Abstract.
Impaired oxygen delivery and/or consumption in the retinal tissue underlies the pathophysiology of many retinal diseases. However, the essential tools for measuring oxygen concentration in retinal capillaries and studying oxygen transport to retinal tissue are still lacking. We show that two-photon phosphorescence lifetime microscopy can be used to map absolute partial pressures of oxygen () in the retinal capillary plexus. Measurements were performed at various retinal depths in anesthetized mice under systemic normoxic and hyperoxic conditions. We used a newly developed two-photon phosphorescent oxygen probe, based on a two-photon absorbing platinum tetraphthalimidoporphyrin, and commercially available optics without correction for optical aberrations of the eye. The transverse and axial distances within the tissue volume were calibrated using a model of the eye’s optical system. We believe this is the first demonstration of in vivo depth-resolved imaging of in retinal capillaries. Application of this method has the potential to advance our understanding of oxygen delivery on the microvascular scale and help elucidate mechanisms underlying various retinal diseases.
Keywords: two-photon microscopy, phosphorescence quenching, oxygen partial pressure, retinal imaging
1. Introduction
The retina has complex microvascular architecture and requires ample oxygen delivery to maintain its high metabolic activity.1 Insufficient blood supply to the retina can cause impaired vision and blindness2,3 due to common retinal diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy. According to the National Eye Institute, in the United States alone 7.7 million people with diabetic retinopathy were reported in 2010, and this number is expected to double by 2050.4 However, despite the urgent need to prevent vision loss, the knowledge of how disease development and progression is related to impaired oxygen delivery and consumption is still limited.5 This knowledge gap persists in part due to the lack of techniques for measuring oxygen concentration in the retina with high spatiotemporal resolution. Previous studies have shown that retinal in rodents varies across the total depth of the retinal tissue, although less so in the inner retina.6–8 However, physiological challenges and/or diseases may differentially affect in the inner retinal capillary layers. For example, light flicker stimulation differentially affects vessel dilation and blood flux at the inner retina capillary layers in rats.9 Recent studies have also demonstrated elevation in the inner-retinal levels in diabetic rats10 as well as variations in perfusion of different inner-retinal capillary layers in humans affected by diabetic retinopathy.11,12 Therefore, there is a need for development of techniques for depth-resolved measurements in the retina, which will help in unraveling mechanisms underlying neurovascular coupling and retinal diseases.
Various methods have been reported for in vivo assessment of retinal oxygenation in rodents. Currently, oxygen microelectrode is considered the gold standard of retinal extravascular (tissue) measurements with high depth resolution.6,7 However, this technique is invasive, and measurements are limited to single point locations in the retina, where the local microenvironment is potentially being disturbed by the electrodes. Numerous techniques for assessment of retinal intravascular oxygenation are based on optical absorption spectroscopy of hemoglobin, including spectrophotometric oximetry,13 photoacoustic imaging,14 and visible light optical coherence tomography.15–17 While all these methods can be relatively easily translated to the clinic, they suffer from common limitations. First, hemoglobin-based techniques report oxygen only in the blood, but not at the sites of the actual oxygen consumption. Second, hemoglobin-based measurements are better suited for accessing oxygenation in major arteries and veins and do not provide reliable measurements within retinal microvessels and capillaries.
Another optical approach to imaging retinal intravascular oxygenation is based on oxygen-dependent quenching of phosphorescence.18 Originally, this method was used for assessment of oxygen levels in retinal and choroidal vessels by wide-field time-domain phosphorescence lifetime imaging,19 and later extended to the frequency domain.20 A number of retinal oxygen imaging studies by us and other groups followed, typically using gated CCD cameras and phosphorescent probes based on Pd porphyrins20–25 and, more recently, an Ir(III) complex.26 By using the laser-line illumination approach, we have also demonstrated the feasibility of 3-D imaging of both the retinal vascular 27,28 and retinal extravascular with high lateral resolution,29,30 though depth resolution was limited by scattering. To date, depth-resolved measurements in the retinal microvasculature with truly microscopic resolution have not been demonstrated. Such measurements are essential for assessment of oxygenation in capillaries where the earliest retinal vasculopathies occur, providing critical information about oxygen delivery to the retinal cells.
Here, we performed for the first time high-resolution absolute measurements in superficial, intermediate, and deep retinal microvascular plexus by two-photon phosphorescence lifetime microscopy (2PLM)31 using a recently developed probe based on a bright two-photon-absorbing platinum tetraphthalimidoporphyrin.32 We measured intravascular in major arteries and veins as well as in precapillary arterioles, capillaries, and postcapillary venules within the retinal microvascular plexus in the retina of healthy anesthetized mice under normoxia and hyperoxia. Noteworthy, our two-photon microscope33 was equipped with a commercially available objective lens with a long working distance, having no additional tools (e.g., adaptive optics) for correcting optical aberrations of the eye. We constructed the ray transfer matrix of the mouse eye based on optical parameters (refractive index, thickness, curvature, etc.) that were previously reported in the literature, and accordingly calibrated the lateral and axial retinal distances in our measurements. The new method has the potential to provide information that will be invaluable for understanding retinal vasculopathies occurring in diabetic retinopathy and similar diseases of the eye.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Optical Setup
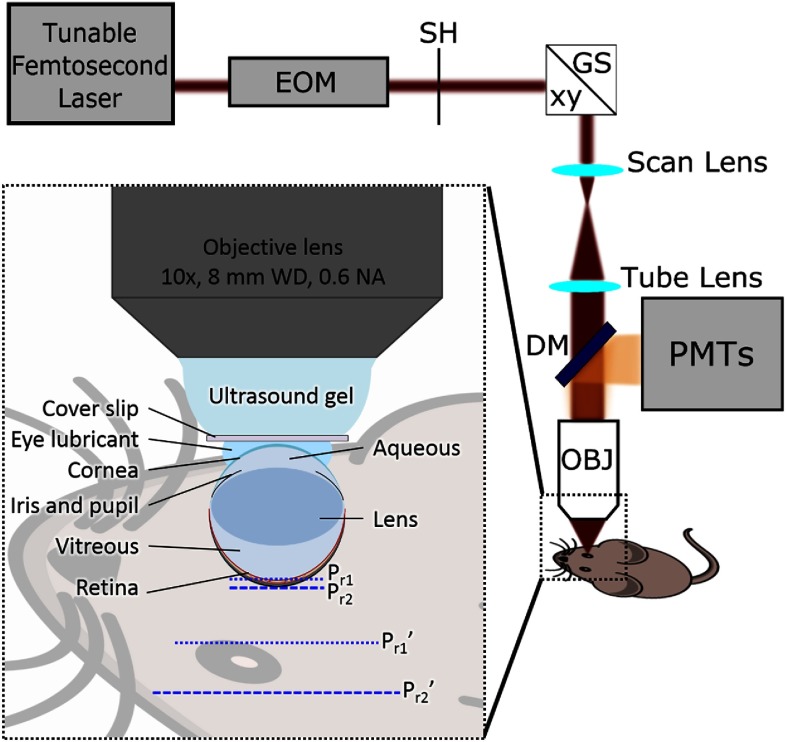
The custom-built 2PM system (Fig. 1)33 was used for both 3-D retinal microvasculature angiography and measurements of . All measurements were performed in the dark.
Fig. 1.
Optical setup for 2PM imaging of in mouse retinal microvasculature. EOM, electro-optic modulator; SH, shutter; GS, galvanometer scanner; DM, dichroic mirror; OBJ, microscope objective lens; PMTs, four-channel detector unit. The inset illustrates the coupling of the long-working-distance microscope objective with the mouse eye and eye anatomical features considered, when modeling the propagation of the optical rays. and are top and bottom retina planes, respectively. and are virtual images of and , respectively, created by the compound optical system of the mouse eye.
Two-photon excitation was performed using a tunable femtosecond laser (InSight, Spectra-Physics, 680 to 1300 nm, 80 MHz rep. rate). The power level and temporal gating of the excitation beam were controlled by an electro-optic modulator (EOM) (ConOptics, 350 to 160). The beam was steered in the lateral plane ( and ) by two galvanometer mirrors (Cambridge Technologies, 6215HB) and focused onto a desired retina layer by an objective lens (Olympus, XLPLN10XSVMP, , 0.6 NA, water immersion), which was separated from the mouse cornea by transparent ultrasound gel, a glass cover slip, and a thin layer of eye lubricant (see Fig. 1 inset). The working distance () of the objective lens was chosen to be significantly longer than the physical cornea-to-retina distance (),34–36 since the apparent optical depth of the retina position is higher due to the optical properties of the eye. The emission originating from the retinal microvasculature was collected by the objective lens, reflected by an epidichroic mirror (Semrock Inc., FF875-Di01-25x36), passed through a short-pass filter (Semrock Inc., FF01-890/SP-50), and split into two channels. One was directed to a photon-counting photomultiplier tube (PMT) (PMT, Hamamatsu, H10770PA-50) through a bandpass filter (Semrock Inc., FF01-795/150-25) and used for recording the phosphorescence of the probe. Another was passed through a band-pass filter (Semrock Inc., FF01-525/50-25) and directed into analog PMT (Hamamatsu, R3896), for recording the fluorescence of vascular markers [e.g., fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran] in order to construct microvascular angiograms of the regions of interest.
2.2. Animal Preparation
All surgeries and experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the guidelines established by the MGH Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). We used three female C57BL/six mice (Charles River Laboratories, 3-months old, 22 to 23 g). Mice were anesthetized during surgery using 1.5% to 2% isoflurane in a mixture of air and oxygen, as they underwent tracheotomy for ventilation and femoral artery cannulation for measuring the blood pressure and heart rate, injection of the contrast agents (probes), and blood gas measurements. The body temperature was maintained at 37°C using a heating blanket and monitored by a rectal thermometer.
Prior to imaging, the pupils were dilated using 1% tropicamide eye drops, and an eye lubricant gel (Goniovisc Hypromellose Ophthalmic solution USP 25 mg, 2.5%) was applied over the cornea. Animals were placed in a prone position; the head was slightly tilted and restrained using a metal bar previously attached to the skull with dental cement to minimize motion artifacts induced by respiration and heartbeat. A microscope coverslip was placed over the right cornea. The coverslip was in contact with the eye lubricant gel, providing a flat surface, and it was optically coupled with the objective lens by using ultrasound gel. A mixture of the phosphorescent probe [molecular weight (MW) , 0.1 mL, ] and dextran-conjugated fluorescein (FITC, 0.1 mL, ) was administered into the blood plasma via a femoral artery cannula. The mice were kept anesthetized during imaging using 1% isoflurane in a mixture of air and oxygen. The average power limit for ocular safety (based on ANSI 2000)37 was calculated to be 61 mW in our imaging configuration (-long excitation gate at 950 nm). The average laser power after the objective during application of the excitation gate (high-repetition-rate pulse train) was 1.3 to 58 mW. We induced hyperoxic and normoxic conditions by manipulating the concentration in the inhaled mixture of and air (: 21% during normoxia and 100% during hyperoxia) and confirmed the results through systemic arterial blood gas measurements. The animal blood pressure (BP), heart rate, body temperature, and expired were monitored continuously during the experiments. The range of BP and systemic during the experiments were 67 to 90 mmHg and 30 to 37.5 mmHg, respectively. Surgical preparations took to 45 min and moving the animal to the microscope, positioning of the animal, injection of contrast agent, and testing blood gasses took additional 30 to 45 min.
2.3. Depth-Resolved Imaging of Retinal Microvasculature Using Two-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy
In order to visualize retinal microvasculature, high-resolution volumetric angiograms were recorded by means of 2PM fluorescence imaging of the FITC-labeled blood plasma. We started our measurements by selecting a region of interest (ROI) using an air-coupled, low-resolution objective (Olympus, XLFLUOR4x/340, , 0.28 NA, 30-mm WD) with a large field-of-view. Then we switched to a high-resolution water-immersion objective (Olympus XLPLN10XSVMP, , 0.6 NA, 8-mm WD) to record the angiograms. The excitation beam (840 nm) was raster scanned with a dwell time of . The FITC fluorescence was recorded at multiple planes through the retinal depth by translating the imaging objective along the optical axis.
2.4. Depth-Resolved Measurement of Absolute in Retinal Microvasculature Using Two-Photon Phosphorescence Lifetime Microscopy
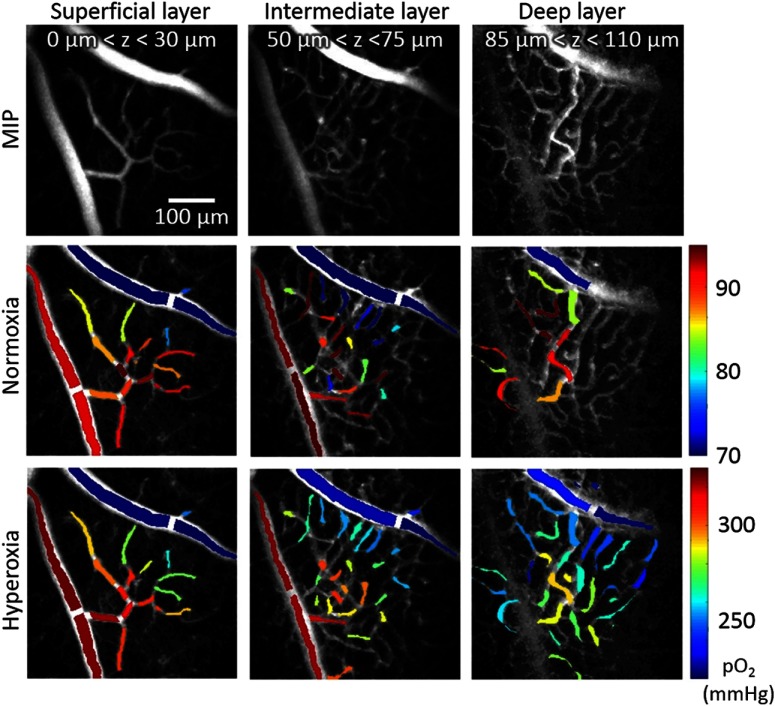
Intravascular was quantified using oxygen-dependent quenching of phosphorescence and a new probe based on a new highly two-photon absorbing Pt(II) tetraphthalimidoporphyrin.32 The probe does not cross the blood brain barrier and/or cellular membranes and can be used for both intravascular and extravascular oxygen imaging. The new probe belongs to the class of dendritically protected phosphorescent probes38 and is characterized by high two-photon absorption cross-section ( at 950 nm) and high phosphorescence quantum yield ( in aqueous solution at 22°C). Before recording phosphorescence decays in selected locations, the excitation beam (950 nm) was raster scanned in the corresponding axial plane, and a two-dimensional phosphorescence intensity image (survey image) of the ROI was recorded. This survey scan helped to position the beam at the desired location(s) for collection of the time-resolved phosphorescence data. We used -long interexcitation cycles, during which the EOM was in the opened state during the initial to provide an excitation gate, followed by a -long phosphorescence collection period. We averaged 500 interexcitation cycles during to collect the decay at each measurement location. In each imaging plane, we selected 30 to 60 locations inside the microvascular segments. Measurement of at selected locations took 5 to 10 s. The digital acquisition card (National Instruments, PCIe-6537) was used at a acquisition rate to collect PMT photon counts after the discriminator (Hamamatsu, C9744). The photon counts were binned into bins. The first of the data after the end of the excitation gate were rejected to match the probe calibration conditions and the remaining of phosphorescence decays were fitted with a single exponential function to calculate the decay time. The phosphorescence decay times (lifetimes) were converted to absolute values using a Stern–Volmer-like expression obtained in independent calibration experiments, which were performed using solutions of the probe in a physiological buffer (phosphate, 20 mM) at 36.6°C. Throughout the range assessed by our calibrations ( to 160 mmHg), the probe displayed nearly ideally linear Stern–Volmer behavior, i.e., the quenching rate constant changed linearly with . In the hyperoxia experiments, we assumed that this linearity is retained at values above 160 mmHg, and thus the hyperoxia values shown in Fig. 5 were obtained by extrapolation of the oxygen titration curve to the higher region. This extrapolation was justified by the linearity of the Stern–Volmer plot throughout the physiological range (0 to 160 mmHg) and the fact that the Stern–Volmer approximation, i.e., the assumption about zero-order of the quenching reaction with respect to quencher (), should become even more justified physically at higher oxygen concentrations. The objective was translated along the optical axis as measurements were proceeded to different axial planes (typically six to seven per experiment). The measurement results were classified according to three retinal depth ranges. The survey intensity images in each group were merged by maximum intensity projection (MIP), i.e., selecting the maximum intensity value per pixel. The resulting MIP image was contrast enhanced for better visualization and segmentation of the microvascular branches. The resulting MIP images and measurements were overlaid. Within each vessel segment, was typically measured in one to five locations (as shown in Fig. 4), then the average values were computed per vessel segment if more than one point was measured. Finally, the colors (using MATLAB colormap “jet”) were assigned to the entire vessel segments showing average in mmHg (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
distribution in the retinal microvasculature during normoxia and hyperoxia. Survey images (top) and measurements superimposed on these images during normoxia (middle row) and hyperoxia (bottom row). Columns represent different microvascular layers: superficial (first column), intermediate (middle column), and deep layer (third column). Vascular segment colors in second and third rows represent average of all point measurements within the vascular segment (colorbar in mmHg). Color-coded masks were overlaid on the gray-scaled MIP survey scan images. Both the imaging depth ranges () and the dimensions of the FOV were estimated using the calibration curves presented in Fig. 2. Note that the ranges during normoxia and hyperoxia are far apart, so we used separate color scales to aid visualization of distributions in the retinal microvasculature at these two conditions.
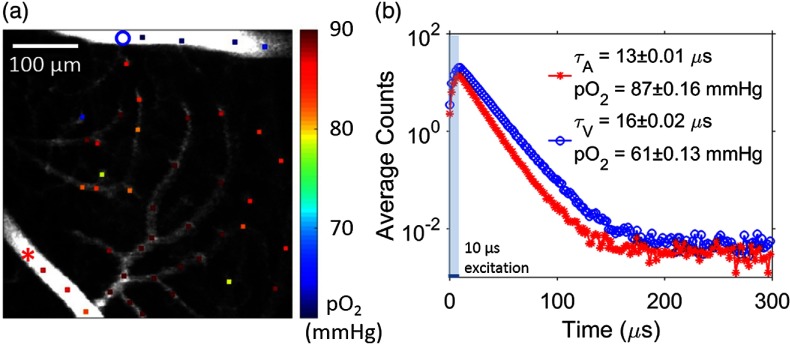
Fig. 4.
Two-photon imaging of retinal microvascular . (a) Intravascular (color coded, color bar in mmHg) at various locations within retinal microvasculature. measurement locations are marked by colored dots on the gray-scale survey intensity image. (b) Examples of phosphorescence decays measured within the artery (red) and vein (blue). The measurement locations corresponding to the decays shown were marked on image (a) with a red star and a blue circle, respectively. -long laser excitation gate was marked with the shaded area at the beginning of the interexcitation interval. Fitted phosphorescence lifetimes in arteriole and venule ( and , respectively) and their corresponding values are provided inside the panel. Values are presented as error of mean (SEM).
2.5. Statistics
The individual measurements with standard error higher than 15% were rejected. Reported values within major vessels were presented as (SD), where mean and its standard deviation were calculated across multiple measurements within a vascular segment.
3. Results
3.1. Calibration of the Compound Eye-Objective Optical System
The compound optical system, which consisted of the imaging objective and the intrinsic optical system of the eye, was calibrated in order to quantify the distances within the measured tissue volume in both lateral and axial dimensions. The optical system of the mouse eye, i.e., cornea, aqueous chamber, lens, vitreous chamber, and retina, can be represented by volumes with different refractive indices separated by curved interfaces (Fig. 1, inset).
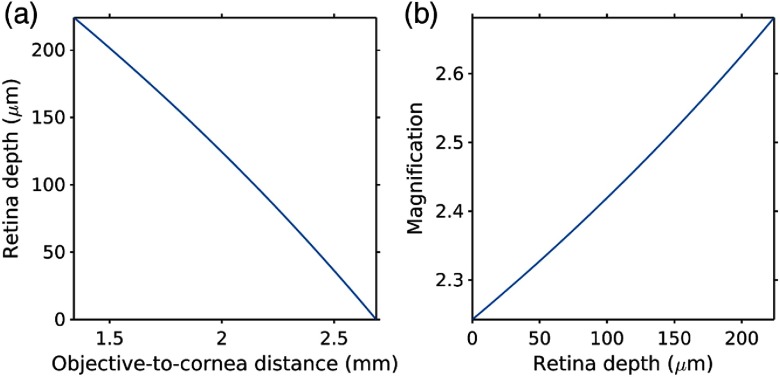
The dimensions of the mouse eye and hence its optical properties vary with age and strain. We used the previously published data34–36 to estimate the optical properties of the eye of the 3-month-old C57BL/6 mice that were used in our experiments (see Table 1) at the excitation wavelength of 950 nm. We constructed the compound ray transfer matrix of the mouse eye, using the previously published approach,36 taking into account the propagation of light through the cornea, lens, aqueous, and vitreous chambers, and the diffraction at the interfaces between them. The whole eye was modeled as a single optical element (i.e., a thick lens). Marginal rays were traced from both directions (cornea-to-retina and retina-to-cornea) in order to calculate front and back focal points, principal planes, and effective focal length (3.1 mm). We then used the lens equation to estimate the distances [Fig. 2(a)] and magnification [Fig. 2(b)] in our measurements. To determine the lateral dimensions, we focused the excitation beam on the inner-retina surface, translated the animal in - and -directions at known distances and recorded fluorescence images of the vasculature (using FITC-dextran as vascular marker) at each position. The shifts between the images in - and -dimensions were quantified and scaled with the depth-dependent magnification factor [Fig. 2(b)].
Table 1.
Optical parameters used to calculate the depth of the imaging plane within the retina and corresponding lateral magnification.34–36
| Effective focal length | Retina | Vitreous chamber | Lens | Aqueous chamber | Cornea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness/depth | |||||
| Refractive index | 1.33 | 1.33 | 1.64 | 1.33 | 1.39 |
| Radius of curvature at the interface | Anterior: ; posterior: | N/A | Anterior: 1.21 mm; posterior: | N/A | Anterior: 1.41 mm; posterior: 1.42 mm |
Fig. 2.
Calibration of the compound eye-objective optical system. (a) Calibrated retina depth as a function of the distance between the objective lens and the cornea surface. (b) Calibrated lateral magnification introduced by mouse eye optics as a function of imaging plane depth inside the retina.
The working distance of the objective lens was quickly depleted as deeper layers of retina were imaged [Fig. 2(a)]. The entire retinal depth () was accessible by adjusting the gap between the surfaces of the objective lens and the cornea from 2.7 to 1.6 mm. Upon lowering the focal plane deeper into the retina, the magnification factor induced by the eye optics changed from 2.2 to 2.7. These calibration experiments revealed that our optical system had sufficient working distance and could be used to image through the entire retinal microvascular plexus.
3.2. Depth-Resolved Imaging of Retinal Microvasculature
After the optical system was calibrated, we demonstrated the capability of our imaging setup to generate high-resolution volumetric angiograms by two-photon excited fluorescence of FITC-labeled blood plasma.
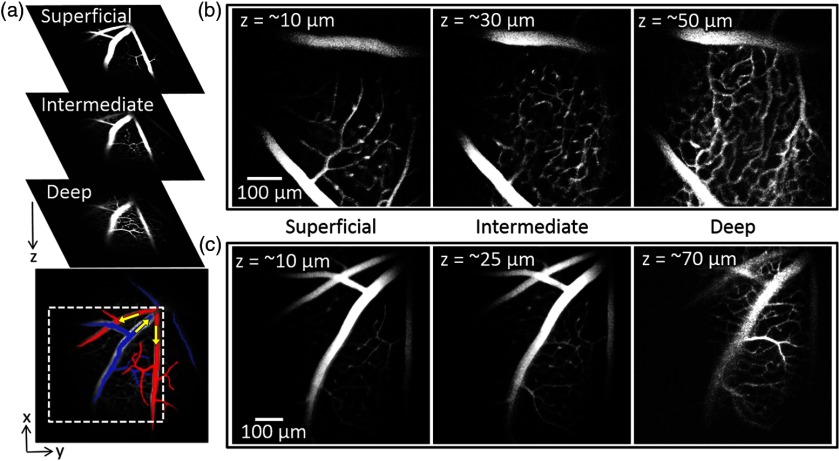
Mouse retina is holangiotic, i.e., it does not have an avascular central region, unlike human retina.39 Major retinal vessels on the superficial layer are arranged in a radiating star-like pattern consisting of arteries and veins in alternating order [Fig. 3(a)]. The total retinal thickness is ,34 and the outer retinal layers ( thick) are avascular and positioned close to the choroid plexus.15,40 The inner retinal layers ( thick) comprise three microvascular layers.41 Starting from the retinal surface, these layers are: (1) the superficial layer, which is rich in arterioles and located in the ganglion cell layer; (2) the intermediate layer, located in the inner plexiform layer; and (3) the deep layer, which is rich in venules and located in the outer plexiform layer.40–43
Fig. 3.
Two-photon depth-resolved retinal microvasculature imaging. (a) Microvascular structures, as imaged using a low-magnification objective, of the three main microvascular layers in the mouse retina: superficial, intermediate, and the deep. The superficial microvascular layer shows a radiating pattern of major arteries and veins falsely colored in red and blue, respectively. Yellow arrows indicate the direction of the blood flow. ROI is shown by white-dashed square. (b) and (c) Retinal microvasculature layers of two mice, imaged using high-magnification objective. Three imaging depths () in (b) and (c) show microvascular structure in three retinal microvascular layers. The imaging depths () shown in the graphs represent calculated values based on the calibrations (see the main text and Fig. 2 for details).
Figures 3(b) and 3(c) show images of the retinal microvasculature in two mice. The microvascular structures shown in three panels in Figs. 3(b) and 3(c) represent mostly microvascular segments from the three individual retinal microvascular layers, with little overlap with the vasculature from the adjacent microvascular layers. This confirms that our setup is capable of high-resolution 3-D imaging in the eye and able to distinguish between individual arterioles, venules, and capillaries from different microvascular layers as well as between major arteries and veins.
3.3. Depth-Resolved Measurement of in Retinal Microvasculature
We quantified absolute in the blood-plasma using the phosphorescence quenching method.
A representative phosphorescence intensity image and the locations of the local microvascular measurements in the superficial layer are shown in Fig. 4(a). was measured in a large set of microvascular segments within field-of-view (FOV), including in arterioles, venules, and capillaries. Representative phosphorescence decays (average photon counts during interexcitation interval of ) corresponding to a major artery and a vein under normoxia (systemic arterial according to blood gas analyzer) are shown in Fig. 4(b). These decays were fitted with single exponentials to derive the phosphorescence lifetimes and subsequently the values.
Depth-resolved measurements in the retinal microvasculature, performed in the same mouse during normoxia and hyperoxia, are shown in Fig. 5. We measured in a major artery, a major vein, a number of arterioles, venules, and capillaries within the superficial, intermediate, and deep retinal microvascular plexus. During normoxia, the mean values in the major artery and vein were () and (), respectively. The arterial value was consistent with the systemic arterial , measured using a blood gas analyzer. Longitudinal gradients, starting from high in the major artery at the superficial retinal layer, could be visualized along the precapillary arterioles as approaching lower values in the capillaries close to the postcapillary venules, and finally to the major vein.
We subsequently perturbed the microvascular oxygenation in the retina by inducing hyperoxia, whereby the systemic arteriolar was increased to 334 mmHg. Similar to the measurements under normoxia, the longitudinal gradients of intravascular could be visualized between the major artery (, ) and vein (, ) in the superficial retinal layer, i.e., the small vascular segments close to the major artery were more oxygenated than those close to the major vein.
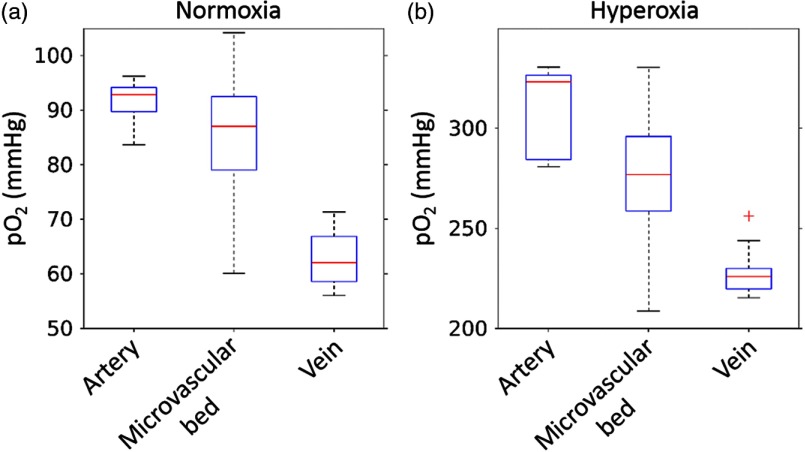
The values in the major artery and vein, as well as in the combined superficial, intermediate, and deep microvascular plexus (microvascular bed) under normoxia and hyperoxia are shown in Fig. 6. During normoxia, the median values in the major artery, vein, and in the microvascular bed were 93, 62, and 87 mmHg, respectively, with the microvascular bed distribution being highly heterogeneous, spanning the range of values from arteriolar to venular .
Fig. 6.
distribution across different retinal compartments: artery, vein, and microvascular bed in between, under (a) normoxic and (b) hyperoxic conditions (same data as in Fig. 5). The top and bottom edges of the boxes (shown in blue) mark the 75th and 25th percentiles; the error bars show the extreme ends of the data spread (red + symbols), excluding outliers, and the red-center lines mark the medians.
Using the Hill equation with coefficients characteristic of C57BL/6 mice ( and ),44 we calculated the hemoglobin oxygen saturation () in the major artery and vein during normoxia. The corresponding values were 90% and 75%, respectively. These results suggest that the oxygen extraction fraction was 16%. During hyperoxia, the median in the artery, vein, and the microvascular bed were 323, 226, and 277 mmHg, respectively, with the microvascular bed distribution, as in the normoxic case, being highly heterogeneous and spanning the range of values from arteriolar to venular .
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Here, we performed in vivo measurements of absolute in major retinal vessels, and, for the first time, in arterioles, venules, and capillaries within three depth-resolved microvascular plexus, by 2PLM, using a potent two-photon phosphorescent oxygen probe. Oxygen measurements by phosphorescence quenching are based on the probe’s triplet decay time (phosphorescence lifetime), and as such they are unaffected neither by variations in the local probe concentration nor by optical properties of the medium (tissue).45 Compared to an earlier two-photon oxygen probe PtP-C343.31 Pt tetraphthalimidoporphyrin32 has a significantly red-shifted emission spectrum, centered at 757 nm and - to 100-fold higher two-photon brightness. As a result, it allows much deeper and faster measurements of in vivo. In this pilot study, we conservatively averaged 500 decays at each measurement location (e.g., 150 ms per point measurement); however, in the future it should be possible to shorten the acquisition time by reducing the number of cycles per location, while still maintaining adequate signal-to-noise ratio for accurate determination.
In vivo 2PM imaging of the retinal tissue with high spatial resolution presents specific challenges to the optical setup design due to the intrinsic optical properties of the eye. When imaging the retina in an intact eye through the pupil, one should consider that: (1) the imaging plane is located deeper than expected from the physical distance between the surface of the cornea and the retina ( in mice) due to the refractive properties of the eye itself; (2) when using objectives with large numerical apertures (NA), the diameter of the pupil may limit the aperture size of the imaging system and compromise resolution; (3) the compound (objective plus eye) imaging system is prone to strong aberrations limiting the useful FOV.
The crystalline lens of the eye works together with the imaging objective to focus the excitation beam on a more anterior plane within the eye than expected from the objective working distance. Therefore, traditional 2PM objectives with working distances of 2 to 3 mm are not suitable for retinal imaging. This challenge has been addressed in the past by using adaptive optics combined with an animal-specific contact lenses laid over the cornea,46 or using a more flexible periscope design.47 Bar-Noam et al.48 placed a convex electrically tunable lens and a concave offset lens before a water-immersion microscope objective (WD 1.8 mm or 3.5 mm) in order to extend their imaging depth to cover the entire retinal range. However, using either tunable lens or adaptive optics substantially increases the complexity of the imaging setup. Being able to perform 2PM imaging of the retina with a standard 2PM system should be advantageous. We used a commercially available 2PM objective with large working distance, which was coupled to the surface of the cornea to image retinal microvascular layers. Using this objective, we were able to image throughout the entire retinal depth although the working distance was effectively shortened by the optics of the eye. It should be noted that the eye’s iris limits the aperture and hence the FOV and the effective NA of the overall imaging system. Therefore, in spite of the fact that imaging was performed through a dilated pupil ( in diameter), full NA of the objective was not utilized.
During in vivo imaging of retina, contributions of the eye optics to the imaging cannot be avoided. Therefore, the compound optical system needs to be calibrated to ensure correct estimation of imaging dimensions and depths. This was achieved in the past by: (1) using histological images of the retina as a reference to scale the corresponding in vivo imaged en face planes;46,49 (2) assuming the focal length of the eye lens and scaling the magnification factor of the combined optical system accordingly;47 and (3) employing ray tracing or software, such as Zemax (Zemax, LLC) in combination with the assumed optical properties of the eye.48 In our approach, at the time of coupling, the distance between the objective and the cornea was not known. We used the star-shaped pattern of the major vessels as a guide to set the focus on the retina surface. We then assigned the depth at which focusing occurred as a reference and calculated the axial distances and magnifications relative to this depth using a ray matrix model of the optics of the mouse eye. Furthermore, we calibrated the lateral distances by introducing known displacements in the lateral plane (X - Y) while the beam was focused on the retinal surface, and subsequently scaled them using the previously calculated depth-dependent magnification factor.
Our 2PM setup has an axial resolution of and lateral resolution of 33 for measurements. Despite additional challenges (optical aberrations, etc.) induced by imaging through the eye, the spatial resolution of our imaging system was sufficient to visualize different retinal microvascular layers. The relatively sparse configuration of the capillaries within the retinal microvascular bed also helped to avoid potential artifacts due to the overlaps between the sampled volumes when the beam was focused at neighboring vessels.
We validated our system’s capability to assess retinal oxygenation by measuring intravascular during normoxia and hyperoxia. Systemic arterial and retinal arterial measurements were in good agreement under normoxia (112 versus 93 mmHg) and under hyperoxia (334 versus 327 mmHg). It could be expected that the systemic arterial would be somewhat higher than the in retinal arterioles due to the oxygen extraction from the arterioles. Previous results from our group and others revealed longitudinal gradients in arterioles50–52 as well as gradients in periarteriolar tissue.51,53–55 Under both normoxia and hyperoxia, we were able to visualize longitudinal gradients throughout the microvascular bed. However, in the case of hyperoxia, the gradients could be in part due to the change in the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved in the blood plasma, without significant change in , since blood hemoglobin would be almost fully saturated with oxygen under hyperoxic conditions. Motion artifacts due to heavy breathing as well as reduced tissue transparency after prolonged anesthesia may hamper measurements in every capillary as displayed in the deep retina layer (Fig. 5, normoxia).
Several studies have previously reported measurements in major retinal arteries and veins of mice using phosphorescence lifetime imaging of different single-photon excited oxyphors. In one of our earlier studies,25 we used a phosphorescent probe based on Pd tetracarboxyphenylporphyrin (Frontier Scientific, Logan, Utah, single-photon excitation at 532 nm) to measure intravascular in 3-month-old C57BL\6J mice under ketamine/xylazine anesthesia, and reported arterial of and venular of (). Wilson et al.21 measured retinal intravascular using Oxyphor G256,57 in mice under ketamine/xylazine anesthesia with single-photon excitation at 450 nm. The reported values in arterioles, venules, and capillary regions were 60 to 80, 30 to 45, and 50 to 100 mmHg, respectively.21 Prior to that, Shonat and Kight20 performed imaging using single-photon excitation at 524 nm and reported values of in arterioles, in venules, and () in capillary bed halothane-anesthetized C57BL\6 mice.20 The values reported here are generally higher than those found in the previous studies.20,21,25 It is possible that the choice of animal strain, age, and, importantly, type and duration of anesthesia, contributed to this difference. It is also important to note that the measurement methods used in all of the previous studies had limited depth resolution, and thus the reported values may have been effectively convolutions of the values at different depths throughout the sampled volumes of the retina.
Although in major vessels close to the retinal surface has been quantified previously, our work is the first demonstration of measurements in retinal capillaries at different depths with single-capillary resolution. This advance is important because the main oxygen transport to tissue occurs at the capillary sites. Moreover, the early-phase clinical indications of retinal pathologies are associated with capillaries, and our method may open up a new avenue to study baseline and transient in capillaries in health and various mouse models of retinal diseases.
In this work, extrapolation of the probe calibration to the hyperoxia regime may have resulted in a slight, most likely constant overestimation of the values at s above 160 mmHg. However, this discrepancy, even if present, should not change the key result of our proof-of-principle hyperoxia experiments, i.e., the ability of our setup to detect perturbations in retinal oxygenation as well as longitudinal gradients from arterioles to capillaries to venules. In the future, with sufficient interest in quantification of biological hyperoxia, we may perform detailed calibrations of our probes in the upper range.
Mouse eye has no apparent sensitivity in the spectral range of our excitation and emission (950 nm/757 nm).58 Thus, we presume that our measurements did not cause direct visual stimulation. On the other hand, a few endogenous chromophores in the retina (e.g., melanin and lipofuscin) have measurable two-photon absorption cross-sections near 950 nm as well as one-photon absorption spectra near 757 nm.59 Hence, it is possible that some indirect visual stimulation during the experiment affected the retinal metabolism. However, melanin and lipofuscin accumulations are mostly confined to the retinal pigment epithelial and subretinal microglia cells60 that are positioned significantly below the focal planes imaged in our experiments. In addition, lipofuscin accumulation in retina is insignificant in animals younger than 12 months.60 It is important to note that our measurements are not compromised by autofluorescence, since they rely on the triplet decay that is orders of magnitude longer than the time scale of any potential tissue autofluorescence.
Our method can be combined with other imaging techniques that can be used, e.g., for measurements of microvascular blood flow, as previously demonstrated in brain.33,61–67 Furthermore, oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent probes can be delivered to the retinal extravascular space.29,30 Therefore, we anticipate that 2PLM can be used in the future to perform depth-resolved extravascular retinal as well, similarly to how it was done previously in the rodent brain cortex.53,33 Overall, we anticipate that our method for measuring in retinal microvasculature will stimulate new studies of the pathophysiology of the eye and lead to better understanding of the mechanisms underlying various retinal disorders.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health (NIH) Grant Nos. EY017918, NS092986, EB018464, NS091230, NS055104, HL133362, MH111359, AG042026, and AA027097.
Biographies
İkbal Şencan is a research fellow in Optics@Martinos at MGH and Harvard Medical School. She completed her BSc degree in electronics engineering at Fatih University as valedictorian. She received her MSc and PhD degrees in electrical engineering from UCLA. She worked at Yale School of Medicine as a postdoctoral associate for two years. She coauthored three book chapters, two patents, 19 peer-reviewed journal articles, >50 conference presentations, and has an h-index of 15 with >1550 citations.
Biographies for the authors are not available.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Country M. W., “Retinal metabolism: a comparative look at energetics in the retina,” Brain Res. 1672(Suppl. C), 50–57 (2017). 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.07.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wong T. Y., et al. , “Diabetic retinopathy,” Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2, 16012 (2016). 10.1038/nrdp.2016.12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shah C. A., “Diabetic retinopathy: a comprehensive review,” Indian J. Med. Sci. 62(12), 500–519 (2008). 10.4103/0019-5359.48562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.“Statistics and Data|National Eye Institute,” https://nei.nih.gov/eyedata (19 April 2018).
- 5.Eshaq R. S., Wright W. S., Harris N. R., “Oxygen delivery, consumption, and conversion to reactive oxygen species in experimental models of diabetic retinopathy,” Redox Biol. 2, 661–666 (2014). 10.1016/j.redox.2014.04.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yu D.-Y., Cringle S. J., “Oxygen distribution in the mouse retina,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47(3), 1109–1112 (2006). 10.1167/iovs.05-1118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lau J. C. M., Linsenmeier R. A., “Oxygen consumption and distribution in the Long-Evans rat retina,” Exp. Eye Res. 102, 50–58 (2012). 10.1016/j.exer.2012.07.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cringle S. J., et al. , “Intraretinal oxygen consumption in the rat in vivo,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 43(6), 1922–1927 (2002). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kornfield T. E., Newman E. A., “Regulation of blood flow in the retinal trilaminar vascular network,” J. Neurosci. 34(34), 11504–11513 (2014). 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1971-14.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lau J. C. M., Linsenmeier R. A., “Increased intraretinal in short-term diabetic rats,” Diabetes 63(12), 4338–4342 (2014). 10.2337/db14-0101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hwang T. S., et al. , “Automated quantification of nonperfusion areas in 3 vascular plexuses with optical coherence tomography angiography in eyes of patients with diabetes,” JAMA Ophthalmol. 136(8), 929–936 (2018). 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.2257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Onishi A. C., et al. , “Importance of considering the middle capillary plexus on OCT angiography in diabetic retinopathy,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 59(5), 2167–2176 (2018). 10.1167/iovs.17-23304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hardarson S. H., et al. , “Automatic retinal oximetry,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47(11), 5011–5016 (2006). 10.1167/iovs.06-0039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hariri A., et al. , “In vivo photoacoustic imaging of chorioretinal oxygen gradients,” J. Biomed. Opt. 23(3), 036005 (2018). 10.1117/1.JBO.23.3.036005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yi J., et al. , “Visible light optical coherence tomography measures retinal oxygen metabolic response to systemic oxygenation,” Light Sci. Appl. 4(9), e334 (2015). 10.1038/lsa.2015.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chong S. P., et al. , “Quantitative microvascular hemoglobin mapping using visible light spectroscopic optical coherence tomography,” Biomed. Opt. Express 6(4), 1429–1450 (2015). 10.1364/BOE.6.001429 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chong S. P., et al. , “Ultrahigh resolution retinal imaging by visible light OCT with longitudinal achromatization,” Biomed. Opt. Express 9(4), 1477–1491 (2018). 10.1364/BOE.9.001477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vanderkooi J. M., et al. , “An optical method for measurement of dioxygen concentration based upon quenching of phosphorescence,” J. Biol. Chem. 262(12), 5476–5482 (1987). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shonat R. D., et al. , “Oxygen distribution in the retinal and choroidal vessels of the cat as measured by a new phosphorescence imaging method,” Appl. Opt. 31(19), 3711–3718 (1992). 10.1364/AO.31.003711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shonat R. D., Kight A. C., “Oxygen tension imaging in the mouse retina,” Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31(9), 1084–1096 (2003). 10.1114/1.1603256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wilson D. F., et al. , “Oxygen distribution and vascular injury in the mouse eye measured by phosphorescence-lifetime imaging,” Appl. Opt. 44(25), 5239–5248 (2005). 10.1364/AO.44.005239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shahidi M., et al. , “A method for chorioretinal oxygen tension measurement,” Curr. Eye Res. 31(4), 357–366 (2006). 10.1080/02713680600599446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wanek J., et al. , “Inner retinal metabolic rate of oxygen by oxygen tension and blood flow imaging in rat,” Biomed. Opt. Express 2(9), 2562–2568 (2011). 10.1364/BOE.2.002562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wanek J., et al. , “Inner retinal oxygen delivery and metabolism under normoxia and hypoxia in rat,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54(7), 5012–5019 (2013). 10.1167/iovs.13-11887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Blair N. P., et al. , “Inner retinal oxygen delivery, metabolism, and extraction fraction in ins2akita diabetic mice,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 57(14), 5903–5909 (2016). 10.1167/iovs.16-20082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Akiyama H., et al. , “Ir(III) complex-based oxygen imaging of living cells and ocular fundus with a gated ICCD camera,” Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 17(6), 846–853 (2018). 10.1039/C8PP00122G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shahidi M., et al. , “Three-Dimensional mapping of chorioretinal vascular oxygen tension in the rat,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50(2), 820–825 (2009). 10.1167/iovs.08-2343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Teng P., et al. , “Oxygen tension and gradient measurements in the retinal microvasculature of rats,” Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 250(3), 361–367 (2012). 10.1007/s00417-011-1859-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shahidi M., et al. , “Retinal tissue oxygen tension imaging in the rat,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51(9), 4766–4770 (2010). 10.1167/iovs.09-4710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Felder A. E., et al. , “A method for volumetric retinal tissue oxygen tension imaging,” Curr. Eye Res. 43(1), 122–127 (2018). 10.1080/02713683.2017.1373823 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Finikova O. S., et al. , “Oxygen microscopy by two-photon-excited phosphorescence,” Chem. Phys. Chem. 9(12), 1673–1679 (2008). 10.1002/cphc.v9:12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Esipova T. V., et al. , “Stabilizing g-states in centrosymmetric tetrapyrroles: two-photon-absorbing porphyrins with bright phosphorescence,” J. Phys. Chem. A 121(33), 6243–6255 (2017). 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b04333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yaseen M. A., et al. , “Multimodal optical imaging system for in vivo investigation of cerebral oxygen delivery and energy metabolism,” Biomed. Opt. Express 6(12), 4994–5007 (2015). 10.1364/BOE.6.004994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schmucker C., Schaeffel F., “A paraxial schematic eye model for the growing C57BL/6 mouse,” Vision Res. 44(16), 1857–1867 (2004). 10.1016/j.visres.2004.03.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang H., et al. , “The measurement of corneal thickness from center to limbus in vivo in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice using two-photon imaging,” Exp. Eye Res. 115, 255–262 (2013). 10.1016/j.exer.2013.07.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bawa G., et al. , “Variational analysis of the mouse and rat eye optical parameters,” Biomed. Opt. Express 4(11), 2585–2595 (2013). 10.1364/BOE.4.002585 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Delori F. C., Webb R. H., Sliney D. H., “Maximum permissible exposures for ocular safety (ANSI 2000), with emphasis on ophthalmic devices,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 24(5), 1250–1265 (2007). 10.1364/JOSAA.24.001250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lebedev A. Y., et al. , “Dendritic phosphorescent probes for oxygen imaging in biological systems,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1(6), 1292–1304 (2009). 10.1021/am9001698 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lossi L., et al. , “Anatomical features for an adequate choice of experimental animal model in biomedicine: II. Small laboratory rodents, rabbit, and pig,” Ann. Anat. 204, 11–28 (2016). 10.1016/j.aanat.2015.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cuthbertson R. A., Mandel T. E., “Anatomy of the mouse retina. Endothelial cell-pericyte ratio and capillary distribution,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 27(11), 1659–1664 (1986). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ramos D., et al. , “The use of confocal laser microscopy to analyze mouse retinal blood vessels” (2013).
- 42.Paques M., et al. , “Structural and hemodynamic analysis of the mouse retinal microcirculation,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44(11), 4960–4967 (2003). 10.1167/iovs.02-0738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Simmons A. B., Fuerst P. G., “Analysis of retinal vascular plexuses and interplexus connections,” Methods Mol. Biol. 1753, 317–330 (2018). 10.1007/978-1-4939-7720-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Uchida K., Reilly M. P., Asakura T., “Molecular stability and function of mouse hemoglobins,” Zool. Sci. 15(5), 703–706 (1998). 10.2108/zsj.15.703 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vinogradov S. A., Wilson D. F., “Porphyrin dendrimers as biological oxygen sensors,” in Designing Dendrimers, Campagna S., Ceroni P., Puntoriero F., Eds., pp. 463–504, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey: (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 46.Palczewska G., et al. , “Noninvasive two-photon microscopy imaging of mouse retina and retinal pigment epithelium through the pupil of the eye,” Nat. Med. 20(7), 785–789 (2014). 10.1038/nm.3590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Stremplewski P., et al. , “Periscope for noninvasive two-photon imaging of murine retina in vivo,” Biomed. Opt. Express 6(9), 3352–3361 (2015). 10.1364/BOE.6.003352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bar-Noam A. S., Farah N., Shoham S., “Correction-free remotely scanned two-photon in vivo mouse retinal imaging,” Light Sci. Appl. 5(1), e16007 (2016). 10.1038/lsa.2016.7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Geng Y., et al. , “Adaptive optics retinal imaging in the living mouse eye,” Biomed. Opt. Express 3(4), 715–734 (2012). 10.1364/BOE.3.000715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sakadžić S., et al. , “Large arteriolar component of oxygen delivery implies safe margin of oxygen supply to cerebral tissue,” Nat. Commun. 5, 5734 (2014). 10.1038/ncomms6734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Moeini M., et al. , “Compromised microvascular oxygen delivery increases brain tissue vulnerability with age,” Sci. Rep. 8(1), 8219 (2018). 10.1038/s41598-018-26543-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Vovenko E. P., Chuikin A. E., “Oxygen tension in rat cerebral cortex microvessels in acute anemia,” Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 38(5), 493–500 (2008). 10.1007/s11055-008-9007-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Devor A., et al. , “‘Overshoot’ of is required to maintain baseline tissue oxygenation at locations distal to blood vessels,” J. Neurosci. 31(38), 13676–13681 (2011). 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1968-11.2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Vovenko E., “Distribution of oxygen tension on the surface of arterioles, capillaries and venules of brain cortex and in tissue in normoxia: an experimental study on rats,” Pflugers Arch. 437(4), 617–623 (1999). 10.1007/s004240050825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sakadžić S., et al. , “Two-photon microscopy measurement of cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen using periarteriolar oxygen concentration gradients,” Neurophotonics 3(4), 045005 (2016). 10.1117/1.NPh.3.4.045005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rietveld I. B., Kim E., Vinogradov S. A., “Dendrimers with tetrabenzoporphyrin cores: near infrared phosphors for in vivo oxygen imaging,” Tetrahedron 59(22), 3821–3831 (2003). 10.1016/S0040-4020(03)00432-0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dunphy I., Vinogradov S. A., Wilson D. F., “Oxyphor R2 and G2: phosphors for measuring oxygen by oxygen-dependent quenching of phosphorescence,” Anal. Biochem. 310(2), 191–198 (2002). 10.1016/S0003-2697(02)00384-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Peirson S. N., et al. , “Light and the laboratory mouse,” J. Neurosci. Methods 300, 26–36 (2018). 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.04.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dysli C., et al. , “Fluorescence lifetime imaging ophthalmoscopy,” Prog. Retinal Eye Res. 60(Suppl. C), 120–143 (2017). 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2017.06.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Xu H., et al. , “Age-dependent accumulation of lipofuscin in perivascular and subretinal microglia in experimental mice,” Aging Cell 7(1), 58–68 (2008). 10.1111/ace.2008.7.issue-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lecoq J., et al. , “Simultaneous two-photon imaging of oxygen and blood flow in deep cerebral vessels,” Nat. Med. 17(7), 893–898 (2011). 10.1038/nm.2394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yaseen M. A., et al. , “Microvascular oxygen tension and flow measurements in rodent cerebral cortex during baseline conditions and functional activation,” J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 31(4), 1051–1063 (2011). 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Srinivasan V. J., et al. , “Depth-resolved microscopy of cortical hemodynamics with optical coherence tomography,” Opt. Lett. 34(20), 3086–3088 (2009). 10.1364/OL.34.003086 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jeong B., et al. , “Combined two-photon microscopy and optical coherence tomography using individually optimized sources,” Opt. Express 19(14), 13089–13096 (2011). 10.1364/OE.19.013089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kim B., et al. , “Combined two-photon microscopy and angiographic optical coherence tomography,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(8), 80502 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.8.080502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bouchard M. B., et al. , “Ultra-fast multispectral optical imaging of cortical oxygenation, blood flow, and intracellular calcium dynamics,” Opt. Express 17(18), 15670–15678 (2009). 10.1364/OE.17.015670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Dunn A. K., et al. , “Simultaneous imaging of total cerebral hemoglobin concentration, oxygenation, and blood flow during functional activation,” Opt. Lett. 28(1), 28–30 (2003). 10.1364/OL.28.000028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]