In the title imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives, N-tert-butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine, (I), and N-tert-butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine, (II), the 4-methoxyphenyl ring in (I) and the 4-(dimethylamino)phenyl ring in (II) are inclined to the mean planes of the respective imidazole rings by 26.69 (9) and 31.35 (10)°.
Keywords: crystal structure; imidazole; imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives; N—H⋯N hydrogen bonding; C—H⋯π interactions; offset π–π interactions; Hirshfeld surface analysis; fingerprint plots
Abstract
In the title imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives, N-tert-butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine, C19H23N3O, (I), and N-tert-butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine, C19H24N4, (II), the 4-methoxyphenyl ring in (I) and the 4-(dimethylamino)phenyl ring in (II) are inclined to the respective imidazole rings by 26.69 (9) and 31.35 (10)°. In the crystal of (I), molecules are linked by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along the [001] direction. The chains are linked by C—H⋯π interactions, forming layers parallel to the (010) plane. In (II), the crystal packing also features N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, which together with C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link molecules to form chains propagating along the c-axis direction. The chains are linked by C—H⋯π interactions to form layers parallel to the (100) plane. Inversion-related layers are linked by offset π–π interactions [intercentroid distance = 3.577 (1) Å]. The intermolecular interactions of both compounds were analyzed using Hirshfeld surface analysis and two-dimensional fingerprint plots.
Chemical context
Imidazoles are heterocyclic compounds which show important pharmacological and biochemical properties. They exhibit anti-fungal (Banfi et al., 2006 ▸), anti-bacterial (Jackson et al., 2000 ▸), anti-tumour (Dooley et al., 1992 ▸; Cui et al., 2003 ▸), anti-protozoal (Biftu et al., 2006 ▸), anti-herpes (Gudmundsson & Johns, 2007 ▸), anti-inflammatory (Rupert et al., 2003 ▸), anti-ulcerative, anti-hypertensive, anti-histaminic and anti-helminthic properties (Spasov et al., 1999 ▸). They also exhibit different therapeutic (Silvestre et al., 1998 ▸; Lhassani et al., 1999 ▸; Ertl et al., 2000 ▸) and fluorescence properties (Kawai et al., 2001 ▸; Abdullah, 2005 ▸). Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines have been shown to be highly active against human cytomegalovirus and varicella-zoster virus (Gueffier et al., 1998 ▸; Mavel et al., 2002 ▸). In the present study, we report the synthesis, the single crystal X-ray diffraction studies, and Hirshfeld surface analysis of two new novel imidazole derivatives, N-tert-butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine, (I), and N-tert-butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine, (II).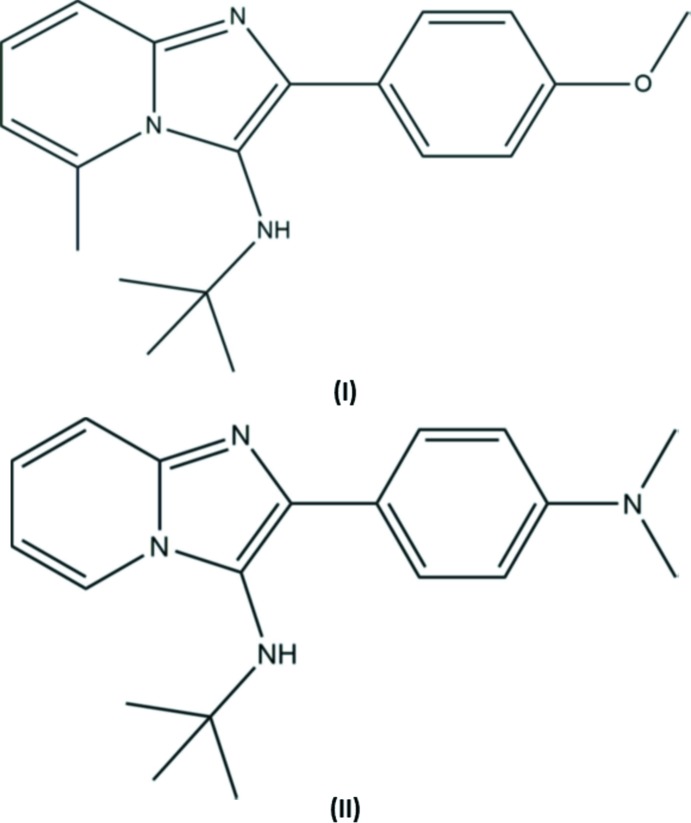
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of compound (I) is shown in Fig. 1 ▸, and that of compound (II) in Fig. 2 ▸. The overall conformation of the two molecules is similar, as shown in the structural overlap drawing, Fig. 3 ▸. In compound (I), the imidazole ring system is planar with an r.m.s deviation of 0.062 Å and a maximum deviation of 0.071 (2) Å for atom C1. In compound (II), the imidazole ring system is planar with an r.m.s deviation of 0.029 Å and a maximum deviation of 0.031 (2) Å for atom N2. In (I) the pyridine ring (N2/C1–C5) of the imidazole ring system makes a dihedral angle of 4.91 (11)° with the five-membered ring (N2/N3/C5–C7), while the corresponding angle in (II) is 2.90 (13)°. In both compounds, the difference in endocyclic angles [129.27 (19)° for bond angle C4—C5—N3 and 132.33 (17)° for bond angle C1—N2—C6 in compound (I), and 131.1 (2) and 130.4 (2)°, respectively, in compound (II)] of the imidazole ring systems are due to the merging of five- and six-membered rings and the strain is taken up by angular distortion rather than by bond length distortion.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I), with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II), with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 3.
A structural overlap view of molecules (I) and (II).
The dihedral angle between the pyridine (N2/C1–C5) and the benzene (C8–C13) rings is 25.04 (10)° in (I) and 31.11 (12) ° in (II). In (I) the methoxy group (C11/O1/C14) lies in the plane of the benzene ring (C8–C13) to which it is attached, with a dihedral angle of 0.6 (2)°. In (II) the dimethylamine group (N4/C14/C15) also lies close to the plane of the benzene ring (C8–C13) with a dihedral angle of 1.42 (19)°. The dihedral angle between atoms N1/C16/C18 and the imidazole ring mean plane is 80.28 (19)° in (I) and 84.6 (2)° in (II). The sum of the bond angles around atom N2 is 359.87 ° in (I), and the sums around atoms N2 and N4 in (II) are 359.85 and 360.0°, respectively, indicating sp 2 hybridization. In compound (I) the torsion angles C10—C9—C8—C7 and C18—C16—N1—C6 are −178.9 (2) and 170.52 (18)°, respectively, while the corresponding torsion angles in compound (II) are −177.9 (2) and 179.4 (2)°, respectively. This shows that for both compounds the imidazole ring is (−) antiperiplanar with the benzene ring and (+) antiperiplanar with the side-chain atoms N1, C16 and C18.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal of (I), molecules are linked by N1—H1A⋯N3i hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸), forming C(8) chains propagating along the c-axis direction, as shown in Fig. 4 ▸. The chains are linked by C—H⋯π interactions, forming layers lying parallel to the ac plane (Fig. 4 ▸, Table 1 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg4 is the centroid of the imidazole ring system N2/N3/C1–C7.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯N3i | 0.84 (2) | 2.41 (2) | 3.226 (2) | 163.6 (19) |
| C14—H14A⋯Cg4ii | 0.96 | 2.93 | 3.862 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 4.
The crystal packing of compound (I) viewed along the b axis, showing the intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds as dashed lines (Table 1 ▸). The C—H⋯π interactions are also represented by cyan dashed lines (Table 1 ▸).
In the crystal of (II), molecules are linked by N1—H1A⋯N3i and C13—H13⋯N3i hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸), forming chains propagating along the [001] direction, as shown in Fig. 5 ▸. The chains are also linked by C—H⋯π interactions, forming layers lying parallel to the bc plane (Fig. 5 ▸, Table 2 ▸). Inversion-related layers are linked by offset π–π interactions involving the pyridine ring of the imidazole ring system: Cg2⋯Cg2iii = 3.577 (1) Å, Cg2 is the centroid of the pyridine ring (N2/C1–C5), α = 0.0 (1)°, β = 22.3°, interplanar distance = 3.309 (1) Å, offset = 1.357 Å; symmetry code (iii) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
Cg3 is the centroid of benzene ring C8–C13.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯N3i | 0.86 (3) | 2.56 (3) | 3.412 (3) | 167 (2) |
| C13—H13⋯N3i | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.467 (3) | 161 |
| C19—H19B⋯Cg3ii | 0.96 | 2.87 | 3.829 (4) | 174 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 5.
The crystal packing of compound (II) viewed along the a axis, showing the intermolecular N—H⋯N and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions as dashed lines (Table 2 ▸).
Hirshfeld Surface Analysis
Hirshfeld surface analysis was used to quantify the intermolecular contacts of the title compounds, using the software CrystalExplorer17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). The bright-red spots on the Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm [Fig. 6 ▸(a) and 7(a)], show the presence of N—H⋯N and C—H⋯ N interactions with neighbouring molecules. The surfaces mapped over the electrostatic potential are illustrated in Fig. 6 ▸(b) and 7(b), while Fig. 6 ▸(c) and 7(c) show the intermolecular contacts. The presence of red and blue triangles on the shape index map [Fig. 7 ▸(d)], indicates the presence of π–π stacking interactions in compound (II), and their absence in Fig. 6 ▸(d) shows that such interactions are absent in compound (I). The large flat region in Fig. 7 ▸(e), shown on the curvature map, confirms the presence of C—H⋯π interactions in compound (II). The fragment patches on the Hirshfeld surface [Figs. 6 ▸(f) and 7(f) ▸] show the coordination environments of the molecules. The complete two-dimensional fingerprint plots are shown in Fig. 8 ▸(a) and 9(a). The H⋯H, C⋯H, N⋯H, C⋯N, H⋯O and C⋯C interactions are illustrated in Fig. 8 ▸(b)–8(e) for (I) and Fig. 9 ▸(b)–9(e) for (II). The H⋯H interactions make the largest contributions [Fig. 8 ▸(b) and 9(b)] to the overall Hirshfeld surfaces [68.3% for compound (I) and 71.6% for compound (II)]. The C⋯H interactions appear as two wings in the fingerprint plot [Fig. 8 ▸(c) and 9(c)], showing a contribution of 18.2% for compound (I) and 17.7% for compound (II) of the Hirshfeld surfaces. The contribution from the N⋯H contacts, corresponding to C—H⋯N interactions, is represented by a pair of sharp spikes with a contribution of 7.1% for compound (I) and 8.2% for compound (II) of the Hirshfeld surfaces [Fig. 8 ▸(d) and 9(d)]. The H⋯O contacts have a contribution of 5.4% of the Hirshfeld surface for compound (I). The C⋯C contacts, which refers to π–π interactions, contribute 1.8% of the Hirshfeld surfaces for compound (II). This can be seen in the shape of a butterfly at d e = d i 1.7Å [Fig. 9 ▸(e)].
Figure 6.
View of the Hirshfeld surface for compound (I), mapped over: (a) d norm; (b) electrostatic potential; (c) intermolecular contacts; (d) shape index; (e) curvature; (f) fragment patches.
Figure 7.
View of the Hirshfeld surface for compound (II), mapped over: (a) d norm; (b) electrostatic potential; (c) intermolecular contacts; (d) shape index; (e) curvature; (f) fragment patches.
Figure 8.
Two-dimensional fingerprint plots for compound (I): (a) all intermolecular interactions; (b) H⋯H contacts; (c) C⋯·H contacts; (d) H⋯ N contacts; (e) H⋯O contacts.
Figure 9.
Two-dimensional fingerprint plots for compound (II): (a) all intermolecular interactions; (b) H⋯H contacts; (c) H⋯C contacts; (d) N⋯ H contacts; (e) C⋯C contacts.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, version 5.39, last update August 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) revealed 29 hits for substructure imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine and 16 hits for 5-methyl imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine. Two compounds, (5-methylimidazo-[1,2-a]pyridin-2-yl)methanol (CSD refcode PONVUL; Elaatiaoui et al., 2014 ▸), and ethyl 5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylate (DUSWOE; Yao et al., 2010 ▸) are close analogues of compound (I). A third compound, (E)-2-phenyl-N-(thiophen-2-ylmethylidene)-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (OLEBOY; Elaatiaoui et al., 2016 ▸), is a close analogue of compound (II). The crystal packing of compounds (I) and (II) are stabilized by N—H⋯N, C—H⋯N and C—H⋯π interactions, but the above mentioned crystal structures exhibit in general C—H⋯O, O—H⋯N and π–π interactions.
An interesting pyrazine analogue of compound (II) has been reported, i.e. N-tert-butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-amine (WIGKOO; Fatima et al., 2013 ▸). Here the pyrazine and benzene rings are inclined to each other by 16.96 (7)°, compared to the corresponding dihedral angle of 31.11 (12)° involving the pyridine and benzene rings in (II). In the crystal, molecules are linked via N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [010], which in turn are linked by C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds forming layers parallel to the ab plane. This is very similar to the crystal-packing arrangement observed for compound (II).
Synthesis and crystallization
Compound (I)
5-Methyl-2-aminopyridine (10 mmol) and 4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1 eq.) were solubilized in ethanol. To this solution, tert-butyl isocyanide (1 eq.) and iodine (0.5 mmol %) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. The white precipitate that had formed was filtered off and purified further using silica-gel column chromatography to give a white solid in 60% yield.
Compound (II)
2-Aminopyridine (10 mmol) and 4-(dimethylamino) benzaldehyde (1 eq.) were solubilized in ethanol. To this solution, tert-butyl isocyanide (1 eq.) and iodine (0.5 mmol %) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. The white precipitate that formed was filtered off and purified further using silica-gel column chromatography to give a yellow solid (yield 0.282 g, 91%).
Spectroscopic data : NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker 400 MHz NMR spectrophotometer in CdCl3 and chemical shifts were recorded in parts per million relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS), used as an internal standard.
Compound (I)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 8.57 (ddd, J = 4.9, 1.8, 0.9, 1H), 8.14 (dt, J = 8.0, 1.0, 1H), 7.77 (td, J = 7.7, 1.8, 1H), 7.40 (d, J = 9.0, 1H), 7.16 (ddd, J = 7.5, 4.9, 1.2, 1H), 7.01 (dd, J = 9.0, 6.7, 1H), 6.46–6.41 (m, 1H), 4.99 (s, 1H), 2.96 (s, 3H), 0.93 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.31, 148.37, 142.86, 138.16, 137.65, 137.35, 136.54, 130.34, 124.28, 121.80, 121.79, 115.58, 113.91, 105.48, 57.20, 28.97, 20.21.
Compound (II)
1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz): dH 1.05 [s, 9H, –C(CH3)3], 2.97 [s, 6H, Ar-N(CH3)2], 6.69 (t, 1H, -Ar-H), 6.77 (d, 2H, J = 8.40 Hz, –Ar-H), 7.17 (t, 1H, –Ar-H, –Ar-H), 7.53 (d, 1H, J = 8.40 Hz, –Ar-H), 7.8 (d, 2H, J = 4.5 Hz, –Ar-H), 8.19 (d, 1H, J = 8.40 Hz, –Ar-H). ESI–MS: calculated for C19H24N4 [M + H]+ 308.2007; found: 308.27.
Crystals of compounds (I) and (II), suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis, were obtained by slow evaporation from ethyl alcohol (EtOH) solution at room temperature.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. For both compounds the NH H atoms were located in difference-Fourier maps and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding: C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C19H23N3O | C19H24N4 |
| M r | 309.40 | 308.42 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.2357 (7), 15.6388 (12), 11.984 (1) | 34.9185 (14), 8.4656 (5), 11.8361 (6) |
| β (°) | 93.998 (3) | 91.061 (5) |
| V (Å3) | 1726.7 (2) | 3498.2 (3) |
| Z | 4 | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.10 | 0.15 × 0.10 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.552, 0.746 | 0.697, 0.745 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 16458, 3208, 2109 | 32313, 3259, 1834 |
| R int | 0.044 | 0.071 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.606 | 0.606 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.047, 0.119, 1.03 | 0.049, 0.159, 1.02 |
| No. of reflections | 3208 | 3259 |
| No. of parameters | 218 | 218 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.15, −0.13 | 0.22, −0.18 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016651/su5459sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016651/su5459Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016651/su5459IIsup3.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the SAIF, IIT, Madras for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Crystal data
| C19H23N3O | F(000) = 664 |
| Mr = 309.40 | Dx = 1.190 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.2357 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 3732 reflections |
| b = 15.6388 (12) Å | θ = 2.6–29.2° |
| c = 11.984 (1) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 93.998 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1726.7 (2) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3208 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2109 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.044 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.552, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −18→18 |
| 16458 measured reflections | l = −14→13 |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0386P)2 + 0.6929P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3208 reflections | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 218 parameters | Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2018 (Sheldrick, 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0063 (11) |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.02423 (18) | 0.88980 (13) | 0.62308 (14) | 0.0800 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.58139 (18) | 0.64812 (11) | 0.72686 (14) | 0.0385 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.560 (2) | 0.6854 (13) | 0.7736 (17) | 0.045 (6)* | |
| N2 | 0.71475 (16) | 0.66024 (10) | 0.55928 (13) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.55442 (18) | 0.72815 (11) | 0.43982 (13) | 0.0417 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.8497 (2) | 0.62484 (14) | 0.59167 (19) | 0.0480 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.9389 (2) | 0.60796 (16) | 0.5092 (2) | 0.0618 (7) | |
| H2 | 1.028199 | 0.582474 | 0.528113 | 0.074* | |
| C3 | 0.9016 (3) | 0.62747 (17) | 0.3962 (2) | 0.0633 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.963493 | 0.611842 | 0.341717 | 0.076* | |
| C4 | 0.7768 (2) | 0.66868 (14) | 0.36672 (18) | 0.0524 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.754319 | 0.684394 | 0.292687 | 0.063* | |
| C5 | 0.6809 (2) | 0.68762 (13) | 0.44948 (16) | 0.0401 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.5944 (2) | 0.68161 (12) | 0.61971 (15) | 0.0345 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.5016 (2) | 0.72552 (12) | 0.54407 (15) | 0.0361 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.3630 (2) | 0.76695 (12) | 0.56396 (15) | 0.0367 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.2546 (2) | 0.77465 (15) | 0.47894 (17) | 0.0516 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.270036 | 0.752223 | 0.408881 | 0.062* | |
| C10 | 0.1244 (2) | 0.81454 (16) | 0.49472 (18) | 0.0574 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.053459 | 0.818460 | 0.435930 | 0.069* | |
| C11 | 0.0997 (2) | 0.84844 (15) | 0.59730 (18) | 0.0512 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.2067 (2) | 0.84190 (15) | 0.68339 (18) | 0.0540 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.190965 | 0.864567 | 0.753249 | 0.065* | |
| C13 | 0.3361 (2) | 0.80227 (14) | 0.66681 (17) | 0.0463 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.407187 | 0.799021 | 0.725600 | 0.056* | |
| C14 | −0.1377 (3) | 0.8996 (2) | 0.5385 (2) | 0.0848 (9) | |
| H14A | −0.170048 | 0.844251 | 0.512568 | 0.127* | |
| H14B | −0.102994 | 0.931447 | 0.477349 | 0.127* | |
| H14C | −0.217011 | 0.929636 | 0.568295 | 0.127* | |
| C15 | 0.8957 (3) | 0.61354 (19) | 0.7129 (2) | 0.0712 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.992141 | 0.590353 | 0.720247 | 0.107* | |
| H15B | 0.830116 | 0.575101 | 0.746182 | 0.107* | |
| H15C | 0.894405 | 0.667913 | 0.749953 | 0.107* | |
| C16 | 0.4969 (2) | 0.56772 (13) | 0.73775 (17) | 0.0478 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.3348 (3) | 0.58040 (18) | 0.7103 (3) | 0.0830 (9) | |
| H17A | 0.318020 | 0.596991 | 0.633344 | 0.124* | |
| H17B | 0.299696 | 0.624313 | 0.757429 | 0.124* | |
| H17C | 0.284589 | 0.527895 | 0.722769 | 0.124* | |
| C18 | 0.5237 (3) | 0.53949 (16) | 0.85894 (19) | 0.0676 (7) | |
| H18A | 0.491235 | 0.583342 | 0.907398 | 0.101* | |
| H18B | 0.625574 | 0.529685 | 0.875337 | 0.101* | |
| H18C | 0.471174 | 0.487645 | 0.870558 | 0.101* | |
| C19 | 0.5532 (3) | 0.50019 (15) | 0.6600 (2) | 0.0712 (8) | |
| H19A | 0.654518 | 0.490342 | 0.679215 | 0.107* | |
| H19B | 0.540247 | 0.519762 | 0.584077 | 0.107* | |
| H19C | 0.500409 | 0.447913 | 0.667862 | 0.107* |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0547 (10) | 0.1337 (17) | 0.0507 (11) | 0.0372 (11) | −0.0036 (8) | −0.0104 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0478 (10) | 0.0425 (10) | 0.0246 (9) | −0.0031 (8) | −0.0024 (7) | −0.0012 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0392 (9) | 0.0403 (9) | 0.0346 (10) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0022 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0473 (10) | 0.0488 (10) | 0.0290 (9) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0027 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0412 (12) | 0.0509 (13) | 0.0513 (14) | 0.0026 (10) | −0.0018 (10) | −0.0050 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0425 (13) | 0.0714 (17) | 0.0720 (18) | 0.0081 (12) | 0.0084 (12) | −0.0068 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0550 (15) | 0.0765 (17) | 0.0612 (17) | 0.0001 (13) | 0.0240 (13) | −0.0099 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0582 (15) | 0.0613 (15) | 0.0392 (13) | −0.0063 (12) | 0.0147 (11) | −0.0027 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0430 (11) | 0.0307 (11) | −0.0073 (10) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0019 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0374 (10) | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0263 (10) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0019 (8) | −0.0040 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0416 (11) | 0.0407 (11) | 0.0257 (10) | −0.0025 (9) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0400 (11) | 0.0428 (11) | 0.0267 (10) | −0.0002 (9) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0032 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0536 (13) | 0.0747 (16) | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0113 (12) | −0.0037 (10) | −0.0055 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0494 (13) | 0.0846 (17) | 0.0363 (13) | 0.0130 (12) | −0.0114 (10) | −0.0019 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0428 (12) | 0.0695 (15) | 0.0410 (13) | 0.0112 (11) | 0.0000 (10) | 0.0011 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0516 (13) | 0.0801 (16) | 0.0300 (12) | 0.0137 (12) | 0.0002 (10) | −0.0098 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0457 (12) | 0.0609 (14) | 0.0307 (12) | 0.0066 (10) | −0.0090 (9) | −0.0043 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0514 (15) | 0.127 (3) | 0.074 (2) | 0.0277 (16) | −0.0128 (14) | −0.0110 (18) |
| C15 | 0.0511 (14) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0626 (17) | 0.0198 (14) | −0.0146 (12) | −0.0050 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0568 (13) | 0.0468 (12) | 0.0386 (12) | −0.0101 (11) | −0.0062 (10) | 0.0059 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0623 (17) | 0.0747 (18) | 0.109 (2) | −0.0249 (14) | −0.0135 (16) | 0.0225 (17) |
| C18 | 0.097 (2) | 0.0635 (16) | 0.0422 (14) | −0.0124 (14) | 0.0028 (13) | 0.0133 (12) |
| C19 | 0.112 (2) | 0.0494 (14) | 0.0506 (15) | −0.0149 (15) | −0.0056 (14) | −0.0033 (12) |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C11 | 1.368 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.372 (3) |
| O1—C14 | 1.414 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C6 | 1.400 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.382 (3) |
| N1—C16 | 1.490 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.373 (3) |
| N1—H1A | 0.84 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C1 | 1.394 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C5 | 1.398 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C6 | 1.409 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N3—C5 | 1.327 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N3—C7 | 1.373 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.355 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C15 | 1.495 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.407 (3) | C16—C18 | 1.522 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C16—C19 | 1.523 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.346 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.523 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.407 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.385 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.469 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.383 (3) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C13 | 1.389 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.380 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C11—O1—C14 | 118.61 (19) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C6—N1—C16 | 118.36 (16) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C6—N1—H1A | 112.9 (14) | C12—C13—C8 | 121.27 (19) |
| C16—N1—H1A | 112.4 (14) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C1—N2—C5 | 121.38 (17) | C8—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C1—N2—C6 | 132.33 (17) | O1—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C5—N2—C6 | 106.16 (15) | O1—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—N3—C7 | 105.83 (16) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N2 | 116.8 (2) | O1—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C15 | 122.6 (2) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—C15 | 120.36 (19) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.6 (2) | C1—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 118.7 | C1—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 118.7 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.3 (2) | C1—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.0 (2) | N1—C16—C18 | 106.10 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.5 | N1—C16—C19 | 109.17 (18) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.5 | C18—C16—C19 | 110.05 (19) |
| N3—C5—N2 | 111.49 (16) | N1—C16—C17 | 112.57 (18) |
| N3—C5—C4 | 129.27 (19) | C18—C16—C17 | 109.6 (2) |
| N2—C5—C4 | 119.23 (19) | C19—C16—C17 | 109.3 (2) |
| C7—C6—N1 | 134.20 (17) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—N2 | 104.80 (15) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—N2 | 120.27 (17) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C6 | 111.55 (17) | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 120.23 (17) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 128.23 (17) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 117.03 (18) | C16—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.86 (17) | C16—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 122.08 (18) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 122.11 (19) | C16—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 118.9 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 118.9 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.9 (2) | C16—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 | C16—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| O1—C11—C10 | 125.4 (2) | C16—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| O1—C11—C12 | 115.63 (19) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.0 (2) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.7 (2) | ||
| C5—N2—C1—C2 | −8.4 (3) | N1—C6—C7—N3 | −166.5 (2) |
| C6—N2—C1—C2 | 176.4 (2) | N2—C6—C7—N3 | 3.3 (2) |
| C5—N2—C1—C15 | 166.7 (2) | N1—C6—C7—C8 | 14.0 (4) |
| C6—N2—C1—C15 | −8.5 (3) | N2—C6—C7—C8 | −176.20 (18) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | 2.2 (3) | N3—C7—C8—C9 | 29.4 (3) |
| C15—C1—C2—C3 | −172.7 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −151.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 3.7 (4) | N3—C7—C8—C13 | −148.62 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −3.5 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C13 | 30.8 (3) |
| C7—N3—C5—N2 | −1.7 (2) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (3) |
| C7—N3—C5—C4 | 176.8 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.9 (2) |
| C1—N2—C5—N3 | −172.63 (17) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.3 (4) |
| C6—N2—C5—N3 | 3.7 (2) | C14—O1—C11—C10 | −0.2 (4) |
| C1—N2—C5—C4 | 8.7 (3) | C14—O1—C11—C12 | 179.3 (2) |
| C6—N2—C5—C4 | −174.96 (18) | C9—C10—C11—O1 | 179.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N3 | 179.1 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.0 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—N2 | −2.5 (3) | O1—C11—C12—C13 | −179.5 (2) |
| C16—N1—C6—C7 | 75.4 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.1 (4) |
| C16—N1—C6—N2 | −93.2 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.6 (4) |
| C1—N2—C6—C7 | 171.71 (19) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.9 (3) |
| C5—N2—C6—C7 | −4.1 (2) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 179.0 (2) |
| C1—N2—C6—N1 | −16.7 (3) | C6—N1—C16—C18 | 170.52 (18) |
| C5—N2—C6—N1 | 167.46 (17) | C6—N1—C16—C19 | 52.0 (2) |
| C5—N3—C7—C6 | −1.1 (2) | C6—N1—C16—C17 | −69.6 (3) |
| C5—N3—C7—C8 | 178.47 (17) |
N-tert-Butyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (I) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg4 is the centroid of the imidazole ring system N2/N3/C1–C7.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···N3i | 0.84 (2) | 2.41 (2) | 3.226 (2) | 163.6 (19) |
| C14—H14A···Cg4ii | 0.96 | 2.93 | 3.862 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y, z.
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Crystal data
| C19H24N4 | F(000) = 1328 |
| Mr = 308.42 | Dx = 1.171 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 34.9185 (14) Å | Cell parameters from 4941 reflections |
| b = 8.4656 (5) Å | θ = 2.3–21.5° |
| c = 11.8361 (6) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| β = 91.061 (5)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 3498.2 (3) Å3 | Block, brown |
| Z = 8 | 0.15 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3259 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1834 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.071 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016) | h = −42→42 |
| Tmin = 0.697, Tmax = 0.745 | k = −10→10 |
| 32313 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.159 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0675P)2 + 2.4598P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3259 reflections | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 218 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2018 (Sheldrick, 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0021 (4) |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.58246 (6) | 0.2712 (2) | 0.25418 (17) | 0.0442 (6) | |
| H1A | 0.5872 (7) | 0.328 (3) | 0.196 (2) | 0.059 (8)* | |
| N2 | 0.55040 (5) | 0.3250 (2) | 0.42684 (15) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.58530 (6) | 0.5154 (2) | 0.50989 (15) | 0.0438 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.72538 (7) | 0.8380 (3) | 0.2431 (2) | 0.0757 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.52002 (7) | 0.2237 (3) | 0.4153 (2) | 0.0508 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.517019 | 0.162595 | 0.350459 | 0.061* | |
| C2 | 0.49463 (8) | 0.2134 (3) | 0.4987 (2) | 0.0571 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.473839 | 0.145323 | 0.491098 | 0.068* | |
| C3 | 0.49907 (8) | 0.3043 (3) | 0.5975 (2) | 0.0582 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.481526 | 0.294650 | 0.655271 | 0.070* | |
| C4 | 0.52893 (7) | 0.4063 (3) | 0.6088 (2) | 0.0534 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.531869 | 0.466408 | 0.674089 | 0.064* | |
| C5 | 0.55533 (7) | 0.4205 (3) | 0.52145 (18) | 0.0421 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.57963 (7) | 0.3602 (3) | 0.35289 (18) | 0.0393 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.60021 (6) | 0.4794 (3) | 0.40559 (18) | 0.0401 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.63292 (7) | 0.5687 (3) | 0.36299 (18) | 0.0402 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.66073 (7) | 0.6297 (3) | 0.4354 (2) | 0.0497 (7) | |
| H9 | 0.658973 | 0.610551 | 0.512451 | 0.060* | |
| C10 | 0.69081 (8) | 0.7177 (3) | 0.3970 (2) | 0.0553 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.708854 | 0.756665 | 0.448615 | 0.066* | |
| C11 | 0.69492 (7) | 0.7499 (3) | 0.2825 (2) | 0.0508 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.66718 (7) | 0.6877 (3) | 0.2090 (2) | 0.0508 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.669089 | 0.705457 | 0.131802 | 0.061* | |
| C13 | 0.63701 (7) | 0.6006 (3) | 0.24861 (19) | 0.0462 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.618807 | 0.561903 | 0.197371 | 0.055* | |
| C14 | 0.75347 (10) | 0.8995 (5) | 0.3193 (3) | 0.1142 (15) | |
| H14A | 0.741602 | 0.971727 | 0.370444 | 0.171* | |
| H14B | 0.772753 | 0.954037 | 0.277596 | 0.171* | |
| H14C | 0.765061 | 0.814507 | 0.361250 | 0.171* | |
| C15 | 0.72835 (11) | 0.8749 (5) | 0.1261 (3) | 0.1039 (13) | |
| H15A | 0.727624 | 0.779098 | 0.082673 | 0.156* | |
| H15B | 0.752067 | 0.928862 | 0.113508 | 0.156* | |
| H15C | 0.707347 | 0.941516 | 0.103264 | 0.156* | |
| C16 | 0.60865 (8) | 0.1322 (3) | 0.25466 (19) | 0.0507 (7) | |
| C17 | 0.64993 (10) | 0.1807 (4) | 0.2766 (4) | 0.1032 (13) | |
| H17A | 0.657379 | 0.256783 | 0.220981 | 0.155* | |
| H17B | 0.666177 | 0.089525 | 0.272039 | 0.155* | |
| H17C | 0.652367 | 0.226531 | 0.350538 | 0.155* | |
| C18 | 0.60542 (11) | 0.0597 (4) | 0.1387 (2) | 0.0899 (12) | |
| H18A | 0.579787 | 0.021809 | 0.125922 | 0.135* | |
| H18B | 0.623086 | −0.026745 | 0.133299 | 0.135* | |
| H18C | 0.611317 | 0.137832 | 0.082842 | 0.135* | |
| C19 | 0.59690 (11) | 0.0154 (4) | 0.3429 (3) | 0.0996 (13) | |
| H19A | 0.597112 | 0.065823 | 0.415539 | 0.149* | |
| H19B | 0.614509 | −0.071669 | 0.344110 | 0.149* | |
| H19C | 0.571574 | −0.022513 | 0.325394 | 0.149* |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0602 (14) | 0.0398 (12) | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0071 (10) | 0.0018 (10) | −0.0009 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0434 (12) | 0.0376 (11) | 0.0417 (11) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0017 (9) | −0.0031 (9) |
| N3 | 0.0492 (12) | 0.0451 (12) | 0.0372 (11) | −0.0053 (10) | 0.0044 (9) | −0.0036 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0694 (17) | 0.0800 (19) | 0.0784 (18) | −0.0236 (15) | 0.0188 (14) | 0.0092 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0549 (16) | 0.0452 (15) | 0.0524 (16) | −0.0078 (13) | −0.0015 (13) | −0.0073 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0529 (17) | 0.0563 (17) | 0.0623 (17) | −0.0120 (14) | 0.0069 (14) | −0.0029 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0564 (17) | 0.0631 (18) | 0.0556 (17) | −0.0070 (15) | 0.0144 (13) | 0.0000 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0596 (17) | 0.0574 (17) | 0.0434 (14) | −0.0049 (15) | 0.0107 (12) | −0.0057 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0490 (15) | 0.0422 (14) | 0.0350 (13) | −0.0032 (12) | 0.0017 (11) | −0.0043 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0462 (14) | 0.0375 (13) | 0.0343 (12) | 0.0014 (11) | 0.0017 (11) | −0.0019 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0438 (14) | 0.0400 (13) | 0.0365 (13) | 0.0026 (11) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0013 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0437 (14) | 0.0388 (13) | 0.0384 (13) | 0.0017 (12) | 0.0037 (10) | −0.0016 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0542 (16) | 0.0538 (16) | 0.0411 (14) | −0.0058 (14) | 0.0017 (12) | −0.0010 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0514 (16) | 0.0569 (17) | 0.0575 (17) | −0.0098 (14) | 0.0015 (13) | −0.0036 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0501 (16) | 0.0431 (15) | 0.0596 (17) | −0.0023 (13) | 0.0114 (13) | −0.0004 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0621 (17) | 0.0482 (15) | 0.0426 (14) | 0.0011 (14) | 0.0128 (13) | 0.0041 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0516 (16) | 0.0464 (15) | 0.0407 (14) | −0.0017 (13) | 0.0015 (11) | 0.0005 (11) |
| C14 | 0.082 (3) | 0.131 (4) | 0.129 (3) | −0.059 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.019 (3) |
| C15 | 0.107 (3) | 0.115 (3) | 0.092 (3) | −0.034 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C16 | 0.0687 (18) | 0.0412 (14) | 0.0422 (14) | 0.0131 (13) | 0.0054 (12) | −0.0005 (11) |
| C17 | 0.074 (2) | 0.082 (3) | 0.154 (4) | 0.029 (2) | −0.012 (2) | −0.021 (2) |
| C18 | 0.145 (3) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0538 (18) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0069 (19) | −0.0116 (16) |
| C19 | 0.150 (3) | 0.066 (2) | 0.084 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0315 (19) |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C6 | 1.395 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.393 (3) |
| N1—C16 | 1.491 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1A | 0.86 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.393 (4) |
| N2—C1 | 1.369 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.375 (3) |
| N2—C6 | 1.389 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C5 | 1.389 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C5 | 1.329 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N3—C7 | 1.383 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N4—C11 | 1.387 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N4—C14 | 1.419 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| N4—C15 | 1.425 (4) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.342 (4) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C16—C19 | 1.500 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.406 (4) | C16—C18 | 1.506 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C16—C17 | 1.516 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.358 (4) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.403 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.381 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.467 (3) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.383 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C13 | 1.390 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.372 (3) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | ||
| C6—N1—C16 | 118.45 (19) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.2 (2) |
| C6—N1—H1A | 112.8 (17) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| C16—N1—H1A | 108.6 (17) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| C1—N2—C6 | 130.4 (2) | C12—C13—C8 | 121.9 (2) |
| C1—N2—C5 | 121.9 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.0 |
| C6—N2—C5 | 107.55 (18) | C8—C13—H13 | 119.0 |
| C5—N3—C7 | 105.59 (18) | N4—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C11—N4—C14 | 120.6 (3) | N4—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C11—N4—C15 | 121.0 (3) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C14—N4—C15 | 118.4 (3) | N4—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N2 | 119.2 (2) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.4 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—H1 | 120.4 | N4—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.8 (3) | N4—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | N4—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.1 (2) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | N1—C16—C19 | 110.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.7 (2) | N1—C16—C18 | 106.4 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C19—C16—C18 | 110.4 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | N1—C16—C17 | 111.6 (2) |
| N3—C5—N2 | 110.80 (19) | C19—C16—C17 | 109.3 (3) |
| N3—C5—C4 | 131.1 (2) | C18—C16—C17 | 108.7 (3) |
| N2—C5—C4 | 118.1 (2) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—N2 | 104.74 (19) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—N1 | 136.7 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N2—C6—N1 | 118.4 (2) | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—N3 | 111.3 (2) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 128.5 (2) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 120.1 (2) | C16—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 116.5 (2) | C16—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.5 (2) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 122.0 (2) | C16—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 122.1 (2) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.0 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.0 | C16—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 121.5 (2) | C16—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.3 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.3 | C16—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N4—C11—C10 | 121.7 (2) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N4—C11—C12 | 121.5 (2) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 116.8 (2) | ||
| C6—N2—C1—C2 | −178.1 (2) | C5—N3—C7—C6 | −0.7 (3) |
| C5—N2—C1—C2 | −1.4 (4) | C5—N3—C7—C8 | 177.1 (2) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −150.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.2 (4) | N3—C7—C8—C9 | 32.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C13 | 31.5 (4) |
| C7—N3—C5—N2 | −0.4 (2) | N3—C7—C8—C13 | −145.9 (2) |
| C7—N3—C5—C4 | −178.6 (3) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.2 (4) |
| C1—N2—C5—N3 | −175.9 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −177.9 (2) |
| C6—N2—C5—N3 | 1.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.1 (4) |
| C1—N2—C5—C4 | 2.5 (3) | C14—N4—C11—C10 | −0.4 (4) |
| C6—N2—C5—C4 | 179.9 (2) | C15—N4—C11—C10 | −177.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N3 | 176.3 (3) | C14—N4—C11—C12 | −179.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N2 | −1.8 (4) | C15—N4—C11—C12 | 3.2 (4) |
| C1—N2—C6—C7 | 175.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N4 | −179.6 (3) |
| C5—N2—C6—C7 | −1.7 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.4 (4) |
| C1—N2—C6—N1 | −7.4 (4) | N4—C11—C12—C13 | −179.9 (2) |
| C5—N2—C6—N1 | 175.56 (19) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.8 (4) |
| C16—N1—C6—C7 | 81.8 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.8 (4) |
| C16—N1—C6—N2 | −94.4 (3) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.3 (4) |
| N2—C6—C7—N3 | 1.6 (3) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 178.3 (2) |
| N1—C6—C7—N3 | −175.0 (2) | C6—N1—C16—C19 | 59.6 (3) |
| N2—C6—C7—C8 | −176.1 (2) | C6—N1—C16—C18 | 179.4 (2) |
| N1—C6—C7—C8 | 7.4 (4) | C6—N1—C16—C17 | −62.1 (3) |
N-tert-Butyl-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-amine (II) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg3 is the centroid of benzene ring C8–C13.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···N3i | 0.86 (3) | 2.56 (3) | 3.412 (3) | 167 (2) |
| C13—H13···N3i | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.467 (3) | 161 |
| C19—H19B···Cg3ii | 0.96 | 2.87 | 3.829 (4) | 174 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1, z−1/2; (ii) x, y−1, z.
References
- Abdullah, Z. (2005). Int. J. Chem. Sci. 3, 9–15.
- Banfi, E., Scialino, G., Zampieri, D., Mamolo, M. G., Vio, L., Ferrone, M., Fermeglia, M., Paneni, M. S. & Pricl, S. (2006). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58, 76–84. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Biftu, T., Feng, D., Fisher, M., Liang, G. B., Qian, X., Scribner, A., Dennis, R., Lee, S., Liberator, P. A., Brown, C., Gurnett, A., Leavitt, P. S., Thompson, D., Mathew, J., Misura, A., Samaras, S., Tamas, T., Sina, J. F., McNulty, K. A., McKnight, C. G., Schmatz, D. M. & Wyvratt, M. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 2479–2483. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2016). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA..
- Cui, B., Zheng, B. L., He, K. & Zheng, Q. Y. (2003). J. Nat. Prod. 66, 1101–1103. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dooley, S. W., Jarvis, W. R., Martone, W. J. & Snider, D. E. Jr (1992). Ann. Intern. Med. 117, 257–259. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elaatiaoui, A., Elkalai, F., Benchat, N., Saadi, M. & El Ammari, L. (2016). IUCrData, 1, x160723.
- Elaatiaoui, A., Koudad, M., Saddik, R., Benchat, N. & El Ammari, L. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o1189–o1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ertl, P., Rohde, B. & Selzer, P. (2000). J. Med. Chem. 43, 3714–3717. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Fatima, Z., Srinivasan, T., Koorathota, S., Thennarasu, S. & Velmurugan, D. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o612–o613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, K. S. & Johns, B. A. (2007). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 2735–2739. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gueiffier, A., Mavel, S., Lhassani, M., Elhakmaoui, A., Snoeck, R., Andrei, G., Chavignon, O., Teulade, J. C., Witvrouw, M., Balzarini, J., De Clercq, E. & Chapat, J. (1998). J. Med. Chem. 41, 5108–5112. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C. J., Lamb, D. C., Kelly, D. E. & Kelly, S. L. (2000). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 192, 159–162. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kawai, M., Lee, M. J., Evans, K. O. & Nordlund, T. M. (2001). J. Fluoresc. 11, 23–32.
- Lhassani, M., Chavignon, O., Chezal, J. M., Teulade, J. C., Chapat, J. P., Snoeck, R., Andrei, G., Balzarini, J., De Clercq, E. & Gueiffier, A. (1999). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 34, 271–274. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mavel, S., Renou, J. L., Galtier, C., Allouchi, H., Snoeck, R., Andrei, G., De Clercq, E., Balzarini, J. & Gueiffier, A. (2002). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 10, 941–946. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rupert, K. C., Henry, J. R., Dodd, J. H., Wadsworth, S. A., Cavender, D. E., Olini, G. C., Fahmy, B. & Siekierka, J. J. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13, 347–350. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Silvestre, J., Leeson, P. A. & Castañer, J. (1998). Drugs Fut. 23, 598–601.
- Spasov, A. A., Yozhitsa, I. N., Bugaeva, L. I. & Anisimova, V. A. (1999). Pharm. Chem. J. 33, 232–243.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., MacKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17.5. University of Western Australia, Perth.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Yao, J., Wang, L., Guo, B., An, K. & Guan, J. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016651/su5459sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016651/su5459Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018016651/su5459IIsup3.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report











