF‐κB ligand (RANKL) (100 ng·mL−1) (Sigma‐Aldrich) for 6 days. The medium was changed every 2 days.
Analysis of tartrate‐resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and TRAP activity
Isolated macrophage‐like osteoclast precursor cells were cultured in 24‐well plates with α‐MEM containing 10% FBS, penicillin/streptomycin and http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=5066, in the absence or presence of 3′‐SL and methotrexate (MTX). After 6 days, the cells were washed with PBS and lysed. Whole cell lysate (50 μg protein) was used for measurement of TRAP activity using the TRACP & ALP Assay Kit (TaKaRa Bio, Shiga, Japan). Absorbance was measured at 405 nm using an ELISA microplate reader (VICTOR X3; PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). TRAP staining was performed using the Acid Phosphatase, Leukocyte (TRAP) Kit (Sigma‐Aldrich). In brief, cells were washed with PBS, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min and stained with TRAP staining solution for 1 h in the dark. TRAP‐positive cells were analysed using light microscopy.
FLS viability analysis
CD90.2+ FLS were seeded in 96‐well dishes (9 × 103 cells per well) for 48 h prior to the addition of 3′‐SL at various concentrations (10, 50, 100 and 250 μM). The cells were then incubated for 24 h in DMEM without FBS. Cytotoxicity was analysed using the EZ‐CyTox Cell viability assay kit (DoGen, Seoul, South Korea) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 2‐(4‐iodophenyl)‐3‐(4‐nitrophenyl)‐5‐(2,4‐disulphophenyl)‐2H‐tetrazolium (WST‐1) solution mixed with serum‐free DMEM (1:100, v·v−1) was added to the cultured cells for 3 h, after which viability was measured using a microplate reader (VICTOR X3; PerkinElmer) at 450 nm.
RT‐PCR and quantitative (q)RT‐PCR
Total RNA was isolated from mouse CD90.2+ FLS using TRIzol (Molecular Research Center Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA). Isolated total RNA was reverse‐transcribed, and the resulting cDNA was amplified by PCR (Intron Biotechnology, Gyeonggi‐do, South Korea). PCR primers for Mmps, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines are summarized in Supporting Information Table S1. Transcript levels of target genes were quantified by qRT‐PCR using SYBR® premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa Bio). For each target gene, transcript levels were normalised to those of GAPDH and expressed as fold changes relative to the indicated controls.
Western blotting
Total proteins were extracted using lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 1% NP‐40, 50 mM Tris pH 8.0, 0.2% SDS and 5 mM NaF) supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Madison, WI, USA). http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=1630 and http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=6656 were detected after trichloroacetic acid precipitation, as previously described (Ryu et al., 2014). Each protein was visualized using SuperSignal West Dura (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Western blot analysis was performed using the following antibodies: mouse anti‐p65 (8342; Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA), mouse anti‐phosphorylated p65 (pp65) (3033; Cell Signaling Technology), and mouse anti‐β‐actin (LF‐PA0207; Abfrontier, Seoul, Korea).
Reporter gene assay
NF‐κB reporter gene constructs (1.0 μg) and β‐galactosidase vector (0.1 μg) were transfected into mouse CD90.2+ FLS using Lipofectamine® Plus (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) as previously described (Ueberla et al., 1993). The transfected cells were cultured in complete medium for 24 h. Luciferase activity was determined using an assay kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and subsequently normalized to β‐galactosidase activity measured at 420 nm by an ELISA microplate reader (VICTOR X3; PerkinElmer).
Collagen‐induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model and gavage
Experimental RA was induced in 8‐week‐old male DBA/1 mice (n = 56). Before CIA induction, all mice were anaesthetized with 100 mg·kg−1 ketamine and 5 mg·kg−1 xylazine by i.p. injection, according to Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. The mice were then s.c. injected with complete Freund's adjuvant (Chondrex, Inc, Redmond, WA, USA) only (control, n = 8) or complete Freund's adjuvant containing 100 mg of collagen type II (Chondrex, Inc.) at the tail base. On day 21 after the first boost, a second boost was administered by s.c. injection of type II collagen emulsified 1:1 (v·v−1) with incomplete Freud's adjuvant (Chondrex, Inc.), and the mice were maintained for an additional 2 weeks. The incidence and severity of RA were assessed every 2 days after the second immunization. The mice with RA were given 3′‐SL (100 mg·kg−1; n = 8 or 500 mg·kg−1; n = 8), PBS (1 mL; n = 8), lactose (250 mg·kg−1; n = 8), sialic acid (250 mg·kg−1; n = 8) or MTX (1 mg·kg−1; n = 8), by gavage at 2 day intervals for 4 weeks for prophylactic effects and 2 weeks for therapeutic effects. The animals were killed by CO2 inhalation 48 days after the first boost.
ELISA
To compare the cytokine levels between the arthritic control and oral feeding groups, blood samples were collected from mice at 21 and 48 days after the first immunization and stored at −80°C until analysis. Serum levels of IL‐1β, TNF‐α and IL‐6 at 48 days were measured using an ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul, South Korea) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Total autoantibody concentrations in serum at 21 and 48 days were determined using another ELISA kit (ILC Lab., Portland, OR, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Each serum sample was assessed by comparing to a standard curve. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using an ELISA microplate reader (VICTOR X3; PerkinElmer).
Evaluation of synovitis, pannus formation and arthritis
We used clinical scores (0–4) based on the degree of inflammation, as previously described, to evaluate RA severity (Ryu et al., 2014). The ankle and knee joints of the mice were fixed in paraformaldehyde and then decalcified for 2 weeks. Samples were embedded in paraffin and sectioned (5 μm thick). To evaluate severity, we used clinical scoring (0–3), according to the following criteria: 0 = normal, 1 = oedema or swelling of one joint, 2 = swelling of two or more joints and 3 = swelling of all joints or deformity. The scores of four limbs were added together to obtain the clinical index (maximum score = 12). Synovitis and pannus formation were scored (0–4) after haematoxylin staining, with or without safranin‐O staining of cartilage, as previously described (Ryu et al., 2014). Cartilage destruction was determined by safranin‐O staining and scored using Mankin's method. Ankle diameters were measured for paw swelling with a digital Vernier calliper (Mitutoyo, Kawasaki, Japan).
Immunohistochemical analysis
Mouse joint and knee tissues were sectioned into 5 μm thick samples. Antigen retrieval was performed by incubating the section with 0.1% trypsin for 40 min at 37°C or with citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 20 min at 95°C. Anti‐CD90.2 (140 301; BioLegend), anti‐CCL2 (ab25124, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), anti‐ CXCL1 (LS‐B13384; LifeSpan BioSciences, Inc. Seattle, WA, USA), anti‐IL‐6 (ab9324, Abcam), anti‐COX2 (SC‐1745, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), anti‐MMP3 (ab52915, Abcam), anti‐MMP13 (ab51072, Abcam), anti‐elastase (Ab21593, Abcam), anti‐CD68 (ab31630, Abcam), anti‐pp65 (3033, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti‐cleaved caspase 3 (9664s, Cell Signaling Technology) were used in the analysis. All immunohistochemistry signals were quantified by ImageJ software v1.60 (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Collagenase activity assay and PGE2 assay
CD90.2+ FLS were seeded in 6‐well dishes (2 × 105 cells per well) for 24 h prior to adding 3′‐SL at various concentrations. The cells were incubated for 24 h in DMEM without FBS. Culture medium was collected and equal volumes were concentrated using Viva® spin columns (Sartorius Stedim Biotech, Goettingen, Germany) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Concentrated samples were assayed for total collagenase activity using EnzCheck Gelatinase/Collagenase Assay kits (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA). Collagenase activity was measured as fluorescent signals using a VICTOR X3 microplate reader (PerkinElmer) at Ex/Em = 495/515 nm. http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=1883 production was assessed using PGE2 immunoassay kits (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Briefly, CD90.2+ FLS were seeded in 6‐well plates (2 × 105 cells per well). The levels of secreted and cellular PGE2 were quantified in total cell lysates by absorbance at 560 nm, according to the manufacturer's protocol.
LC–MS experiments
The samples were injected into an ultra‐performance LC ethylene bridged hybrid amide column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm particle size, Waters) equilibrated with 0.1% (v·v−1) ammonia solution (solvent A) and eluted with a gradient of 0.1% (v·v−1) ammonia in acetonitrile (solvent B) at a flow rate of 0.3 mL·min−1 for 10 min. Gradient conditions were 0.0–3.0 min, 10–25% (A); 3.0–8.0 min, 25–40% (A); 8.0–8.1 min, 40–10% (A); and 8.1–10.0 min, 10% (A). The injection volume was 1 μL. The column was maintained at 30°C, and samples were kept at 4°C. Eluents were analysed by quadrupole time‐of‐flight/MS in electrospray ionization‐negative mode. Instrument parameters were set as follows: sheath gas temperature: 350°C, sheath gas flow: 11 L·min−1, nebulizer: 40 psig, dry gas temperature: 250°C and dry gas flow: 12 L·min−1. The fragmentor was operated at 120°C. MS scan data were collected at 1 spectrum/s from 50–1000 m/z. All MS scan data were collected with MassHunter Data Acquisition Version B.06.01 (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA).
Data and statistical analysis
The data and statistical analysis comply with the recommendations on experimental design and analysis in pharmacology (Curtis et al., 2018). Data are presented as means ± SEM. All the histology samples were scored blindly and independently by two investigators. Each experiment was conducted independently at least five times. Data were analysed by one‐way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc multiple comparison tests or two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni posthoc tests. Statistical analyses were performed with PRISM 5 software and significance was accepted when P ≤ 0.05.
Materials
3′‐SL and recombinant proteins (IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17 and TNF‐α) were purchased from GeneChem Inc. (Daejeon, South Korea) and GenScript (Piscataway, NJ, USA) respectively. All reagents were dissolved in sterilized water prior to use. Human RA‐FLS (Cell Applications, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) and mouse CD90.2+ FLS were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1), IL‐6 (50 ng·mL−1), IL‐17 (10 ng·mL−1), TNF‐α (50 ng·mL−1) and 3′‐SL (50, 100 or 250 μM) for 24 h before they were harvested. http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4815, lactose, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4644, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=5019, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=2341 and A23187 were purchased from Sigma‐Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Nomenclature of targets and ligands
Key protein targets and ligands in this article are hyperlinked to corresponding entries in http://www.guidetopharmacology.org, the common portal for data from the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY (Harding et al., 2018), and are permanently archived in the Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/18 (Alexander et al., 2017).
Results
3′‐SL shows both prophylactic and therapeutic effects on CIA progression
To evaluate both prophylactic and therapeutic effects of 3′‐SL in CIA progression, we tested whether 3′‐SL could inhibit RA symptoms in a mouse model of CIA. Mice were first treated with 3′‐SL p. o., three times per week before onset of CIA to confirm the prophylactic effect (Figure 1A), which continued until the end of the experiment. Consistent with the macroscopic evidence (Figure 1B), measurements of paw swelling (Figure 1C; left), clinical score (Figure 1C; middle) and incidence rate (Figure 1C; right), 3′‐SL showed a marked prophylactic effect against RA pathogenesis in mice with CIA.
Figure 1.
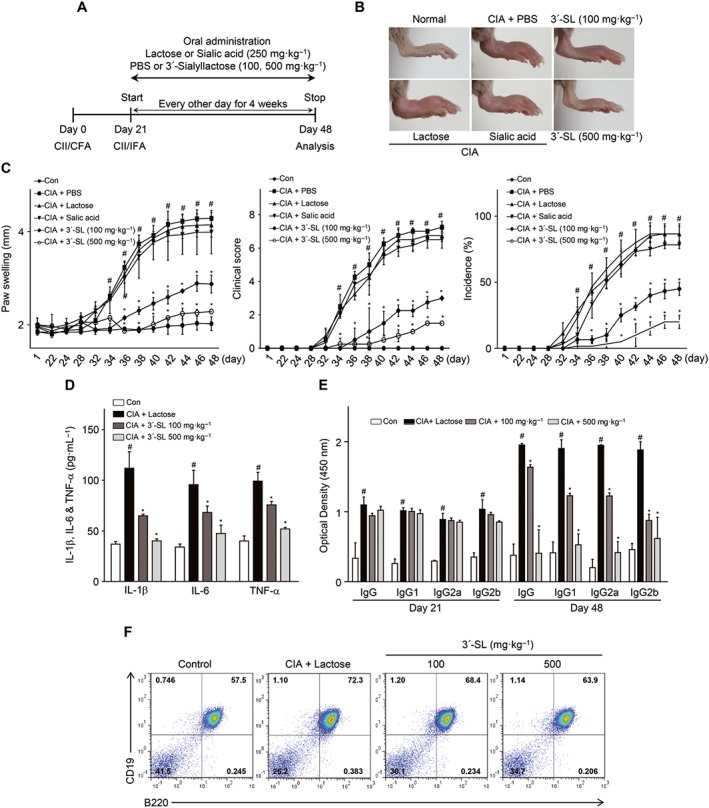
Prophylactic effect of 3′‐SL in CIA. (A) Experimental scheme for the analysis of CIA. DBA/1 mice were immunized on days 0 and 21 and were administered 3′‐SL at 2‐day intervals for 4 weeks after the second immunization. (B) Representative hind paws from each treatment group (4 weeks after induction of arthritis). (C) Paw swelling (left), clinical score (middle) and incidence (right) in mice with CIA that were administrated PBS, lactose, sialic acid or 3′‐SL. (D, E) Production of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (D) and CII‐specific autoantibodies (E) in the sera of mice with CIA that were administered lactose or 3′‐SL. Serum samples were collected on day 21 or 48 from mice with CIA and those administered 3′‐SL. Production of autoantibodies and cytokines was measured by ELISA. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 8 mice per group). (F) Percentage of CD19+B220+ B cells in the spleens from CIA mice treated with lactose or 3′‐SL. # P < 0.05, significantly different from control group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from CIA group (given lactose).
We also checked whether 3′‐SL has therapeutic effects. After onset of CIA, mice were orally treated with 3′‐SL and MTX and analysed by microscopy. As shown in Supporting Information Figure S1, 3′‐SL and MTX also have therapeutic effects for CIA (Supporting Information Figure S1A–C). One rheumatoid factor in RA is autoantibody production, which has been evaluated previously in the CIA mouse model (Ryu et al., 2014). To test the effect of 3′‐SL on autoantibody production, we analysed type II collagen (CII)‐reactive total IgG and its subclasses, such as IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b. As shown in Figure 1D and Supporting Information Figure S1D, CII‐reactive total IgG and IgG isotype levels were markedly reduced by 3′‐SL and MTX in the CIA mouse model. Furthermore, beta cell proliferation was diminished by 3′‐SL administration (Figure 1E and Supporting Information Figure S1E).
Prior to studying in vivo functions of 3′‐SL, we checked whether 3′‐SL was metabolized in vivo. As shown in Supporting Information Figure S3, 3′‐SL could be detected by extracted‐ion chromatogram (EIC) after 3′‐SL administration, whereas metabolites of 3′‐SL were difficult to measure between 10 min and 6 h. To elucidate the mechanism by which CIA severity was reduced, we measured the plasma levels of pro‐inflammatory cytokines in the 3′‐SL‐treated mice. The levels of IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α in serum were measured by ELISA at the end of the experiment. Consistent with the paw swelling, clinical score and incidence rate, plasma levels of IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α decreased in 3′‐SL‐ and in MTX‐treated mice with CIA, but not in lactose‐treated mice with CIA (Figure 1F and Supporting Information Figure S1F). These results suggest that 3′‐SL shows both prophylactic and therapeutic effects by reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines and autoantibodies.
3′‐SL alleviates CIA by reducing synovitis, pannus formation and proliferation of CD90.2+ FLS and immune cells
To validate the protective effect of 3′‐SL in RA progression, ankle and knee joints were stained with haematoxylin and safranin‐O. As shown in Figure 2 and Supporting Information Figure S2, 3′‐SL suppressed synovial hyperplasia and mononuclear cell infiltration into the synovial ankle (Figure 2A and Supporting Information Figure S2A) and knee (Figure 2C and Supporting Information Figure S2C) joints. In addition, CIA‐induced synovitis (Figure 2B,D, Supporting Information Figure S2B,D; upper panel) and pannus formation (Figure 2B,D, Supporting Information Figure S2B and S2D; lower panel) were markedly inhibited by treatment with 3′‐SL or MTX. Moreover, the increased number of BrdU‐incorporating, proliferating, CD90.2+ FLS and the number of infiltrated macrophages and neutrophils induced by CIA were markedly attenuated by 3′‐SL treatment (Figure 2E–J, Supporting Information Figure S4). We also demonstrated that the inhibition of CD90.2+ FLS proliferation by 3′‐SL was not caused by apoptosis (Supporting Information Figure S5). These data strongly suggest that 3′‐SL delays the onset and reduces the severity of RA by inhibiting proliferation of CD90.2+ FLS and reducing the number of infiltrated macrophages and neutrophils in CIA mice.
Figure 2.

Amelioration of CIA severity by oral 3′‐SL via suppression of CD90.2+ FLS, macrophages and neutrophils. CIA severity was assessed by histological analysis. (A–D) Levels of infiltrated mononuclear cells into synovium of ankle (A) and knee (C) joints were analysed by haematoxylin and safranin‐O staining. Quantification of synovitis (B and D; upper panels) and pannus formation (B and D; lower panels) in ankle (B) and knee (D) joints was assessed using clinical scores. (E–G) Increased CD90.2+ FLS, macrophages and neutrophils were stained with anti‐CD90.2, ‐CD68 and ‐elastase in synovial tissues respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. (H–J) Quantification of increased FLS (H), macrophages (I) and neutrophils (J) in ankle (left) and knee (right) joints. Numbers of increased FLS, macrophages and neutrophils were quantified by ImageJ software v1.60. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 8 mice per group). # P < 0.05, significantly different from control group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from CIA group (given lactose).
3′‐SL reduces expression of chemokines and pro‐inflammatory cytokines in IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐stimulated CD90.2+ FLS
We investigated whether 3′‐SL has anti‐chemokine and anti‐inflammatory effects under in vitro RA conditions. Prior to this analysis, we checked the purity of mouse CD90.2+ FLS (CD90.2+CD14−) and their contamination with bone marrow fibroblasts (Collagen type 1+CD45+) by FACS analysis (Supporting Information Figure S6) and then verified the absence of cytotoxicity of 3′‐SL against CD90.2+ FLS using WST‐1 assays (Supporting Information Figure S7). Furthermore, there was no difference between sialic acid and lactose as controls for 3’‐SL in our in vitro analysis (Supporting Information Figure S7). Thus, 3′‐SL was used at concentrations of 0–250 μM in subsequent in vitro experiments. To investigate the effect of 3′‐SL against IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐induced chemokines (i.e. http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4406, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4412, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=759, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=819, http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=827 and http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=829), pro‐inflammatory cytokines (IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α) and COX2 expression, IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐stimulated human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS were co‐treated with 3′‐SL (100 or 250 μM) for 24 h. As shown in Figure 3A,B, and Supporting Information Figure S8, 3′‐SL markedly reduced the expression of chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines and COX2 in IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐stimulated human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. COX2 production is induced in response to the release of various chemokines and inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, PGE synthase converts COX2‐derived PGH2 to PGE2, which is an inflammatory mediator. As shown in Figure 3C, PGE2 production in the cell lysate was also suppressed by 3′‐SL in a concentration‐dependent manner.
Figure 3.
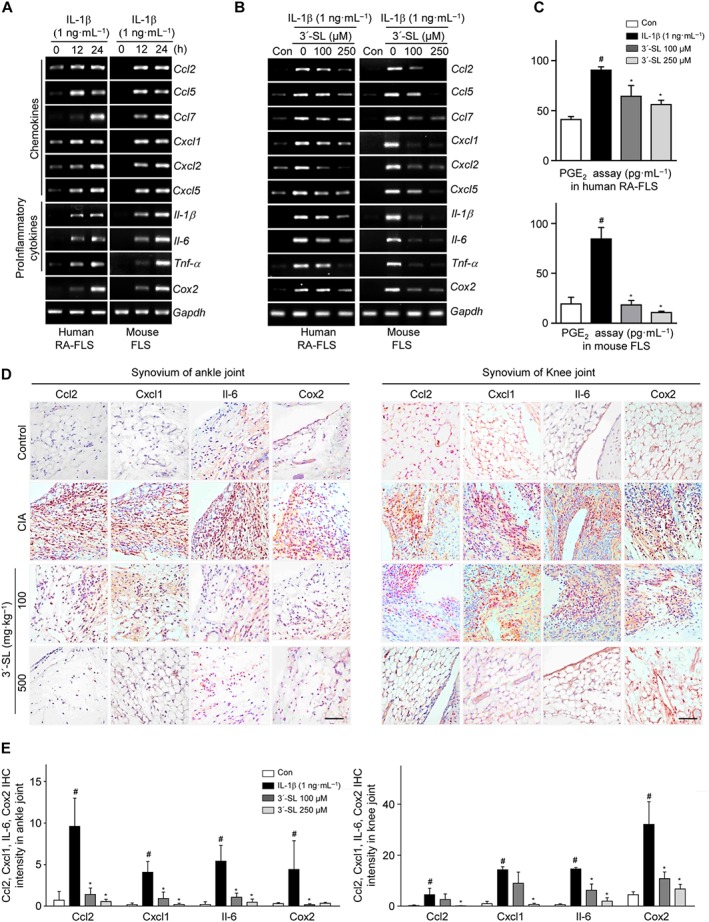
Effect of 3′‐SL on expression of chemokines and pro‐inflammatory cytokines in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. (A) Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) for the indicated times. Chemokine (CCL2, CCL5, CCL7, CXCL1, CXCL2 and CXCL5), pro‐inflammatory cytokine (IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α) and COX2 mRNA were detected by RT‐PCR. (B) Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) with or without various concentrations of 3′‐SL for 24 h. RT‐PCR was carried out to evaluate expression of chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines and COX2. (C) PGE2 production was detected in human RA‐FLS (upper panel) and mouse CD90.2+ FLS (lower panel) after treatment with IL‐1β and 3′‐SL. (D) Immunohistochemical staining of representative chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines and COX2 in the synovial tissues of ankle (left) and knee (right) joints. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) Quantification of CCL2, CXCL1, IL‐6 and COX2 expression in the ankle (left) and knee (right) joints. Values are presented as means ± SEM (in vivo, 8 mice per group; in vitro, n = 5). # P < 0.05, significantly different from control group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from IL‐1β‐treated group or CIA group (given lactose).
The in vivo analysis showed that the expression of IL‐6, CCL2, CXCL1 and COX2 as a representative pro‐inflammatory cytokine, chemokines and pro‐inflammatory enzyme respectively, were reduced in the ankle and knee synovial tissues of 3′‐SL‐treated CIA mice, compared with those of control CIA mice (Figure 3D and E). These data indicate that 3′‐SL attenuated the production of chemokines, inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators secreted by IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐stimulated CD90.2+ FLS and in mice with CIA.
3′‐SL inhibits activation of T cells and monocytes and suppresses osteoclastogenesis
Results of the in vivo experiments demonstrated that 3′‐SL modulated pannus formation (Figure 2E), which mainly contains extensive infiltrates of immune cells (T cells, macrophages, monocytes and FLS) and increased numbers of osteoclasts (Roberts et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2017). To further confirm activation of T cells, monocytes and of osteoclastogenesis by 3′‐SL, we evaluated inhibition by 3′‐SL of the regulation of pro‐inflammatory cytokine expression by inflammatory immune cells (T cells and monocytes) and the suppression of osteoclastogenesis. As shown in Figure 4A and B, increased IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α levels were markedly reduced by 3′‐SL or MTX treatment in T cells and monocytes activated by PMA/A23187 and LPS respectively. Osteoclast precursor cells are differentiated into TRAP‐positive multinuclear osteoclasts upon RANKL stimulation. To investigate the effect of 3′‐SL on osteoclast differentiation, osteoclast precursor cells treated with M‐CSF (100 ng·mL−1) were co‐treated with RANKL (100 ng·mL−1) and various concentration of 3′‐SL and MTX for 6 days. TRAP activity and multinucleated osteoclasts were analysed. As shown in Figure 4C and D, 3′‐SL or MTX significantly reduced the formation of multinuclear osteoclasts and TRAP activity.
Figure 4.

The effects of 3′‐SL on the activation of T cells, monocytes and osteoclastogenesis. (A) Human Jurkat T cells and (B) Human THP‐1 monocytes cultured with PMA/A23187 (P/A) and LPS, respectively, were treated with or without various concentrations of 3′‐SL and MTX for 24 h. The transcript and protein levels of IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α were determined by qRT‐PCR (A, B; left panel) and ELISA (A, B; right panel). (C) Osteoclast precursor cells were stimulated with RANKL and co‐treated with different concentrations of 3′‐SL and MTX for 6 days. The cells were stained using TRAP staining solution and photographed under light microscopy. (×40; left panel) and TRAP‐positive osteoclasts were counted (right panel). (D) TRAP activity was measured by absorbance at 405 nm using an ELISA microplate reader. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05, significantly different from control group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from stimulated group.
3′‐SL reduces matrix degradation by inhibiting MMP3 and MMP13 activation
MMPs secreted by FLS are also involved in cartilage destruction, which is a characteristic feature of RA. Therefore, we investigated whether 3′‐SL blocked cartilage destruction through regulation of MMP3 and MMP13 expression during CIA pathogenesis. As shown in Figure 5A and Supporting Information Figure S2, 3′‐SL protected against ankle and knee cartilage destruction, which was also evident from the significantly lower Mankin scores in the control group (Figure 5B and Supporting Information Figure S2B). Furthermore, expression of MMP3 and MMP13 was reduced in the ankle and knee synovial tissues of 3′‐SL‐treated CIA mice, but not in those of CIA mice (Figure 5C and D). In addition, expression of MMP3 and MMP13 was increased by IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17 and TNF‐α in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS (Figure 5E and Supporting Information Figure S8). To determine whether 3′‐SL blocks IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17 and TNF‐α induced MMP3 and MMP13 expression in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS, we treated the cells with IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17 and TNF‐α for 24 h in either the absence or presence of 3′‐SL. The expression of MMP3 and MMP13 were markedly decreased by 3′‐SL in a concentration‐dependent manner (Figure 5F and Supporting Information Figure S9). Accordingly, increased collagenase activity due to MMP activation in the conditioned medium was suppressed by 3′‐SL in a concentration‐dependent manner (Figure 5G). These results are consistent with the hypothesis that 3′‐SL ameliorates cartilage destruction in RA by inhibiting MMP3 and MMP13 expression.
Figure 5.

Protective effect of 3′‐SL against cartilage destruction in CIA development via suppression of MMP expression. (A) Mice with CIA were treated with 3′‐SL at 2 day intervals for 4 weeks with lactose or 3′‐SL, given by gavage. Cartilage destruction in ankle and knee joints was detected by haematoxylin and safranin‐O staining. (B) Cartilage destruction in ankle (left panel) and knee (right panel) joints was quantified using Mankin scores. (C) Immunohistochemical staining of MMP3 and MMP13 in synovial tissues of ankle and knee joints of mice that were administered lactose or 3′‐SL. Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Quantification of MMP3 and MMP13 in ankle (upper panel) and knee (lower panel) joints. (E) Human RA‐FLS (upper panel) and mouse CD90.2+ FLS (lower panel) were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) for the indicated times. Transcript levels of MMP3 and MMP13 were detected by RT‐PCR. (F) Inhibition of IL‐1β‐induced MMP3, MMP13 and COX2 expression in human RA‐FLS (upper panel) and mouse CD90.2+ FLS (lower panel) by 3′‐SL. CD90.2+ FLS were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) with or without various concentrations of 3′‐SL for 24 h. The expression of MMP3, MMP13 and COX2 was determined by RT‐PCR. GAPDH was used as loading control. (G) Collagenase activity was detected in human RA‐FLS (left) and mouse CD90.2+ FLS (right) treated with IL‐1β and 3′‐SL. Values are presented as means ± SEM (in vivo, 8 mice per group; in vitro, n = 5). # P < 0.05, significantly different from control group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from CIA group (given lactose) or IL‐1β‐treated group.
3′‐SL modulates NF‐κB signalling to alleviate CIA
We first verified that NF‐κB activation in IL‐1β‐stimulated CD90.2+ FLS was suppressed by 3′‐SL or MTX treatment. NF‐κB reporter assays demonstrated that treatment of CD90.2+ FLS with IL‐1β led to activation of NF‐κB‐dependent transcription, whereas IL‐1β‐induced activation of NF‐κB was clearly blocked by 3′‐SL or MTX, in a concentration‐dependent manner (Figure 6A and Supporting Information Figure S2E). We next performed Western blotting to evaluate the phosphorylation of p65, an NF‐κB subunit. CD90.2+ FLS were pre‐incubated for 12 h with or without 3′‐SL and were then exposed to IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) for 10 min to activate NF‐κB signalling. As shown in Figure 6B and Supporting Information Figure S2F, p65 phosphorylation was markedly decreased by 3′‐SL or MTX. Furthermore, the level of pp65 was reduced in 3′‐SL or MTX‐treated CIA mice, but not in control CIA mice (Figure 6E,F, Supporting Information Figure S2G and H). Taken together, our results indicate that 3′‐SL suppresses expression of chemokines, MMPs and COX2 through inhibition of NF‐κB signalling in CIA pathogenesis.
Figure 6.
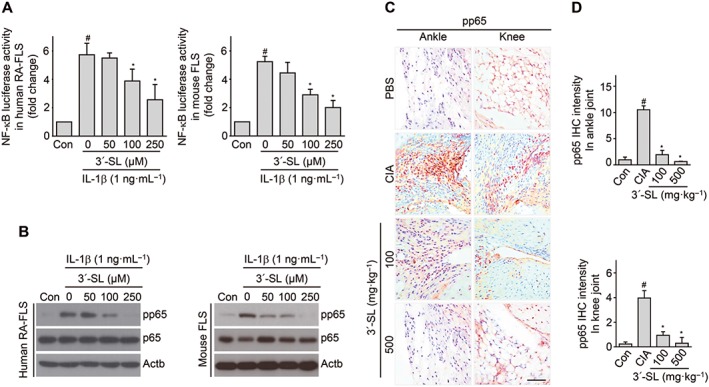
Blocking NF‐κB activity by 3′‐SL in RA models in vitro and in vivo. (A) Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS transfected with NF‐κB reporter gene constructs and β‐galactosidase vector were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) with or without 3′‐SL. NF‐κB transcriptional activity was determined by reporter gene assay. (B) Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS were co‐treated with different concentrations of 3′‐SL for 24 h with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1). Phosphorylation of p65 was detected by Western blots. (C) Immunohistochemical staining for pp65 in synovial tissues of ankle and knee joints after oral administration of 3′‐SL to mice with CIA. Scale bar = 50 μm. (D) Quantification of pp65 expression in ankle (upper panel) and knee (lower panel) joints. Values are presented as means ± SEM (in vivo, 8 mice per group; in vitro, n = 5). # P < 0.05, significantly different from control; *P < 0.05, significantly different from IL‐1β‐treated group or CIA group (given lactose).
Discussion
During RA pathogenesis, chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines and MMPs secreted by FLS and inflammatory immune cells play crucial roles in immune cell recruitment, inflammation induction and cartilage destruction respectively (Bartok and Firestein, 2010). Among heterogeneous FLS in the RA synovium, a distinct subset of PDPN+CD34−THY1+ fibroblasts has potential roles in matrix invasion, immune cell recruitment and osteoclastogenesis (Mizoguchi et al., 2018).
The current strategy used in RA treatment focuses on specifically targeting inflammatory mediators secreted by FLS and inflammatory cells or protecting the synovium from inflammation (Noss and Brenner, 2008). Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs and disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs are the most commonly prescribed medications for RA treatment. However, these drugs can cause severe side effects, such as peptic ulcers, intestinal bleeding and heart attacks (Quan et al., 2008).
3′‐SL is commercially available and occurs naturally in human milk (Zivkovic and Barile, 2011). Previous reports focused on the use of 3′‐SL as a prebiotic, as well as its effect on bacterial colonization in the gut and pathogenesis of viral diseases (Izquierdo‐Useros et al., 2012; Donovan and Comstock, 2016). For example, 3′‐SL influences colitis by colonizing commensal bacteria in the colon and it also plays important roles in promoting growth and activity of beneficial intestinal bacteria to develop a strong immune system in neonates (Fuhrer et al., 2010; Donovan and Comstock, 2016). Moreover, 3′‐SL binds to several viruses, such as influenza, HIV‐1, retrovirus and polyomavirus (Coppa et al., 2006; Izquierdo‐Useros et al., 2012; Stencel‐Baerenwald et al., 2014). The function of 3′‐SL involves not only its prebiotic and immune homeostatic activities but also its ability to regulate anti‐inflammatory responses (Zenhom et al., 2011). 3′‐SL regulates pro‐inflammatory cytokines via activation of PPARγ and increases levels of peptidoglycan recognition protein 3in intestinal inflammation (Zenhom et al., 2011). After a careful examination of earlier reports, it was clear that, although there was evidence that 3′‐SL could treat RA by regulating pro‐inflammatory cytokines and immune homeostasis, the overall effects of 3′‐SL on RA pathogenesis were largely unknown. In the current study, we have characterized these prophylactic and therapeutic effects with in both in vitro and in vivo models of CIA.
The most common characteristics of RA are joint swelling, pain and deformity by synovial hyperplasia, FLS activation, production of inflammatory cytokines and autoantibody production (Noss and Brenner, 2008). Our results obtained in the CIA mouse model demonstrated that 3′‐SL detected by EIC, after systemic administration of 3′‐SL, alleviated RA symptoms by reducing paw swelling, clinical scores, incidence and production of inflammatory cytokines and autoantibodies in the serum of the mice. Moreover, increased proliferation and numbers of CD90.2+ FLS, macrophages, B cells, and neutrophils in the synovial membranes of mice with CIA were markedly reduced by 3′‐SL treatment.
Inflammation involved in expression of chemokines and pro‐inflammatory cytokines is a causal factor in RA pathogenesis (Gomez et al., 2005, Choy, 2012). Chemokines induce chemotaxis of nearby responsive immune cells for recruitment to inflammatory sites and to induce inflammation in synovial tissues (Noss and Brenner, 2008; Smith et al., 2008; McGettrick et al., 2009). Although chemokines have been classified into four main subfamilies, the CC and CXC families, which are secreted by FLS and immune cells, secreted have been well characterized in RA pathogenesis (Koch, 2005; Noss and Brenner, 2008; Szekanecz et al., 2010). Thus CC chemokines trigger movement of monocytes, NK cells and dendritic cells (Shi and Pamer, 2014). Particularly, CCL‐2, ‐5 and ‐7 recruit various immune cells to inflamed joint synovial membranes (Shadidi et al., 2003; Szekanecz et al., 2010). CXCL‐1, ‐2 and ‐5 are small cytokines belonging to the CXC chemokine family (Koch, 2005). They are secreted by FLS and immune cells and mediate their biological effects via GPCRs, including the receptors CXCR‐1, ‐2 and ‐5, which appear to play major roles in neutrophil recruitment during RA pathogenesis (Han, 2014). Among various pro‐inflammatory cytokines, TNF‐α, IL‐6 and IL‐1β are mainly secreted into the synovial fluid by FLS, and they are known to play roles in inflammation and cartilage destruction during RA pathogenesis (Choy, 2012).
In a previous study, the possibility of arthritis induction by cytokines was analysed by injecting recombinant cytokines into rabbit and rodent knee joints. The results of that study provided evidence that IL‐1β, IL‐6 and IL‐17 are important cytokines in both arthritis and cartilage destruction and that TNF‐α is an inflammatory mediator (Lee et al., 2013; Calabrese and Rose‐John, 2014: Ryu et al., 2014). Several studies have shown that IL‐6 expression is increased in the serum and synovial fluid in RA and that its level correlates with disease severity and joint destruction (Nowell et al., 2009; Calabrese and Rose‐John, 2014). We, therefore, assessed the inhibitory effect of 3′‐SL on CIA inflammation by evaluating the expression of chemokines and pro‐inflammatory cytokines. In our experiments, 3′‐SL suppressed the activation of chemokines (CCL2, CCL5, CCL7, CXCL1, CXCL2 and CXCL5) and inflammatory cytokines (IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α) both in vitro and in vivo. COX2 induced by pro‐inflammatory cytokines is associated with increased production of PGE2, known as an inflammatory mediator in synovial and joint pain (Gomez et al., 2005). Although regulation of COX2 expression is a critical target when developing therapeutic approaches to RA, currently developed COX2 inhibitors have serious side effects (Sundy, 2001). However, as a compound found in human milk, 3′‐SL is already known to have no toxicity in humans (Mysore et al., 1999), and it has been used as a prebiotic, to promote immune homeostasis (Zenhom et al., 2011). The role of 3′‐SL as a novel form of COX2 inhibitor for arthritis treatment was further confirmed by evaluating COX2 expression and PGE2 production. In the present study, we found that COX2 expression and the subsequent PGE2 production were reduced by 3′‐SL in IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐stimulated CD90.2+ FLS, as well as in the CIA mouse model.
MMP3 and MMP13 are proteolytic enzymes known to be responsible for cartilage destruction and are regulated by pro‐inflammatory cytokines (IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α) (Choy, 2012; Ryu et al., 2014). COX2‐dependent PGE2 production also promotes MMP synthesis via NF‐κB signalling (Steenport et al., 2009). Therefore, increased MMP3 and MMP13 in RA synovial fluid are able to cleave cartilage ECM components, such as collagen α1(II) and aggrecan (Yoshihara et al., 2000). Here, we have shown that increased collagenase activity by MMP expression was also suppressed by 3′‐SL in IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐ and TNF‐α‐stimulated human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS.
Although inflammatory cytokines and MMPs were mainly expressed in CD34+ and CD34+THY1− fibroblasts, respectively, in human RA synovium (Mizoguchi et al., 2018), CD90.2+ FLS, known to be THY1+, isolated from mouse knee joints showed increased inflammatory cytokine and MMP expression in our data.
Cartilage destruction not only occurs via inflammatory cytokine‐induced MMP expression but also via regulation of osteoclastogenesis (Tanaka, 2013). Our results strongly suggest that 3′‐SL suppresses formation of multinuclear osteoclasts and TRAP activity.
Inflammation induced by expression of chemokines and inflammatory cytokines, cartilage destruction by MMP expression, osteoclastogenesis and autoantibody production are commonly regulated by NF‐κB through direct binding to its consensus sequences in the promoters of related genes (‐GGGRNYYCC‐) (Ueberla et al., 1993; Gerondakis and Siebenlist, 2010; Boyce et al., 2015). In many studies, NF‐κB activation is reported to be involved in a variety of cellular signalling pathways, including inflammation and cell survival, proliferation and differentiation (Simmonds and Foxwell, 2008). NF‐κB is particularly activated during RA pathogenesis and is one of the major regulators of inflammatory cytokine production in RA (Gomez et al., 2005). Moreover, IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17 and TNF‐α stimulate NF‐κB activation to contribute to joint inflammation and cartilage destruction (Simmonds and Foxwell, 2008; Choy, 2012). In contrast, inhibition of p65 phosphorylation suppresses RA pathogenesis (Roman‐Blas and Jimenez, 2006). In this study, we found that 3′‐SL inhibited NF‐κB activity and blocked p65 phosphorylation in IL‐1β‐stimulated human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Additionally, phosphorylation of p65 was reduced by 3′‐SL in the synovial tissues of mice with CIA.
In summary, the results from our in vivo and in vitro experiments support the potent effects of 3′‐SL on RA. Specifically, chemokines (CCL2, CCL5, CCL7, CXCL1, CXCL2 and CXCL5), inflammatory cytokines (IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α) and MMPs (MMP3 and MMP13) that are secreted by human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS are regulated by 3′‐SL through modulation of NF‐κB transcriptional activity. Therefore, it appears that 3′‐SL has the potential to be developed into novel prophylactic and therapeutic agents for RA treatment, without the usual side effects caused by current anti‐arthritic drugs.
Author contributions
L.J.K., E.S.K., K.M.L. and S.Y. were responsible for conception, design, analysis and interpretation of data. L.J.K., E.S.K., K.M.L., C.C. and J.J. performed the in vivo and in vitro experiments. T.H.Y., M.R.C., S.Y.J, S.R.L. and W.K. contributed reagents, materials and analytical tools for the study. J.I.L. and Y.B.R. performed metabolite analyses. L.J.K., E.S.K., K.M.L. and S.Y. wrote the paper. L.J.K. and S.Y. have full access to the data and take responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of the data analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Declaration of transparency and scientific rigour
This http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.13405/abstract acknowledges that this paper adheres to the principles for transparent reporting and scientific rigour of preclinical research recommended by funding agencies, publishers and other organisations engaged with supporting research.
Supporting information
Figure S1 Therapeutic effect of 3′‐SL after onset of CIA. (A) Experimental scheme for CIA analysis. Eight‐week‐old DBA/1 mice were immunised on days 0 and 21. Oral administration of 3′‐SL, lactose, sialic acid, and MTX occurred at 2‐day intervals for 2 weeks after onset of CIA. (B) Representative hind paws from each treatment group are shown (2 weeks after induction of arthritis). (C) Paw swelling (left), clinical score (middle), and incidence (right) in mice with CIA that were administered lactose, sialic acid, MTX, or 3′‐SL. (D, E) Production of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (D) and type II collagen‐specific autoantibodies (E) in sera of mice with CIA that were treated as indicated. Serum samples were collected on day 21 or 48. Production of autoantibodies and cytokines was measured by ELISA. (F) Percentage of CD19+B220+ B cells in spleens from CIA mice administered lactose or 3′‐SL. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 8 mice per group). # P < 0.05 compared with control group; *P < 0.05 compared with CIA group (Lactose administration).
Figure S2 Attenuation of CIA progression after onset of CIA by 3′‐SL and MTX via blocking NF‐κB activation. (A‐D) Immune cell infiltrations into synovium of ankle (A) and knee (C) joints were analysed by haematoxylin and safranin‐O staining. Quantification of synovitis and pannus formation in ankle (B) and knee (C) joints was assessed by clinical scores. (E) Mouse CD90.2+ FLS transfected with NF‐κB reporter gene plasmid were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) in absence or presence of 3′‐SL and MTX. NF‐κB transcriptional activity was measured by reporter gene assay. (F) Mouse CD90.2+ FLS were co‐treated with different concentrations of 3′‐SL and MTX for 24 h and IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) for 10 min. Phosphorylation of p65 was detected by western blotting. (G) Immunohistochemical staining of pp65 in synovial tissues of ankle and knee joints after oral administration of 3′‐SL or MTX to mice with CIA. Scale bar = 50 μm. (H) Quantification of pp65 expression in ankle (upper panel) and knee (lower panel) joints. # P < 0.05 compared with control; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐treated or CIA group (Lactose administration).
Figure S3 (A) Extracted‐ion chromatogram (EIC) of 3′‐SL standard in negative ion mode ([M‐H]−); (B) MS spectra of 3′‐SL standard in negative ion mode ([M‐H]−); (C) – (F) MS spectra of 3′‐SL for 10 min to 6 h in treated serum.
Figure S4 Mice were administered BrdU for 2 days. Isolated cells from the ankle and knee were labelled with anti‐CD90.2 (A), anti‐CD68 (B), or anti‐CD11b+Ly6G+ (C) for FLS, macrophages, and neutrophils, respectively, and analysed by FACS.
Figure S5 Annexin V and 7‐AAD double‐positive staining show the proportion of apoptotic cells in ankle and knee joints. Cells were isolated from ankle and knee joints and labelled with anti‐CD90.2 (A), anti‐CD68 (B), or anti‐CD11b+Ly6G+ (C). (D) Immunohistochemical staining of representative cleaved caspase 3 in the synovial tissues of ankle (left) and knee (right) joints. (E) Quantification of cleaved caspase 3 expression in ankle (left panel) and knee (right panel) joints.
Figure S6 FACS analysis of mouse CD90.2+ FLS surface marker expression with increasing passages. Mouse CD90.2+ FLS were maintained as described in the Methods section. (A, B) Mouse CD90.2+ FLS were harvested and stained with anti‐CD90.2, anti‐CD14, anti‐CD45, and anti‐collagen type 1 antibodies in different passage conditions. Percentages of CD90.2+ (A), CD14+ (B), and collagen type 1+CD45+ (C) were analysed by FACS analysis.
Figure S7 Effect of 3′‐SL on CD90.2+ FLS viability. (A) Chemical structure of 3′‐SL. (B) Effect of 3′‐SL on CD90.2+ FLS viability and proliferation was determined by WST‐1 assay. CD90.2+ FLS were cultured with various concentrations of 3′‐SL for 24 h. Cell viability was then determined by WST‐1 assay. (C) Effect of lactose, sialic acid, and 3′‐SL in IL‐1β‐treated mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05 compared with control; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐treated group.
Figure S8 Chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, and COX2 expression induced by IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17, and TNF‐α are suppressed by 3′‐SL in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) (A), IL‐6 (50 ng·mL−1) (B), IL‐17 (10 ng·mL−1) (C), and TNF‐α (50 ng·mL−1) (D) were co‐treated with 3′‐SL or MTX for 24 h at the indicated concentrations. Expression of chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, and COX2 was determined by qRT‐PCR. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05 compared with control group; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐, and TNF‐α‐treated groups.
Figure S9 MMP expression induced by IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17, and TNF‐α was inhibited by 3′‐SL in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) (A), IL‐6 (50 ng·mL−1) (B), IL‐17 (10 ng·mL−1) (C), and TNF‐α (50 ng·mL−1) (D) were co‐treated with 3′‐SL or MTX for 24 h at the indicated concentrations. Expression of MMP3 and MMP13 was determined by qRT‐PCR. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05 compared with control group; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐, and TNF‐α‐treated groups.
Table S1 Primer sequence and PCR conditions.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Ministry of Science and ICT (2016R1E1A1A01941213 and SRC 2017R1A5A1014560), the Korea Health Technology R&D project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (HI14C2126, HI15C2407 and HI16C0992), and Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology Research Initiative Program.
Kang, L.‐J. , Kwon, E.‐S. , Lee, K. M. , Cho, C. , Lee, J.‐I. , Ryu, Y. B. , Youm, T. H. , Jeon, J. , Cho, M. R. , Jeong, S.‐Y. , Lee, S.‐R. , Kim, W. , and Yang, S. (2018) 3′‐Sialyllactose as an inhibitor of p65 phosphorylation ameliorates the progression of experimental rheumatoid arthritis. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175: 4295–4309. 10.1111/bph.14486.
References
- Alexander SP, Fabbro D, Kelly E, Marrion NV, Peters JA, Faccenda E et al (2017). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/2018: Enzymes. Br J Pharmacol 174: S272–S359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartok B, Firestein GS (2010). Fibroblast like synovicotytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 233: 233–255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce BF, Xiu Y, Li J, Xing L, Yao Z (2015). NF‐κB‐mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 30: 35–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese LH, Rose‐John S (2014). IL‐6 biology: implications for clinical targeting in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10: 720–727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy E (2012). Understanding the dynamics: pathways involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51: v3–v11. 10.1093/rheumatology/kes113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppa GV, Zampini L, Galeazzi T, Facinelli B, Ferrante L, Capretti R et al (2006). Human milk oligosaccharides inhibit the adhesion to Caco‐2 cells of diarrheal pathogens: Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholera, and Salmonella fyris. Pediatr Res 59: 377–382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis MJ, Alexander S, Cirino G, Docherty JR, George CH, Giembycz MA et al (2018). Experimental design and analysis and their reporting II: updated and simplified guidance for authors and peer reviewers. Brit J Pharmacol 175: 987–993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan SM, Comstock SS (2016). Human milk oligosaccharides influence neonatal mucosal and systemic immunity. Ann Nutr Metab 69: 42–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer A, Sprenger N, Kurakevich E, Borsig L, Chassard C, Hennet T (2010). Milk sialyllactose influences colitis in mice through selective intestinal bacterial colonization. J Exp Med 207: 2843–2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S, Siebenlist U (2010). Roles of the NF‐κB pathway in lymphocyte development and function. Cold Spring Harb Rerspect Biol 2: a000182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez PF, Pillinger MH, Attur M, Marjanovic N, Dave M, Park J et al (2005). Resolution of inflammation: prostaglandin E2 dissociates nuclear trafficking of individual NF‐κB subunit (p65,p50) in stimulated rheumatoid synovial fibroblast. J Immunol 175: 6924–6930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han X (2014). Constitutively active chemokine CXC receptors. Adv Pharmacol 70: 265–301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding SD, Sharman JL, Faccenda E, Southan C, Pawson AJ, Ireland S et al (2018). The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2018: updates and expansion to encompass the new guide to IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY. Nucl Acids Res 46: D1091–D1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo‐Useros N, Lorizate M, Contreras FX, Rodriguez‐Plata MT, Glass B, Erkizia I et al (2012). Sialyllactose in viral memebrane gangliosides is a novel molecular recognition pattern for mature dendritic cell capture of HIV‐1. PLoS Biol 10: e1001315 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010). Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. Br J Pharmacol 160: 1577–1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch AE (2005). Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: future targets? Arthritis Rheum 52: 710–721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A, Qiao Y, Grigoriev G, Chen J, Park‐Min KH, Park SH et al (2013). Tumor necrosis factor α induces sustained signaling and a prolonged and unremitting inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthrtis Rheum 65: 928–938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo J, Nordvang RT, Morthenesen ST, Zeuner B, Meyer AS, Mikkelsen JD et al (2014). An integrated membrane system for the biocatalytic production of 3'‐sialyllactose from dairy by‐products. Bioresour Technol 166: 9–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGettrick HM, Smith E, Filer A, Kissane S, Salmon M, Buckley CD et al (2009). Fibroblasts from different sites may promote or inhibit recruitment of flowing lymphocytes by endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol 39: 113–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath JC, Lilley E (2015). Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): new requirements for publication in BJP. Br J Pharmacol 172: 3189–3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi F, Slowikowski K, Wei K, Marshall JL, Rao DA et al (2018). Functionally distinct disease‐associated fibroblast subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun 9: 789: 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mysore JV, Wigginton T, Simon PM, Zopf D, Heman‐Ackah LM, Dubois A (1999). Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in rhesus monkeys using a novel antiadhesion compound. Gastroenterology 177: 1316–1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noss EH, Brenner MB (2008). The role and therapeutic implications of fibroblast‐like synoviocytes in inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 223: 252–270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell MA, Williams AS, Carty SA, Scheller J, Hayes AJ, Jones GW et al (2009). Therapeutic targeting of IL‐6 trans signaling counteracts STAT3 control of experimental inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol 182: 613–622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan LD, Thiele GM, Tian J, Wang D (2008). The development of novel therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Ther Pat 18: 723–738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts CA, Dickinson AK, Taams LS (2015). The interplay between monocyte/macrophages and CD4(+)T cell subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 6: 571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman‐Blas JA, Jimenez SA (2006). NF‐κB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 14: 839–848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu JH, Chae CS, Kwak JS, Oh H, Shin Y, Huh YH et al (2014). Hypoxia‐inducible factor‐2α is an essential catabolic regulator of inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS Biol 12: e1001881 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadidi KR, Aarvak T, Henriksen JE, Natvig JB, Thompson KM (2003). The chemokines CCL5, CCL2 and CXCL12 play significant roles in the migration of Th1 cells into rheumatoid synovial tissue. Scand J Immunol 57: 192–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi C, Pamer EG (2014). Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 11: 762–774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds RE, Foxwell BM (2008). Signalling, inflammation and arthritis: NF‐κB and its relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 584–590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E, McGettrick HM, Stone MA, Shaw JS, Middleton J, Nash GB et al (2008). Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines and CXCL5 are essential for the recruitment of neutrophils in a multicellular model of rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum 58: 1968–1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenport M, Khan KM, Du B, Barnhard SE, Dannenberg AJ, Falcone DJ (2009). Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)‐1 and MMP‐3 induce macrophage MMP‐9: evidence for the role of TNF‐α and cyclooxygenase‐2. J Immunol 183: 8119–8127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stencel‐Baerenwald JE, Reiss K, Reiter DM, Stehle T, Dermody TS (2014). The sweet spot: defining virus‐sialic acid interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 12: 739–749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundy JS (2001). COX‐2 inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 3: 86–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekanecz Z, Vegvari A, Szabo Z, Koch AE (2010). Chemokines and chemokine receptors in arthritis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2: 153–167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S (2013). Regulation of bone destruction I rheumatoid arthritis through RANKL‐RANK pathways. World J Orthop 4: 1–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueberla K, Lu Y, Chung E, Haseltine WA (1993). The NF‐κB p65 promoter. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 6: 227–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q, Wang L, Wu L, Zhang M, Hu S, Wang R et al (2017). Paroxetine alleviates T lymphocyte activation and infiltration to joints of collagen‐induced arthritis. Sci Rep 28: 45364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara Y, Nakamura H, Obata K, Yamada H, Hayakawa T, Fujikawa K et al (2000). Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 59: 455–461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenhom M, Hyder A, de Vrese M, Heller KJ, Roeder T, Schrezenmeir J (2011). Prebiotic oligosaccharides reduce proinflammatory cytokines in intestinal Caco‐2 cells via activation of PPARγ and peptidoglycan recognition protein 3. J Nutr 141: 971–977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zivkovic AM, Barile D (2011). Bovine milk as a source of functional oligosaccharides for improving human health. Adv Nutr 2: 284–289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1 Therapeutic effect of 3′‐SL after onset of CIA. (A) Experimental scheme for CIA analysis. Eight‐week‐old DBA/1 mice were immunised on days 0 and 21. Oral administration of 3′‐SL, lactose, sialic acid, and MTX occurred at 2‐day intervals for 2 weeks after onset of CIA. (B) Representative hind paws from each treatment group are shown (2 weeks after induction of arthritis). (C) Paw swelling (left), clinical score (middle), and incidence (right) in mice with CIA that were administered lactose, sialic acid, MTX, or 3′‐SL. (D, E) Production of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (D) and type II collagen‐specific autoantibodies (E) in sera of mice with CIA that were treated as indicated. Serum samples were collected on day 21 or 48. Production of autoantibodies and cytokines was measured by ELISA. (F) Percentage of CD19+B220+ B cells in spleens from CIA mice administered lactose or 3′‐SL. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 8 mice per group). # P < 0.05 compared with control group; *P < 0.05 compared with CIA group (Lactose administration).
Figure S2 Attenuation of CIA progression after onset of CIA by 3′‐SL and MTX via blocking NF‐κB activation. (A‐D) Immune cell infiltrations into synovium of ankle (A) and knee (C) joints were analysed by haematoxylin and safranin‐O staining. Quantification of synovitis and pannus formation in ankle (B) and knee (C) joints was assessed by clinical scores. (E) Mouse CD90.2+ FLS transfected with NF‐κB reporter gene plasmid were treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) in absence or presence of 3′‐SL and MTX. NF‐κB transcriptional activity was measured by reporter gene assay. (F) Mouse CD90.2+ FLS were co‐treated with different concentrations of 3′‐SL and MTX for 24 h and IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) for 10 min. Phosphorylation of p65 was detected by western blotting. (G) Immunohistochemical staining of pp65 in synovial tissues of ankle and knee joints after oral administration of 3′‐SL or MTX to mice with CIA. Scale bar = 50 μm. (H) Quantification of pp65 expression in ankle (upper panel) and knee (lower panel) joints. # P < 0.05 compared with control; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐treated or CIA group (Lactose administration).
Figure S3 (A) Extracted‐ion chromatogram (EIC) of 3′‐SL standard in negative ion mode ([M‐H]−); (B) MS spectra of 3′‐SL standard in negative ion mode ([M‐H]−); (C) – (F) MS spectra of 3′‐SL for 10 min to 6 h in treated serum.
Figure S4 Mice were administered BrdU for 2 days. Isolated cells from the ankle and knee were labelled with anti‐CD90.2 (A), anti‐CD68 (B), or anti‐CD11b+Ly6G+ (C) for FLS, macrophages, and neutrophils, respectively, and analysed by FACS.
Figure S5 Annexin V and 7‐AAD double‐positive staining show the proportion of apoptotic cells in ankle and knee joints. Cells were isolated from ankle and knee joints and labelled with anti‐CD90.2 (A), anti‐CD68 (B), or anti‐CD11b+Ly6G+ (C). (D) Immunohistochemical staining of representative cleaved caspase 3 in the synovial tissues of ankle (left) and knee (right) joints. (E) Quantification of cleaved caspase 3 expression in ankle (left panel) and knee (right panel) joints.
Figure S6 FACS analysis of mouse CD90.2+ FLS surface marker expression with increasing passages. Mouse CD90.2+ FLS were maintained as described in the Methods section. (A, B) Mouse CD90.2+ FLS were harvested and stained with anti‐CD90.2, anti‐CD14, anti‐CD45, and anti‐collagen type 1 antibodies in different passage conditions. Percentages of CD90.2+ (A), CD14+ (B), and collagen type 1+CD45+ (C) were analysed by FACS analysis.
Figure S7 Effect of 3′‐SL on CD90.2+ FLS viability. (A) Chemical structure of 3′‐SL. (B) Effect of 3′‐SL on CD90.2+ FLS viability and proliferation was determined by WST‐1 assay. CD90.2+ FLS were cultured with various concentrations of 3′‐SL for 24 h. Cell viability was then determined by WST‐1 assay. (C) Effect of lactose, sialic acid, and 3′‐SL in IL‐1β‐treated mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05 compared with control; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐treated group.
Figure S8 Chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, and COX2 expression induced by IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17, and TNF‐α are suppressed by 3′‐SL in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) (A), IL‐6 (50 ng·mL−1) (B), IL‐17 (10 ng·mL−1) (C), and TNF‐α (50 ng·mL−1) (D) were co‐treated with 3′‐SL or MTX for 24 h at the indicated concentrations. Expression of chemokines, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, and COX2 was determined by qRT‐PCR. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05 compared with control group; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐, and TNF‐α‐treated groups.
Figure S9 MMP expression induced by IL‐1β, IL‐6, IL‐17, and TNF‐α was inhibited by 3′‐SL in human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS. Human RA‐FLS and mouse CD90.2+ FLS treated with IL‐1β (1 ng·mL−1) (A), IL‐6 (50 ng·mL−1) (B), IL‐17 (10 ng·mL−1) (C), and TNF‐α (50 ng·mL−1) (D) were co‐treated with 3′‐SL or MTX for 24 h at the indicated concentrations. Expression of MMP3 and MMP13 was determined by qRT‐PCR. Values are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5). # P < 0.05 compared with control group; *P < 0.05 compared with IL‐1β‐, IL‐6‐, IL‐17‐, and TNF‐α‐treated groups.
Table S1 Primer sequence and PCR conditions.


