Abstract
Background & Aims
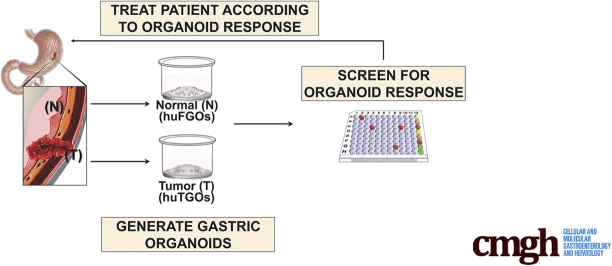
Our goal was to develop an initial study for the proof of concept whereby gastric cancer organoids are used as an approach to predict the tumor response in individual patients.
Methods
Organoids were derived from resected gastric cancer tumors (huTGOs) or normal stomach tissue collected from sleeve gastrectomies (huFGOs). Organoid cultures were treated with standard-of-care chemotherapeutic drugs corresponding to patient treatment: epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-fluorouracil. Organoid response to chemotherapeutic treatment was correlated with the tumor response in each patient from whom the huTGOs were derived. HuTGOs were orthotopically transplanted into the gastric mucosa of NOD scid gamma mice.
Results
Whereas huFGOs exhibited a half maximal inhibitory concentration that was similar among organoid lines, divergent responses and varying half maximal inhibitory concentration values among the huTGO lines were observed in response to chemotherapeutic drugs. HuTGOs that were sensitive to treatment were derived from a patient with a near complete tumor response to chemotherapy. However, organoids resistant to treatment were derived from patients who exhibited no response to chemotherapy. Orthotropic transplantation of organoids resulted in the engraftment and development of human adenocarcinoma. RNA sequencing revealed that huTGOs closely resembled the patient's native tumor tissue and not commonly used gastric cancer cell lines and cell lines derived from the organoid cultures.
Conclusions
The treatment of patient-derived organoids alongside patients from whom cultures were derived will ultimately test their usefulness to predict individual therapy response and patient outcome.
Keywords: Stomach, Organoids, Gastroids, Chemotherapy
Abbreviations used in this paper: CK, cytokeratin; DPBS, Dulbecco phosphate-buffered saline; EdU, 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; huFGO, human-derived normal fundic gastric organoid; huTGO, human-derived tumor gastric organoid; IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1
Graphical abstract
Summary.
This study tests the potential of gastric cancer–derived organoids as an approach to predict in vivo tumor responses. Effect of standard-of-care therapies on organoids was correlated with results of in vivo treatment. The data suggest that patient-derived organoids will be useful in developing individualized therapies.
Gastric cancer is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths, with a 5-year survival rate of only 29%.1 The incidence of gastric cancer is 4 times more common in Japan than in the United Kingdom and United States and occurs at a younger age.2 Because of the poor response of gastric cancer to various existing treatments, there is a need for approaches to predict the efficacy of therapy for individuals. We report here the generation of patient-derived gastric cancer organoids that may be useful for the prediction of patient responses to chemotherapy treatment.
Randomized data have clearly established that surgery alone for the treatment of gastric cancer results in reduced survival and increased recurrence rates when compared with multimodality therapy.1 A current limitation for the treatment of gastric cancer is the lack of a reliable approach to identify which treatment options are most effective for each individual patient. For example, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression is used as a biomarker for the prediction of response to anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody trastuzumab in patients with metastatic gastric cancer.3 Currently, HER2 expression is determined by immunohistochemistry or by the detection of HER2 gene amplification by fluorescence in situ hybridization.4, 5 However, because of tumor heterogeneity these approaches may represent inaccuracy in HER2 testing.6 Thus, further approaches are required to improve reliability of HER2 testing to ensure that patients receive the appropriate therapy for their individual disease.
Although cancer cell lines have proven valuable in the investigation of fundamental cancer research mechanisms, these models have the significant disadvantage of bearing little resemblance to the intended patient tumor.7, 8, 9, 10, 11 The development of high-throughput analytical methods now enables us to address the clinical relevance of these human cancer-derived cell lines. At the genomic level, driver mutations may be retained within cancer cell lines. However, several studies reveal a drift at the transcriptomic level, demonstrating that cancer cell lines carry more resemblance to each other rather than to the clinical samples from which they were originally derived.9, 10 Our study reports the use of three-dimensional organoids as a potential tool used for the prediction of targeted therapies for gastric cancer patients.
Results
Individual Patient-Derived Gastric Cancer Organoids Display Unique Responses to Chemotherapeutic Drugs and Targeted Therapy
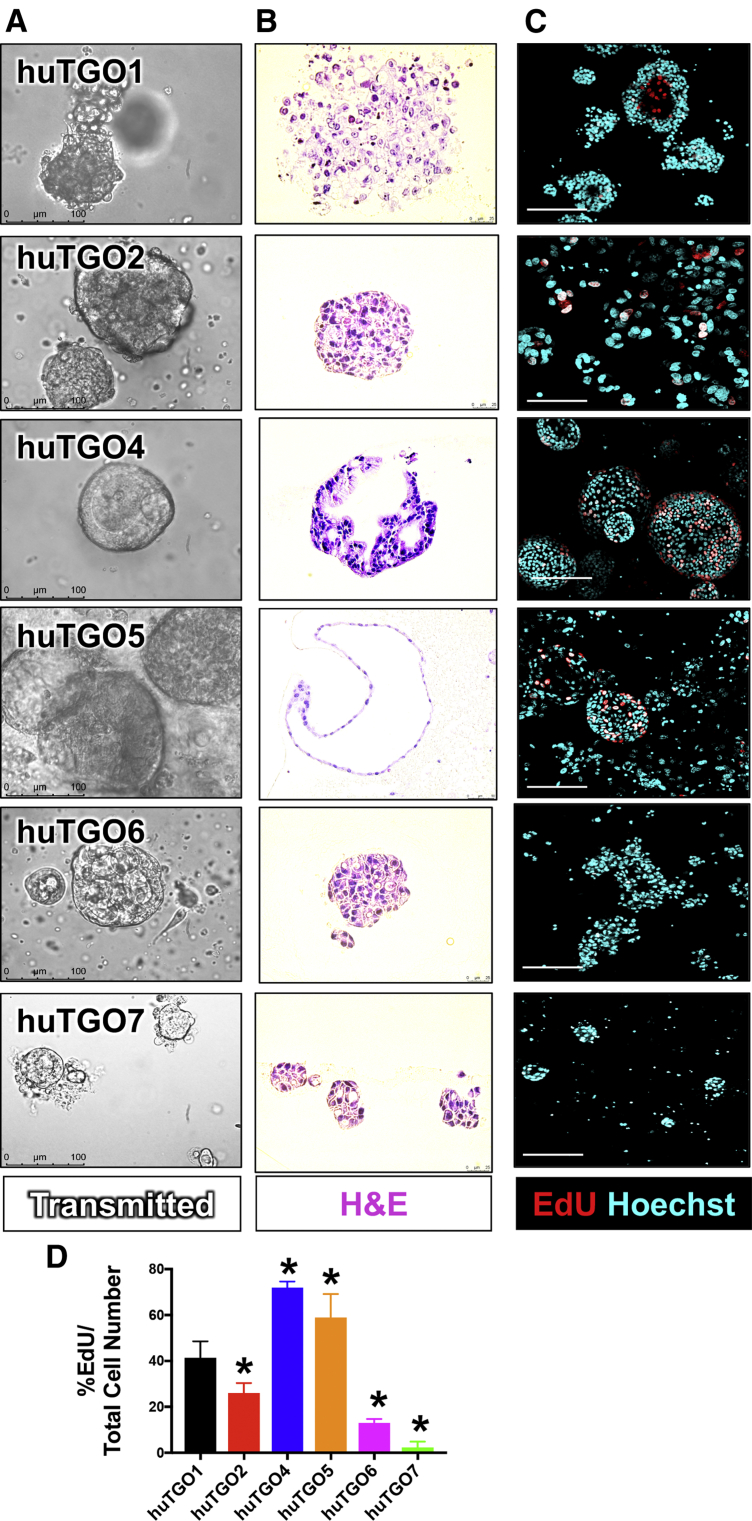
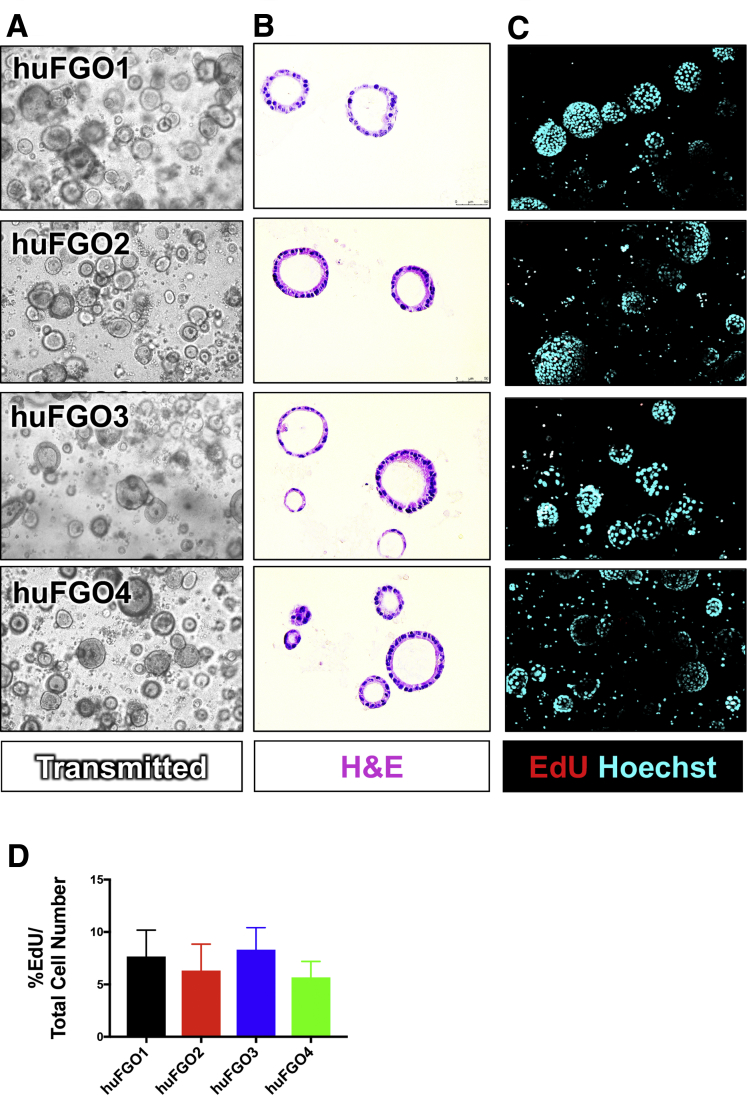
We generated an initial bank of gastric cancer organoids from tumors obtained from 7 patients (Table 1). For each patient from whom the organoids were derived, patient treatment, cancer staging, and tumor response and recurrence were recorded when available (Table 1). The morphology of each patient-derived organoid line (huTGO) was unique (Figure 1A and B). Specifically, we observed that whereas huTGO1 and 2 appeared as spherical nests with a central lumen lined by multiple layers of cells, huTGO4 exhibited a cribriform glandular morphology with cells forming multiple lumens of varying sizes (Figure 1A and B). HuTGO5 formed large spheres that consisted of a single epithelial layer by H&E staining (Figure 1A and B). All huTGO lines were passaged and re-formed organoids efficiently except for the huTGO3 line that lasted for only 4 passages before the line no longer persisted. Thus, we were unable to study the huTGO3 in the drug response assays. The proliferative response of each huTGO was measured by 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine (EdU) uptake. This analysis revealed a divergent and significantly different proliferative rate among the different organoid lines (Figure 1C and D). In contrast to the huTGOs, normal human-derived normal fundic gastric organoid (huFGO) lines displayed similar morphologies both in culture (Figure 2A) and by H&E staining (Figure 2B). In addition, the proliferative rates of the huFGOs were not statistically different among the different organoid lines (Figure 2C and D).
Table 1.
Histologic Classification, Tumor Response, Number of Cases, and Organoid Lines Derived From Patients With Gastric Cancer
| Histologic classification | No. of cases | Organoid line | Patient treatment and tumor response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuse/intestinal | 1 | 1: huTGO1 | EOX, T3N1M1, no evaluation of tumor response |
| Diffuse | 3 | 1: huTGO3 (Baylor) | Unknown |
| 2: No cell growth | Unknown | ||
| 3: huTGO6 | No chemo, T2N3aM1, no evaluation of tumor response | ||
| Intestinal | 3 | 1: huTGO2 | No chemo, T1bN0M0, no evaluation of tumor response |
| 2: huTGO5 | EOX, T3N0M0, no response to EOX (grade 3) | ||
| 3: huTGO7 | EOX, T3N3M0, complete response (grade 1) | ||
| Signet-ring cell | 2 | 1: No cell growth | Unknown |
| 2: No cell growth | Unknown | ||
| Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with diffuse and signet-ring patterns | 1 | 1: huTGO4 | EOX, T4N3M0, no response to EOX (grade 3) |
NOTE. Based on the criteria by the College of American Pathologists: grade 1: complete (0% residual tumor; grade 1a) or subtotal tumor regression (10% residual tumor per tumor bed; grade 1b); grade 2, partial tumor regression (10%–50% residual tumor per tumor bed); and grade 3, minimal or no tumor regression (50% residual tumor per tumor bed) (Becker et al, Cancer 2003;98:1521–1530).
Figure 1.
Morphologic differences and proliferative rate of patient-derived gastric cancer organoids (huTGOs). (A) Light micrographs of patient-derived gastric cancer organoid lines. (B) H&E staining of gastric cancer organoids. (C) Proliferation of huTGO lines as measured by EdU (red) uptake (Hoechst, cyan). (D) Quantification of proliferation as measured by %EdU expressing cells/total cell number in huTGOs. *P < .05 compared with huTGO1; n = 6 individual organoids were quantified per line.
Figure 2.
Morphologic differences and proliferative rate of patient-derived gastric organoids (huFGOs). (A) Light micrographs of patient-derived gastric organoid lines. (B) H&E staining of gastric organoids. (C) Proliferation of huFGO lines as measured by EdU (red) uptake (Hoechst, cyan). (D) Quantification of proliferation as measured by %EdU expressing cells/total cell number in huFGOs. *P < .05 compared with huTGO1; n = 6 individual organoids were quantified per line.
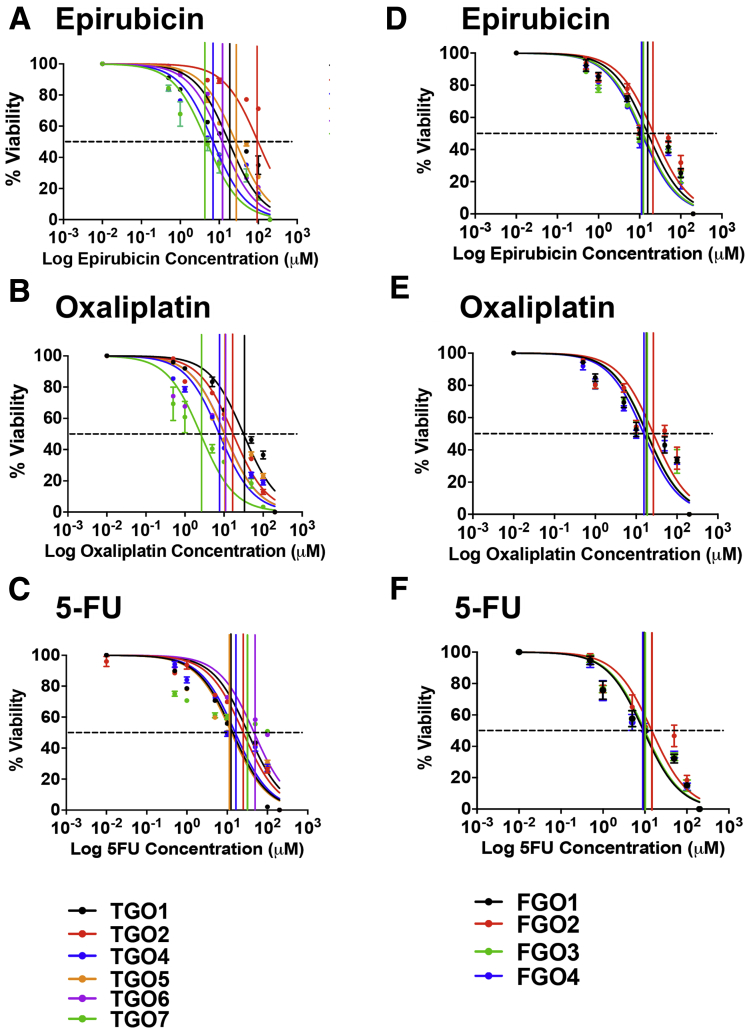
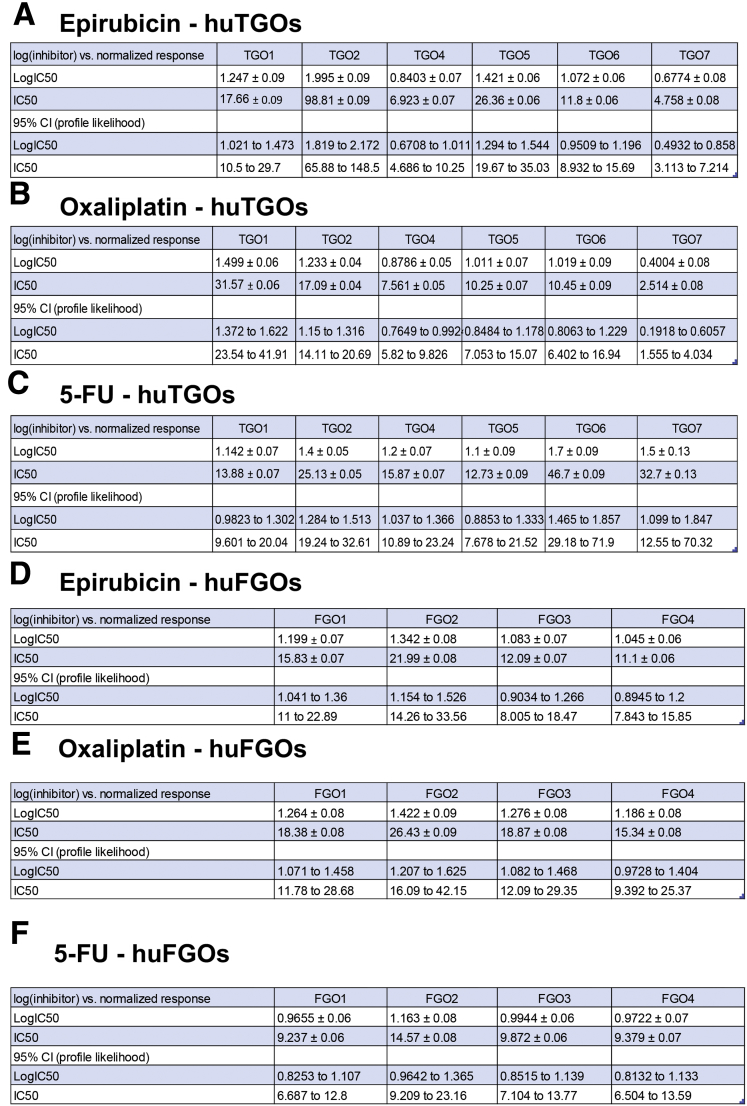
To investigate whether huTGOs are a potential in vitro platform to study the efficacy of standard-of-care chemotherapeutic agents, organoids were treated with drugs that gastric cancer patients are typically treated with (epirubicin, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil [5-FU]) (Figure 3A–C). As a comparison, organoids generated from normal gastric tissue (huFGOs) were treated with the same drugs (Figure 3D–F). In the huFGO lines it was observed that the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values, as documented by an MTS cell viability assay, were similar among the organoid lines for each drug that was tested (Figure 3D–F). Statistical analysis revealed an overlapping 95% confidence interval between each huFGO line (Figure 4D–F), thus demonstrating that the IC50 concentrations were not statistically different among these organoids. However, cell viability assays documented divergent responses and varying IC50 values to drug treatments among the huTGO lines (Figure 3A–C, Figure 4A–C). Note that a shift of the curve to the right indicates a higher IC50 (ie, more resistant to that particular drug). Cell viability assays were normalized to vehicle-treated controls to ensure that toxicity was specific to the drug effects.
Figure 3.
Drug responses of patient-derived gastric cancer and normal organoids. Dose-response curves generated from patient-derived (A–C) gastric cancer (huTGO) and (D–F) normal (huFGO) organoid lines treated with epirubicin, oxaliplatin, or 5-FU. These plots demonstrate the percent of viable cells as measured by an MTS assay in response to micromolar doses of chemotherapeutic agents. Each assay was run in triplicate for each individual organoid line.
Figure 4.
IC50 values for huTGO and huFGO dose-response curves. IC50 values for tumor-derived gastric organoids (huTGO) treated with (A) epirubicin, (B) oxaliplatin, and (C) 5-FU. IC50 values for normal gastric tissue (huFGOs) treated with (D) epirubicin, (E) oxaliplatin, and (F) 5-FU. CI, confidence interval.
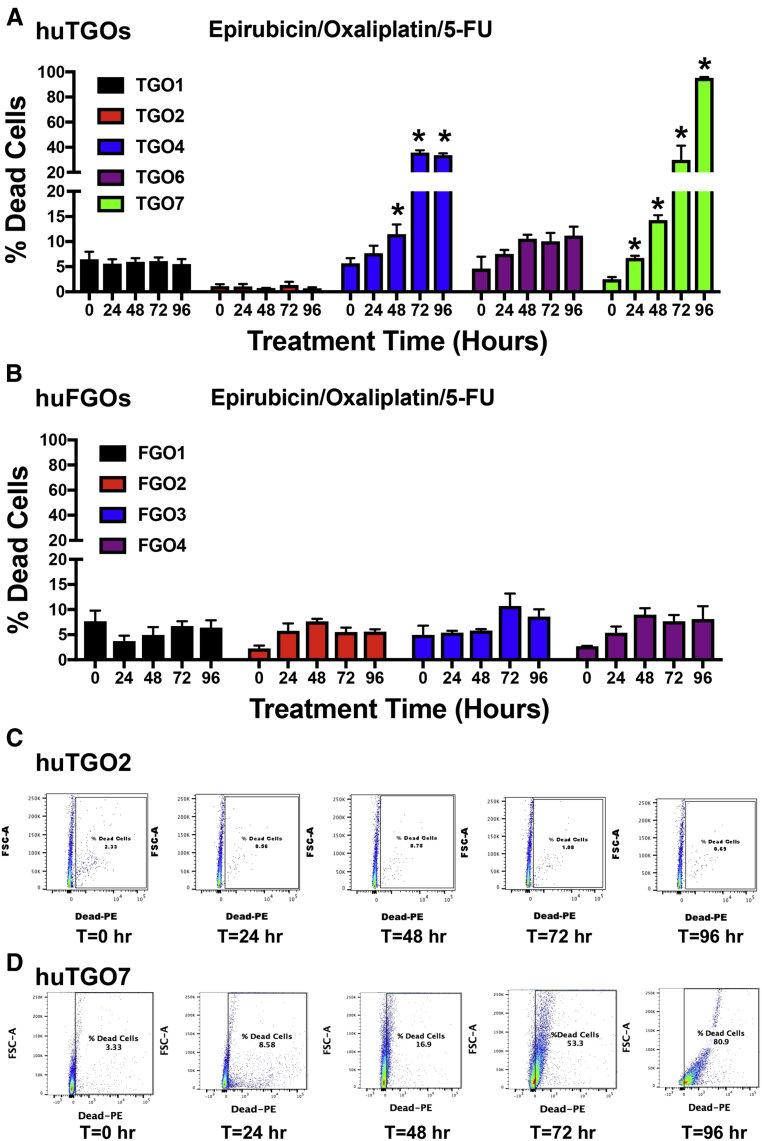
We wanted to next correlate the drug response of each huTGO line to the corresponding patient's tumor response from whom the cultures were derived. Lines huTGO1, huTGO2, and huTGO6 were among the more resistant to chemotherapeutic drug treatment. Resistance was documented on the basis of decreased percentage of dead cells in organoid response to combination treatment with epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU through the use of a fluorescence-based live/dead cell viability assay (Figure 5A and C). Unfortunately, evaluation of tumor response in these patients was not performed (Table 1). This is because (1) the patient from whom huTGO1 organoids were derived exhibited metastatic gastric cancer and the tumor was not resected, and (2) the patients from whom huTGO2 and huTGO6 organoids were derived did not receive chemotherapy and therefore tumor response was not evaluated (Table 1). The huTGO4 line displayed decreased resistance in response to chemotherapeutic drug treatment; however, this particular patient did not respond to chemotherapy (Table 1). Also, compared with huTGO1, 2, and 6, huTGO4 responded partially to the combination in vitro treatment of the organoids as documented by the significant increase in the percent of dead cells within the organoid cultures within 48 hours of treatment (Figure 5A). However, huTGO7 was highly responsive to drug treatment, and similarly the patient's tumor exhibited a near complete response to the same chemotherapy combination therapy (Table 1, Figure 5A and D). Importantly, whereas the huTGO lines exhibited differences in the response to drug treatment, huFGOs showed similar response to the combination drug treatment (Figure 5B). We were unable to perform a similar analysis on huTGO5 because this culture did not persist. Our studies suggest that each organoid line may be useful to help determine an active chemotherapeutic drug(s) for patient treatment. However, just as important is our ability to define drugs for which a patient has a resistance and may predominantly be causing side effects with little therapeutic response.
Figure 5.
Organoid responses to combined treatment with epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU. Quantification of flow cytometric cell viability analysis at 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours after treatment with combined epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU of (A) huTGOs and (B) huFGOs. Representative flow cytometry dot plots at 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours after treatment with combined epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU in (C) huTGO2 and (D) huTGO7. *P < .05 compared with t = 0 hours. Each assay was run in triplicate for each individual organoid line.
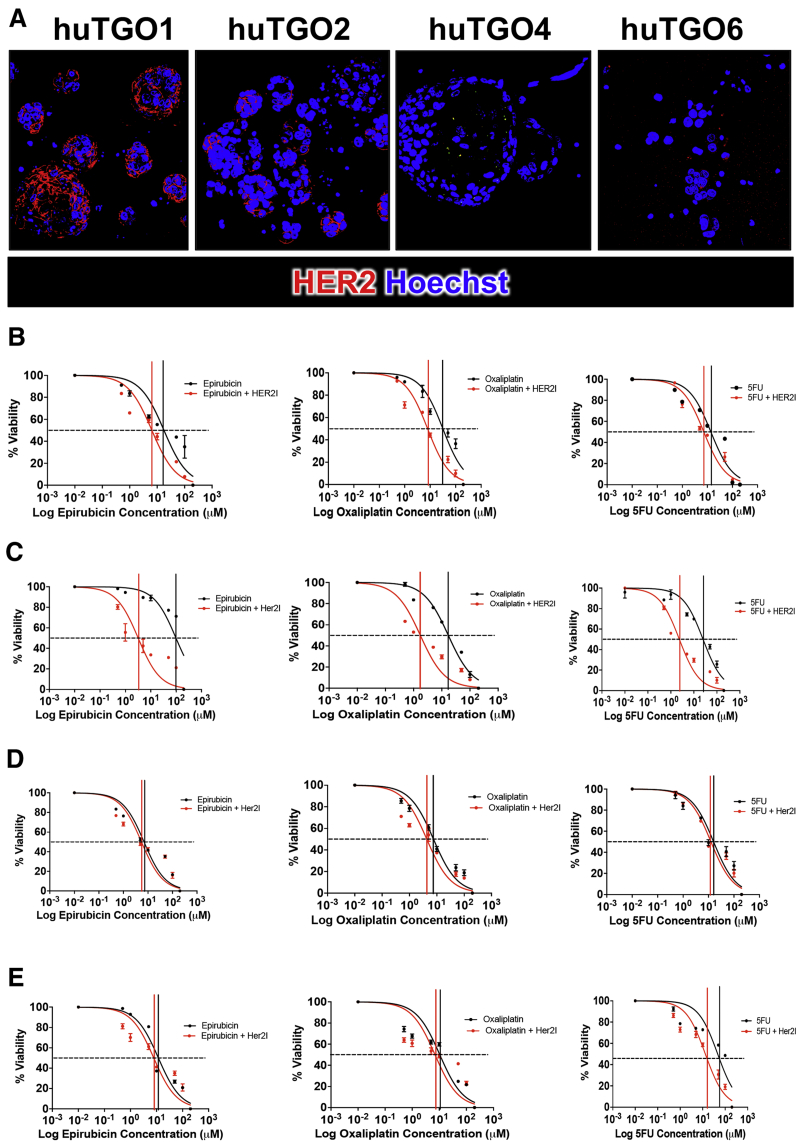
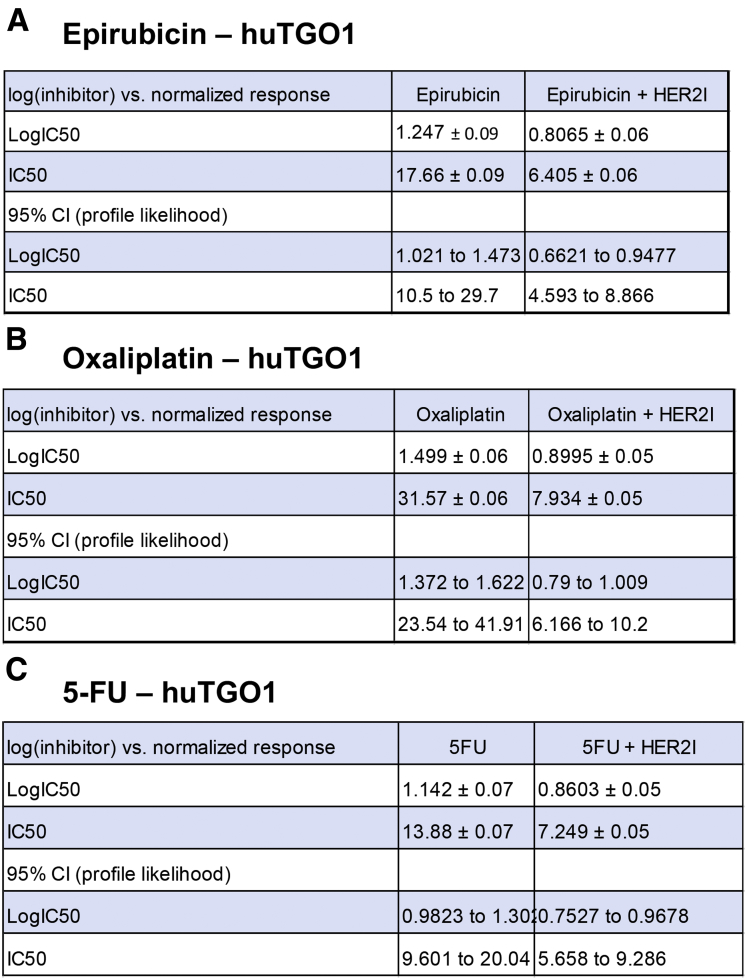
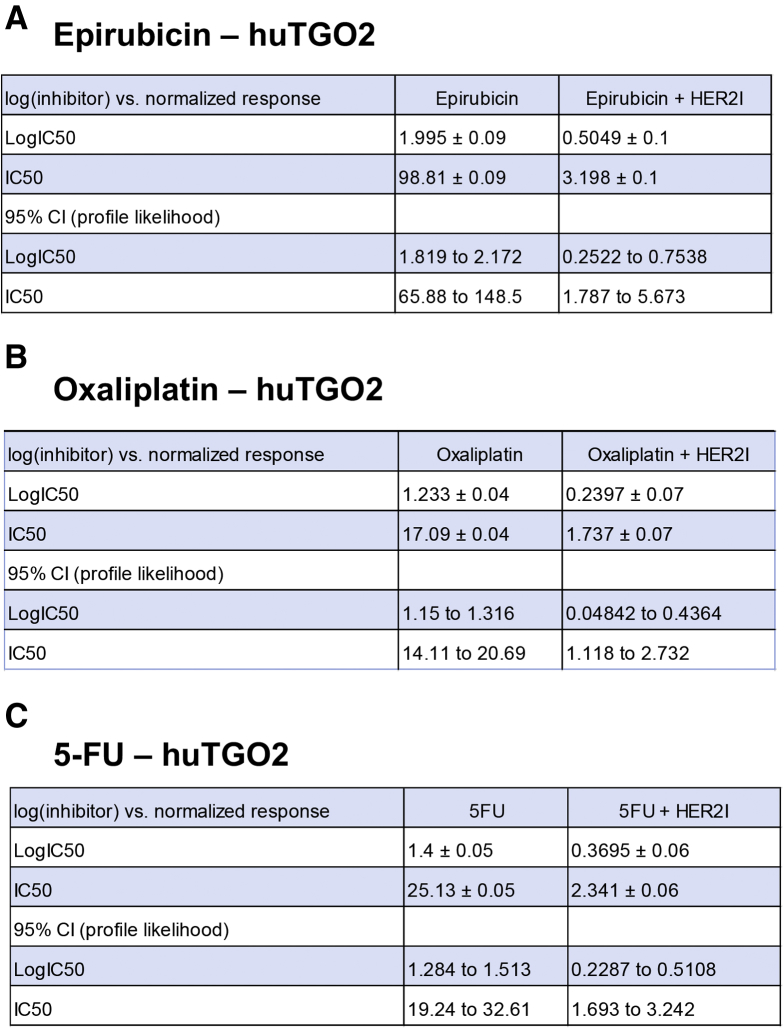
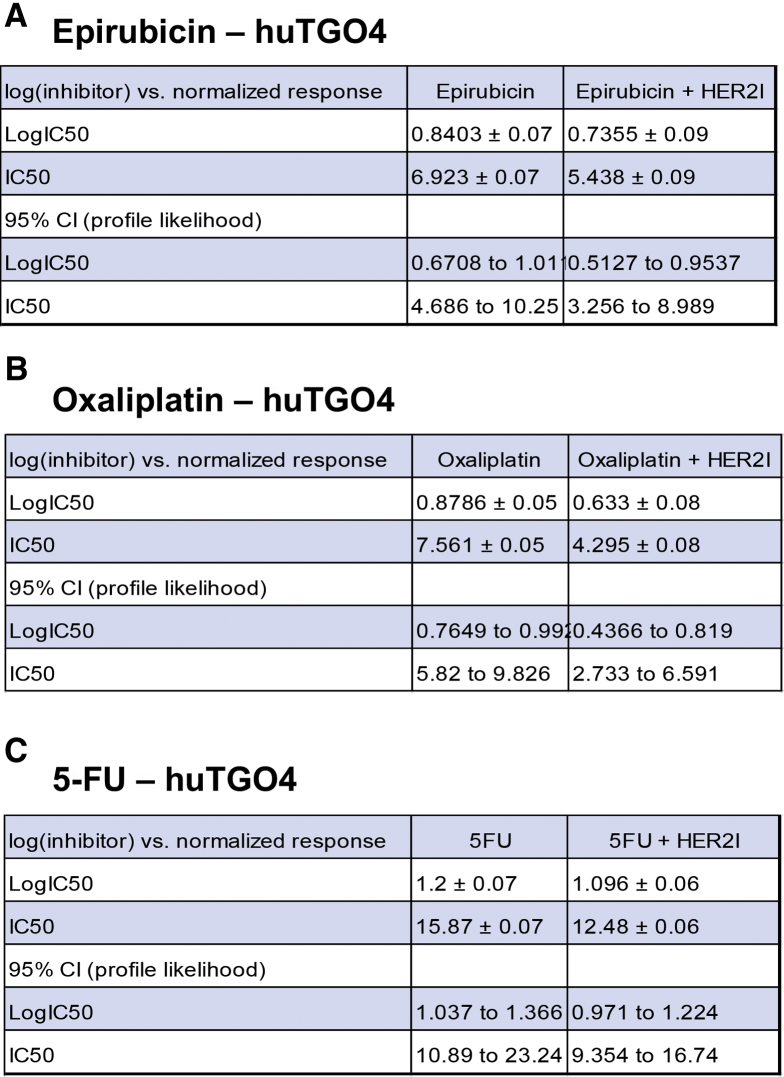
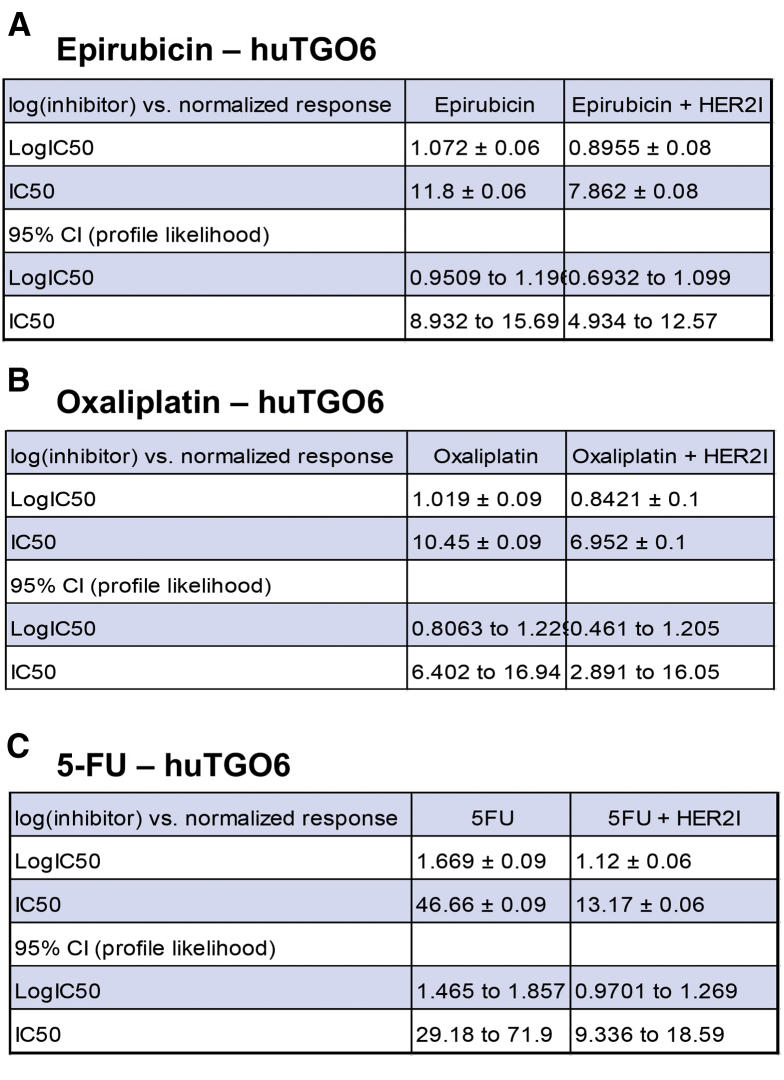
We observed that the huTGO1 and huTGO2 organoid lines expressed HER2, whereas huTGO4 and huTGO6 did not express this protein (Figure 6A). This observation was contradictory to the pathologist's observations of the tumor tissue that reported all patients to be negative for HER2. The patient from whom huTGO1 was derived did not undergo tumor resection, but rather HER2 status was determined on the basis of tissue collected from the metastatic tumor. We tested whether HER2 inhibition sensitized the huTGOs to epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU treatment (Figure 6B–E). For example, huTGO1 was most resistant to epirubicin (IC50, 17.66 ± 0.09), oxaliplatin (IC50, 31.57 ± 0.06), and 5-FU (IC50, 13.88 ± 0.07) (Figure 6B, Figure 7). However, when huTGO1s were pretreated with HER2 inhibitor, the IC50 decreased to 6.05 ± 0.06, 7.93 ± 0.05, and 7.25 ± 0.05 in response to epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU, respectively (Figure 6B, Figure 7). Similarly, pretreatment of huTGO2s with HER2 inhibitor also sensitized the organoids to epirubicin (IC50 epirubicin, 98.8 ± 0.09; IC50 epirubicin + HER2I, 3.19 ± 0.10), oxaliplatin (IC50 oxaliplatin, 17.09 ± 0.04; IC50 oxaliplatin + HER2I, 1.74 ± 0.07), and 5-FU (IC50 5-FU, 25.13 ± 0.05; IC50 5-FU + HER2I, 2.34 ± 0.06) (Figure 6C, Figure 8). The huTGO4 and 6 lines did not express HER2 (Figure 6A) and were not responsive to HER2 inhibitor pretreatment (Figure 6D and E, Figures 9 and 10). It is important to note that Mubritinib specifically inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of HER2 signaling and cannot reproduce the effects that trastuzumab has on host immune surveillance.12 Including the patient's immune cell in an organoid co-culture is part of our future plans. Thus, we may propose that on the basis of our observations, patient-derived gastric cancer organoids may serve as a platform for testing the efficacy of targeted therapies in individual patients.
Figure 6.
HER2 expression and responsiveness to HER2 inhibition in patient-derived gastric cancer organoids. (A) Immunofluorescence of HER2 expression (red) in huTGOs. Dose-response curves generated by using (B) huTGO1, (C) huTGO2, (D) huTGO4, and (E) huTGO6 organoid lines in response to epirubicin, oxaliplatin, or 5-FU with or without HER2 inhibitor (HER2I). Each assay was run in triplicate for each individual organoid line.
Figure 7.
IC50 values for huTGO1 dose-response curves. IC50 values for tumor-derived gastric organoids (huTGO) treated with (A) epirubicin with or without HER2I, (B) oxaliplatin with or without HER2I, or (C) 5-FU with or without HER2I. CI, confidence interval.
Figure 8.
IC50 values for huTGO2 dose-response curves. IC50 values for tumor-derived gastric organoids (huTGO) treated with (A) epirubicin with or without HER2I, (B) oxaliplatin with or without HER2I, or (C) 5-FU with or without HER2I. CI, confidence interval.
Figure 9.
IC50 values for huTGO4 dose-response curves. IC50 values for tumor-derived gastric organoids (huTGO) treated with (A) epirubicin with or without HER2I, (B) oxaliplatin with or without HER2I, or (C) 5-FU with or without HER2I. CI, confidence interval.
Figure 10.
IC50 values for huTGO6 dose-response curves. IC50 values for tumor-derived gastric organoids (huTGO) treated with (A) epirubicin with or without HER2I, (B) oxaliplatin with or without HER2I, or (C) 5-FU with or without HER2I. CI, confidence interval.
Patient-Derived Gastric Cancer Organoids Phenotypically Resemble the Native Tumor Tissue
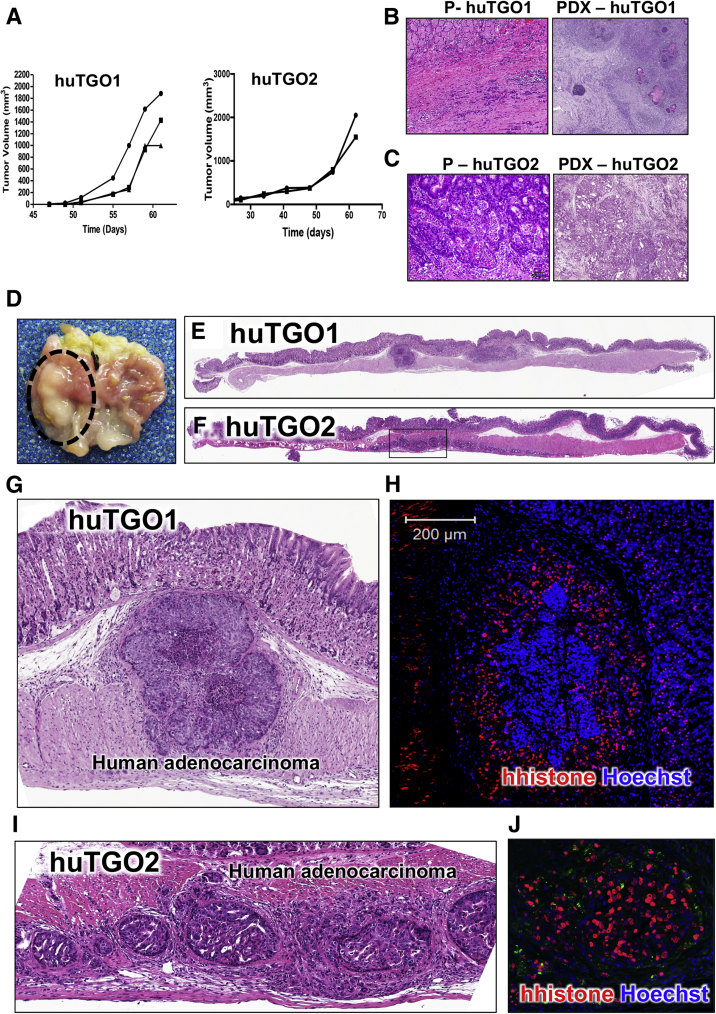
In support of carcinogenesis, these cultures also rapidly developed tumors in an in vivo xenograft mouse model (Figure 11A). We questioned the extent to which huTGOs recapitulate their original tumor histology in vivo. HuTGO1 and 2 were xenotransplanted subcutaneously into NSG mice (Figure 11B and C). Notably, histologic and differentiation patterns of the patient tumor tissue were highly recapitulated in the xenograft tumors established from the organoids (Figure 11B and C). For example, huTGO2 derived from well-differentiated intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma is composed of glandular structures (Figure 11C, PDX-huTGO2) and is similar to patient's specimen (Figure 11C, P-huTGO2). Organoids derived from mixed poorly differentiated diffuse and intestinal-type gastric cancer tissues (huTGO1) formed similar morphologies in vivo including infiltrating single tumor cells (diffuse-type) and adjacent cancer glands (intestinal-type) (Figure 11B, PDX-huTGO1).
Figure 11.
Analysis of patient-derived gastric cancer organoid xenografts and orthotopic transplants. (A) Tumor volume measured over time of patient-derived xenografts (PDX). H&E staining of patient tumor tissue and patient-derived xenografts from (B) P1; PDX-huTGO1 and (C) P2; PDX-huTGO2. (D) Gross morphology of gastric tumor 30 days after orthotopic transplantation of patient-derived gastric cancer organoids in NSG mice. H&E staining of NSG mouse stomachs orthotopically transplanted with (E) huTGO1 and (F) huTGO2 30 days after injection. High-power magnification of human adenocarcinoma within submucosa of mice transplanted with (G) huTGO1 and (I) huTGO2. Immunofluorescence staining of human histone (red) and nuclear staining (Hoescht, blue) in NSG mouse stomachs orthotopically transplanted with (H) huTGO1 or (J) huTGO2.
Patient-Derived Gastric Cancer Organoids Engraft Within the Gastric Epithelium of a Mouse and Form Adenocarcinoma
Investigating the impact of the endogenous environment of the stomach on tumor growth is part of our future research plans. Thus, we sought to develop an orthotopic transplantation model using patient-derived gastric cancer organoids. HuTGO1 and 2 organoid lines were transplanted into the submucosa of the gastric epithelium of NSG mice (Figure 11D–F). After organoid transplantation we observed the development of adenocarcinoma with areas of cells invading the epithelium (Figure 11D–H). Of note, human cells were detected in areas of adenocarcinoma and the epithelium of the mouse gastric mucosa with the use of an antibody specific for human histone protein (Figure 11H and J).
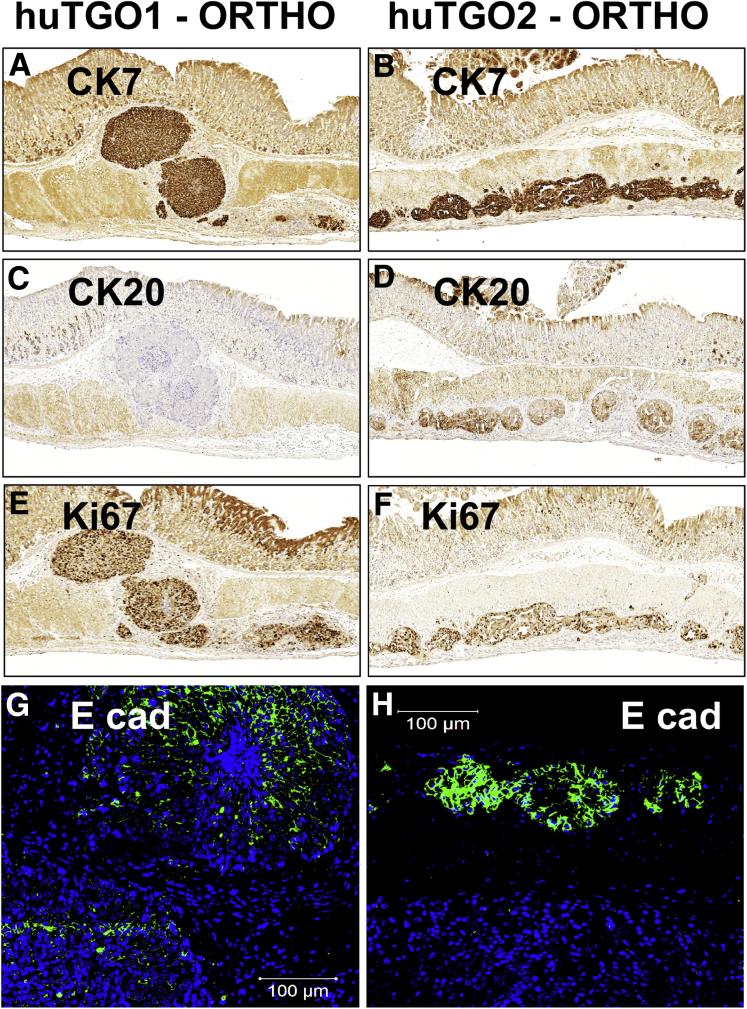
The expression of cytokeratin (CK) 7 and CK20 is often used for the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Immunohistochemical staining revealed high expression of CK7 within the lesions originating from the huTGO1 (Figure 12A) and huTGO2 (Figure 12B) organoid orthotopic transplantations. In contrast, CK20 was only detected in the stomachs of mice transplanted with huTGO2 (Figure 12D) compared with those animals transplanted with huTGO1 (Figure 12C). Lesions arising from huTGO1 and huTGO2 were highly proliferative (Figure 12E and F). Expression of E-cadherin (Figure 12G and H) was also detected within these lesions of mice transplanted with huTGO1 and 2 organoids. The negative control for the human-specific histone immunofluorescence is shown in Figure 13. Collectively, these data suggest that transplantation of patient-derived gastric cancer organoids engraft within the gastric epithelium and mimic their parental histology.
Figure 12.
Engraftment and immunostaining of adenocarcinoma arising from orthotopically transplanted patient-derived gastric cancer organoids. Immunohistochemical evaluation of CK7 in orthotopic (A) huTGO1 or (B) huTGO2 transplanted mouse stomachs. Immunohistochemical analysis of CK20 in orthotopic (C) huTGO1 or (D) huTGO2 transplanted mouse stomachs. Immunohistochemistry of Ki67 expression in orthotopic (E) huTGO1 or (F) huTGO2 transplanted mouse stomachs. Immunofluorescence of E-cadherin expression (E cad, green) in orthotopic (G) huTGO1 or (H) huTGO2 transplanted mouse stomachs.
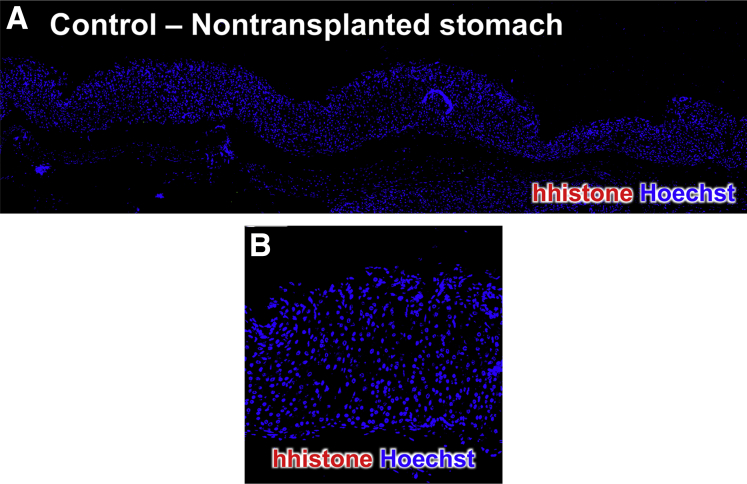
Figure 13.
Human histone immunofluorescence of nontransplanted mouse stomach. (A) Immunofluorescence of nontransplanted mouse stomach using an antibody specific for human histone (red) and Hoechst (blue). (B) Higher magnification is shown.
Gastric Cancer Organoids Resemble the Patient's Tumor Tissue From Which They Are Derived
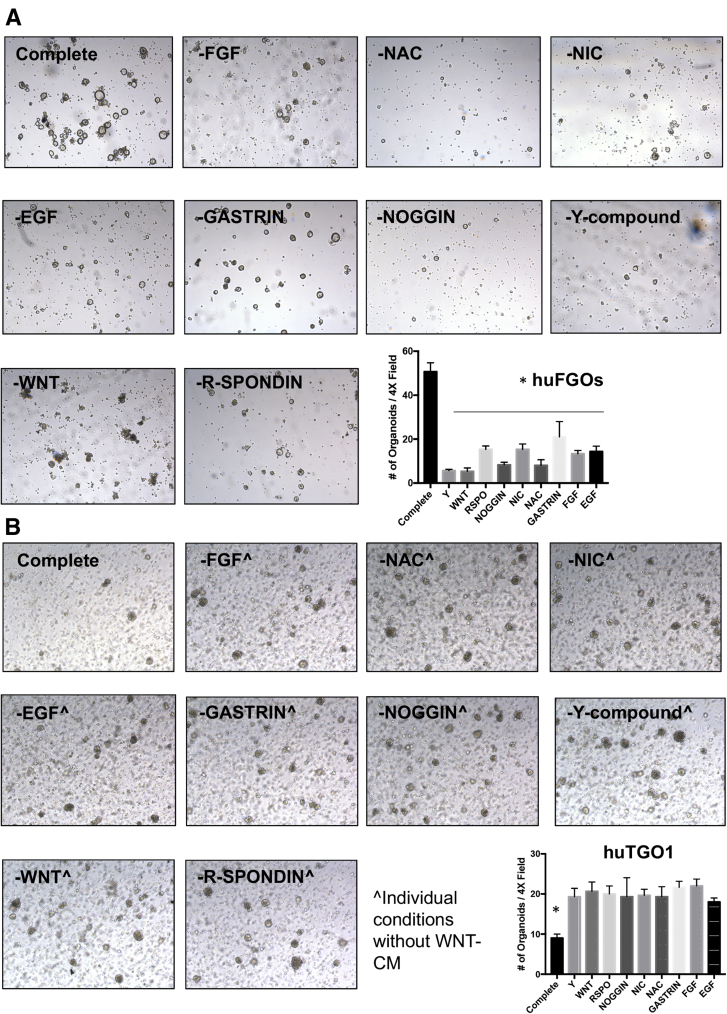
HuTGO1-7 organoid lines were able to grow efficiently without organoid media and rapidly formed cell lines. To test the dependence of normal (huFGOs, organoids derived from normal human gastric tissue) and tumor-derived gastric organoids (huTGOs) on key growth factors supplied in the organoid growth medium, organoids were dissociated to single cells and re-suspended in organoid media with or without the key growth factors. HuTGOs grew in a growth factor–independent manner relative to control organoids (Figure 14A and B).
Figure 14.
Growth factor independent growth of gastric cancer organoids. Light micrographs of organoids derived from (A) normal (huFGOs) or (B) gastric cancer (huTGO1) organoid line in various growth factor conditions. Quantification of number of organoids per 4× field is shown for both huFGOs and huTGO1. *P < .05 compared with complete media condition, n = 3 individual organoid lines.
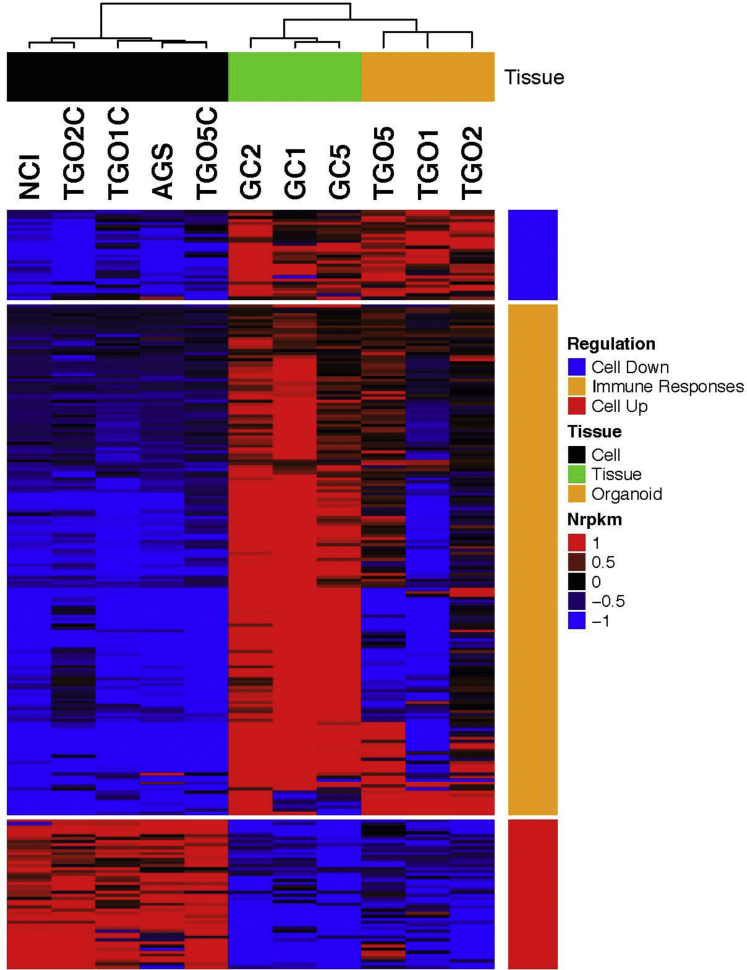
RNA sequencing followed by patient-matched statistical analysis identified 251 genes differentially expressed between samples derived from organoids and tissue samples and samples derived from two-dimensional cultures (false discovery rate <0.1). Hierarchical clustering analysis of differentially expressed genes (Figure 15) and samples, including the samples from 2 commonly used gastric cancer cell lines (AGS and NCI-N87), revealed 3 major patterns of expression: genes down-regulated in two-dimensional cultures, genes up-regulated in two-dimensional cultures, and genes that were down-regulated in both TGO and two-dimensional cultures. Interestingly, genes down-regulated in both TGO and two-dimensional cultures were enriched by genes with several immune-response Gene Ontology categories (Table 2). This is consistent with the lack of the immune response within organoid and cell line cultures. Furthermore, gene expression profiles from AGS and NCI-N87 gastric cell lines were virtually identical to profiles of our two-dimensional cultures and different from TGO and cancer tissue samples, although these samples were not used in the selection of differentially expressed genes.
Figure 15.
RNA sequencing analysis of gastric cancer patient tissue (GC), organoid (TGOs), and cell lines (AGS, NCI, or TGOC). RNA sequencing analysis of gastric cancer cell lines (NCI, AGS), organoid-derived gastric cancer cell lines (TGO1C, TGO2C, TGO5C), patient tissue (GC1, GC2, GC5), and patient-derived gastric cancer organoids (TGO1, TGO2, TGO5).
Table 2.
Immune Response GO Categories Identified in the Enrichment Analysis of the Genes in the Immune Responses Cluster in Figure 15
| GO | GO names | Differentially expressed | In GO category | False discovery rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0006955 | Immune response | 46 | 771 | 4.69*10–10 |
| GO:0002682 | Regulation of immune system process | 42 | 653 | 4.69*10–10 |
| GO:0050776 | Regulation of immune response | 31 | 408 | 1.00*10–8 |
| GO:0044421 | Extracellular region part | 42 | 739 | 1.40*10–8 |
| GO:0050778 | Positive regulation of immune response | 24 | 281 | 1.37*10–7 |
| GO:0002429 | Immune response-activating cell surface receptor signaling pathway | 16 | 120 | 2.36*10–7 |
| GO:0002504 | Antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II | 8 | 19 | 3.41*10–7 |
| GO:0002768 | Immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway | 16 | 125 | 3.41*10–7 |
| GO:0042613 | MHC class II protein complex | 7 | 13 | 3.92*10–7 |
| GO:0001775 | Cell activation | 34 | 590 | 4.39*10–7 |
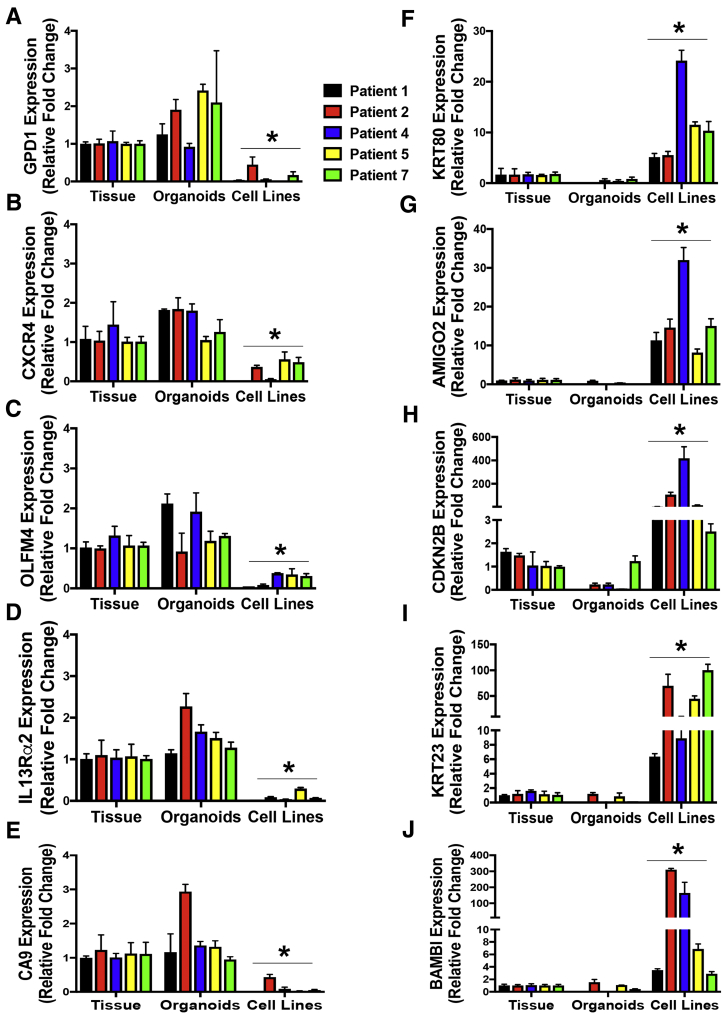
The genes that were highly expressed in gastric cancer tissue and organoids (TGOs) included GPD1, CXCR4, OLFM4, IL13Rα2, and carbonic anhydrase (CA9). Genes that were identified as being uniquely expressed in the cell lines included KRT80, AMIGO2, CDKN2B, KRT23, and BAMBI. The expression of the genes among gastric cancer tissue 1, 2, 4, 5, and 7, TGO1, 2, 4, 5 and 7 lines, and cell lines was verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (Figure 16). Collectively, these data suggest that gastric cancer organoids resemble the patient's tumor tissue from which they were derived.
Figure 16.
Validation of RNA sequencing data. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction using RNA collected from gastric cancer tissue (GC), huTGOs, cell lines derived from huTGOs (huTGOC), and AGS and NCI-N87 (NCI) cell lines for the expression of (A) GPD1, (B) CXCR4, (C) OLFM4, (D) IL13Rα2, (E) CA9, (F) KRT80, (G) AMIGO2, (H) CDKN2B, (I) KRT23, and (J) BAMBI. *P < .05 compared with GC samples, n = 3 assays per sample.
Discussion
We demonstrate the proof of concept for the use of gastric cancer organoids as a preclinical model to potentially evaluate the efficacy of cancer therapeutics. The development of these organoid cultures represents the first step that is required to establish in vivo and in vitro patient-derived organoid-based platforms for personalized medicine. Cell lines have been the most frequently used models in cancer research, and their use has certainly advanced our understanding of cancer biology. As opposed to standard-of-care chemotherapeutic agents, targeted therapy is applied to the percentage of patients expressing a specific molecular abnormality. Thus, a large part of our ability to develop personalized medicine depends on cultures that capture this genetic heterogeneity. However, many studies report genomic differences between cancer cell lines and tissue samples from which they are derived.7, 8, 9, 10, 11 On the basis of RNA sequencing data and hierarchical clustering, we document a phenotypical similarity between the organoids and the patient's tumor tissue. This is in stark contrast to a cell line derived from the gastric cancer organoids, which has a similar transcriptional program to that of the well-established gastric cancer cell lines AGS and NCI-N87 cells. Importantly, a limitation of the organoid and cell line cultures is the lack of the immune component that is found within the patient's tumor environment. These findings are of significance because tumors can evade immune surveillance by expressing molecules such as programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) that interacts with PD-1 and subsequently inhibiting CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte proliferation, survival, and effector function.13, 14, 15 On average, PD-L1 expression is detected in approximately 42.2% of gastric adenocarcinomas.16 Although anti-PD1 antibodies are already in clinical trials for gastric cancer treatment,17, 18, 19 there are currently no preclinical models that allow us to test the efficacy of therapy to predict patient treatment response and outcome. Refining the organoid culture system to include the patient's own immune response would be beneficial to identifying the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients. Collectively, our data and published studies direct us toward developing in vitro models, such as the gastric cancer organoids, that would help to better predict the success or failure of chemotherapeutic agents and targeted therapies. Of importance, we have optimized these cultures such that organoids can be directly grown in a 96-well plate format and used for drug testing within 3 days of the patient's surgery. Thus, it is feasible to inform the clinician of possible treatment options within 5–6 days of surgery.
Investigating the impact of the endogenous environment of the stomach on tumor growth is an important direction of our future research plans. An orthotopic transplantation model using patient-derived gastric cancer organoids was developed. Organoids that were transplanted into the submucosa below the gastric epithelium of NSG mouse stomachs developed into adenocarcinoma, and this was confirmed by a board-certified pathologist. The lesions were originated from human organoids as documented by the positive immunostaining using anti-human histone antibody. Organoid-derived lesions were highly proliferative, and huTGO1 and huTGO2 differentially expressed CK7 and CK20. The expressions of CK7 and CK20 are often used as prognostic markers for gastric cancer.20 Cytokeratin (CK), an intermediate filament that is expressed in epithelial cells, plays an important role as a cytoskeletal component in the maintenance of cell morphology. The CK gene has 20 subtypes, and the expression of CK depends primarily on the epithelial cell type and the degree of differentiation.21 Early studies report that the expression of CK7 and/or CK20 showed a tendency toward a high positive rate in the differentiated type of gastric cancer.20 Our data showed that whereas CK7 was highly expressed in lesions arising from the transplant of TGO1 and 2 organoid lines, CK20 was not expressed in TGO1-derived transplants. This is significant because TGO1 was an organoid line derived from a patient with a mixed, poorly differentiated, and intestinal-type gastric cancer. In support of our studies, a recent study demonstrated the development of an orthotopic mouse model whereby gastric cancer cell lines tagged with luciferase and injected into the subserosa of the stomach allows for monitoring of primary tumor growth and metastasis in real-time.22 Our RNA sequencing data suggest that the use of gastric cancer cell lines may be a limitation because the patient-derived organoids express a transcriptional profile more similar to the patient's primary tumor tissue than the profile of gastric cancer cell lines. Thus, we advance these recent studies by demonstrating that orthotopic transplantation of cancer-derived organoid lines is clinically relevant and may recapitulate tumor growth and metastasis in vivo.
The current work supports the finding that cancer organoids derived from resected gastric cancer tumors may capture the response to standard-of-care chemotherapeutics of the patient's native tumor. Our data showed that each huTGO line exhibited a unique response to epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU, when compared with the non-divergent responses of huFGOs to the same drugs. These results may be attributed to the heterogeneity in each cancer organoid line exhibiting various mutations that do not exist in organoids derived from normal tissue. A recent study also reporting the development of gastric cancer organoids supports our findings.23 Seidlitz et al23 report that human-derived cancer organoids represent typical characteristics and altered pathways of gastric cancer. Although the report also documents that gastric cancer organoids derived from individual patients exhibit divergent drug responses, this study fails to address the original patient's tumor responses to treatment. Although a limitation of our current study is the small sample size, we report a potential correlation between organoid responses to chemotherapy with the patient's own tumor response from which the cultures were derived. In support of this, huTGO7 organoid line was highly chemosensitive to the combination treatment of epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU (Figure 5A). Importantly, huTGO7 was derived from a patient who was diagnosed with a complete response to chemotherapy (Table 1). In contrast, huTGO4 responded partially to the combination in vitro treatment of the organoids (Figure 5A); however, this patient did not respond to chemotherapy treatment (Table 1). One potential explanation for these data is the absence of the patient's immune component in the culture system. Immune dysregulation may contribute to tumor progression in gastric cancer. For example, it has been shown that the infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells contributes not only to the suppression of T-cell activation but also the impairment of the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.24, 25 Thus, we may speculate that if the patient from whom huTGO4 was derived exhibited high infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells, then the patient's tumor response would be poor. However, in vitro in the absence of these immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, it may be expected that the huTGO4 cultures would exhibit increased chemosensitivity. Thus, our future studies will include co-culturing patient-derived immune cells and tumor organoids to investigate the potential effect of immune-tumor cell cross talk on treatment response. Importantly, our plans also entail using a larger patient sample size to truly predict patient outcome based on an organoid-based response to chemotherapy.
Our data suggest that gastric cancer organoids may be used to help predict patient response to targeted therapies such as HER2 inhibition. Expression of HER2 within organoid cultures (huTGO1 and huTGO2) that were 2 of the resistant lines to chemotherapy treatment was sensitized to these chemotherapeutic agents with HER2 inhibitor pretreatment. HER2 overexpression is becoming recognized as a frequent molecular abnormality in gastric cancer.26 Amplification of the HER2 gene was first discovered in breast cancer and is significantly associated with worse prognosis.27 With the recent introduction of HER2 molecular targeted therapy for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, determination of HER2 status is crucial to select patients who may benefit from this treatment. However, HER2 testing in gastric cancer differs from testing in breast cancer because of inherent differences in tumor biology, tumor heterogeneity of HER2 expression, and incomplete membrane staining that are commonly observed in gastric cancers.6 The organoid culture system may provide a reliable method for identifying HER2-positive patients because the culture is designed to select for the cancer stem cells. Treating organoids alongside the patients from whom the cultures were derived will ultimately test their usefulness to predict individual therapy response and patient outcome.
Materials and Methods
Generating Human Fundic Gastric Organoids
Human fundus was collected from sleeve gastrectomies (IRB protocol number: 2015-5537, University of Cincinnati and 2014-0427, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center), and gastric glands were generated as previously described.28, 29 Briefly, epithelial tissue was separated from the muscle layer, cut into small fragments, and washed in Dulbecco phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) without Ca2+/Mg2+. Tissue fragments were placed in a buffer containing collagenase (1 mg/mL) from Clostridium histolyticum and bovine serum albumin (2 mg/mL) for 30 minutes at 37°C. Gastric glands were suspended in 50 μL Matrigel (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and cultured in freshly generated human gastric organoid media (DMEM/F12 (Thermo Fisher Scientific), HEPES (10 mmol/L), 1X L-glutamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1X Pen/Strep, 1X N2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1X B27 (Thermo Fisher Scientific), N-acetylcysteine (1 mmol/L; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO), nicotinamide (10 mmol/L; Sigma-Aldrich), epidermal growth factor (50 ng/mL; PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ), noggin (100 ng/mL; PeproTech), R-spondin conditioned media, wnt conditioned media, FGF10 (200 ng/mL; PeproTech), gastrin (1 nmol/L; Tocris Bioscience, Bristol, United Kingdom), Y-27632 (10 μmol/L; Sigma-Aldrich), 1X amphotericin B/gentamicin, 1X kanamycin). Organoids were harvested after 4–7 days of growth.
Organoids Derived From Gastric Cancer Tissue
Tumor tissue was obtained from patients undergoing surgical resection for gastric cancer (IRB protocol number: 2015-5537, University of Cincinnati and H-35094, Baylor College of Medicine). Tumor organoids were generated as previously described.30 Briefly, tumor tissue was washed well in DPBS without Ca2+ and Mg2+ supplemented with antibiotics and minced into small pieces. Tumor fragments were placed in pre-warmed stripping buffer: Hank’s balanced salt solution, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (5 mmol/L), HEPES (25 mmol/L), 10% fetal calf serum. Fragments were incubated for 10 minutes in a shaking incubator at 37°C. The fragments were supplied fresh stripping buffer and incubated for an additional 5 minutes in a shaking incubator at 37°C. The tissue fragments were washed with Hank’s balanced salt solution twice, and pre-warmed incubation buffer (RPMI supplemented with collagenase [1.5 mg/mL] and hyaluronidase [20 μg/mL]) was added to the fragments and incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes in a shaking incubator. The digest was diluted with 20 mL DPBS without Ca2+ and Mg2+ supplemented with antibiotics and filtered through a 70-μm filter. The cells were centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 minutes and embedded into Matrigel supplemented with gastric growth medium as described above.
Orthotopic Transplantation of Gastric Organoids
All mouse studies were approved by the University of Cincinnati Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee that maintains an American Association of Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care facility. Orthotopic transplantation of gastric organoids was performed in NOD scid gamma (NSG) mice according to a previously published protocol.29 Briefly, an acetic acid injury was induced. After injury, approximately 500 organoids were resuspended in 1:1 Matrigel/PBS solution and injected within the submucosa. Stomach tissues were collected 14, 30, and 60 days after transplantation.
Mouse Xenograft Assay
Xenograft assays were performed by injecting approximately 500 organoids subcutaneously in the right flank of NSG mice. Tumor dimensions were measured every 3–7 days.
Immunofluorescence
Stomach tissues were collected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 16 hours, and longitudinal sections were paraffin-embedded and sectioned at 5 μm. Tissue slides were deparaffinized and boiled in antigen citrate buffer (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA; H3300) for 10 minutes. Sections were then blocked with 20% donkey serum for 20 minutes and immunostained with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with secondary antibodies for 1 hour. Whole mount staining of gastric organoids derived from fresh tissue was performed as previously described.28 Briefly, organoids were fixed in 3.7% formaldehyde for 15 minutes at room temperature. Organoids were permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 20 minutes at room temperature. Organoids were incubated with primary antibody overnight and washed in PBS containing 0.01% Triton-X 100. Secondary antibody incubation was also performed overnight in gastric organoids and subsequently immunostained for cell nuclei using 10 μg/mL Hoechst. The following primary antibodies and dilutions were used: 1:100 human-specific rabbit anti histone (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom; ab125027), 1:100 rabbit anti-HER2 (Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO; NBP1-84584), and 1:400 goat anti-Ecad (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN; AF648). For measurement of proliferation, EdU solution was added to the organoid medium of huTGOs or huFGOs for 1-hour uptake. EdU staining was performed by using the Click-iT Alexa Fluor 594 Imaging Kit, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). Coverslips were mounted onto slides with Vectashield Mounting Medium (Vector Laboratories; H-1400), and slides and whole mount organoids were imaged on a Zeiss LSM710 LIVE (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) duo confocal microscope.
Immunohistochemistry
Stomach sections spanning both the fundic and antral regions collected from mice orthotopically transplanted with huTGOs were fixed for 16 hours in 4% paraformaldehyde, paraffin embedded, and sectioned at 5 μmol/L. Prepared slides were deparaffinized with antigen retrieval performed by submerging in boiling solution (1:100 dilution Antigen Unmasking Solution in dH2O; Vector Laboratories; H-3300) for 10 minutes, followed by 20 minutes at room temperature. Sections were then blocked and immunostained with 1:100 CK7 (Novus Biologicals; NBP2-44814), 1:100 CK20 (Novus Biologicals; NBP1-85599), or 1:400 Ki67 (Thermo Fisher Scientific; RM-9106-SO). Slides were incubated with biotinylated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit secondary antibodies for 30 minutes, followed by additional 30-minute incubation with ABC reagent (Vectastain ABC kit; Vector Laboratories). Color was developed with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) using the DAB Substrate Kit (Vector Laboratories), and slides were then counterstained with hematoxylin (Fisher Scientific Company, Kalamazoo, MI). Immunohistochemical slides were dehydrated and mounted using Permount (Fisher Scientific), and images were viewed and captured under light microscopy (Olympus BX60 with Diagnostic Instruments “Spot” Camera; Tokyo, Japan).
Drug Assay in Tumor-Derived Organoids
Organoids were grown in 96-well plates and treated with epirubicin, oxaliplatin, or 5-FU (EOX) (Selleckchem, Houston, TX) at concentrations of 0, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, and 200 μmol/L for 48 hours. In a separate series of experiments, organoids were pretreated with HER2 inhibitor Mubritinib (Sigma-Aldrich) at concentrations of 0, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, and 200 μmol/L for 2 hours before epirubicin, oxaliplatin, or 5-FU treatment at the calculated IC50 for each drug for an additional 48 hours. After 48 hours, organoid proliferation was measured by using MTS Assay (Promega 93582; Madison, WI). Dose-response curves were calculated on the basis of the absorbance readings collected from the MTS assay relative to drug concentrations. Absorbance was normalized to the vehicle controls, and drug concentrations were converted to logarithms by using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA).
In a separate series of experiments, huTGO or huFGO lines were grown in a 48-well plate and treated with a combination of epirubicin/oxaliplatin/5-FU at IC50 concentrations calculated for each organoid line. Organoids were then dissociated to single cells by using Accutase for 10–15 minutes at 37°C at 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours after drug treatment. Organoids treated with vehicle were harvested at the same time points. Cell viability was then assayed by flow cytometry using the LIVE/DEAD Viability/Cytoxicity Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific; L3224). The % dead cells was calculated on the basis of the ability of ethidium homodimer-1 (ex/em approximately 495/635 nm) to enter the cells with damaged membranes. All calculations were normalized to the number % live/dead cells in vehicle controls. Samples were run on the CANTO 3 and analyzed by FlowJo software.
RNA Sequencing
RNA was isolated from patient tumor tissue, gastric organoids using TRIzol (Molecular Research Center Inc, Cincinnati, OH) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA-seq data were aligned to the reference human genome (hg19), and expression levels of all genes were quantified by using the standard Bioconductor workflow.31 The differential expression analysis between sample types was performed on the basis of the negative-binomial statistical model of read counts as implemented in the DESeq Bioconductor package.32, 33 The differential expression analysis between sample types was performed on the basis of the negative-binomial statistical model of read counts as implemented in the edgeR Bioconductor package.34 A two-factor generalized linear model was used to identify genes differentially expressed between 2 groups of samples, TGO and cancer tissues samples vs two-dimensional cultures, adjusted for the patient effect. The comparison was made. False discovery rates were calculated,33 and genes with false discovery rates <0.1 were considered statistically significant. Cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes was performed by using Bayesian infinite mixture model-based clustering35 of the normalized log-2 rpkm gene expression profiles after adjusting for the patient effect. The enrichment analysis of the clusters of differentially expressed genes was performed by using the CLEAN package.36
Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Total RNA was isolated from tissue, organoids, or cell lines by using TRIzol according to manufacturer’s protocol (Life Technologies). The High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) was used for cDNA synthesis of RNA following the recommended protocol. For each sample, 60 ng RNA was reverse transcribed to yield approximately 2 μg total cDNA that was then used for the real-time polymerase chain reaction. Pre-designed real-time polymerase chain reaction assays were purchased for the following genes (Thermo Fisher, Applied Biosystems): GAPDH (Hs02786624_g1), CXCR4 (Hs00607978_s1), GPD1 (Hs01100039_m1), CA9 (Hs00154208_m1), IL13RA2 (Hs00152924_m1), OLFM4 (Hs00197437), KRT80 (Hs01372365_m1), AMIGO2 (Hs05001325_s1), CDKN2B (Hs00793225_m1), KRT23 (Hs00210096_m1), BAMBI (Hs03044164_m1). Polymerase chain reaction amplifications were performed in a total volume of 20 μL containing 20X TaqMan Expression Assay primers, 2X TaqMan Universal Master Mix (Applied Biosystems; TaqMan Gene Expression Systems), and cDNA template. Each polymerase chain reaction amplification was performed in duplicate wells in a StepOne Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) by using the following conditions: 50oC 2 minutes, 95oC 10 minutes, 95oC 15 seconds (denature) and 60°C 1 minute (anneal/extend) for 40 cycles. Fold change was calculated as the following: (Ct–Ct high) = n target, 2ntarget/2nHPRT = fold change where Ct = threshold cycle. The results were expressed as average fold change in gene expression relative to control, with GAPDH used as an internal control according to Livak and Schmittgen.37
Statistical Analyses
The significance of the results was tested by two-way analysis of variance or Student t test by using commercially available software (GraphPad Prism). A P value <.05 was considered significant.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the assistance of Chet Closson (Live Microscopy Core, University of Cincinnati). The authors thank Lisa McMillin (Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Pathology Research Core) for her assistance with organoid embedding and processing; Kathy McClinchey and the McClinchey Histology Lab Inc and Glenn Doerman (Cancer Biology, Graphic Design, Illustrations, Presentations and Desktop Publishing) for helping us prepare the figures for submission. The authors acknowledge Dr Joel Gabre for his insightful conversation. Finally, the authors thank the patients who consented to donate tissue and blood for the development of the gastric organoids. Without their willingness to participate in the study, this work would not be possible.
Footnotes
Author contributions N.S., J.W., J.C., L.H., J.B.: study concept and design; acquisition of data; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; statistical analysis; technical or material support. J.C., L.M.N., J.H., M.M., N.S.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; technical or material support. N.S., M.M., M.H., S.A.: study concept and design; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; technical or material support. Y.Z.: study concept and design; acquisition of data; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; statistical analysis; obtained funding; study supervision.
Conflicts of interest The authors disclose no conflicts.
Funding Supported by NIH (NIDDK) 2 R01 DK083402-06A1 grant, College of Medicine Bridge Funding Program (Y.Z.) and NIH 1U19AI116491-01 (Weis and J.W., Y.Z. Project Leader), and the University of Cincinnati Graduate School Dean’s Fellowship and Albert J. Ryan Fellowship and 2T32GM105526-04 (N.G.S.). This project was supported in part by PHS Grant P30 DK078392 (Integrative Morphology Core) of the Digestive Diseases Research Core Center in Cincinnati.
References
- 1.Ahmad S.A., Xia B.T., Bailey C.E., Abbott D.E., Helmink B.A., Daly M.C., Thota R., Schlegal C., Winer L.K., Ahmad S.A., Al Humaidi A.H., Parikh A.A. An update on gastric cancer. Curr Probl Surg. 2016;53:449–490. doi: 10.1067/j.cpsurg.2016.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Neugut A.I., Hayek M., Howe G. Epidemiology of gastric cancer. Semin Oncol. 1996;23:281–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gunturu K.S., Woo Y., Beaubier N., Remotti H.E., Saif M.W. Gastric cancer and trastuzumab: first biologic therapy in gastric cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2013;5:143–151. doi: 10.1177/1758834012469429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Manion E., Hornick J.L., Lester S.C., Brock J.E. A comparison of equivocal immunohistochemical results with anti-HER2/neu antibodies A0485 and SP3 with corresponding FISH results in routine clinical practice. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135:845–851. doi: 10.1309/AJCPIP5LOO3NGDJG. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yano T., Doi T., Ohtsu A., Boku N., Hashizume K., Nakanishi M., Ochiai A. Comparison of HER2 gene amplification assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and HER2 protein expression assessed by immunohistochemistry in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abrahao-Machado L.F., Jacome A.A., Wohnrath D.R., dos Santos J.S., Carneseca E.C., Fregnani J.H., Scapulatempo-Neto C. HER2 in gastric cancer: comparative analysis of three different antibodies using whole-tissue sections and tissue microarrays. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:6438–6446. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Domcke S., Sinha R., Levine D.A., Sander C., Schultz N. Evaluating cell lines as tumour models by comparison of genomic profiles. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2126. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ertel A., Verghese A., Byers S.W., Ochs M., Tozeren A. Pathway-specific differences between tumor cell lines and normal and tumor tissue cells. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:55. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gillet J.P., Calcagno A.M., Varma S., Marino M., Green L.J., Vora M.I., Patel C., Orina J.N., Eliseeva T.A., Singal V., Padmanabhan R., Davidson B., Ganapathi R., Sood A.K., Rueda B.R., Ambudkar S.V., Gottesman M.M. Redefining the relevance of established cancer cell lines to the study of mechanisms of clinical anti-cancer drug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:18708–18713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111840108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sandberg R., Ernberg I. Assessment of tumor characteristic gene expression in cell lines using a tissue similarity index (TSI) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:2052–2057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408105102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stein W.D., Bates S.E., Fojo T. Intractable cancers: the many faces of multidrug resistance and the many targets it presents for therapeutic attack. Curr Drug Targets. 2004;5:333–346. doi: 10.2174/1389450043345489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bianchini G., Gianni L. The immune system and response to HER2-targeted treatment in breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e58–e68. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70477-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ahmadzadeh M., Johnson L.A., Heemskerk B., Wunderlich J.R., Dudley M.E., White D.E., Rosenberg S.A. Tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood. 2009;114:1537–1544. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-195792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Z., Chen X., Zhou E., Chen G., Qian K., Wu X., Miao X., Tang Z. Intratumoral CD8(+) cytotoxic lymphocyte is a favorable prognostic marker in node-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9:e95475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reissfelder C., Stamova S., Gossmann C., Braun M., Bonertz A., Walliczek U., Grimm M., Rahbari N.N., Koch M., Saadati M., Benner A., Buchler M.W., Jager D., Halama N., Khazaie K., Weitz J., Beckhove P. Tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity determines colorectal cancer patient prognosis. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:739–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI74894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wu C., Zhu Y., Jiang J., Zhao J., Zhang X.G., Xu N. Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Acta Histochem. 2006;108:19–24. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2006.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abdel-Rahman O. PD-L1 expression and outcome of advanced melanoma patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents: a meta-analysis. Immunotherapy. 2016;8:1081–1089. doi: 10.2217/imt-2016-0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Abdel-Rahman O. Correlation between PD-L1 expression and outcome of NSCLC patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents: a meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;101:75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abdel-Rahman O. Immune checkpoints aberrations and gastric cancer: assessment of prognostic value and evaluation of therapeutic potentials. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;97:65–71. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Takami H., Sentani K., Matsuda M., Oue N., Sakamoto N., Yasui W. Cytokeratin expression profiling in gastric carcinoma: clinicopathologic significance and comparison with tumor-associated molecules. Pathobiology. 2012;79:154–161. doi: 10.1159/000335694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chu P.G., Weiss L.M. Keratin expression in human tissues and neoplasms. Histopathology. 2002;40:403–439. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2002.01387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Busuttil R.A., Liu D.S., Di Costanzo N., Schroder J., Mitchell C., Boussioutas A. An orthotopic mouse model of gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Sci Rep. 2018;8:825. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19025-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Seidlitz T., Merker S.R., Rothe A., Zakrzewski F., von Neubeck C., Grutzmann K., Sommer U., Schweitzer C., Scholch S., Uhlemann H., Gaebler A.M., Werner K., Krause M., Baretton G.B., Welsch T., Koo B.K., Aust D.E., Klink B., Weitz J., Stange D.E. Human gastric cancer modelling using organoids. Gut. 2018 doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314549. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang L., Chang E.W., Wong S.C., Ong S.M., Chong D.Q., Ling K.L. Increased myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastric cancer correlate with cancer stage and plasma S100A8/A9 proinflammatory proteins. J Immunol. 2013;190:794–804. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shoji H., Tada K., Kitano S., Nishimura T., Shimada Y., Nagashima K., Aoki K., Hiraoka N., Honma Y., Iwasa S., Takashima A., Kato K., Boku N., Honda K., Yamada T., Heike Y., Hamaguchi T. The peripheral immune status of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlates the survival in advanced gastric cancer patients receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 2017;8:95083–95094. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ruschoff J., Dietel M., Baretton G., Arbogast S., Walch A., Monges G., Chenard M.P., Penault-Llorca F., Nagelmeier I., Schlake W., Hofler H., Kreipe H.H. HER2 diagnostics in gastric cancer-guideline validation and development of standardized immunohistochemical testing. Virchows Arch. 2010;457:299–307. doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0952-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Slamon D.J., Clark G.M., Wong S.G., Levin W.J., Ullrich A., McGuire W.L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bertaux-Skeirik N., Feng R., Schumacher M.A., Li J., Mahe M.M., Engevik A.C., Javier J.E., Peek R.M., Jr., Ottemann K., Orian-Rousseau V., Boivin G.P., Helmrath M.A., Zavros Y. CD44 plays a functional role in Helicobacter pylori-induced epithelial cell proliferation. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004663. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Engevik A.C., Feng R., Choi E., White S., Bertaux-Skeirik N., Li J., Mahe M.M., Aihara E., Yang L., DiPasquale B., Oh S., Engevik K.A., Giraud A.S., Montrose M.H., Medvedovic M., Helmrath M.A., Goldenring J.R., Zavros Y. The development of spasmolytic polypeptide/TFF2-expressing metaplasia (SPEM) during gastric repair is absent in the aged stomach. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;2:605–624. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2016.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bertaux-Skeirik N., Centeno J., Gao J., Gao J., Gabre J., Zavros Y. Oncogenic transformation of human-derived gastric organoids. Methods Mol Biol. 2016:1–9. doi: 10.1007/7651_2016_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Huber W., Carey V.J., Gentleman R., Anders S., Carlson M., Carvalho B.S., Bravo H.C., Davis S., Gatto L., Girke T., Gottardo R., Hahne F., Hansen K.D., Irizarry R.A., Lawrence M., Love M.I., MacDonald J., Obenchain V., Oles A.K., Pages H., Reyes A., Shannon P., Smyth G.K., Tenenbaum D., Waldron L., Morgan M. Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat Meth. 2015;12:115–121. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Anders S., Huber W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R106. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc B. 1995;57:289–300. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Robinson M.D., McCarthy D.J., Smyth G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Freudenberg J.M., Sivaganesan S., Wagner M., Medvedovic M. A semi-parametric Bayesian model for unsupervised differential co-expression analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:234. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Freudenberg J.M., Joshi V.K., Hu Z., Medvedovic M. CLEAN: CLustering Enrichment ANalysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:234. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Livak K., Schmittgen T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]