Abstract
The Serra da Mantiqueira is one of the least inventoried physiographic areas of southeastern Brazil. There is great potential for detection of endemic species for which little or nothing is known about basic aspects of natural history. The Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio (PESP) within the Serra da Mantiqueira is an area of extreme biological importance because it houses mixed formations of grasslands, ombrophilous forests, and enclaves of Araucaria forests (mixed ombrophilous forest). Currently, the mixed ombrophilous forest covers less than 5% of its original range and areas occupied by this forest type, and associated ecosystems constitute refuges, housing several endemic, high altitude species. Between September 2015 and April 2016, field samplings were performed in the PESP using four distinct methods. The objective was to determine the composition and natural history of snakes from an isolated, high altitude area of the Serra da Mantiqueira. In PESP and surrounding areas, 80 individuals representing 24 species, 19 genera, and three families were recorded. Data are presented on abundance, habitat, daily activity, diet, reproduction, and defense. Comparison of the PESP snake assemblage with 30 other Atlantic Forest areas in southeastern Brazil indicate the Serra da Mantiqueira presents particular characteristics regarding snake composition.
Keywords: Araucaria Forests, Atlantic Rainforest, cluster analysis, Serpentes , southeastern Brazil
Introduction
The structure of a snake community can be influenced by historical factors, such as biogeography (Cadle and Greene 1993, Martins and Oliveira 1998, Marques 1998, Sawaya et al. 2008), and ecological factors, such as competition (Inger and Colwell 1977, Henderson et al. 1979, Vitt and Vangilder 1983, Pianka 1989, Krebs 2001), predation (Connel 1975, Krebs 2001), and the influence of species natural history on the assemblage evolution (Schoener 1968, 1983, Wiens 1977). However, the basic natural history and biology for many snake species remains unknown. This is compounded by loss of such information with the reduction of habitat (Marques 1998). Description of snake communities with the intention of understanding interactions between species, patterns of diversity (e.g., species richness, dominance and relative abundance), and the processes that influence community structure is becoming increasingly important.
Snake fauna of tropical areas is typically characterized by high species richness, low abundance, and complex ecological interactions (Duellman 1978, Henderson et al. 1979). These features pose challenges to quantitative and comprehensive study of these populations. There have been several efforts to describe the ecology and natural history of snakes in Brazil (e.g., Amazon Forest: Cunha and Nascimento 1978, Martins and Oliveira 1998, Pantanal: Strüsmann and Sazima 1993, Cerrado: Nogueira 2001, Sawaya et al. 2008, Caatinga: Mesquita et al. 2013, Guedes et al. 2014; Atlantic Forest: Marques 1998, Cicchi et al. 2007, Centeno 2008, Cicchi et al. 2009, Hartmann et al. 2009a, b, Trevine et al. 2014). Although these studies have advanced our understanding of snake fauna in various ecosystems, studies focusing on snake communities in high altitude areas and the Araucaria forests remain scarce. Studies with this focus are mainly concentrated in the Serra do Mar of São Paulo State (e. g., Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar: Hartmann et al. 2009b; Parque Natural Municipal Nascentes de Paranapiacaba: Trevine et al. 2014; Parque Nacional da Serra da Bocaina: Ortiz et al. (2017) and southern Brazil (e.g., Centro de Pesquisas e Conservação da Natureza Pró-Mata: Di-Bernardo 1998; Parque Nacional de Aparados da Serra: Deiques 2009). However, there is a lack of knowledge about the Serra da Mantiqueira snake fauna.
The Serra da Mantiqueira is one of the least well-understood physiographic areas of southeastern Brazil. There is considerable potential for the record of remarkable and endemic species, for which basic natural history has yet to be described. To date only a single study reports on a snake assemblage in this region (Cardoso 2011). This work presented the ecological aspects of a snake community in Munhoz (southern Minas Gerais) and provided the first insight into the composition and natural history of snakes in this region. Here we report on the snake composition of the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio (PESP), Minas Gerais, Southeastern Brazil, a high altitude area of the Serra da Mantiqueira. We describe the species observed, natural history data, altitudinal distribution, as well as an identification key for the recognition of snake species in the area. Finally, we compare the snake fauna composition of PESP with those of 30 other Atlantic forest areas in southeastern Brazil, including the states of Minas Gerais (MG), Rio de Janeiro (RJ) and São Paulo (SP).
Materials and methods
Study area
This study was conducted in the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio (PESP) (22°8'33"S, 44°43'43"W, ca. 22.900 ha) located at Serra da Mantiqueira, southern Minas Gerais State, southeastern Brazil. The PESP overlaps the municipalities of Aiuruoca, Alagoa, Baependi, Itamonte and Pouso Alto within MG, and has an altitudinal range from 1200–2359 m above sea level (Silva et al. 2008). Southward, the PESP contacts the Itatiaia National Park, forming an ecological corridor between the forests of southern Minas Gerais with those of the coastal mountain ridges (= Serra do Mar) in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo States. The park presents little-disturbed vegetation, within five vegetation zones: 1 - Ombrophilous Dense High Montane Forest (nebular forest), covering altitudes above 1800 m a.s.l.; 2 - Ombrophilous Dense Montane Forest, covering altitudes below 1800 m a.s.l.; 3 - Mixed Ombrophilous Forest, concentrated in valleys along watercourses at 1600 m a.s.l.; 4 – High altitude grasslands, covering parts with altitudinal heights between 1300 and 1800 m a.s.l. and 5 - Rocky Fields, associated with rocky outcrops above 2000 m a.s.l. (Silva et al. 2008). According to Köppen`s classification, the predominant climate is mesothermal tropical of altitude, with a cold and dry winter, and high rainfall levels in the summer. The average annual precipitation exceeds 1500 mm, with 80% occurring from October to March. Winter temperatures range from 0 °C to 10 °C and frost and drought can occur during in this period. Summer is mild with temperatures ranging up to 30 °C (Silva et al. 2008).
Sampling design
Snake sampling lasted eight months, from September 2015 to April 2016. We sampled between altitudes 1600 and 2359 m a.s.l. across all of the available vegetation types. Field trips of four to seven days at a time were made monthly for a total of 40 days of field observation. Four different sampling methods were used to capture snakes:
1) Pitfall traps with drift fences (Greenberg et al. 1994, Cechin and Martins 2000) were installed in three types of vegetation: Ombrophilous Dense Montane Forest, Mixed Ombrophilous Forest, and High Altitude Grasslands. Two sets of traps were used, each comprised of two 50-meter lines, separated from each other by 100 m. Each line consisted of five 60-L buckets, joined by an approximately 50 cm high drift fence. The buckets were drilled in the bottom to avoid accumulation of rainwater. Inside each bucket, we also put foliage together with a styrofoam plate to serve as a refuge for the fallen animals (Mesquita et al. 2013). The drift fence was buried 20 cm below the ground and held upright by wood stakes. These traps were opened for the four to seven days of each monthly field trip, except for May, June, July, and August. They were inspected daily, totaling 40 days of open traps (2400 bucket days).
2) Time-constrained search was also employed (Campbell and Christman 1982, Martins and Oliveira 1998). Trails were covered on foot, searching all possible shelters and microhabitats that might be used by snakes. In total, 360 hours of visual searching was performed in the study area vegetation types.
3) Accidental encounter (Sawaya et al. 2008) of live or dead specimens sampled opportunistically, with no methodology like pitfall traps or time-constrained search. Here we included individuals found in the PESP and the surrounding areas. Snakes found in the surroundings were included in the list only when recorded above 1600 m (lower altitude of our sampling site) and if they presented literature records at equal to or higher elevations. This methodology was used primarily on roads BR 354, LMG 881, and an unpaved road that links Itamonte, MG, to the PESP headquarters.
4) Records made by local people (Martins and Nogueira 2012). Snakes found by local people from the PESP area and surroundings were also incorporated in the sampling. To get more information about the specimens found, we delivered record sheets for registering information on snakes, such as time and site of the encounter (open area, forest edge, and forest interior), behavior and posture (moving, stationary, coiled or stretched).
For each specimen, we recorded: date and time of observation, habitat, microhabitat, mass (g), sex, diet, reproduction, activity, and defensive behavior. Snake size was categorized according to Marques et al. (2001). Diet was characterized in two different ways. Collected snakes had their stomach examined through a ventral incision along the posterior two-thirds of the body (Martins and Gordo 1993). However, most individuals were not collected and so they were submitted to regurgitation through soft palpation on the abdomen in an antiperistaltic movement (Shine 1995). These animals were subsequently released at the site of capture. Whenever diet items were found, they were identified to the lowest possible taxonomic level using identification keys, comparison with other specimens from zoological collections, and expert assistance. To describe the reproductive condition, we recorded the number of follicles in secondary vitellogenesis or eggs/embryos present in females (Almeida-Santos et al. 2014). The specimens collected during this study were deposited in two zoological collections: Coleção Herpetológica Alphonse Richard Hoge of Instituto Butantan (IBSP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil and in Museu de Zoologia João Moojen (MZUFV), Viçosa, MG, Brazil.
Data analysis
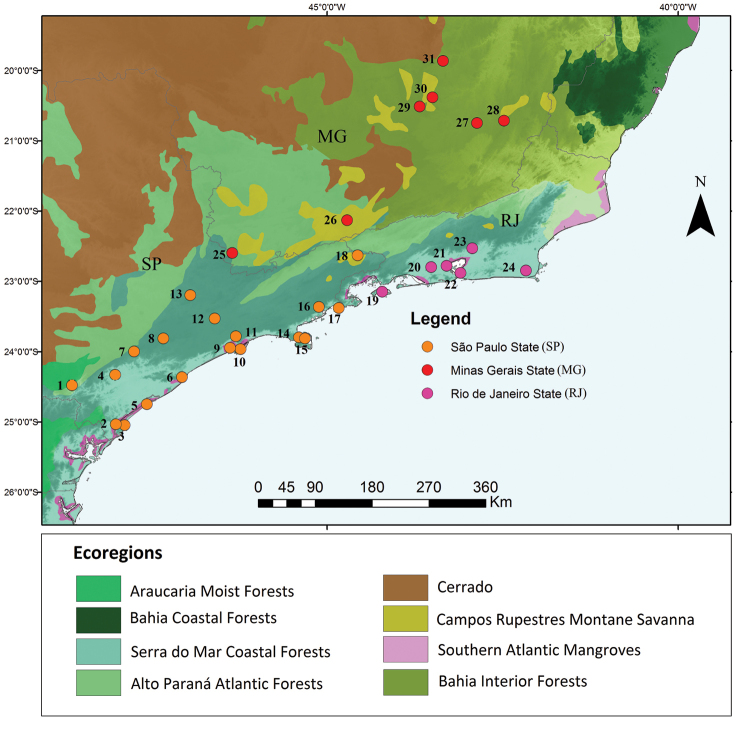
We compared the snake assemblage from Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio with those of 30 other localities in the Atlantic forest, in southeastern Brazil (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Areas used for the analysis of similarity between snake assemblages.The following snake assemblages were included in the analyzes: São Paulo State: 1 Parque Estadual Turístico do Alto Ribeira (Araújo et al. 2010) 2 Ilha da Cananéia (Cicchi et al. 2007) 3 Parque Estadual Ilha do Cardoso (Rocha et al. 2008) 4 Fazenda Etá (Fiorillo 2016) 5 Ilha Comprida (Cicchi et al. 2007) 6 Estação Ecológica Juréia-Itatins (Marques and Sazima 2004) 7 Parque Estadual Carlos Botelho (Forlani et al. 2010) 8 Municipalities of Tapiraí and Piedade (Condez et al. 2009) 9 São Sebastião (Centeno et al. 2008) 10 Ilhabela (Centeno et al. 2008) 11 Parque Municipal de Paranapiacaba (Trevine et al. 2014) 12 São Paulo (Barbo et al. 2011) 13 Parque Estadual da Serra do Japi (Sazima and Haddad 1992) 14 São Vicente Island (Cicchi et al. 2007) 15 Santo Amaro Island (Cicchi et al. 2007) 16 Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar (Núcleo Santa Virgínia) (Hartmann et al. 2009a) 17 Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar (Núcleo Picinguaba) (Hartmann et al. 2009b) 18 São José do Barreiro (Ortiz et al. 2017); Rio de Janeiro State 19 Ilha Grande (Rocha and Van-Sluys 2006) 20 Parque Natural Municipal da Serra do Mendanha (Pontes et al. 2009) 21 Duque de Caxias (Salles and Silva-Soares 2010) 22 Niterói (Citeli et al. 2016) 23 Estação Ecológica do Paraíso (Vrcibradic et al. 2011) 24 Núcleo Experimental de Iguaba Grande (Martins et al. 2012) Minas Gerais State 25 Munhoz (Cardoso 2011) 26 Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio (This study) 27 Parque Estadual da Serra do Brigadeiro (Moura et al. 2012) 28 Viçosa (Costa et al. 2010) 29 Ouro Branco (São-Pedro and Pires 2009) 30 Ouro Preto and surroundings (Silveira et al. 2010) 31 Estação Ambiental de Peti (Bertoluci et al. 2009).
With this data set, we generated a binary presence/absence matrix of 120 species. To compare snake assemblages, we used this matrix to run a Cluster Analysis, using the Jaccard’s similarity index, and the Pair Group Average Method (UPGMA) as the grouping method. We also calculated the cophenetic correlation coefficient to indicate the similarity matrix degree of representation in the dendrogram. In this index, values greater than or equal to 0.8 allow considering the dendrogram as adequate to the similarity matrix (Rohlf 2000). The result of this analysis was visually compared, allowing the identification of groups clustered together by the similarities of species composition from different localities.
Finally, a Nonmetric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) was used for another view of the Jaccard index clusters. The stress value was used as a representative measure of the groupings, and values <0.20 were considered acceptable (Clarke and Warnick 1994). Multivariate analyzes were performed in R software (R Core Team 2014), using the vegan package (Oksanen et al. 2015).
Taxonomic accounts
Several nomenclature changes have been proposed to the taxonomy of Neotropical snakes in recent years. To provide consistency during similarity analysis we present a brief list of species that have had names changes and identify the name used in this report. The name “Taeniophallusgr.occipitalis” was used for specimens traditionally referred to as Taeniophallusoccipitalis (Jan, 1863) because more than one species often fall under this designation (Santos-Jr. 2008). Specimens identified as Mussuranamontana (Franco, Marques & Puorto, 1997) by Hartmann et al. (2009b) belong to Pseudoboaserrana Morato, Moura-Leite, Prudente & Bérnils, 1995 (Francísco Luís Franco pers. obs.). Specimens identified as Atractus sp. by Hartmann et al. (2009b) were described as Atractusfrancoi Passos, Fernandes, Bérnils and Moura-Leite, 2010. Specimens referred to as Dipsas sp. by Hartmann et al. (2009a) were described as Dipsassazimai Fernandes, Marques & Argôlo, 2010. Specimens identified as Dipsasindica Laurenti, 1768 by Hartmann et al. (2009a) were considered Dipsaspetersi Hoge & Romano, 1975, according to Harvey and Embert (2008). The specimen referred to as Helicops sp. by Costa et al. (2010) was described as Helicopsnentur Costa, Santana, Leal, Koroiva and Garcia 2016. The specimen identified as Tropidophiscf.paucisquamis by Silveira et al. (2010) was described as Tropidophispreciosus Curcio, Nunes, Argôlo, Skuk & Rodrigues, 2012. The specimen identified as Philodryasoligolepis Gomes in Amaral, 1921 by Silveira et al. (2010) belongs to Philodryaslaticeps Werner, 1900 (Zaher et al. 2008). Specimens identified as Thamnodynastes sp. by Salles and Silva-Soares (2010) belong to Thamnodynastesnattereri (Mikan, 1820) (Franco and Ferreira 2002), as well as the specimens cited as Thamnodynastescf.nattereri by Marques and Sazima (2004), Centeno et al. (2008), Pontes et al. (2008), Bertoluci et al. (2009), Hartmann et al. (2009b), Silveira et al. (2010), Vrcibradic et al. (2011), Moura et al. (2012) and Citeli et al. (2016). Specimens considered as Chironiusflavolineatus (Jan, 1863) by Condez et al. (2009), São Pedro and Pires (2009), Forlani et al. (2010) and Silveira et al. (2010) were described as Chironiusbrazili Hamdan & Fernandes, 2015 (Hamdan and Fernandes 2015). The specimen considered Micrurusibiboboca (Merrem, 1820) by Martins et al. (2012) corresponds to a new species which is being described (Francisco Luís Franco, unpubl. data). The specimen regarded as Dipsasincerta (Jan, 1863) by Citeli et al. (2016) corresponds to Dipsasalternans (Fischer, 1885) (Passos et al. 2004). The specimen cited as Epicrates sp. by Moura et al. (2012) was considered Epicratescenchria (Linnaeus, 1758) according to the own comments on Moura et al. (2012). Specimens addressed as Dipsasneivai Amaral, 1926 by Centeno et al. (2008) correspond to Dipsasvariegata (Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854) (Harvey and Embert 2008). The specimens cited as Chironiuscf.quadricarinatus and Liophiscf.almadensis by Bertoluci et al. (2009) were considered Chironiusquadricarinatus (Boie, 1827) and Erythrolamprusalmadensis (Wagler, 1824), respectively. Specimens identified as Tantillacf.melanocephala by Barbo et al. (2011) are here considered Tantillamelanocephala (Linnaeus 1758). The specimen “IBSP 30496” regarded as Cleliarustica (Cope, 1878) by Franco et al. (1997), corresponds to a new species that is being described (Francisco Luís Franco, unpubl. data). Taxonomy on family level follows Grazziotin et al. (2012).
Results
Species composition
We recorded 80 snakes during the eight month period of fieldwork through all sampling methods. In this group we separated 24 species of 19 genera, of which 67% are dipsadids, 19% viperids, and 14% colubrids (Table 1). The five most abundant species in the study area were dipsadids Atractuszebrinus and Thamnodynastesstrigatus (each 18.5% of the records), followed by Philodryaspatagoniensis (11.2%), Gomsesophisbrasiliensis (10%), and the viperid Bothropsfonsecai (8.7%). Among viperid records, the most abundant species was B.fonsecai (n = 7; 63%), followed by B.jararaca (n = 2; 18%), and B.neuwiedi and Crotalusdurissus (n = 1; 9% each).
Table 1.
List of species found in the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Abbreviations: abundance (N), relative frequency of each species (f%), environment (1 - High altitude grassland, 2 - Rocky Field, 3 - Dense Montane Ombrophilous Forest, 4 - Mixed Ombrophilous Forest), habitat (aa - open area, bf - forest edge, da – disturbed areas, fl - forest, lo - lotic environment, le - lentic environment), and habits (F-fossorial, C-cryptozoic, SAQ-sub-aquatic, T-terrestrial, SA-sub-arboreal, and A-arboreal). Species registered outside the park area (*).
| Family/ Species | N | F% | Environments | Habitat | Habit | Altitudinal variation (m) | New record altitudinal (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COLUBRIDAE | |||||||
| Chironiusbicarinatus (Wied, 1820) | 1 | 1.2 | 1,3 | bf, at | SA | 0–1850 | – |
| Chironiusbrazili Hamdan & Fernandes, 2015 | 1 | 1,2 | 1,3 | Bf, fl, at | SA | 200–2030 | – |
| Spílotes pullatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | fl | SA | 0–1100 | 1630 |
| DIPSADIDAE | |||||||
| Apostolepisassimilis (Reinhardt, 1861)* | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | Aa, at | F, T | 170–1610 | – |
| Atractuszebrinus (Jan, 1962) | 15 | 18.7 | 1,2,3 | Aa, fl, at | F, T | 20–1610 | 1730 |
| Boirunamaculata (Boulenger, 1896) | 1 | 1.2 | 3 | fl | T | 0–1880 | – |
| Echinantheracephalostriata Di-Bernardo, 1996 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | Bf, fl | C, T | 0–1610 | 1730 |
| Erythrolamprusmiliaris (Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 1.2 | 3 | Fl, le | SAQ | – | 1643 |
| Gomesophisbrasiliensis (Gomes, 1918) | 8 | 10 | 1 | Aa, lo, le, at | SAQ | 430–1650 | 1750 |
| Mussuranamontana (Franco, Marques & Puorto, 1997)* | 1 | 1.2 | 4 | fl | T | 750–1610 | 1740 |
| Oxyrhopusclathratus Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854* | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | Aa, at | T | 0–1610 | – |
| Oxyrhopusrhombifer Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854 | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | Aa, at | T | 0–1330 | 1730 |
| Philodryasaestiva (Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854) | 2 | 2.5 | 1,2 | aa | T | 0–1730 | 1800 |
| Philodryaspatagoniensis (Girard, 1858) | 9 | 11.2 | 1,2 | Aa, at | T | 0–1600 | 2200 |
| Sibynomorphusmikanii (Schlegel, 1837) | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | Aa, at | T | 110–1350 | 1630 |
| Taeniophallusaffinis (Günther, 1858) | 3 | 3.7 | 1,3 | aa | T, C | 0–1600 | 1760 |
| Taeniophallusgr.occipitalis* | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | bf | T, C | – | 1600 |
| Thamnodynastesstrigatus (Günther, 1858) | 15 | 18.7 | 1,3,4 | Aa, fl, bf, at | SAQ | 0–2450 | – |
| Tomodondorsatus Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854 | 2 | 2.5 | 3,4 | fl | T | 0–1610 | 1730 |
| Xenodonmerremii (Wagler in Spix, 1824) | 1 | 1.2 | 1,2 | aa | T | 0–1300 | 1610 |
| VIPERIDAE | |||||||
| Bothropsfonsecai Hoge & Belluomini, 1959 | 7 | 8.7 | 1,2,3,4 | Aa, bf, fl | T | 440–1730 | 2175 |
| Bothropsjararaca (Wied, 1824) | 2 | 2.5 | 1,2,3,4 | Bf, fl | T | 0–1640 | 2150 |
| Bothropsneuwiedi Wagler in Spix, 1824 | 1 | 1.2 | 1,2 | Aa, bf | T | 0–1600 | 2150 |
| Crotalusdurissus Linnaeus, 1758 | 1 | 1.2 | 1,2 | Aa, bf | T | 0–1400 | 1950 |
| Total | 80 | 100 | |||||
Comparison with other snake assemblages from the Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil
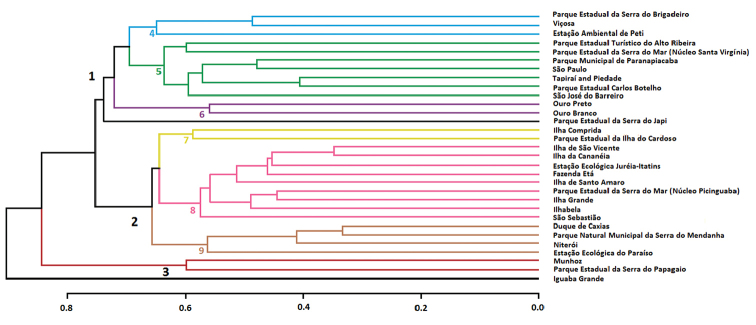
The cluster analysis (cophenetic correlation coefficient = 0.8381) based on 120 snake species recorded at 31 localities, including Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio, resulted in three main groupings (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Cluster analysis based on snake species composition from 31 localities of the Atlantic Forest, southeastern Brazil.
Group 1 was composed generally by localities of mid to high altitudes (> 600 m): the coastal forests of Serra do Mar and Bahia Interior Forests (Olson et al. 2001), covering the Paranapiacaba, Cantareira and Bocaina Mountains in São Paulo, and the Mantiqueira and extreme south of Espinhaço mountains in Minas Gerais. An exception was the Parque Estadual da Serra do Japi, which has remained isolated from the other localities. Three subgroups can be visualized in this grouping. The first (4) is formed by areas in the northern portion of Serra da Mantiqueira and surroundings (Parque Estadual da Serra do Brigadeiro and Viçosa), in Minas Gerais state, as well as a locality in southern Espinhaço Mountains (Estação Ambiental de Peti). The second (5) is comprised of the mountains in São Paulo State. The third (6) is composed of two localities in the southern region of Serra do Espinhaço (Municipalities of Ouro Branco and Ouro Preto and surroundings).
Group 2 consisted of low areas (< 400 m a.s.l.) of the Coastal Forests of Serra do Mar, comprising island and continental regions in the coastal strip of São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro states. In this group, three subgroups can also be observed. The first (7) consists of two continental islands on the south coast of São Paulo state (Ilha do Cardoso and Ilha Comprida). The second (8) composed by the other insular and lowland locations of the Atlantic Forest in São Paulo state, in addition to an island in Rio de Janeiro State (Ilha Grande). Geographically, this subgroup is close to the Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar (Picinguaba, São Paulo State), with which it shares several snake species. The third (9) is composed of lowland locations in the state of Rio de Janeiro, east of Serra dos Órgãos, for which similarities have already been described by Citeli et al. (2016).
Group 3 is composed of only two high altitude localities (> 1100 m a.s.l.) in the southern Mantiqueira Mountains: the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio and Munhoz.
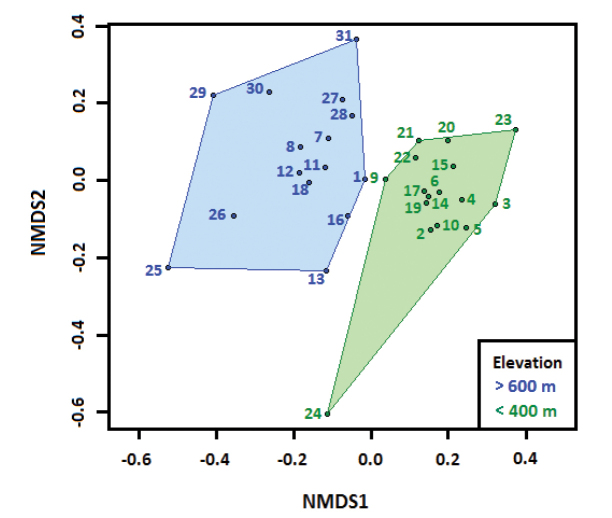
The NMDS ordering analysis (stress 0.1547) graphically depicts the relative position of localities in a two-dimensional space (Fig. 3). It suggests the clustering pattern found between the locations is associated with the spatial distribution, mainly altitudinal, in the study area and corroborates the results of the cluster analysis.
Figure 3.
Groupings formed through NMDS analysis (stress 0.1547). The relationship between altitude and the composition of snake species in the Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil is shown. The numbers correspond to the same localities as in figure 1.
Natural history information about the species
Colubridae Oppel, 1811
Chironius bicarinatus
(Wied, 1820)
0D8CBAAC-CD35-5A49-9D4B-5E2EEC89A447
Natural history notes.
Medium-sized snake (n = 1), diurnal and semi-arboreal (Marques et al. 2001). An individual was observed on the ground during the day (12:00 h) in March, next to a small fragment of disturbed forest. Upon detecting the observer’s approach, the snake fled into the forest. Sazima and Haddad (1992) also mention the presence of C.bicarinatus in fragments of disturbed forests. The diet is specialized in anurans, composed mainly of hylids and leptodactylids (Dixon et al. 1993). Reproduction is seasonal, with copulation in early autumn and between 4 – 14 eggs laid at the end of winter (Marques et al. 2009, Pontes and Rocha 2008).
Altitudinal variation.
From sea level, from the northern coast of Rio Grande do Sul to Bahia, to a maximum altitude of 1610 m in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). In this study, the maximum altitudinal record was 1730 m, in Baependi, MG. Dixon et al. (1993) cited the species in “Brazil, Rio de Janeiro, Marombe [sic], Itatiaia,” at 1850 m a.s.l.. The Maromba region encompasses altitudes from 500 to 2000 m. Despite several records of this species in elevated areas (above 800 m a.s.l.) (Bérnils 2009), Chironiusbicarinatus is thought to occupy predominantly plains (Dixon et al. 1993, Carreira et al. 2005).
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, central-west, southeast and south of Brazil (Bahia, Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul), Argentina, and Uruguay (Bérnils 2009, Wallach et al. 2014). This species inhabits all forest formations and open areas such as pampas, cerrado, restingas (Sazima and Haddad 1992, Dixon et al. 1993, Carreira et al. 2005) and rocky fields.
Chironius brazili
Hamdan & Fernandes, 2015
D96C0A19-0ABC-537B-9B86-63B35D13AB83
Figure 4.
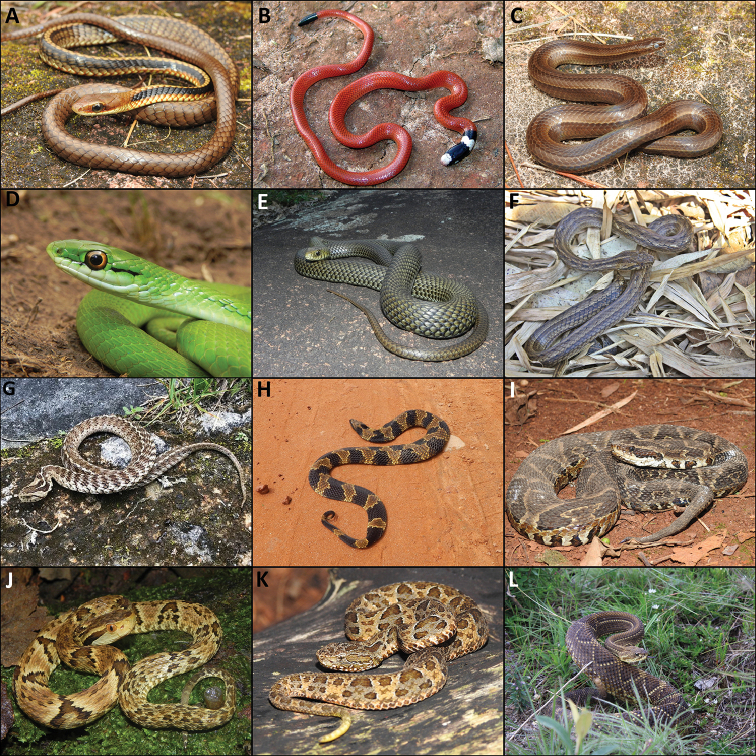
Snakes from the Serra do Papagaio. AChironiusbraziliBApostolepisassimilisCGomesophisbrasiliensisDPhilodryasaestivaEPhilodryaspatagoniensisFThamnodynastesstrigatusGTomodondorsatusHXenodonmerremiiIBothropsfonsecaiJBothropsjararacaKBothropsneuwiediLCrotalusdurissus. Photographs by Mário Sacramento, Frederico de Alcântara Menezes, Arthur Diesel Abegg, and Leonardo Chaves.
Natural history notes.
Medium-size species (n = 1), diurnal and semi-arboreal (Dixon et al. 1993, Marques et al 2015). Five observations of C.brazili were made (one during fieldwork and four outside the sampling period). Three individuals were observed between the stones of a waterfall (10:00 – 15:00 h). A recently road-killed adult male was found during the day (11:00 h) in a forest area. Additionally, we observed an individual at rest, coiled over the vegetation at 1.30 m above the ground during the day (16:30 h). All records occurred near watercourses. Abegg et al. (2016) also mention the occurrence of C.brazili in riparian forests. No data on the diet was obtained from the examined specimen. However, as in the other species of the genus, it is likely that C.brazili preys primarily on anurans, mainly hylids (Dixon et al. 1993). We could observe the following defensive behaviors for C.brazili: head elevation and neck S-coil.
Altitudinal variation.
The maximum altitudinal record for the species was at 2030 m a.s.l. at Pico do Inficionado, Catas Altas, MG (Bérnils 2009). In the present study, the maximum altitudinal record was at 1600 m a.s.l., in Baependi, MG.
Distribution and habitat.
Central-west, southeast and south of Brazil (Federal District, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Rio Grande do Sul) (Hamdan and Fernandes 2015). This species is thought to live in habitats similar to those of C.flavolineatus and inhabits riverine forests and forest borders near open areas (Hamdan and Fernandes 2015).
Spilotes pullatus
(Linnaeus, 1758)
BB9F9CC3-61BA-5794-89E7-77E4F5B3A2EC
Natural history notes.
A large species (n = 1), with semi-arboreal habits, and diurnal activity (Marques et al. 2001, Marques and Sazima 2004). Both of our records were made in the same place, during the day (12:00 and 12:10 h), in September and October, respectively, indicating that it may be the same individual. On both occasions, the individuals were on the ground, in a forest area. The diet is mainly composed of mammals (Marques et al. 2014), but S.pullatus also feeds on lizards, birds and their eggs, and anurans (Martins and Oliveira 1998, Marques and Sazima 2004, Bernarde and Abe 2006). This species lays five to twelve eggs (Amaral 1930, Marques et al. 2014). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
In Brazil, range spans at minimum of sea level from the coast of Santa Catarina to Bahia to a maximum of 1100 m a.s.l., Brasília, Federal District (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record of this species for Brazil is expanded here by our observations at 1630 m a.s.l.. From the toponyms surveyed, Bérnils (2009) recorded only 8% in areas higher than 800 m a.s.l. and 57% between the range of sea level and 400 m a.s.l.
Distribution and habitat.
This species can be found in all Brazilian states, and in Argentina and Paraguay (Wallach et al. 2014). It lives in open formations associated with riparian, dense and seasonal ombrophilous forests (Bérnils 2009).
Dipsadidae Bonaparte, 1838
Apostolepis assimilis
(Reinhardt, 1861)
74709F12-A0F6-5B1E-9628-E639A348F1FA
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 1), with nocturnal activity and cryptozoic or fossorial habits (Ferrarezzi et al. 2005, Marques et al. 2015). In December, an adult was seen at 07:30 h. moving in an open area. The record occurred in Aiuruoca-MG, near the PESP. The diet is composed of amphisbaenids and other elongate vertebrates (Ferrarezzi et al. 2005). Barbo (2011) mentions two females with four and six vitellogenic follicles in November and March. No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of 170 m a.s.l., in Cuiabá, Mato Grosso and maximum of 1610 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). In this study, the record occurred outside the park limits at 1100 m a.s.l., in Aiuruoca, MG.
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Goiás, Distrito Federal, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná), southeast Paraguay, northern Argentina, and Bolivia (Bérnils 2009; Wallach et al. 2014). This species is typical of the Cerrado morphoclimatic domain, also occurring in adjacent forested areas (Ferrarezzi et al. 2005).
Atractus zebrinus
(Jan, 1862)
A9FAA999-C31E-52E8-B697-9F9C6B47424B
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 15), nocturnal, with fossorial habits (Marques et al. 2001). Data on A.zebrinu activity and habitat use are available from sparse records and inferred from ecological attributes of other species of the genus (e.g., Atractuspantostictus and A.reticulatus). The species was considered abundant in the study area and was found in all the sampled vegetation types. The exception was mixed ombrophilous forest, which are located in valleys along water courses and undergo seasonal flooding in the rainy season. This species was often captured in pitfall traps (open area = 7, forest area = 8, pitfall = 8). Seven individuals were found during the day (09:30–18:00 h.), all at rest; three under trunks, three were buried and came up when a tractor revolved the soil, and one was basking. An adult female was observed at 20:00 h. crossing the road in a forest area. This information reinforces the conclusion that this species is nocturnal and a generalist for vegetation use, because it was found in both open and forested areas. Similar to other Atractus species, the diet is composed of annelids (Marques et al. 2001). Of the seven individuals examined, two had earthworms in their stomachs. This species was found in all sampling months at similar numbers. There is no information in the literature regarding reproduction. A female collected in October (SVL = 425 mm; TL = 34 mm) presented four vitellogenic follicles and another female was found in December (SVL = 480 mm; TL = 40 mm) with 12 undeveloped follicles. In June, two young individuals (approx SVL = 200 mm) were found together when a tractor revolved the earth. Passos et al. (2016) observed aggregation of juveniles after parturition in Atractuspotschi. As defensive tactics, we observed cloacal discharge and head hiding.
Altitudinal variation.
Found at a minimum of 20 m a.s.l. in Itaboraí, RJ and maximum of 1610 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitude of the species is expanded here by individuals we observed at 1730 m a.s.l.
Distribution and habitat.
South and southeast of Brazil (Santa Catarina, Paraná, São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais and Espírito Santo) (Bérnils 2009, Wallach et al. 2014). The toponyms occupied by this species are concentrated in the coastal mountain ranges of Paraná and São Paulo States: Paranapiacaba, Órgaos, Mantiqueira, and Espinhaço mountain ranges. The species is found in areas with predominantly dense ombrophilous forests, mixed ombrophilous forest, seasonal forest (Bérnils 2009), and high altitude grasslands.
Boiruna maculata
(Boulenger, 1896)
DB195237-CF9C-5204-AAD9-E4A809957BCE
Natural history notes.
A large species (n = 1), terrestrial (Marques et al. 2015), although there is one record of arboreal substrate (Gallardo et al. 2006). In October, a juvenile was collected at 07:30 h. while crossing an unpaved road in a forested area. Data on daily activity are scarce. In the literature, there are two observations of activity at night, one during twilight, and one during the day (Gallardo et al. 2006, Hartmann and Giasson 2008, Gaiarsa et al. 2013). Although the specimen was found active in the early hours of the day, it is thought that the species is predominantly nocturnal, similar to other Pseudoboine species (Marques 1998, Sawaya et al. 2008). A recently ingested lizard (Ophiodes sp.), swallowed head-first, was found in the digestive tract of this specimen. Previous studies indicate this species is a generalist, feeding primarily on snakes, but also birds, small mammals, anurans, and lizards (Lema et al. 1983, Carreira 2002, Gallardo et al. 2006, Hartmann and Giasson 2008, Gaiarsa et al. 2013). This is the first record of an Ophiodes as prey for B.maculata. No reproductive data were obtained from the examined specimen. However, the species is known to lay from four to 15 eggs (Sawaya et al. 2008). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
Species records indicate a minimum of sea level in Rio Grande do Sul and maximum of 1240 m a.s.l. in Serra do Salitre, MG (Bérnils 2009). In Brazil, the maximum altitudinal record of the species is for the study area (at 1600 m a.s.l.). Observations at toponyms below 400 m a.s.l. were recorded only on the coast, from Uruguay to Rio Grande do Sul, and in the western and southernmost parts of its distribution (Negro, Jacuí, Uruguay, Paraguay, and Paraná basins) (Bérnils 2009). Quinteros-Muñoz (2006) collected an individual at 1880 m a.s.l. in the National Park La Yunga, Bolivia in a region that encompasses altitudes ranging from 1000 to 4000 m a.s.l.
Distribution and habitat.
North, central-west, southeast and south of Brazil (Amazonas, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Rio Grande do Sul, São Paulo), Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay (Bérnils 2009, Wallach et al. 2014). Typically, this is a species of open areas (cerrados, savannas, chacos, and pampas) with records near adjacent forests (Bérnils et al. 2007).
Echinanthera cephalostriata
Di-Bernardo, 1996
CE558160-9BF1-5FAC-92EA-EC2FF3B648A0
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 2), predominantly diurnal, terrestrial and cryptozoic (Marques et al. 2001). Feeds on anurans (Marques et al. 2001, Forlani et al. 2010). In September, a female was found in the early afternoon (12:00 h), inside a bromeliad (Aechmeaaiuruocensis Leme) on the forest floor. In its digestive tract, we found a Physalaemusolfersii (Lichtenstein & Martens, 1856) (ingested by the leg), and three anuran eggs. Moura-Leite et al. (2003) recorded a specimen with 32 anuran eggs in the stomach. The second individual, another female, was found resting during the day. The record was made in November, at the forest edge, near a swamp area. This individual had ingested three Physalaemusjordanensis Bokermann, 1967 (two were ingested head-first and the last by the leg). Pontes et al. (2008) found E.cephalostriata only in primary and secondary forests. The presence of P.jordanensis (found in PESP just in open area marshes, F. Menezes pers. obs.) as prey of E.cephalostriata, indicates this snake also forages in open areas and lentic environments. Reproduction data of the species are scarce. The female collected in September (SVL = 490 mm; TL = 210 mm) presented nine vitellogenic follicles. Fiorillo (2016) refers to a female from Iguape, with eight vitellogenic follicles in November. No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
Found at altitude minimum of sea level from Santa Catarina coast to Rio de Janeiro and maximum of 1610 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitude for this species is recorded here, with two individuals found at 1730 m a.s.l.. Bérnils (2009) mentioned that more than 80% of the toponyms come from hill and plateau areas. Although the distribution range is concentrated in mountains and plateau areas, this species is also frequent in lower altitudes (see Hartmann 2005, Fiorillo 2016).
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, southeast, and southern Brazil (Bahia, Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro, Santa Catarina and São Paulo) (Wallach et al. 2014). Occurs in dense and mixed ombrophilous forest formations, as well as in semi-deciduous forests (Di-Bernardo 1996, Bérnils 2009).
Erythrolamprus miliaris
(Linnaeus, 1758)
D5720AC6-FCF3-5FB9-A4DB-F535C75BFC85
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 1), predominantly diurnal and semi-aquatic (Marques et al. 2001), although there are reports of activity at night (Sazima and Haddad 1992). In September, an individual was found standing still on the forest floor during the day (15:00 h) at a swamp border. This species feeds mainly on amphibians, fish, and tadpoles (Marques and Souza 1993, Marques and Sazima 2004), although it can occasionally feed on other reptiles (Marques and Sazima 2004, Bonfiglio and Lema 2007, Hartmann et al. 2009a). Pizzatto and Marques (2006) reported a continuous reproductive cycle in a population of southern Bahia state coast (northern distribution) and seasonal reproductive cycles in populations of both inland and coastal São Paulo and Paraná states (southern distribution). Fecundity is six to seventeen eggs, with individuals reaching sexual maturity at twelve months (Vitt 1992, Pizzatto and Marques 2006). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
We found no information in the literature regarding the altitudinal variation of the species. In this study, the maximum altitudinal record was at 1643 m a.s.l., in Baependi-MG.
Distribution and habitat.
Northern, northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Alagoas, Amapá, Amazonas, Bahia, Ceará, Espírito Santo, Goiás, Maranhão, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Pará, Paraná, Pernambuco, Piauí, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande Do Sul, Rondônia, Santa Catarina, São Paulo, Sergipe) (Wallach et al. 2014). This species occurs in semi-deciduous, dense, and mixed ombrophilous forests, as well as in adjacent open areas, from the Amazon to the Atlantic Forest (Gans 1964).
Gomesophis brasiliensis
(Gomes, 1918)
B33C87BE-F5CF-5FF4-8801-9FC7DD3A6DEF
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 8). This species is considered nocturnal and aquatic, associating with lentic watercourses (Gomes 1918, Marques et al. 2001, Gonzalez et al. 2014). During our fieldwork, it was found during all months of sampling in similar numbers and all observations occurred during the day in open areas. Five individuals were found active: four were moving from a river edge towards a swamp (10:00 h, 16:00 h, 17:00 h, 17:30 h) and one towards a creek (14:00 h). Three individuals were found at rest; one on a creek edge (9:00 h.), one in a muddy area (15:00 h) and another in a swamp (16:00 h). Fortes et al. (2010) recorded two active individuals at 21:00 h swimming on the surface of an 80-cm-deep turbid water lagoon. A male (SVL = 420 mm; TL = 75 mm) was kept in a 70cm × 30cm × 45cm terrarium for 10 consecutive days. During this period, it was monitored by camera 24 hours/day, to study its activity. It presented a unimodal activity pattern, with 96.4% of activity records during the day and peak activity from 9:30 to 17:00 h. Data obtained in the laboratory and field observations indicate this species is predominantly diurnal and semi-aquatic. G.brasiliensis frequently uses the ground (instead of the water), mainly during the day, to move between lentic and lotic environments. Of the three specimens examined, one had an earthworm in its stomach. Our results are consistent with the study by Oliveira et al. (2003) who also found traces of earthworm in the digestive tract of G.brasiliensis. Earthworms are sensitive to light and ultraviolet radiation (Edwards and Lofty 1977), so they are predominantly nocturnal, coming to the surface at night or during periods of very low light intensity during the day (Lee 1985). The diurnal activity of G.brasiliensis does not match its prey activity period. G.brasiliensis may hunt and capture its prey underground, during the day, possibly on the borders of marshes where the concentration of earthworms is higher (Frederico Menezes, pers. obs.). No information about reproduction of the examined specimens was recorded, except for a pregnant female in February. The species has seasonal reproduction associated with the rainy season, with juvenile recruitment between February and March (Oliveira et al. 2003). The defensive repertoire is described in Menezes et al. (2017).
Altitudinal variation.
Found at a minimum of 430 m a.s.l. in Encruzilhada do Sul, RS and maximum of 1650 m a.s.l. in the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio, Alagoa, MG. The maximum altitudinal record derives from the same are in this study, where most individuals were recorded at 1750 m altitude, in the PESP, Baependi, MG. The toponyms obtained for this species occur in two altitudinal ranges: 51% are located between 430 and 800 meters and 49% above this range (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
This species occurs in natural field areas (Amaral 1977, Ghizoni-Jr et al. 2009) in southern and southeastern Brazil (Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, and São Paulo) (Gonzalez et al. 2014).
Mussurana montana
(Franco, Marques & Puorto, 1997)
3DD664B0-487C-55E6-B130-BB5ECC6C1160
Natural history notes.
A large species (n = 1), terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001, Gaiarsa et al. 2013). There is no information on the time of activity for this species (Gaiarsa et al. 2013). In October, an adult was seen resting at 11:20 h, coiled in the middle of plant litter, in a forested area. The record occurred in an adjacent conservation area: RPP Alto Montana, Itamonte-MG. Literature data indicate its diet is composed of snakes and lizards (Franco et al. 1997). Regarding the reproduction, Franco et al. (1997) recorded two females: one with seven and the other with 11 eggs. No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of 750 m a.s.l. in Guaratinguetá, SP and maximum of 1610 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record of the species was 1740 m a.s.l., at RPPN Alto Montana, Itamonte, MG. Bérnils (2009) stated all toponyms found to occur in areas above 750 m a.s.l..
Distribution and habitat.
Southeast Brazil (Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro, and São Paulo) (Wallach et al. 2014). This species occurs in fields, close to ombrophilous and seasonal forests (Bérnils 2009).
Oxyrhopus clathratus
Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854
F065370C-24BD-5386-81BF-9B3D2B070250
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 1), terrestrial and nocturnal (Marques et al. 2001). A recently road-killed adult male was found in an open area near the PESP, during the morning. There was no evidence of diet or reproduction of the examined specimen. The available information in the literature indicates a diet composed mainly of mammals, although lizards and birds can also be prey (Hartmann et al. 2009b, Gaiarsa et al. 2013). Reproduction is seasonal, with a reproductive peak in the summer (Marques and Sazima 2004). Fecundity varies from four to 16 eggs (Gaiarsa et al. 2013). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
The species is found at a minimum of sea level from the coast of Rio Grande do Sul to Rio de Janeiro, and a maximum of 1610 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). In this study, we found this species outside the PESP limits, at 1000 m a.s.l. in the Aiuruoca, MG. Total altitudinal range is broad with 31.7% of toponyms found from the sea level up to 400 m a.s.l., 36.6% between 401 and 800 m a.s.l. and 31.7% above 801 m a.s.l. (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast and southeast Brazil (Bahia, Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, São Paulo), and Argentina (Wallach et al. 2014, Bernardo et al. 2012). It occurs in dense, mixed ombrophilous and seasonal semidecidual forests (Bernardo et al. 2012).
Oxyrhopus rhombifer
Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854
2EA88614-498D-51F6-A035-D056B30418F9
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 1), nocturnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001). An individual was found resting during the day (9:30 h) in a pasture area. This species occurs mainly in open areas (Cechin 1999, Sawaya et al. 2008), but may be found in forested areas near fields (Lema 1994, Cardoso 2011). It is a generalist species, feeding mainly on lizards, but also small mammals and snakes (Cechin 1999, Carreira 2002, Maschio et al. 2003, Sawaya et al. 2008). It is oviparous, with litter varying from two to 12 eggs (Gaiarsa et al. 2013). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
This species is found at a minimum of sea level in Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul, and south of Santa Catarina, and at a maximum of 1330 m a.s.l. in Liberdade, MG (Bérnils 2009). This study provides a new maximum altitudinal record of the species with an individual found at 1730 m a.s.l., Baependi, MG. The records located below 400 m a.s.l. occurred only from the Prata Basin to Santa Catarina (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Ceará, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Pará, Paraná, Pernambuco, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondônia, Santa Catarina and São Paulo), Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay (Wallach et al. 2014). The species was predominantly found in areas with open formations of Pampa, plateau fields, rupestrian fields, restingas, and at the southern portions of the cerrado (Bérnils 2009, Ghizoni-Jr et al. 2009).
Philodryas aestiva
(Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854)
00578F1D-616A-550A-A9DC-CBA66D8847B4
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 2), diurnal, often found on the ground in open areas (Di-Bernardo 1998, Marques et al. 2001, Sawaya et al. 2008). A recently road-killed adult male was found in an open field during the morning. The other record is of an adult’s shed skin, located at the grassland, in a rock outcrop, at 1800 m a.s.l.. There is no information on diet and reproduction of the examined specimen. Machado-Filho (2015) describes this species as generalist, feeding on mammals (40%), birds (25%), lizards (20%) and anurans (15%). Vitellogenesis occurs between April and December and ovulation between July and December (Fowler et al. 1998). There is a record of a captive female with eleven eggs (Fowler et al. 1998). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of sea level from the coast of Uruguay to Santa Catarina and maximum of 1730 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record for this species is presented here, with a specimen recorded at 1800 m a.s.l.. Bérnils (2009) mentioned the species occurs at sea level only from Uruguay to Santa Catarina. All other localities where this species was found are plateau areas.
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, and São Paulo), Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay (Wallach et al. 2014). This species was predominantly found in open areas of pampas, plateau fields, cerrados, and restingas, with records to adjacent forests (Giraudo and Scrocchi 2002, Bérnils 2009).
Philodryas patagoniensis
(Girard, 1858)
74586C83-0EDB-546B-8EBF-FC31B6996A88
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 9), diurnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001, Hartmann and Marques 2005). All observations occurred in open areas during the day. Seven individuals were found between 14:00 and 17:00 h, and two were found in the morning. According to Sazima and Haddad (1992), and Hartmann and Marques (2005), this species is active mainly during the hottest hours of the day. In December, during the day (14:00 h), we found two adults (male and female) about two meters away from each other. Both were coiled at rest and showed evidence of being in the shedding process.
In September, an adult was observed at 14:00 h near a ravine, while it was being attacked by two different birds (Poospiza sp. and an unidentified Passeriformes), possibly in defense of a nearby nest. In July, an adult was observed at 15:00 h, while it was ingesting a rodent. Out of the four examined specimens, two presented rodents in their stomach. Machado-Filho (2015) suggest this species is generalist, feeding on anurans (27%), lizards (25.8%), mammals (19.4%), snakes (10.9%), birds (8%), spiders (4%), fish (0.4%) and amphibians (0.4%). P.patagoniensis was found during all seasons of the year with higher frequency in December (n = 4). There is no information on reproduction of the examined individuals. Previous records indicate reproduction is seasonal, with three to nine eggs, secondary vitellogenesis between August and December, and ovulation between October and December (Fowler et al. 1998, Sawaya et al. 2008). As defensive tactics of this species, we observed cloacal discharge, head elevation, head triangulation, and neck S-coiling.
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of sea level from the coast of Argentina to the state of Espírito Santo and maximum of 1660 m a.s.l. in Umuarama, Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record for this species is from the area in this study, where an individual was recorded at 2200 m a.s.l. altitude, in the Alagoa, MG.
Distribution and habitat.
North, northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Pará, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondônia, and São Paulo), Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay (Wallach et al. 2014). This species can be found in open mountain areas, pampas, plateau fields, chacos, cerrados, restingas and deforested areas (Giraudo and Scrocchi 2002, Bérnils et al. 2007).
Sibynomorphus mikanii
(Schlegel, 1837)
3B734F43-9D7E-519F-A0DC-8A4B70ACAFA5
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 1), nocturnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001). A recently road-killed individual was found in an open area during the day. No diet or reproduction data was recovered for the examined specimen. Available information indicates this species is a specialist in mollusks (Marques et al. 2001). Fecundity varies from three to 10 eggs, which may be laid in communal spawning (Albuquerque and Ferrarezzi 2004, Pizzatto et al. 2008a). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of 110 m a.s.l., in Puerto Bemberg, Iguazú, Argentina and maximum of 1350 m a.s.l. in the Serra do Ouro Branco, Ouro Branco, MG (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitude for the species is expanded in this work, where a record occurred at 1630 m a.s.l., in the Baependi, MG. Total altitudinal range is broad with 12.3% of toponyms found below 400 m a.s.l., 30.5% above 801 m a.s.l., and 57.2% in the range between 401 and 800 m a.s.l. (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Goiás, Maranhão, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Pará, Paraná, Norte and São Paulo), Argentina and Paraguay (Bérnils 2009, Wallach et al. 2014). The species is common in forested formations from the Amazon Forest to the Atlantic Forest, in semidecidual and riverine forests and savannah formations of cerrado (Bérnils 2009, Freitas et al. 2014).
Taeniophallus affinis
(Günther, 1858)
D209AEE4-C505-52F1-887D-F25D29431578
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 3), diurnal, terrestrial and cryptozoic (Marques et al. 2001). Two recently road-killed individuals were found during the day at 9:00 h and 14:00 h: one in an open area and the other in a forested area. A third individual was also found during the day in an open area, apparently at rest, near a watercourse. Of the three examined specimens, one presented fragments of anurans in its digestive tract. Available information indicates the diet is composed of anurans primarily, but also by lizards and amphisbaenians (Marques et al. 2001, Barbo and Marques 2003). There is no information in the literature regarding the reproduction of the species. A female (SVL = 397 mm TL = 125 mm) presented five vitellogenic follicles in September. No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
This species is found at a minimum of sea level from the coast of Rio Grande do Sul to Rio de Janeiro and maximum at 1600 m a.s.l. in Parque Estadual Ibitipoca, Lima Duarte, MG (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitude for the species is increased, where individuals were observed at 1760 m a.s.l., in Baependi, MG. Bérnils (2009) points out that more than 80% of the toponyms are located in mountains and plateaus above 800 m.
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, southeast and southern Brazil (Alagoas, Bahia, Ceará, Espírito Santo, SE Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, São Paulo) (Wallach et al. 2014). This species was reported in areas with predominantly dense and mixed ombrophilous forests (Bérnils 2009).
Taeniophallus gr. occipitalis
92474224-3288-54C5-931D-72C2F9A414FC
Natural history notes.
Species of small size (n = 1), diurnal and cryptozoic (Sawaya et al. 2008). This individual was killed during the day by a domestic cat, near a forested area. There is no information on diet or reproduction for the examined specimen. There are no records of reproduction or altitudinal variation in T.gr.occipitalis. Prior reports are limited on diet, indicating only lizards as prey (Cechin 1999). No defensive behavior was observed for this species.
Altitudinal variation.
In this study, the maximum record was at 1600 m a.s.l., in the Aiuruoca, MG.
Distribution and habitat.
North, northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Ceará, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Pará, Paraíba, Paraná, Piauí, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondônia, São Paulo and Sergipe), Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay, Peru and Uruguay (Wallach et al. 2014, Santos-Jr et al. 2008). Taeniophallusgr.occipitalis occurs in open (cerrados, amazon savannas, plateau fields and pampas) and forested areas (western Amazon Forest and northeastern Atlantic Forest, in Brazil) (Santos-Jr et al. 2008).
Thamnodynastes strigatus
(Günther, 1858)
DB7E9E89-EE32-55F3-9268-4997D42A3A0F
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 15), nocturnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001, Barbo et al. 2011). The species was frequently found in November, December, and January. Ten individuals were observed resting during the day between 9:00 and 15:00 h; nine were in open areas and one on a forest border. Three individuals were found active at 22:00 h, foraging on the margin of a marsh with intense anuran vocal activity. Bernarde et al. (2000a) also observed this aggregation in T.strigatus in a permanent pond in Parque Estadual da Mata dos Godoy, Londrina, Paraná State. A juvenile was collected at 15:00 h while crossing an unpaved road after heavy rain. An adult was observed, also during the day (9:00 h), as it had captured by the leg and was attempting to prey on a Leptodactylus sp. Histological features of the retina of T.strigatus (i.e., presence of cones, but absence of rods) (Hauzman et al. 2014) along with activity data obtained in captivity (Torello-Vieira and Marques 2017) reinforce the idea this snake exhibits significant activity during the day. Of the seven individuals examined, three presented stomach contents: lizard scales (in a young individual), a Physalaemus sp., and a Rhinella sp. (this last one also showed traces of an unidentified exoskeleton - possibly a secondary prey). Bernarde et al. (2000b) suggested T.strigatus is a generalist, feeding primarily on anurans (71.4%), but also rodents (14.3%), fish (3.6%), and lizards (3.6%). In regard to reproduction, one female (SVL = 585 mm; TL = 155 mm, collected in December) possessed 14 vitellogenic follicles and a young individual (SVL = 200mm; TL = 65 mm) was recorded in January. Barbo et al. (2011) mentioned observations of two females: one with 15 vitellogenic follicles in February and another one in November with 24 embryos. We could observe the following defensive behaviors for this species: cloacal discharge, head triangulation, body flattening, strike, and biting.
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of sea level and maximum of 2450 a.s.l. in Itatiaia National Park, state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (Winkler et al. 2011). In this study, the maximum altitudinal record of the species was at 1730 m a.s.l., in the Baependi, MG.
Distribution and environment.
Southern, southeast, and northern Brazil (Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Pará, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro, Santa Catarina, Rio Grande do Sul, Roraima and São Paulo), Paraguay, Uruguay and Argentina (Franco and Ferreira 2003).
Tomodon dorsatus
Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854
A542CA2B-ECC0-5081-AD76-BB783FBE5E78
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 2), diurnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001). Two individuals were found in forested areas during the day, one active at 12:30 h and the other a recently road-kill found at 10:30 h. These records were observed in September and October. We found no data on diet or reproduction of the examined specimens. Prior literature accounts suggest feeding exclusively on slugs. The reproductive cycle is seasonal, with births occurring from January to June (Bizerra et al. 2005). We observed the following defensive behaviors for T.dorsatus: cloacal discharge, head triangulation, body flattening, strike and biting.
Altitudinal variation.
This species is found at a minimum of sea level from the coast of Rio Grande do Sul to Rio de Janeiro, and a maximum of 1610 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). We contribute a new maximum altitudinal record for our study area, where an individual was observed at 1730 m a.s.l., in Baependi, MG.
Distribution and habitat.
Central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, and São Paulo), Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay (Bérnils 2009, Wallach et al. 2014). This species is common in the Atlantic forest areas, with some records to open adjacent areas (Bérnils 2009).
Xenodon merremii
(Wagler, 1824)
A303DFDA-FBAA-59F0-963F-727178B9402F
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 1), diurnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001). In January, an individual was found at 14:00 h crossing an unpaved road in an open area. Prior records indicate this species specialize in anurans, mainly the toxic Rhinella spp. (Vitt and Vangilder 1983, Jordão 1997). X.merremii has a long reproductive cycle, from the beginning of the dry season to the middle of the rainy season. Fecundity varies between six and 44 eggs with recruitment between January and May (Pizzatto et al. 2008). As a defensive tactic of X.merremii, we observed the following behavior: body flattening.
Altitudinal variation.
This species is found at a minimum of sea level from the northern coast of Rio Grande do Sul to the extreme south of Santa Catarina, São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Espírito Santo, and Bahia. Maximum altitude recorded is 1300 m a.s.l. in the Parque Estadual de Itacolomi, Ouro Preto, MG (Bérnils 2009). This study expands the maximum altitudinal record for this species with an individual registered at 1610 m a.s.l. from the Aiuruoca, MG. This species occupies a large variety of habitats, both vegetal and altitudinal. The recorded toponyms corresponds to the altitudinal gradient with 35.3% of toponyms between sea level and 400 m a.s.l., 33.2% between 401 and 800 m a.s.l. and 31.5% above 801 m a.s.l. (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
North, northeast, central-west, southeast, and southern Brazil (Bahia, Brasília, Ceará, Goiás, Mato Grosso, Pará, Paraiba, Paraná, Pernambuco, Rondônia, São Paulo, and Tocantins), Bolivia and Paraguay (Wallach et al. 2014). This species occurs mainly in open areas (e.g., Cerrado, Chaco, plateau fields, rocky fields and Caatinga), but is also present in arboreal formations, such as seasonal forests, secondary forests, riverine forests and restingas (Bérnils 2009).
Viperidae Oppel, 1811
Bothrops fonsecai
Hoge & Belluomini, 1959
11AF9127-5AE3-5B6F-8065-456D985CD825
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 7), nocturnal and terrestrial (Marques et al. 2001). We collected twelve specimens of B.fonsecai, (seven during fieldwork and five outside of designated fieldwork periods. Individuals were more frequently observed in February and March. All observations occurred during the day. Ten adults were observed. Seven were at rest, five in open areas (at 9:00, 9:30, 10:00, 14:00, 14:10 h) and two at a forest edge (9:00 and 11:30 h). Three were found moving, two in open areas (10:00 and 14:00 h) and one entering a forested area (14:50 h). In November, we found an adult female, at rest at 9:00 h, 50 m away from a forested area. This female was about to shed. We found the same individual again at 14:00 h at the same place, with the skin-shed next to it. At 17:00 h, it had already retreated under the bush (goat’s beard), remaining coiled in a stalking position. All individuals found in open areas were at most 100 m from a forested area. Two juveniles were found in forested areas, one coiled on the ground in the light-shade mosaics made by the sunlight (12:40 h) and another stretched over the first branches of a bromeliad (Vrieseasceptrum Mez)(9:30 h). This individual (SVL = 263 mm; TL = 38 mm; M = 18 g) was collected and contained a freshly ingested rodent (M = 6 g). B.fonsecai preys exclusively on rodents (Martins et al. 2001). In PESP, B.fonsecai can often be found among ferns (Pteridiumarachnoides (Kaulf.)) growing near forested areas (Frederico Menezes, pers. obs.), and occasionally in swamp areas. Only juveniles were found within a forest (about 150 m inside). This difference in habitat use may be related to milder temperatures and protection against visually oriented predators. The reproductive cycle has been described by Menezes et al. (in press). We observed the following defensive tactic behaviors: tail vibrating (against the substrate and its own body), cloacal discharge, hiding the head under the body coils and striking.
Altitudinal variation.
This species is found at a minimum of 400 m a.s.l. in Barra Mansa, RJ and a maximum of 1730 m a.s.l. in Campos do Jordão, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record for this study area is 2175 m a.s.l. in Itamonte, MG. Most of the toponyms where this species can be found (about 65%) are located at altitudes above 800 m a.s.l.
Distribution and habitat.
Southeastern Brazil (Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro, and São Paulo) (Peters and Orejas-Miranda 1970, Wallach et al. 2014). It occurs in mixed ombrophilous forests and adjacent natural fields (Campbell and Lamar 2004, Bérnils 2009).
Bothrops jararaca
(Wied, 1824)
D8F6AB4A-FBAD-56F2-8E58-517EB7DE11C1
Natural history notes.
A species of medium size (n = 2), semi-arboreal and mainly nocturnal (Sazima 1992, Marques et al. 2001). In January, a recently road-killed adult male was found in the morning in a forested area. In March, an adult was seen at 10:40 h. above a rock outcrop at 2150 m a.s.l. near a forested area. When the observer approached, it fled into the forest. We did not obtain information on diet or reproduction from the observed specimen. Available information on diet from prior studies indicates that B.jararaca is a specialist, with ontogenetic variation. When juvenile, it often feeds on ectothermic prey (amphibians). This shifts to endothermic prey during adulthood (Sazima 1992). The reproductive cycle is seasonal and biennial. Pregnant females can be found from November to March (Almeida-Santos and Salomão 2002). Gestation ranges from 152 to 239 days, with fecundity from three to 36 snakelets (Alves et al. 2000, Almeida-Santos and Salomão 2002).
Altitudinal variation.
This species was found at a minimum of sea level between Rio Grande do Sul and Bahia with a maximum of 1640 m a.s.l. in Parque Nacional da Serra da Bocaina, SP (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record for this species from this study area is an individual recorded at 2150 m a.s.l., in Baependi-MG. Of the surveyed toponyms, 33% occur at low elevations (0–400 m a.s.l.) and 41.5% at intermediate altitudes (400–800 m a.s.l.) (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
Central-west, northeast, southeast, and southern Brazil (Bahia, Espírito Santo, Mato Grosso, Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Sul, São Paulo, and Santa Catarina), Paraguay and Argentina (Wallach et al. 2014). This species is common in ombrophilous and seasonal forests, although it can also be found in secondary forests and disturbed areas (Bérnils 2009).
Bothrops neuwiedi
Wagler in Spix, 1824
DE647BF8-11D6-5281-836C-49B17871A096
Natural history notes.
Medium-sized snake (n = 1), terrestrial and nocturnal (Marques et al. 2016). We spotted an adult during the day (12:50 h) in March, in a rocky field area. It was basking near a forest fragment at 2150 m a.s.l. When the observer approached, it fled into the forest. The available data in the literature indicates it was found mainly in fields and other open formations (Borges and Araújo 1998, Valdujo et al. 2002, Bérnils 2009). Diet is composed primarily of mammals (Martins et al. 2001, Valdujo et al. 2002).
Altitudinal variation.
The neuwiedi complex species was found at a minimum of sea level in the coast of Rio de Janeiro State, and a maximum of 1600 m a.s.l. in Parque Estadual do Ibitipoca, MG (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record for this species is extended here, with an individual observed at 2150 m a.s.l. in the PESP, Baependi, MG. Bérnils (2009) states more than 80% of the surveyed toponyms are located in mountain and plateau areas, and only five toponyms have been recorded at sea level.
Distribution and habitat.
Northeast, central-west, southeast and southern Brazil (Bahia, Goiás, Minas Gerais, Paraiba, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Santa Catarina) (Wallach et al. 2014). Like other taxa of the neuwiedi complex, this species occurs in open formations, such as savannas, rocky fields, and steppes (Bérnils 2009).
Crotalus durissus
Linnaeus, 1758
C6852B44-983D-5676-A489-33FFA7797082
Natural history notes.
Species of medium size (n = 1), with terrestrial and nocturnal habits (Marques et al. 2001). In January, an adult male was found during the day (13:00 h) in a high altitude grassland area. It was moving from the edge of a small forested area, towards an open field. Diurnal habits of this species have been described in reports by Sawaya et al. (2008) and Tozetti and Martins (2013) as well. No information of diet or reproduction was obtained from the specimen we observed. Available data indicates Crotalus has specialized in mammals, but may also ingest lizards (Sant’Anna 1999, Almeida-Santos and Germano 1996, Hoyos 2006). Interestingly, we found feces from an unidentified feline near the site of observation (at 2000 m a.s.l.) that contained a rattle and rattlesnake’s scales, indicating feline predation. Reproduction is viviparous, with a biennial reproductive cycle. Vitellogenesis starts in March and gestation goes through October and January and recruitment happens between January and March (Almeida-Santos and Salomão 1997, Almeida-Santos and Orsi 2002). This specimen presented the following defensive behaviors: cloacal discharge, rattle vibration, s-coil formation, and strike.
Altitudinal variation.
This species is found at a minimum of sea level for the coasts of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul and Bahia and maximum of 1400 m a.s.l. at Taquaral Farm, Paraty, RJ (Bérnils 2009). The maximum altitudinal record for this species in this study area is an individual recorded at 1950 m a.s.l., in the Baependi, MG. Most of the surveyed toponyms occur at intermediate altitudes. Only 21% were found between 0–400 m a.s.l.; 51% between 401 and 800 m a.s.l. and 28% above 801 m a.s.l. (Bérnils 2009).
Distribution and habitat.
Southern and southeastern Brazil (Amapá, Amazonas, Bahia, Ceará, Goiás, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Maranhão, Minas Gerais, Pará, Paraíba, Paraná, Pernambuco, Piauí, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondônia, Roraima, Santa Catarina, São Paulo), Netherlands Antilles (Aruba), Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Uruguay, Bolivia and Paraguay (Bérnils 2009, Wallach et al. 2014). This species is typically found in open formations, with little vegetation, such as savannas and steppes (Campbell and Lamar 2004).
Discussion
Species composition
The 24 snake species recorded in this study correspond to approximately 11% of the 219 species known from the phytogeographical domain of the Atlantic Forest (Moura et al. 2016). In general, the observed richness to the PESP is similar than that of other sites in the low-elevated Southeast Atlantic Forest (e.g., Marques and Sazima 2004, Centeno et al. 2008, Pontes and Rocha 2008, Hartmann et al. 2009a,b, São Pedro and Pires 2009, Moura et al. 2012, Trevine et al. 2014). Given the altitude increments of this sampling effort, several high-altitude species are expected to be found in the area, such as Ditaxodontaeniatus (Peters in Hensel, 1868), with a record to the Campos do Jordão - SP, approximately 100 km from the study area (see Thomas et al. 2006); Philodryasarnaldoi (Amaral, 1933), with two records for the Franca - SP, approximately 330 km away from the study site (Bérnils 2009). Despite the distance, Franca is directly connected to the extreme west of Serra da Mantiqueira (Bérnils 2009), so both places may present common elements in their faunas (R.S. Bérnils pers. comm.). Other possible species are (for details, see Bérnils 2009): Micrurusdecoratus (Jan, 1858) with a record for Caxambu – MG (ca. 27 km) (Gonzalez et al. 2014b); Ptychophisflavovirgatus Gomes, 1915, with a record for Liberdade - MG (ca. 45 km) (Gonzalez et al. 2014a); Siphlophislongicaudatus (Andersson, 1901), with a record for Munhoz - MG (ca 55 km); Phalotrisreticulatus (Perters, 1960), also for Munhoz - MG; Erythrolamprusjaegeri (Günther, 1858), recorded for Campos do Jordão – SP (ca. 100 km); Pseudoboaserrana Morato, Moura-Leite, Prudente & Bérnils, 1995, recorded for Bocaina de Minas – MG (ca. 35 km); Echinantheraamoena (Jan, 1863), recorded for Baependi – MG (ca. 25 km); E.melanostigma (Wagler 1824), recorded for Lambari - MG (ca. 65 km); E.undulata (Wied-Neuwied, 1824), recorded for Campos do Jordão - SP (ca. 100 km); Taeniophallusbilineatus (Fischer, 1885), recorded for Campos do Jordão - SP (ca. 100 km) and T.persimilis (Cope, 1869), recorded for Bananal - SP (ca. 70 km) (Bérnils 2009).
In any study, the relative frequency of snakes may be influenced by the sampling method (Marques 1998; Martins and Oliveira 1998). Here, the high frequency of Atractuszebrinus may be related to the use of pitfall traps, which accounted for 53% of records for that species. Nevertheless, disregarding pitfall trap records, A.zebrinus remains among the four most frequently observed species in the study area with seven records. Despite the considerable sample effort (2002 to 2007), Cardoso (2011) did not record A.zebrinus in a neighboring area (Farm Santa Elisa, Munhoz, MG, at 1320–1640 m a.s.l.). A possible explanation for this discrepancy is a lack of pitfall trappin method in that study effort. However, A.zebrinus has a confirmed voucher in the same farm in the Butantan Institute Collection (Frederico Menezes, pers. obs.). We propose this species simply may not be abundant in the study area covered by Cardoso (2011). In a similar discrepancy at Núcleo Curucutu, SP, Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar, Batista (2017) did not register A.zebrinus for this locality despite the use of pitfall traps. While, in an earlier study, Barbo et al. (2008) collected a specimen in the area. It is possible the altitudinal gradient influences species abundance, as noted by Lawton et al. (1987). Atractuszebrinus was the most abundant species in two inventories which were carried out at 1500 meters above the sea level: Ortiz et al. (2017), in Serra da Bocaina, with seven individuals (none captured by pitfall traps), and the present study, in Serra da Mantiqueira, with 15 individuals. However, this interpretation remains speculative and we suggest further tests, with a larger data set, to investigate this possibility.
In contrast to other Neotropical snake community studies (Cardoso 2011, Fiorillo 2016, Hartmann 2009a, b, Marques 1998, Cechin 1999, Sawaya et al. 2008, Costa et al. 2010), the family Viperidae was not the most abundant in this study. Our findins are more similar to the observations from temperate areas of Araucaria Forests and associated ecosystems (Di-Bernardo 2007, Deiques 2009). This may reflect a pattern for elevated areas. In this context, several factors may account for the predominance of B.fonsecai over other viperids (B.jararaca, B.neuwiedi, and C.durissus), which are somewhat common and easy to find (see Sazima 1988, Sazima 1992, Marques and Sazima 2004, Sawaya et al. 2008, Hartmann 2009a,b). Climatic factors, especially temperature, can act directly on the abundance of species that coexist in a given locality (Vitt 1987). We hypothesize that B.fonsecai is more tolerant of lower average temperatures, and as a result predominates in this study area where temperature may be a limiting factor for abundance of other vipers. For example, B.jararaca is very abundant in sites between 0 - 800 m altitude and yet rare in higher localities of Serra da Mantiqueira and Araucaria Plateau (Bérnils 2009). Altitude also seems to influence the population density of species Chironiusbicarinatus, E.miliaris, O.clathratus, S.mikanii, and S.pullatus. These species are well-represented in inventories carried out at lower altitudes (e.g., Hartmann et al. 2009a,b, Marques 1998, Fiorillo 2016, Trevine et al. 2014), but are rare in the study area, with only one record each. Regarding viperids Bothropsfonsecai and B.alternatus specifically, the later was not recorded in the PESP (1600 to 2359 m als). Hoge and Belluomini (1964) have discussed allopatry between these two species for the state of São Paulo and in areas near Minas Gerais State. Bérnils (2009) affirmed the allopatry proposed by these authors was not accurate, since, in these states some areas where B.fonsecai occur within areas where B.alternatus is dominant. However, sympatry could not be confirmed for these locations primarily because the specimens, housed in zoological collections, do not contain precise georeferences (Bérnils 2009). Bothropsalternatus is confirmed for Aiuruoca (IBSP data), at Ponte Coberta Farm (between 900 and 1000 m a.s.l.). In the same municipality, we recorded a B.fonsecai at approximately 1900 m a.s.l., which indicates sympatry between these species in the area. B.fonsecai is likely to be restricted to the higher altitudes, with different microclimatic conditions, and where there are still well-preserved forest fragments (Frederico Menezes pers. obs.). As for B.alternatus, this species is concentrated in lower open areas (Bérnils 2009).
The high species richness registered for the PESP might be related to environmental heterogeneity and the mix of habitats allowing more species of reptiles to coexist (Pianka 1969). However, comparing abundance data across altitude suggests this might have the greater effect on the number of individuals found. The frequency of individuals obtained in the PESP was at least 5.7 times lower than in Marques (1998), 3.5 times lower than Hartmann (2009a), 3.3 times lower than Fiorillo (2016), and only larger than Trevine et al. (2014). It is necessary to consider that these inventories were not performed uniformly and this could be a bias in comparing the abundance of snakes between these localities. Though decrease in abundance and species richness as altitude increases has been observed in other animal groups (Lawton et al. 1987, Moraes et al. 2017), it remains to be explored for snakes (Marques 1998). Undoubtedly, factors influencing species abundance across altitude are complex and differ for species and altitudinal transects. Although this hypothesis is speculative, we encourage further research to test this relationship in Brazilian snakes through systematic samplings at different altitudinal gradients.
Comparison with other snake assemblages from the Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil
The species composition of the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio is very similar to the Munhoz, which is also in southern Serra da Mantiqueira. These areas have very similar vegetation types. Both are present in the Alto Paraná Atlantic Forest, which contains rocky fields, savannahs, and montane forests (sensu Olson et al. 2001). The only other locality with similar vegetation to PESP and Munhoz is the São José do Barreiro, in São Paulo State (Ortiz et al. 2017). However, this locality belongs to another topographical complex: the Serra da Bocaina, which is separated from the Serra da Mantiqueira by the Paranapiacaba valley. This valley may pose a geographical barrier to the dispersal of the snake fauna (Ortiz et al. 2017, this study). Thus, the Serra da Mantiqueira seems to contain a sui generis composition of snake species, resulting in group 3 of our cluster analysis.
The other two main groups are composed of plateau areas (1) in the states of São Paulo and Minas Gerais (except localities in southern Serra da Mantiqueira); and (2) lowland areas and in São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro states. The formation of a cluster containing low coastal localities has already been described for anurans (Pombal Jr. et al. 2004, Bertoluci et al. 2007, Forlani et al. 2010). Coastal climatic conditions and other environmental characteristics may be the primary factors acting on formation of a particular fauna. These are certainly different between different areas of the Atlantic Forest (Dixo and Verdade 2006, Forlani et al. 2010). The presence of snake species found only in higher areas of the Atlantic Forest had already been highlighted by previous studies (e.g., Bérnils 2009). Thus, a more significant similarity was expected between these highlands. This is especially true of the Planalto Paulista, due to the number of localities inserted in the Ecological Continuous of Serra de Paranapiacaba, one of the largest preserved fragments of Atlantic Forest in São Paulo State (Pisciotta 2002).
Conservation
The Serra da Mantiqueria is defined as an area of particular biological importance, and it stands out in the region as one of the most important areas for biodiversity conservation in the state of Minas Gerais. This status is justified by the high abundance of rare and threatened species (Drummond et al. 2005). The Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio is located within the Serra da Mantiqueiria and carries many different types of vegetation, including fields, forests, and ombrophilous mixed forest (Olson et al. 2001, Silva et al. 2001). As it is one of the few areas in Minas Gerais protecting this variety of vegetation, it is regarded as an area of extreme biological importance (Silva et al. 2008). Currently, the mixed ombrophilous forest has been reduced to less than 5% of its original size (SOS Mata Atlântica and INPE, 2014). These remaining areas constitute the last refuges, sheltering several high altitude species (Backes 2009, Cardoso 2011). Bothropsfonsecai is endemic to an area that covers approximately 120,000 km2, in the mountainous portions of São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro States (Barbo 2012). Of the viper species found in this study, B.fonsecai was the only one which was not located outside the PESP limits. It appears to be relatively common in protected areas, but rare in unprotected areas. The absence of this species in disturbed areas suggests it may be sensitive to environmental degradation and/or may benefit from the protection. Either of these contributes to a critical situation that demands immediate efforts for conservation. Additionally, little is known about the ecology of B.fonsecai. Although we have collected field data about its natural history, a detailed study is still necessary to describe its displacements, home range, habitat use, and reproduction (e. g. Hartmann et al. 2003, Tozetti and Martins 2008).
The dipsadid Mussuranamontana is another species of interest found in this area. This species is endemic to a region that covers about 16,000 km2 in the mountainous portions of São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro states (Barbo 2012). According to Costa et al. (2015), it is susceptible to habitat disturbance. In the national assessment of the Brazilian fauna risk of extinction, M.Montana was classified as “least concern” (MMA 2014). Regional classification of M.montana is “vulnerable” and “near threatened” in the states of São Paulo and Minas Gerais, respectively (Biodiversitas 2007, Bérnils et al. 2009). Recently, Costa et al. (2015) presented three new records of this species in protected areas of the State of Minas Gerais, increasing its known range considerably and supporting the lower conservation status in Minas Gerais. M.montana is known only to inhabit tropical ombrophilous or seasonal forest formations of montain ranges from Bocaina, Mantiqueira and Órgãos, between 750–1,610 m a.s.l. (Bérnils 2009, Costa et al. 2015). However, sampling in potentially suitable areas for the species did not yield encounters (Costa et al. 2015). This may mean that M.montana is present over a smaller range and more specific habitat than was previously expected. If true, this reinforces the need for conservation in areas where it occurs.
The present study provides data on the occurrence and natural history of snakes in the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio. However, additional field research is encouraged. New inventories could contribute additional knowledge about the natural history of the species of this region, especially those of which ecological, biological, and morphological data are scarce, such as Mussuranamontana. Our ordination analysis shows a remarkable difference between the compositions of snake faunas between different altitudinal gradients in the Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest. The Serra da Mantiqueira, where the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio is located, seems to present a very unique composition of snake species, most of which are not shared with others localities from the southeast of Brazil. The diverse vegetation types found in this region permits the existence and maintenance of diverse species of animals. Additionally, the protected areas belonging to the Atlantic Forest affords greater potential to find rare and endemic species. These facts together make an argument for prioritizing the conservation of this park. Nevertheless, even if recognized as a conservation unit, the park continues to suffer depredation of its flora and fauna, mainly through illegal hunting. Regrettably, this alarming scenario is widely observable in Brazil due to the scientific scrapping and the neglect of the Brazilian government to control its natural resources (Bockmann et al. 2018).
Key to the snake species from Serra do Papagaio State Park – MG
| 1 | Loreal pit present; solenoglyphous dentition | Viperidae |
| – | Loreal pit absent, aglyphous or opisthoglyphous | 2 |
| 2 | Aglyphous dentition; even number of dorsal scale rows | Colubridae |
| – | Aglyphous or opisthoglyphous dentition; odd number of dorsal scale rows | Dipsadidae |
Viperidae
| 1 | Rattle at the tip of the tail; with some enlarged shields on top of the head | Crotalus durissus |
| – | No rattle at the tip of the tail; tiny shields on top of the head | 2 |
| 2 | Inverted v-shaped spots along the dorsum; second supralabial fusioned with the prelaculal | Bothrops jararaca |
| – | Trapezoid spots along the dorsum; second supralabial not fused with the prelaculal | 3 |
| 3 | Non-fragmented trapezoid spots along the dorsum; black venter | Bothrops fonsecai |
| – | Trapezoid spots are fragmented at the midline to ventrals; venter cream, with several tiny brown spots | Bothrops neuwiedi |
Colubridae
| 1 | 12 scale rows at mid-body | 2 |
| – | More than 12 scale rows at mid-body | Spilotes pullatus |
| 2 | 2-4 rows of keeled dorsal scales; first third of body black or dark gray, vertebral stripe yellowish or cream; top of the head tan to brown (distinct from the background color of the body); venter cream, with black bordered scales | Chironius brazili |
| – | Two rows of keeled dorsal; olive green at the first third of the body; head color similar to the body; venter yellow, without black bordered scales | Chironius bicarinatus |
Dipsadidae
| 1 | 17 or fewer scale rows at mid-body | 2 |
| – | 19 scale rows at mid-body | 10 |
| 2 | 15 scale rows at mid-body | 3 |
| – | 17 scale rows at mid-body | 5 |
| 3 | Internasal shields absent; body almost uniformly red, with black tail | Apostolepis assimilis |
| – | Internasal shields present; without red color on the dorsum | 4 |
| 4 | Black eyes, indistinguishable pupil; venter white, with black spots | Sibynomorphus mikanii |
| – | Eyes with brown background color and round pupil, easily distinguishable; venter immaculate yellow | Taeniophallus gr. occipitalis |
| 5 | Dark lining, loreal shield absent | Tomodon dorsatus |
| – | Light lining, loreal shield present | 6 |
| 6 | Dorsal color brown, with a lighter longitudinal line on each side; three supralabials in contact with the eyeball | Gomesophis brasiliensis |
| – | Coloration not as above; two supralabials in contact with the eyeball | 7 |
| 7 | Dorsal scales with black borders and light centers; venter cream yellow, base of ventral scales with black edges | Erythrolamprus miliaris |
| – | Coloration not as above | 8 |
| 8 | Stout and short body; small eyes | Atractus zebrinus |
| – | Slender and elongate body; large eyes | 9 |
| 9 | Fourth row of dorsal scales with white dots that, together, form a continuous line along the body; brown top of the head and body; ventral scales with transverse band | Echinanthera cephalostriata |
| – | The fourth row of dorsals without white dots; top of the head black, contrasting with the brown body; ventral scales without transverse band | Taeniophallus affinis |
| 10 | Two apical pits | 11 |
| – | Single apical pit | 14 |
| 11 | Red iris | 12 |
| – | Black or dark brown irish, never red | 13 |
| 12 | Juveniles are brick red, with a dark brown longitudinal vertebral stripe; adults are entirely dark brown | Mussurana montana |
| – | Coral color pattern, with black triangular spots, bordered with white, background color red | Oxyrhopus rhombifer |
| 13 | Loreal shield usually absent; contact between frontal and preocular absent | Oxyrhopus clathratus |
| – | Loreal shield present; contact between frontal and preocular present | Boiruna maculata |
| 14 | Keeled dorsal scales; dorsum uniform green | Philodryas aestiva |
| – | Smooth dorsal scales; dorsum never green | 15 |
| 15 | Canthusrostralis very evident; without postocular stripe | Philodryas patagoniensis |
| – | Canthusrostralis not evident; conspicuous postocular stripe | 16 |
| 16 | With two large post-diastemal fangs, aglyphous; venter cream, without longitudinal lines | Xenodon merremii |
| – | Without two large post-diastemal fangs, but opisthoglyphous; venter cream, with two to four longitudinal lines | Thamnodynastes strigatus |
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Instituto Butantan for the infrastructure offered, Instituto Estadual de Florestas (IEF) for permission to work at the park, Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis (IBAMA) for authorizing snake capture (47749–3), CAPES and Christiane Sarkis de Alcântara for financial support; Emmanuel M. J. Landroz, Marcos Lopez Menezes and all his family, Roseli, Darci, Rita and Marcilei Lopes Menezes for fieldwork assistance; Renato S. Bérnils, for the valuable comments throughout the development of the study.
Citation
Menezes FA, Abegg AD, Silva BR, Franco FL, Feio RN (2018) Composition and natural history of the snakes from the Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio, southern Minas Gerais, Serra da Mantiqueira, Brazil. ZooKeys 797: 117–160. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.797.24549
Funding Statement
CAPES
References
- Abegg AD, Borges LM, Mario-da-Rosa C, Entiauspe-Neto OM, Arocha NM, Santos-Jr AP. (2016) Included, excluded and re-included: Chironiusbrazili (Serpentes, Colubridae) in Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. Neotropical Biology and Conservation 11: 198–203. 10.4013/nbc.2016.113.11 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque CE, Ferrarezzi H. (2004) A case of communal nesting in the Neotropical snake Sibynomorphusmikanii (Serpentes, Colubridae). Phyllomedusa 3: 73–77. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v3i1p73-77 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida-Santos SM, Orsi AM. (2002) Ciclo reprodutivo de Crotalusdurissus e Bothropsjararaca (SerpentesViperidae): morfologia e função dos ovidutos. Revista Brasileira de Reprodução Animal 26: 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida-Santos SM, Salomão MG. (2002) Reproduction in Neotropical Pitvipers with emphasis on species of genus Bothrops. In: Schuett GW, Höggren M, Douglas ME, Greene HW. (Eds) Biology of the Vipers.Eagle Mountain Publishing, LC, 445–462.
- Almeida-Santos SM, Braz HB, Santos LC, Sueiro LR, Barros VA, Rojas CA, Kasperoviczus KN. (2014) Biologia reprodutiva de serpentes: recomendações para a coleta e análise de dados. Herpetologia Brasileira 3: 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida-Santos SM, Germano VJ. (1996) Crotalusdurissus (Neotropical Ratlesnake). Prey. Herpetological Review 27: 255–255.
- Alves MLM, Araujo ML, Witt AA. (2000) Aspectos da Biologia Reprodutiva de Bothropsjararaca em Cativeiro (Serpentes: Viperidae). Iheringia, Série Zoologia 89: 187–192. 10.1590/S0073-47212000000200009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Amaral A. (1930) Notes on Spilotespullatus. Bulletin of the Antivenin Institute of America 3: 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral A. (1977) Serpentes do Brasil. Iconografia Colorida. Melhoramentos e Editora da Universidade de São Paulo, 247 pp.
- Araújo CDO, Condez TH, Bovo RP, Centeno FDC, Luiz AM. (2010) Amphibians and reptiles of the Parque Estadual Turístico do Alto Ribeira (PETAR), SP: an Atlantic Forest remnant of southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 10: 257–274. 10.1590/S1676-06032010000400031 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Backes A. (2009) Distribuição geográfica atual da Floresta com Araucária: condicionamento climático. Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo, Brazil, 39–44.
- Barbo FE, Marques OAV. (2003) Do aglyphous colubrid snakes prey on live amphisbaenids able to bite? Phyllomedusa 2: 113–114. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v2i2p113-114 [DOI]
- Barbo FE, Malagoli LR, Bajestero FB, Whately M. (2008) Os Répteis no Município de São Paulo: aspectos históricos, diversidade e conservação. Além do Concreto: contribuições para a proteção da biodiversidade paulistana (Malagoli LR, Bajestero FB, Whately M.). Editora Instituto Socioambiental, São Paulo 234–267.
- Barbo FE, Marques OAV, Sawaya RJ. (2011) Diversity, natural history, and distribution of snakes in the municipality of São Paulo. South American Journal of Herpetology 6: 135–160. 10.2994/057.006.0301 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Barbo FE. (2012) Biogeografia Histórica e Conservação das Serpentes da Floresta Pluvial Atlântica Costeira do Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho, Rio Claro.
- Batista SF. (2017) Diversidade e distribuição de serpentes e lagartos em um mosaico de fisionomias na Serra do Mar, estado de São Paulo. PhD Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho, São José do Rio Preto.
- Bernarde PS, Kokubum MN, Marques OAV. (2000a) Utilização de hábitat e atividade em Thamnodynastesstrigatus (Günther, 1858) no sul do Brasil (Serpentes, Colubridae). Museu Nacional.
- Bernarde PS, Moura-Leite JC, Machado RA, Kokobum MNC. (2000b) Diet of the colubrid snake, Thamnodynastesstrigatus (Günther, 1858) from Paraná State, Brazil, with field notes on anuran predation. Revista Brasileira de Biologia 60: 695–699. 10.1590/S0034-71082000000400022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernarde PS, Abe AS. (2010) Food habits of snakes from Espigão do Oeste, Rondônia, Brazil. Biota Neotropica 10: 167–173. 10.1590/S1676-06032010000100017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo PH, Machado FA, Murphy RW, Zaher H. (2012) Redescription and morphological variation of Oxyrhopusclathratus Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854 (Serpentes: Dipsadidae: Xenodontinae). South American Journal of Herpetology 7: 134–148. 10.2994/057.007.0203 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bérnils RS, Giraudo AR, Carreira S, Cechin Z. (2007) Répteis das porções subtropical e temperada da Região Neotropical. Ciência & Ambiente 6: 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bérnils RS. (2009) Composição e Padrões de Distribuição de Caenophidia (Squamata, Serpentes) das Serras Atlânticas e Planaltos do Sudeste da América do Sul [master’s thesis]. Rio de Janeiro (RJ): Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro.
- Bérnils RS, Sawaya RJ, Nogueira CC, Marques OAV, Ferrarezzi H, Franco FL, Germano VJ, Rodrigues MTU, Zaher HE, Molina FB, Martins M. (2009) Fauna ameaçada de extinção no Estado de São Paulo. São Paulo: Fundação Parque Zoológico de São Paulo, Secretaria do Meio Ambiente.
- Bertoluci J, Brassaloti RA, Ribeiro Júnior JW, Vilela VMD, Sawakuchi HO. (2007) Species composition and similarities among anuran assemblages of forest sites in southeastern Brazil. Scientia Agricola 64: 364–374. 10.1590/S0103-90162007000400007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoluci J, Canelas MAS, Eisemberg CC, Palmuti CFDS, Montingelli GG. (2009) Herpetofauna da Estação Ambiental de Peti, um fragmento de Mata Atlântica do estado de Minas Gerais, sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotropica 9: 1. 10.1590/S1676-06032009000100017 [DOI]
- Biodiversitas Fundação (2007) Revisão das Listas das Espécies da Flora e da Fauna Ameaçadas de Extinção do Estado de Minas Gerais – Relatório Final, Vol 3.: Fundação Biodiversitas, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 104–142.
- Bizerra AF, Marques OAV, Sazima I. (2005) Reproduction and feeding of the colubrid snake Tomodondorsatus from southeastern Brazil. Amphibia-Reptilia 26: 33–38. 10.1163/1568538053693350 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bockmann FO, Rodrigues MT, Kohsldorf T, Straker LC, Grant T, Pinna MCC, Mantelatto FLM, Datovo A, Pombal Jr JP, Mcnamara JC, Almeida EAB, Klein W, Hsiou AS, Groppo ME, Castro RMC, Souza-Amorim D. (2018) Brazil’s government attacks biodiversity. Science 360(6391): 865 10.1126/science.aat7540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfiglio F, Lema T. (2007) Ofiofagia em Liophismiliaris (Serpentes, Colubridae). Biociências 14: 2. [on-line]
- Borges RC, Araujo AFB. (1998) Seleção de hábitat em duas espécies de jararacas (Bothropsmoojeni Hoge e B.neuwiedi Wagler). Revista Brasileira de Biologia 58: 489–493. 10.1590/S0034-71081998000400006 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cadle JE, Greene HW. (1993) Phylogenetic patterns, biogeography, and the ecological structure of Neotropical snake assemblages. Species diversity in ecological communities: historical and geographical perspectives. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 281–293.
- Campbell HW, Christman SP. (1982) Field techniques for herpetofaunal community analysis. In: Scott Jr NJ. (Ed.) Herpetological Communities: a Symposium of the Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles and the Herpetologist’s League.US Fish Wild, 13, 193–200.
- Campbell JA, Lamar WW. (2004) The venomous reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. Vol. 2, Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca, 45–50.
- Cardoso SRT. (2011) História natural das serpentes da região de Munhoz, sul de Minas Gerais, Serra da Mantiqueira. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo.
- Carreira Vidal S. (2002) Alimentación de los Ofidios de Uruguay. Montevideo. Asociación Herpetológica Española, Monografías de Herpetología 6: 127.
- Carreira S, Meneghel M, Achaval F. (2005) Reptiles de Uruguay. Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de La República, Montevideo, 639 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Cechin SZ. (1999) História natural de uma comunidade de serpentes na região da depressão central (Santa Maria) Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Pontífica Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul.
- Cechin SZ, Martins M. (2000) Eficiência de armadilhas de queda (Pitfall traps) em amostragens de anfíbios e répteis no Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia 17: 729–749. 10.1590/S0101-81752000000300017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Centeno FDC, Sawaya RJ, Marques OAV. (2008) Snake assemblage of Ilha de São Sebastião, southeastern Brazil: comparison to mainland. Biota Neotropica 8: 63–68. 10.1590/S1676-06032008000300005 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchi PJP, Sena MA, Peccinini-Seale DM, Duarte MR. (2007) Snakes from coastal islands of state of São Paulo, Southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 7: 227–240. 10.1590/S1676-06032007000200026 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchi PJP, Serafim H, Sena MA, Centeno FDC, Jim J. (2009) Herpetofauna em uma área de Floresta Atlântica na Ilha Anchieta, município de Ubatuba, sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotropica 9: 201–212. 10.1590/S1676-06032009000200019 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cechin SZ, Martins M. (2000) Eficiencia de marmadilhas de queda (pitfall traps) em amostragens de anfíbios e répteis no Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia 17: 729–740. 10.1590/S0101-81752000000300017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Citeli N, Hamdan B, Guedes T. (2016) Snake richness in urban forest fragments from Niterói and surroundings, state of Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil. Biodiversity Data Journal 4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Clarke KR, Warwick RM. (1994) Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analyses and Interpretation. Natural Environment Research Council, Plymouth, 144 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Condez TH, Sawaya RJ, Dixo M. (2009) Herpetofauna dos remanescentes de Mata Atlântica da região de Tapiraí e Piedade, SP, sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotropica 9: 157–185. 10.1590/S1676-06032009000100018 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Connell JH. (1975) Some mechanisms producing structure in natural communities: a model and evidence from field experiments. In: Cody ML, Diamond JM. (Eds) Ecology and Evolution of Communities.Belknap Press of Harvard University, 460–490.
- Costa HC, Pantoja DL, Pontes JL, Feio RN. (2010) Serpentes do município de Viçosa, Mata Atlântica do sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotropica 10: 353–377. 10.1590/S1676-06032010000300033 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Costa HC, Santos PS, Laia WP, Garcia PC, Bérnils RS. (2015) Mussuranamontana (Franco, Marques & Puorto, 1997) (Serpentes: Dipsadidae): noteworthy records and an updated distribution map. Check List 11: 1657. 10.15560/11.3.1657 [DOI]
- Cunha OR, Nascimento FP. (1978) Ofídios da Amazônia X. As cobras da região leste do Pará. Publicações Avulsas do Museu Goeldi 31: 1–218. [Google Scholar]
- Deiques CH. (2009) Répteis da floresta com araucária. In: Fonseca CR, Souza AF, Leal-Zanchet AM, Dutra TL, Backes A, Ganade G. (Eds) Floresta com araucária: ecologia, conservação e desenvolvimento sustentável.Holos Editora, Ribeirão Preto, 185–190.
- Di-Bernardo M. (1996) A new species of the Neotropical snake genus Echinanthera Cope, 1894 from Southeastern Brazil (Serpentes, Colubridae). Snake-Nittagun 27: 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Di-Bernardo M. (1998) História Natural de uma comunidade de serpentes da borda oriental do planalto das Araucárias Rio Grande do Sul Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista.
- Di-Bernardo M, Borges-Martins M, Oliveira RD, Pontes GMF, Nascimento LB, Oliveira ME. (2007) Taxocenoses de serpentes de regiões temperadas do Brasil. In: Nascimento LB, Bernardes AT, Cotta GA. (Eds) Herpetologia no Brasil 2.PUCMG, Belo Horizonte, 222–263
- Dixon JR, Wiest Jr JA, Cei JM. (1993) Revision of the Neotropical snake genus Chironius Fitizinger (Serpentes, Colubridae). Monografie Museo Regionale di Scienze Naturali di Torino 13: 1279.
- Dixo M, Verdade VK. (2006) Leaf litter herpetofauna of the Reserva Florestal de Morro Grande, Cotia (SP). Biota Neotropica 6: 1–20. 10.1590/S1676-06032006000200009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond GM, Martins CS, Machado AM, Sebaio FA, Antonini YO. (2005) Biodiversidade em Minas Gerais: um atlas para sua conservação. Fundação Biodiversitas, Belo Horizonte, 222.
- Drummond G, Martins C, Mendonca M. (2007) Revisão das listas das espécies da flora e da fauna ameaçadas de extinção do Estado de Minas Gerais – Relatório Final, Vol 3. Fundação Biodiversitas, Belo Horizonte, 104–142.
- Duellman WE. (1978) The Biology of an Equatorial Herpetofauna in Amazonian Ecuador. University of Kansas, Lawrence, 352 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards CA, Lofty JR. (1977) Biology of Earthworms. Chapman and Hall. London, 333 pp. 10.1007/978-1-4613-3382-1 [DOI]
- Ferrarezzi H, Barbo FE, Albuquerque CE. (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of a new species of Apostolepis from Brazilian Cerrado with notes on the assimilis group (Serpentes: Colubridae: Xenodontinae: Elapomorphini). Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia 45: 215–229. 10.1590/S0031-10492005001600001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorillo BF. (2016) Estrutura da comunidade de Serpentes da Região da Fazenda Etá. PhD Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho, São José do Rio Preto.
- Forlani MC, Bernardo PH, Haddad CFB, Zaher H. (2010) Herpetofauna do Parque Estadual Carlos Botelho, São Paulo, Brasil. Biota Neotropica 10: 265–309. 10.1590/S1676-06032010000300028 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fortes VB, Lucas EM, Caldart VM. (2010) Reptilia, Serpentes, Dipsadidae, Gomesophisbrasiliensis (Gomes, 1918): Distribution extension in state of Santa Catarina, Brazil. Check List 415–416. 10.15560/6.3.414 [DOI]
- Fowler IR, Salomão MG, Jordão RS. (1998) A description of the female reproductive cycle in four species from the neotropical colubrid snake Philodryas (ColubridaeXenodontinae). Snake-Nittagun 28: 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Franco FL, Marques OAV, Puorto G. (1997) Two new species of colubrid snakes of the genus Clelia from Brazil. Journal of Herpetology 31: 483–490. 10.2307/1565599 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Franco FL, Ferreira TG. (2002) Descrição de uma nova espécie de Thamnodynastes Wagler, 1830 (Serpentes, Colubridae) do nordeste brasileiro, com comentários sobre o gênero. Phyllomedusa 1: 57–74. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v1i2p57-74 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Franco FL, Ferreira TG. (2003) Ocorrência de Thamnodynastesstrigatus (Serpentes, Colubridae) no Escudo das Guianas, estados do Pará e Roraima, Brasil. Phyllomedusa: Journal of Herpetology 2: 117–119. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v2i2p117-119 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas MA, Almeida BA, Almeida MSA, Danin TS, Moura GJB. (2014) Rediscovery and first record of Sibynomorphusmikaniiseptentrionalis (Cunha, Nascimento & Hoge, 1980), (Squamata; Serpentes) for the state of Pará. Check List 10: 1246–1248. 10.15560/10.5.1246 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gaiarsa MP, Alencar LRV, Martins M. (2013) Natural History of Pseudoboine Snakes. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia 53: 261–283. 10.1590/S0031-10492013001900001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo G, Scrocchi GJ, Di Giacomo A, Giraudo A. (2006) Boirunamaculata (Mussurana, Víbora luta, mamona). Prey and predation behavior. Herpetological Review 37: 349–350.
- Gans C. (1964) A redescription of, and geographic variation in Liophismiliaris Linné, the common water snake of southeastern South America. American Museum Novitates 2178: 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ghizoni-Junior IR, Kunz TS, Cherem JJ, Bérnils RS. (2009) Registros notáveis de répteis de áreas abertas naturais do planalto e litoral do Estado de Santa Catarina, sul do Brasil. Biotemas 22: 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudo AR, Scrocchi GJ. (2002) Argentinian snakes: an annoted checklist. Smithsonian Herpetological Information Service 132: 1–53. 10.5479/si.23317515.132.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes JF. (1918) Contribuição para o conhecimento dos ofídios do Brasil III. Descrição de duas espécies novas. Memórias do Instituto Butantan 1: 57–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez RC, Prudente AL, Franco FL. (2014a) Morphological variation of Gomesophisbrasiliensis and Ptychophisflavovirgatus (Serpentes, Dipsadidae, Xenodontinae). Salamandra 50: 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez RC, Silva-Soares T, de Castro TM, Bérnils RS. (2014b) Review of the geographic distribution of Micrurusdecoratus (Jan, 1858) (Serpentes: Elapidae). Phyllomedusa Journal of Herpetology 13: 29–39. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v13i1p29-39 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Grazziotin FG, Zaher H, Murphy RW, Scrocchi G, Benavides MA, Zhang YP, Bonatto SL. (2012) Molecular phylogeny of the new world Dipsadidae (Serpentes: Colubroidea): a reappraisal. Cladistics 28: 437–459. 10.1111/j.1096-0031.2012.00393.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg CH, Neary DG, Harris LD. (1994) A comparison of herpetofaunal sampling effectiveness of pitfall single-ended and double-ended funnel traps used with drift fences. Journal of Herpetology 28: 319–324. 10.2307/1564530 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Guedes TB, Nogueira C, Marques OAV. (2014) Diversity, natural history, and geographic distribution of snakes in the Caatinga, Northeastern Brazil. Zootaxa 3863: 1–93. 10.11646/zootaxa.3863.1.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan B, Srnandes D. (2015) Taxonomic revision of Chironiusflavolineatus (Jan, 1863) with description of a new species (Serpentes: Colubridae). Zootaxa 4012: 97–119. 10.11646/zootaxa.4012.1.5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann PA, Hartmann MT, Giasson LOM. (2003) Uso do hábitat e alimentação em juvenis de Bothropsjararaca (Serpentes, Viperidae) na Mata Atlântica do sudeste do Brasil. Phyllomedusa 2(1): 35–41. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v2i1p35-41 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann PA. (2005) História natural e ecologia de duas taxocenosis de serpentes na Mata Atlântica. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho, Rio Claro.
- Hartmann PA, Marques OA. (2005) Diet and habitat use of two sympatric species of Philodryas (Colubridae), in south Brazil. Amphibia-Reptilia 26: 25–31. 10.1163/1568538053693251 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann PA, Giasson LO. (2008) Répteis. In: Cherem JJ, Kammers M. (Eds) A fauna das áreas de influência da usina hidrelétrica Quebra Queixo.Editora Habilis, Erechim, 111–130.
- Hartmann PA, Hartmann MT, Martins M. (2009a) Ecologia e história natural de uma taxocenose de serpentes no Núcleo Santa Virgínia do Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar, no sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotropica 9: 173–184. 10.1590/S1676-06032009000300018 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann PA, Hartmann MT, Martins M. (2009b) Ecology of a snake assemblage in the Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia 49: 343–360. [Google Scholar]
- Hauzman E, Bonci DM, Grotzner SR, Mela M, Liber AM, Martins SL, Ventura DF. (2014) Comparative study of photoreceptor and retinal ganglion cell topography and spatial resolving power in Dipsadidae snakes. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 84: 197–213. 10.1159/000365275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey MB, Embert D. (2008) Review of Bolivian Dipsas (Serpentes: Colubridae), with comments on other South American species. Herpetological Monographs 22(1): 54–105. 10.1655/07-023.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson RW, Dixon JR, Soini P. (1979) Resource partitioning in Amazonian Sanke communities. Milwaukee Public Museum Contributions in Biology and Geology 22: 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Heyer WR. (1967) A herpetofauna study of an ecological transect through the Cordillera de Tilaran, Costa Rica. Copeia 1967: 259–271. 10.2307/1442113 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge AR, Belluomini HE. (1964) Notas sobre Bothropsfonsecai Hoge e Belluomini, Bothropsalternatus Duméril, Bibron and Duméril e Bothropscotiara Gomes. Memórias do Instituto Butantan 30: 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos MA. (2006) Ecologia da cascavel (Viperidae, Crotalusdurissus) no Cerrado brasileiro. PhD Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, Distrito Federal.
- Inger RF, Colweel RF. (1977) Organization of contiguous communities of amphibians and reptiles in Thailand. Ecological Monographs 47: 229–253. 10.2307/1942516 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jordão RS. (1997) Estudo comparativo da alimentação e da reprodução de Waglerophismerremii e Xenodonneuwiedii (Serpentes: Colubridae). PhD Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo.
- Krebs CJ. (2001) Ecology: The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance. Benjamin Cummings.
- Lawton JH, MacGarvin M, Heads PA. (1987) Effects of altitude on the abundance and species richness of insect herbivores on bracken. The Journal of Animal Ecology 56(1): 147–160 10.2307/4805 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lee KE. (1985) Earthworms.Their ecology and relationships with soils and land use. Academic, Sydney, Australia, 411 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Lema T, Araújo ML, Azevedo ACP. (1983) Contribuição ao conhecimento da alimentação e do modo alimentar de serpentes do Brasil. Comunicações do Museu de Ciências da PUCRS 26: 41–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lema T. (1994) Lista comentada dos répteis ocorrentes no Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Comunicações do Museu de Ciências da Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul. Iheringia, Série Zoologia 7: 41–150. [Google Scholar]
- Machado-Filho PR. (2015) Evolução do hábito alimentar e utilização do substrato pelo gênero Philodryas Wagler, 1830. PhD Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho, São José do Rio Preto.
- Marques OAV, Souza VC. (1993) Nota sobre a atividade alimentar de Liophismiliaris no ambiente marinho (Serpentes, Colubridae). Revista Brasileira de Biologia 53: 645–648. [Google Scholar]
- Marques OAV. (1998) Composição faunística, história natural e ecologia de serpentes da mata Atlântica, na região da estação ecológica Juréia-Itatins. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo.
- Marques OAV, Eterovic A, Sazima I. (2001) Serpentes da Mata Atlântica: guia ilustrado para a Serra do Mar. Holos Editora, São Paulo.
- Marques OAV, Sazima I. (2004) História natural dos répteis da Estação Ecológica Juréia-Itatins. In Marques OAV, Duleba W (Eds) Estação Ecológica Juréia-Itatins: ambiente físico, flora e fauna. Holos Editora, Ribeirão Preto, 257–277.
- Marques OAV, Almeida-Santos SM, Rodrigues MG, Camargo R. (2009a) Mating and Reproductive Cycle in the Neotropical Colubrid Snake Chironiusbicarinatus. South American Journal of Herpetology 4: 76–80. 10.2994/057.004.0110 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Marques OAV, Nogueira CC, Sawaya RJ, Bérnils RS, Martins M, Molina FB, Ferrarezzi H, Franco FL, Germano VJ. (2009b) Répteis. In: Bressan P, Kierulff MCM, Sugieda AM. (Eds) Fauna Ameaçada de Extinção no estado de São Paulo.Fundação Parque Zoológico de São Paulo/Secretaria do Meio Ambiente, 285–327.
- Marques OAV, Eterovic A, Strüssmann C, Sazima I. (2015) Serpentes do Cerrado: guia ilustrado. Holos Editora, São Paulo, 239 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Marques OAV, Muniz-DA-Silva DF, Barbo FE, Cardoso SRT, Maia DC, Almeida-Santos SM. (2014) Ecology of the Colubrid Snake Spilotespullatus from the Atlantic Forest of Southeastern Brazil. Herpetologica 70: 407–416. 10.1655/HERPETOLOGICA-D-14-00012 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Martins MRC, Gordo M. (1993) Bothropsatrox. Herpetological Review 24: 151–152.
- Martins M, Oliveira ME. (1998) Natural history of snakes in forests of the Manaus region, Central Amazonia, Brazil. Herpetological Natural History 6: 78–150. [Google Scholar]
- Martins M, Araújo MS, Sawaya RJ, Nunes R. (2001) Diversity and evolution of macrohabitat use body size and morphology in a monophyletic group of neotropical pitvipers (Bothrops). Journal of Zoology 254: 529–538. 10.1017/S0952836901001030 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Machado ABM, Martins CS, Drummond GM. (2005) Lista da fauna Brasileira ameaçada de extinção, incluindo as listas das espécies quase ameaçadas e deficientes de dados, Fundação Biodiversitas, Belo Horizonte, 160 pp.
- Martins M, Nogueira CC. (2012) Collaboration with local people for sampling reptiles. In: Roy W, McDiarmid MS, Foster CGJ, Whitfield G, Neil Chernoff C (Eds) Reptile Biodiversity Standard Methods for Inventory and Monitoring. University of California Press, Berkeley, 424 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Martins AR, Bruno SF, Navegantes AQ. (2012) Herpetofauna of Núcleo Experimental de Iguaba Grande, Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology 72: 553–562. 10.1590/S1519-69842012000300018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maschio GF, Di-Bernardo M, Melchiors J. (2003) Oxyrhopusrhombiferrhombifer (Falsa-coral). Diet. Herpetological Review 35: 71.
- Menezes FA, Fiorillo BF, Feio RN. (2017) Repertoire of antipredator displays in the poorly known Atlantic forest snake, Gomesophisbrasiliensis (Gomes, 1918). Herpetology Notes 10: 245–247. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes FA, Almeida-Santos SM, Feio RN. (in press) Reproductive cycle of Bothropsfonsecai Hoge & Belluomini, 1959. Herpetology Review.
- Mesquita PC, Passos DC, Borges-Nojosa DM, Cechin SZ. (2013) Ecologia e história natural das serpentes de uma área de Caatinga no nordeste brasileiro. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia 53: 99–113. 10.1590/S0031-10492013000800001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- MMA (Ministério do Meio Ambiente) (2014) Fauna brasileira ameaçada de extinção. portaria nº 444, de 17 de dezembro de 2014. http://www.icmbio.gov.br/portal.
- Moraes LJ, Almeida AP, Fraga R, Rojas RR, Pirani RM, Silva AA, Carvalho VT, Gordo M, Werneck FP. (2017) Integrative overview of the herpetofauna from Serra da Mocidade, a granitic mountain range in northern Brazil. ZooKeys 715: 103–159. 10.3897/zookeys.715.20288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura MR, Motta AP, Fernandes VD, Feio RN. (2012) Herpetofauna da Serra do Brigadeiro, um Remanescete de Mata Atlântica em Minas Gerais, sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotropica 12: 209–235. 10.1590/S1676-06032012000100017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Moura MR, Argôlo AJ, Costa HC. (2016) Historical and contemporary correlates of snake biogeographical subregions in the Atlantic Forest hotspot. Journal of Biogeography 44(3): 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Moura-Leite JC, Bérnils RS, Morato SAA, Langone JA. (2003) Echinantheracephalostriata. Diet. Herpetological Review 34: 149.
- Nogueira CC. (2001) New records of squamate reptiles in Central Brazilian Cerrado II: Brasília region. Herpetological Review 32: 285–287. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen JF, Blanchet G, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H. (2015) Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package. Version 2.2–1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
- Oliveira JL, Borges M, Marques OAV. (2003) Gomesophisbrasiliensis (NCN). Reproduction and diet. Herpetology Review 34: 251–252.
- Olson DM, Dinerstein E, Wikramanayake ED, Burgess ND, Powell GVN. (2001) Terrestrial ecoregions of the world: a new map of life on Earth. Bioscience 51: 933–938. 10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0933:TEOTWA]2.0.CO;2 [DOI]
- Ortiz FR, Serafim H, Rodrigues AP, Abegg AD, Franco FL. (2017) Snakes from Municipality of São José do Barreiro, State of São Paulo, Brazil. Herpetology Notes 10: 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Passos P, Fernandes DS, Caramaschi U. (2004) The taxonomic status of Leptognathusincertus Jan, 1863, with revalidation of Dipsasalternans (Fischer, 1885) (Serpentes: Colubridae: Dipsadinae). Amphibia–Reptilia 25: 381–393. 10.1163/1568538042788951 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Passos P, Martins A, Pinto-Coelho D. (2016) Population Morphological Variation and Natural History of Atractuspotschi (Serpentes: Dipsadidae) in Northeastern Brazil. South American Journal of Herpetology 11: 188–211. 10.2994/SAJH-D-16-00034.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Peters JA, Orejas-Miranda B. (1970) Catalogue of the Neotropical Squamata Part I. Snakes. United States National Museum Bulletin 297.
- Pianka ER. (1969) Habitat specificity, speciation, and species density in Australian desert lizards. Ecology 50(3): 498–502. 10.2307/1933908 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pianka ER. (1989) Latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 4: 223. 10.1016/0169-5347(89)90163-8 [DOI]
- Pinto C, Lema T. (2002) Comportamento alimentar e dieta de serpentes, gêneros Boiruna e Clelia (Serpentes, Colubridae). Iheringia, Série Zoologia 92: 9–19. 10.1590/S0073-47212002000200002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pisciotta K. (2002) The Paranapiacaba forest fragment. Censuses of vertebrates in Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest area: The Paranapiacaba fragment. Barcelona: Centre de Recursos de Biodiversitat Animal–Universitat de Barcelona, 43–69.
- Pizzatto L. (2005) Body size, reproductive biology and abundance of the rare pseudoboini snakes genera Clelia and Boiruna (Serpentes, Colubridae) in Brazil. Phyllomedusa 4: 111–122. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v4i2p111-122 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzatto L, Cantor M, Oliveira JL, Marques OAV, Capovilla V, Martins M. (2008a) Reproductive Ecology of Dipsadine Snakes, with Emphasis on South American Species. Herpetologica 64: 168–179. 10.1655/07-031.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzatto L, Jordão RS, Marques OAV. (2008) Overview of reproductive strategies in Xenodontini (Serpentes: Colubridae: Xenodontinae) with new data for Xenodonneuwiedii and Waglerophismerremii. Journal of Herpetology 42: 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzatto L, Marques OAV. (2006) Interpopulational variation in reproductive cycles and activity of the water snake Liophismiliaris (Colubridae) in Brazil. Herpetological Journal 16: 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Pombal Jr JP, Gordo JP, Marques OAV. (2004) Anfíbios anuros da Juréia. Estação Ecológica Juréia-Itatins. Ambiente Físico, Flora e Fauna, 243–256.
- Pontes JÁ, Figueredo L, Pontes JP, Rocha CFD. (2008) Snakes from the Atlantic Rainforest area of Serra do Mendanha, in Rio de Janeiro state, southeastern Brazil: a first approximation to the taxocenosis composition. Brazilian Journal of Biology 68: 601–608. 10.1590/S1519-69842008000300018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontes JAL, Pontes RC, Rocha CFD. (2009) The snake community of Serra do Mendanha, in Rio de Janeiro State, southeastern Brazil: composition, abundance, richness and diversity in areas with different conservation degrees. Brazilian Journal of Biology 69: 795–804. 10.1590/S1519-69842009000400006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinteros-Muñoz O. (2015) A new prey item for the snake Boirunamaculata (Serpentes: Dipsadidae) in the yungas of Bolivia. Phyllomedusa 14: 79–81. 10.11606/issn.2316-9079.v14i1p79-81 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha CFD, Van Sluys M. (2006) New records of reptiles from Ilha Grande Island in Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Herpetological Review 37: 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha CFD, Bergallo HG, Conde V, Fabiane C, Bittencourt EB, Santos HDC. (2008) Richness, abundance, and mass in snake assemblages from two Atlantic Rainforest sites (Ilha do Cardoso, São Paulo) with differences in environmental productivity. Biota Neotropica 8: 117–122. 10.1590/S1676-06032008000300011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf FJ. (2000) NTSYS. Version 2.1: Numerical taxonomic and multivariate analysis system, version 2.1. Exeter Software Setauket, New York. https://www.exetersoftware.com/downloads/ntsysguide21.pdf
- Salles ROL, Silva-Soares T. (2010) Répteis do município de Duque de Caxias, Baixada Fluminense, Rio de Janeiro, Sudeste do Brasil. Biotemas 23: 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Jr AP, Di-Bernardo M, Lema T. (2008) New species of the Taeniophallusoccipitalis group (Serpentes, Colubridae) from eastern Amazonia, Brazil. Journal of Herpetology 42: 419–426. 10.1670/06-215.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- São-Pedro VA, Pires MRS. (2009) As Serpentes da Região de Ouro Branco, extremo sul da Cadeia do Espinhaço, Minas Gerais. Revista Ceres 56: 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaya RJ, Marques OAV, Martins M. (2008) Composition and natural history of a Cerrado snake assemblage at Itirapina, São Paulo state, southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 8: 127–149. 10.1590/S1676-06032008000200015 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sazima I. (1988) Um estudo de biologia comportamental da jararaca, Bothropsjararaca, com uso de marcas naturais. Memórias do Instituto Butantan 50: 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Sazima I. (1992) Natural history of the jararaca pitviper, Bothropsjararaca, in southeastern Brazil. Biology of the Pitvipers 199–216.
- Sazima I, Haddad CFB. (1992) Répteis da Serra do Japi: notas sobre história natural. In História natural da Serra do Japi: ecologia e preservação de uma área florestal no sudeste do Brasil 28–49.
- Schoener TW. (1968) Size of feeding territories among birds. Ecology 49: 123–141. 10.2307/1933567 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Schoener TW. (1983) Field experiments on interspecific competition. The American Naturalist 122: 240–285. 10.1086/284133 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Scott Jr NJ, Maxwell TC, Thornton-jr OW, Fitzgerald LA, Flury JW. (1989) Distribution habitat and future of Harter’s Water Snake Nerodiaharteri in Texas. J. Herpetology 23: 373–389. 10.2307/1564049 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shine R. (1995) Australian Snakes. A Natural History. Cornell University Press, 42–50.
- Silva LVC, Viana PL, Mota NFO. (2008) Plano de Manejo do Parque Estadual da Serra do Papagaio, Minas Gerais, Brasil. Belo Horizonte, Instituto Estadual de Florestas, 66 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira AL, Pires MRS, Cotta GA. (2010) Serpentes de uma área de transição entre o cerrado e a mata atlântica no sudeste do Brasil. Arquivos do Museu Nacional do Rio de Janeiro 68: 79–110. [Google Scholar]
- SOS Mata Atlântica and INPE. (2014) Atlas dos remanescentes florestais da Mata Atlântica. Período 2012–2013. Fundação SOS Mata Atlântica, São Paulo, 61 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Strussmann C, Sazima I. (1993) The snake assemblage of the Pantanal at Paconé, western Brasil: faunal composition and ecological summary. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Evironment 28: 157–168. 10.1080/01650529309360900 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas RA, Bérnils RS, Moura-Leite JC, Morato SAA. (2006) Redescription of Ditaxodontaeniatus (Hensel, 1868) (Serpentes, Colubridae, Xenodontinae): variation, relationships, and distribution. South American Journal of Herpetology 1: 94–101. 10.2994/1808-9798(2006)1[94:RODTHS]2.0.CO;2 [DOI]
- Torello-Viera NF, Marques OAV. (2017) Daily Activity of Neotropical Dipsadid Snakes. South American Journal of Herpetology 12: 128–135. 10.2994/SAJH-D-16-00023.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tozetti AM, Martins M. (2008) Habitat use by the South‐American rattlesnake (Crotalusdurissus) in south‐eastern Brazil. Journal of Natural History 42(19/20): 1435–1444. 10.1080/00222930802007823 [DOI]
- Tozetti AM, Martins M. (2013) Daily and seasonal activity patterns of free-range South-American rattlesnake (Crotalusdurissus). Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 85: 1047–1052. 10.1590/S0001-37652013005000043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevine V, Forlani MC, Haddad CF, Zaher H. (2014) Herpetofauna of Paranapiacaba: expanding our knowledge on a historical region in the Atlantic forest of southeastern Brazil. Zoologia 31: 126–146. 10.1590/S1984-46702014000200004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Valdujo PH, Nogueira CC, Martins M. (2002) Ecology of Bothropsneuwiedipauloensis (Serpentes: Viperidae: Crotalinae) in the Brazilian Cerrado. Journal of Herpetology 36: 169–176. 10.1670/0022-1511(2002)036[0169:EOBNPS]2.0.CO;2 [DOI]
- Vitt LJ. (1983) Ecology of an anuran-eating guild of terrestrial tropical snake. Herpetologica 39: 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vitt LJ, Vangilder LD. (1983) Ecology of a snake community in northeastern Brazil. Amphibia-Reptilia 4: 273–296. 10.1163/156853883X00148 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vitt LJ. (1987) Communities. In: Seigel RA, Colins JT, Novaks SS. (Eds) Snakes: ecology and evolutionary biology.McGraw–Hill Publishing, New York, 335–365.
- Vitt LJ. (1992) Diversity of reproductive strategies among Brazilian lizards and snakes: the significance of lineage and adaptation. In: Hamlett WC. (Ed.) Reproductive Biology of South American Vertebrates.Springer–Verlag, New York, 135–149. 10.1007/978-1-4612-2866-0_10 [DOI]
- Vrcibradic D, Rocha CFD, Kiefer MC, Hatano FH, Fontes AF, Almeida-Gomes M, Van Sluys M. (2011) Herpetofauna, Estação Ecológica Estadual do Paraíso, State of Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil. Check List 7: 745–749. 10.15560/11013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach V, Williams KL, Boundy J. (2014) Snakes of the World: A Catalogue of Living and Extinct Species. CRC press, 1237 pp. 10.1201/b16901 [DOI]
- Wiens JA. (1977) On Competition and Variable Environments: Populations may experience” ecological crunches” in variable climates, nullifying the assumptions of competition theory and limiting the usefulness of short-term studies of population patterns. American Scientist 65: 590–597. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler FJM, Waltenberg LM, Santos PA, Nascimento DS, Vrcibradic D, Sluys MV. (2011) New records of anuran prey for Thamnodynastesstrigatus (Günther, 1858) (Serpentes: Colubridae) in a high-elevation area of southeast Brazil. Herpetology Notes 4: 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zaher H, Scrocchi G, Masiero R. (2008) Rediscovery and redescription of the type of Philodryaslaticeps Werner, 1900 and the taxonomic status of P.oligolepis Gomes, 1921 (Serpentes, Colubridae). Zootaxa 1940: 25–40. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.