Figure 3.
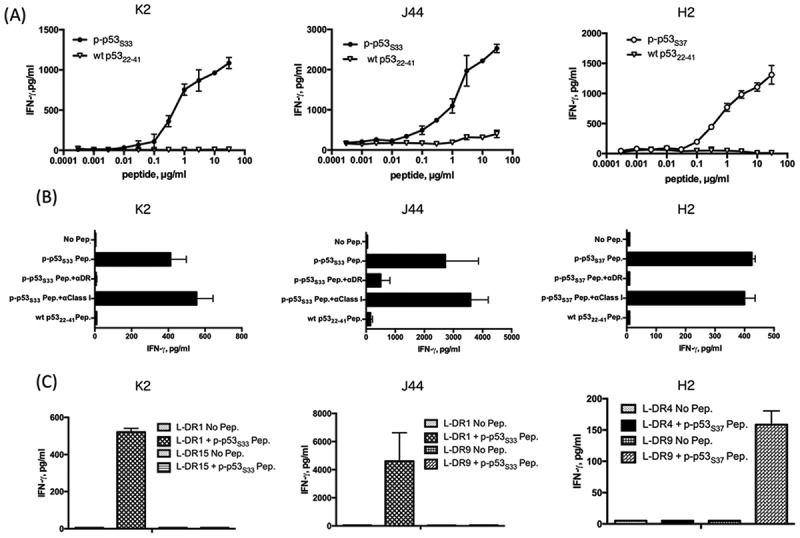
Induction of CD4 T cell responses using the mono-phosphorylated p53 peptide. (A) The phosphorylated peptide p-p53S33-reactive CD4 T cells (K2 and J44) and p-p53S37-reactive CD4 T cells (H2) were assessed for their ability to recognize various concentrations of phosphorylated peptides. Autologous PBMCs were used as APCs. (B) MHC restriction analysis of phosphorylated p53-reactive CD4 T cells. Peptide-induced T cell responses of p-p53S33-reactive (K2 and J44) and p-p53S37 -reactive cells (H2) in the presence of anti-HLA DR mAb L243 or anti-HLA class I mAb W6/32 (negative control) were evaluated. Autologous PBMCs were used as APCs. (C) CD4 T cell responses to p-p53S33-reactive (K2 and J44) and p-p53S37-reactive cells (H2) were assessed using L-cells transfected with individual HLA-DR genes as APCs to determine the restricting HLA class II molecules.
