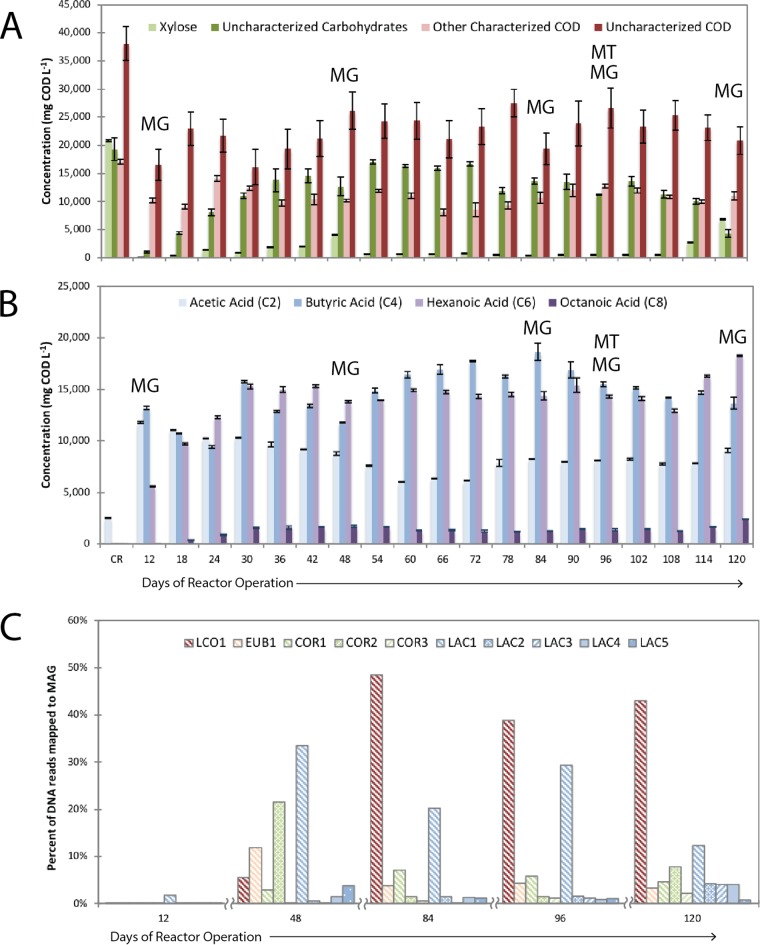
FIG 1.
Transformation of materials in lignocellulosic ethanol conversion residues by an anaerobic microbiome and abundance of MAGs. During 120 days of reactor operation, compounds in conversion residues (CR) were converted to medium-chain fatty acids. In panels A and B, the bars in the first set of bars in the figure indicate the concentrations in the feed (CR), whereas the rest of the bars describe concentrations in the reactor. A more detailed description of the operation of this reactor is presented elsewhere (4). Samples were taken for metagenomic (MG) analysis from five time points (day 12, day 48, day 84, day 96, and day 120) and for metatranscriptomic analysis (MT) from one time point (day 96). Overall, the bioreactor transformed xylose, uncharacterized carbohydrates, and uncharacterized COD to acetic (C2), butyric (C4), hexanoic (C6), and octanoic (C8) acids. The microbial community was enriched in 10 MAGs.