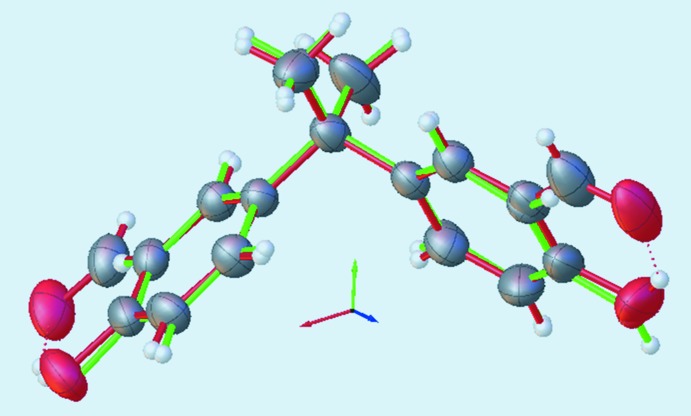
The molecule of (1) presents a >C(CH3)2 group that bridges two nearly planar salicylaldehyde groups, each comprising a planar phenyl ring bonded with a hydroxyl and an aldehyde group. Similarly, molecule (2) presents the same bridging group, but it connects two nearly planar appendants, each comprising a phenyl ring bonded with a hydroxyl and two aldehyde groups. Compound (2) exhibits a strong visible luminescence when excited with ultraviolet radiation.
Keywords: crystal structure; synthesis; photoluminescence; 5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde); 5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde); NMR
Abstract
The title compounds 5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde), C17H16O4, (1), and 5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde), C19H16O6, (2), crystallize with one molecule in the asymmetric unit. In molecule (1), a >C(CH3)2 group bridges two nearly planar salicylaldehyde groups [r.m.s deviations = 0.010 (1) and 0.025 (2) Å], each comprising a planar phenyl ring bonded with a hydroxyl and an aldehyde group. Similarly, compound (2) has the same bridging group, but it connects two nearly planar appendants [r.m.s deviations = 0.034 (1) and 0.035 (1) Å], each comprising a phenyl ring bonded with a hydroxyl and two aldehyde groups. Molecule (1) exhibits a bridge angle of 109.5 (2)° with the salicylaldehyde planes subtending a dihedral angle of 88.4 (1)°. In contrast, molecule (2) presents a bridge angle of 108.9 (2)° with its appendants subtending a dihedral angle of 79.6 (3)°. Both molecules exhibit two intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving the phenolic H atoms and carboxyl O-atom acceptors. In the crystal of (2), O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between one of the hydroxyl H atoms and a carboxyl O atom from a symmetry-related molecule form a chain along [10 ]. In addition, (2) exhibits a strong visible luminescence when excited with ultraviolet radiation.
]. In addition, (2) exhibits a strong visible luminescence when excited with ultraviolet radiation.
Chemical context
As polymers play an undeniable role in our everyday lives, extensive resources and safety evaluations are devoted toward the development and marketing of the most suitable and effective polymer species for a given application (Andrady & Neal 2009 ▸; Fenichell 1996 ▸; Teegarden 2004 ▸). Bisphenols, salicylaldehydes, and their derivatives have fueled much interest in recent years because they are key precursors for many present and future compounds. Bisphenols typically serve as scaffolds for producing thermoplastics and polymer resins, whereas salicylaldehydes and derivatives are commonly used to synthesize metal-chelating agents for analytical, biological, or material science applications (Lim & Tanski, 2007 ▸; Guieu et al., 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸; Barba & Betanzos, 2007 ▸; Vančo et al., 2005 ▸; Baisch et al., 2017 ▸; Kalinowski & Richardson, 2005 ▸, Mounika et al., 2010 ▸). As part of our ongoing work on the synthesis and characterization of novel compounds, as well as our effort to eliminate or replace toxic reagents with greener chemicals in the polymer production process, we have synthesized the title compounds, 5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1) and 5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde (2). These precursor compounds present a >C(CH3)2 group that bridges two salicylaldehyde moieties (1) or two phenyl groups with an hydroxyl and two aldehyde appendants (2). The various functional groups in these molecules determine their chemical and physical properties, and the ability to modify them provides the title compounds with a wide versatility and the multifunctionality required for synthesizing safer and better performance materials for future civilian and military applications. For instance, the title compounds may be used for the non-toxic, isocyanate-free synthesis of polyurethanes (Maisonneuve et al., 2015 ▸). In addition, (2) is a new, solid-state photoluminescence material that emits radiation in the spectroscopic range between 490 and 590 nm upon ultraviolet light excitation, with potential use as an organic light emitting diode, laser frequency harmonic generator, or photoelectric converter.
Structural commentary
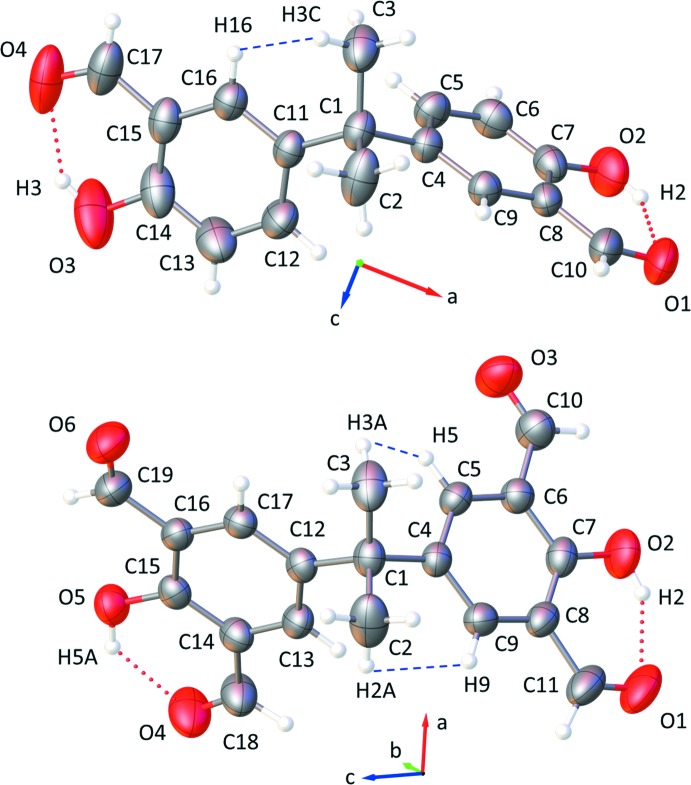
Both title compounds have one molecule in their asymmetric unit. Their molecular structures (Fig. 1 ▸) typify bisphenols and salicylaldehyde derivatives, and their bond lengths and angles are in the usual ranges (Lim & Tanski, 2007 ▸; Guieu et al., 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸; Eriksson & Eriksson, 2001 ▸; Barba & Betanzos, 2007 ▸; Vančo et al., 2005 ▸; Baisch et al., 2017 ▸). In the molecule of (1), the salicylaldehyde fragment containing atom C4 (S1A) is near planar [r.m.s. deviation = 0.010 (1) Å], with a maximum out-of-plane deviation of 0.020 (2) Å for the O1 atom. Similarly, its companion salicylaldehyde fragment (S1B) is near planar [r.m.s. deviation = 0.025 (2)], with a maximum out-of-plane deviation of 0.050 (2) Å for the O3 atom. The bridge angle C4—C1—C11 measures 109.5 (2)° and the S1A and S1B planes subtend a dihedral angle of 88.4 (1)°. Molecule (1) exhibits two intramolecular hydrogen bonds between the phenolic hydrogen atoms and carboxyl O-atom acceptors (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
Molecular conformation and atom-numbering scheme for molecules (1) (top) and (2) (bottom). Non-hydrogen atoms are shown with 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (1) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O1 | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.642 (3) | 145 |
| O3—H3⋯O4 | 0.82 | 1.90 | 2.619 (4) | 145 |
Molecule (2) presents two near planar appendants, denoted A1 and A2 for the appendants containing C4 and C11, respectively, [r.m.s deviation = 0.034 (1) Å (A1) and 0.035 (1) Å (A2), with maximum out-of-plane deviations of 0.068 (2) Å for atom O2 (A1) and −0.060 (2) Å for atom O5 (A2)]. Each appendant comprises a hydroxyl and two aldehyde groups. Similar to (1), the salicylaldehyde fragments with atoms C4–C9/C11/O1/O2 (S2A) or C12–C17/C18/O6/O5 (S2B) in (2) adopt a near planar geometry [r.m.s. deviation = 0.024 (1) Å for S2A and 0.036 (1) Å for S2B]. The additional carbonyl groups C10—O3 and C18—O4 on the phenyl rings are twisted slightly out of the S2A and S2B planes, respectively, as evidenced by their respective torsion angles C5—C6—C10—O3 [−2.9 (4)°] and C13—C14—C18—O4 [−179.1 (3)°]. These additional groups increase the steric hindrance between the appendants and methyl bridge groups in (2), perhaps decreasing both the bridge angle C4—C1—C12 [108.9 (2)°] and the dihedral angle between the A1 and A2 planes [88.4 (1)°] relative to (1). Molecule (2) presents two intramolecular hydrogen bonds involving the phenolic hydrogen atoms with the carboxyl O-atom acceptors (Table 2 ▸), similar to (1).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (2) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O1 | 0.82 | 1.88 | 2.605 (3) | 146 |
| O5—H5A⋯O4 | 0.94 (4) | 2.00 (4) | 2.745 (3) | 135 (3) |
| O5—H5A⋯O3i | 0.94 (4) | 2.14 (4) | 2.841 (2) | 131 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) 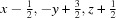 .
.
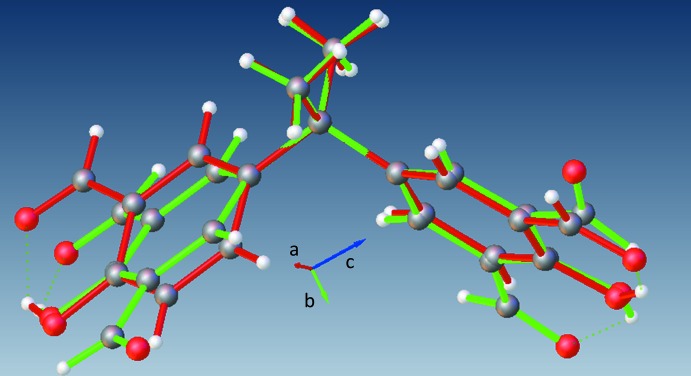
Both (1) and (2) exhibit several intramolecular H⋯H contacts that are shorter than the sum of the H-atom van der Waals radii. These contacts occur between the methyl group H atoms and adjacent phenyl group H atoms [H3C⋯H16 = 2.2538 (1) Å, shortest in (1); H3A⋯H5 = 2.1643 (1) Å and H2A⋯H9 = 2.1890 (1) Å, shorter than others in (2)]. Superimposition of the atoms C1/C2/C3/C4/C11 of (1) with the corresponding atoms of (2) (see Fig. 2 ▸), yields an r.m.s. deviation of 0.011 Å with the S1A and S2B planes subtending a dihedral angle of 9.82 (4)° and the S1B and S2B planes subtending an angle of 35.1 (1)°.
Figure 2.
An overlay of (1) (red) and (2) (green), where the atoms C1/C2/C3/C4/C11 of (1) are superimposed with the corresponding atoms of (2).
Supramolecular features
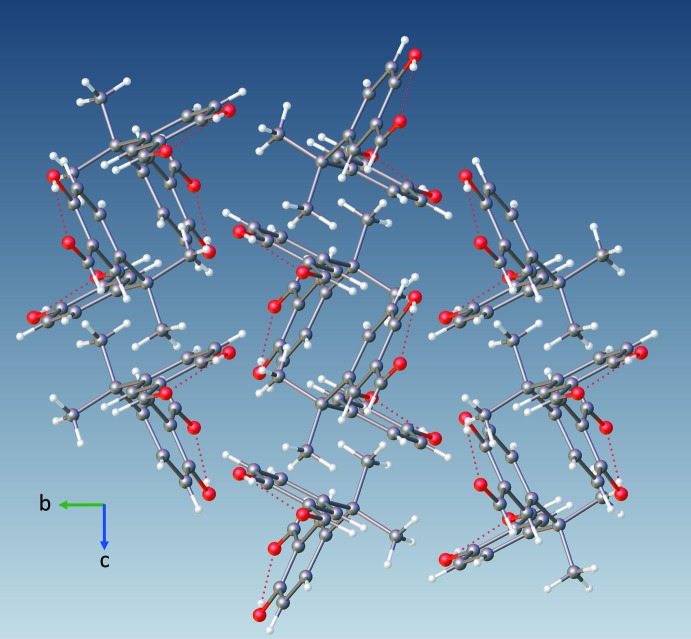
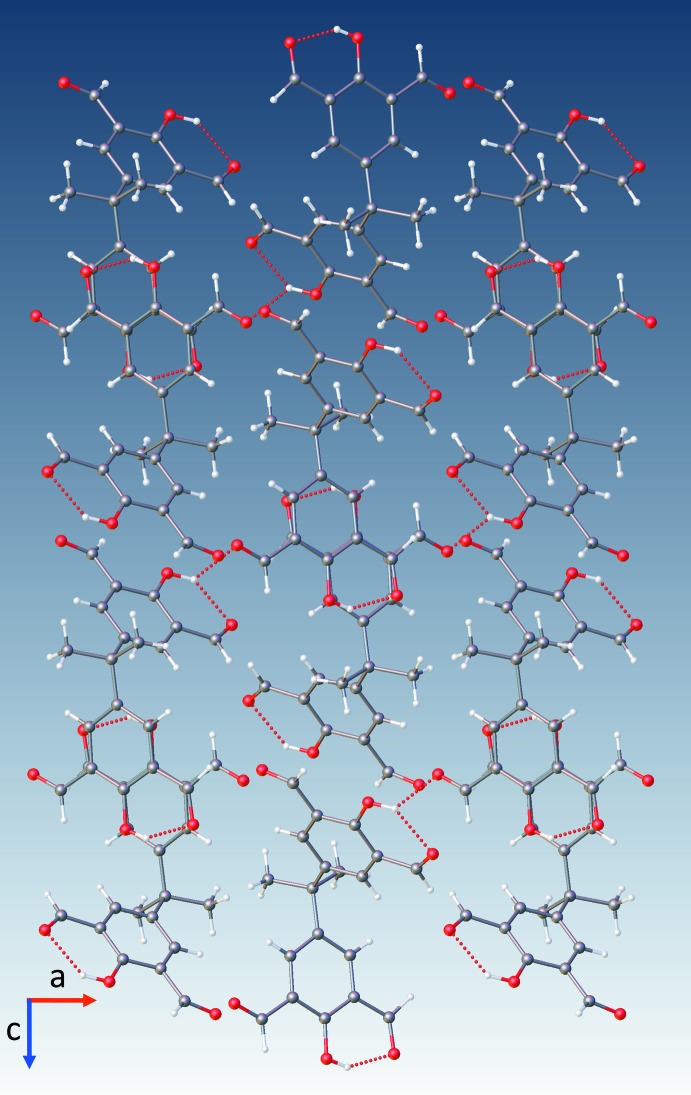
Fig. 3 ▸ shows the packing of (1) along the a axis. van der Waals contacts between the O atoms and H atoms of adjacent molecules [O1⋯H3B
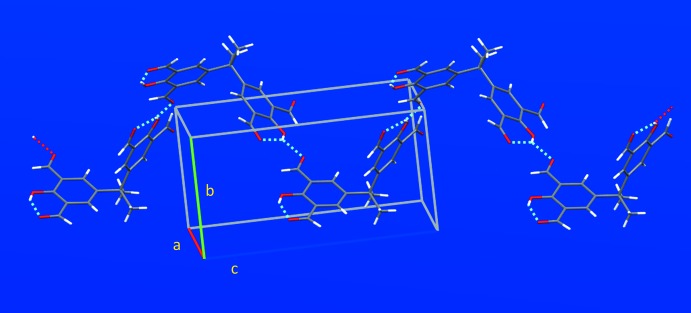
i = 2.628 Å; symmetry code: (i) 1 − x, 1 − y, −z] dominate the intermolecular interactions. In addition, bifurcated contacts between atom C17 and atoms H3 and O3 of adjacent molecules [C17⋯H3ii = 2.887 Å; C17⋯O3ii = 2.811 (4) Å; symmetry code: (ii) x, ½ − y, −½ + z] contribute to the crystal packing. As in molecule (1), O⋯H contacts play a key role in the intermolecular interactions of (2). However, unlike (1), these interactions result mostly from hydrogen bonding between the phenolic hydrogen atoms and the carboxyl oxygen atoms of adjacent molecules [O5—H5A⋯O1 = 2.841 (2) Å; θ = 131 (3)°; Table 2 ▸.) As a result, each molecule becomes both a hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor. This feature links a molecule at both ends with its adjacent inverted molecules, thus forming undulating chains along [10 ] (Figs. 4 ▸ and 5 ▸).
] (Figs. 4 ▸ and 5 ▸).
Figure 3.
Crystal packing of (1) along the a axis. Red dashed lines show the intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Figure 4.
Hydrogen bonding of (2) showing both its intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds, depicted as blue dashed lines.
Figure 5.
Crystal packing of (2) viewed along the b axis showing both the intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds (red dashed lines).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD web interface, August 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) and the Crystallography Open Database (Gražulis et al., 2009 ▸) yields a number of compounds containing the bisphenol or salicylaldehyde group. For examples, see Lim & Tanski, 2007 ▸; Guieu et al., 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸; Eriksson & Eriksson, 2001 ▸; Barba & Betanzos, 2007 ▸; Vančo et al., 2005 ▸; Baisch et al., 2017 ▸. The compounds 4-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenol (3), a common chemical known also as bisphenol A, (Lim & Tanski; CCDC 617706, CEGYOC03) and 5-[(3-formyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (4) (Barba & Betanzos, 2007 ▸; CCDC 642298, VILCID) merit comparison to (1) and (2) and further discussion. Molecule (3) presents a submolecular structure of the title compounds, as it only lacks the aldehyde groups found in (1) or (2). In contrast, (4) exhibits a pair of salicylaldehyde groups as (1) or (2), except that they are linked by a >CH2 bridge, instead of a >C(CH3)2 bridge.
Compound (3) crystallizes with three independent molecules in the asymmetric unit. Each molecule presents a pair of planar phenol fragments [r.m.s. deviations = 0.013 (2) and 0.028 (2) Å; 0.0039 (4) and 0.0078 (5) Å; and 0.0055 (6) and 0.0039 (3) Å] subtending dihedral angles of 77.81 (3), 86.15 (4) and 84.34 (4)°, respectively, and respective bridge angles of 109.2 (1), 109.5 (1), and 108.1 (1)°. In general, both (1) and (2) have similar geometric parameters to (3), although their corresponding phenol groups are less planar than those of (3). This manifestation results most likely because the phenyl groups of the title compounds contain aldehyde groups in addition to the hydroxyl groups. The O atoms of these aldehyde groups participate in hydrogen bonding with the hydroxyl H atoms, thus partially displacing the hydroxyl O atoms away from the phenol planes. A superimposition of the atoms in (1) with the corresponding atoms of one of the three structures of (3) shows that the differences in the atom positions of the two structures are hardly discernible (Fig. 6 ▸) [r.m.s. deviation = 0.115 Å; maximum displacement = 0.217 (2) Å between the O2 atom of (1) and its counterpart of (3)]. An overlay of structure (1) onto either structure two or three of (3) yields comparable results. A similar analysis of structures (2) and (3) yields a r.m.s. deviation of 1.14 Å with maximum displacement of 0.605 (2) Å for the C6 atom of (2) and its counterpart in (3). Again, we obtain comparable results overlaying either structure two or three of (3) onto (1).
Figure 6.
Superimposition of the non-hydrogen atoms of (3) (green) onto the corresponding atoms of (1) (red).
Molecule (4) exhibits a pair of near planar salicylaldehyde fragments [r.m.s. deviation = 0.0153 (2) and 0.0238 (9) Å] forming a dihedral angle of 85.96 (4)°, similar to (1). Its bridge angle of 113.6 (1)° is much greater than that of (1) or (2), however. A superimposition of the salicylaldehyde group atoms of (4) (C4 through C9, C10, O1, and O2) with corresponding atoms of (1) reveals nearly identical atomic positions of the two groups [r.m.s. deviation = 0.0160 Å], with the companion salicylaldehyde group planes [centroid-to-centroid distance measuring = 4.68 (2) Å] subtending a dihedral angle of 6.81°. A similar analysis for structures (2) and (4) yields a r.m.s. deviation = 0.027 Å with companion salicylaldehyde groups planes [centroid-to-centroid distance measuring = 4.21 (1) Å] forming a dihedral angle of 7.4 (1)°.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compounds were synthesized following modified literature procedures (Özdemir et al., 2015 ▸ and Masurier et al., 2008 ▸ for compounds (1) and (2), respectively).
Compound (1): A combination of compound (3) (10.0 g, 43.8 mmol, 1.0 equiv.), paraformaldehyde (16.7 g, 556.1 mmol, 12.7 equiv.), and magnesium(II) chloride (35.2 g, 173.1 mmol, 4.0 equiv.) were suspended in tetrahydrofuran (THF, 500 mL), placed under a stream of N2, and stirred. Then, triethylamine (49 mL, 351.6 mmol, 8.0 equiv.) was added dropwise to the reaction mixture at ambient temperature and stirred under reflux for 16 h. At the conclusion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to room temperature before the addition of diethyl ether (500 mL). The organic solution was sequentially extracted with aqueous 1 M HCl (3 × 500 mL) and water (3 × 500 mL), dried over Na2SO4 or MgSO4, filtered, and the volatiles were removed under reduced pressure. The solid residue was purified with a series of hexane washes and then dried under vacuum to afford the desired product (1) as a white solid (11.3 g, 39.7 mmol, 91% yield). Slow diffusion of hexanes into a benzene solution saturated with (1) afforded single crystals of (1).
Compound (2): A mixture of (3) (10.0 g, 43.8 mmol, 1.0 equiv.) and hexamethylenetetramine (19.1 g, 183.3 mmol, 4.2 equiv.) was dissolved in trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, 60 mL) under ambient conditions. The reaction mixture was stirred at 403 K for 2.5 h and subsequently cooled to room temperature before aqueous HCl (3M, 150 mL) was added slowly. The reaction mixture was stirred at 383 K for 16 h, cooled to room temperature, and the resulting organic phase extracted with dichloromethane (DCM, 3 × 150 mL). Then, this organic phase was dried over MgSO4, filtered, and the volatiles were removed under reduced pressure. The resulting solid was purified with a series of hexanes washes and dried under vacuum to afford the novel product (2) as a neon yellow solid (9.97 g, 29.3 mmol, 67% yield). Slow evaporation of a DCM solution saturated with (2) afforded single crystals suitable for X-ray diffractometry.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker 400 MHz spectrometer. Chemical shifts (δ) are given in ppm: (1) 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400.13 MHz): δ 1.70 (s, 6H), 6.92 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (dd, J 1 = 8.7 Hz, J 2 = 2.5 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 2H), 9.86 (s, 2H), 10.93 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3, 100.62 MHz): δ 30.47, 41.86, 117.85, 120.15, 130.92, 136.20, 141.67, 160.10, 196.74 ppm. (2) 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400.13 MHz): δ 1.75 (s, 6H), 7.81 (s, 4H), 10.19 (s, 4H), 11.53 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3, 100.62 MHz): δ 30.31, 30.59, 42.08, 123.05, 135.53, 141.31, 162.20, 191.99 ppm; low-resolution mass spectrometry (atmospheric pressure ionization); Thermo Fisher Scientific (ISQ–EC): m/z [M]+: calculated = 340.33; measured: 340; and luminescence spectrum (Horiba Jobin Yvon Fluoromax 3 Spectrofluorimeter): 10−5 M/acetonitrile; λexc = 356 nm; λem = 539 nm (full width half maximum = 100 nm).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. The hydrogen atoms for (1) and most in (2) were refined in a riding-model approximation with C—H = 0.93 or 0.96 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) or 1.5U eq(Cmethyl) and O—H = 0.82 Å and U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O). In (2), atoms H10, H11, H18, and H5A were refined independently with isotropic displacement parameters.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C17H16O4 | C19H16O6 |
| M r | 284.30 | 340.32 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 298 | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 16.6108 (6), 12.0803 (6), 7.0946 (4) | 13.4327 (4), 7.9920 (3), 15.2062 (5) |
| β (°) | 90.396 (4) | 90.348 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1423.59 (12) | 1632.42 (9) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.3 × 0.28 | 0.34 × 0.32 × 0.28 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Dualflex, EosS2 | Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Dualflex, EosS2 |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Bourhis et al., 2015 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Bourhis et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.861, 1.000 | 0.810, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 6271, 2589, 2036 | 13629, 3331, 2586 |
| R int | 0.017 | 0.029 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.602 | 0.625 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.051, 0.122, 1.10 | 0.056, 0.167, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 2589 | 3331 |
| No. of parameters | 195 | 249 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.21, −0.20 | 0.25, −0.27 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 1, 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016316/lh5885sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016316/lh58851sup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016316/lh58852sup5.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr J. Orlicki for the use of the Fluoromax Spectrofluorimeter and helpful discussions regarding this work and Mr E. Napadensky for helping acquire the mass spectra. This research was supported in part by an appointment to the Postgraduate Research Participation Program at the US Army Research Laboratory by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education through an interagency agreement between the US Department of Energy and the USARL.
supplementary crystallographic information
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Crystal data
| C17H16O4 | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 284.30 | Dx = 1.326 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 16.6108 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 2453 reflections |
| b = 12.0803 (6) Å | θ = 2.1–25.2° |
| c = 7.0946 (4) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 90.396 (4)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1423.59 (12) Å3 | Irregular, clear colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.35 × 0.3 × 0.28 mm |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Data collection
| Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Dualflex, EosS2 diffractometer | 2036 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 8.0945 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.017 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Bourhis et al., 2015) | h = −20→20 |
| Tmin = 0.861, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −11→14 |
| 6271 measured reflections | l = −8→6 |
| 2589 independent reflections |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0347P)2 + 0.7348P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.10 | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 2589 reflections | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| 195 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL-2016/4 (Sheldrick 2016), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0035 (12) |
| Primary atom site location: dual |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.60832 (9) | 0.41639 (19) | 0.2405 (3) | 0.0801 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.52036 (10) | 0.26273 (16) | 0.0724 (3) | 0.0736 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.562402 | 0.293270 | 0.104187 | 0.110* | |
| O3 | 0.01645 (12) | 0.31117 (19) | 0.6564 (4) | 0.1054 (9) | |
| H3 | −0.028389 | 0.315525 | 0.607948 | 0.158* | |
| O4 | −0.08657 (10) | 0.34768 (16) | 0.3823 (4) | 0.0932 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.24872 (11) | 0.53761 (17) | 0.2163 (3) | 0.0461 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.26777 (14) | 0.6426 (2) | 0.3303 (4) | 0.0721 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.218770 | 0.681998 | 0.354821 | 0.108* | |
| H2B | 0.303523 | 0.688954 | 0.259696 | 0.108* | |
| H2C | 0.292921 | 0.622372 | 0.447559 | 0.108* | |
| C3 | 0.21711 (14) | 0.5742 (2) | 0.0216 (4) | 0.0662 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.199791 | 0.510478 | −0.048481 | 0.099* | |
| H3B | 0.259284 | 0.611212 | −0.045502 | 0.099* | |
| H3C | 0.172540 | 0.623899 | 0.037436 | 0.099* | |
| C4 | 0.32352 (11) | 0.46576 (17) | 0.1856 (3) | 0.0411 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.31596 (13) | 0.36340 (18) | 0.0949 (3) | 0.0482 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.264923 | 0.339291 | 0.059134 | 0.058* | |
| C6 | 0.38080 (13) | 0.29743 (19) | 0.0566 (3) | 0.0524 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.373339 | 0.230404 | −0.005545 | 0.063* | |
| C7 | 0.45731 (12) | 0.33011 (19) | 0.1102 (3) | 0.0486 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.46721 (11) | 0.43126 (19) | 0.2017 (3) | 0.0448 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.40007 (11) | 0.49711 (18) | 0.2366 (3) | 0.0430 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.407386 | 0.564808 | 0.296766 | 0.052* | |
| C10 | 0.54638 (13) | 0.4685 (2) | 0.2607 (3) | 0.0600 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.550084 | 0.537495 | 0.318412 | 0.072* | |
| C11 | 0.18592 (11) | 0.47158 (16) | 0.3248 (3) | 0.0420 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.20564 (13) | 0.4232 (2) | 0.4976 (3) | 0.0569 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.258393 | 0.428440 | 0.541446 | 0.068* | |
| C13 | 0.15019 (15) | 0.3682 (2) | 0.6053 (4) | 0.0699 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.165623 | 0.336218 | 0.719130 | 0.084* | |
| C14 | 0.07106 (14) | 0.36060 (19) | 0.5433 (4) | 0.0651 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.04964 (12) | 0.40537 (18) | 0.3714 (4) | 0.0519 (6) | |
| C16 | 0.10733 (12) | 0.45953 (18) | 0.2658 (3) | 0.0469 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.092278 | 0.489091 | 0.149790 | 0.056* | |
| C17 | −0.03227 (14) | 0.3944 (2) | 0.3020 (5) | 0.0717 (8) | |
| H17 | −0.044107 | 0.426019 | 0.185508 | 0.086* |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0374 (9) | 0.1197 (17) | 0.0831 (13) | 0.0130 (10) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0127 (12) |
| O2 | 0.0616 (10) | 0.0765 (13) | 0.0828 (13) | 0.0281 (9) | 0.0117 (10) | −0.0046 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0797 (13) | 0.0857 (15) | 0.152 (2) | 0.0139 (12) | 0.0501 (14) | 0.0595 (15) |
| O4 | 0.0470 (10) | 0.0713 (13) | 0.162 (2) | −0.0120 (9) | 0.0304 (12) | −0.0243 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0356 (10) | 0.0403 (11) | 0.0624 (14) | 0.0016 (9) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0008 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0487 (13) | 0.0455 (14) | 0.122 (2) | 0.0000 (11) | 0.0113 (14) | −0.0231 (15) |
| C3 | 0.0496 (13) | 0.0670 (17) | 0.0819 (18) | 0.0083 (12) | 0.0080 (12) | 0.0270 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0368 (10) | 0.0402 (11) | 0.0463 (12) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0021 (8) | 0.0001 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0461 (13) | 0.0543 (13) | −0.0033 (10) | −0.0030 (10) | −0.0045 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0619 (14) | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0527 (13) | 0.0055 (11) | 0.0038 (11) | −0.0083 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0479 (12) | 0.0526 (14) | 0.0456 (12) | 0.0123 (10) | 0.0096 (9) | 0.0050 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0372 (10) | 0.0559 (13) | 0.0413 (12) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0039 (8) | 0.0064 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0412 (11) | 0.0419 (11) | 0.0459 (12) | −0.0021 (9) | 0.0021 (9) | −0.0013 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0406 (12) | 0.0845 (18) | 0.0551 (14) | −0.0010 (12) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0087 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0357 (10) | 0.0377 (11) | 0.0526 (13) | 0.0041 (8) | 0.0020 (9) | −0.0049 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0436 (12) | 0.0644 (15) | 0.0625 (15) | 0.0130 (11) | −0.0022 (11) | 0.0059 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0669 (16) | 0.0731 (18) | 0.0698 (17) | 0.0226 (13) | 0.0113 (13) | 0.0274 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0550 (14) | 0.0443 (14) | 0.096 (2) | 0.0109 (11) | 0.0266 (14) | 0.0164 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0404 (11) | 0.0390 (12) | 0.0762 (17) | 0.0021 (9) | 0.0084 (11) | −0.0042 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0408 (11) | 0.0457 (12) | 0.0543 (13) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0011 (9) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0424 (13) | 0.0641 (17) | 0.109 (2) | −0.0049 (12) | 0.0080 (14) | −0.0208 (16) |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C10 | 1.216 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.368 (3) |
| O2—H2 | 0.8200 | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C7 | 1.355 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.381 (3) |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | C7—C8 | 1.393 (3) |
| O3—C14 | 1.354 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.393 (3) |
| O4—C17 | 1.210 (3) | C8—C10 | 1.449 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.536 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C3 | 1.539 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C4 | 1.532 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.395 (3) |
| C1—C11 | 1.526 (3) | C11—C16 | 1.376 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9600 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9600 | C12—C13 | 1.372 (3) |
| C2—H2C | 0.9600 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9600 | C13—C14 | 1.386 (4) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9600 | C14—C15 | 1.379 (4) |
| C3—H3C | 0.9600 | C15—C16 | 1.385 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.399 (3) | C15—C17 | 1.450 (3) |
| C4—C9 | 1.373 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C7—O2—H2 | 109.5 | C6—C7—C8 | 118.96 (19) |
| C14—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C7—C8—C9 | 119.45 (19) |
| C2—C1—C3 | 107.6 (2) | C7—C8—C10 | 120.7 (2) |
| C4—C1—C2 | 112.22 (17) | C9—C8—C10 | 119.8 (2) |
| C4—C1—C3 | 107.89 (18) | C4—C9—C8 | 122.5 (2) |
| C11—C1—C2 | 107.77 (18) | C4—C9—H9 | 118.8 |
| C11—C1—C3 | 111.89 (17) | C8—C9—H9 | 118.8 |
| C11—C1—C4 | 109.48 (16) | O1—C10—C8 | 124.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | O1—C10—H10 | 117.6 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C8—C10—H10 | 117.6 |
| C1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C12—C11—C1 | 120.33 (18) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C16—C11—C1 | 123.53 (19) |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C16—C11—C12 | 116.1 (2) |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 118.7 |
| C1—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 122.5 (2) |
| C1—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 118.7 |
| C1—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.2 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C12—C13—C14 | 119.6 (2) |
| H3A—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.2 |
| H3B—C3—H3C | 109.5 | O3—C14—C13 | 118.6 (3) |
| C5—C4—C1 | 119.71 (17) | O3—C14—C15 | 121.8 (2) |
| C9—C4—C1 | 123.83 (18) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.5 (2) |
| C9—C4—C5 | 116.42 (18) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.7 | C14—C15—C17 | 120.0 (2) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 122.5 (2) | C16—C15—C17 | 120.7 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.7 | C11—C16—C15 | 123.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C11—C16—H16 | 118.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.2 (2) | C15—C16—H16 | 118.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.9 | O4—C17—C15 | 125.7 (3) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 119.0 (2) | O4—C17—H17 | 117.2 |
| O2—C7—C8 | 122.0 (2) | C15—C17—H17 | 117.2 |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | 180.0 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.5 (3) |
| O2—C7—C8—C10 | 0.0 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.2 (3) |
| O3—C14—C15—C16 | 176.9 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C10 | 179.8 (2) |
| O3—C14—C15—C17 | −3.8 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.6 (3) |
| C1—C4—C5—C6 | 177.4 (2) | C7—C8—C10—O1 | −1.6 (4) |
| C1—C4—C9—C8 | −178.02 (19) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (3) |
| C1—C11—C12—C13 | 176.4 (2) | C9—C8—C10—O1 | 178.4 (2) |
| C1—C11—C16—C15 | −175.8 (2) | C10—C8—C9—C4 | −179.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C4—C5 | 175.9 (2) | C11—C1—C4—C5 | 56.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C4—C9 | −6.4 (3) | C11—C1—C4—C9 | −126.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—C11—C12 | −67.3 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.7 (4) |
| C2—C1—C11—C16 | 109.9 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.6 (3) |
| C3—C1—C4—C5 | −65.7 (2) | C12—C13—C14—O3 | −176.5 (2) |
| C3—C1—C4—C9 | 112.0 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 2.1 (4) |
| C3—C1—C11—C12 | 174.6 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.6 (4) |
| C3—C1—C11—C16 | −8.2 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C17 | 177.7 (2) |
| C4—C1—C11—C12 | 55.0 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.3 (3) |
| C4—C1—C11—C16 | −127.7 (2) | C14—C15—C17—O4 | −0.2 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.9 (3) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (3) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | −0.3 (3) | C16—C15—C17—O4 | 179.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | 179.3 (2) | C17—C15—C16—C11 | −179.6 (2) |
5,5'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) (1). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O1 | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.642 (3) | 145 |
| O3—H3···O4 | 0.82 | 1.90 | 2.619 (4) | 145 |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Crystal data
| C19H16O6 | F(000) = 712 |
| Mr = 340.32 | Dx = 1.385 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 13.4327 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 4266 reflections |
| b = 7.9920 (3) Å | θ = 2.0–26.0° |
| c = 15.2062 (5) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 90.348 (3)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1632.42 (9) Å3 | Irregular, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.34 × 0.32 × 0.28 mm |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Data collection
| Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Dualflex, EosS2 diffractometer | 3331 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube, Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2586 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| Detector resolution: 8.0945 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.0° |
| ω scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Bourhis et al., 2015) | k = −8→9 |
| Tmin = 0.810, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −19→19 |
| 13629 measured reflections |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.167 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.085P)2 + 0.540P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3331 reflections | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 249 parameters | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.56797 (16) | 0.2277 (3) | 0.75859 (13) | 0.0451 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.5020 (3) | 0.0866 (3) | 0.79457 (17) | 0.0744 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.433239 | 0.115432 | 0.786234 | 0.112* | |
| H2B | 0.515438 | 0.071710 | 0.856159 | 0.112* | |
| H2C | 0.516230 | −0.015436 | 0.763805 | 0.112* | |
| C3 | 0.67756 (19) | 0.1817 (3) | 0.77738 (16) | 0.0650 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.719548 | 0.274519 | 0.762469 | 0.098* | |
| H3B | 0.695707 | 0.086163 | 0.742724 | 0.098* | |
| H3C | 0.685618 | 0.155720 | 0.838652 | 0.098* | |
| C4 | 0.55349 (14) | 0.2495 (2) | 0.65879 (12) | 0.0398 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.62192 (14) | 0.3416 (3) | 0.61068 (13) | 0.0425 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.674345 | 0.392670 | 0.640554 | 0.051* | |
| C6 | 0.61570 (15) | 0.3610 (3) | 0.51995 (13) | 0.0442 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.53582 (16) | 0.2880 (3) | 0.47460 (13) | 0.0477 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.46395 (15) | 0.2017 (3) | 0.52114 (14) | 0.0470 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.47444 (15) | 0.1818 (3) | 0.61219 (14) | 0.0458 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.426579 | 0.120883 | 0.642407 | 0.055* | |
| C10 | 0.69131 (19) | 0.4569 (3) | 0.47277 (17) | 0.0598 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.683 (2) | 0.462 (3) | 0.4070 (19) | 0.073 (8)* | |
| C11 | 0.37722 (19) | 0.1293 (4) | 0.4765 (2) | 0.0669 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.324 (2) | 0.068 (3) | 0.5214 (17) | 0.065 (7)* | |
| C12 | 0.53648 (14) | 0.3898 (3) | 0.80494 (12) | 0.0400 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.44519 (15) | 0.4626 (3) | 0.78465 (13) | 0.0449 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.407023 | 0.415913 | 0.739712 | 0.054* | |
| C14 | 0.40839 (15) | 0.6016 (3) | 0.82828 (13) | 0.0460 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.46436 (15) | 0.6737 (3) | 0.89671 (13) | 0.0421 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.55783 (14) | 0.6066 (3) | 0.91700 (13) | 0.0426 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.59223 (14) | 0.4663 (3) | 0.87119 (12) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.654434 | 0.422634 | 0.885479 | 0.051* | |
| C18 | 0.31154 (19) | 0.6673 (4) | 0.80118 (17) | 0.0662 (7) | |
| H18 | 0.277 (2) | 0.595 (4) | 0.755 (2) | 0.087 (9)* | |
| C19 | 0.61762 (17) | 0.6814 (3) | 0.98792 (16) | 0.0571 (6) | |
| H19 | 0.5921 (19) | 0.790 (3) | 1.0142 (17) | 0.067 (7)* | |
| O1 | 0.36389 (14) | 0.1404 (3) | 0.39694 (14) | 0.0851 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.53075 (14) | 0.3050 (3) | 0.38619 (10) | 0.0706 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.479652 | 0.260776 | 0.367754 | 0.106* | |
| O3 | 0.75935 (14) | 0.5285 (3) | 0.50684 (12) | 0.0779 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.27133 (14) | 0.7886 (3) | 0.83289 (13) | 0.0869 (7) | |
| O5 | 0.43151 (13) | 0.8023 (2) | 0.94557 (11) | 0.0565 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.366 (3) | 0.834 (4) | 0.932 (2) | 0.096 (10)* | |
| O6 | 0.69410 (13) | 0.6221 (3) | 1.01611 (13) | 0.0749 (6) |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0571 (12) | 0.0433 (12) | 0.0349 (10) | 0.0031 (9) | −0.0028 (8) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C2 | 0.119 (2) | 0.0514 (15) | 0.0532 (14) | −0.0140 (15) | 0.0114 (14) | 0.0062 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0797 (16) | 0.0667 (16) | 0.0484 (13) | 0.0329 (13) | −0.0166 (12) | −0.0045 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0436 (10) | 0.0397 (11) | 0.0362 (10) | 0.0046 (8) | −0.0029 (8) | −0.0034 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0428 (10) | 0.0440 (11) | 0.0405 (11) | −0.0006 (9) | −0.0066 (8) | −0.0020 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0460 (10) | 0.0449 (12) | 0.0417 (11) | 0.0012 (9) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0007 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0560 (12) | 0.0477 (12) | 0.0392 (11) | 0.0097 (10) | −0.0085 (9) | −0.0048 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0479 (12) | 0.0503 (12) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0095 (9) | −0.0094 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0422 (10) | 0.0467 (12) | 0.0486 (12) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0004 (9) | −0.0036 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0656 (14) | 0.0639 (16) | 0.0498 (13) | −0.0071 (12) | −0.0004 (11) | 0.0063 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0536 (13) | 0.0721 (17) | 0.0746 (18) | 0.0058 (12) | −0.0217 (13) | −0.0220 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0458 (10) | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0309 (9) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0046 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0458 (10) | 0.0547 (13) | 0.0343 (10) | 0.0009 (9) | −0.0045 (8) | −0.0014 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0433 (10) | 0.0585 (13) | 0.0362 (10) | 0.0051 (9) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0039 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0458 (10) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0374 (10) | −0.0001 (9) | 0.0060 (8) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0480 (12) | 0.0373 (10) | −0.0043 (9) | 0.0007 (8) | 0.0004 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0395 (9) | 0.0497 (12) | 0.0373 (10) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0034 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0561 (13) | 0.0870 (19) | 0.0555 (14) | 0.0234 (13) | −0.0084 (11) | −0.0153 (14) |
| C19 | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0662 (16) | 0.0578 (14) | −0.0025 (11) | −0.0040 (10) | −0.0106 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0752 (12) | 0.1010 (15) | 0.0786 (13) | 0.0110 (11) | −0.0387 (10) | −0.0277 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0875 (13) | 0.0870 (14) | 0.0371 (8) | 0.0030 (10) | −0.0139 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0766 (12) | 0.0875 (14) | 0.0697 (12) | −0.0279 (11) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0071 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0695 (11) | 0.1126 (16) | 0.0784 (13) | 0.0418 (11) | −0.0131 (10) | −0.0226 (12) |
| O5 | 0.0581 (9) | 0.0565 (10) | 0.0550 (9) | 0.0090 (8) | 0.0009 (7) | −0.0105 (8) |
| O6 | 0.0604 (10) | 0.0890 (14) | 0.0753 (12) | 0.0004 (9) | −0.0174 (9) | −0.0135 (10) |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.537 (3) | C12—C1 | 1.536 (3) |
| C1—C3 | 1.542 (3) | C12—C17 | 1.393 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9600 | C13—C12 | 1.390 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9600 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2C | 0.9600 | C13—C14 | 1.386 (3) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9600 | C14—C18 | 1.460 (3) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9600 | C15—C14 | 1.404 (3) |
| C3—H3C | 0.9600 | C16—C15 | 1.398 (3) |
| C4—C1 | 1.539 (3) | C16—C19 | 1.468 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.389 (3) | C17—C16 | 1.400 (3) |
| C4—C9 | 1.383 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 1.02 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (3) | C19—H19 | 1.02 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.399 (3) | O1—C11 | 1.225 (3) |
| C6—C10 | 1.464 (3) | O2—C7 | 1.353 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.384 (3) | O2—H2 | 0.8200 |
| C8—C9 | 1.400 (3) | O3—C10 | 1.194 (3) |
| C8—C11 | 1.464 (3) | O4—C18 | 1.211 (3) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | O5—C15 | 1.344 (3) |
| C10—H10 | 1.01 (3) | O5—H5A | 0.94 (3) |
| C11—H11 | 1.10 (3) | O6—C19 | 1.208 (3) |
| C2—C1—C3 | 108.1 (2) | C4—C9—H9 | 118.8 |
| C2—C1—C4 | 111.37 (18) | C8—C9—H9 | 118.8 |
| C4—C1—C3 | 108.94 (17) | C6—C10—H10 | 115.5 (16) |
| C12—C1—C2 | 107.15 (18) | O3—C10—C6 | 124.8 (2) |
| C12—C1—C3 | 112.43 (17) | O3—C10—H10 | 119.8 (16) |
| C12—C1—C4 | 108.90 (16) | C8—C11—H11 | 113.7 (13) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | O1—C11—C8 | 122.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | O1—C11—H11 | 123.6 (13) |
| C1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C13—C12—C1 | 119.75 (17) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C13—C12—C17 | 116.53 (19) |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C17—C12—C1 | 123.62 (17) |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 118.5 |
| C1—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C14—C13—C12 | 123.06 (18) |
| C1—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 118.5 |
| C1—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C13—C14—C15 | 119.53 (18) |
| H3B—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C13—C14—C18 | 118.2 (2) |
| H3B—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C15—C14—C18 | 122.3 (2) |
| H3C—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 118.81 (19) |
| C5—C4—C1 | 119.94 (17) | O5—C15—C14 | 123.20 (19) |
| C9—C4—C1 | 123.58 (18) | O5—C15—C16 | 117.97 (19) |
| C9—C4—C5 | 116.48 (18) | C15—C16—C17 | 119.76 (18) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.5 | C15—C16—C19 | 119.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 123.06 (18) | C17—C16—C19 | 120.73 (19) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.5 | C12—C17—C16 | 122.25 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.93 (19) | C12—C17—H17 | 118.9 |
| C5—C6—C10 | 120.46 (19) | C16—C17—H17 | 118.9 |
| C7—C6—C10 | 120.6 (2) | C14—C18—H18 | 113.3 (17) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.40 (18) | O4—C18—C14 | 125.1 (2) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 118.8 (2) | O4—C18—H18 | 121.4 (17) |
| O2—C7—C8 | 121.82 (19) | C16—C19—H19 | 116.9 (14) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.73 (18) | O6—C19—C16 | 124.2 (2) |
| C7—C8—C11 | 121.0 (2) | O6—C19—H19 | 119.0 (15) |
| C9—C8—C11 | 119.3 (2) | C7—O2—H2 | 109.5 |
| C4—C9—C8 | 122.31 (19) | C15—O5—H5A | 113 (2) |
| C1—C4—C5—C6 | 177.43 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C18 | 179.9 (2) |
| C1—C4—C9—C8 | −179.08 (19) | C12—C17—C16—C15 | 0.2 (3) |
| C1—C12—C17—C16 | −174.81 (18) | C12—C17—C16—C19 | 178.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.5 (3) | C13—C12—C1—C2 | −71.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C10 | −178.8 (2) | C13—C12—C1—C3 | 170.37 (19) |
| C5—C4—C1—C2 | −164.9 (2) | C13—C12—C1—C4 | 49.6 (2) |
| C5—C4—C1—C3 | −45.8 (3) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | 1.6 (3) |
| C5—C4—C1—C12 | 77.2 (2) | C13—C14—C18—O4 | −179.1 (3) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | 1.0 (3) | C14—C13—C12—C1 | 175.04 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.5 (3) | C14—C13—C12—C17 | −1.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | −179.06 (19) | C15—C14—C18—O4 | 1.2 (4) |
| C5—C6—C10—O3 | −2.9 (4) | C15—C16—C19—O6 | 172.1 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −3.0 (3) | C16—C15—C14—C13 | 2.2 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C11 | 177.5 (2) | C16—C15—C14—C18 | −178.1 (2) |
| C7—C6—C10—O3 | 176.9 (2) | C17—C12—C1—C2 | 105.3 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C4 | 1.8 (3) | C17—C12—C1—C3 | −13.3 (3) |
| C7—C8—C11—O1 | 0.3 (4) | C17—C12—C1—C4 | −134.15 (19) |
| C9—C4—C1—C2 | 15.2 (3) | C17—C16—C15—C14 | −2.2 (3) |
| C9—C4—C1—C3 | 134.4 (2) | C17—C16—C15—O5 | 176.20 (18) |
| C9—C4—C1—C12 | −102.7 (2) | C17—C16—C19—O6 | −6.2 (4) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −2.7 (3) | C19—C16—C15—C14 | 179.5 (2) |
| C9—C8—C11—O1 | −179.2 (2) | C19—C16—C15—O5 | −2.1 (3) |
| C10—C6—C7—C8 | −178.3 (2) | O2—C7—C8—C9 | 177.5 (2) |
| C10—C6—C7—O2 | 1.2 (3) | O2—C7—C8—C11 | −1.9 (3) |
| C11—C8—C9—C4 | −178.8 (2) | O5—C15—C14—C13 | −176.02 (19) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.4 (3) | O5—C15—C14—C18 | 3.6 (3) |
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde) (2). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O1 | 0.82 | 1.88 | 2.605 (3) | 146 |
| O5—H5A···O4 | 0.94 (4) | 2.00 (4) | 2.745 (3) | 135 (3) |
| O5—H5A···O3i | 0.94 (4) | 2.14 (4) | 2.841 (2) | 131 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
References
- Andrady, A. L. & Neal, M. A. (2009). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 364, 1977–1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Baisch, U., Scicluna, M. C., Näther, C. & Vella-Zarb, L. (2017). Acta Cryst. E73, 155–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Barba, V. & Betanzos, I. J. (2007). Organomet. Chem. 692, 4903–4908.
- Bourhis, L. J., Dolomanov, O. V., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2015). Acta Cryst. A71, 59–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Eriksson, J. & Eriksson, L. (2001). Acta Cryst. C57, 1308–1312. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fenichell, S. (1996). Plastic: the Making of a Synthetic Century. New York: HarperBusiness.
- Gražulis, S., Chateigner, D., Downs, R. T., Yokochi, A. F. T., Quirós, M., Lutterotti, L., Manakova, E., Butkus, J., Moeck, P. & Le Bail, A. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 726–729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Guieu, S., Brandão, P., Rocha, J. & Silva, A. M. S. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Guieu, S., Rocha, J. & Silva, A. M. S. (2013). Tetrahedron, 69, 9329–9334.
- Kalinowski, D. S. & Richardson, D. R. (2005). Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 547–583. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lim, C. F. & Tanski, J. M. (2007). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 37, 587–595.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Maisonneuve, L., Lamarzelle, O., Rix, E., Grau, E. & Cramail, H. (2015). Chem. Rev. 115, 12407–12439. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Masurier, N., Moreau, E., Lartigue, C., Gaumet, V., Chezal, J., Heitz, A., Teulade, J. & Chavignon, O. (2008). J. Org. Chem. 73, 5989–5992. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mounika, K., Pragathi, A. & Gyanakumari, C. (2010). J. Sci. Res. 2, 513–524.
- Özdemir, H. S., Şahin, E., Çakıcı, M. & Kılıç, H. (2015). Tetrahedron, 71, 2882–2890.
- Rigaku OD (2015). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Teegarden, D. M. (2004). Polymer Chemistry: Introduction to an Indispensable Science. Arlington, VA: NSTA Press.
- Vančo, J., Marek, J. & Švajlenová, O. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o4209–o4211.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 1, 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016316/lh5885sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016316/lh58851sup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016316/lh58852sup5.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report