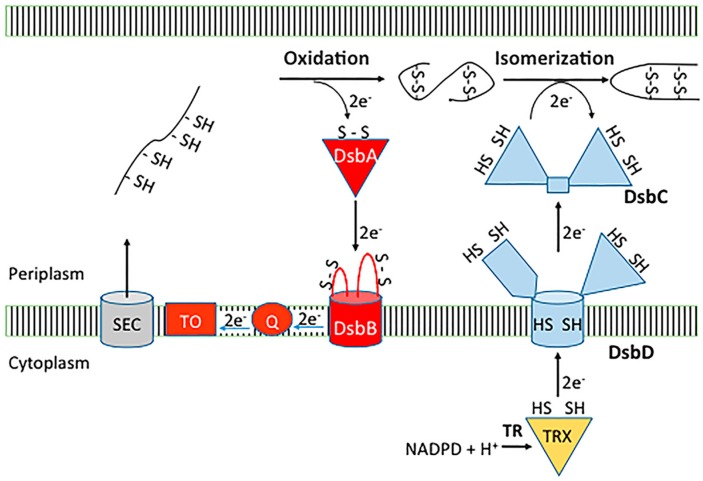
Figure 1.
Escherichia coli K-12 disulfide catalytic pathways. In the oxidase pathway the thioredoxin-like oxidase DsbA introduces disulfide bonds into proteins that are translocated to the periplasm via the SEC machinery (the plotted line with the -SH and S-S symbols represents the amino acid chain of the DsbA substrate protein). Upon oxidising a substrate, DsbA becomes reduced and is re-oxidized by the partner membrane protein DsbB, which transfers electrons to quinones (Q) and terminal oxidases (TO). In the isomerase pathway, incorrectly formed disulfide bonds are corrected by the isomerases DsbC and DsbG, which are maintained in a reduced form by the inner membrane reductase DsbD. This multidomain protein is reduced by cytoplasmic thioredoxin, which in turn is reduced by thioredoxin reductase (TR) in a NADPH-dependent manner.