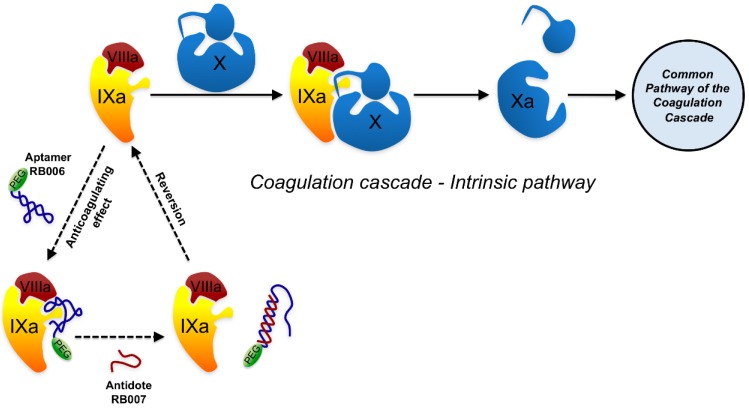
Figure 4.
Mechanism of the apatamer-antidote pair for anticoagulant therapy.The intrinsic pathway of the blood coagulation cascade involves the activation of factor X. Anticoagulation system REG1 consists of RB006 (drug), an injectable RNA aptamer that specifically binds to activated factor IX (IXa) and prevents the proteolytic cleavage of factor X; and RB007 (antidote), a RNA antisense oligonucleotide that neutralizes the anticoagulating effect of the aptamer RB006. In the presence of the antidote, the aptamer is released from factor IXa and clotting parameters return to normal. Together with activated factor VIII (VIIIa), factor IXa catalyzes the cleavage of factor X (pro-enzyme) to yield activated factor X (Xa), which is required for the blood clotting cascade.