The title molecular salts are stilbazole, or 4-styrylpyridine, derivatives in which the cation has a methyl group attached to the pyridine ring N atom and a diethyl amine group attached to the benzene ring. In salt (I), the cadmium atom of the [CdI4]2− dianion is located on a twofold rotation axis and the compound crystallizes with one cation in the asymmetric unit. In salt(II), the anion consists of a 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate ion, and it crystallizes as a monohydrate.
Keywords: crystal structure, stilbazole, 4-styrylpyridine derivatives, tetraiodocadmate, hydrogen bonding, ring motif, π-π interactions
Abstract
The title molecular salts, (C18H23N2)2[CdI4], (I), and C18H23N2 +·C7H7O4S−·H2O, (II), are stilbazole, or 4-styrylpyridine, derivatives. The cation, (E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium, has a methyl group attached to pyridine ring and a diethyl amine group attached to the benzene ring. The asymmetric unit of salt (I), comprises one cationic molecule and half a CdI4 dianion. The Cd atom is situated on a twofold rotation axis and has a slightly distorted tetrahedral coordination sphere. In (II), the anion consists of a 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate and it crystallizes as a monohydrate. In both salts, the cations adopt an E configuration with respect to the C=C bond and the pyridine and benzene rings are inclined to each other by 10.7 (4)° in (I) and 4.6 (2)° in (II). In the crystals of both salts, the packing is consolidated by offset π–π stacking interactions involving the pyridinium and benzene rings, with centroid–centroid distances of 3.627 (4) Å in (I) and 3.614 (3) Å in (II). In the crystal of (II), a pair of 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate anions are bridged by Owater—H⋯Osulfonate hydrogen bonds, forming loops with an R 2 4(8) motif. These four-membered units are then linked to the cations by a number of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming slabs lying parallel to the ab plane.
Chemical context
Stilbene-based compounds have been reported to possess a wide range of biological applications including antibacterial (Chanawanno et al., 2010 ▸) and antioxidant (Frombaum et al., 2012 ▸) activities. The antibacterial activities of a series of pyridine stilbene benzenesulfonates have been studied against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (Chanawanno et al., 2010 ▸). Pyridine and its derivatives play an important role in drugs including antiviral, antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, antioxidant and antidiabetic agents (Ghattas et al., 2017 ▸). They have a variety of biological activities and a number of such compounds are in clinical use (Altaf et al., 2015 ▸). The antibacterial activity of pyridinium derivatives have also been studied (Chanawanno et al., 2010 ▸). The title salts, bis[(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium] tetraiodidocadmate (I) and (E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate (II) were tested for the level of cytotoxicity and anticancer analysis on normal VERO and MCF-7 cells. From an MTT assay it was found that the reported compounds have IC50 values of 31.2 µg mL−1 and 125 µg mL−1, respectively, against MCF-7 cell lines, whereas the IC50 value of crystals against normal VERO cells was found to be 1000 µg mL−1. This shows that both compounds exhibit very good anticancer activity, which implies that they may be suitable for biomedical applications.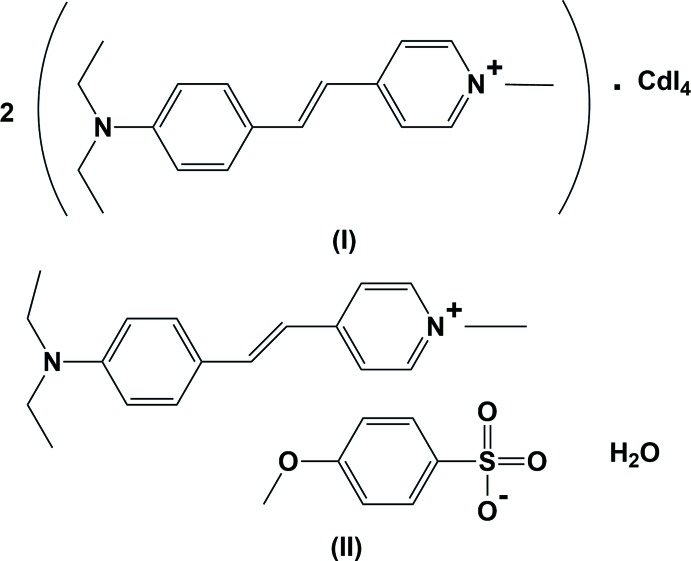
Structural commentary
The title molecular salts consist of the same cationic stilbazole derivative, (E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium. Their molecular structures are illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸ for (I) and Fig. 2 ▸ for (II). Salt (I) crystallizes with one 4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium cation and half a [CdI4]2− anion in the asymmetric unit, the cadmium atom being located on a twofold rotation axis. The cadmium atom is surrounded by four iodine atoms with a slightly distorted tetrahedral coordination sphere. In salt (II), the anion is 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate and it crystallizes as a monohydrate. In the cations of both salts, the configuration about the C7=C8 bond is E, with the C4—C7=C8—C9 torsion angle being 179.6 (6) ° in (I) and 178.7 (4)° in (II).
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of salt (I), with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level. [symmetry code: (i) −x, y, −z +  .]
.]
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of salt (II), with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
The dihedral angles between the mean planes of the pyridinium (N1/C2–C6) and benzene (C9–C14) rings are 10.7 (4) and 4.6 (2)° in (I) and (II), respectively. The C1—N1—C6—C5 torsion angles are −179.9 (7) and 179.1 (4)°, in (I) and (II), respectively, indicating that the methyl substituent (atom C1) at N1 is coplanar with the pyridine ring. The nitrogen atom (N2) deviates from the benzene ring (C9–C14) plane by 0.023 (7) and 0.079 (3) Å in (I) and (II), respectively. The two ethyl units are orthogonal to the benzene ring, as indicated by torsion angle C17—C18—N2—C12, which is 89.1 (8)° in (I) and −81.7 (5)° in (II). The title salts exhibit structural similarities with related structures, as described in the Database survey below.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal of (I), pairs of cations are arranged head-to-tail and the only significant intermolecular interactions present are offset π–π interactions (Fig. 3 ▸). These involve the benzene (C9–C14; centroid Cg2) and pyridine (N1/C2–C6; centroid Cg1) rings [Cg2⋯Cg1i = 3.627 (4) Å, α = 10.7 (4)°, β = 25.0°, interplanar distances are 3.287 (3) and 3.503 (3) Å, offset = 0.941 Å, symmetry code: (i) −x +  , −y +
, −y +  , −z + 1].
, −z + 1].
Figure 3.
The crystal packing of salt (I), viewed along the b axis, showing the π–π interactions as double-headed blue arrows. For clarity, all of the H atoms have omitted.
In the crystal of (II), a pair of 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate anions are bridged by Owater—H⋯Osulfonate hydrogen bonds, forming loops with an  (8) graph-set motif (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 4 ▸). These four-membered units are then linked to the cations by a number of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming slabs lying parallel to the ab plane (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 4 ▸). Within the slabs there are offset π–π interactions present involving adjacent cations [Cg2⋯Cg1ii = 3.614 (3) Å, α = 4.6 (2)°, β = 15.5°, interplanar distances are 3.425 (2) and 3.484 (2) Å, offset = 0.963 Å, symmetry code: (ii) x − 1, y, z].
(8) graph-set motif (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 4 ▸). These four-membered units are then linked to the cations by a number of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming slabs lying parallel to the ab plane (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 4 ▸). Within the slabs there are offset π–π interactions present involving adjacent cations [Cg2⋯Cg1ii = 3.614 (3) Å, α = 4.6 (2)°, β = 15.5°, interplanar distances are 3.425 (2) and 3.484 (2) Å, offset = 0.963 Å, symmetry code: (ii) x − 1, y, z].
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5A⋯O3 | 0.85 | 2.06 | 2.891 (6) | 165 |
| O5—H5B⋯O3i | 0.85 | 2.06 | 2.882 (6) | 162 |
| C3—H14⋯O5ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.394 (6) | 163 |
| C6—H17⋯O4iii | 0.93 | 2.33 | 3.247 (6) | 169 |
| C7—H12⋯O2iv | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.476 (6) | 162 |
| C19—H19A⋯O2ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.423 (6) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Figure 4.
The crystal packing of salt (II), viewed along the b-axis, showing the hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) as dashed lines. Only the H atoms (grey balls) involved in these interactions have been included.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, version 5.39, latest update August 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for salts containing the title cation, 4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium, gave 12 hits; atomic coordinates are available for only 10 compounds. In the triiodide salt (CSD refcode EWUDUV; Tan et al., 2004 ▸), the pyridinium and benzene rings are inclined to each other by ca 4.08°, while in the tetraphenylborate salt (QECXON; Li et al., 2012 ▸), the same dihedral angle is ca 14.33°, and in the iodide dihydrate salt (WOWGOE; Wang et al., 2000 ▸) it is ca 8.77°. The corresponding dihedral angle in salt (I) is 10.7 (4)°. In the crystals of these compounds, π–π stacking interactions dominate, as in the crystal of (I).
There is only one salt reported with the title cation and a sulfonate anion, namely the p-toluenesulfonate monohydrate salt (IBOWIG; Zhou et al., 2004 ▸). Here the dihedral angle between the pyridinium and benzene rings in the cation is ca 6.88°, compared to 4.6 (2)° in salt (II). The crystal packing is very similar to that of salt (II): a pair of water molecules bridge a pair of p-toluenesulfonate anions via O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming an  (8) ring motif; these four-membered units are linked to the cations by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a network structure.
(8) ring motif; these four-membered units are linked to the cations by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a network structure.
Synthesis and crystallization
Compound (I)
(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methyl-pyridinium-iodide (0.788 g, 2 mmol) and cadmium iodide (0.732 g, 2 mmol) were dissolved in a composite solvent, 2:1 ratio of acetonitrile and double-distilled water. The mixture was stirred well at 343 K and then allowed to cool naturally to room temperature. The solution was filtered and the filtrate left for the solvent to slowly evaporate at room temperature. After 3–4 weeks, dark-brown block-like crystals of compound (I) were obtained.
Compound (II)
(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridinium iodide (0.7885 g, 2 mmol) was mixed with sodium 4-methoxybenzenesulfonate (0.418 g, 2 mmol) in distilled water and heated at 373 K for 30 min. The mixture immediately yielded a grey precipitate of sodium iodide. After stirring the mixture for 30 min, the sodium iodide precipitate was removed. The filtrate was left to slowly evaporate and gave a deep-red solid. Red block-like crystals of compound (II), suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis, were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution in methanol after 2-3 weeks.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details for salts (I), and (II) are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The hydrogen atoms were located in difference electron-density maps. During refinement they were placed in idealized positions and allowed to ride on the parent atoms: C—H = 0.93–0.97Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2U eq(C,N) for other H atoms. The rotation angles for the methyl groups were optimized by least-squares. In compound (II), the hydrogen atoms of the water molecule were treated as riding with d(O—H) = 0.85 Å and U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | (C18H23N2)2[CdI4] | C18H23N2 +·C7H7O4S−·H2O |
| M r | 1154.77 | 472.59 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 21.6649 (18), 14.9748 (12), 14.9744 (11) | 8.2481 (6), 9.7963 (9), 15.5409 (14) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 123.621 (2), 90 | 94.283 (5), 101.647 (5), 99.112 (5) |
| V (Å3) | 4045.4 (6) | 1206.93 (18) |
| Z | 4 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 3.62 | 0.17 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.10 | 0.38 × 0.30 × 0.18 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.613, 0.713 | 0.940, 0.969 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 37329, 5003, 2802 | 25709, 4253, 2396 |
| R int | 0.070 | 0.167 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.666 | 0.595 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.043, 0.091, 1.02 | 0.080, 0.161, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 5003 | 4253 |
| No. of parameters | 207 | 306 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.23, −0.87 | 0.30, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462IIsup4.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr P. K. Sudadevi Antharjanam, SAIF, IIT, Chennai, India, for the X-ray intensity data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Crystal data
| (C18H23N2)2[CdI4] | F(000) = 2200 |
| Mr = 1154.77 | Dx = 1.896 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2 y c | Cell parameters from 5003 reflections |
| a = 21.6649 (18) Å | θ = 1.9–28.3° |
| b = 14.9748 (12) Å | µ = 3.62 mm−1 |
| c = 14.9744 (11) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 123.621 (2)° | Block, brown |
| V = 4045.4 (6) Å3 | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 5003 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2802 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.070 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −28→28 |
| Tmin = 0.613, Tmax = 0.713 | k = −19→19 |
| 37329 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.091 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0128P)2 + 39.5734P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5003 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 207 parameters | Δρmax = 1.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.87 e Å−3 |
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.1450 (5) | 0.3509 (5) | 0.0481 (6) | 0.075 (2) | |
| H1A | 0.1669 | 0.3954 | 0.0279 | 0.112* | |
| H1B | 0.0941 | 0.3660 | 0.0187 | 0.112* | |
| H1C | 0.1474 | 0.2938 | 0.0210 | 0.112* | |
| C2 | 0.2429 (4) | 0.2922 (5) | 0.2212 (6) | 0.0576 (19) | |
| H2 | 0.2568 | 0.2556 | 0.1849 | 0.069* | |
| C3 | 0.2816 (4) | 0.2883 (4) | 0.3292 (6) | 0.0539 (18) | |
| H3 | 0.3221 | 0.2501 | 0.3657 | 0.065* | |
| C4 | 0.2626 (4) | 0.3397 (4) | 0.3867 (5) | 0.0456 (16) | |
| C5 | 0.2005 (4) | 0.3962 (5) | 0.3255 (6) | 0.0563 (18) | |
| H5 | 0.1847 | 0.4320 | 0.3598 | 0.068* | |
| C6 | 0.1639 (4) | 0.3987 (5) | 0.2171 (6) | 0.0568 (18) | |
| H6 | 0.1234 | 0.4365 | 0.1779 | 0.068* | |
| C7 | 0.3041 (4) | 0.3361 (4) | 0.5024 (6) | 0.0536 (18) | |
| H7 | 0.3467 | 0.3011 | 0.5376 | 0.064* | |
| C8 | 0.2859 (4) | 0.3792 (4) | 0.5622 (6) | 0.0533 (18) | |
| H8 | 0.2433 | 0.4139 | 0.5247 | 0.064* | |
| C9 | 0.3236 (4) | 0.3796 (4) | 0.6780 (6) | 0.0509 (17) | |
| C10 | 0.3910 (4) | 0.3350 (5) | 0.7473 (6) | 0.0554 (18) | |
| H10 | 0.4143 | 0.3050 | 0.7193 | 0.067* | |
| C11 | 0.4228 (4) | 0.3355 (5) | 0.8562 (6) | 0.0575 (19) | |
| H11 | 0.4678 | 0.3063 | 0.9005 | 0.069* | |
| C12 | 0.3896 (4) | 0.3791 (4) | 0.9033 (5) | 0.0476 (16) | |
| C13 | 0.3215 (4) | 0.4221 (4) | 0.8322 (6) | 0.0534 (18) | |
| H13 | 0.2971 | 0.4509 | 0.8592 | 0.064* | |
| C14 | 0.2905 (4) | 0.4221 (5) | 0.7236 (6) | 0.0549 (18) | |
| H14 | 0.2458 | 0.4517 | 0.6790 | 0.066* | |
| C15 | 0.4916 (4) | 0.3359 (5) | 1.0878 (6) | 0.065 (2) | |
| H15A | 0.4971 | 0.2833 | 1.0550 | 0.078* | |
| H15B | 0.4927 | 0.3168 | 1.1506 | 0.078* | |
| C16 | 0.5558 (5) | 0.3987 (6) | 1.1222 (7) | 0.094 (3) | |
| H16A | 0.5564 | 0.4153 | 1.0608 | 0.142* | |
| H16B | 0.6014 | 0.3694 | 1.1738 | 0.142* | |
| H16C | 0.5501 | 0.4512 | 1.1537 | 0.142* | |
| C17 | 0.3302 (4) | 0.3824 (6) | 1.0656 (7) | 0.080 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.2889 | 0.3694 | 0.9943 | 0.120* | |
| H17B | 0.3141 | 0.4196 | 1.1011 | 0.120* | |
| H17C | 0.3501 | 0.3278 | 1.1049 | 0.120* | |
| C18 | 0.3893 (4) | 0.4305 (5) | 1.0603 (6) | 0.066 (2) | |
| H18A | 0.3684 | 0.4851 | 1.0194 | 0.079* | |
| H18B | 0.4292 | 0.4470 | 1.1324 | 0.079* | |
| N1 | 0.1855 (3) | 0.3468 (4) | 0.1655 (5) | 0.0519 (14) | |
| N2 | 0.4199 (3) | 0.3780 (4) | 1.0116 (5) | 0.0603 (16) | |
| Cd1 | 0.0000 | 0.51199 (4) | 0.2500 | 0.04358 (18) | |
| I1 | 0.10734 (3) | 0.62756 (3) | 0.26682 (4) | 0.05415 (14) | |
| I2 | −0.05786 (3) | 0.40088 (4) | 0.07160 (4) | 0.06612 (17) |
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.095 (6) | 0.063 (5) | 0.070 (5) | −0.007 (5) | 0.047 (5) | −0.014 (4) |
| C2 | 0.063 (5) | 0.042 (4) | 0.085 (6) | 0.008 (4) | 0.052 (5) | −0.003 (4) |
| C3 | 0.056 (4) | 0.042 (4) | 0.073 (5) | 0.006 (3) | 0.041 (4) | 0.004 (4) |
| C4 | 0.049 (4) | 0.029 (3) | 0.061 (4) | −0.005 (3) | 0.031 (4) | 0.003 (3) |
| C5 | 0.063 (5) | 0.056 (5) | 0.061 (5) | 0.004 (4) | 0.041 (4) | −0.008 (4) |
| C6 | 0.053 (4) | 0.049 (4) | 0.078 (5) | 0.004 (3) | 0.042 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C7 | 0.057 (5) | 0.033 (4) | 0.076 (5) | 0.003 (3) | 0.041 (4) | 0.006 (3) |
| C8 | 0.048 (4) | 0.044 (4) | 0.071 (5) | −0.004 (3) | 0.035 (4) | 0.006 (4) |
| C9 | 0.043 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.067 (5) | 0.000 (3) | 0.031 (4) | 0.009 (3) |
| C10 | 0.055 (5) | 0.055 (5) | 0.070 (5) | −0.001 (4) | 0.043 (4) | −0.003 (4) |
| C11 | 0.048 (4) | 0.050 (4) | 0.077 (5) | 0.008 (3) | 0.036 (4) | 0.004 (4) |
| C12 | 0.046 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.054 (4) | 0.000 (3) | 0.027 (4) | 0.002 (3) |
| C13 | 0.050 (4) | 0.046 (4) | 0.063 (5) | 0.012 (3) | 0.031 (4) | 0.009 (3) |
| C14 | 0.048 (4) | 0.049 (4) | 0.064 (5) | 0.007 (3) | 0.028 (4) | 0.009 (4) |
| C15 | 0.058 (5) | 0.062 (5) | 0.064 (5) | 0.017 (4) | 0.027 (4) | 0.013 (4) |
| C16 | 0.060 (6) | 0.096 (7) | 0.104 (7) | 0.001 (5) | 0.031 (5) | 0.004 (6) |
| C17 | 0.070 (6) | 0.091 (7) | 0.091 (6) | 0.004 (5) | 0.052 (5) | 0.004 (5) |
| C18 | 0.061 (5) | 0.067 (5) | 0.057 (5) | 0.012 (4) | 0.025 (4) | −0.004 (4) |
| N1 | 0.056 (4) | 0.045 (4) | 0.061 (4) | −0.008 (3) | 0.037 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| N2 | 0.049 (4) | 0.067 (4) | 0.062 (4) | 0.011 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| Cd1 | 0.0366 (4) | 0.0423 (4) | 0.0472 (4) | 0.000 | 0.0202 (3) | 0.000 |
| I1 | 0.0507 (3) | 0.0489 (3) | 0.0651 (3) | −0.0079 (2) | 0.0335 (2) | −0.0002 (2) |
| I2 | 0.0539 (3) | 0.0672 (4) | 0.0688 (3) | −0.0091 (3) | 0.0287 (3) | −0.0258 (3) |
Bis{(E)-4-[4-(diethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridin-1-ium} tetraiodidocadmium(II) (I) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.468 (9) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C12—N2 | 1.371 (8) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C12—C13 | 1.409 (9) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C13—C14 | 1.373 (9) |
| C2—N1 | 1.328 (8) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.349 (9) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C15—N2 | 1.467 (8) |
| C3—C4 | 1.377 (9) | C15—C16 | 1.513 (10) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.414 (9) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C7 | 1.445 (9) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.356 (9) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C6—N1 | 1.349 (8) | C17—C18 | 1.508 (10) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.328 (9) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.452 (9) | C18—N2 | 1.458 (9) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C9—C14 | 1.388 (9) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.407 (9) | Cd1—I2i | 2.7871 (6) |
| C10—C11 | 1.374 (9) | Cd1—I2 | 2.7871 (6) |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | Cd1—I1i | 2.7960 (6) |
| C11—C12 | 1.416 (9) | Cd1—I1 | 2.7961 (6) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C13—C14—C9 | 122.4 (7) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14 | 118.8 |
| N1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C9—C14—H14 | 118.8 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | N2—C15—C16 | 112.0 (6) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | N2—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.6 (7) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| N1—C2—H2 | 119.2 | N2—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.2 | C16—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.5 (7) | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.9 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 115.8 (6) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 121.7 (6) | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 122.5 (6) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.6 (6) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C18—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C18—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 120.8 (7) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H6 | 119.6 | C18—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.6 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C4 | 124.7 (7) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 117.6 | N2—C18—C17 | 113.8 (6) |
| C4—C7—H7 | 117.6 | N2—C18—H18A | 108.8 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 128.8 (7) | C17—C18—H18A | 108.8 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 115.6 | N2—C18—H18B | 108.8 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 115.6 | C17—C18—H18B | 108.8 |
| C14—C9—C10 | 117.5 (7) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.7 |
| C14—C9—C8 | 119.3 (6) | C2—N1—C6 | 119.8 (6) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 123.2 (7) | C2—N1—C1 | 120.6 (6) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.4 (7) | C6—N1—C1 | 119.6 (6) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C12—N2—C18 | 122.2 (6) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C12—N2—C15 | 122.2 (6) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 122.3 (7) | C18—N2—C15 | 114.9 (6) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 118.8 | I2i—Cd1—I2 | 106.69 (3) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 118.8 | I2i—Cd1—I1i | 111.478 (16) |
| N2—C12—C13 | 121.0 (6) | I2—Cd1—I1i | 111.895 (15) |
| N2—C12—C11 | 122.7 (6) | I2i—Cd1—I1 | 111.894 (15) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 116.3 (6) | I2—Cd1—I1 | 111.476 (16) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 121.0 (7) | I1i—Cd1—I1 | 103.52 (3) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.5 | ||
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.3 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.9 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.2 (10) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.7 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −179.6 (6) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.3 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.7 (10) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | 177.4 (6) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 178.8 (6) | C3—C2—N1—C6 | −1.5 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 0.5 (11) | C3—C2—N1—C1 | 179.0 (7) |
| C3—C4—C7—C8 | −175.3 (6) | C5—C6—N1—C2 | 0.6 (10) |
| C5—C4—C7—C8 | 5.3 (10) | C5—C6—N1—C1 | −179.9 (7) |
| C4—C7—C8—C9 | 179.6 (6) | C13—C12—N2—C18 | −8.3 (10) |
| C7—C8—C9—C14 | −173.2 (7) | C11—C12—N2—C18 | 173.6 (7) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 3.7 (11) | C13—C12—N2—C15 | −178.4 (6) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.1 (10) | C11—C12—N2—C15 | 3.6 (10) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −178.0 (6) | C17—C18—N2—C12 | 89.1 (8) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.9 (11) | C17—C18—N2—C15 | −100.2 (8) |
| C10—C11—C12—N2 | 178.3 (7) | C16—C15—N2—C12 | 85.9 (9) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.1 (10) | C16—C15—N2—C18 | −84.8 (8) |
| N2—C12—C13—C14 | −179.1 (7) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, y, −z+1/2.
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Crystal data
| C18H23N2+·C7H7O4S−·H2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 472.59 | F(000) = 504 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.300 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.2481 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 4253 reflections |
| b = 9.7963 (9) Å | θ = 3.0–25.0° |
| c = 15.5409 (14) Å | µ = 0.17 mm−1 |
| α = 94.283 (5)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 101.647 (5)° | Block, red |
| γ = 99.112 (5)° | 0.38 × 0.30 × 0.18 mm |
| V = 1206.93 (18) Å3 |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4253 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2396 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.167 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.940, Tmax = 0.969 | k = −11→11 |
| 25709 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.080 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.161 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0418P)2 + 1.3526P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4253 reflections | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 306 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0075 (14) |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 1.8223 (5) | 0.6523 (6) | 0.4728 (3) | 0.0666 (16) | |
| H16A | 1.8691 | 0.5725 | 0.4575 | 0.100* | |
| H16B | 1.8368 | 0.6672 | 0.5359 | 0.100* | |
| H16C | 1.8788 | 0.7327 | 0.4522 | 0.100* | |
| C2 | 1.5563 (5) | 0.7352 (5) | 0.4278 (3) | 0.0565 (14) | |
| H15 | 1.6137 | 0.8236 | 0.4519 | 0.068* | |
| C3 | 1.3901 (5) | 0.7177 (5) | 0.3904 (3) | 0.0505 (13) | |
| H14 | 1.3355 | 0.7938 | 0.3893 | 0.061* | |
| C4 | 1.3003 (5) | 0.5865 (5) | 0.3536 (3) | 0.0360 (11) | |
| C5 | 1.3915 (5) | 0.4783 (5) | 0.3598 (3) | 0.0444 (12) | |
| H18 | 1.3367 | 0.3883 | 0.3379 | 0.053* | |
| C6 | 1.5597 (5) | 0.5008 (5) | 0.3973 (3) | 0.0466 (12) | |
| H17 | 1.6180 | 0.4268 | 0.3994 | 0.056* | |
| C7 | 1.1240 (5) | 0.5583 (5) | 0.3109 (3) | 0.0409 (11) | |
| H12 | 1.0741 | 0.4656 | 0.2943 | 0.049* | |
| C8 | 1.0267 (5) | 0.6531 (5) | 0.2931 (3) | 0.0400 (11) | |
| H11 | 1.0770 | 0.7455 | 0.3109 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | 0.8504 (5) | 0.6276 (5) | 0.2488 (3) | 0.0346 (10) | |
| C10 | 0.7625 (5) | 0.7379 (4) | 0.2380 (3) | 0.0392 (11) | |
| H9 | 0.8197 | 0.8277 | 0.2585 | 0.047* | |
| C11 | 0.5938 (5) | 0.7186 (4) | 0.1981 (3) | 0.0377 (11) | |
| H6 | 0.5404 | 0.7951 | 0.1914 | 0.045* | |
| C12 | 0.5027 (5) | 0.5848 (4) | 0.1678 (3) | 0.0342 (10) | |
| C13 | 0.5919 (5) | 0.4738 (4) | 0.1788 (3) | 0.0375 (11) | |
| H7 | 0.5354 | 0.3835 | 0.1592 | 0.045* | |
| C14 | 0.7586 (5) | 0.4953 (4) | 0.2173 (3) | 0.0368 (11) | |
| H8 | 0.8130 | 0.4192 | 0.2228 | 0.044* | |
| C15 | 0.2459 (5) | 0.6762 (5) | 0.1087 (3) | 0.0469 (12) | |
| H2A | 0.2845 | 0.7525 | 0.1557 | 0.056* | |
| H2B | 0.1265 | 0.6458 | 0.1044 | 0.056* | |
| C16 | 0.2708 (7) | 0.7292 (5) | 0.0234 (3) | 0.0673 (15) | |
| H1A | 0.3878 | 0.7656 | 0.0282 | 0.101* | |
| H1B | 0.2063 | 0.8016 | 0.0109 | 0.101* | |
| H1C | 0.2343 | 0.6545 | −0.0236 | 0.101* | |
| C17 | 0.2467 (6) | 0.3604 (5) | 0.0164 (3) | 0.0712 (16) | |
| H3A | 0.1996 | 0.4155 | −0.0275 | 0.107* | |
| H3B | 0.1848 | 0.2669 | 0.0045 | 0.107* | |
| H3C | 0.3622 | 0.3598 | 0.0146 | 0.107* | |
| C18 | 0.2363 (5) | 0.4213 (5) | 0.1064 (3) | 0.0510 (13) | |
| H4A | 0.1193 | 0.4231 | 0.1070 | 0.061* | |
| H4B | 0.2765 | 0.3610 | 0.1496 | 0.061* | |
| C19 | 0.9837 (5) | 0.9933 (6) | 0.8722 (3) | 0.0708 (17) | |
| H19A | 0.9936 | 0.9136 | 0.8351 | 0.106* | |
| H19B | 1.0760 | 1.0114 | 0.9227 | 0.106* | |
| H19C | 0.9854 | 1.0726 | 0.8395 | 0.106* | |
| C20 | 0.6835 (5) | 0.9375 (4) | 0.8384 (3) | 0.0351 (10) | |
| C21 | 0.5389 (5) | 0.9182 (4) | 0.8707 (3) | 0.0396 (11) | |
| H21 | 0.5454 | 0.9266 | 0.9313 | 0.048* | |
| C22 | 0.3847 (5) | 0.8864 (4) | 0.8129 (3) | 0.0393 (11) | |
| H22 | 0.2873 | 0.8715 | 0.8349 | 0.047* | |
| C23 | 0.3731 (5) | 0.8764 (4) | 0.7233 (3) | 0.0348 (10) | |
| C24 | 0.5190 (6) | 0.8983 (5) | 0.6920 (3) | 0.0495 (12) | |
| H24 | 0.5121 | 0.8918 | 0.6313 | 0.059* | |
| C25 | 0.6738 (5) | 0.9292 (5) | 0.7482 (3) | 0.0467 (12) | |
| H25 | 0.7710 | 0.9444 | 0.7261 | 0.056* | |
| N1 | 1.6404 (4) | 0.6282 (4) | 0.4310 (2) | 0.0452 (10) | |
| N2 | 0.3330 (4) | 0.5618 (4) | 0.1330 (2) | 0.0407 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.8308 (3) | 0.9673 (3) | 0.90069 (18) | 0.0489 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.0530 (4) | 0.7905 (4) | 0.6988 (2) | 0.0754 (11) | |
| O3 | 0.1484 (4) | 0.9579 (4) | 0.6101 (3) | 0.0907 (14) | |
| O4 | 0.1904 (4) | 0.7254 (4) | 0.5852 (2) | 0.0862 (13) | |
| O5 | 0.1888 (5) | 0.9840 (5) | 0.4312 (3) | 0.0791 (12) | |
| H5A | 0.1915 | 0.9678 | 0.4844 | 0.119* | |
| H5B | 0.0903 | 0.9951 | 0.4070 | 0.119* | |
| S1 | 0.17473 (14) | 0.83367 (13) | 0.64771 (8) | 0.0441 (4) |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.031 (2) | 0.110 (5) | 0.057 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.013 (3) |
| C2 | 0.040 (3) | 0.057 (4) | 0.064 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.004 (3) |
| C3 | 0.038 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.066 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.005 (3) |
| C4 | 0.031 (2) | 0.049 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.0116 (19) | 0.006 (2) |
| C5 | 0.041 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C6 | 0.043 (3) | 0.068 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.009 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.031 (2) | 0.053 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.0069 (19) | 0.001 (2) |
| C8 | 0.037 (2) | 0.046 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C9 | 0.032 (2) | 0.043 (3) | 0.029 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.0075 (18) | 0.004 (2) |
| C10 | 0.039 (2) | 0.029 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C11 | 0.036 (2) | 0.032 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.013 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C12 | 0.033 (2) | 0.038 (3) | 0.032 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.0063 (18) | 0.007 (2) |
| C13 | 0.037 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.0047 (19) | 0.006 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C14 | 0.039 (2) | 0.037 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.014 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C15 | 0.037 (2) | 0.049 (3) | 0.056 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.003 (3) |
| C16 | 0.091 (4) | 0.057 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.033 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.015 (3) |
| C17 | 0.080 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.005 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C18 | 0.040 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.007 (3) |
| C19 | 0.035 (3) | 0.104 (5) | 0.066 (4) | 0.000 (3) | 0.007 (2) | −0.003 (3) |
| C20 | 0.037 (2) | 0.030 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.0075 (19) | 0.004 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C21 | 0.044 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C22 | 0.035 (2) | 0.039 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.007 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| C23 | 0.041 (2) | 0.029 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.0110 (19) | 0.0020 (19) | 0.006 (2) |
| C24 | 0.060 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C25 | 0.041 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.010 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0282 (19) | 0.066 (3) | 0.041 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.0063 (17) | 0.003 (2) |
| N2 | 0.0310 (18) | 0.033 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0067 (16) | 0.0003 (16) | 0.0042 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0372 (17) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0427 (19) | 0.0038 (15) | −0.0012 (14) | 0.0009 (16) |
| O2 | 0.0422 (19) | 0.102 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.0049 (19) | −0.0002 (18) | 0.002 (2) |
| O3 | 0.084 (3) | 0.063 (3) | 0.108 (3) | 0.019 (2) | −0.032 (2) | 0.032 (2) |
| O4 | 0.057 (2) | 0.106 (3) | 0.078 (3) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0189 (18) | −0.047 (2) |
| O5 | 0.071 (2) | 0.094 (3) | 0.088 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.025 (3) |
| S1 | 0.0407 (7) | 0.0404 (8) | 0.0454 (7) | 0.0147 (5) | −0.0075 (5) | −0.0015 (6) |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.484 (5) | C15—H2B | 0.9700 |
| C1—H16A | 0.9600 | C16—H1A | 0.9600 |
| C1—H16B | 0.9600 | C16—H1B | 0.9600 |
| C1—H16C | 0.9600 | C16—H1C | 0.9600 |
| C2—N1 | 1.344 (6) | C17—C18 | 1.503 (6) |
| C2—C3 | 1.354 (6) | C17—H3A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H15 | 0.9300 | C17—H3B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.395 (6) | C17—H3C | 0.9600 |
| C3—H14 | 0.9300 | C18—N2 | 1.461 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.393 (5) | C18—H4A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C7 | 1.445 (5) | C18—H4B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.367 (5) | C19—O1 | 1.411 (5) |
| C5—H18 | 0.9300 | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C6—N1 | 1.332 (5) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H17 | 0.9300 | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.329 (5) | C20—O1 | 1.367 (4) |
| C7—H12 | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.377 (5) |
| C8—C9 | 1.452 (5) | C20—C25 | 1.383 (6) |
| C8—H11 | 0.9300 | C21—C22 | 1.375 (5) |
| C9—C14 | 1.392 (5) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.395 (5) | C22—C23 | 1.372 (5) |
| C10—C11 | 1.381 (5) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H9 | 0.9300 | C23—C24 | 1.379 (6) |
| C11—C12 | 1.399 (5) | C23—S1 | 1.779 (4) |
| C11—H6 | 0.9300 | C24—C25 | 1.368 (6) |
| C12—N2 | 1.371 (5) | C24—H24 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.409 (5) | C25—H25 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.360 (5) | O2—S1 | 1.434 (4) |
| C13—H7 | 0.9300 | O3—S1 | 1.418 (3) |
| C14—H8 | 0.9300 | O4—S1 | 1.423 (3) |
| C15—N2 | 1.457 (5) | O5—H5A | 0.8498 |
| C15—C16 | 1.500 (6) | O5—H5B | 0.8501 |
| C15—H2A | 0.9700 | ||
| N1—C1—H16A | 109.5 | C15—C16—H1C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H16B | 109.5 | H1A—C16—H1C | 109.5 |
| H16A—C1—H16B | 109.5 | H1B—C16—H1C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H16C | 109.5 | C18—C17—H3A | 109.5 |
| H16A—C1—H16C | 109.5 | C18—C17—H3B | 109.5 |
| H16B—C1—H16C | 109.5 | H3A—C17—H3B | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.8 (4) | C18—C17—H3C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—H15 | 119.1 | H3A—C17—H3C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H15 | 119.1 | H3B—C17—H3C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.6 (4) | N2—C18—C17 | 114.1 (4) |
| C2—C3—H14 | 119.7 | N2—C18—H4A | 108.7 |
| C4—C3—H14 | 119.7 | C17—C18—H4A | 108.7 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 115.8 (4) | N2—C18—H4B | 108.7 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 119.7 (4) | C17—C18—H4B | 108.7 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 124.5 (4) | H4A—C18—H4B | 107.6 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.7 (4) | O1—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H18 | 119.1 | O1—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H18 | 119.1 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 120.3 (4) | O1—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H17 | 119.9 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H17 | 119.9 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C4 | 125.8 (4) | O1—C20—C21 | 115.6 (4) |
| C8—C7—H12 | 117.1 | O1—C20—C25 | 124.2 (4) |
| C4—C7—H12 | 117.1 | C21—C20—C25 | 120.1 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 126.9 (4) | C22—C21—C20 | 119.8 (4) |
| C7—C8—H11 | 116.6 | C22—C21—H21 | 120.1 |
| C9—C8—H11 | 116.6 | C20—C21—H21 | 120.1 |
| C14—C9—C10 | 116.4 (4) | C23—C22—C21 | 120.8 (4) |
| C14—C9—C8 | 123.3 (4) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.6 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.3 (4) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.6 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 122.5 (4) | C22—C23—C24 | 118.8 (4) |
| C11—C10—H9 | 118.8 | C22—C23—S1 | 121.3 (3) |
| C9—C10—H9 | 118.8 | C24—C23—S1 | 119.9 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.5 (4) | C25—C24—C23 | 121.5 (4) |
| C10—C11—H6 | 119.8 | C25—C24—H24 | 119.3 |
| C12—C11—H6 | 119.8 | C23—C24—H24 | 119.3 |
| N2—C12—C11 | 121.7 (4) | C24—C25—C20 | 119.1 (4) |
| N2—C12—C13 | 121.3 (4) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 116.9 (4) | C20—C25—H25 | 120.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 121.7 (4) | C6—N1—C2 | 119.9 (4) |
| C14—C13—H7 | 119.2 | C6—N1—C1 | 120.3 (4) |
| C12—C13—H7 | 119.2 | C2—N1—C1 | 119.9 (4) |
| C13—C14—C9 | 122.1 (4) | C12—N2—C15 | 121.1 (3) |
| C13—C14—H8 | 118.9 | C12—N2—C18 | 121.6 (3) |
| C9—C14—H8 | 118.9 | C15—N2—C18 | 116.6 (3) |
| N2—C15—C16 | 114.5 (4) | C20—O1—C19 | 118.6 (3) |
| N2—C15—H2A | 108.6 | H5A—O5—H5B | 109.4 |
| C16—C15—H2A | 108.6 | O3—S1—O4 | 113.3 (3) |
| N2—C15—H2B | 108.6 | O3—S1—O2 | 111.9 (2) |
| C16—C15—H2B | 108.6 | O4—S1—O2 | 113.0 (2) |
| H2A—C15—H2B | 107.6 | O3—S1—C23 | 105.6 (2) |
| C15—C16—H1A | 109.5 | O4—S1—C23 | 105.90 (19) |
| C15—C16—H1B | 109.5 | O2—S1—C23 | 106.5 (2) |
| H1A—C16—H1B | 109.5 | ||
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (7) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.1 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.2 (7) | S1—C23—C24—C25 | −179.0 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −178.7 (4) | C23—C24—C25—C20 | 0.5 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.9 (6) | O1—C20—C25—C24 | 179.9 (4) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 178.0 (4) | C21—C20—C25—C24 | −1.5 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 1.5 (7) | C5—C6—N1—C2 | −0.2 (6) |
| C5—C4—C7—C8 | −173.2 (4) | C5—C6—N1—C1 | 179.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C7—C8 | 6.7 (7) | C3—C2—N1—C6 | −0.5 (7) |
| C4—C7—C8—C9 | 178.7 (4) | C3—C2—N1—C1 | −179.8 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C14 | −0.9 (7) | C11—C12—N2—C15 | 13.1 (6) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 177.3 (4) | C13—C12—N2—C15 | −170.1 (4) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −0.2 (6) | C11—C12—N2—C18 | −176.2 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −178.5 (4) | C13—C12—N2—C18 | 0.6 (6) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.1 (6) | C16—C15—N2—C12 | 77.0 (5) |
| C10—C11—C12—N2 | 175.9 (4) | C16—C15—N2—C18 | −94.1 (5) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (6) | C17—C18—N2—C12 | −81.7 (5) |
| N2—C12—C13—C14 | −176.7 (4) | C17—C18—N2—C15 | 89.4 (5) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.3 (6) | C21—C20—O1—C19 | −177.8 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.6 (6) | C25—C20—O1—C19 | 0.9 (6) |
| C10—C9—C14—C13 | −0.6 (6) | C22—C23—S1—O3 | 108.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—C14—C13 | 177.6 (4) | C24—C23—S1—O3 | −72.3 (4) |
| O1—C20—C21—C22 | −179.3 (4) | C22—C23—S1—O4 | −131.0 (4) |
| C25—C20—C21—C22 | 2.0 (6) | C24—C23—S1—O4 | 48.1 (4) |
| C20—C21—C22—C23 | −1.3 (6) | C22—C23—S1—O2 | −10.4 (4) |
| C21—C22—C23—C24 | 0.3 (6) | C24—C23—S1—O2 | 168.6 (4) |
| C21—C22—C23—S1 | 179.4 (3) |
4-{2-[4-(Diethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridin-1-ium 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonate monohydrate (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5A···O3 | 0.85 | 2.06 | 2.891 (6) | 165 |
| O5—H5B···O3i | 0.85 | 2.06 | 2.882 (6) | 162 |
| C3—H14···O5ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.394 (6) | 163 |
| C6—H17···O4iii | 0.93 | 2.33 | 3.247 (6) | 169 |
| C7—H12···O2iv | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.476 (6) | 162 |
| C19—H19A···O2ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.423 (6) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by University Grants Commission grant F1–17.1/2017–18/MANF-2017–18-KER-83185 to Priya Antony. Science and Engineering Research Board grant SR/S2/LOP-29/2013.
References
- Altaf, A. A., Shahzad, A., Gul, Z., Rasool, N., Badshah, A., Lal, B. & Khan, E. (2015). J. Drug Design Med. Chem. 1, 1–11.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chanawanno, K., Chantrapromma, S., Anantapong, T., Kanjana-Opas, A. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 4199–4208. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Frombaum, M., Le Clanche, S., Bonnefont-Rousselot, D. & Borderie, D. (2012). Biochimie, 94, 269–276. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ghattas, A.-E.-B. A. G., Khodairy, A., Moustafa, H. M., Hussein, B. R. M., Farghaly, M. M. & Aboelez, M. O. (2017). Pharma. Chem. J. , 30, 652–660.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, D.-D., Li, R. & Li, S.-L. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2694.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.-J., Sun, S.-X., Yu, W.-T., Xing, D.-X., Wang, Y.-G. & Qi, C.-G. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, o1054–o1056.
- Wang, X.-M., Zhou, Y.-F., Yu, W.-T., Wang, C., Fang, Q., Jiang, M.-H., Lei, H. & Wang, H.-W. (2000). J. Mater. Chem. 10, 2698–2703.
- Zhou, H.-P., Hao, F.-Y., Zhang, J.-Z., Zhao, Z.-Z., Dong, M.-L., Wu, J.-Y., Tian, Y.-P. & Fun, K.-F. (2004). Wuji Huaxue Xuebao, 20, 1165.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016808/su5462IIsup4.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






