The structures of the hydrogen-bonded 1:1 co-crystal of chloranilic acid with ethyleneurea and the 1:2 co-crystal of chloranilic acid with hydantoin have been determined at 180 K. In the crystals of both compounds, the base molecules are in the lactam form and no acid–base interaction involving H-atom transfer is observed. The acid and base molecules are linked by short O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure; chloranilic acid; ethyleneurea; imidazolidin-2-one; hydantoin; imidazolidine-2,4-dione; hydrogen bond
Abstract
The structures of the hydrogen-bonded 1:1 co-crystal of chloranilic acid (systematic name: 2,5-dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone) with ethyleneurea (systematic name: imidazolidin-2-one), C6H2Cl2O4·C3H6N2O, (I), and the 1:2 co-crystal of chloranilic acid with hydantoin (systematic name: imidazolidine-2,4-dione), C6H2Cl2O4·2C3H4N2O2, (II), have been determined at 180 K. In the crystals of both compounds, the base molecules are in the lactam form and no acid–base interaction involving H-atom transfer is observed. The asymmetric unit of (I) consists of two independent half-molecules of chloranilic acid, with each of the acid molecules lying about an inversion centre, and one ethyleneurea molecule. The asymmetric unit of (II) consists of one half-molecule of chloranilic acid, which lies about an inversion centre, and one hydantoin molecule. In the crystal of (I), the acid and base molecules are linked via O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming an undulating sheet structure parallel to the ab plane. In (II), the base molecules form an inversion dimer via a pair of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, and the base dimers are further linked through another N—H⋯O hydrogen bond into a layer structure parallel to ( 01). The acid molecule and the base molecule are linked via an O—H⋯O hydrogen bond.
01). The acid molecule and the base molecule are linked via an O—H⋯O hydrogen bond.
Chemical context
Chloranilic acid, a dibasic acid with hydrogen-bond donor as well as acceptor groups, appears particularly attractive as a template for generating tightly bound self-assemblies with various organic bases, and also as a model compound for investigating hydrogen-transfer motions in O—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen-bonded systems (Zaman et al., 2004 ▸; Seliger et al., 2009 ▸; Asaji et al. 2010 ▸; Molčanov & Kojić-Prodić, 2010 ▸). In the present study, we have prepared two hydrogen-bonded compounds of chloranilic acid–ethyleneurea (1/1) and chloranilic acid–hydantoin (1/2) in order to extend our study on D—H⋯A hydrogen bonding (D = N, O, or C; A = N, O or Cl) in chloranilic acid–organic base systems (Gotoh & Ishida, 2017a
▸,b
▸, and references therein).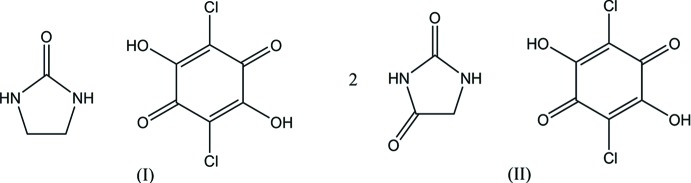
Structural commentary
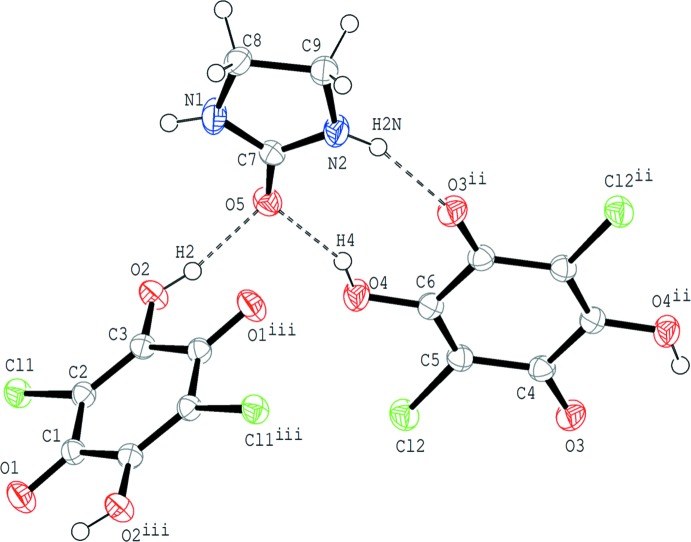
In compound (I), the base molecule is in the lactam form and no acid–base interaction involving H-atom transfer is observed (Fig. 1 ▸). In the asymmetric unit, there is one ethyleneurea molecule and two crystallographically independent half-molecules of chloranilic acid, with each of the acid molecules lying about an inversion centre. The O atom of ethyleneurea participates in two O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds as an acceptor for two O—H groups of chloranilic acid (O2—H2⋯O5 and O4—H4⋯O5; Table 1 ▸). The base ring (C7/N1/C8/C9/N2) is essentially planar and makes dihedral angles of 88.75 (6) and 3.27 (6)°, respectively, with the acid C1–C3/C1iii–C3iii and C4–C6/C4ii–C6ii rings [symmetry codes: (ii) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iii) −x + 1, −y, −z + 1].
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I), showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids of non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level and H atoms are drawn as small spheres of arbitrary radii. O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines. [Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iii) −x + 1, −y, −z + 1.]
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O5 | 0.81 (2) | 1.82 (2) | 2.6090 (11) | 164 (2) |
| O4—H4⋯O5 | 0.86 (2) | 1.88 (2) | 2.6635 (12) | 151.0 (19) |
| N1—H1N⋯O1i | 0.85 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.9003 (15) | 168 (2) |
| N2—H2N⋯O3ii | 0.85 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.8654 (15) | 158.6 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 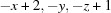 ; (ii)
; (ii) 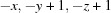 .
.
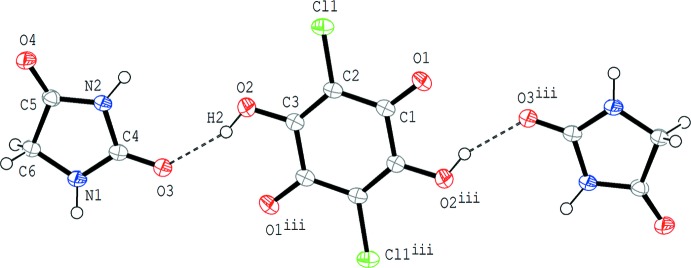
In compound (II), the base molecule is also in the lactam form and no acid–base interaction involving H-atom transfer is observed (Fig. 2 ▸). The chloranilic acid molecule is located on an inversion centre and the asymmetric unit consists of one hydantoin molecule and a half-molecule of chloranilic acid. The acid and base molecules are linked via an O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (O2—H2⋯O3; Table 2 ▸), forming a centrosymmetric 1:2 aggregate of the acid and the base. The 1:2 unit is approximately planar with a dihedral angle of 5.42 (5)° between the acid and base rings.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II), showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids of non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level and H atoms are drawn as small spheres of arbitrary radii. O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines. [Symmetry code: (iii) −x + 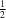 , −y +
, −y +  , −z + 1.]
, −z + 1.]
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O3 | 0.86 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.7917 (15) | 160 (2) |
| N1—H1N⋯O3i | 0.91 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.8927 (13) | 165 (2) |
| N2—H2N⋯O4ii | 0.91 (2) | 1.85 (2) | 2.7560 (14) | 176 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 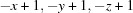 ; (ii)
; (ii) 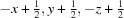 .
.
Supramolecular features
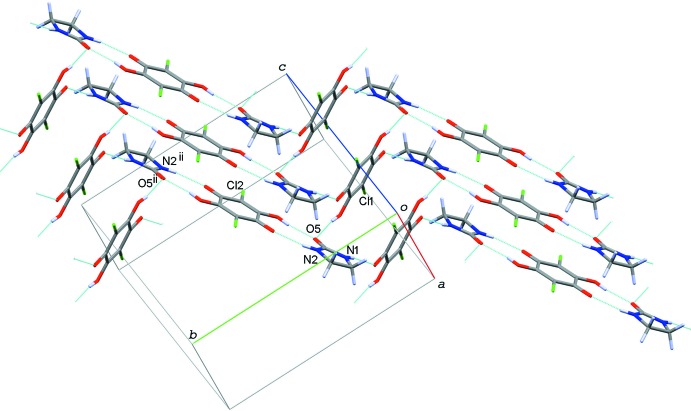
In the crystal of compound (I), the acid and base molecules are alternately arranged through O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (O4—H4⋯O5, N1—H1N⋯O1i, N2—H2H⋯O3ii; symmetry codes as in Table 1 ▸), forming an undulating tape structure along [3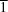 0]. The tapes are stacked along the a axis via another O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (O2—H2—O5; Table 1 ▸) into a sheet structure parallel to the ab plane (Fig. 3 ▸).
0]. The tapes are stacked along the a axis via another O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (O2—H2—O5; Table 1 ▸) into a sheet structure parallel to the ab plane (Fig. 3 ▸).
Figure 3.
A partial packing diagram of compound (I), showing the undulating sheet structure formed by O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (light-blue dotted lines). [Symmetry code: (ii) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1.]
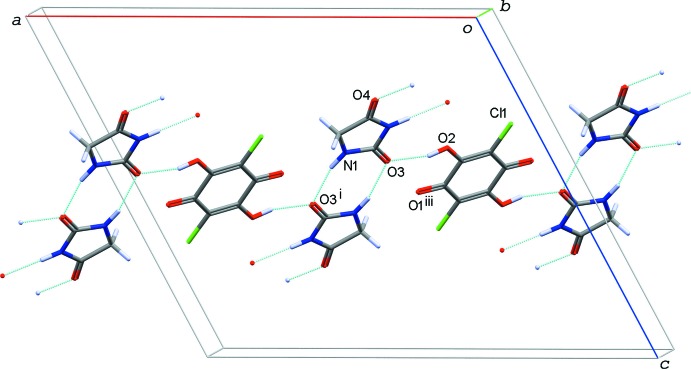
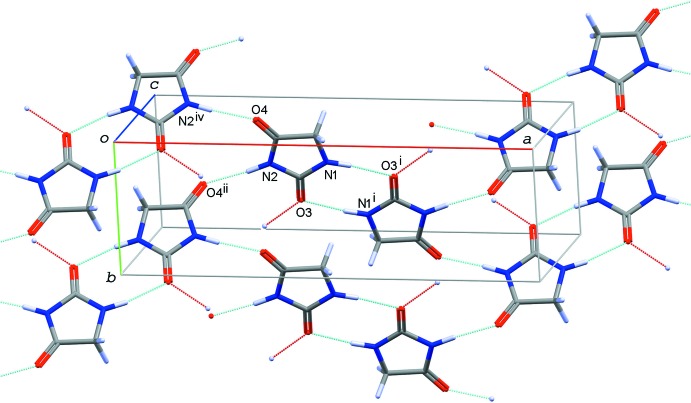
In the crystal of (II), two adjacent base molecules, which are related by an inversion centre, form a dimer via a pair of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (N1—H1N⋯O3i; symmetry code as in Table 2 ▸), and the base dimer and the acid molecule are alternately linked through an O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (O2—H2⋯O3; Table 2 ▸), forming a flat tape structure along the a-axis direction (Fig. 4 ▸). The base dimers are assembled via another N—H⋯O hydrogen bond (N2—H2N⋯O4ii; symmetry code as in Table 2 ▸), forming a layer parallel to (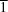 01) as shown in Fig. 5 ▸. The O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (O2—H2⋯O3; Table 2 ▸) formed between the acid and base molecules links the layers.
01) as shown in Fig. 5 ▸. The O—H⋯O hydrogen bond (O2—H2⋯O3; Table 2 ▸) formed between the acid and base molecules links the layers.
Figure 4.
A partial packing diagram of compound (II) viewed approximately along the b axis, showing a hydrogen-bonded tape structure formed by acid molecules and pairs of base molecules. O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown by light-blue dotted lines. [Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iii) −x + 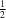 , −y +
, −y +  , −z + 1.]
, −z + 1.]
Figure 5.
A partial packing diagram of compound (II), showing hydrogen-bonding scheme in the layer formed by base molecules. N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the base molecules are shown by light-blue dotted lines, while O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the base and acid molecules are shown by red dotted lines. [Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (ii) −x + 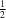 , y +
, y + 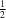 , −z +
, −z + 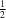 ; (iv) −x +
; (iv) −x + 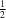 , y −
, y − 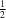 , −z +
, −z + 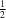 .]
.]
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.39, last update August 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for organic crystals of chloranilic acid with lactam-form base molecules gave ten hits. In the seven crystals of these compounds, O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the O—H group of chloranilic acid and the carbonyl group of base are observed [refcodes ACOJIO (Gotoh & Ishida, 2017a ▸), AJAGIB (Luo & Palmore, 2002 ▸), HUFZUE (Jasinski et al., 2010 ▸), ODIHIU, SADTIC, SADTOI and SADTUO (Gotoh & Ishida, 2011 ▸)]. In particular, the compounds of chloranilic acid with 2-pyridone (ACOJIO), gabapentin-lactum (HUFZUE), pyrrolidin-2-one (ODIHIU) and piperidin-2-one (SADTUO) show short O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (O⋯O shorter than 2.5 Å). In the O—H⋯O hydrogen bond [O⋯O = 2.4484 (10) Å] of chloranilic acid–piperidin-2-one (1/2) (SADTUO), the H atom is disordered over two positions.
Synthesis and crystallization
Single crystals of compound (I) were obtained by slow evaporation from an acetonitrile solution (150 ml) of chloranilic acid (330 mg) with ethyleneurea (140 mg) at room temperature. Crystals of compound (II) were obtained by slow evaporation from an acetonitrile solution (250 ml) of chloranilic acid (350 mg) with hydantoin (340 mg) at room temperature.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms in compounds (I) and (II) were found in difference Fourier maps. The O- and N-bound H atoms were freely refined. C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.99 Å) and were treated as riding with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C6H2Cl2O4·C3H6N2O | C6H2Cl2O4·2C3H4N2O2 |
| M r | 295.08 | 409.14 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 180 | 180 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 5.0180 (4), 14.6142 (10), 15.8882 (11) | 19.5690 (8), 5.18661 (10), 16.6103 (3) |
| β (°) | 105.563 (3) | 117.965 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1122.43 (15) | 1489.03 (8) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.59 | 0.49 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.45 × 0.29 × 0.23 | 0.49 × 0.33 × 0.24 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII |
| Absorption correction | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.716, 0.873 | 0.808, 0.888 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 21546, 3266, 3040 | 14622, 2181, 2029 |
| R int | 0.057 | 0.072 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.704 | 0.704 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.033, 0.092, 1.07 | 0.036, 0.100, 1.08 |
| No. of reflections | 3266 | 2181 |
| No. of parameters | 179 | 130 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.54, −0.31 | 0.44, −0.40 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) General, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Crystal data
| C6H2Cl2O4·C3H6N2O | F(000) = 600.00 |
| Mr = 295.08 | Dx = 1.746 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 5.0180 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 19204 reflections |
| b = 14.6142 (10) Å | θ = 3.0–30.1° |
| c = 15.8882 (11) Å | µ = 0.59 mm−1 |
| β = 105.563 (3)° | T = 180 K |
| V = 1122.43 (15) Å3 | Block, brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.45 × 0.29 × 0.23 mm |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 3040 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.057 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.716, Tmax = 0.873 | k = −20→19 |
| 21546 measured reflections | l = −21→22 |
| 3266 independent reflections |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0573P)2 + 0.2007P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3266 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 179 parameters | Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 1.06653 (5) | 0.00389 (2) | 0.64704 (2) | 0.02517 (9) | |
| Cl2 | 0.28647 (6) | 0.43040 (2) | 0.69108 (2) | 0.03101 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.64834 (18) | −0.14266 (6) | 0.60507 (6) | 0.03198 (19) | |
| O2 | 0.83758 (17) | 0.15225 (5) | 0.51887 (5) | 0.02612 (17) | |
| O3 | −0.17821 (19) | 0.55990 (6) | 0.63245 (6) | 0.03138 (19) | |
| O4 | 0.43441 (18) | 0.37722 (6) | 0.52805 (6) | 0.03039 (19) | |
| O5 | 0.70481 (17) | 0.29928 (5) | 0.42370 (5) | 0.02644 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.8521 (2) | 0.24152 (9) | 0.30842 (7) | 0.0372 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.4933 (2) | 0.33134 (8) | 0.27881 (7) | 0.0323 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.5873 (2) | −0.07583 (7) | 0.55745 (7) | 0.02118 (19) | |
| C2 | 0.7619 (2) | 0.00483 (7) | 0.56565 (7) | 0.02058 (19) | |
| C3 | 0.6846 (2) | 0.07805 (7) | 0.51226 (6) | 0.02064 (19) | |
| C4 | −0.0902 (2) | 0.53136 (7) | 0.57314 (7) | 0.0233 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.1390 (2) | 0.46653 (7) | 0.58624 (7) | 0.0238 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.2263 (2) | 0.43578 (7) | 0.51801 (7) | 0.0236 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.6858 (2) | 0.29121 (7) | 0.34329 (7) | 0.0224 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.7865 (2) | 0.24974 (8) | 0.21442 (8) | 0.0275 (2) | |
| H8A | 0.737465 | 0.189643 | 0.185683 | 0.033* | |
| H8B | 0.943169 | 0.276222 | 0.195803 | 0.033* | |
| C9 | 0.5369 (3) | 0.31466 (9) | 0.19376 (8) | 0.0325 (2) | |
| H9A | 0.578932 | 0.372186 | 0.166986 | 0.039* | |
| H9B | 0.372898 | 0.285493 | 0.153938 | 0.039* | |
| H1N | 0.989 (4) | 0.2121 (14) | 0.3405 (14) | 0.059 (6)* | |
| H2N | 0.381 (4) | 0.3687 (13) | 0.2915 (12) | 0.041 (5)* | |
| H2 | 0.766 (4) | 0.1933 (16) | 0.4861 (14) | 0.056 (6)* | |
| H4 | 0.476 (4) | 0.3613 (13) | 0.4811 (13) | 0.045 (5)* |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.02251 (14) | 0.02897 (15) | 0.02081 (14) | −0.00049 (8) | 0.00027 (10) | 0.00183 (8) |
| Cl2 | 0.03685 (16) | 0.03457 (16) | 0.02165 (15) | 0.00812 (10) | 0.00789 (11) | 0.00275 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0284 (4) | 0.0277 (4) | 0.0345 (4) | −0.0009 (3) | −0.0007 (3) | 0.0114 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0273 (4) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0252 (4) | −0.0031 (3) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0039 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0355 (4) | 0.0356 (4) | 0.0262 (4) | 0.0082 (3) | 0.0138 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0333 (4) | 0.0350 (4) | 0.0243 (4) | 0.0124 (3) | 0.0100 (3) | 0.0016 (3) |
| O5 | 0.0319 (4) | 0.0244 (4) | 0.0230 (4) | 0.0017 (3) | 0.0071 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0378 (6) | 0.0468 (6) | 0.0272 (5) | 0.0224 (5) | 0.0093 (4) | 0.0057 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0336 (5) | 0.0411 (5) | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0106 (4) | 0.0045 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0207 (4) | 0.0220 (4) | 0.0204 (4) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0047 (3) | 0.0012 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0192 (4) | 0.0236 (5) | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0012 (3) | 0.0029 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0215 (4) | 0.0221 (4) | 0.0181 (4) | 0.0003 (3) | 0.0049 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0225 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0083 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0260 (5) | 0.0245 (5) | 0.0213 (5) | 0.0019 (4) | 0.0070 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0016 (3) | 0.0077 (4) | 0.0002 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0239 (4) | 0.0191 (4) | 0.0246 (5) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0070 (4) | 0.0021 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0315 (5) | 0.0275 (5) | 0.0034 (4) | 0.0100 (4) | −0.0007 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0346 (6) | 0.0416 (6) | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0125 (5) | 0.0127 (4) | 0.0075 (4) |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C2 | 1.7169 (10) | N2—C9 | 1.4464 (15) |
| Cl2—C5 | 1.7145 (11) | N2—H2N | 0.849 (19) |
| O1—C1 | 1.2230 (13) | C1—C2 | 1.4537 (14) |
| O2—C3 | 1.3165 (12) | C1—C3i | 1.5092 (14) |
| O2—H2 | 0.81 (2) | C2—C3 | 1.3560 (14) |
| O3—C4 | 1.2168 (13) | C4—C5 | 1.4612 (14) |
| O4—C6 | 1.3264 (12) | C4—C6ii | 1.5045 (15) |
| O4—H4 | 0.86 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.3504 (15) |
| O5—C7 | 1.2609 (13) | C8—C9 | 1.5348 (15) |
| N1—C7 | 1.3338 (14) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C8 | 1.4455 (15) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| N1—H1N | 0.85 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C7 | 1.3397 (14) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C3—O2—H2 | 114.1 (14) | C6—C5—Cl2 | 121.94 (8) |
| C6—O4—H4 | 115.8 (13) | C4—C5—Cl2 | 117.13 (8) |
| C7—N1—C8 | 112.92 (10) | O4—C6—C5 | 122.18 (10) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 121.2 (15) | O4—C6—C4ii | 117.46 (9) |
| C8—N1—H1N | 125.7 (15) | C5—C6—C4ii | 120.35 (9) |
| C7—N2—C9 | 112.46 (10) | O5—C7—N1 | 125.87 (10) |
| C7—N2—H2N | 119.3 (12) | O5—C7—N2 | 125.24 (10) |
| C9—N2—H2N | 127.5 (12) | N1—C7—N2 | 108.88 (10) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 123.17 (9) | N1—C8—C9 | 102.65 (9) |
| O1—C1—C3i | 117.64 (9) | N1—C8—H8A | 111.2 |
| C2—C1—C3i | 119.19 (8) | C9—C8—H8A | 111.2 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.28 (9) | N1—C8—H8B | 111.2 |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 121.68 (8) | C9—C8—H8B | 111.2 |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 117.03 (7) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| O2—C3—C2 | 122.48 (9) | N2—C9—C8 | 102.92 (9) |
| O2—C3—C1i | 117.99 (9) | N2—C9—H9A | 111.2 |
| C2—C3—C1i | 119.53 (9) | C8—C9—H9A | 111.2 |
| O3—C4—C5 | 123.19 (10) | N2—C9—H9B | 111.2 |
| O3—C4—C6ii | 118.08 (10) | C8—C9—H9B | 111.2 |
| C5—C4—C6ii | 118.73 (9) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.92 (9) | ||
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.04 (11) | C4—C5—C6—O4 | 179.73 (10) |
| C3i—C1—C2—C3 | 0.34 (16) | Cl2—C5—C6—O4 | −1.31 (16) |
| O1—C1—C2—Cl1 | −0.19 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C4ii | 0.61 (17) |
| C3i—C1—C2—Cl1 | 179.19 (7) | Cl2—C5—C6—C4ii | 179.57 (8) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | 179.32 (9) | C8—N1—C7—O5 | −176.92 (10) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—O2 | 0.52 (15) | C8—N1—C7—N2 | 3.23 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C1i | −0.34 (16) | C9—N2—C7—O5 | 175.71 (11) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C1i | −179.14 (7) | C9—N2—C7—N1 | −4.43 (15) |
| O3—C4—C5—C6 | 178.94 (11) | C7—N1—C8—C9 | −0.84 (14) |
| C6ii—C4—C5—C6 | −0.60 (17) | C7—N2—C9—C8 | 3.73 (14) |
| O3—C4—C5—Cl2 | −0.07 (15) | N1—C8—C9—N2 | −1.64 (13) |
| C6ii—C4—C5—Cl2 | −179.61 (8) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidin-2-one (1/1) (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O5 | 0.81 (2) | 1.82 (2) | 2.6090 (11) | 164 (2) |
| O4—H4···O5 | 0.86 (2) | 1.88 (2) | 2.6635 (12) | 151.0 (19) |
| N1—H1N···O1iii | 0.85 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.9003 (15) | 168 (2) |
| N2—H2N···O3ii | 0.85 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.8654 (15) | 158.6 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Crystal data
| C6H2Cl2O4·2C3H4N2O2 | F(000) = 832.00 |
| Mr = 409.14 | Dx = 1.825 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 19.5690 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 13670 reflections |
| b = 5.18661 (10) Å | θ = 3.3–30.2° |
| c = 16.6103 (3) Å | µ = 0.49 mm−1 |
| β = 117.965 (3)° | T = 180 K |
| V = 1489.03 (8) Å3 | Block, brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.49 × 0.33 × 0.24 mm |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 2029 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.072 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 4.1° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −27→27 |
| Tmin = 0.808, Tmax = 0.888 | k = −7→7 |
| 14622 measured reflections | l = −22→23 |
| 2181 independent reflections |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.08 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0633P)2 + 0.4572P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2181 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 130 parameters | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement was performed using all reflections. The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.09683 (2) | 1.02553 (6) | 0.33978 (2) | 0.02980 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.11596 (5) | 1.47273 (17) | 0.45960 (6) | 0.0313 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.25729 (5) | 0.82514 (16) | 0.40485 (6) | 0.02794 (19) | |
| O3 | 0.39430 (5) | 0.57413 (17) | 0.43836 (6) | 0.02824 (19) | |
| O4 | 0.31705 (4) | −0.10296 (18) | 0.23989 (6) | 0.0296 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.46359 (5) | 0.26895 (19) | 0.40528 (6) | 0.0269 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.33612 (5) | 0.25929 (18) | 0.32811 (6) | 0.02336 (19) | |
| C1 | 0.17655 (6) | 1.3650 (2) | 0.47556 (7) | 0.0229 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.18138 (6) | 1.1410 (2) | 0.42588 (7) | 0.0228 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.25018 (6) | 1.0302 (2) | 0.44779 (7) | 0.0223 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.39913 (6) | 0.3869 (2) | 0.39566 (7) | 0.0226 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.35871 (6) | 0.0519 (2) | 0.29613 (7) | 0.0229 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.44610 (6) | 0.0494 (2) | 0.34539 (8) | 0.0255 (2) | |
| H6A | 0.466307 | −0.112237 | 0.380266 | 0.031* | |
| H6B | 0.467588 | 0.070964 | 0.302420 | 0.031* | |
| H1N | 0.5127 (12) | 0.308 (4) | 0.4484 (15) | 0.054 (5)* | |
| H2 | 0.3043 (12) | 0.772 (4) | 0.4269 (14) | 0.049 (5)* | |
| H2N | 0.2861 (11) | 0.313 (4) | 0.3055 (13) | 0.045 (5)* |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.02000 (16) | 0.03480 (18) | 0.02881 (17) | −0.00423 (8) | 0.00662 (12) | −0.00241 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0206 (4) | 0.0327 (4) | 0.0358 (4) | 0.0052 (3) | 0.0091 (3) | −0.0012 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0237 (4) | 0.0269 (4) | 0.0314 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0114 (3) | −0.0036 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0219 (4) | 0.0300 (4) | 0.0288 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0085 (3) | −0.0058 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0198 (4) | 0.0324 (4) | 0.0321 (4) | −0.0038 (3) | 0.0085 (3) | −0.0086 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0312 (5) | 0.0288 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0067 (3) | −0.0071 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0158 (4) | 0.0268 (4) | 0.0239 (4) | 0.0003 (3) | 0.0063 (3) | −0.0025 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0191 (4) | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0009 (3) | 0.0084 (4) | 0.0032 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0177 (4) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.0220 (4) | −0.0009 (3) | 0.0069 (3) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0205 (4) | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0094 (4) | 0.0021 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0256 (5) | 0.0221 (4) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0076 (3) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0262 (5) | 0.0239 (5) | −0.0002 (3) | 0.0086 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0276 (5) | 0.0295 (5) | −0.0008 (3) | 0.0079 (4) | −0.0049 (4) |
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C2 | 1.7094 (10) | N2—C5 | 1.3620 (14) |
| O1—C1 | 1.2222 (12) | N2—C4 | 1.3857 (13) |
| O2—C3 | 1.3237 (13) | N2—H2N | 0.912 (18) |
| O2—H2 | 0.86 (2) | C1—C2 | 1.4536 (15) |
| O3—C4 | 1.2318 (14) | C1—C3i | 1.5035 (14) |
| O4—C5 | 1.2117 (13) | C2—C3 | 1.3475 (14) |
| N1—C4 | 1.3425 (13) | C5—C6 | 1.5106 (14) |
| N1—C6 | 1.4436 (14) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| N1—H1N | 0.91 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| C3—O2—H2 | 112.8 (14) | O2—C3—C1i | 116.58 (9) |
| C4—N1—C6 | 111.82 (8) | C2—C3—C1i | 120.65 (9) |
| C4—N1—H1N | 125.3 (13) | O3—C4—N1 | 127.75 (10) |
| C6—N1—H1N | 122.5 (13) | O3—C4—N2 | 124.29 (9) |
| C5—N2—C4 | 111.40 (8) | N1—C4—N2 | 107.95 (9) |
| C5—N2—H2N | 124.3 (12) | O4—C5—N2 | 126.87 (10) |
| C4—N2—H2N | 124.2 (12) | O4—C5—C6 | 126.41 (10) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 123.86 (10) | N2—C5—C6 | 106.71 (9) |
| O1—C1—C3i | 117.46 (10) | N1—C6—C5 | 102.06 (8) |
| C2—C1—C3i | 118.67 (8) | N1—C6—H6A | 111.4 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.68 (9) | C5—C6—H6A | 111.4 |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 121.94 (8) | N1—C6—H6B | 111.4 |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 117.37 (7) | C5—C6—H6B | 111.4 |
| O2—C3—C2 | 122.77 (10) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109.2 |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.33 (10) | C6—N1—C4—N2 | −1.64 (12) |
| C3i—C1—C2—C3 | −0.32 (16) | C5—N2—C4—O3 | −176.84 (11) |
| O1—C1—C2—Cl1 | 0.48 (15) | C5—N2—C4—N1 | 2.61 (12) |
| C3i—C1—C2—Cl1 | 179.49 (7) | C4—N2—C5—O4 | 176.75 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | 179.56 (9) | C4—N2—C5—C6 | −2.45 (12) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—O2 | −0.24 (15) | C4—N1—C6—C5 | 0.19 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C1i | 0.32 (16) | O4—C5—C6—N1 | −177.85 (11) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C1i | −179.48 (7) | N2—C5—C6—N1 | 1.35 (11) |
| C6—N1—C4—O3 | 177.78 (11) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1/2, −y+5/2, −z+1.
2,5-Dichloro-3,6-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone–imidazolidine-2,4-dione (1/2) (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O3 | 0.86 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.7917 (15) | 160 (2) |
| N1—H1N···O3ii | 0.91 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.8927 (13) | 165 (2) |
| N2—H2N···O4iii | 0.91 (2) | 1.85 (2) | 2.7560 (14) | 176 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Asaji, T., Seliger, J., Žagar, V. & Ishida, H. (2010). Magn. Reson. Chem. 48, 531–536. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2011). Acta Cryst. C67, o500–o504. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2017a). Acta Cryst. E73, 1546–1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2017b). Acta Cryst. E73, 1840–1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. (1999). NUMABS. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Jasinski, J. P., Butcher, R. J., Hakim Al-arique, Q. N. M., Yathirajan, H. S. & Narayana, B. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o163–o164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Luo, T. M. & Palmore, G. T. R. (2002). Cryst. Growth Des. 2, 337–350.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Molčanov, K. & Kojić-Prodić, B. (2010). CrystEngComm, 12, 925–939.
- Rigaku (2006). RAPID-AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2018). CrystalStructure. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Seliger, J., Žagar, V., Gotoh, K., Ishida, H., Konnai, A., Amino, D. & Asaji, T. (2009). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 2281–2286. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 9–18. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zaman, Md. B., Udachin, K. A. & Ripmeester, J. A. (2004). Cryst. Growth Des. 4, 585–589.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) General, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901801561X/lh5884IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report