Abstract
Some animals, such as the bombardier beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae: Brachinini), have evolved chemical defences against predators. When attacked, bombardier beetles can discharge noxious chemicals at temperatures of approximately 100 °C from the tip of their abdomens, “bombing” their attackers. Although many studies to date have investigated how bombardier beetles discharge defensive chemicals against predators, relatively little research has examined how predators modify their attacks on bombardier beetles to avoid being bombed. In this study, I observed the black-spotted pond frog Pelophylax nigromaculatus (Anura: Ranidae) attacking the bombardier beetle Pheropsophus jessoensis under laboratory conditions. In Japan, Pe. nigromaculatus is a generalist predator in grasslands where the bombardier beetle frequently occurs. Almost all the frogs (92.9%) observed rejected live bombardier beetles; 67.9% stopped their attacks once their tongues touched the beetles, and 25.0% spat out the beetles immediately after taking the beetles into their mouths. No beetle bombed a frog before being taken into a frog’s mouth. All beetles taken into mouths bombed the frogs. Only 7.1% of the frogs swallowed live bombardier beetles after being bombed in the mouth. When dead beetles were provided instead, 85.7% of the frogs rejected the dead beetles, 71.4% stopped their attacks after their tongues touched the beetles, and 14.3% spat out the beetles. Only 14.3% of the frogs swallowed the dead beetles. The results suggest that the frogs tended to stop their predatory attack before receiving a bombing response from the beetles. Therefore, bombing was not essential for the beetles to successfully defend against the frogs. Using its tongue, Pe. nigromaculatus may be able to rapidly detect a deterrent chemical or physical characteristics of its potential prey Ph. jessoensis and thus avoid injury by stopping its predatory attack before the beetle bombs it.
Keywords: Carabidae, Chemical defence, Predator, Prey
Introduction
Physical and chemical defences have evolved in many organisms to protect against natural enemies (Edmunds, 1974; Eisner, Eisner & Siegler, 2005). For example, some plant and animal species have developed physical deterrents such as thorns and spines (Edmunds, 1974; Cooper & Owen-Smith, 1986; Eisner, 2003; Sugiura & Yamazaki, 2014; Sugiura, 2016; Ito, Taniguchi & Billen, 2016), while other species produce defensive chemicals, including toxic substances, to prevent themselves from being eaten (Eisner, 2003; Eisner, Eisner & Siegler, 2005; Derby, 2007; Mithöfer & Boland, 2012). Organisms whose defence mechanisms can cause severe injury to their natural enemies have also evolved warning signals, such as conspicuous body colouration or particular sounds (Lev-Yadun, 2001; Ruxton, Sherratt & Speed, 2004; Inbar & Lev-Yadun, 2005; Bonacci et al., 2008; Lev-Yadun, 2009; Bura, Kawahara & Yack, 2016; Sugiura & Takanashi, 2018). In response, predators have evolved specific abilities to avoid such well-defended prey by recognising warning colouration or detecting chemical signals (Edmunds, 1974; Endler, 1991; Ruxton, Sherratt & Speed, 2004; Skelhorn & Rowe, 2006; Williams et al., 2010).
Adult bombardier beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae: Brachinini) bomb, i.e., discharge noxious chemicals from the tip of their abdomens at temperatures of approximately 100 °C, when they are disturbed or attacked (Aneshansley et al., 1969; Dean, 1979; Eisner, 2003; Eisner, Eisner & Siegler, 2005; Arndt et al., 2015). Such ejection of hot chemicals is only known in the coleopteran family Carabidae. Previous studies have investigated how bombardier beetles successfully defend against predators (Eisner, 1958; Eisner & Meinwald, 1966; Eisner & Dean, 1976; Dean, 1980a; Eisner, Eisner & Aneshansley, 2005; Eisner et al., 2006). Bombardier beetles can aim their abdominal discharge in virtually any direction, spraying various parts of their own bodies (e.g., legs and dorsal surface) with the toxic chemicals (Eisner & Aneshansley, 1999). Dean (1980b) reported that predators displayed intense responses to the unheated chemical discharges of bombardier beetles in experiments. This suggests that the cooled chemicals coating the beetles’ body surfaces function as the primary defence against predators. Successful defence mediated by chemicals on the body surfaces of beetles may reduce the costs of spraying (bombing). Further research is needed to clarify the relative importance of chemical toxicity and heat for overall successful anti-predatory defence.
Frogs and toads are important predators of carabid beetles (Larochelle, 1974a; Larochelle, 1974b). However, bombardier beetles have rarely been found in the gut contents and faeces of frogs and toads (Larochelle, 1974a; Larochelle, 1974b; Sarashina, Yoshihisa & Yoshida, 2011; except Mori, 2008), suggesting that bombing prevents toads and frogs from swallowing and ingesting beetles (Eisner & Meinwald, 1966; Dean, 1980a; Eisner, 2003; Sugiura & Sato, 2018). Still, only a few studies have investigated the factors that cause anuran predators to stop preying on bombardier beetles (Dean, 1980b). Elucidating these ecological factors would contribute to a better understanding of the evolution of anti-predatory defences in insects.
This study aims to investigate the responses of the black-spotted pond frog Pelophylax nigromaculatus (Hallowell) (Anura: Ranidae) to the defensive behaviour of the bombardier beetle Pheropsophus jessoensis (Morawitz). Pheropsophus jessoensis is a bombardier beetle found in East Asia (Ueno, Kurosawa & Sato, 1985; Jung et al., 2012); the beetle is a common inhabitant of farmlands, grasslands, and forest edges in Japan (Habu & Sadanaga, 1965; Ueno, Kurosawa & Sato, 1985; Yahiro et al., 1992; Ishitani & Yano, 1994; Fujisawa, Lee & Ishii, 2012; Ohwaki, Kaneko & Ikeda, 2015; Sugiura & Sato, 2018). Adult Ph. jessoensis eject toxic chemicals (1,4-benzoquinone and 2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone) at a temperature of approximately 100 °C from their rear ends in response to predator attacks (Video S1; Kanehisa & Murase, 1977; Kanehisa, 1996). Pelophylax nigromaculatus is a true frog inhabiting wetlands and farmlands of East Asia (Liu et al., 2010; Tsuji et al., 2011; Komaki et al., 2015), being one of the most abundant frog species of traditional agricultural landscapes including farmlands, grasslands, and forest edges (Hirai, 2002; Honma, Oku & Nishida, 2006; Tsuji et al., 2011; Matsuhashi & Okuyama, 2015). Using its tongue, Pe. nigromaculatus readily catches and swallows smaller prey (Video S2; Honma, Oku & Nishida, 2006). Pelophylax nigromaculatus is a generalist predator that has been reported to prey on carabid beetles (Maeda & Matsui, 1999; Hirai & Matsui, 1999; Sano & Shinohara, 2012; Sarashina, Yoshihisa & Yoshida, 2011). As Ph. jessoensis and Pe. nigromaculatus co-occur in the same grassland habitats, this frog species is a potential predator of adult Ph. jessoensis. In early June 2016, I offered an adult Ph. jessoensis to an adult Pe. nigromaculatus under laboratory conditions. The frog attacked the beetle, but stopped the attack immediately after its tongue touched the beetle. No bombing sounds were heard, suggesting that the frog ceased its attack before the beetle bombed. Therefore, I hypothesised that bombing is not essential when Ph. jessoensis seeks to avoid being swallowed by Pe. nigromaculatus. To test this hypothesis, I observed Pe. nigromaculatus attacking Ph. jessoensis under laboratory conditions using a digital video camera. Acceptance or rejection of prey was carefully investigated using slow-motion videos. Furthermore, both dead and live beetles were used to test whether bombing is essential for successful defence against predatory attacks by Pe. nigromaculatus. Finally, I discuss the importance of primary and secondary defences in terms of overall anti-predation defence.
Materials and Methods
Sampling
Approximately 100 adult Ph. jessoensis were collected from grasslands and forest edges in Kato-shi (34°54′N, 135°02′E, 120 m above sea level), Hyogo Prefecture, central Japan, from May to August in 2016, 2017, and 2018 (cf. Sugiura & Sato, 2018). Body weight was measured to the nearest 0.1 mg using an electronic balance (PA64JP, Ohaus, Tokyo, Japan). Study individuals were maintained separately in plastic cases (diameter: 85 mm; height: 25 mm) with wet tissue paper in the laboratory at 25 °C. Dead larvae of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) were provided as food (Sugiura & Sato, 2018). Beetles were not used repeatedly in different feeding experiments. All experiments were conducted 22.6 ± 4.0 (means ± standard errors; range: 4–69) days after the beetles were collected.
Approximately 100 individuals of Pe. nigromaculatus were collected from wetlands and forest edges in Takarazuka-shi (34°53′N, 135°17′E, 230 m above sea level), Sanda-shi (34°57′N, 135°11′E, 180 m above sea level), and Sayo-cho (35°02′N, 134°20′E, 180 m above sea level), Hyogo Prefecture, central Japan, from May to August in 2016, 2017, and 2018. The distances between these sites and the sampling site of Ph. jessoensis ranged from 15.6 to 65.4 km. Although Pe. nigromaculatus has recently been classified as near threatened (NT) in the Japanese Red Data List (Ministry of the Environment of Japan, 2017), this species was abundant at the collection sites. Both juveniles and adults were collected. Body weight was measured to the closest 0.01 g using an electronic balance (EK-120A, A&D, Tokyo). Small and large frogs were maintained separately in small (120 × 85 × 130 mm, length × width × height) and large plastic cages (120 × 185 × 130 mm, length × width × height), respectively, in the laboratory at 25 °C. Live larvae of S. litura, Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), and Zophobas atratus Fabricius (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) were provided as food. Frogs were starved for 24 h before the feeding experiments to standardise their hunger level (cf. Honma, Oku & Nishida, 2006). As with the beetles, individual frogs were not used repeatedly. The experiments were conducted 18.6 ± 2.5 (means ± standard errors; range: 4–66) days after the frogs were collected. The frogs were released after the experiments were completed.
Feeding experiments
Feeding experiments were all conducted at 25 °C. To start, a frog was placed in a transparent plastic container (120 × 85 × 130 mm, length × width × height). Then, a transparent glass petri dish (45 mm in diameter, 15 mm in height) containing a live bombardier beetle was placed outside the plastic container where the frog could see it. Frogs that did not try to attack the beetle (34.1%) were not used for the feeding experiments. However, frogs that ignored Ph. jessoensis did not respond to other prey (i.e., T. molitor larvae). If a frog displayed attacking behaviour (i.e., opening the mouth and shooting out the tongue to capture prey; Video S2), a live beetle was then placed in the container with the frog. The resulting behaviours were recorded on video using a digital camera (iPhone 6 plus, Apple) at 240 frames per second. If the frog did not swallow the beetle, palatable prey (a T. molitor larva) was offered to the frog several minutes after beetle rejection to determine whether the frog was hungry. If a frog swallowed the bombardier beetle, I observed whether it vomited the beetle within 330 min of swallowing it (cf. Sugiura & Sato, 2018). Vomited beetles were checked to see whether they were still alive. Frogs that did not vomit after swallowing were considered to have digested the beetle. Frog faeces were examined after the experiment to confirm whether the beetles were digested. In total, 28 frogs and 28 live bombardier beetles were used in the experiments. The means ± standard errors of the frog and live beetle body weights were 10.23 ± 1.39 g (n = 28) and 213.0 ± 10.0 mg (n = 28), respectively.
A second set of frogs were presented with dead adult beetles to test whether the bombing response is essential for deterring a predatory attack. Pelophylax nigromaculatus usually does not attack motionless prey. However, in a pilot test, an individual of Pe. nigromaculatus attacked and ingested a dead caterpillar (S. litura) when forceps were used to move the caterpillar within the frog’s field of view. For this experiment, the bombardier beetles were killed in a freezer at −15 °C. First, a dead beetle was placed in the plastic container (120 × 85 × 130 mm, length × width × height) within the frog’s field of view. If the frog did not initially respond to the beetle, forceps were used to move the dead beetle within the frog’s field of view again. Frogs that did not attack the dead beetles (29.2%) were not used in these experiments; frogs that ignored Ph. jessoensis did not respond to other prey (i.e., T. molitor larvae). The predatory behaviours of the frogs were recorded using the same digital video camera. Frogs that did not swallow dead beetles were offered T. molitor larvae several minutes after beetle rejection to check whether they were hungry. Twenty-eight frogs and 28 dead beetles were used in this experiment. The means ± standard errors of the frog and dead beetle body weights were 8.65 ± 1.25 g (n = 28) and 214.8 ± 7.6 mg (n = 28), respectively. The mean body weight of frogs that attacked dead beetles did not differ significantly from the mean body weight of frogs that attacked live beetles (t-test, t = 0.84, P = 0.40). The mean body weight of dead beetles did not differ significantly from the mean body weight of live beetles (t-test, t = − 0.14, P = 0.89)
Videos of frogs responding to live and dead beetles were played back using QuickTime Player version 10.4 (Apple, Inc.). Frog responses to the bombardier beetles were grouped into four categories (cf. Ito, Taniguchi & Billen, 2016; Matsubara & Sugiura, 2017; Sugiura & Sato, 2018): (1) frogs that touched the beetles with their tongues but did not take the beetles into their mouths; (2) frogs that spat out the beetles after taking them into the mouth; (3) frogs that swallowed beetles but vomited them later; and (4) frogs that swallowed and digested the beetles. I also assessed whether frogs that rejected beetles (1–2) resumed their attacks within 10 s.
All experiments were performed in accordance with the Kobe University Animal Experimentation Regulations (Kobe University Animal Care and Use Committee, 27–01, 30–01). No frogs were seriously injured or killed during the feeding experiments. My study also complies with the current laws of Japan.
Data analysis
Generalised linear models (GLMs) featuring binomial error distributions and logit links (i.e., logistic regressions) were used to identify factors that contributed to frogs’ successful swallowing and digestion of the bombardier beetles. The success or failure (1/0) of frogs’ swallowing and digesting beetles was used as the response variable. Frog weight, beetle weight, the frog weight × beetle weight interaction, and beetle condition (live or dead) were treated as fixed factors. When the residual deviance was larger (overdispersion) or smaller (underdispersion) than the residual degrees of freedom, a quasi-binomial error distribution was used rather than a binomial error distribution. Furthermore, fixed factors were subjected to likelihood ratio testing when marginal significance was evident. Thus, the significance of models with and without the factors of interest were compared using the GLMs. All analyses were performed using R version 3.3.2 (R Development Core Team, 2016).
Results
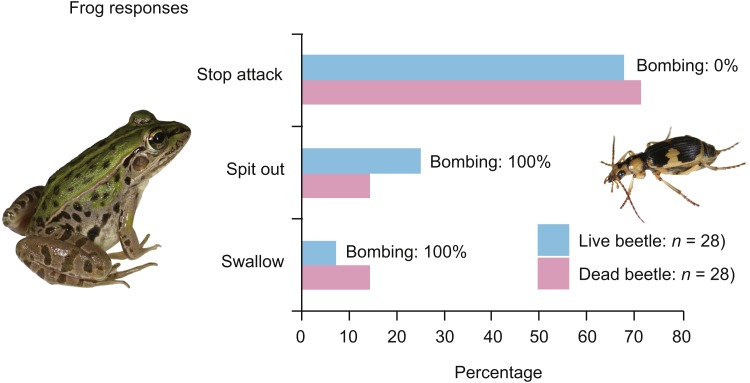
In the experiment using live adult bombardier beetles (n = 28), 26 frogs (92.9%) rejected the beetles without swallowing them (Fig. 1); 19 frogs (67.9%) stopped attacking the beetles immediately after touching the beetles with their tongues (Fig. 2; Video S3), and seven frogs (25.0%) spat out the beetles after taking the beetles into their mouths (Fig. 3; Video S4). No beetle bombed a frog before being taken into the frog’s mouth. All beetles that were taken into frog mouths bombed (Video S4). Only two frogs (7.1%) were observed to swallow the bombardier beetles (Table 1) after being bombed in the mouth; one of the frogs successfully digested the beetle, but the other frog vomited the beetle 18 min after swallowing it (Table 1). The vomited beetle was still alive. Of the frogs that took the beetles into their mouths, 88.9% (n = 8/9) initially stopped attacking the beetles when their tongues first touched the beetles, but resumed their predatory attack soon thereafter (Fig. 3; Video S4). Frogs that did not swallow beetles consumed other prey (i.e., T. molitor larvae) soon thereafter.
Figure 1. Behavioural responses of the black-spotted pond frog Pelophylax nigromaculatus to live and dead adult individuals of the bombardier beetle Pheropsophus jessoensis.
‘Stop attack’: the frogs stopped their attacks after their tongues touched the beetles. ‘Spit out’: the frogs spat out the beetles immediately after taking the beetles into their mouths. ‘Swallow’: the frogs successfully swallowed the beetles. ‘Bombing’: the beetles could be heard bombing. Photo credit: Shinji Sugiura.
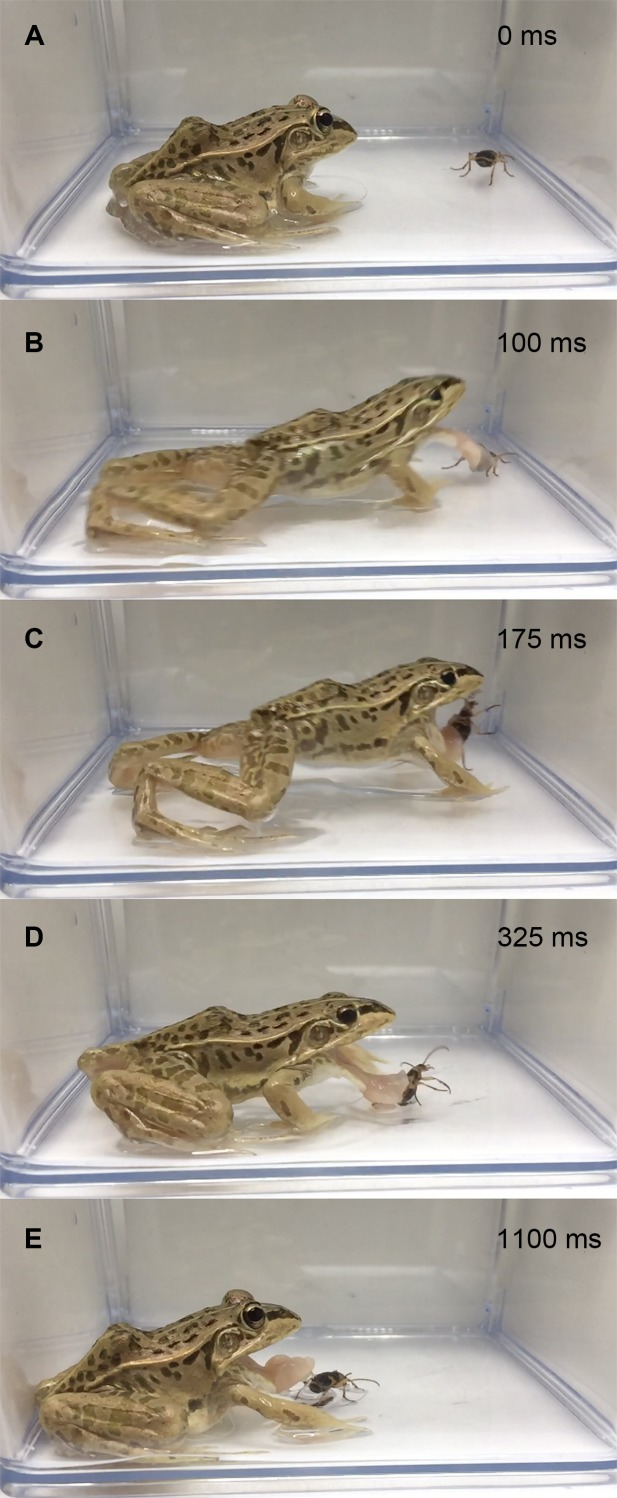
Figure 2. Temporal sequence of the frog Pelophylaxnigromaculatus rejecting a live adult Pheropsophus jessoensis without taking the beetle into its mouth.
(A) 0 ms. (B) 100 ms. (C) 175 ms. (D) 325 ms. (E) 1,100 ms. The frog stopped the attack immediately after its tongue touched the beetle. No bombing sounds were heard (see Video S3). Credit: Shinji Sugiura.
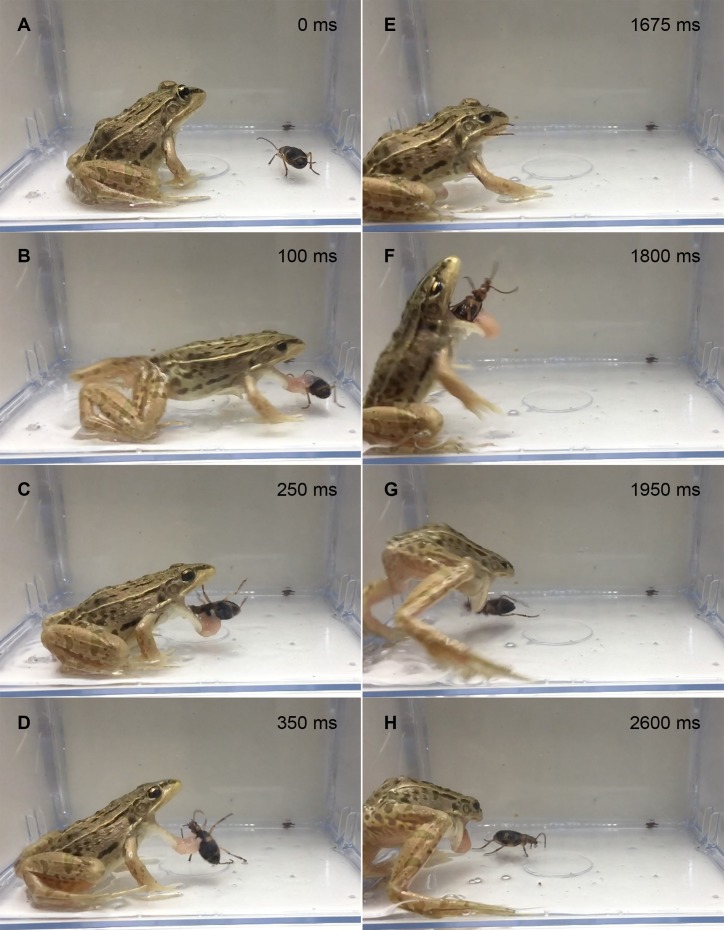
Figure 3. Temporal sequence of the frog Pelophylaxnigromaculatus spitting out a live adult Pheropsophus jessoensis after taking the beetle into its mouth.
(A) 0 ms. (B) 100 ms. (C) 250 ms. (D) 350 ms. (E) 1,675 ms. (F) 1,800 ms. (G) 1,950 ms (H) 2,600 ms. Bombing by the beetle was audible just before the frog spat out the beetle (1,675–1,800 ms; see Video S4). Credit: Shinji Sugiura.
Table 1. Results of a generalised linear model (GLM) testing potential factors influencing whether the frog Pelophylax nigromaculatus successfully swallowed the bombardier beetle Pheropsophus jessoensis in feeding experiments.
| Response variable | Explanatory variable (fixed effect) | Coefficient estimate | SE | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swallowing successa | Intercept | 7.601881 | 4.454207 | 1.707 | 0.094 |
| Frog weight | −0.420817 | 0.290774 | −1.447 | 0.154 | |
| Beetle weight | −0.060781 | 0.025084 | −2.423 | 0.019 | |
| Frog weight × Beetle weight | 0.002637 | 0.001457 | 1.81 | 0.076c | |
| Beetle treatmentb | 1.387536 | 0.855616 | 1.622 | 0.111 |
Notes.
As the residual deviance was smaller than the residual degrees of freedom, a quasi-binomial error distribution (rather than a binomial error distribution) was employed. Two and four live and dead beetles, respectively, were swallowed.
Live beetles were used as a reference.
The significance of this factor was checked using the likelihood ratio test (P = 0.063).
When dead beetles were used (n = 28), 24 frogs (85.7%) rejected the dead beetles without swallowing them (Fig. 1); 20 frogs (71.4%) stopped attacking the beetles after their tongues touched the dead beetles (Video S5), and four frogs (14.3%) spat out the beetles after taking the beetles into their mouths (Fig. 1). Only four frogs (14.3%) swallowed the dead beetles. Similar to the experiment using live beetles, 87.5% of the frogs that took beetles into their mouths (n = 7/8) were initially deterred when their tongues first touched the beetles, but continued with their predatory behaviour soon afterwards. The frogs that did not swallow beetles ate other prey (i.e., T. molitor larvae) soon thereafter.
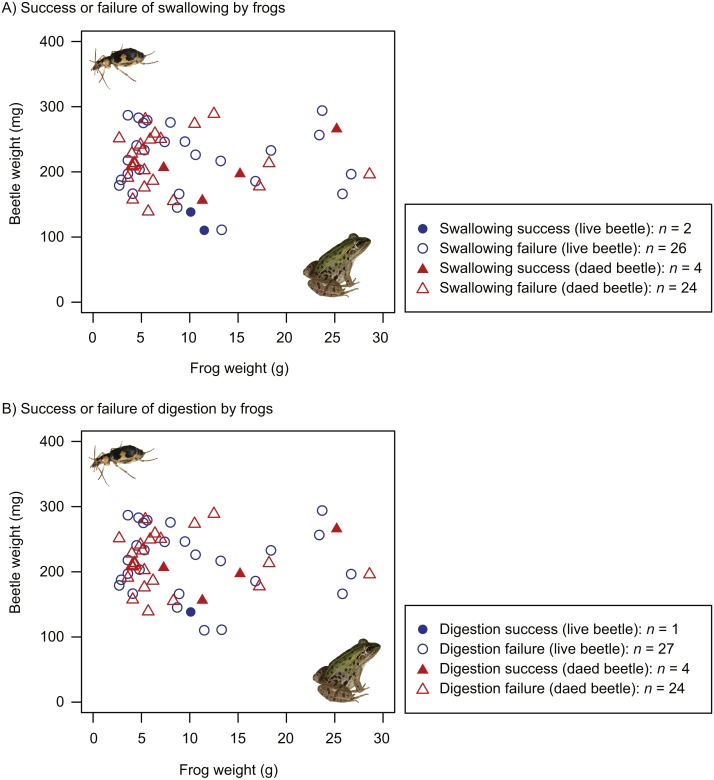
The proportion of dead beetles swallowed by frogs (14.3%) was higher than that of live beetles (7.1%). However, the GLM results indicated that the frog swallowing rates of live and dead beetles did not significantly differ (Table 1). Whether beetles were swallowed or not was associated with beetle size, but not frog size (Table 1). Beetles were more likely to be swallowed as beetle size decreased (Fig. 4A). The interaction of frog and beetle weight was not significant (Fig. 4A).
Figure 4. Body size relationships between predator frogs (Pelophylax nigromaculatus) and prey beetles (Pheropsophus jessoensis).
(A) Success or failure of swallowing by frogs. (B) Success or failure of digestion by frogs. Closed circles and triangles indicate the swallow (or digestion) success of live and dead beetles, respectively. Open circles and triangles indicate the swallow (or digestion) failure of live and dead beetles, respectively. Photo credit: Shinji Sugiura.
The proportion of dead beetles digested by frogs (14.3%) was higher than the proportion of live beetles swallowed (3.6%). The GLMs indicated that the difference between the digestion rates of live and dead beetles was significant (Table 2). Beetle size affected the digestion rate (Table 2, Fig. 4B).
Table 2. Results of a generalised linear model (GLM) testing potential factors influencing whether the frog Pelophylax nigromaculatus successfully digested the bombardier beetle Pheropsophus jessoensis in feeding experiments.
| Response variable | Explanatory variable (fixed effect) | Coefficient estimate | SE | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestion successa | Intercept | 4.471889 | 4.45551 | 1.004 | 0.32 |
| Frog weight | −0.370908 | 0.30261 | −1.226 | 0.226 | |
| Beetle weight | −0.04681 | 0.023848 | −1.963 | 0.055c | |
| Frog weight × Beetle weight | 0.002329 | 0.00146 | 1.596 | 0.117 | |
| Beetle treatmentb | 2.011385 | 1.033049 | 1.947 | 0.057d |
Notes.
As the residual deviance was smaller than the residual degrees of freedom, a quasi-binomial error distribution (rather than a binomial error distribution) was employed. One and four live and dead beetles, respectively, were digested.
Live beetles were used as a reference.
The significance of this factor was checked using the likelihood ratio test (P = 0.028).
The significance of this factor was checked using the likelihood ratio test (P = 0.029).
Disussion
Here, I found that Pe. nigromaculatus frequently rejected Ph. jessoensis without attempting to swallow the beetles (Fig. 1). Around 70% of frogs stopped attacking both live and dead beetles immediately after touching the beetles with their tongues. Although the high-speed release of hot noxious chemicals (bombing) protected Ph. jessoensis from digestion by the frog Pe. nigromaculatus (Figs. 1 and 3; Video S4), my findings support the hypothesis that bombing is not essential for Ph. jessoensis to successfully evade being swallowed by Pe. nigromaculatus (Figs. 1 and 3; Video S3). Which factors, then, stopped the frogs from attacking? Three potential reasons can be considered: (1) the frogs recognised the warning colouration of the beetles; (2) the body size of the beetles was too large for the frog to accommodate; and (3) the frogs reflexively avoided the beetles after detecting toxic substances or other deterrent characteristics on the beetles’ body surfaces.
The bombardier beetle Ph. jessoensis does have a striking yellow and black pattern on its body that could serve as warning colouration (Fig. 1), although this has not been empirically demonstrated. Anuran predators can avoid toxic prey by recognising certain colours or other morphological characteristics and then ignoring those prey (Brower, Brower & Westcott, 1960; Brower & Brower, 1962; Dean, 1980a; Taniguchi et al., 2005; Ito, Taniguchi & Billen, 2016). In fact, 34.1 and 29.2% of frogs did not seek to attack live or dead beetles, respectively, before the feeding experiments commenced, suggesting that Pe. nigromaculatus may recognise the body pattern and shape of Ph. jessoensis and interpret these as warning signals. However, frogs that ignored Ph. jessoensis did not respond to other prey (i.e., T. molitor larvae). Therefore, the experimental conditions used may not be appropriate for analysing foraging by certain frogs. Alternatively, the yellow-and-black pattern of Ph. jessoensis may serve as disruptive camouflage; flightless Ph. jessoensis walk on soil of forest edges, grasslands, and agricultural fields. Further work is needed to explore the significance of Ph. jessoensis colour as a defensive trait.
GLM analysis indicated that beetle size was correlated with beetle-swallowing frequency of frogs (Table 1). Pelophylax nigromaculatus has been reported to spit out large prey that they were unable to swallow after taking the prey into their mouths (Honma, 2004; Honma, Oku & Nishida, 2006). However, 67.9% of the frogs in the experiment with live beetles and 71.4% of the frogs in the experiment with dead beetles stopped their predatory attacks before taking the beetles into their mouths (Figs. 1 and 2; Video S3, Video S5). Thus, my results do not provide strong evidence that the frogs could not ingest large beetles. Rather, the amount of chemicals on the beetle body surface may increase with beetle size (see below).
The rapid responses of the frog species Pe. nigromaculatus to bombardier beetles (Fig. 2) could be considered a reflex action of the frogs’ tongues (cf. Kumai, 1981a; Kumai, 1981b; Hirakawa, 1989). Frogs are known to use their tongues as a chemical detector (Dean, 1980b; Kumai, 1981a; Kumai, 1981b; Barlow, 1998) as well as a prey-catching tool (Noel et al., 2017). For example, chemical or electrical stimulation of the tongue can generate reflex responses in Pe. nigromaculatus (Kusano & Sato, 1957; Kumai, 1981a; Kumai, 1981b; Suzuki & Nomura, 1985; Takeuchi, Satou & Ueda, 1986; Hirakawa, 1989). Because Pe. nigromaculatus is a generalist predator that can attack a variety of arthropods within its field of view (Hirai & Matsui, 1999; Honma, 2004; Honma, Oku & Nishida, 2006; Sano & Shinohara, 2012; Sarashina, Yoshihisa & Yoshida, 2011), Pe. nigromaculatus may have evolved specific responses to toxic prey to avoid being injured by trying to eat them. The results of this study suggest that the tongues of Pe. nigromaculatus may be able to rapidly detect toxic substances or other characteristics on the body surface of the bombardier beetles, and the frogs subsequently avoid the beetles to prevent themselves from being bombed and injured. Previous studies have focused on how frogs and toads use their tongues to catch prey (Ewert, 1970; Nishikawa & Gans, 1996; Monroy & Nishikawa, 2010; Noel et al., 2017). Few reports have explored how frogs and toads use their tongues to detect toxins in/on potential prey (but see Dean, 1980b). Therefore, the tongue responses that I describe in Pe. nigromaculatus will likely be evident in other frogs such as the tree frog Hyla japonica (Günther) (Taniguchi et al., 2005; Ito, Taniguchi & Billen, 2016; Matsubara & Sugiura, 2017).
Conclusions
In one study, the chemicals produced by bombardier beetles’ bombing did not stimulate the tongues of toads any less intensely than did the heat from the chemical reaction (Dean, 1980b). Other than this study, the relative importance of the toxic chemicals and heat produced by bombing for the successful escape of bombardier beetles from predators has been largely unexplored. My results support the hypothesis that bombing is not essential when bombardier beetles defend themselves against frog attacks. Furthermore, my findings suggest that (cool) toxic chemicals on the beetles’ bodies alone may cause frogs to desist from an attack; thus, chemicals on the body may serve as a primary defence and bombing as a secondary defence. Successful defence by chemicals on the body would reduce the costs associated with bombing, suggesting that beetles may have evolved to use chemicals on the body surface as their primary defence. However, further experiments are required to validate this hypothesis; for example, dead beetles with body surfaces cleaned of chemicals, or palatable prey coated with toxic chemicals, should be offered to frogs.
Many prey animals exhibit multiple anti-predator defences (Edmunds, 1974). Predation pressures imposed by different enemies may encourage prey to diversify defence strategies. Further studies are needed.
Supplemental Information
The beetle discharged toxic chemicals when its eggs were pinched with a pair of forceps.
The frog stopped the attack immediately after its tongue touched the beetle.
The frog took the beetle into its mouth but immediately spat out the beetle.
The frog stopped its attack immediately after its tongue touched the dead beetle.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to K. Sakagami, K. Uchida, and A. Ushimaru for providing valuable information about the collection sites. I thank K. Sakagami, W. Higashikawa, and M. Ito for helping to collect the study animals, and S. Matsubara and Y. Maeda for helping to maintain them. T. Takanashi provided valuable advice on this research. M. Bulbert and two anonymous reviewers provided helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Funding Statement
This study was financially supported by the Fujiwara Natural History Foundation (H28-23) and the Graduate School of Agriculture, Kobe University. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Additional Information and Declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Author Contributions
Shinji Sugiura conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools, prepared figures and/or tables, authored or reviewed drafts of the paper, approved the final draft.
Animal Ethics
The following information was supplied relating to ethical approvals (i.e., approving body and any reference numbers):
The experiments were undertaken in accordance with the Kobe University Animal Experimentation Regulations (Kobe University’s Animal Care and Use Committee, 27–01, 30–01).
Data Availability
The following information was supplied regarding data availability:
References
- Aneshansley et al. (1969).Aneshansley DT, Eisner T, Widom JM, Widom B. Biochemistry at 100 °C: explosive secretory discharge of bombardier beetles (Brachinus) Science. 1969;165:61–63. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3888.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt et al. (2015).Arndt EM, Moore W, Lee WK, Ortiz C. Mechanistic origins of bombardier beetle (Brachinini) explosion-induced defensive spray pulsation. Science. 2015;348:563–567. doi: 10.1126/science.1261166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow (1998).Barlow LA. The biology of amphibian taste. In: Heatwole H, Dawley E, editors. Amphibian biology, volume 3: sensory perception. Surrey Beatty & Sons; Chipping Norton: 1998. pp. 743–782. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacci et al. (2008).Bonacci T, Aloise G, Brandmayr P, Brandmayr TZ, Capula M. Testing the predatory behaviour of Podarcis sicula (Reptilia: Lacertidae) towards aposematic and non-aposematic preys. Amphibia-Reptilia. 2008;29:449–453. doi: 10.1163/156853808785111986. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Brower & Brower (1962).Brower JVZ, Brower LP. Experimental studies of mimicry. 6. The reaction of toads (Bufo terrestris) to honeybees (Apis mellifera) and their dronefly mimics (Eristalis vinetorum) The American Naturalist. 1962;96:297–307. doi: 10.1086/282237. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Brower, Brower & Westcott (1960).Brower LP, Brower JVZ, Westcott PW. Experimental studies of mimicry. 5. The reactions of toads (Bufo terrestris) to bumblebees (Bombus americanorum) and their robberfly mimics (Mallophora bomboides), with a discussion of aggressive mimicry. The American Naturalist. 1960;94:343–355. doi: 10.1086/282137. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bura, Kawahara & Yack (2016).Bura BL, Kawahara A, Yack J. A comparative analysis of sonic defences in Bombycoidea caterpillars. Scientific Reports. 2016;6:31469. doi: 10.1038/srep31469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper & Owen-Smith (1986).Cooper SM, Owen-Smith N. Effects of plant spinescence on large mammalian herbivores. Oecologia. 1986;68:446–455. doi: 10.1007/BF01036753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean (1979).Dean J. Defensive reaction time of bombardier beetles: an investigation of the speed of a chemical defense. Journal of Chemical Ecology. 1979;5:691–701. doi: 10.1007/BF00986554. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dean (1980a).Dean J. Encounters between bombardier beetles and two species of toads (Bufo americanus, B. marinus): speed of prey-capture does not determine success. Journal of Comparative Physiology. 1980a;133:41–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00660180. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dean (1980b).Dean J. Effects of thermal and chemical components of bombardier beetle chemical defense: glossopharyngeal response in two species of toads (Bufo americanus, B. marinus) Journal of Comparative Physiology. 1980b;133:51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00660181. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Derby (2007).Derby CD. Escape by inking and secreting: marine molluscs avoid predators through a rich array of chemicals and mechanisms. Biological Bulletin. 2007;213:274–289. doi: 10.2307/25066645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds (1974).Edmunds M. Defense in animals. Longman; Harlow: 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Eisner (1958).Eisner T. The protective role of the spray mechanism of the bombardier beetle, Brachynus ballistarius Lec. Journal of Insect Physiology. 1958;2:215–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(58)90006-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner (2003).Eisner T. For love of insects. The Belknap Press of the Harvard University Press; Cambridge: 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eisner & Aneshansley (1999).Eisner T, Aneshansley DJ. Spray aiming in the bombardier beetle: photographic evidence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96:9705–9709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner et al. (2006).Eisner T, Aneshansley DJ, del Campo ML, Eisner M, Frank JH, Deyrup M. Effect of bombardier beetle spray on a wolf spider: repellency and leg autotomy. Chemoecology. 2006;16:185–189. doi: 10.1007/s00049-006-0346-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner & Dean (1976).Eisner T, Dean J. Ploy and counterploy in predator–prey interactions: orb-weaving spiders versus bombardier beetles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1976;73:1365–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner, Eisner & Aneshansley (2005).Eisner T, Eisner M, Aneshansley DJ. Pre-ingestive treatment of bombardier beetles by jays: food preparation by “anting” and “sand-wiping”. Chemoecology. 2005;15:227–233. doi: 10.1007/s00049-005-0316-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner, Eisner & Siegler (2005).Eisner T, Eisner M, Siegler M. Secret weapons: defenses of insects, spiders, scorpions, and other many-legged creatures. The Belknap Press of the Harvard University Press; Cambridge: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Eisner & Meinwald (1966).Eisner T, Meinwald J. Defensive secretions of arthropods. Science. 1966;153:1341–1350. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3742.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endler (1991).Endler JA. Interactions between predators and prey. In: Krebs JR, Davies NB, editors. Behavioural ecology: an evolutionary approach. Blackwell; London, Paris, Berlin, Vienna: 1991. pp. 169–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ewert (1970).Ewert JP. Neural mechanisms of prey-catching and avoidance behaviour in the toad (Bufo bufo L.) Brain, Behavior and Evolution. 1970;3:36–56. doi: 10.1159/000125462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, Lee & Ishii (2012).Fujisawa T, Lee CM, Ishii M. Species diversity of ground beetle assemblages in the distinctive landscapes of the Yodo River flowing through northern Osaka Prefecture, central Japan. Japanese Journal of Environmental Entomology and Zoology. 2012;23:89–100. doi: 10.11257/jjeez.23.89. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Habu & Sadanaga (1965).Habu A, Sadanaga K. Illustrations for identification of larvae of the Carabidae found in cultivated fields and paddy-fields (III) Bulletin of the National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Series C: Plant Pathology and Entomology. 1965;19:81–216. (in Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hirai (2002).Hirai T. Ontogenetic change in the diet of the pond frog, Rana nigromaculata. Ecological Research. 2002;17:639–644. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1703.2002.00521.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai & Matsui (1999).Hirai T, Matsui M. Feeding habits of the pond frog, Rana nigromaculata, inhabiting rice fields in Kyoto, Japan. Copeia. 1999;1999:940–947. doi: 10.2307/1447969. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakawa (1989).Hirakawa T. A study of averaged waves of reflex discharges in the frog hypoglossal nerve elicited by electrical stimulation of glossopharyngeal afferent. Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society. 1989;43:693–709. doi: 10.2504/kds.43.693. (in Japanese with English summary) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Honma (2004).Honma A. MOMO VideoArchives: momo040902cj01b. 2004. http://movspec.mus-nh.city.osaka.jp/ethol/showdetail.php?movieid=momo040902cj01b. [28 January 2018]. http://movspec.mus-nh.city.osaka.jp/ethol/showdetail.php?movieid=momo040902cj01b
- Honma, Oku & Nishida (2006).Honma A, Oku S, Nishida T. Adaptive significance of death feigning posture as a specialized inducible defence against gape-limited predators. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Science. 2006;273:1631–1636. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar & Lev-Yadun (2005).Inbar M, Lev-Yadun S. Conspicuous and aposematic spines in the animal kingdom. Naturwissenschaften. 2005;92:170–172. doi: 10.1007/s00114-005-0608-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitani & Yano (1994).Ishitani M, Yano K. Species composition and seasonal activities of ground beetles (Coleoptera) in a fig orchard. Japanese Journal of Entomology. 1994;62:201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Taniguchi & Billen (2016).Ito F, Taniguchi K, Billen J. Defensive function of petiole spines in queens and workers of the formicine ant Polyrhachis lamellidens (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) against an ant predator, the Japanese tree frog Hyla japonica. Asian Myrmecology. 2016;8:1–6. doi: 10.20362/am.008014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jung et al. (2012).Jung JK, Kim ST, Lee SY, Park CK, Lee EH, Lee JH. Ground beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) assemblage in the urban landscape, Korea. Journal of Ecology and Field Biology. 2012;35:79–89. doi: 10.5141/JEFB.2012.012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa (1996).Kanehisa K. Secretion of defensive substance by Carabidae and Brachinidae. Bulletin of the Research Institute for Bioresources, Okayama University. 1996;4:9–23. (in Japanese with English summary) [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa & Murase (1977).Kanehisa K, Murase M. Comparative study of the pygidial defensive systems of carabid beetles. Applied Entomology and Zoology. 1977;12:225–235. doi: 10.1303/aez.12.225. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Komaki et al. (2015).Komaki S, Igawa T, Lin SM, Tojo K, Min MS, Sumida M. Robust molecular phylogeny and palaeodistribution modelling resolve a complex evolutionary history: glacial cycling drove recurrent mtDNA introgression among Pelophylax frogs in East Asia. Journal of Biogeography. 2015;42:2159–2171. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12584. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kumai (1981a).Kumai T. Reflex response of the hypoglossal nerve induced by gustatory stimulation of the frog tongue. Brain Research. 1981a;208:432–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90572-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumai (1981b).Kumai T. Reflex response of the hypoglossal nerve induced by chemical stimulation of the tongue and electrical stimulation of the glossopharyngeal nerve in the frog. Japanese Journal of Physiology. 1981b;31:625–637. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.31.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano & Sato (1957).Kusano K, Sato M. Properties of fungiform papillae in frog’s tongue. Japanese Journal of Physiology. 1957;157:324–338. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larochelle (1974a).Larochelle A. The American toad as champion carabid beetle collector. The Pan-Pacic Entomologist. 1974a;50:203–204. [Google Scholar]
- Larochelle (1974b).Larochelle A. Carabid beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) as prey of North American frogs. The Great Lakes Entomolosit. 1974b;7:147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lev-Yadun (2001).Lev-Yadun S. Aposematic (warning) coloration associated with thorns in higher plants. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2001;210:385–388. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2001.2315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev-Yadun (2009).Lev-Yadun S. Aposematic (warning) coloration in plants. In: Baluska F, editor. Plant-environment interactions. From sensory plant biology to active plant behavior. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2009. pp. 167–202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liu et al. (2010).Liu K, Wang F, Chen W, Tu L, Min MS, Bi K, Fu J. Rampant historical mitochondrial genome introgression between two species of green pond frogs, Pelophylax nigromaculatus and P. plancyi. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 2010;10:201. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda & Matsui (1999).Maeda N, Matsui M. Frogs and toads of Japan. Revised edition Bun-ichi Sogo Shuppan; Tokyo: 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara & Sugiura (2017).Matsubara S, Sugiura S. Chemical defence of turnip sawfly larvae against Japanese tree frogs. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology. 2017;20:225–227. doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2017.01.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi & Okuyama (2015).Matsuhashi T, Okuyama F. Frogs and toads of Japan. Yamakei; Tokyo: 2015. (in Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Mithöfer & Boland (2012).Mithöfer A, Boland W. Plant defense against herbivores: chemical aspects. Annual Review of Plant Biology. 2012;63:431–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy & Nishikawa (2010).Monroy JA, Nishikawa K. Prey capture in frogs: alternative strategies, biomechanical trade-offs, and hierarchical decision making. Journal of Experimental Zoology. 2010;315:61–71. doi: 10.1002/jez.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori (2008).Mori I. Predation by introduced bullfrog Rana catesbeiana on a breeding male of Rhacophorus schlegelii and the other animals. Bulletin of the Okayama Prefecture Nature Conservation Center. 2008;16:61–62. (in Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa & Gans (1996).Nishikawa KC, Gans C. Mechanisms of tongue protraction and narial closure in the marine toad Bufo marinus. Journal of Experimental Biology. 1996;199:2511–2529. doi: 10.1242/jeb.199.11.2511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel et al. (2017).Noel AC, Guo HY, Mandica M, Hu DL. Frogs use a viscoelastic tongue and non-Newtonian saliva to catch prey. Journal of the Royal Society Interface. 2017;14 doi: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0764. Article 20160764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohwaki, Kaneko & Ikeda (2015).Ohwaki A, Kaneko Y, Ikeda H. Seasonal variability in the response of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) to a forest edge in a heterogeneous agricultural landscape in Japan. European Journal of Entomology. 2015;112:135–144. doi: 10.14411/eje.2015.022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team (2016).R Development Core Team R, a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing 2016
- Ruxton, Sherratt & Speed (2004).Ruxton GD, Sherratt TN, Speed MP. Avoiding attack: the evolutionary ecology of crypsis, aposematism, and mimicry. Oxford University Press; Oxford: 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sano & Shinohara (2012).Sano M, Shinohara M. Species comparison of frogs food habits during mating seasons in Uenohara, Yamanashi Pref., Japan. Bulletin of Teikyo University of Science and Technology. 2012;8:101–111. (in Japanese with English summary) [Google Scholar]
- Sarashina, Yoshihisa & Yoshida (2011).Sarashina M, Yoshihisa Y, Yoshida T. Stomach contents of invasive Black-spotted Pond frog (Rana nigromaculata) in urban landscape of Sapporo City. Journal of Rakuno Gakuen University. 2011;36:81–86. (in Japanese with English summary) [Google Scholar]
- Skelhorn & Rowe (2006).Skelhorn J, Rowe C. Taste-rejection by predators and the evolution of unpalatability in prey. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 2006;60:550–555. doi: 10.1007/s00265-006-0199-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura (2016).Sugiura S. Bagworm bags as portable armour against invertebrate predators. PeerJ. 2016;4:e1686. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura & Sato (2018).Sugiura S, Sato T. Successful escape of bombardier beetles from predator digestive systems. Biology Letters. 2018;14 doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2017.0647. Article 20170647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura & Takanashi (2018).Sugiura S, Takanashi T. Hornworm counterattacks: defensive strikes and sound production in response to invertebrate attackers. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 2018;123:496–505. doi: 10.1093/biolinnean/blx156. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura & Yamazaki (2014).Sugiura S, Yamazaki K. Caterpillar hair as a physical barrier against invertebrate predators. Behavioral Ecology. 2014;25:975–983. doi: 10.1093/beheco/aru080. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki & Nomura (1985).Suzuki H, Nomura H. Input–output relation in gustatory linguo-hypoglossal reflex in the frog. Matsumoto Shigaku: Journal of the Matsumoto Dental College Society. 1985;11:13–17. (in Japanese with English summary) [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, Satou & Ueda (1986).Takeuchi H, Satou M, Ueda K. EMG analysis of head muscle during naturally-occurring and electrically- evoked snapping, rejecting and avoiding behavior in the Japanese toad . Abstract 992Zoological Science. 1986;3 [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi et al. (2005).Taniguchi K, Maruyama M, Ichikawa T, Ito F. A case of Batesian mimicry between myrmecophilous staphylinid beetle, Pella comes, and its host ant, Lasius (Dendrolasius) spathepus: an experiment using the Japanese tree frog Hyla japonica as a real predator. Insectes Sociaux. 2005;52:320–322. doi: 10.1007/s00040-005-0813-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji et al. (2011).Tsuji M, Ushimaru A, Osawa T, Mitsuhashi H. Paddy-associated frog declines via urbanization: a test of the dispersal-dependent-decline hypothesis. Landscape and Urban Planning. 2011;103:318–325. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2011.08.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, Kurosawa & Sato (1985).Ueno S, Kurosawa Y, Sato M, editors. The Coleoptera of Japan in color II. Hoikusha; Osaka: 1985. (in Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Williams et al. (2010).Williams BL, Hanifin CT, Brodie Jr ED, Brodie III ED. Tetrodotoxin affects survival probability of rough-skinned newts (Taricha granulosa) faced with TTX-resistant garter snake predators (Thamnophis sirtalis) Chemoecology. 2010;20:285–290. doi: 10.1007/s00049-010-0057-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yahiro et al. (1992).Yahiro K, Fujimoto T, Tokuda M, Yano K. Species composition and seasonal abundance of ground beetles (Coleoptera) in paddy fields. Japanese Journal of Entomology. 1992;60:805–813. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The beetle discharged toxic chemicals when its eggs were pinched with a pair of forceps.
The frog stopped the attack immediately after its tongue touched the beetle.
The frog took the beetle into its mouth but immediately spat out the beetle.
The frog stopped its attack immediately after its tongue touched the dead beetle.
Data Availability Statement
The following information was supplied regarding data availability: