Abstract
Introduction
Obesity and related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are an emerging health care issue that imposes substantial morbidity to individuals. Growth and differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) limits food uptake, body weight, and energy balance by modulation of GDNF-family receptor α-like (GFRAL) signalling in the hindbrain. However, the regulation of GDF15 expression in obesity and NAFLD is incompletely understood. We sought to define the impact of weight loss achieved by laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) on hepatic and adipose GDF15 expression in a cohort of severely obese patients.
Methods
We analysed GDF15 expression of liver and subcutaneous adipose tissue before and 6 months after LAGB in severely obese patients undergoing LAGB by quantitative real-time PCR. To assess the role of inflammation on GDF15 expression, we analysed Hep G2 hepatocytes stimulated with cytokines such as IL-1β, TNFα, IL-6, LPS, or cellular stressors such as tunicamycin.
Results
GDF15 expression was mostly confined to the liver compared to adipose tissue in severely obese patients. Weight loss induced by LAGB was associated with reduced hepatic (but not adipose tissue) expression of GDF15. Stimulation with IL-1β or tunicamycin induced hepatic GDF15 expression in hepatocytes. In line with this, hepatic GDF15 expression directly correlated with IL-1β expression and steatosis severity in NAFLD. These data demonstrated that amelioration of metabolic inflammation and weight loss reduced hepatic GDF15 expression.
Conclusion
Based on recent mechanistic findings, our data suggest that hepatic GDF15 may serve as a negative feedback mechanism to control energy balance in NAFLD.
1. Introduction
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and obesity are dramatically increasing worldwide. Systemic inflammation and tissue inflammation represent a critical driver of disease processes in obesity and its related disorders including NAFLD [1, 2]. We previously described that hepatic inflammation in NAFLD patients could be reversed by weight loss that was achieved by laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB). LAGB not only improved metabolic dysregulation but also liver disease [3, 4].
Growth and differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), also known as MIC-1, is a member of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family. Increased tumor-derived GDF15 concentrations mediated cachexia by modulation of food intake in mice [5]. In line with these findings, overexpression of GDF15 in mice reduced food intake and body weight while genetic deletion of GDF15 evoked obesity [6, 7], and administration of recombinant GDF15 ameliorated diet-induced obesity in mice [8]. Only recently, a mechanism of GDF15-controlled food intake and body mass has been revealed in a series of reports in Nature Medicine [9–11]. These studies demonstrated that GDNF-family receptor α-like (GFRAL) served as a receptor of GDF15 signalling in the hindbrain (i.e., area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarius) which was required for the metabolic effects of GDF15 [9–11]. Specifically, mice exposed to a high-fat diet exhibited decreased food intake and body weight when they were treated with recombinant GDF15 which was likely mediated by signalling in the brain [9]. In line with this notion, intracerebroventricular GDF15 application in rats similarly resulted in reduced food intake [11]. Knockout models established that GFRAL signalling particularly protected against diet-induced obesity, while no phenotype was observed at baseline [9–11]. These data suggest that GDF15/GFRAL signalling critically controls energy balance in a situation with unrestricted dietary access to high-caloric food. In line with this, GDF15-mediated GFRAL signalling at the brainstem regulated food intake and energy expenditure in metabolic and toxic-induced stress [12]. As such, clear evidence accumulated that GDF15 allows limitation of food intake to control body weight under calorie-rich dietary conditions.
Based on these data, GDF15/GFRAL signalling emerges as a promising target to treat obesity in the future. However, the regulation of GDF15 in obesity-related human disease processes is poorly understood. GDF15 is expressed in the liver [13], and patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis exhibited increased systemic GDF15 level when compared to healthy controls or patients without simple steatosis [14]. In this cohort of NAFLD patients, systemic GDF15 concentrations increased with hepatic fibrosis and correlated with liver stiffness measured by elastography [14]. Although GDF15 emerges as a critical driver of metabolism in diet-induced obesity, the impact of body weight on hepatic GDF15 expression remains unexplored. We tracked a cohort of 28 severely obese patients that underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) and analysed the impact of weight loss on GDF15 expression in the liver and subcutaneous adipose tissue. We found that GDF15 expression was mostly confined to the liver and that weight loss induced by LAGB was associated with reduced hepatic (but not adipose tissue) expression of GDF15. Mediators of metabolic inflammation such as IL-1β and tunicamycin induced hepatic GDF15 expression in hepatocytes and IL-1β expression correlated with GDF15 expression in the liver of NAFLD patients. As such, weight loss and reduction in low-grade inflammation induced by LAGB in severely obese patients impact on hepatic GDF15 expression [3, 15]. In light of recent studies [9–12], our findings suggest that hepatic GDF15 may serve as a feedback mechanism to control energy balance in NAFLD.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
Evaluation for LAGB was performed at the Department of Medicine, Innsbruck Medical University, Innsbruck, Austria. In this study, twenty-eight patients (21 females, 7 male) with a BMI of more than 35 kg/m2 were included between 2003 and 2007 [4]. Patients with alcohol intake of more than 20 g per week, statin treatment, or other cause of chronic liver diseases (autoimmune or viral hepatitis, PBC, PSC, haemochromatosis, and Wilson's disease) were excluded from the study. The protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Medical University Innsbruck, and patients provided written informed consent before LAGB and sample collection. Liver and abdominal subcutaneous tissue specimens were taken intraoperatively at LAGB and per biopsy six months after LAGB along with blood samples from the fasting state. Clinical parameters were assessed, and blood and biopsy specimen were stored at −80°C. Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients before and after LAGB.
| Before LAGB | After LAGB | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (female/male) | 28 (21/7) | — | — |
| Age | 38 [19–66] | — | — |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 43.01 ± 3.70 | 35.7 ± 4.53 | P < 0.001 |
| Weight loss (kg) | 21.90 ± 9.76 | — | — |
| % excessive weight loss | 39.57 ± 17.92 | — | — |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | 103.02±17.81 | 89.47 ± 9.17 | P < 0.001 |
| Insulin (U/I) | 20.85 ± 15.06 | 11.89 ± 7.87 | P > 0.001 |
| HOMA | 5.53 ± 4.54 | 2.71 ± 2.05 | P < 0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 30.59 ± 12.93 | 25.44 ± 7.14 | P=0.058 |
| ALT (U/L) | 36.45 ± 27.90 | 23.89 ± 12.30 | P < 0.05 |
| GGT (U/L) | 36.04 ± 24.57 | 25.64 ± 16.41 | P < 0.01 |
| AP (U/L) | 66.86 ± 17.87 | 66.00 ± 11.37 | P=0.838 |
| CRP (mg/dl) | 1.01 ± 0.73 | 0.63 ± 0.35 | P < 0.05 |
| Leukocyte count (G/L) | 7.32 ± 1.88 | 6.48 ± 1.39 | P < 0.05 |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BMI, body mass index; CRP, C-reactive protein; HOMA, homeostasis model assessment (calculated as Insulin (µU/ml) × glucose (mmol/l)/22.5); GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase.
2.2. Quantification of Hepatic and Adipose mRNA Expression
Expression analysis was performed as previously reported [4]. Tissue samples were thawed and total RNA was extracted using TRIzol® Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California). RNA was reverse transcribed using Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MLV) reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California). Quantitative real-time PCRs were performed with mesa green master mix (Eurogentec, Seraign, Belgium) on an Mx3000 qPCR Cycler (Stratagene, La Jolla, California). Expression was normalised to the housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). The following primer sequences were used: GAPDH, forward: GTC GCC AGC CGA GCC; GAPDH reverse: CCC AAT ACG ACC AAA TCC GT; GDF15, forward: GAC CCT CAG AGT TGC ACT CC; and GDF15, reverse: GCC TGG TTA GCA GGT CCT C.
2.3. Culture and Stimulation of Hep G2 Hepatocytes
Hep G2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells were purchased from ATCC (HB-8065; Middlesex, UK) and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS 100 ng/ml; Invivogen, San Diego, California), recombinant human TNFα (50 ng/ml; Peprotech), rec. IL-1β (1 ng/ml, Peprotech, 200-01B), rec. IL-6 (10 ng/ml, Peprotech, 200-06), or tunicamycin (1 µg/ml, Sigma, T7765) for 24–48 hours overnight.
2.4. Histological Analysis of Hepatic Biopsies
Hepatic biopsies were formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. A blinded pathologist scored the severity of steatosis (0–4) as previously described [15].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Results are expressed mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) or dot blot where appropriate. Statistical significance between two groups was determined by a two-tailed Student's t-test, a Wilcoxon signed-rank test, or a two-way ANOVA where appropriate and considered significant at P < 0.05. Linear regression was analysed by GraphPad Prism version 6.0.
3. Results
3.1. LAGB Ameliorates Metabolic Inflammation
We hypothesised that weight loss induced by laparoscopic gastric banding impacted on GDF15 expression. We analysed hepatic and subcutaneous fat expression before and 6 months after laparoscopic gastric banding in severely obese patients in a longitudinal fashion [4]. Our cohort comprised 28 patients with an average age of 38 years who had lost 21.9 kg ± 9.76 kg 6 months after LAGB (Table 1) [4]. Weight loss was paralleled by reduced low grade systemic inflammation indicated by leukocyte counts and C-reactive protein (CRP). Furthermore, weight loss was associated with reduced hepatic injury indicated by a reduction in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT). In line with this, metabolic inflammation improved after 6 months as demonstrated by an improved homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) index and reduced hepatic expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-6 (Table 1 and [3, 16, 17]).
3.2. LAGB-Induced Weight Loss in Obese Patients is Associated with Reduced Hepatic GDF15 Expression
We utilised this cohort to analyse the expression of GDF15 in liver and subcutaneous adipose tissue specimens before and 6 months after LAGB. Hepatic GDF15 expression was largely confined to the liver in obese patients before LAGB (Figure 1(a)). Six months after LAGB, hepatic GDF15 expression substantially decreased in all individuals while we observed no demonstrable effect in subcutaneous adipose tissue (Figures 1(b) and 1(c)).
Figure 1.
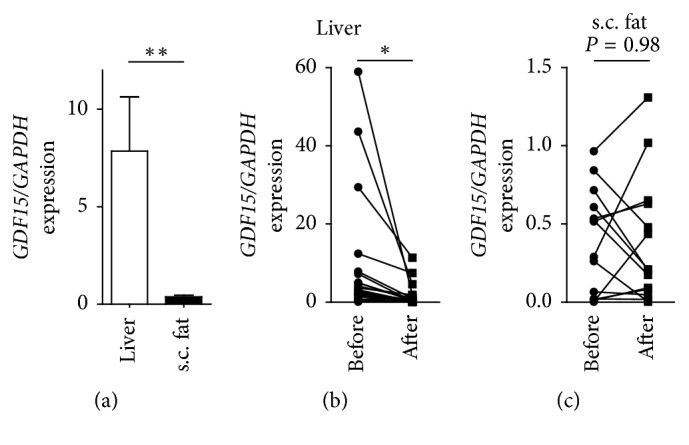
GDF15 is strongly expressed in the liver of obese subjects and decreases after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. (a) Hepatic and subcutaneous adipose tissue GDF15 expression in obese patients determined by qPCR and normalised to GAPDH. (b, c) Hepatic (b) and subcutaneous adipose tissue (c) GDF15 expression in obese patients before and 6 months after LAGB determined by qPCR and normalised to GAPDH. ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01.
3.3. Inflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induce GDF15 Expression
To understand the effect of weight loss on hepatic GDF15 expression, we utilised Hep G2 hepatocytes as a model system. As hepatic inflammation ameliorated 6 months after LAGB [3, 16, 17], we hypothesised that cytokines and cellular stress may induce the expression of GDF15. To address the impact of cytokines and cellular stress on GDF15 expression, we stimulated Hep G2 cells with IL1-β, TNFα, IL-6, LPS, and tunicamycin, the latter being an inducer of endoplasmic reticulum stress [18]. We noted that IL-1β, but not TNFα, IL-6 or LPS, induced the expression of GDF15 in hepatocytes (Figure 2(a), Supplementary Figure 1). Furthermore, endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by tunicamycin increased the expression of GDF15 in Hep G2 hepatocytes (Figure 2(b)). These data indicated that hepatic inflammation contributed to increased GDF15 expression in obese patients [14] which could be reversed by LAGB-induced weight loss.
Figure 2.
IL-1β and tunicamycin promote GDF15 expression in hepatocytes. (a, b) GDF15 expression in Hep G2 hepatocytes over the course of 48 hours stimulation with interleukin 1b (a) or the endoplasmic reticulum stressor tunicamycin (b) determined by qPCR and normalised to GAPDH. Data from 3 independent experiments are shown. ∗ P < 0.05.
3.4. GDF15 Expression Correlates with Hepatic Steatosis and IL-1β Expression in NAFLD
To assess a relationship between the regulation of GDF15 and metabolic inflammation in NAFLD, we correlated clinical parameters with GDF15 expression before LAGB. We did not note a correlation between hepatic GDF15 expression and BMI, HOMA, liver injury, systemic inflammation (C-reactive protein), or hepatic TNFα expression (Supplementary Figures 2(A)–2(E)). In contrast, we noted a direct correlation between hepatic GDF15 expression and steatosis assessed by histologic means (Figure 3(a)). Furthermore, hepatic expression of GDF15 correlated with IL-1β (Figure 3(b)). These data indicated a direct relationship between features of NAFLD and hepatic GDF15 expression.
Figure 3.
Correlation of hepatic GDF15 expression with steatosis and inflammation. (a, b) Hepatic GDF15 mRNA expressions correlated with histologically quantified steatosis (a) and IL-1β expression (b). Respective R values and level of significance are shown in each panel. Each dot represents individual patient before or after LAGB.
4. Discussion
GDF15 limits food uptake and obesity in experimental models. However, the regulation in and impact on obesity and related diseases in humans are incompletely understood. A previous study demonstrated increased circulating GDF15 concentrations in advanced NAFLD [14]. We report that hepatic (but not adipose tissue) GDF15 expression decreased after LAGB-induced weight loss. In hepatocytes, GDF15 expression was promoted by IL-1β signalling and ER stress both of which have been implicated in the development of NAFLD [19, 20]. A previous study demonstrated that palmitic acid impacted on GDF15 expression particularly in Kupffer cells [14]. Collectively, these findings may explain why LAGB-induced weight loss was associated with reduced hepatic GDF15 expression as we previously noted reduced hepatic inflammation (i.e., IL-1β expression) and improved metabolic dysfunction consequent to bariatric surgery in this cohort [3,15–17].
Previous studies convincingly demonstrated that GDF15 shapes the susceptibility to developing obesity and that GDF15 treatment ameliorated diet-induced obesity [8–12]. These data provide the basis for a model in which hepatic GDF15 is strongly expressed in NAFLD [14] to limit food intake and diet-induced obesity. In line with this, a recent study demonstrated increased hepatic GDF15 expression in NASH animal models and humans which may protect against NAFLD [21]. GDF15 signalling may act locally (e.g., in the liver) or systemically which we cannot address in this study. Specifically, we were unable to provide systemic GDF15 level in our cohort due to lack of sample availability, and GFRAL was neither expressed in the liver (as previously demonstrated [10]) nor in adipose tissue of our cohort (data not shown). After LAGB-induced weight loss, which is in part mediated by restricted food uptake [22], a compensatory expression of GDF15 in the liver may be less pronounced. In line this with notion, GDF15 expression directly correlated with steatosis severity in our study, a critical feature of NAFLD which could be reverted by weight loss [17]. As such, GDF15 treatment may be beneficial in obese patients and after LAGB as many patients relapse [22]. In this context, a local inflammatory milieu (e.g., hepatic MIC-1 expression) may also impact on the regulation of body weight [5].
To further explore a therapeutic benefit of GDF15 in metabolic diseases and NAFLD, additional experimental studies are needed. It may be plausible that GDF15 mediated actions other than regulation of food intake control susceptibility to obesity and related disorders. For example, GDF15 may act anti-inflammatory by limiting neutrophilic inflammation as seen in myocardial infarction [23]. This observation appears important in NAFLD, as advanced stages are characterised by hepatic neutrophilic inflammation [24]. Moreover, GDF15 controls hepatic hepcidin expression and iron overload which may set the susceptibility to NAFLD [25, 26]. Interestingly, GDF15 serum level is a predictor of all-cause mortality which highlights the importance of GDF15 signalling in many disease processes [27].
In conclusion, our study demonstrated that weight loss induced by LAGB reduced hepatic GDF15 expression in patients with NAFLD which may be mediated by a reduction in low-grade inflammation [16]. Based on previous findings [6,9–12], these observations suggest that GDF15 expression in NAFLD [14] occurs in a compensatory manner and that targeting this pathway may ameliorate obesity and related disorders.
Acknowledgments
H. T. was supported by the excellence initiative (Competence Centers for Excellent Technologies: COMET) of the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG: Research Center of Excellence in Vascular Ageing Tyrol, VASCage (K-Project no. 843536) funded by the BMVIT, BMWFW, the Wirtschaftsagentur Wien, and the Standortagentur Tirol; T. E. A. by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) P 29379-B28 and the Austrian Society of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (ÖGGH); and A. R. M. by the Christian Doppler research foundation, the Austrian Federal Ministry of Science, Research and Economy, and the National Foundation for Research, Technology and Development.
Abbreviations
- ALT:
Alanine aminotransferase
- BMI:
Body mass index
- GDF15:
Growth differentiation factor 15
- GGT:
c-Glutamyl transferase
- HOMA:
Homeostasis model assessment
- LAGB:
Laparoscopic gastric banding
- NAFLD:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Additional Points
(i) GDF15 is strongly expressed in the liver compared to adipose tissue in obesity. (ii) Weight loss induced by LAGB is associated with reduced hepatic GDF15 expression in obese patients. (iii) Inflammatory signals such as IL-1β or unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress induce GDF15 expression in hepatocytes. (iv) Hepatic GDF15 expression directly correlates with features of human NAFLD i.e., IL-1β expression and steatosis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors' Contributions
T.E.A. designed and analysed all experiments. F.G., L.M., C.G., and B.E. helped preparing the manuscript and performed experimentation. A.R.M. and H.T. developed and coordinated the project and prepared the manuscript.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figure 1: IL-6, TNF, and LPS do not impact on GDF15 expression in hepatocytes. GDF15 expression in Hep G2 hepatocytes over the course of 24 hours stimulation with IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) determined by qPCR and normalised to GAPDH. Data from 3 independent experiments are shown. Supplementary Figure 2: correlation of hepatic GDF15 expression with clinical features. (A–E) Hepatic GDF15 mRNA expressions did not correlate with body mass index (BMI) (A), homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) index (B), liver injury (C), systemic inflammation (D), and hepatic TNFα expression (E). Respective R values and level of significance are shown in each panel. Each dot represents an individual patient before or after LAGB.
References
- 1.Guh D. P., Zhang W., Bansback N., Amarsi Z., Birmingham C. L., Anis A. H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:p. 88. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tilg H., Moschen A. R. Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2006;6(10):772–783. doi: 10.1038/nri1937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moschen A. R., Molnar C., Geiger S., et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of excessive weight loss: potent suppression of adipose interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha expression. Gut. 2010;59(9):1259–1264. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.214577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wieser V., Adolph T. E., Enrich B., Moser P., Moschen A. R., Tilg H. Weight loss induced by bariatric surgery restores adipose tissue PNPLA3 expression. Liver International. 2017;37(2):299–306. doi: 10.1111/liv.13222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Johnen H., Lin S., Kuffner T., et al. Tumor-induced anorexia and weight loss are mediated by the TGF-β superfamily cytokine MIC-1. Nature Medicine. 2007;13(11):1333–1340. doi: 10.1038/nm1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Macia L., Tsai V. W., Nguyen A. D., et al. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1 (MIC-1/GDF15) decreases food intake, body weight and improves glucose tolerance in mice on normal & obesogenic diets. PLoS One. 2012;7(4) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034868.e34868 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tsai V. W., Macia L., Johnen H., et al. TGF-b superfamily cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 is a physiological appetite and body weight regulator. PLoS One. 2013;8(2) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055174.e55174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tsai V. W., Zhang H. P., Manandhar R., et al. Treatment with the TGF-b superfamily cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 reduces the adiposity and corrects the metabolic dysfunction of mice with diet-induced obesity. International Journal of Obesity. 2017;42(3):561–571. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2017.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mullican S. E., Lin-Schmidt X., Chin C. N., et al. GFRAL is the receptor for GDF15 and the ligand promotes weight loss in mice and nonhuman primates. Nature Medicine. 2017;23(10):1150–1157. doi: 10.1038/nm.4392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Emmerson P. J., Wang F., Du Y., et al. The metabolic effects of GDF15 are mediated by the orphan receptor GFRAL. Nature Medicine. 2017;23(10):1215–1219. doi: 10.1038/nm.4393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yang L., Chang C. C., Sun Z., et al. GFRAL is the receptor for GDF15 and is required for the anti-obesity effects of the ligand. Nature Medicine. 2017;23(10):1158–1166. doi: 10.1038/nm.4394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hsu J. Y., Crawley S., Chen M., et al. Non-homeostatic body weight regulation through a brainstem-restricted receptor for GDF15 . Nature. 2017;550(7675):255–259. doi: 10.1038/nature24042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tsai V. W., Lin S., Brown D. A., Salis A., Breit S. N. Anorexia-cachexia and obesity treatment may be two sides of the same coin: role of the TGF-b superfamily cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 . International Journal of Obesity. 2016;40(2):193–197. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Koo B. K., Um S. H., Seo D. S., et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 predicts advanced fibrosis in biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver International. 2017;38(4):695–705. doi: 10.1111/liv.13587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moschen A. R., Wieser V., Gerner R. R., et al. Adipose tissue and liver expression of SIRT1, 3, and 6 increase after extensive weight loss in morbid obesity. Journal of Hepatology. 2013;59(6):1315–1322. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moschen A. R., Molnar C., Enrich B., Geiger S., Ebenbichler C. F., Tilg H. Adipose and liver expression of interleukin (IL)-1 family members in morbid obesity and effects of weight loss. Molecular Medicine. 2011;17(7-8):840–845. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moschen A. R., Molnar C., Wolf A. M., et al. Effects of weight loss induced by bariatric surgery on hepatic adipocytokine expression. Journal of Hepatology. 2009;51(4):765–777. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pagliassotti M. J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annual Review of Nutrition. 2012;32(1):17–33. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071811-150644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tilg H., Moschen A. R., Szabo G. Interleukin-1 and inflammasomes in alcoholic liver disease/acute alcoholic hepatitis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2016;64(3):955–965. doi: 10.1002/hep.28456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dara L., Ji C., Kaplowitz N. The contribution of endoplasmic reticulum stress to liver diseases. Hepatology. 2011;53(5):1752–1763. doi: 10.1002/hep.24279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim K. H., Kim S. H., Han D. H., Jo Y. S., Lee Y. H., Lee M. S. Growth differentiation factor 15 ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and related metabolic disorders in mice. Scientific Reports. 2018;8(1):p. 6789. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25098-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee S. J., Shin S. W. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. New England Journal of Medicine. 2017;376(15):1490–1492. doi: 10.1056/nejmc1701944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kempf T., Zarbock A., Widera C., et al. GDF-15 is an inhibitor of leukocyte integrin activation required for survival after myocardial infarction in mice. Nature Medicine. 2011;17(5):581–588. doi: 10.1038/nm.2354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xu R., Huang H., Zhang Z., Wang F. S. The role of neutrophils in the development of liver diseases. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2014;11(3):224–231. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tanno T., Bhanu N. V., Oneal P. A., et al. High levels of GDF15 in thalassemia suppress expression of the iron regulatory protein hepcidin. Nature Medicine. 2007;13(9):1096–1101. doi: 10.1038/nm1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Datz C., Muller E., Aigner E. Iron overload and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Minerva Endocrinologica. 2017;42(2):173–183. doi: 10.23736/S0391-1977.16.02565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Corre J., Hébraud B., Bourin P. Concise review: growth differentiation factor 15 in pathology: a clinical role? STEM CELLS Translational Medicine. 2013;2(12):946–952. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2013-0055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figure 1: IL-6, TNF, and LPS do not impact on GDF15 expression in hepatocytes. GDF15 expression in Hep G2 hepatocytes over the course of 24 hours stimulation with IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) determined by qPCR and normalised to GAPDH. Data from 3 independent experiments are shown. Supplementary Figure 2: correlation of hepatic GDF15 expression with clinical features. (A–E) Hepatic GDF15 mRNA expressions did not correlate with body mass index (BMI) (A), homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) index (B), liver injury (C), systemic inflammation (D), and hepatic TNFα expression (E). Respective R values and level of significance are shown in each panel. Each dot represents an individual patient before or after LAGB.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.




