Abstract
Genome mining is an effective tool used to discover novel natural products from actinomycetes. Genome sequence analysis of Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 revealed the presence of one putative type II polyketide gene cluster (ABX), which may correspond to type II polyketide products including BE-24566B and its chloro-derivatives. The addition of natural humus acid successfully activated the biosynthsis of the abx gene cluster. BE-24566B and its chloro-derivatives, named zunyimycin A, were also detected. The targeted deletion of the polyketide skeleton synthesis genes such as abxp, abxk, and abxs was performed in the wild strain to identify the gene cluster for BE-24566B biosynthesis.
Keywords: polyketide synthases, genome mining, genetic engineering, anthrabenzoxocinones, gene cluster
1. Introduction
Aromatic polyketides are an important class of natural products with various biological activities, including antibacterial [1,2], antitumor [3,4], and antiviral effects [5]. These polyketides are isolated from plants or microorganisms [6,7]. Actinomycete-derived aromatic polyketides are mainly synthesized by type II polyketide synthases (PKSs) [8,9]. Malonyl-CoA is exclusively used as the extender unit during type II polyketide biosynthesis [10,11]. Starter units vary in different aromatic polyketide biosynthesis pathways, leading to various polyketide backbones [12,13]. Enzymes, such as ketoreductases [14,15], oxygenases [16,17], cyclases [18,19], methyltransferases [20], halogenase [21,22], and glycosyltransferases [23], function on the skeleton to form aromatic structures or provide novel biological activities once the polyketide chains are formed by PKSs [24].
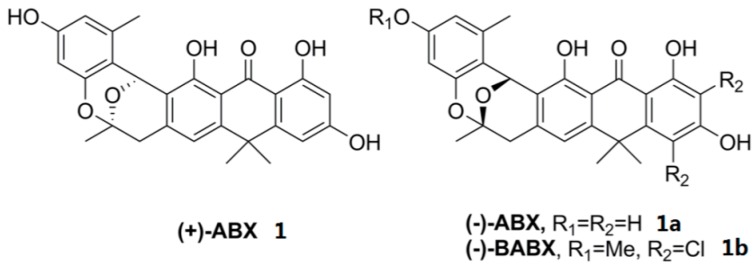
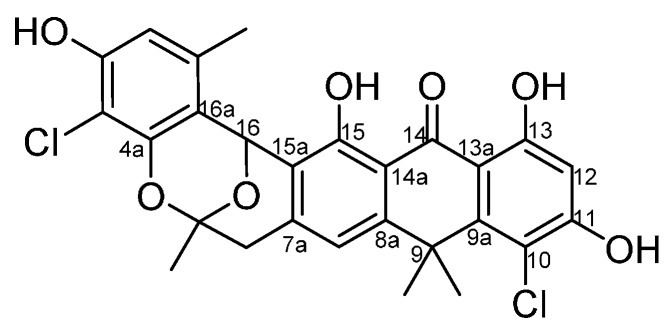
Anthrabenzoxocinones (ABXs) are a group of hexacyclic aromatic ketones with bioactivities, such as antibacterial activity [25,26,27], anti-hypertensive activity [28], cholesterol-reducing activity [27] and nuclear hormone receptors [25]. ABX family members such as (+)-anthrabenzoxocinone ((+)-ABX) (BE-24566B, also named 1.264C,1), (−)-anthrabenzoxocinone ((−)-ABX)(1a), as well as (−)-bischloroanthrabenzoxocinone ((−)-BABX)(1b), (Figure 1) have been isolated from Streptomyces sp. (MA6657), Streptomyces sp. FXJ1.264, or Streptomyces violaceusniger, and Actinomyces sp. MA7150, respectively [29].
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of ABXs.
2. Results
2.1. Comparative Analysis of ABX Gene Clusters
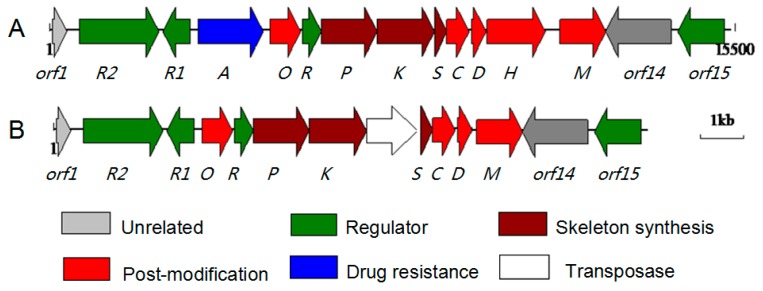
The draft genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 contains 11595310 bp, with a GC content of 70.73%. A total of 10877 putative protein coding sequences (CDSs) were identified in the draft genome covering 8840283 bp, accounting for 76.2% of the genome. Prediction of biosynthetic gene clusters on the whole genome level deduced by antiSMASH online reveals that the genome contains 23 secondary metabolism gene clusters such as polyketide synthase systems of every formally classified families (types I and II PKS), nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS), PKS-NRPS hybrids, terpenes, siderophores, lantibiotics, aminocyclitol, melanin, ectoine, bacteriocin, and so on. As shown in Figure 2, genome sequencing and comparative analysis revealed that Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 contains only one putative type II polyketide gene cluster (GenBank accession No. KU243130). This gene cluster shares a high similarity to its homologous gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. FXJ1.264 at the amino acid sequence (from 86.3% to 94.5%), gene content, and gene order levels (Table 1). Thirteen open reading frames are involved in the ABX polyketide backbone biosynthesis (abxp, abxk, and abxs), regulation (abxR2, abxR1, and abxR), drug resistance (abxA), cyclization (abxC and abxD), methylation (abxM), and halogenation (abxO and abxH) within the gene cluster of Streptomyces sp. 31-2 (Figure 2A). Ten homologous genes were found in Streptomyces sp. 1.264 (Figure 2B).
Figure 2.
Organization of the ABX clusters from Streptomyces sp. FJS 31-2 (A) and Streptomyces sp. FXJ 1.264 (B).
Table 1.
Homologous analysis of abx gene cluster from Streptomyces strains.
| S. sp. FJS31-2 | S. sp. FXJ1.264 | Identit % | Deduced Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | Size aa | Protein | Size aa | ||
| Orf1 | 87 | 1.264DNAGM006278 | 87 | 93 | Hypothetical protein. |
| 1.264DNAGM006279 | 319 | Cation efflux family | |||
| AbxR2 | 616 | 1.264DNAGM006280 | 616 | 91 | SARP transcriptional regulator |
| AbxR2 | 207 | 1.264DNAGM006281 | 219 | 88 | TetR transcriptional regulator |
| AbxA | 490 | MFS transporter | |||
| AbxO | 227 | 1.264DNAGM006282 | 231 | 90.5 | Monooxygenase |
| AbxR | 141 | 1.264DNAGM006283 | 141 | 93.6 | AraC transcriptional regulator |
| AbxP | 421 | 1.264DNAGM006284 | 421 | 96 | Beta-ketoacyl_synthase, t2PKS |
| AbxK | 426 | 1.264DNAGM006285 | 424 | 90.3 | Beta-ketoacyl_synthase, t2PKS |
| 1.264DNAGM006286 | 394 | Transposase | |||
| AbxS | 85 | 1.264DNAGM006287 | 88 | 86.4 | Acyl carrier protein |
| AbxC | 167 | 1.264DNAGM006288 | 168 | 86.3 | cyclase/dehydrase |
| AbxD | 113 | 1.264DNAGM006289 | 113 | 88.5 | Polyketide synthesis cyclase |
| AbxH | 436 | tryptophan halogenase | |||
| AbxM | 343 | 1.264DNAGM006290 | 349 | 91.4 | O-methyltransferase |
| Orf14 | 491 | 1.264DNAGM006291 | 490 | 91.0 | Lipase maturation factor |
| Orf15 | 348 | 1.264DNAGM006292 | 348 | 94.5 | LacI transcription regulator |
2.2. Characterization of the ABX Gene Cluster
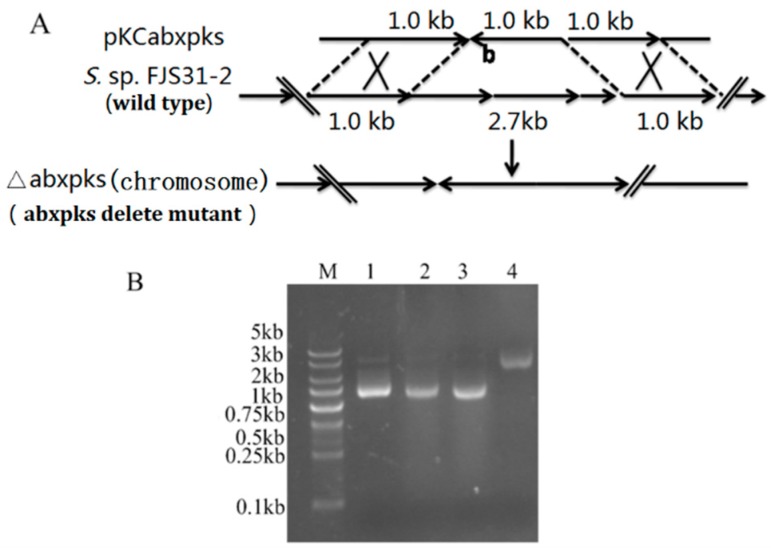
Results of PCR products sequencing of the three open reading fragments, namely, abxp, abxk and abxs, from the knockout mutant strain (△abxpks) indicated that the 2.7 kp DNA fragment was replaced by the kanamycin resistance gene (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Deleted mutation of abxp, abxk, and abxs. (A) Mutation strategies of abxp, abxk, and abxs. (B) Analysis of abxp, abxk, and abxs deletion by PCR (lanes 1, 2, and 3: abxpks-deleted mutants; lane 4: wild-type strain; and M: DNA marker).
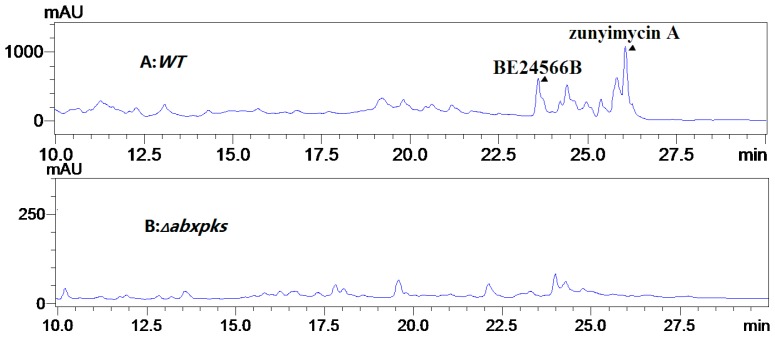
Wild-type Streptomyces sp. FJS 31-2 and its abxpks-deleted mutant strain (△abxpks) were fermented, isolated, and chemically prepared under the same conditions, followed by high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) detection. The result of the metabolite profiling analysis showed that the mutant ceased to produce BE-24566B. However, BE-24566B was still detected in the wild-type strain; this finding confirms that abxp, abxk, and abxs are involved in the biosynthesis of BE-2456B (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Metabolite profiling analysis of ABX biosynthesis. (A) Wild-type strain; (B) abxpks-deleted mutant strain.
2.3. Chemical Identification of BE-24566B and Zunyimycin A
Chromatography and preparative high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) yielded two compounds from strain Streptomyces sp. FJS 31-2. The NMR data of the two compounds were obtained in MeOD solvent. Compound 1 was obtained as a pale yellow powder. The 13C-NMR and DEPT spectra of 1 displayed signal for eighteen aromatic carbons at δC 167.7, 167.4, 159.6, 159.0, 157.0, 154.5, 152.4, 144.8, 138.0, 125.5, 119.5, 115.8, 113.2, 109.1, 108.4, 103.0, and 1012.7, which implied that the component 1 contained three benzene rings. Further, combining the signal of the carbonyl group at δC 192.8, the methane group at δC 35.0, the quaternary carbon at δC 35.0, and the carbon proton at δC 99.7 indicated that Compound 1 was BE-24566B. Except for the above information, the 1H-NMR spectra of 1 displayed signal at 13.5 (1H, s), 12.8 (1H, s), 7.16 (1H, s), 6.75 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz), 6.33 1H, d, J = 2.1 Hz), 6.27 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz), 6.16 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz), 2.52 (3H, s), 1.95 (3H, s), 1.88 (3H, s), 1.64 (3H, s), 3.24 (1H, d, J = 18.0Hz), and 3.24 (1H, d, J = 18.0Hz). This also demonstrated that the constituent was ABX.
Compound 2 was obtained as a pale yellow powder. The IR spectrum of 2 showed absorption at 3385 cm−1 and 1608 cm−1, indicative of the presence of hydroxyl and carbonyl groups, and the absorption at 1421 cm−1 and 1384 cm−1 illustrated the existence of a benzene ring. Its HR-TOF-MS ion at m/z 528.0714 [M]− indicated the molecular formula to be C27H22Cl2O7, implying sixteen degrees of unsaturation, respectively. The 13C-NMR and DEPT spectra of 2 displayed signal for eighteen aromatic carbons at δC 164.5, 163.0, 156.9, 153.2, 152.6, 150.6, 148.3, 141.9, 133.4, 122.1, 117.7, 115.4, 112.6, 109.9, 107.6, 102.6, and 101.6, which implied the component 2 contained three benzene rings. Further, combining the signal of the carbonyl group at δC 190.8, the methane group at δC 39.6, the quaternary carbon at δC 39.5, and the carbon proton at δC 98.2 indicated that Compound 2 had the skeleton of BE-24566B. Except for the above information, the 1H-NMR spectra of 2 displayed signal at 7.01 (1H, s), 6.45 (1H, s), 6.27 (1H, s), 6.24 (1H, s), 2.52 (3H, s), 1.95 (3H, s), 1.88 (3H, s), 1.64 (3H, s), 3.24 (1H, d, J = 18.0Hz) and 3.24 (1H, d, J = 18.0). This also demonstrated the presence of BE-24566B.
The HMBC experiment showed a correlation between the proton at δH 7.01 and carbons at δC 39.6, 39.5, 109.9, and 122.1, which indicated that one hydroxyl atom connected with the C-8 position. The signal at δH 6.45 (1H, s), the carbons at δC 164.5, 112.6, and 164.5, and, combined with the ROSEY spectra, the δH 6.45 (1H, s) had no correlation, which implied that the signal at δH 6.45 connected with a benzene ring at position C-12. The proton signal at δH 6.27 (1H, s) correlated with δC 152.6, 150.6, and 115.4, which indicated that the signal at δH 6.27 connected with a benzene ring at position C-4. The proton signal at δH 6.24 (1H, s) had a key correlation with the signal at δC 98.2, which indicated that the signal at δH 6.24 connected with a benzene ring at position C-16. According to the above information, the relative structure of 2 was substituted by chlorine atoms at the C-2 and C-10 positions of BE-24566B; therefore, Compound 2 was named zunyimycin A (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
The structure of zunyimycin A.
3. Discussion
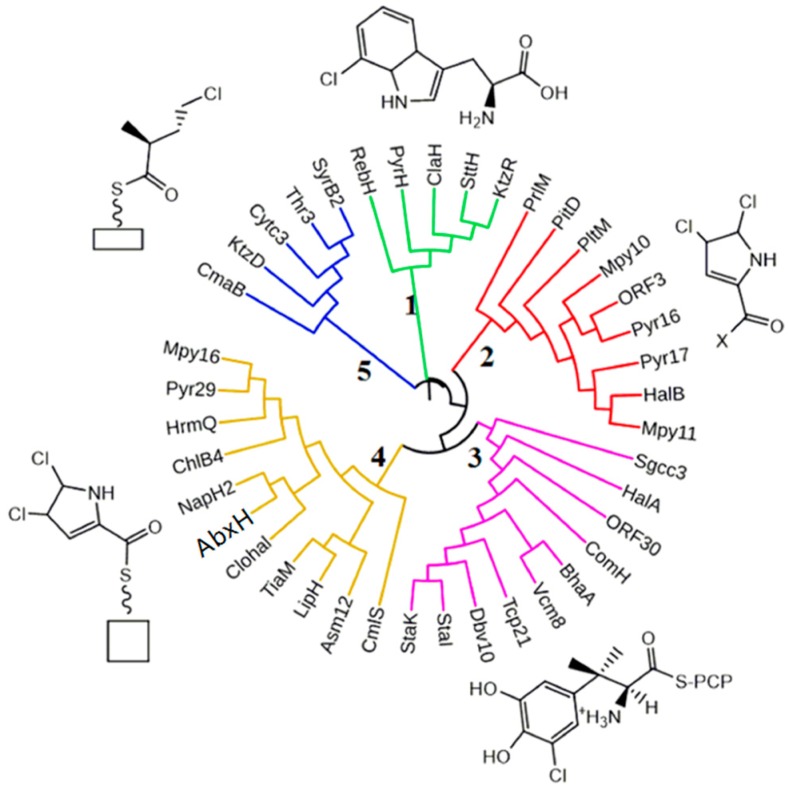
Cluster analysis results show that AbxH is clustered with the identified halogenases involved in the halogenated modification of pyrrole or its derivatives. Furthermore, AbxH exhibits the highest similarity (i.e., 49% at the amino acid sequence level) to NapH2 (Figure 6), which is involved in the halogenation reaction of napyradiomycin [29]. These results suggest that AbxH may possess a capacity for the halogenation reaction of polyketide. No abxH homologous gene was predicted in the genome, and no halogenated natural product was detected from the fermented products of Streptomyces sp. 1.264; hence, abxH (halogenase) may play a vital role in zunyimycin biosynthesis (Scheme 1).
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic analysis of identified halogenases from actinomycetes.
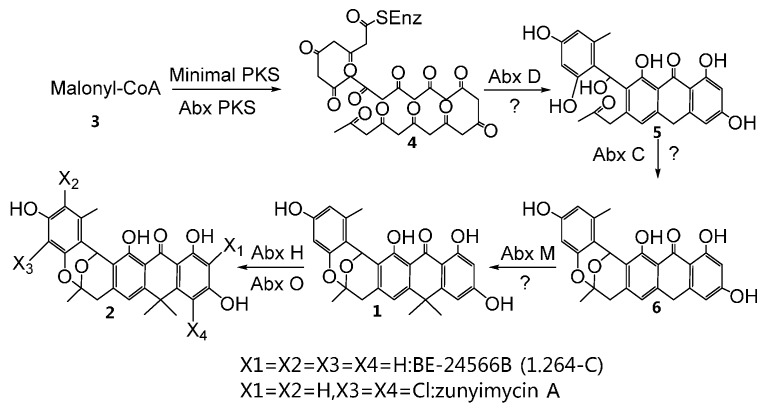
Scheme 1.
Proposed biosynthetic pathway of zunyimycin A.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Reagents
Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 was isolated from a soil sample collected from the Fanjing Mountain of the Guizhou Province at an altitude of 800 m in October 2012. The strain was deposited in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under accession number CGMCC 4.7321; the strain exhibits biological activities against Candida albicans, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Micrococcus luteus. The nucleotide sequencing was performed by BGI (Shenzhen, China) using an Illumina/Hiseq 2000 sequencer. Assembly was performed using SOAP de novo software [30]. Genomic DNA was directly extracted from the expanded culture of the ISP 2 liquid medium and used for genome sequencing and genomic library construction [31]. The bacterial strain EPI300-T1R and the plasmid pCC2FOS were obtained from Epicentre (Madison, WI, USA) and used to construct a genomic library by using CopyControl™ HTP Fosmid Library Production Kit (Cat. No. CCFOS059; Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Cloning plasmids, namely, pMD18-T and pSIMPLE-18 EcoR V/BAP, were purchased from Takara Biotechnology Company (Dalian, China) and used to construct a sub-clone library. Restriction enzymes, T4 DNA ligase, DNA end blunting kination ligation, and PCR kits were also purchased from the same company. The primers used for gene cloning and DNA sequencing were synthesized by Beijing Invitrogen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). The DNA gel extraction kit was obtained from Axygen Biosciences, Inc. (Hangzhou, China).
4.2. DNA Isolation, Manipulation, and Sequencing
Genomic DNA was isolated from Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 by using the standard method described by Hopwood [32]. Molecular manipulation was conducted according to the standard methods described by Sambrook and Russel [33]. Plasmid and fosmid sequencing was performed on the 3730xl DNA analyzer at Beijing Invitrogen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. by using the shotgun cloning strategy. The pCC2/pEpiFOS forward and reverse primers (sequences in the CopyControl protocol) were used to sequence the fosmid ends. Moreover, the M13 primers were used to sequence the subclone ends. Draft genome sequencing of Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 was performed on Illumina HiSeq2000 (BGI Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Shenzhen, China) by using a proprietary reversible terminator-based strategy.
4.3. The Genomic Library and Subclone Library Construction and Screening
The full-length sequence of the predicted lobophorin biosynthetic gene cluster was obtained by constructing the genomic library of Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 in CopyControl pCC2FOS according to the manufacturer′s instructions. The library contains more than 6000 clones with approximately 40 kb inserted genomic DNA fragments. The genomic library was screened through colony PCR with primer pairs designed based on the nucleic acid sequences of abxH according to the results of the predictive analysis of the draft genome sequencing. The end of the positive clone was sequenced to confirm that the clone was located in the abx cluster. Next-round screening was performed with primer pairs designed based on the end sequences of the last round of screening results until three positive clones overlapping one another were obtained. Accordingly, 1 μg of fosmid DNA was fragmented using an ultrasonic cell disruptor under 200 W for 1 s on ice. DNA fragments within 2–4 kb size were recovered using the AxyPrep DNA gel extraction kit. The fragments were cloned into pSIMPLE-18 EcoR V/BAP vector to construct subclone libraries after being end blunted and 5′-phosphorylated. PCR screening was performed using sequence-specific primers designed based on the end sequences of each gap. The positive clones were then sequenced with M13-47F/M13-48R and specific primers.
4.4. Analysis of the Anthrabenzoxocinone Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
A 16.5-kb contiguous DNA segment was obtained by subcloned library sequencing and deposited in GenBank under accession number KU243130. The sequence was uploaded to the antiSMASH website [34] and used to determine gene content and order. The open reading frames proposed for the biosynthesis pathway of the anthrabenzoxocinone skeleton, post modification, and regulation were deduced based on functional gene analysis. The analysis was performed by comparing the sequence homology with its homologous clusters by using BlastP. These clusters were found by antiSMASH. The comparative analysis and the global rearrangement structure of the two anthrabenzoxocinone biosynthetic gene clusters were conducted using Mauve software [35].
4.5. Inactivation of the Anthrabenzoxocinone Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
A 2.7-kb DNA fragment (from 6165 nt to 8872 nt of KU243130) encoding the ABX polyketide backbone biosynthesis (abxp, abxk, and abxs) was replaced by the kanamycin resistance protein-coding region (AAF85969.1). This region was constructed by PCR, inserted into the pKC1139 plasmid, and transformed into E. coli ET12567. The constructs for gene inactivation were introduced into Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 by conjugal transfer following the procedure of Hopwood2. Disruption was confirmed by PCR analysis. HPLC (LC20AT, Shimadzu, Beijing, China) was used to confirm the abolishment of anthrabenzoxocinone production.
4.6. Fermentation, Isolation, and Chemical Identification of BE-24566B and Zunyimycin A
Streptomyces sp. FJS31-2 was cultured using 140 × 500 mL shake flasks containing 100 mL of ISP 2 agar medium with 10% natural humus acid water extracts and then incubated for 15 d at 28 °C. The solid culture was mashed and extracted three times with 140 L of ethanol after cultivation. The organic portion was then concentrated in vacuo to remove the solvent. The crude extract was applied to silica gel column chromatography using the CHCl3/MeOH gradient to obtain the crude products. Further purification was conducted using Sephadex LH-20 (GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan) (MeOH) column and RP-HPLC (Shimadzu SPD-M20A with Xbridge ODS 10 mm × 150 mm column). Compounds were identified with an HRESI-MS (Waters Xevo G2 QTOF mass spectrometer (Waters corportion, Milford, MA, USA) and NMR (Bruker AV 600 MHz) (Bruker Corporation, Karlsruhe, Germany) analyses.
5. Conclusions
In summary, a cryptic anthrabenzoxocinone gene cluster was identified by genome mining. This cluster was successfully activated by adding natural humus acid. Novel halogenated natural products were isolated, characterized, and named as zunyimycin A. Furthermore, the results indicated that halogenase AbxH is responsible for the halogenation reaction of zunyimycin A and may provide potential for the halogenation of natural products.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31160004, 31460006), the Program for Innovative Research Team in Guizhou Province (No. QKH-RCTD-20134035) and the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (No. (2010)2156), (2012)2348), (2013) 3013) and (2015)4026).
Author Contributions
Changwu Yue and Yuhong Lü designed the study, prepared the manuscript, and wrote the paper; Changwu Yue, Yuhong Lü, and Miao Wang performed the biological experiments; Meiyun Shao, Xiaoqian Li, and Yinyin Wang performed chemistry experiments; Shengyan Qian and Ning Liu did the data analyses; Minghao Liu helped perform the analysis of gene clusters; Changwu Yue, Yuhong Lü, Yuxin Bao, and Ying Huang were the principal investigators of the project and provided the research funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds zunyimycin A and BE24566B are available from the authors.
References
- 1.Kallifidas D., Kang H.S., Brady S.F. Tetarimycin A, an MRSA-active antibiotic identified through induced expression of environmental DNA gene clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:19552–19555. doi: 10.1021/ja3093828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arasu M.V., Duraipandiyan V., Ignacimuthu S. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of polyketide metabolite from marine Streptomyces sp. AP-123 and its cytotoxic effect. Chemosphere. 2013;90:479–487. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liu W., Christenson S.D., Standage S., Shen B. Biosynthesis of the enediyne antitumor antibiotic C-1027. Science. 2002;297:1170–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.1072110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rui Z., Petrícková K., Skanta F., Pospísil S., Yang Y., Chen C.Y., Tsai S.F., Floss H.G., Petrícek M., Yu T.W. Biochemical and genetic insights into asukamycin biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:24915–24924. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zaleta-Rivera K., Charkoudian L.K., Ridley C.P., Khosla C. Cloning, sequencing, heterologous expression, and mechanistic analysis of A-74528 biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:9122–9128. doi: 10.1021/ja102519v. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shen B. Polyketide biosynthesis beyond the type I, II and III polyketide synthase paradigms. Curr. Opin Chem. Biol. 2003;7:285–295. doi: 10.1016/S1367-5931(03)00020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hopwood D.A., Khosla C. Genes for polyketide secondary metabolic pathways in microorganisms and plants. Ciba. Found Symp. 1992;171:88–106. doi: 10.1002/9780470514344.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gao X., Wang P., Tang Y. Engineered polyketide biosynthesis and biocatalysis in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010;88:1233–1242. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2860-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hertweck C., Luzhetskyy A., Rebets Y., Bechthold A. Type II polyketide synthases: Gaining a deeper insight into enzymatic teamwork. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007;24:62–90. doi: 10.1039/B507395M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Van Lanen S.G., Shen B. Advances in polyketide synthase structure and function. Curr. Opin Drug Discov. Devel. 2008;11:186–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Caldara-Festin G., Jackson D.R., Barajas J.F., Valentic T.R., Patel A.B., Aguilar S., Nguyen M., Vo M., Khanna A., Sasaki E., et al. Structural and functional analysis of two di-domain aromatase/cyclases from type II polyketide synthases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:E6844–E6851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512976112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hillenmeyer M.E., Vandova G.A., Berlew E.E., Charkoudian L.K. Evolution of chemical diversity by coordinated gene swaps in type II polyketide gene clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:13952–13957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511688112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jackson D.R., Tu S.S., Nguyen M., Barajas J.F., Schaub A.J., Krug D., Pistorius D., Luo R., Müller R., Tsai S.C. Structural Insights into Anthranilate Priming during Type II Polyketide Biosynthesis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016;11:95–103. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bailey C.B., Pasman M.E., Keatinge-Clay A.T. Substrate structure-activity relationships guide rational engineering of modular polyketide synthase ketoreductases. Chem. Commun. 2015;52:792–795. doi: 10.1039/C5CC07315D. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mugnai M.L., Shi Y., Keatinge-Clay A.T., Elber R. Molecular dynamics studies of modular polyketide synthase ketoreductase stereospecificity. Biochemistry. 2015;54:2346–2359. doi: 10.1021/bi501401g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sciara G., Kendrew S.G., Miele A.E., Marsh N.G., Federici L., Malatesta F., Schimperna G., Savino C., Vallone B. The structure of ActVA-Orf6, a novel type of monooxygenase involved in actinorhodin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2003;22:205–215. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Watanabe K. Effective use of heterologous hosts for characterization of biosynthetic enzymes allows production of natural products and promotes new natural product discovery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014;62:1153–1165. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c14-00471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Thompson T.B., Katayama K., Watanabe K., Hutchinson C.R., Rayment I.J. Structural and Functional Analysis of Tetracenomycin F2 Cyclase from Streptomyces glaucescens a type II polyketide cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:37956–37963. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406144200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fritzsche K., Ishida K., Hertweck C. Orchestration of discoid polyketide cyclization in the resistomycin pathway. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:8307–8316. doi: 10.1021/ja800251m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lopez P., Hornung A., Welzel K., Unsin C., Wohlleben W., Weber T., Pelzer S. Isolation of the lysolipin gene cluster of Streptomyces tendae Tü 4042. Gene. 2010;461:5–14. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Akey D.L., Gehret J.J., Khare D., Smith J.L. Insights from the sea: Structural biology of marine polyketide synthases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012;29:1038–1049. doi: 10.1039/c2np20016c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhu T., Cheng X., Liu Y., Deng Z., You D. Deciphering and engineering of the final step halogenase for improved chlortetracycline biosynthesis in industrial Streptomyces aureofaciens. Metab. Eng. 2013;19:69–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2013.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Siitonen V., Claesson M., Patrikainen P., Aromaa M., Mäntsälä P., Schneider G., Metsä-Ketelä M. Identification of late-stage glycosylation steps in the biosynthetic pathway of the anthracycline nogalamycin. ChemBioChem. 2012;13:120–128. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ma M., Kwong T., Lim S.K., Ju J., Lohman J.R., Shen B. Post-polyketide synthase steps in iso-migrastatin biosynthesis, featuring tailoring enzymes with broad substrate specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:2489–2492. doi: 10.1021/ja4002635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kojiri K., Nakajima S., Fuse A., Suzuki H., Suda H. BE-24566B, a new antibiotic produced by streptomyces violaceusniger. J. Antibiot. 1995;48:1506–1508. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.48.1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Herath K.B., Jayasuriya H., Guan Z., Schulman M., Ruby C., Sharma N., MacNaul K., Menke J.G., Kodali S., Galgoci A., et al. Anthrabenzoxocinones from Streptomyces sp. as liver X receptor ligands and antibacterial agents. J. Nat. Prod. 2005;68:1437–1440. doi: 10.1021/np050176k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kodali S., Galgoci A., Young K., Painter R., Silver L.L., Herath K.B., Singh S.B., Cully D., Barrett J.F., Schmatz D., Wang J. Determination of selectivity and efficacy of fatty acid synthesis inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:1669–1677. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406848200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lam Y.K.T., Hensens O., Helms G., Williams D.J., Nallin M., Smith J., Gartner S., Rodriguez L.H., Stevens-Miles S. L-755,805, a new polyketide endothelin binding inhibitor from an actinomycete. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:2013–2016. doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)00215-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Winter J.M., Moffitt M.C., Zazopoulos E., McAlpine J.B., Dorrestein P.C., Moore B.S. Molecular basis for chloronium-mediated meroterpene cyclization: Cloning, sequencing, and heterologous expression of the napyradiomycin biosynthetic gene cluster. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:16362–16368. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611046200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li R., Zhu H., Ruan J., Qian W., Fang X., Shi Z., Li Y., Li S., Shan G., Kristiansen K., et al. De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res. 2010;20:265–272. doi: 10.1101/gr.097261.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shirling E.B., Gottlieb D. Methods for characterizing Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1966;16:313–340. doi: 10.1099/00207713-16-3-313. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hopwood D.A. Genetic manipulation of Streptomyces polyketide synthase genes for novel secondary metabolite production. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1995;16:233–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1995.tb00169.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sambrook J., Russell D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor; New York, NY, USA: 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Blin K., Medema M.H., Kazempour D., Fischbach M.A., Breitling R., Takano E., Weber T. antiSMASH 2.0—A versatile platform for genome mining of secondary metabolite producers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Darling A.E., Mau B., Perna N.T. Progressive mauve: Multiplegenome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e11147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]