Abstract
Impairment of the immune system is a developing concern in evaluating the toxicity of cadmium (Cd). In the present study, we investigated if Cd could impair cutaneous wound healing through interfering with inflammation after injury. We found that exposure of mice to CdCl2 through drinking water at doses of 10, 30, and 50 mg/l for 8 weeks significantly impaired cutaneous wound healing. Chronic 30 mg/l CdCl2 treatment elevated murine blood Cd level comparable to that of low dose Cd-exposed humans, had no effect on blood total and differential leukocyte counts, but reduced neutrophil infiltration, chemokines (CXCL1 and CXCL2), and proinflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6) expression in wounded tissue at early stage after injury. Wounded tissue homogenates from CdCl2-treated mice had lower chemotactic activity for neutrophils than those from untreated mice. Mechanistic studies showed that chronic Cd treatment suppressed ERK1/2 and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation in wounded tissue at early stage after injury. Compared with neutrophils isolated from untreated mice, neutrophils from CdCl2 treated mice and normal neutrophils treated with CdCl2 invitro both had lower chemotactic response, calcium mobilization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation upon chemoattractant stimulation. Collectively, our study indicate that chronic low-dose Cd exposure impaired cutaneous wound healing by reducing neutrophil infiltration through inhibiting chemokine expression and neutrophil chemotactic response, and suppressing proinflammatory cytokine expression. Cd may suppress chemokine and proinflammatory expression through inactivating ERK1/2 and NF-κB, and inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis by attenuating calcium mobilization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in response to chemoattractants.
Keywords: cadmium, wound healing, neutrophil, chemokine, proinflammatory cytokine
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic metal existing in the environment naturally and as a pollutant from industrial and agricultural sources. Humans are exposed to Cd through food chain and tobacco smoke. Cd has a decades-long half-life in humans and significant accumulation occurs with chronic dietary intake. Chronic low-dose Cd exposure is associated with a range of chronic diseases, including renal dysfunction, osteoporosis, certain types of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes (Edwards and Ackerman, 2016; Johri etal., 2010; Kazantzis, 2004; Nawrot etal., 2015; Tellez-Plaza etal., 2013).
Apart from aforementioned diseases, impairment of the immune system by Cd is a developing concern. Acute exposure to Cd results in neutrophilia in industrially exposed workers (Amdur and Caputi, 1953; Beton etal., 1966). Acute exposure of animals to high-dose Cd not only causes neutrophilia, but also induces neutrophil infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine expression in tissues and organs (Djokic etal., 2014; Horiguchi etal., 2000; Stosic etal., 2010). Chronic or subchronic exposure of animals to low-dose Cd also induces leukocyte infiltration (Kirschvink etal., 2006), proinflammatory cytokine expression (Lee and Lim, 2011; Yazihan etal., 2011), and JNK, AP-1, NF-κB activation (Lee and Lim, 2011). Most invitro studies show that Cd in micromolar concentrations has pro-inflammatory properties in immune and non-immune cells (Olszowski etal., 2012). Macrophages exposed to Cd have lower phagocytic activity (Nelson etal., 1982; Wei etal., 1998). Collectively, data from invivo and invitro studies indicate that Cd is a pathogenic factor leading to excess mobilization and dysfunction of innate immune cells, as well as overexpression of proinflammatory cytokines. Cd may cause adverse health effects by disturbing the innate immune system. However, the effect of chronic low-dose Cd on innate immune response is largely unknown.
Wound healing encompasses 3 phases: inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling phases. Inflammatory response, an innate immune response after injury is critical for establishing an environment that facilitates the subsequent stages of the healing process. The initial event during the inflammatory phase is the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages into the wound site to phagocytose bacteria and cellular debris. Neutrophils and macrophages are recruited to wounded tissues by classic chemoattractants (formyl peptides, leukotriene B4, complement fragments) and chemokines (CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL8, and CCL2) produced by bacteria, injured tissues, and immune cells (Lammermann etal., 2013; Liu etal., 2014; Martins-Green etal., 2013; Su and Richmond, 2015). Neutrophils and macrophages are major sources and targets of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are crucial mediators during cutaneous inflammatory process (Hübner etal., 1996). Dysregulation of leukocyte recruitment or chemokine and proinflammatory cytokine expression may delay wound healing (Ashcroft etal., 2012; Behm etal., 2012; Ebaid 2014; Gallucci etal., 2000; Koh and DiPietro, 2011; Mirza etal., 2009). Lansdown etal. (2001) reported that topically exposure of murine skin wounds to 1.0% CdCl2 impaired wound healing with persistent inflammatory cell infiltration, edema, and aberrant epidermal cell growth. It is not clear if chronic low-dose oral Cd exposure could impair wound healing through disturbing early inflammatory response after injury.
Many epidemiological studies reported elevated blood Cd concentrations in workers professionally exposed to Cd or in peoples living near the Cd-polluted area. For example, blood Cd concentrations of Cd exposed workers in Netherland (Verschoor etal., 1987), Singapore (Chia etal.,1989), and China (Chen etal., 2006) were 18.8 to −154.9 nmol/l (2.11–17.41 µg/l), 7.57 ± 5.89 and 7.53–11.43 µg/l, respectively. About 30.30% of 539 children living near a lead smelter in Brazil had blood Cd levels higher than 0.15 µmol/l (16.86 µg/l) (Carvalho etal., 1986). People living near a copper smelter in Poland had Cd blood levels of 44 ± 17 µg/l in 1985 and 28 ± 7 µg/l in 1990 (n = 60) (Andrzejak etal., 1993). Thijssen etal. (2007) reported that C57BL/6 mice exposed to 10, 20, and 100 mg/l CdCl2 through drinking water for 8 weeks had blood Cd concentrations of 6.19 ± 0.73, 11.18 ± 1.44, and 56.31 ± 8.79 µg/l, respectively. In the present study, we found that chronically exposure of mice to CdCl2 at doses of 10, 30, and 50 mg/l through drinking water impaired skin wound healing. The blood Cd levels of mice exposed 10 and 30 mg/l for 8 weeks were similar to those of Cd-exposed humans. Mechanistic studies revealed that in contrast to its proinflammatory effect reported before, chronic Cd exposure inhibited early inflammation after skin injury with defective neutrophil infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine expression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and treatment
Male C57BL/6 mice were obtained from Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Institute for Nutritional Sciences, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Seven- to eight-week-old mice were maintained in temperature- and humidity-controlled conditions with a 12 h light/dark cycle, and were allowed ad libitum access to food and water containing different concentrations of CdCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) for different periods of time. Mice were anaesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 2,2,2-tribromoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and the back was shaved and sterilized with 75% ethanol. Full-thickness wounds were made using a sterile biopsy punch with a diameter of 6 mm (AcuPunch, Fort Lauderdale, FL) in the right and left upper paravertebral regions of each animal. Wounds were photographed using a Nikon D70s digital camera (Nikon, Japan) at indicated time points during healing. Changes in wound area over time were calculated using an image-pro plus 6.0 software (Media Cybernetics, Inc, MD).
At indicated time points after wounding, the animals were sacrificed and the wounds and surrounding skin tissues (1 mm from the border of wound) were sampled by a biopsy punch. The excised wounded tissues were frozen at −80 °C for further examination of target gene expression at mRNA and protein levels, or immediately fixed in 4% polyformaldehyde for further histological and immunohistochemical assays.
Histology and immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence
Fixed wounded tissues were processed for embedding in paraffin and sectioned at 3 µm. The sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E). Additionally, sections were used for immunohistochemical or immunofluoresence staining of myeloperoxidase (MPO) or F4/80 to detect infiltrated neutrophils and macrophages in wounded tissues. Briefly, tissues were incubated with rabbit anti-MPO antibody (Proteintech Group Inc., IL) or anti-F4/80 antibody (Santa Cruz, CA, USA) at 4 °C for 24 h and then with HRP conjugated secondary antibody (Proteintech Group Inc., IL) or Cy3 labeled goat-anti-rabbit antibody (Jackson immunoResearch, West Grove, PA) for 2 h. All simultaneously stained sections were examined under light microscope, or fluorescence microscope and photomicrographs were taken with a digital camera (Olympus, Japan). Apoptotic cells in wounded tissues were detected with TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit (FITC) (Roche Basel, Switzerland). MPO, F4/80 or TUNEL positive cells were analyzed using Image-Pro Plus (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD).
MPO activity assay
MPO activity of wounded tissues was determined using MPO Assay Kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China). Briefly, wounds and surrounding tissues (1 mm from the border of wound) were homogenized in PBS and centrifuged. The supernatant was collected and measured protein concentration using BCA Kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, China). About 10 µl of the supernatant was added to 10 µl PBS containing 0.17 mg/ml 3,3′-dimethoxybenzidine and 0.0005% H2O2. MPO activity was determined by measuring absorbance at 460 nm. MPO activity was expressed as units per gram of total protein.
Cd determination
The content of Cd in skin tissue and blood was measured with Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS). Briefly, 200 mg skin tissue or 200 µl whole blood was digested with 5 ml HNO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) for 24 h, evaporated to 500 µl, and then diluted with 2 ml 2% HNO3. The Cd level in the solution was measured with Agilent 7700X ICP-MS (Agilent Technologies, Tokyo, Japan).
Peripheral blood cell counts and biochemistry analysis
Total blood erythrocyte, total and differential blood leukocyte, and platelet counts were determined using COULTER LH 750 Hematology Analyzer (Beckman Coulter Inc., Brea, CA). Blood glucose, creatinine, uric acid, and urea concentrations were measured with ADIVA2400 Chemistry System (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc., Berlin and Munich, Germany).
RNA isolation and real time RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from excised wounds and surrounding skin tissues or neutrophils using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Total RNA (2 µg) was reverse transcribed to cDNA using MMLV-reverse transcriptase (TAKARA, Japan). Real time PCR was performed by using ABI Prism 7900 sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA) with SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA). Transcriptional levels for mRNA were normalized to RPLP2. The relative expression of mRNA was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method. Primer sequences used for qRT- PCR are listed in the Supplementary Table 1.
Western blot
The excised wounds and surrounding skin tissues or neutrophils were homogenized or lysed in lysis buffer and centrifuged to remove the debris. The supernatants were collected and measured for protein concentration with BCA Kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, China). Western blotting was carried out according to standard protocols. Target proteins were detected with SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA). Primary antibodies against phosphorylated and total forms of NF-κB p65 and MAP kinases (p38, JNK, and ERK1/2) (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MD) were used. The phosphorylated proteins were quantified with Image-Pro Plus 6.0 (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD) and normalized to corresponding total proteins.
Cytokine determination by ELISA
The excised wounds and surrounding skin tissues were homogenized in PBS and centrifuged. The supernatants were collected to measure the concentrations of chemokines (CXCL1, CXCL2), proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNFα, and IL-6) and IL-10 using ELISA kits (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The supernatants at different dilutions were also examined for chemotactic activity to neutrophils.
Neutrophil isolation and chemotaxis assay
Neutrophils were isolated form mice bone marrow as previously described (Swamydas etal., 2015). Briefly, mice were euthanized and bone marrow was harvested by flushing the tibias and femurs with PBS. Neutrophils were purified from bone marrow cell suspension using Histopaque 1077/1119 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) density gradient centrifugation. The chemotaxis of neutrophils was analyzed using polycarbonate membranes with 3 µm pore size in 48-well chambers (NeuroProbe, Gaithersburg, MD) as described previously (Liu etal., 2014). Briefly, different concentrations of fMLF (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) or WKYMVm (W peptide, R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) were placed in the lower wells of the chamber, neutrophils suspended in RPMI 1640 with 0.5% BSA (2 × 106 cells/ml) were placed in the upper wells. After incubation at 37 °C for 1 h, the membranes were removed, rinsed with PBS, fixed, and stained with Diff-Quik 3-step stain solution (Richard Allan Scientific, Waltham, MA). Migrated cells were counted in 3 random fields at 200 magnification under light microscopy using Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD), the results are presented as mean ± SD of triplicate wells.
Ca2+ flux assay
Ca2+ mobilization was measured with BioTek Synergy NEO (Bio Tek Instruments, Inc, Winooski, VT). Neutrophils (2×106 cell/ml) were incubated with 1 ng/ml Fluo 3-AM (Molecular Probes, Waltham, MA, USA) in loading medium (0.005% pluronic-127 and 10% FBS in RPMI1640) at 37 °C for 20 min in dark, washed and resuspended at 4 × 106 cells/ml in emission buffer (10 mM CaCl2, 7.6 mM MgCl2, 50 mM glucose) with vehicle or different concentrations of CdCl2 for 30 min. The fluorescence before and after stimulation with different concentrations of fMLF was measured with the excitation wavelength at 488 nm and the emission wavelength at 525 nm. Results were presented as relative fluorescence unit (RFU) which was calculated with the following formula: RFU (%) = (fluorescence after fMLF stimulation– basal fluorescence)/basal fluorescence × 100.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed at least 3 times. Data were expressed as mean ± SE or mean ± SD as indicated in figure legends. Statistical differences between testing and control groups were analyzed by Student’s t-test. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered as significantly different.
RESULTS
Chronic Cd Exposure Impairs Wound Healing in Mice
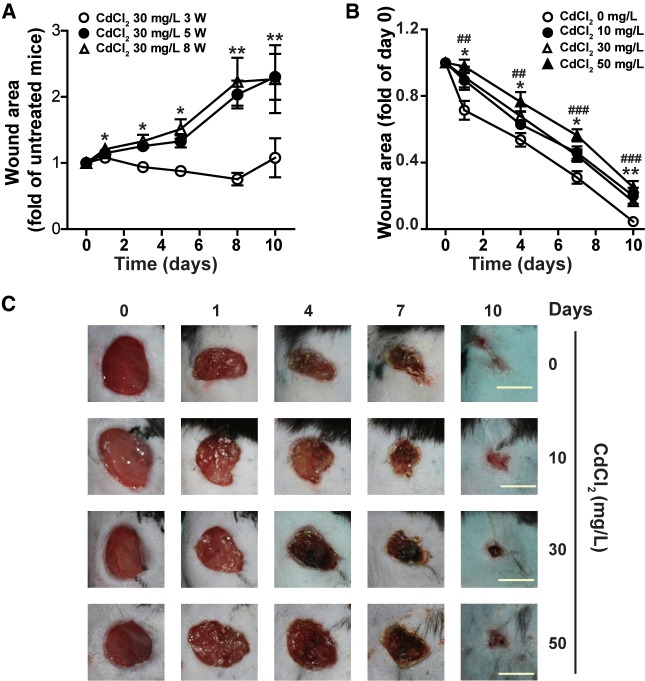
To investigate the effect of chronic Cd exposure on mice skin wound healing, we first exposed mice to Cd through drinking water containing 30 mg/l CdCl2 for different periods of time, and observed the repair of skin wounds made by biopsy punch. Compared with the wound areas of mice drinking normal water, exposure to 30 mg/l CdCl2 for 3 weeks had no significant effect on wound healing. However, exposure to 30 mg/l CdCl2 for 5 or 8 weeks significantly delayed wound healing (Figure 1A). We then examined the dose–response effect of Cd on wound healing. As shown in Figures 1B and 1C, CdCl2 at dose as low as 10 mg/l significantly impaired wound healing, and the impairment of Cd on wound healing was observed as early as 1 day after wounding. CdCl2 at 10 and 30 mg/l had similar inhibitory effect on wound healing, but 50 mg/l CdCl2 had more severe impact on wound healing. Exposure of mice to 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks significantly increased Cd levels in skin (0.08 ± 0.004 µg/g) and blood (11.33 ± 1.05 µg/l), but had no significant effect on body weight, food and water intake, blood glucose level, and serum renal function markers (Table 1, Supplementary Figure 1, and data not shown). Taken together, these results demonstrate that chronic low-dose Cd exposure delays skin wound healing in mice. It has been reported that mice exposed to 10 mg/l CdCl2 for 8 weeks resulted in 6.19 ± 0.073 µg/l Cd in blood (Thijssen etal., 2007). The blood Cd levels in mice exposed to 10 and 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks was similar to those of humans working or living near a Cd-polluted environment (Andrzejak etal., 1993; Carvalho etal., 1986; Chen etal., 2006; Verschoor etal., 1987). 30 mg/l CdCl2 was used in the following experiments to explore the mechanisms involved in the inhibitory effect of Cd on wound healing.
Figure 1.
Chronic cadmium exposure delays skin wound healing in mice. C57B/L6 mice were given 0 or 30 mg/l CdCl2 for different periods of time (A), or different concentrations of CdCl2 for 8 weeks (B) through drinking water, 6-mm diameter wounds were made on the back, and the wound areas were measured at different times after injury. Data in (A) and (B) are expressed as mean ± SE, n = 5 per group. All experiments were repeated at least 3 times with similar results and representative data are shown. *P < .05, **P < .01, compared mice treated with 30 mg/l CdCl2 for 5 or 8 weeks with corresponding untreated mice (A); compared mice treated with 10 or 30 mg/l CdCl2 with untreated mice (B); ##P < .01, ###P < .001, compared 50 mg/l CdCl2 treated mice with untreated mice, at the same time points (B). (C) Representative pictures of skin wound healing of mice exposed to different concentrations of CdCl2 for 8 weeks. Bar = 5 mm.
Table 1.
Effect of Chronic Cadmium (Cd) Exposure on Skin and Blood Cd Levels, Peripheral Blood Cell Counts, Blood Glucose Level, and Renal Function Markers in Mice
| Untreated Control | CdCl2 (30 mg/l) | |
|---|---|---|
| Skin Cd (µg/g) | <0.001 | 0.08 ± 0.004*** |
| Blood Cd (µg/l) | 0.35 ± 0.08 | 11.33 ± 1.05*** |
| White blood cell (109/l) | 2.0 ± 1.26 | 2.0 ±1.05 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 4.70 ± 2.73 | 7.26 ± 1.87 |
| Monocyte (%) | 8.29 ± 6.99 | 6.20 ± 2.84 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 86.43 ± 8.98 | 85.19 ± 5.60 |
| Basophil (%) | 0.025 ± 0.01 | 0.027 ± 0.01 |
| Eosinophil (%) | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 0.25 ± 0.11 |
| Red blood cell (1012/l) | 8.92 ± 0.30 | 9.01 ± 0.27 |
| Hemoglobin (g/l) | 132.80 ± 4.87 | 133.60 ± 4.76 |
| Platelet (109/l) | 993.20 ± 80.89 | 920.0 ± 169.46 |
| Serum creatinine (µmol/l) | 18.0 ± 4.69 | 23.0 ± 5.76 |
| Blood glucose (mmol/l | 6.50 ± 0.25 | 6.32 ± 0.29 |
| Serum uric acid (µmol/l) | 82.0 ± 28.01 | 122.80 ± 42.75 |
| Serum urea (mmol/l) | 15.20 ± 1.49 | 14.74 ± 2.63 |
Mice were exposed to 0, 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks. Values are expressed as means ± SE. n = 5 per group.
P < .001, compared with untreated control mice.
Chronic Exposure to Cd Inhibited Neutrophil Infiltration Into Wounded Tissues
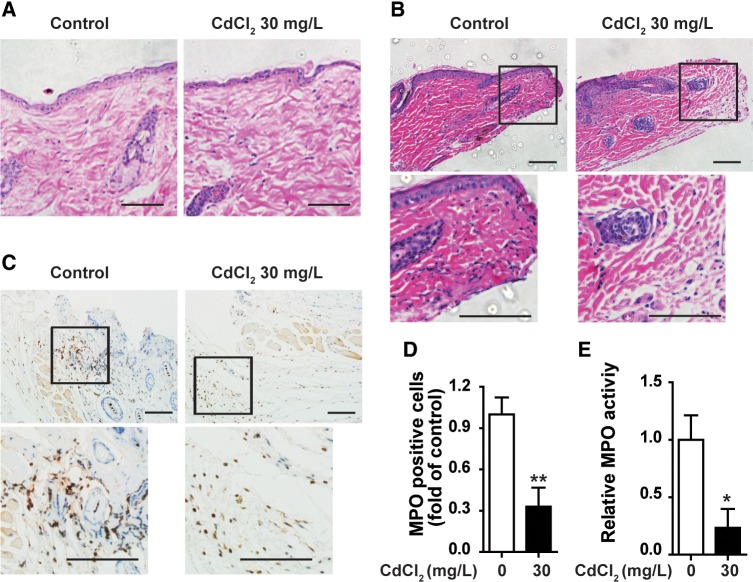
The influx of neutrophils to wounded tissue at the early inflammatory phase is one of the notable events during wound healing. As we observed that chronic exposure of low-dose Cd impaired wound healing at early stage, we examined the effect of chronic Cd exposure on neutrophil infiltration into wounded tissues at 3 h after skin punch. H & E staining showed that the skin structure and cell distribution had no difference between untreated control mice and mice exposed to 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks (Figure 2A). In the wounded tissues of untreated control mice, there was significant neutrophil infiltration at 3 h after skin injury. Exposure of 30 mg/l CdCl2 for 8 weeks decreased neutrophils in the wounded tissues at 3 h after skin injury (Figure 2B). Immunostaining of MPO, a biomarker of neutrophils, showed that there were fewer neutrophils in wounded tissues of CdCl2 treated mice than those of control mice (Figs. 2C and 2D). Consistently, the MPO activity in the wounded tissues of Cd exposed mice was lower than that of control mice (Figure 2E). These results showed that chronic exposure of low-dose Cd reduced neutrophil infiltration into wounded tissues. Peripheral blood cell analysis showed that there was no significant difference of erythrocyte count and hemoglobin level, total and differential leukocyte counts, as well as platelet count between untreated and Cd exposed mice (Table 1), indicating that the lower infiltration of neutrophils in wounded tissues of Cd treated mice is not due to the alteration of neutrophil levels in the peripheral blood. To check if reduced neutrophil infiltration in wounded tissues of Cd-exposed mice is due to neutrophil apoptosis, dual immunofluorescence staining of MPO and TUNEL was performed. Overlay analysis showed that in control mice, there were very few apoptotic neutrophils in wounded tissues at 3 h after skin injury, chronic Cd-exposure had no significant effect on neutrophil apoptosis in wounded skin tissues (Supplementary Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Chronic cadmium exposure reduced neutrophil infiltration in the wounds of mice. Mice were given drinking water containing 0 or 30 mg/l CdCl2 for 8 weeks. A, H & E staining of uninjured skin tissues. Wounded tissues at 3 h after skin punch were examined for neutrophil infiltration by H & E staining (B), myeloperoxidase (MPO) immunostaining (C,D), and MPO activity assay (E). All experiments were repeated at least 3 times with similar results and representative data are shown. MPO positive cells were analyzed in 3 random fields under microscope for each section using Image-Pro Plus. Five sections from 5 animals each group were analyzed. (A–C) show representative images of H & E staining and MPO immunostaining, respectively, scale bar = 50 µm. Data in (D) and (E) are mean ± SE, n = 5 per group. *P < .05, **P < .01, compared with untreated mice.
We also examined the effect of chronic Cd exposure on recruitment of macrophages in wounded tissues by immunostaining of macrophage marker F4/80 in wounded tissues at different time points after skin punch. As shown in Supplementary Figure 3, the infiltration of macrophage into wounded tissues increased in a time-dependent manner, chronic Cd exposure had no significant effect on macrophage infiltration in wounded tissues at 3, 24, and 72 h after skin injury. Therefore, chronic Cd exposure had no significant effect on macrophage infiltration into wounded tissues at early stage of wound healing.
Chronic Exposure to Cd Reduces Chemokine Expression and Chemotactic Activity in Wounded Tissues
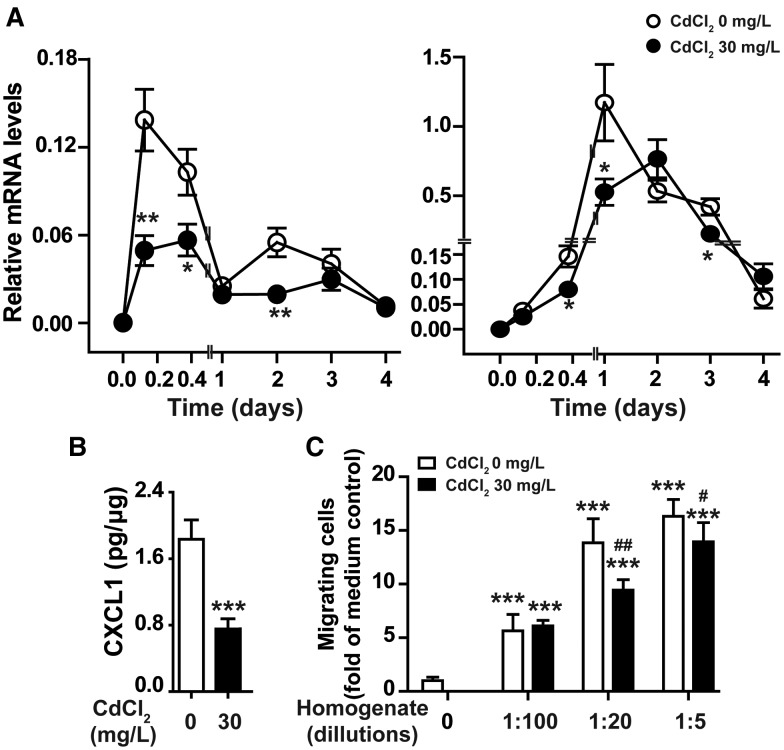
During the inflammation stage, injured skin tissues produce chemokines and other chemoattractants that guide neutrophils to navigate into the wounding sites (Su and Richmond, 2015). We examined the effect of chronic Cd exposure on the expression of chemokines recruiting leukocytes to wounded tissues, including CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL12, CCL3, CCL4, and CCL5, at different times after skin injury. Exposure of mice to 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks had no significant effect on basal expression of these chemokines in uninjured skin tissues (time 0 of Figure 3A and Supplementary Figure 4). The mRNA levels of these chemokines were significantly increased in wounded tissues of control mice after skin injury. However, compared with untreated mice, CXCL1 expression was significantly reduced at 3 h, 9 h, and 2 days; CXCL2 expression was significantly reduced at 1 and 3 days after skin injury in Cd treated mice (Figure 3A). The reduction of CXCL1 in wounded tissues of Cd exposed mice was confirmed at protein level at 3 h after skin injury (Figure 3B). These results indicate that chronic Cd exposure reduced the production of CXCL1 and CXCL2 which are required for the recruitment of neutrophils to wounded tissues at early stage of wound healing. We then checked the chemotactic activity of wounded tissues at 3 h after skin punch. As shown in Figure 3C, neutrophils isolated from normal mice showed marked chemotactic response to wounded tissue homogenates of untreated mice, but less response to wounded tissue homogenates of Cd treated mice, supporting that chronic Cd exposure reduced chemoattractant production in wounded tissue at the early stage after skin injury. Collectively, these results indicate that chronic low-dose Cd exposure reduces neutrophil infiltration into wounds through inhibiting chemoattractant production by injured skin tissues, including chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2.
Figure 3.
Chronic cadmium exposure reduced chemokine production and chemotactic activity of skin wounded tissues. Wounded tissues of mice taking CdCl2 in drinking water (0, 30 mg/l) for 8 weeks were examined for the expression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 at mRNA level at different time points after skin injury (A), at protein level 3 h after injury (B), and for chemotactic activity to neutrophils isolated from untreated mice (C). Data in (A) and (B) are expressed as mean ± SE, n = 10 per group. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared with untreated control mice at same time points. Data in (C) are mean ± SD, representative results of experiment with 5 animals in each group. ***P < .001 compared with cell migration in response to medium control (0); #P < .05, ##P < .01, compared with chemotactic response to wounded tissue homogenates from untreated mice with same dilution.
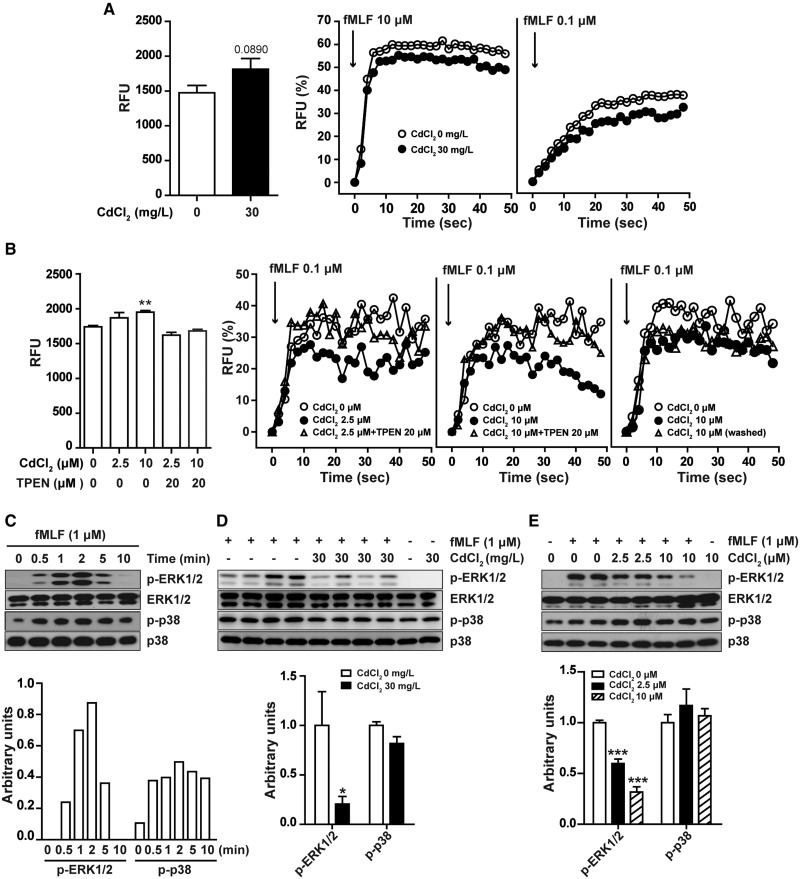
Cd Exposure Impairs Neutrophil Chemotaxis, Calcium Mobilization, and ERK Phosphorylation in Response to Chemoattractants
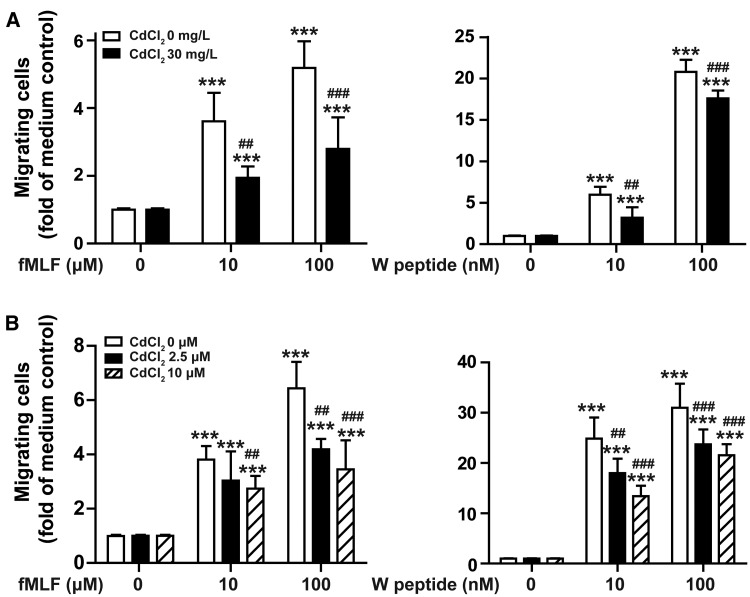
In addition to chemokines, chemoattractants produced by injured skin tissues, such as formylpeptides, also play important roles in neutrophil infiltration into skin wounds. To examine whether chronic Cd exposure impairs neutrophil chemotactic response, we measured neutrophil migration in response to agonists for formyl peptide receptors Fpr1 and Fpr2 by invitro chemotaxis assay. As shown in Figure 4A, fMLF (a ligand for Fpr1) and W peptide (a high affinity ligand for Fpr2) both dose-dependently induce migration of neutrophils isolated from untreated mice and mice exposed to 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks, but neutrophils from Cd treated mice had lower chemotactic response to fMLF and W peptide. We then investigated if Cd had acute, direct effect on neutrophil chemotactic response to fMLF and W peptide. As shown in Figure 4B, treatment of neutrophils from untreated mice with different concentrations of CdCl2 for 30 min also significantly inhibited cell migration to fMLF and W peptide. Typan staining showed that exposure of neutrophils to CdCl2 up to 10 µM for 4 h had no significant effect on cell viability (Supplementary Figure 5). These results demonstrate that exposure of Cd chronically invivo and acutely invitro could inhibit Fpr1- and Fpr2-mediated neutrophil migration, and indicate that Cd exposure may reduce neutrophil infiltration into wounds through impairing neutrophil chemotactic response to chemoattractants.
Figure 4.
Cadmium inhibited neutrophil chemotactic response to chemoattractants. A, Neutrophils were isolated from bone marrow of untreated mice or mice exposed to Cd (30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water) for 8 weeks, and examined for migration in response to different concentrations of fMLF or WKYMVm (W peptide). B, Neutrophils from untreated mice were incubated with different concentrations of CdCl2 for 30 min, and then examined for chemotactic response to fMLF or W peptide. Data are mean ± SD, data in (A) are representative results of 2 experiments with 5 animals in each group. Data in (B) are representative results of 5 animals. ***P < .001, compared with migrating neutrophils from untreated mice in response to medium control; ##P < .01, ###P < .001, compared with untreated neutrophils in response to same concentration of fMLF or W peptide.
We further examined the mechanisms involved in the inhibitory effect of Cd on neutrophil chemotactic response to fMLF. It is well-known that fMLF induces neutrophil migration through calcium mobilization and activation of MAP Kinases p38 and ERK1/2 (Niggli, 2003; Selvatici etal., 2006). We used Fluo-3AM to detect intracellular Ca2+ level and found that Flu3-AM fluorescence density had a tendency to increase in neutrophils isolated form Cd-treated mice and slightly increased in neutrophils treated with Cd invitro (Figs. 5A and 5B). fMLF dose-dependently induced calcium flux in neutrophils isolated from untreated control mice and mice chronically exposed to Cd (30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks). However, neutrophils from Cd treated mice had lower response to same concentrations of fMLF (Figure 5A). Acute treatment of neutrophils isolated from untreated mice with Cd for 30 min also dose-dependently inhibited fMLF induced calcium mobilization (Figure 5B). We further found that the inhibitory effect of Cd was reversed by pretreating neutrophils with TPEN, a chelator of Cd. Remove extracellular Cd from Cd-treated neutrophils by washing had no significant effect on the inhibition of fMLF-induced calcium mobilization by Cd (Figure 5B), indicating that Cd interfered with intracellular calcium mobilization rather than extracellular calcium influx induced by fMLF. These results showed that Cd could inhibit neutrophil calcium mobilization in response to fMLF. We also examined the effect of Cd on fMLF-induced ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation. Treatment of neutrophils isolated from untreated mice with fMLF induced p38 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner, with a maximum response at 2 min after stimulation (Figure 5C). Compared with neutrophils from control mice, neutrophils from mice exposed to 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks had lower levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and similar levels of p38 (Figure 5D). Similarly, treatment of neutrophils from untreated mice with 2.5 and 10 µM CdCl2 for 30 min dose-dependently inhibited fMLF-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation but had no significant effect on p38 phosphorylation (Figure 5E). Taken together, Cd treatment, chronically invivo or acutely invitro, inhibits fMLF-induced calcium mobilization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in neutrophils, which may result in lower neutrophil chemotactic response to formyl peptides.
Figure 5.
Cadmium inhibited calcium mobilization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation induced by fMLF in neutrophils. Neutrophils from control mice or mice taking Cd in drinking water (30 mg/l CdCl2) for 8 weeks were examined for basal intracellular Ca2+ level and Ca2+ mobilization in response to different concentrations of fMLF (A), ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation in response to 1 µM fMLF for 2 min (D). Neutrophils from untreated mice pretreated with or without 20 µM TPEM for 10 min were exposed to different concentrations of CdCl2 for 30 min, then were examined for basal intracellular Ca2+ level and Ca2+ mobilization in response to different concentrations of fMLF after extracellular CdCl2 was washed away or not (B), and ERK1/2, p38 phosphorylation in response to 1 µM fMLF for 2 min (E). C, Neutrophils from untreated mice were stimulated with 1 µM fMLF for different periods of time and examined for ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation. A–B: each experiment was performed at least 3 times with similar results. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (A: left panel, n = 5 per group; B: left panel, n = 3), **P < 0.01 compared with untreated neutrophils. C–E, Images shown are representative of 3 independent experiments, data are mean ± SD, n = 5 per group, ***P < .001 compared with Cd untreated neutrophils stimulated with fMLF.
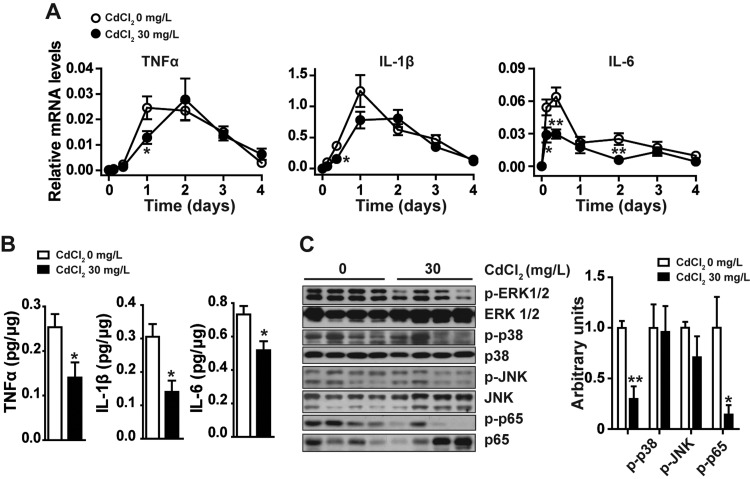
Chronic Cd Exposure Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression, Suppresses ERK1/2 and NF-κB Activation in Wounded Tissue
Proinflammatory cytokines, including TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6, are mainly expressed by neutrophils and macrophages in wounds during the inflammatory phase of healing, and play an important role in wound healing (Behm etal., 2012). We examined the expression of these cytokines at different time points after skin punch. As shown in Figure 6A, the mRNA levels of these cytokines in control mice significantly elevated and reached peak at 1 day after skin injury. Compared with those of untreated mice, the skin wounded tissues of mice exposed to 30 mg/l CdCl2 in drinking water for 8 weeks had lower levels of these cytokines. Consistently, the protein levels of these cytokines also decreased in the wounds of Cd treated mice (Figure 6B). We also examined the expression of IL-10, an important anti-inflammatory cytokine involved in wound healing (Sato etal., 1999) at different time points after skin punch. There was no significant difference of IL-10 mRNA levels in wounded tissues between Cd treated and untreated mice (data not shown). We further examined the activation of MAP kinases and NF-κB, the key molecules regulating proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in wounded tissues by Western blot. Compared with those of control mice, mice exposed to Cd had lower levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and NF-κB p65, and similar levels of phosphorylated p38 and JNK in wounds (Figure 6C). These results indicate that chronic exposure to low-dose Cd may reduce proinflammatory cytokine production in wounded tissues through inhibiting MAP kinases ERK1/2 and NF-κB activation.
Figure 6.
Effect of chronic camium exposure on proinflammatory cytokine production, MAP kinases and NF-κB activation in skin wounded tissues. Skin wounded tissues from mice intake CdCl2 in drinking water (0, 30 mg/l) for 8 weeks were examined for the expression of proinflammatory cytokines at mRNA levels at different times after injury (A), at protein levels 3 h after injury (B), and for phosphorylation of MAP kinases and NF-κB p65 at 3 h after injury by Western blot (C). A, B, Data are expressed as mean ± SE, n = 10 per group. *P < .05, **P < .01 compared with untreated control mice at same time points after skin punch. C, Images shown are representative of 3 independent experiments, data are mean ± SD, n = 5 per group, *P < .05, **P < .01 compared with untreated mice at 3 h after skin injury.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we found that chronic exposure of mice to low-dose Cd inhibited early inflammation after skin injury and impaired wound healing. The inhibitory effect of Cd on wound healing may be mediated by suppressing chemokine and proinflammatory cytokine expression, and reducing neutrophil infiltration in wounded tissues.
We found that exposure of mice to 10, 30, and 50 mg/l CdCl2 through drinking water for 8 weeks impaired skin wound healing. As the blood concentrations of Cd in mice exposed to 10 and 30 mg/l were in accordance with blood concentrations of Cd found in humans working or living in a Cd-polluted environment (Carvalho etal., 1986; Chen etal., 2006; Ikeda etal., 2004; Verschoor etal., 1987). Our study indicates that chronic exposure to Cd polluted environment may delay skin wound healing.
The injured skin tissues produce CXC and CCL chemokines and other chemoattractant molecules which play important role in recruiting neutrophils and other types of leukocytes to the wounding sites. We found that chronic CdCl2 exposure significantly reduced neutrophil infiltration and suppressed chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2 expression. These 2 chemokines have been found to be potent neutrophil chemoattractants in mice. CXCL1 has been reported to be released by recruited neutrophils and to play a critical role in the recruitment of other neutrophils to wounded tissues (Su and Richmond, 2015). CXCR2, the receptor of CXCL1 and CXCL2, is speculated as major chemokine receptor recruiting neutrophils to wounded tissues (Su and Richmond, 2015). Therefore, these results indicate that chronic Cd exposure may inhibit neutrophil infiltration into wounded tissue by reducing CXCL1 and CXCL2 production after injury. We further found that neutrophils chronically exposed to Cd invivo or exposed to Cd invitro had lower chemotactic response to chemoattractants, indicating that Cd has direct inhibitory effect on neutrophil response to chemoattractants and migration to wounded tissues. We further checked if Cd could impair other function of neutrophils. In vitro study showed that acute exposure of neutrophils to 2.5 or 10 µM CdCl2 slightly increased ROS production, pretreatment the cells with 10 µM CdCl2 significantly inhibited fMLF-induced ROS production (Supplementary Figure 6). It has been reported that fMLF induces ROS production in neutrophils through phosphorylation of p47phox, a key component of NADPH oxidase (El-Benna etal., 2009). Regulation of p47phox phosphorylation status is crucial in modulating the effect of fMLF on phagocyte ROS production (Chedid etal., 2012, 2017). Cd induces ROS production by enhancing p47phox phosphorylation and NADPH oxidase activity (Souza etal., 2009). We postulate that pretreatment of neutrophils with Cd phosphorylates p47phox, which may reduce the response of NADPH oxidase to fMLF stimulation and result in lower ROS production. It is commonly understood that ROS produced by neutrophils serve mainly to kill bacteria and prevent wound infection. Inhibition of neutrophil ROS production by Cd may contribute to the impairment of wound healing by Cd.
We further investigated the mechanisms involved in the inhibitory effect of Cd on neutrophil chemotactic response to fMLF. fMLF induces neutrophil polarization and migration through binding FPR1 and increasing cytosolic Ca2+ concentration (Niggli, 2003; Pettit and Fay, 1998). This calcium mobilization is mediated by phospholipase Cβ2 (PLCβ2) which hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate into inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 triggers Ca2+ release from intracellular stores, principally from the endoplasmic reticulum (Cai etal., 2013; Schaff etal., 2010; Smyth etal., 2010). DAG mediates receptor operated Ca2+ entry by direct activation of cell membrane Ca2+ channels (Cai, etal., 2013; Dietrich etal., 2005). In the present study, we found that neutrophils isolated from chronic Cd exposed mice had lower calcium mobilization in response to fMLF than that of untreated mice (Figure 5A). Pretreatment of normal neutrophils with Cd invitro also inhibited fMLF induced-calcium flux (Figure 5B). Studies with lymphocytes and neuronal cells indicate that Cd2+ may inhibit Ca2+-sensitive PLC activity (Grazia Cifone etal., 1989; Vignes etal., 1996). Our studies with cell-permeable Cd chelator TPEN and remove extracellular Cd by washing indicate that Cd inhibit intracellular calcium mobilization in response to fMLF in neutrophils. The inhibition of fMLF-induced Ca2+ mobilization in neutrophils by Cd may also be mediated by suppressing Ca2+-sensitive PLC but needs further investigation. In addition to intracellular Ca2+, MAP kinases ERK1/2 and p38 also play important roles in fMLF-induced neutrophil chemotaxis (Rabiet etal., 2007; Zu etal., 1998). We found that exposure of neutrophils to Cd chronically invivo or acutely invitro had no effect on fMLF-induced p38 phosphorylation, but significantly inhibited fMLF-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation (Figs. 5D and 5E), indicating that Cd exposure inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis through suppressing fMLF-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. It has been reported that fMLF-induced calcium mobilization plays important role in activating ERK1/2 in neutrophils (Elzi etal., 2001), our results showed that Cd2+ exposure significantly reduced Ca2+ mobilization evoked by fMLF in neutrophils. Thus, Cd may inhibit fMLF-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation through suppressing Ca2+ mobilization in neutrophils.
Besides leukocyte infiltration, a subtle balance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines is essential for wound healing. The proinflammatory cytokines, TNFα, IL-1α and -β, are among the first signaling molecules that are released by keratinocytes and leukocytes in response to a disruption of the epidermal barrier, their production is required and beneficial to the wound healing process (Ashcroft etal., 2012; Behm etal., 2012; Efron and Moldawer, 2004). IL-6 is expressed by many cell types in the wounded tissues, especially neutrophils. Studies with IL-6 knockout mice and neutralizing anti-IL-6 antibody reveal the crucial roles of IL-6 in regulating leukocyte infiltration, angiogenesis and collagen accumulation during wound healing (Gallucci etal., 2000; Lin etal., 2003). The anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 has been reported to play an important regulatory role in the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages as well as the production of chemokine/proinflammatory cytokines in the inflammatory response of cutaneous wound healing (Sato etal., 1999). In the present study, we found that chronic treatment of mice with Cd reduced TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 expression but had no effect on IL-10 expression (Figure 6 and data not shown), indicating that Cd impairs wound healing through inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines production at inflammatory stage during wound healing. We further found that chronic Cd exposure reduced ERK1/2 and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation, 2 key molecules contributing to the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, in wounded tissues. Therefore, chronic Cd exposure may inhibit proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression through interfering with ERK1/2 and NF-κB activation after skin injury. Although most of the researches demonstrated that Cd exposure could activate ERK1/2 and NF-κB in various types of cells (Olszowski etal., 2012), it has been reported that Cd inhibited ERK1/2 phosphorylation in osteoblast-like MG63 cells (Hu etal., 2015); treatment of nuclear proteins isolated from TNFα-stimulated A549 cells could inhibit NF-κB binding to DNA (Shumilla etal., 1998); exposure of kidney epithelial cells to Cd could suppress TNFα- stimulated IKKα activity, reduce NF-κB p65 phosphorylation and NF-κB-DNA binding (Xie and Shaikh, 2006). Our studies showed that while stimulation of neutrophils with 1 µM fMLF for 2 min strongly induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation, treatment of neutrophils with 10 µM CdCl2 for up to 8 h had no effect on ERK1/2 phosphorylation (Supplementary Figure 7). Therefore, the different effect of Cd on ERK1/2 and NF-κB may be dependent on cell types or cell activation state. The mechanisms involved in the inhibitory effect of chronic Cd exposure on ERK1/2 and NF-κB activation in wounded tissues remain further investigation.
As described in the “Introduction” paragraph, Cd could promote leukocyte infiltration invivo and induce proinflammatory cytokine expression both invivo and invitro under resting condition. Our studies demonstrated that chronic low-dose Cd exposure alone did not induce leukocyte infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine expression in uninjured skin tissues, but significantly inhibited neutrophil infiltration, NF-κB activation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in wounded skin tissues. Ansari etal. (2015) reported that in collagen-induced arthritis mouse model, exposure of animals to 5 ppm Cd inhibited leukocyte infiltration in synovial membrane and reduced NF-κB p65 and proinflammatory cytokine expression. Recently, Breton etal. (2016) reported that in murine colitis models, exposure of mice to 20 ppm CdCl2 greatly reduced proinflammatory cytokine (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNFα) expression in colon tissues. Therefore, Cd has different effects on inflammatory response when it was used alone or with other stimuli.
In summary, the current study demonstrates that chronic low-dose Cd exposure impairs cutaneous wound healing with negative effects on the early inflammatory response after injury, showing reduced chemokine and proinflammatory cytokine expression and neutrophil infiltration in wounded tissues. Cd may inhibit neutrophil infiltration into the wounded tissues via suppressing chemokine expression and neutrophil chemotactic response to chemoattractants, and inhibit proinflammatory cytokine expression in wounded tissues through inactivating ERK1/2 and NF-κB, and inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis by attenuating calcium mobilization and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in response to chemoattractants. As inflammation is a common feature of wound repair, chronic Cd exposure may also impair tissue repair under pathological conditions, such as trauma, burn, diabetic ulcer, ischemic, or hemorrhagic injury. Understanding the molecular mechanisms involved in the impairment of cutaneous wound healing by Cd may provide critical insight into future intervention strategies to improve wound healing.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary data are available at Toxicological Sciences online.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to thank Dr Xinwei Hou for technical assistance in calcium mobilization assay.
FUNDING
The Science and Technology Service Network Initiative Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-SW-STS-162, KFJ-EW-STS-099, and KFJ-EW-STS-031).
REFERENCES
- Amdur M. L., Caputi R. A. (1953). Cadmium intoxication; clinical report of an acute accidental group exposure. Ind. Med. Surg. 22, 561–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejak R., Antonowicz J., Tomczyk J., Lepetow T., Smolik R. (1993). Lead and cadmium concentrations in blood of people living near a copper smelter in Legnica, Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 134, 233–236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari M. M., Neha, Khan H. A. (2015). Effect of cadmium chloride exposure during the induction of collagen induced arthritis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 238, 55–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft G. S., Jeong M. J., Ashworth J. J., Hardman M., Jin W., Moutsopoulos N., Wild T., McCartney-Francis N., Sim D., McGrady G., et al. (2012). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) is a therapeutic target for impaired cutaneous wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 20, 38–49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behm B., Babilas P., Landthaler M., Schreml S. (2012). Cytokines, chemokines and growth factors in wound healing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 26, 812–820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beton D. C., Andrews G. S., Davies H. J., Howells L., Smith G. F. (1966). Acute cadmium fume poisoning. Five cases with one death from renal necrosis. Br. J. Ind. Med. 23, 292–301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton J., Daniel C., Vignal C., Body-Malapel M., Garat A., Plé C., Foligné B. (2016). Does oral exposure to cadmium and lead mediate susceptibility to colitis? The dark-and-bright sides of heavy metals in gut ecology. Sci. Rep. 6, 19200.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai C., Tang S., Wang X., Cai S., Meng X., Zou W., Zou F. (2013). Requirement for both receptor-operated and store-operated calcium entry in N-formyl-methionine-leucine- phenylalanine-induced neutrophil polarization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 430, 816–821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho F. M., Tavares T. M., Silvany-Neto A. M., Lima M. E., Alt F. (1986). Cadmium concentrations in blood of children living near a lead smelter in Bahia, Brazil. Environ. Res. 40, 437–449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid P., Hurtado-Nedelec M., Marion-Gaber B., Bournier O., Hayem G., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Frystyk J., Flyvbjerg A., El Benna J., Marie J. C. (2012). Adiponectin and its globular fragment differentially modulate the oxidative burst of primary human phagocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 682–692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid P., Boussetta T., Dang P. M., Belambri S. A., Marzaioli V., Fasseau M., Walker F., Couvineau A., El-Benna J., Marie J. C. (2017). Vasoactive intestinal peptide dampens formyl-peptide-induced ROS production and inflammation by targeting a MAPK-p47(phox) phosphorylation pathway in monocytes. Mucosal. Immunol. 10, 332–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Jin T., Huang B., Chang X., Lei L., Nordberg G. F., Nordberg M. (2006). Plasma metallothionein antibody and cadmium-induced renal dysfunction in an occupational population in China. Toxicol. Sci. 91, 104–112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia K. S., Ong C. N., Ong H. Y., Endo G. (1989). Renal tubular function of workers exposed to low levels of cadmium. Br. J. Ind. Med. 46, 165–170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich A., Kalwa H., Rost B. R., Gudermann T. (2005). The diacylgylcerol-sensitive TRPC3/6/7 subfamily of cation channels: Functional characterization and physiological relevance. Pflugers Arch. 451, 72–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djokic J., Ninkov M., Mirkov I., Popov Aleksandrov A., Zolotarevski L., Kataranovski D., Kataranovski M. (2014). Differential effects of cadmium administration on peripheral blood granulocytes in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 37, 210–219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebaid H. (2014). Neutrophil depletion in the early inflammatory phase delayed cutaneous wound healing in older rats: Improvements due to the use of un-denatured camel whey protein. Diagn. Pathol. 9, 46.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J., Ackerman C. (2016). A review of diabetes mellitus and exposure to the environmental toxicant cadmium with an emphasis on likely mechanisms of action. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 12, 252–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efron P. A., Moldawer L. L. (2004). Cytokines and wound healing: The role of cytokine and anticytokine therapy in the repair response. J. Burn. Care Rehabil. 25, 149–160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Benna J., Dang P. M., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Marie J. C., Braut-Boucher F. (2009). p47phox, the phagocyte NADPH oxidase/NOX2 organizer: Structure, phosphorylation and implication in diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 41, 217–225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzi D. J., Bjornsen A. J., MacKenzie T., Wyman T. H., Silliman C. C. (2001). Ionomycin causes activation of p38 and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases in human neutrophils. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 281, C350–C360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallucci R. M., Simeonova P. P., Matheson J. M., Kommineni C., Guriel J. L., Sugawara T., Luster M. I. (2000). Impaired cutaneous wound healing in interleukin-6-deficient and immunosuppressed mice. FASEB J. 14, 2525–2531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grazia Cifone M., Alesse E., Procopio A., Paolini R., Morrone S., Di Eugenio R., Santoni G., Santoni A. (1989). Effects of cadmium on lymphocyte activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1011, 25–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi H., Harada A., Oguma E., Sato M., Homma Y., Kayama F., Fukushima M., Matsushima K. (2000). Cadmium-induced acute hepatic injury is exacerbated in human interleukin-8 transgenic mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 163, 231–239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. H., Li W. X., Sun M. Y., Zhang S. B., Fan C. X., Wu Q., Zhu W., Xu X. (2015). Cadmium induced apoptosis in MG63 cells by increasing ROS, activation of p38 MAPK and inhibition of ERK 1/2 pathways. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 36, 642–654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner G., Brauchle M., Smola H., Madlener M., Fässler R., Werner S. (1996). Differential regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines during wound healing in normal and glucocorticoid-treated mice. Cytokine 8, 548–556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Ezaki T., Tsukahara T., Moriguchi J. (2004). Dietary cadmium intake in polluted and non-polluted areas in Japan in the past and in the present. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 77, 227–234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johri N., Jacquillet G., Unwin R. (2010). Heavy metal poisoning: The effects of cadmium on the kidney. Biometals 23, 783–792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazantzis G. (2004). Cadmium, osteoporosis and calcium metabolism. Biometals 17, 493–498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschvink N., Martin N., Fievez L., Smith N., Marlin D., Gustin P. (2006). Airway inflammation in cadmium-exposed rats is associated with pulmonary oxidative stress and emphysema. Free Radic. Res. 40, 241–250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh T. J., DiPietro L. A. (2011). Inflammation and wound healing: The role of the macrophage. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 13, e23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammermann T., Afonso P. V., Angermann B. R., Wang J. M., Kastenmuller W., Parent C. A., Germain R. N. (2013). Neutrophil swarms require LTB4 and integrins at sites of cell death invivo. Nature 498, 371–375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansdown A. B., Sampson B., Rowe A. (2001). Experimental observations in the rat on the influence of cadmium on skin wound repair. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 82, 35–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Lim K. T. (2011). Preventive effect of phytoglycoprotein (27 kDa) on inflammatory factors at liver injury in cadmium chloride-exposed ICR mice. J. Cell Biochem. 112, 694–703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z. Q., Kondo T., Ishida Y., Takayasu T., Mukaida N. (2003). Essential involvement of IL-6 in the skin wound-healing process as evidenced by delayed wound healing in IL-6-deficient mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 73, 713–721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Chen K., Yoshimura T., Liu Y., Gong W., Le Y., Gao J. L., Zhao J., Wang J. M., Wang A. (2014). Formylpeptide receptors mediate rapid neutrophil mobilization to accelerate wound healing. PLoS One 9, e90613.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins-Green M., Petreaca M., Wang L. (2013). Chemokines and their receptors are key players in the orchestra that regulates wound healing. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2, 327–347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirza R., DiPietro L. A., Koh T. J. (2009). Selective and specific macrophage ablation is detrimental to wound healing in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 175, 2454–2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawrot T. S., Martens D. S., Hara A., Plusquin M., Vangronsveld J., Roels H. A., Staessen J. A. (2015). Association of total cancer and lung cancer with environmental exposure to cadmium: The meta-analytical evidence. Cancer Causes Control 26, 1281–1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. J., Kiremidjian-Schumacher L., Stotzky G. (1982). Effects of cadmium, lead, and zinc on macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity toward tumor cells. Environ Res. 28, 154–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V. (2003). Signaling to migration in neutrophils: Importance of localized pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 35, 1619–1638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszowski T., Baranowska-Bosiacka I., Gutowska I., Chlubek D. (2012). Pro-inflammatory properties of cadmium. Acta Biochim. Pol. 59, 475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit E. J., Fay F. S. (1998). Cytosolic free calcium and the cytoskeleton in the control of leukocyte chemotaxis. Physiol. Rev. 78, 949–967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabiet M. J., Huet E., Boulay F. (2007). The N-formyl peptide receptors and the anaphylatoxin C5a receptors: An overview. Biochimie 89, 1089–1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Ohshima T., Kondo T. (1999). Regulatory role of endogenous interleukin-10 in cutaneous inflammatory response of murine wound healing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 265, 194–199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaff U. Y., Dixit N., Procyk E., Yamayoshi I., Tse T., Simon S. I. (2010). Orai1 regulates intracellular calcium, arrest, and shape polarization during neutrophil recruitment in shear flow. Blood 115, 657–666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvatici R., Falzarano S., Mollica A., Spisani S. (2006). Signal transduction pathways triggered by selective formylpeptide analogues in human neutrophils. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 534, 1–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumilla J. A., Wetterhahn K. E., Barchowsky A. (1998). Inhibition of NF-kappa B binding to DNA by chromium, cadmium, mercury, zinc, and arsenite invitro: Evidence of a thiol mechanism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 349, 356–362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth J. T., Hwang S. Y., Tomita T., DeHaven W. I., Mercer J. C., Putney J. W. (2010). Activation and regulation of store-operated calcium entry. J. Cell Mol. Med. 14, 2337–2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza V., Escobar Mdel C., Bucio L., Hernández E., Gómez-Quiroz L. E., Gutiérrez Ruiz M. C. (2009). NADPH oxidase and ERK1/2 are involved in cadmium induced-STAT3 activation in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 187, 180–186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stosic J., Mirkov I., Belij S., Nikolic M., Popov A., Kataranovski D., Kataranovski M. (2010). Gender differences in pulmonary inflammation following systemic cadmium administration in rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 23, 293–299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y., Richmond A. (2015). Chemokine regulation of neutrophil infiltration of skin wounds. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 4, 631–640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swamydas M., Luo Y., Dorf M. E., Lionakis M. S. (2015). Isolation of mouse neutrophils. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 110, 3.20.1–3.20.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellez-Plaza M., Jones M. R., Dominguez-Lucas A., Guallar E., Navas-Acien A. (2013). Cadmium exposure and clinical cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 15, 356.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thijssen S., Maringwa J., Faes C., Lambrichts I., Van Kerkhove E. (2007). Chronic exposure of mice to environmentally relevant, low doses of cadmium leads to early renal damage, not predicted by blood or urine cadmium levels. Toxicology 229, 145–156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschoor M., Herber R., van Hemmen J., Wibowo A., Zielhuis R. (1987). Renal function of workers with low-level cadmium exposure. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 13, 232–238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignes M., Blanc E., Davos F., Guiramand J., Recasens M. (1996). Cadmium rapidly and irreversibly blocks presynaptic phospholipase C-linked metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neurochem. Int. 29, 371–381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Xue B., Zhang X. (1998). [Effects of cadmium chloride on the function of peritoneal macrophage in mice]. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 32, 159–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie J., Shaikh Z. A. (2006). Cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat kidney epithelial cells involves decrease in nuclear factor-kappa B activity. Toxicol. Sci. 91, 299–308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazihan N., Kocak M. K., Akcil E., Erdem O., Sayal A., Guven C., Akyurek N. (2011). Involvement of galectin-3 in cadmium-induced cardiac toxicity. Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 11, 479–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Y. L., Qi J., Gilchrist A., Fernandez G. A., Vazquez-Abad D., Kreutzer D. L., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. (1998). p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is required for human neutrophil function triggered by TNF-alpha or FMLP stimulation. J. Immunol. 160, 1982–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.