Abstract
The data presented in this article are related to the research article entitled “The alteration landscape of the cerebral cortex” (Cauda et al., 2018). Here, we applied a metric called alteration negentropy (A-negentropy) on a large human neuroimaging dataset, in order to denote the “low structural alteration variety” of the altered brain areas. Furthermore, we reported the overview of the selection strategy, as well as the description and distribution of the selected studies from the voxel-based morphometry database of BrainMap (Vanasse et al., 2018). For all of the analyzed brain areas, we reported the number of pathologies affecting them (both local maxima and mean value), as well as the peak and average values of A-negentropy. Regions altered by a small number of brain disorders exhibit high values of A-negentropy.
Specifications table
| Subject area | Neuroscience |
| More specific subject area | Transdiagnostic Neuroscience |
| Type of data | Table, figure |
| How data were acquired | Data were acquired until March 2016 from BrainMap database using the software application Sleuth 2.4 (http://brainmap.org/sleuth/). |
| Data format | Analyzed |
| Experimental factors | Data were included according to specific inclusion criteria. Data were codified on the basis of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10threvision (ICD-10). |
| Experimental features | We used the negentropy metric to detect brain areas with low alteration variety. |
| Data source location | BrainMap website (http://brainmap.org/sleuth/). BrainMap is a registered trademark of the University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio. |
| Data accessibility | Data are available with this article and on BrainMap database (http://brainmap.org/sleuth/). |
| Related research article | F. Cauda, A. Nani, J. Manuello, D. Liloia, K. Tatu, U. Vercelli, S. Duca, P.T. Fox, T. Costa, The alteration landscape of the cerebral cortex, Neuroimage 184 (2019) 359–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.09.036[1]. |
Value of the data
-
•
Alteration negentropy maps can be compared in meta-analytical studies with alteration patterns of specific disorders or categories of diseases.
-
•
Alteration negentropy maps can be used to select regions of interests for specific investigations about brain disorders.
-
•
Alteration negentropy maps can help researchers to reduce and better define the number of potential pathological causes of structural alterations.
1. Data
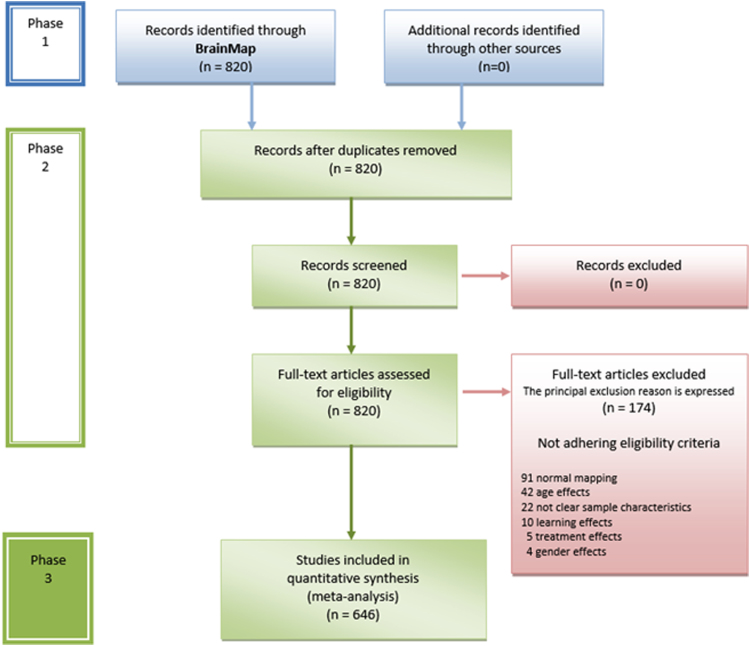
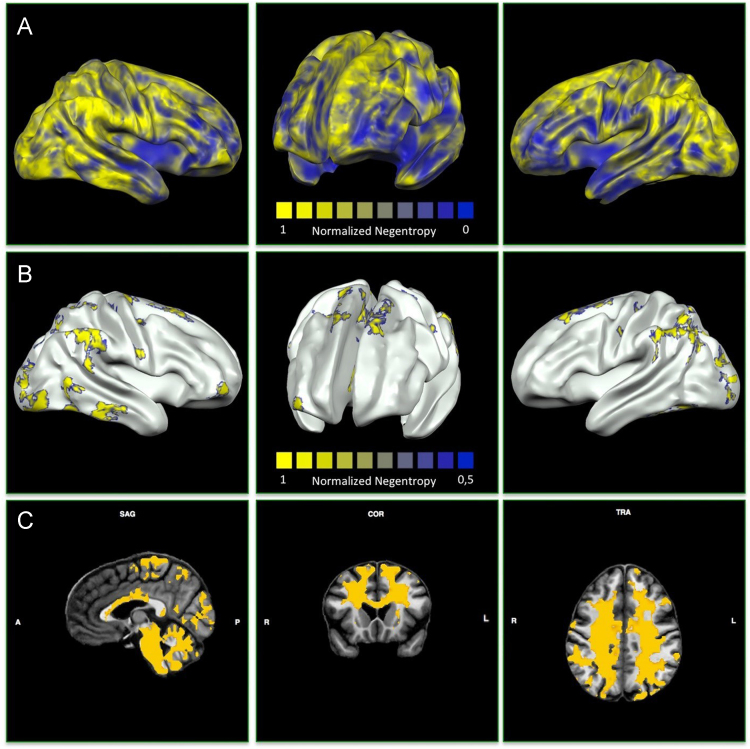
The present data provide a map of the structural alteration variety of the pathological brain. The flow chart of the data selection process is illustrated in Fig. 1. Instead, Fig. 2 shows the areas with high A-negentropy values related to the ICD-10 pathological categories. Detailed data concerning the selected experimental sample and its diagnostic labeling are available in Supplementary Table 1 and Table 1, respectively. Table 2 reports the brain areas affected by the diseases taken into consideration in Cauda et al. [1]. In addition, Table 3 reports peak and average values of normalized A-negentropy for the brain areas (for the details on normalization, please see [1]).
Fig. 1.
PRISMA flow chart. Overview of the selection strategy.
Fig. 2.
3D and 2D visualizations of disease-related alteration negentropy maps. The top panel (A) shows cortical normalized alteration negentropy (A-negentropy) maps related to the ICD-10 pathological categories (for detailed information see also Table 3). The middle panel (B) shows the cortical areas with the highest A-negentropy (i.e., the 10% with the highest values). These areas match with sensorimotor, visual, inferior temporal, and supramarginal regions. The bottom panel (C) shows subcortical normalized A-negentropy maps related to the ICD-10 pathological categories. Of note, a large part of the white matter sites show a high A-negentropy values; this result, however, is to be expected, as we queried the BrainMap database for gray matter alterations only.
Table 1.
Description of the whole experimental sample with the corresponding diagnostic labeling (ICD-10 codes). Subj (N) = number of subjects; Exp (N) = number of experiments.
| Pathological block (ICD-10 Code) | Pathological category (ICD-10 code) | Subj (N) | Exp (N) |
| F20-F25 (N = 4214) | F20: Schizophrenia | 3852 | 208 |
| F29: Psychosis | 327 | 22 | |
| F25: Schizoaffective disorder | 35 | 5 | |
| G30-G32 (N = 3425) | G31: Other degenerative diseases of nervous system | 1918 | 229 |
| G30: Alzheimer׳s disease | 1312 | 138 | |
| F30-F39 (N = 2498) | F33: Major depressive disorder | 1489 | 137 |
| F31: Bipolar disorder | 1009 | 93 | |
| G40-G47 (N = 1722) | G40: Epilepsy and recurrent seizures | 1402 | 137 |
| G47: Sleep disorders | 190 | 15 | |
| G43: Migraines | 93 | 8 | |
| G44: Idiopathic headache disorder | 37 | 3 | |
| G20-G26 (N = 1488) | G20: Parkinson׳s disease | 950 | 95 |
| G24: Dystonia | 223 | 26 | |
| G23: Progressive supranuclear palsy | 160 | 28 | |
| G25: Other extrapyramidal and movement disorders | 155 | 19 | |
| F40-F49 (N = 1016) | F42: Obsessive compulsive disorder | 395 | 44 |
| F43: Reaction to severe stress and adjustment disorders | 374 | 58 | |
| F41: Other anxiety disorders | 247 | 17 | |
| F80-F89 (N = 735) | F84: Pervasive developmental disorders | 642 | 63 |
| F88: Other disorders of psychological development | 48 | 6 | |
| F80: Specific developmental disorders of speech and language | 45 | 6 | |
| G30-G37 (N = 666) | G35: Multiple sclerosis | 666 | 32 |
| G10-G14 (N = 545) | G10: Huntington׳s disease | 236 | 17 |
| G11: Hereditary ataxia | 169 | 25 | |
| G12: Spinal muscular atrophy and related syndromes | 140 | 15 | |
| F90-F98 (N = 363) | F90: Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder | 161 | 13 |
| F91: Conduct disorder | 138 | 20 | |
| F95: Tic disorder | 64 | 5 | |
| G89-G99 (N = 313) | G90: Disorders of autonomic nervous system | 158 | 20 |
| G93: Other disorders of brain | 155 | 11 | |
| E00-E89 (N = 268) | E10: Type I diabetes | 193 | 7 |
| E66: Obesity | 40 | 4 | |
| E70: Disorders of aromatic amino-acid metabolism | 19 | 2 | |
| E23: Hypofunction and other disorders of the pituitary gland | 16 | 6 | |
| F60-F69 (N = 267) | F60: Specific personality disorders | 240 | 55 |
| F65: Paraphilias | 27 | 4 | |
| Z77-Z99 (N = 178) | Z81: Family history of mental and behavioral disorders | 150 | 18 |
| Z89: Acquired absence of limb | 28 | 4 | |
| P00-P96 (N = 176) | P07: Disorders of newborn related to short gestation and low birth weight, not elsewhere classified | 176 | 30 |
| R47-R49 (N = 168) | R48: Dyslexia and other symbolic dysfunctions, not elsewhere classified | 141 | 24 |
| R47: Speech disturbances, not elsewhere classified | 27 | 6 | |
| M00-M99 (N = 158) | M79: Other and unspecified soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified | 80 | 11 |
| M26: Dentofacial anomalies | 34 | 6 | |
| M19: Other and unspecified osteoarthritis | 26 | 5 | |
| M54: Dorsalgia | 18 | 5 | |
| Q90-Q99 (N = 140) | Q93: Monosomies and deletions from autosomes, not elsewhere classified | 91 | 8 |
| Q96: Turner׳s syndrome | 38 | 8 | |
| Q90: Down syndrome | 11 | 2 | |
| N80-N98 (N = 130) | N95: Menopausal and other perimenopausal disorders | 48 | 2 |
| N94: Pain and other conditions associated with female genital Organs and menstrual cycle | 46 | 7 | |
| N80: Endometriosis | 36 | 4 | |
| S00-T88 (N = 113) | S06: Intracranial injury | 73 | 8 |
| T76: Adult and child abuse, neglect and other maltreatment, suspected | 23 | 2 | |
| S24: Injury of nerves and spinal cord at thorax level | 17 | 1 | |
| H60-H95 (N = 105) | H90: Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss | 61 | 4 |
| H93: Other disorders of ear, not elsewhere classified | 28 | 2 | |
| H81: Disorders of vestibular function | 16 | 1 | |
| F10-F19 (N = 68) | F15: Other stimulant related disorders | 44 | 8 |
| F10: Alcohol related disorders | 24 | 1 | |
| F10-F19 (N = 57) | I63: Cerebral infarction | 57 | 3 |
| F70-F79 (N = 54) | F79: Mental retardation | 54 | 6 |
| R51-R69 (N = 54) | R51: Headache | 20 | 1 |
| R55: Syncope and collapse | 18 | 7 | |
| R53: Malaise and fatigue | 16 | 1 | |
| H00-H59 (N = 49) | H54: Blindness and low vision | 25 | 2 |
| H53: Visual disturbances | 13 | 1 | |
| H55: Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements | 11 | 1 | |
| K00-K95 (N = 49) | K58: Irritable bowel syndrome | 49 | 2 |
| R90-R94 (N = 43) | R90: Abnormal findings on diagnostic imaging of central nervous system | 43 | 1 |
| R90-R94 (N = 36) | D57: Sickle-cell disease | 36 | 2 |
| D55-D59 (N = 32) | G50: Disorders of trigeminal nerve | 32 | 5 |
| G80-G83 (N = 26) | G83: Other paralytic syndromes | 26 | 1 |
| C00-D50 (N = 23) | C71: Malignant neoplasm of brain | 13 | 2 |
| C91: Lymphoblastic leukemia | 10 | 4 | |
| R43 (N = 23) | R43: Disturbances of smell and taste | 22 | 2 |
| Q00-Q89 (N = 19) | Q04: Other congenital malformations of brain | 11 | 10 |
| Q85: Phakomatoses, not elsewhere classified | 8 | 1 | |
| L00-L99 (N = 19) | L59: Other disorders of skin and subcutaneous tissue related to radiation | 19 | 2 |
| R25-R29 (N = 17) | R27: Other lack of coordination | 17 | 8 |
| A00-B99 (N = 17) | A81: Atypical virus infections of central nervous system | 17 | 1 |
| F50 (N = 14) | F50: Eating disorders | 14 | 5 |
| B00.4 (N = 8) | B10: Other human herpesviruses | 8 | 1 |
| Total | 19,130 | 1827 |
Table 2.
Maximum number of pathologies (local maxima), average number of pathologies and Talairach coordinates of the different brain areas.
| ID | Brain area |
Local maxima (Talairach) |
Maximum number of pathologies | Mean number of pathologies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| 1 | Right locus coeruleus | 6 | −28 | −8 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | Left pyramis (Cerebellum) | −1 | −77 | −26 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | Left tuber (Cerebellum) | −1 | −75 | −24 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | Left locus Coeruleus | −6 | −27 | −7 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | Left uvula (Cerebellum) | −4 | −60 | −34 | 3 | 1 |
| 6 | Right substantia Nigra | 13 | −17 | −6 | 4 | 1 |
| 7 | Right dentate (Cerebellum) | 18 | −54 | −19 | 4 | 1 |
| 8 | Right fastigium (Cerebellum) | 6 | −48 | −19 | 4 | 1 |
| 9 | Left nodule (Cerebellum) | −6 | −46 | −26 | 5 | 1 |
| 10 | Declive (Cerebellum) | 0 | −75 | −12 | 5 | 1 |
| 11 | Right culmen (Cerebellum) | 6 | −59 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
| 12 | Left dentate (Cerebellum) | −11 | −45 | −22 | 12 | 2 |
| 13 | Right medial geniculum body | 14 | −24 | 2 | 17 | 3 |
| 14 | Right pons | 14 | −14 | −19 | 23 | 1 |
| 15 | Left lingual gyrus (BA 17) | 0 | −84 | 3 | 25 | 2 |
| 16 | Right subthalamic nucleus | 12 | −13 | 2 | 25 | 4 |
| 17 | Right culmen (Cerebellum) | 5 | −33 | −13 | 25 | 2 |
| 18 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 5) | 33 | −39 | 57 | 28 | 4 |
| 19 | Left fastigium (Cerebellum) | −6 | −47 | −19 | 28 | 6 |
| 20 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 1) | 62 | −23 | 34 | 30 | 3 |
| 21 | Left cerebellar lingual | −6 | −45 | −18 | 30 | 4 |
| 22 | Medulla oblongata | 3 | −39 | −42 | 30 | 2 |
| 23 | Left posterior cingulate (BA 29) | −6 | −41 | 22 | 31 | 2 |
| 24 | Left substantia Nigra | −17 | −20 | −6 | 33 | 3 |
| 25 | Left subthalamic nucleus | −11 | −11 | 2 | 38 | 5 |
| 26 | Right precentral gyrus (BA 43) | 54 | −3 | 10 | 39 | 5 |
| 27 | Left lateral geniculum Body | −24 | −26 | −4 | 40 | 16 |
| 28 | Left paracentral lobule (BA 5) | −9 | −42 | 60 | 40 | 5 |
| 29 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 33) | 1 | 22 | 22 | 41 | 10 |
| 30 | Left lingual gyrus (BA 17) | −4 | −84 | 1 | 41 | 2 |
| 31 | Left anterior cingulate (BA 33) | −3 | 22 | 21 | 43 | 9 |
| 32 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 1) | −56 | −25 | 37 | 45 | 3 |
| 33 | Right uvula (Cerebellum) | 20 | −73 | −31 | 45 | 2 |
| 34 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 43) | −57 | −6 | 12 | 46 | 6 |
| 35 | Right lateral geniculum body | 24 | −26 | −3 | 47 | 9 |
| 36 | Right pyramis (Cerebellum) | 23 | −74 | −32 | 47 | 4 |
| 37 | Right inferior semi-lunar lobule (Cerebellum) | 24 | −78 | −35 | 47 | 1 |
| 38 | Right tuber (Cerebellum) | 27 | −75 | −30 | 47 | 2 |
| 39 | Left cerebellar tonsil (Cerebellum) | −24 | −63 | −43 | 47 | 2 |
| 40 | Left inferior semi-lunar lobule (Cerebellum) | −24 | −66 | −39 | 48 | 2 |
| 41 | Right ventral anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | 6 | −4 | 2 | 51 | 18 |
| 42 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 30) | −18 | −42 | −3 | 51 | 6 |
| 43 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 42) | 57 | −30 | 6 | 51 | 5 |
| 44 | Right cingulate gyrus (BA 31) | 6 | −50 | 30 | 51 | 10 |
| 45 | Left tuber (Cerebellum) | −42 | −69 | −23 | 52 | 3 |
| 46 | Right precuneus (BA 7) | 3 | −60 | 36 | 52 | 5 |
| 47 | Right cuneus (BA 19) | 3 | −87 | 25 | 53 | 5 |
| 48 | Left precuneus (BA 31) | −9 | −54 | 30 | 53 | 9 |
| 49 | Left middle occipital gyrus (BA 19) | −36 | −80 | −9 | 55 | 5 |
| 50 | Left culmen (Cerebellum) | −27 | −30 | −19 | 55 | 3 |
| 51 | Left posterior cingulate (BA 23) | −6 | −39 | 27 | 55 | 8 |
| 52 | Left precuneus (BA 7) | −3 | −63 | 36 | 56 | 7 |
| 53 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 27) | −12 | −33 | 3 | 56 | 23 |
| 54 | Right cingulate gyrus (BA 23) | 0 | −33 | 27 | 56 | 8 |
| 55 | Left caudate tail | −35 | −15 | −11 | 56 | 19 |
| 56 | Right inferior temporal gyrus (BA 20) | 30 | −35 | −13 | 56 | 11 |
| 57 | Left red nucleus | −7 | −18 | 2 | 56 | 5 |
| 58 | Right culmen (Cerebellum) | 21 | −25 | −21 | 56 | 3 |
| 59 | Left declive (Cerebellum) | −42 | −69 | −18 | 56 | 4 |
| 60 | Left nucleus Accumbens | −9 | 13 | −8 | 57 | 15 |
| 61 | Right cuneus (BA 18) | 3 | −87 | 24 | 57 | 4 |
| 62 | Right CAudate Tail | 36 | −16 | −6 | 57 | 14 |
| 63 | Left middle temporal gyrus (BA 39) | −51 | −57 | 9 | 57 | 11 |
| 64 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 2) | −54 | −19 | 30 | 58 | 7 |
| 65 | Right ventral posterior lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | 12 | −16 | 10 | 59 | 25 |
| 66 | Right nucleus accumbens | 9 | 12 | −6 | 59 | 38 |
| 67 | Left ventral anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | −6 | −7 | 3 | 59 | 20 |
| 68 | Left middle occipital gyrus (BA 18) | −36 | −81 | −9 | 59 | 4 |
| 69 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 8) | 18 | 44 | 42 | 60 | 10 |
| 70 | Right declive (Cerebellum) | 15 | −60 | −12 | 61 | 5 |
| 71 | Left anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | −6 | −9 | 12 | 62 | 34 |
| 72 | Right lateral globus pallidus | 18 | 0 | −7 | 63 | 21 |
| 73 | Left medial geniculum body | −15 | −24 | 2 | 63 | 21 |
| 74 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 2) | 48 | −24 | 42 | 64 | 8 |
| 75 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 41) | 54 | −24 | 14 | 64 | 12 |
| 76 | Right lateral posterior nucleus (Thalamus) | 13 | −22 | 10 | 66 | 31 |
| 77 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 40) | −57 | −27 | 21 | 66 | 5 |
| 78 | Right ventral posterior medial nucleus (Thalamus) | 12 | −19 | 10 | 67 | 31 |
| 79 | Right medial globus pallidus | 8 | 1 | −3 | 67 | 24 |
| 80 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 3) | −54 | −15 | 30 | 67 | 5 |
| 81 | Right red nucleus (Thalamus) | 4 | −20 | 2 | 68 | 9 |
| 82 | Left ventral lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | −11 | −16 | 6 | 68 | 42 |
| 83 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 3) | 48 | −15 | 42 | 68 | 5 |
| 84 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 27) | 24 | −30 | −7 | 69 | 17 |
| 85 | Right middle frontal gyrus (BA 46) | 42 | 31 | 22 | 69 | 5 |
| 86 | Left lateral dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | −9 | −20 | 14 | 69 | 52 |
| 87 | Right posterior cingulate (BA 29) | 3 | −57 | 9 | 71 | 14 |
| 88 | Right fusiform gyrus (BA 37) | 29 | −36 | −9 | 71 | 12 |
| 89 | Right ventral lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | 10 | −13 | 14 | 71 | 36 |
| 90 | Left hypothalamus | −5 | −3 | −5 | 71 | 32 |
| 91 | Left middle frontal gyrus (BA 8) | −30 | 39 | 39 | 71 | 6 |
| 92 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 37) | −30 | −39 | −12 | 71 | 17 |
| 93 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 22) | 45 | −21 | −3 | 71 | 11 |
| 94 | Right lateral dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | 9 | −20 | 14 | 73 | 56 |
| 95 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 39) | 54 | −54 | 27 | 73 | 4 |
| 96 | Right cerebellar tonsil | 12 | −45 | −42 | 73 | 1 |
| 97 | Right supramarginal gyrus (BA 40) | 54 | −53 | 27 | 74 | 6 |
| 98 | Right putamen | 27 | −9 | 9 | 74 | 26 |
| 99 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 36) | 24 | −29 | −12 | 75 | 24 |
| 100 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 4) | −36 | −13 | 52 | 75 | 8 |
| 101 | Left midline nucleus (Thalamus) | −7 | −19 | 13 | 75 | 57 |
| 102 | Right hypothalamus | 4 | −1 | −6 | 76 | 32 |
| 103 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 11) | 1 | 36 | −11 | 76 | 2 |
| 104 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 6) | 2 | 36 | 33 | 76 | 7 |
| 105 | Left lateral posterior nucleus (Thalamus) | −14 | −21 | 9 | 77 | 44 |
| 106 | Left inferior frontal gyrus (BA 45) | −36 | 23 | 3 | 77 | 8 |
| 107 | Right precentral gyrus (BA 4) | 48 | −12 | 42 | 77 | 5 |
| 108 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 9) | 1 | 36 | 30 | 78 | 11 |
| 109 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 36) | −29 | −14 | −22 | 78 | 32 |
| 110 | Left ventral posterior lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | −15 | −18 | 6 | 78 | 43 |
| 111 | Left medial globus pallidus | −8 | 0 | 0 | 78 | 23 |
| 112 | Right middle temporal gyrus (BA 21) | 48 | 6 | −30 | 78 | 10 |
| 113 | Left caudate body | −9 | 6 | 9 | 78 | 33 |
| 114 | Right midline nucleus (Thalamus) | 6 | −18 | 13 | 78 | 67 |
| 115 | Left cingulate gyrus (BA 32) | −4 | 36 | 29 | 79 | 29 |
| 116 | Left posterior insula (BA 13) | −39 | 3 | 9 | 79 | 19 |
| 117 | Left lateral globus pallidus | −24 | −6 | −7 | 79 | 26 |
| 118 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 35) | 24 | −22 | −14 | 79 | 43 |
| 119 | Right insula (BA 45) | 30 | 23 | 2 | 79 | 8 |
| 120 | Left middle frontal gyrus (BA 10) | −40 | 47 | 14 | 79 | 13 |
| 121 | Left medial frontal gyrus (BA 11) | −2 | 36 | −10 | 79 | 5 |
| 122 | Left inferior temporal gyrus (BA 20) | −28 | −12 | −26 | 79 | 22 |
| 123 | Left middle temporal gyrus (BA 21) | −54 | −15 | −18 | 79 | 14 |
| 124 | Left superior temporal gyrus (BA 22) | −48 | 12 | −6 | 79 | 10 |
| 125 | Left anterior cingulate (BA 24) | −5 | 27 | 24 | 79 | 12 |
| 126 | Left superior temporal gyrus (BA 41) | −48 | −33 | 12 | 79 | 26 |
| 127 | Left middle frontal gyrus (BA 46) | −40 | 48 | 15 | 79 | 10 |
| 128 | Left caudate head | −3 | 6 | −3 | 79 | 49 |
| 129 | Left putamen | −24 | −6 | −6 | 79 | 30 |
| 130 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 10) | 6 | 48 | 9 | 79 | 12 |
| 131 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 24) | 6 | 34 | 18 | 79 | 12 |
| 132 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 24) | 4 | 3 | −3 | 79 | 25 |
| 133 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 32) | 9 | 45 | 0 | 79 | 28 |
| 134 | Right caudate body | 9 | 12 | 9 | 79 | 23 |
| 135 | Right caudate head | 6 | 3 | 1 | 79 | 38 |
| 136 | Right anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | 9 | −12 | 15 | 79 | 34 |
| 137 | Left mammillary body | −9 | −21 | 6 | 79 | 33 |
| 138 | Right mammillary body | 9 | −21 | 6 | 79 | 25 |
| 139 | Left anterior insula (BA 13) | −37 | 14 | −1 | 80 | 56 |
| 140 | Left inferior frontal gyrus (BA 47) | −34 | 17 | −1 | 80 | 18 |
| 141 | Right anterior insula (BA 13) | 42 | 12 | 6 | 80 | 48 |
| 142 | Right posterior insula (BA 13) | 42 | −6 | 6 | 80 | 26 |
| 143 | Left hippocampus | −25 | −10 | −18 | 80 | 57 |
| 144 | Left amygdala | −16 | −5 | −12 | 80 | 77 |
| 145 | Left medial frontal gyrus (BA 9) | −3 | 36 | 30 | 80 | 14 |
| 146 | Left uncus (BA 28) | −15 | −5 | −12 | 80 | 48 |
| 147 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 34) | −18 | 6 | −12 | 80 | 54 |
| 148 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 35) | −21 | −7 | −21 | 80 | 48 |
| 149 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 44) | −41 | 6 | 6 | 80 | 12 |
| 150 | Right amygdala | 29 | 0 | −18 | 80 | 70 |
| 151 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 34) | 30 | 3 | −18 | 80 | 55 |
| 152 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 38) | 30 | 3 | −18 | 80 | 11 |
| 153 | Right precentral gyrus (BA 44) | 42 | 12 | 6 | 80 | 14 |
| 154 | Right anterior insula (BA 13) | 36 | 18 | 1 | 80 | 16 |
| 155 | Right medial dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | 9 | −21 | 12 | 80 | 67 |
| 156 | Right pulvinar | 6 | −24 | 11 | 80 | 37 |
| 157 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 6) | −51 | 0 | 35 | 80 | 9 |
| 158 | Left medial dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | −9 | −21 | 9 | 80 | 67 |
| 159 | Left pulvinar | −9 | −21 | 9 | 80 | 44 |
| 160 | Right hippocampus | 27 | −21 | −9 | 80 | 53 |
Table 3.
Maximum (local maxima) and mean values of normalized alteration negentropy, and Talairach coordinates of the different brain areas.
| ID | Brain area |
Local maxima (Talairach) |
Maximum normalized negentropy | Mean normalized negentropy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| 1 | Left locus coeruleus | −5 | −25 | −7 | 0.987 | 0.996 |
| 2 | Left pyramis (Cerebellum) | −2 | −78 | −27 | 0.974 | 0.997 |
| 3 | Right locus Coeruleus | 6 | −28 | −8 | 0.963 | 0.994 |
| 4 | Left tuber (Cerebellum) | −1 | −75 | −24 | 0.907 | 0.991 |
| 5 | Left uvula (Cerebellum) | −4 | −60 | −34 | 0.836 | 0.994 |
| 6 | Right culmen (Cerebellum) | 6 | −59 | 3 | 0.794 | 0.989 |
| 7 | Right fastigium (Cerebellum) | 6 | −48 | −19 | 0.788 | 0.981 |
| 8 | Right substantia Nigra | 16 | −20 | −6 | 0.786 | 0.981 |
| 9 | Left nodule (Cerebellum) | −6 | −46 | −26 | 0.782 | 0.996 |
| 10 | Left declive (Cerebellum) | 0 | −75 | −12 | 0.683 | 0.972 |
| 11 | Right dentate (Cerebellum) | 18 | −54 | −18 | 0.683 | 0.988 |
| 12 | Right medial geniculum body | 14 | −24 | 2 | 0.525 | 0.927 |
| 13 | Left dentate (Cerebellum) | −12 | −47 | −18 | 0.513 | 0.969 |
| 14 | Right subthalamic nucleus | 11 | −12 | 2 | 0.46 | 0.894 |
| 15 | Left lingual gyrus (BA 17) | 0 | −84 | 3 | 0.44 | 0.908 |
| 16 | Right pons | 14 | −14 | −19 | 0.428 | 0.985 |
| 17 | Left substantia Nigra | −17 | −20 | −6 | 0.375 | 0.926 |
| 18 | Right culmen (Cerebellum) | 5 | −33 | −13 | 0.3 | 0.926 |
| 19 | Left posterior cingulate (BA 29) | −6 | −41 | 22 | 0.259 | 0.922 |
| 20 | Left subthalamic nucleus | −11 | −11 | 2 | 0.258 | 0.817 |
| 21 | Left lateral geniculum body | −24 | −27 | −3 | 0.252 | 0.657 |
| 22 | Left anterior cingulate (BA 33) | −3 | 22 | 21 | 0.247 | 0.797 |
| 23 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 5) | 6 | −46 | 63 | 0.245 | 0.83 |
| 24 | Left fastigium (Cerebellum) | −6 | −47 | −19 | 0.238 | 0.82 |
| 25 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 1) | 62 | −23 | 34 | 0.224 | 0.905 |
| 26 | Left cerebellar lingual | −6 | −45 | −18 | 0.223 | 0.848 |
| 27 | Medulla oblongata | 3 | −39 | −42 | 0.222 | 0.929 |
| 28 | Left lingual gyrus (BA 17) | −4 | −84 | 1 | 0.216 | 0.95 |
| 29 | Right precentral gyrus (BA 43) | 54 | −3 | 12 | 0.197 | 0.787 |
| 30 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 33) | 1 | 22 | 22 | 0.176 | 0.72 |
| 31 | Right uvula (Cerebellum) | 20 | −73 | −31 | 0.162 | 0.943 |
| 32 | Left paracentral lobule (BA 5) | −9 | −42 | 60 | 0.158 | 0.822 |
| 33 | Right lateral geniculum body | 24 | −26 | −3 | 0.144 | 0.806 |
| 34 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 1) | −56 | −25 | 37 | 0.143 | 0.927 |
| 35 | Left red nucleus | −7 | −18 | 2 | 0.137 | 0.854 |
| 36 | Right tuber (Cerebellum) | 33 | −57 | −30 | 0.124 | 0.955 |
| 37 | Left cerebellar tonsil | −24 | −63 | −45 | 0.124 | 0.956 |
| 38 | Right pyramis (Cerebellum) | 29 | −57 | −30 | 0.124 | 0.903 |
| 39 | Right inferior semilunar lobule (Cerebellum) | 24 | −78 | −35 | 0.124 | 0.973 |
| 40 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 43) | −57 | −6 | 12 | 0.124 | 0.772 |
| 41 | Left inferior semilunar lobule (Cerebellum) | −24 | −66 | −39 | 0.119 | 0.957 |
| 42 | Right ventral anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | 12 | −9 | 12 | 0.115 | 0.531 |
| 43 | Right cingulate gyrus (BA 31) | 6 | −57 | 30 | 0.105 | 0.7 |
| 44 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 30) | −18 | −42 | −3 | 0.105 | 0.825 |
| 45 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 27) | −24 | −34 | −3 | 0.104 | 0.467 |
| 46 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 42) | 57 | −30 | 6 | 0.101 | 0.837 |
| 47 | Left tuber (Cerebellum) | −42 | −69 | −23 | 0.1 | 0.924 |
| 48 | Left culmen (Cerebellum) | −24 | −33 | −18 | 0.099 | 0.936 |
| 49 | Right culmen (Cerebellum) | 12 | −63 | −10 | 0.099 | 0.905 |
| 50 | Right precuneus (BA 7) | 0 | −60 | 36 | 0.096 | 0.84 |
| 51 | Right cingulate gyrus (BA 23) | 0 | −33 | 27 | 0.096 | 0.725 |
| 52 | Left nucleus accumbens | −9 | 13 | −8 | 0.094 | 0.497 |
| 53 | Left posterior cingulate (BA 23) | −6 | −39 | 27 | 0.094 | 0.754 |
| 54 | Left precuneus (BA 31) | −9 | −54 | 30 | 0.093 | 0.728 |
| 55 | Right cuneus (BA 19) | 3 | −87 | 25 | 0.093 | 0.83 |
| 56 | Left caudate tail | −36 | −14 | −10 | 0.09 | 0.63 |
| 57 | Left middle occipital gyrus (BA 19) | −54 | −60 | −6 | 0.088 | 0.872 |
| 58 | Right caudate tail | 36 | −16 | −6 | 0.088 | 0.647 |
| 59 | Left declive (Cerebellum) | −42 | −69 | −18 | 0.086 | 0.871 |
| 60 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 2) | −54 | −19 | 30 | 0.085 | 0.8 |
| 61 | Left middle temporal gyrus (BA 39) | −51 | −57 | 9 | 0.084 | 0.76 |
| 62 | Right inferior temporal gyrus (BA 20) | 36 | −6 | −36 | 0.084 | 0.689 |
| 63 | Right ventral posterior lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | 12 | −16 | 10 | 0.082 | 0.512 |
| 64 | Left ventral anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | −6 | −7 | 3 | 0.081 | 0.507 |
| 65 | Left middle occipital gyrus (BA 18) | −36 | −81 | −9 | 0.081 | 0.896 |
| 66 | Left precuneus (BA 7) | −3 | −63 | 36 | 0.079 | 0.764 |
| 67 | Right cuneus (BA 18) | 3 | −87 | 24 | 0.078 | 0.866 |
| 68 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 8) | 3 | 42 | 42 | 0.07 | 0.709 |
| 69 | Right nucleus accumbens | 9 | 12 | −6 | 0.069 | 0.211 |
| 70 | Right lateral posterior nucleus (Thalamus) | 13 | −22 | 12 | 0.069 | 0.427 |
| 71 | Right ventral posterior medial nucleus (Thalamus) | 12 | −19 | 10 | 0.068 | 0.411 |
| 72 | Right declive (Cerebellum) | 15 | −60 | −12 | 0.067 | 0.843 |
| 73 | Left medial geniculum body | −15 | −24 | 2 | 0.065 | 0.466 |
| 74 | Left anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | −6 | −9 | 12 | 0.061 | 0.252 |
| 75 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 41) | 54 | −24 | 14 | 0.057 | 0.66 |
| 76 | Right lateral globus pallidus | 18 | 0 | −7 | 0.057 | 0.534 |
| 77 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 2) | 48 | −24 | 42 | 0.056 | 0.767 |
| 78 | Right red nucleus | 4 | −20 | 2 | 0.053 | 0.791 |
| 79 | Right medial globus pallidus | 9 | 3 | −3 | 0.052 | 0.477 |
| 80 | Left lateral dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | −9 | −20 | 14 | 0.052 | 0.117 |
| 81 | Left ventral lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | −6 | −9 | 6 | 0.048 | 0.242 |
| 82 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 40) | −57 | −27 | 21 | 0.046 | 0.849 |
| 83 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 27) | 24 | −30 | −7 | 0.045 | 0.552 |
| 84 | Right middle frontal gyrus (BA 46) | 42 | 31 | 22 | 0.043 | 0.829 |
| 85 | Left postcentral gyrus (BA 3) | −54 | −15 | 30 | 0.043 | 0.856 |
| 86 | Right postcentral gyrus (BA 3) | 48 | −15 | 42 | 0.042 | 0.821 |
| 87 | Left middle frontal gyrus (BA 8) | −30 | 39 | 39 | 0.038 | 0.825 |
| 88 | Left hypothalamus | −5 | −3 | −5 | 0.037 | 0.352 |
| 89 | Right mammillary body | 8 | −21 | 5 | 0.032 | 0.53 |
| 90 | Right fusiform gyrus (BA 37) | 30 | −36 | −12 | 0.032 | 0.677 |
| 91 | Right lateral dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | 10 | −16 | 15 | 0.032 | 0.131 |
| 92 | Left midline nucleus (Thalamus) | −7 | −20 | 14 | 0.032 | 0.097 |
| 93 | Right ventral lateral nucleus (Thalamus) | 11 | −12 | 15 | 0.031 | 0.323 |
| 94 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 22) | 45 | −21 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.715 |
| 95 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 37) | −30 | −39 | −12 | 0.027 | 0.666 |
| 96 | Right posterior cingulate (BA 29) | 3 | −57 | 9 | 0.025 | 0.671 |
| 97 | Left mammillary body | −8 | −18 | 3 | 0.024 | 0.43 |
| 98 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 39) | 54 | −54 | 27 | 0.023 | 0.86 |
| 99 | Right midline nucleus (Thalamus) | 7 | −15 | 15 | 0.021 | 0.058 |
| 100 | Right putamen | 27 | −9 | 9 | 0.021 | 0.416 |
| 101 | Right supramarginal gyrus (BA 40) | 54 | −53 | 27 | 0.02 | 0.818 |
| 102 | Right cerebellar tonsil | 12 | −45 | −42 | 0.02 | 0.963 |
| 103 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 11) | 1 | 36 | −11 | 0.018 | 0.924 |
| 104 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 4) | −36 | −13 | 52 | 0.017 | 0.794 |
| 105 | Right hypothalamus | 4 | −1 | −6 | 0.016 | 0.401 |
| 106 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 6) | 2 | 36 | 33 | 0.013 | 0.815 |
| 107 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 36) | 24 | −29 | −12 | 0.013 | 0.49 |
| 108 | Right hippocampus | 27 | −22 | −12 | 0.012 | 0.165 |
| 109 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 36) | −28 | −15 | −24 | 0.011 | 0.397 |
| 110 | Right precentral gyrus (BA 4) | 48 | −12 | 42 | 0.01 | 0.84 |
| 111 | Left caudate body | −9 | 6 | 9 | 0.01 | 0.404 |
| 112 | Left lateral posterior nucleus (Thalamus) | −18 | −21 | 9 | 0.01 | 0.241 |
| 113 | Left superior temporal gyrus (BA 22) | −48 | 12 | −6 | 0.009 | 0.709 |
| 114 | Left inferior frontal gyrus (BA 45) | −36 | 24 | 2 | 0.009 | 0.786 |
| 115 | Left lateral globus pallidus | −24 | −6 | −3 | 0.009 | 0.488 |
| 116 | Left putamen | −24 | −6 | −3 | 0.009 | 0.424 |
| 117 | Right caudate body | 9 | 12 | 9 | 0.007 | 0.466 |
| 118 | Right precentral gyrus (BA 44) | 42 | 12 | 6 | 0.007 | 0.635 |
| 119 | Right medial dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | 3 | −21 | 6 | 0.007 | 0.06 |
| 120 | Left medial frontal gyrus (BA 11) | −5 | 36 | −12 | 0.007 | 0.875 |
| 121 | Left medial globus pallidus | −8 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.501 |
| 122 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 44) | −41 | 6 | 6 | 0.006 | 0.683 |
| 123 | Left medial dorsal nucleus (Thalamus) | −6 | −23 | 9 | 0.006 | 0.059 |
| 124 | Left pulvinar | −6 | −24 | 9 | 0.005 | 0.293 |
| 125 | Left anterior cingulate (BA 24) | −3 | 21 | −6 | 0.005 | 0.734 |
| 126 | Left amygdala | −21 | −9 | −18 | 0.005 | 0.025 |
| 127 | Left superior temporal gyrus (BA 42) | −54 | −34 | 18 | 0.005 | 0.719 |
| 128 | Right anterior nucleus (Thalamus) | 9 | −12 | 15 | 0.005 | 0.337 |
| 129 | Left posterior insula (BA 13) | −40 | 0 | 8 | 0.005 | 0.555 |
| 130 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 34) | −21 | −12 | −18 | 0.004 | 0.161 |
| 131 | Right middle temporal gyrus (BA 21) | 48 | 6 | −33 | 0.004 | 0.721 |
| 132 | Left hippocampus | −26 | −12 | −22 | 0.004 | 0.106 |
| 133 | Left caudate head | −6 | 12 | −6 | 0.004 | 0.183 |
| 134 | Right medial frontal gyrus (BA 9) | 1 | 36 | 30 | 0.004 | 0.701 |
| 135 | Right amygdala | 18 | −6 | −21 | 0.003 | 0.046 |
| 136 | Left middle temporal gyrus (BA 21) | −55 | −18 | −15 | 0.003 | 0.661 |
| 137 | Right pulvinar | 4 | −24 | 10 | 0.003 | 0.316 |
| 138 | Left superior temporal gyrus (BA 41) | −48 | −33 | 12 | 0003 | 0.418 |
| 139 | Left uncus (BA 28) | −27 | −12 | −25 | 0.003 | 0.211 |
| 140 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 24) | 1 | 27 | 23 | 0.003 | 0.723 |
| 141 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 32) | 3 | 36 | 21 | 0.002 | 0.456 |
| 142 | Left inferior frontal gyrus (BA 47) | −36 | 24 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.646 |
| 143 | Right superior temporal gyrus (BA 38) | 33 | 18 | -21 | 0.002 | 0.732 |
| 144 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 10) | 6 | 48 | 6 | 0.002 | 0.716 |
| 145 | Left cingulate gyrus (BA 32) | -4 | 36 | 29 | 0.002 | 0.448 |
| 146 | Right posterior insula (BA 13) | 42 | -9 | 3 | 0.002 | 0.465 |
| 147 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 34) | 30 | 3 | -18 | 0.002 | 0.155 |
| 148 | Left parahippocampal gyrus (BA 35) | -24 | -15 | -21 | 0.002 | 0.196 |
| 149 | Right parahippocampal gyrus (BA 35) | 24 | -24 | -14 | 0.002 | 0.298 |
| 150 | Left anterior insula (BA 13) | -39 | 3 | 6 | 0.002 | 0.131 |
| 151 | Right anterior insula (BA 13) | 3−0 | 18 | −3 | 0.001 | 0.673 |
| 152 | Left precentral gyrus (BA 6) | −51 | 0 | 35 | 0.001 | 0.779 |
| 153 | Left inferior temporal gyrus (BA 20) | −57 | −27 | −18 | 0.001 | 0.552 |
| 154 | Left middle frontal gyrus (BA 10) | −39 | 48 | 12 | 0.001 | 0.696 |
| 155 | Right anterior insula (BA 13) | 33 | 16 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.184 |
| 156 | Right insula (BA 45) | 30 | 24 | 3 | 0.001 | 0.806 |
| 157 | Left medial frontal gyrus (BA 9) | −6 | 36 | 30 | 0.001 | 0.645 |
| 158 | Right caudate head | 6 | 3 | −3 | 0.001 | 0.241 |
| 159 | Left middle frontal gyrus (BA 46) | −40 | 48 | 15 | 0.001 | 0.763 |
| 160 | Right anterior cingulate (BA 25) | 4 | 3 | −6 | 0.001 | 0.483 |
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
2.1. Design, materials and method
The pool of all eligible voxel-based morphometry (VBM) experiments was retrieved from the BrainMap database [2], [3], [4]. At the time of selection of studies (March 2016), the whole VBM dataset included 820 independent studies with respective diagnostic labeling (ICD-10 code). Among them, any experiment not meeting inclusion criteria was excluded. Specifically, two researchers reviewed all the full-text articles independently, in order to ensure that: (a) the pathological sample was characterized by gray matter changes of brain parenchyma; (b) the experiments described structural changes visible with whole-brain VBM; (c) the pathological sample was codified on the basis of the ICD-10 classification [5]; (d) the results were reported by using the Talairach or Montreal Neurological Institute stereotactic coordinates; (e) the articles were original works published in a peer-reviewed English language journal.
Based on the aforementioned criteria, 646 studies were included in the meta-analysis (Supplementary Table 1), for a total of 39 pathological blocks and 82 pathological categories (ICD-10 codes), 1827 experiments, 19,130 subjects and 20,238 coordinates of gray matter decrease/increase (Table 1). Descriptive information of interest was extracted from each qualified full-text article. In order to obtain a detailed and transparent description of the selection phase, we have adopted the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement international guidelines [6], [7] (Fig. 1).
2.2. Meta-analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using Matlab®. We first employed an anatomical likelihood estimation (ALE) [8], [9], [10] following the recommendation suggested by Eickhoff et al. [11]. Results were family-wise error-corrected for multiple comparisons and clustered at a level of p < 0.05, with a cluster-forming threshold of p < 0.001 at voxel level. ALE map activations were evaluated with a permutation test that redistributed the same number of foci in the brain and calculated an ALE map. Eventually, the histogram of the scores obtained with this procedure was used to assign a threshold for p-values.
In order to obtain the probability distribution of alteration for every brain area, the untresholded ALE map of each of the 82 pathological categories was used. To find areas of low alteration variety, we used the negentropy metric. The negentropy, which is the reverse of the entropy, is a concept first introduced by Schrödinger in his famous essay “What is Life?“ [12] and further developed by Brillouin [13]. We can therefore define the negentropy as:
where is the expected value of the informational content. This means that the negentropy metric is related to the mean informational content of a random variable. In our case, a voxel with high A-negentropy values is thought to have more mean informational content than a voxel with low A-negentropy values. In other words, a decrease of negentropy corresponds to a loss of information about the system, and vice versa. More detailed information about the statistical analyses are viewable in Cauda et al. [1].
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Fondazione Carlo Molo (F Cauda, PI), Turin; NIH/NIMH grant MH074457 (P Fox, PI) and CDMRP grant W81XWH-14-1-0316 (P Fox, PI).
Footnotes
Transparency data associated with this article can be found in the online version at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.10.142.
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.10.142.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material.
.
Appendix A. Supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1.
.
References
- 1.Cauda F., Nani A., Manuello J., Liloia D., Tatu K., Vercelli U., Duca S., Fox P.T., Costa T. The alteration landscape of the cerebral cortex. NeuroImage. 2019;184:359–371. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.09.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vanasse T.J., Fox P.M., Barron D.S., Robertson M., Eickhoff S.B., Lancaster J.L., Fox P.T. BrainMap VBM: an environment for structural meta-analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018;39:3308–3325. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fox P.T., Lancaster J.L. Opinion: mapping context and content: the BrainMap model. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002;3:319–321. doi: 10.1038/nrn789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Laird A.R., Lancaster J.L., Fox P.T. BrainMap: the social evolution of a human brain mapping database. Neuroinformatics. 2005;3:65–78. doi: 10.1385/ni:3:1:065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 1992. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Liberati A., Altman D.G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P.C., Ioannidis J.P., Clarke M., Devereaux P.J., Kleijnen J., Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009;62:1–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D.G., PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009;62:1006–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eickhoff S.B., Laird A.R., Grefkes C., Wang L.E., Zilles K., Fox P.T. Coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of neuroimaging data: a random-effects approach based on empirical estimates of spatial uncertainty. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009;30:2907–2926. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Eickhoff S.B., Bzdok D., Laird A.R., Kurth F., Fox P.T. Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis revisited. NeuroImage. 2012;59:2349–2361. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Turkeltaub P.E., Eickhoff S.B., Laird A.R., Fox M., Wiener M., Fox P. Minimizing within-experiment and within-group effects in activation likelihood estimation meta-analyses. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012;33:1–13. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eickhoff S.B., Laird A.R., Fox P.M., Lancaster J.L., Fox P.T. Implementation errors in the GingerALE Software: description and recommendations. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017;38:7–11. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schrödinger E. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1944. What Is Life? The Physical Aspect of the Living Cell and Mind. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brillouin L. The negentropy principle of information. J. Appl. Phys. 1953;24:1152–1163. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1.