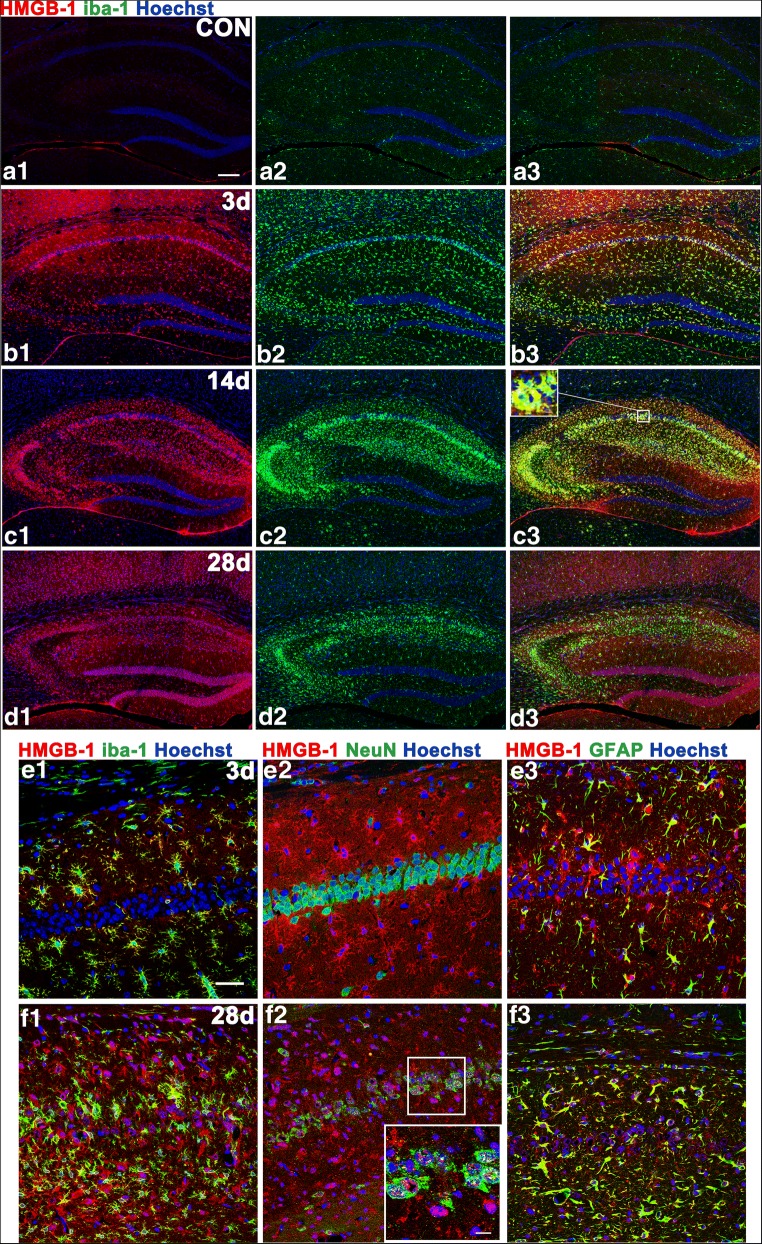
Fig. 3.
Hippocampal expression of HMGB-1 at various time points and in different cell types. In control animals, there were hardly any HMGB-1-immunoreactive cells. HMGB-1 labeling was intense at 14 days after SE and remained to some extent at 28 days. In the acute phase, the HMGB-1-immunoreactive product was found mainly in the cytoplasm of MG/MΦ and astrocytes. In the chronic phase (28 days), HMGB-1 immunoreactivity was also observed in CA1 pyramidal neurons undergoing karyorrhexis. (A1–D3) The distribution of HMGB-1-positive MG/MΦ in the hippocampi of control animals (A1–A3) at 3 days (B1–B3), 14 days (C1–C3), and 28 days (D1–D3) after SE. The inset of (C3) shows strong HMGB-1 labeling in MG/MΦ. (E1–F3) Colocalization of HMGB-1 immunoreactivity with cell-type markers (NeuN for neurons, GFAP for astrocytes, and iba-1 for MG/MΦ) in CA1 at 3 and 28 days. The inset of (F2) shows a higher-magnification view of HMGB-1-labeled karyorrhectic CA1 pyramidal neurons. (A1–B1–C1–D1), HMGB-1 labeling (red); (A2–B2–C2–D2), iba-1 labeling (green); (A3–B3–C3–D3) merged images. Scale bars: (A1–D3) 200 μm; (C) (inset) 12.5 μm; (E1–F3) 50 μm; (F2) (inset) 12.5 μm