1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid and 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide form complex hydrogen-bonded framework structures each containing multiple hydrogen-bond types, but dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate and dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate form simple cyclic dimers containing only C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: synthesis; 1,3-dipolar addition; crystal structure; molecular conformation; disorder; hydrogen bonding; supramolecular assembly
Abstract
Four 1-aryl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate derivatives, one acid, two esters and a dicarbohydrazide have been synthesized starting from 3-aryl sydnones, and structurally characterized. There is an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond in 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid, C11H8N2O4, (I), and the molecules are linked into a three-dimensional framework structure by a combination of O—H⋯O, O—H⋯N, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds. In each of the two esters dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate, C13H12N2O4, (II), and dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate, C14H14N2O4, (III), C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of cyclic centrosymmetric dimers: in (III), one of the methoxycarbonyl groups is disordered over two sets of atomic sites having occupancies 0.71 (2) and 0.29 (2). An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond is present in the structure of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide, C12H14N6O3, (IV), and the molecules are linked into a three-dimensional framework structure by a combination of N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N, N—H⋯π(arene) and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. Comparisons are made with the structures of a number of related compounds.
Chemical context
Pyrazole derivatives have been shown to exhibit a wide range of biological activities including analgesic (Girisha et al., 2010 ▸), anticonvulsant (Owen et al., 1958 ▸), antimicrobial (Satheesha & Kalluraya, 2007 ▸; Asma et al., 2018 ▸), antitumour (Park et al., 2005 ▸), and insecticidal and larvicidal activity (Yang et al., 2018 ▸). Pyrazole carboxylic acids and their derivatives are versatile precursors for the synthesis of numerous substituted analogues (Asma et al., 2018 ▸; Devi et al., 2018 ▸) and, with these considerations in mind, we have now synthesized a series of new pyrazole carboxylate derivatives as intermediates for the synthesis of new pharmacologically active products. Here we report the syntheses, and the molecular and supramolecular structures of four such compounds, namely 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I), dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II), dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) and 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) (Figs. 1 ▸–4 ▸
▸
▸).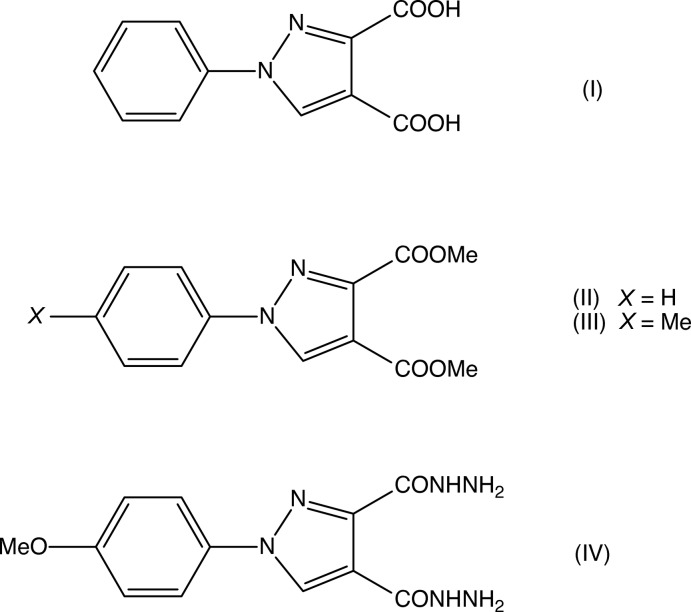
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I) showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II) showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of compound (III) showing the atom-labelling scheme. The major disorder component, occupancy 0.71 (2), is drawn using full lines and the minor component, occupancy 0.29 (2), is drawn using dashed lines. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Figure 4.
The molecular structure of compound (IV) showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
The products (II) and (III) and the intermediate ester (B) (Fig. 5 ▸) used in the formation of compound (IV) were all prepared using the 1,3-dipolar addition reaction between dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate and the 3-arylsyndones [3-aryl-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-5-olates] (A), with loss of carbon dioxide in entropy-driven reactions (Huisgen et al., 1962 ▸) (Fig. 5 ▸). Hydrolysis of the ester (II) gave the dicarboxylic acid (I), while hydrazinolysis of the ester (B) gave the dicarbohyrazide (IV). The sydnone precursors (A) were all prepared from the corresponding anilines via the substituted N-aryl-N-nitrosoglycines (Greco et al., 1962 ▸; Fun et al., 2010 ▸).
Figure 5.
The synthetic routes to compounds (I)–(IV).
Structural commentary
The bond distances in compounds (I)–(IV) show no unexpected values: all are typical of their types (Allen et al., 1987 ▸). However, the molecular conformations show some interesting features. In each of (I) and (IV), the two carboxy substituents on the pyrazole ring are nearly coplanar with this ring, as shown by the leading torsional angles (Table 1 ▸): this is almost certainly a consequence of the presence on an intramolecular O—H⋯O in (I) and an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond in (IV) (Table 2 ▸). In compounds (I) and (III), where such intramolecular interactions are not possible, the carboxyl groups at C3 are by no means coplanar with the pyrazole ring (Table 1 ▸), and in compound (III) the 3-methoxycarbonyl substituent is disordered over two sets of atomic sites having occupancies 0.71 (2) and 0.29 (2) in the crystal selected for data collection: the orientations of the two disorder components are related to one another by a rotation about the C3—C31 bond of approximately 23° (Table 1 ▸). It may be noted here that the ketonic O atom O31 acts as a hydrogen-bond acceptor in each of (I) and (IV), but not in (II) and (III) (Table 2 ▸), and the disorder in (III) may be associated with this.
Table 1. Selected torsional and dihedral angles (°).
φ1 represents the dihedral angle between the planes of the aryl and pyrazole rings and φ2 represents the dihedral angle between the planes (C3,C31,O31A,O32A) and (C3,C31,O31B,O32B)
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—C3—C31—O31 | −178.0 (2) | 44.8 (3) | −12.5 (4) | |
| C4—C3—C31—O32 | 2.1 (4) | −135.9 (2) | ||
| C4—C3—C31—O31A | −129.1 (9) | |||
| C4—C3—C31—O31B | −96.6 (9) | |||
| C4—C3—C31—O32A | 57.5 (6) | |||
| C4—C3—C31—O32B | 71.6 (8) | |||
| C4—C3—C31—N31 | 168.4 (2) | |||
| C3—C4—C41—O41 | −2.5 (4) | −168.5 (2) | 176.5 (2) | −169.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C41—O42 | 178.0 (2) | 12.8 (3) | −3.0 (3) | |
| C3—C4—C41—N41 | 9.8 (4) | |||
| φ1 | 29.38 (8) | 24.38 (12) | 2.78 (12) | 5.82 (13) |
| φ2 | 22.7 (5) |
Table 2. Hydrogen bonds and short intermolecular contacts (Å, °).
Cg1 represents the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| Compound | D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | O32—H32⋯O41 | 1.00 (3) | 1.54 (3) | 3.546 (2) | 178 (2) |
| O42—H42⋯O31i | 0.88 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.660 (2) | 168 (3) | |
| O42—H42⋯N2i | 0.88 (3) | 2.56 (3) | 3.063 (3) | 117 (2) | |
| C14—H14⋯O31ii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.456 (3) | 177 | |
| C12—H12⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.86 | 3.685 (3) | 148 | |
| C15—H15⋯Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.92 | 3.755 (3) | 151 | |
| (II) | C5—H5⋯O41v | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.331 (3) | 170 |
| (III) | C5—H5⋯O41vi | 0.93 | 2.33 | 3.249 (3) | 168 |
| C12—H12⋯O41vi | 0.93 | 2.43 | 3.352 (3) | 173 | |
| (IV) | N31—H31⋯O31vii | 0.88 (2) | 2.04 (2) | 2.851 (3) | 153 (2) |
| N32—H32A⋯O14viii | 0.97 (3) | 2.58 (3) | 3.256 (3) | 127 (2) | |
| N32—H32B⋯N42vii | 1.00 (2) | 2.34 (3) | 3.317 (3) | 165 (2) | |
| N41—H41⋯O31 | 0.95 (3) | 1.78 (3) | 2.714 (3) | 166 (2) | |
| N42—H42A⋯O41ix | 0.95 (3) | 2.21 (3) | 3.120 (3) | 162 (2) | |
| N42—H42B⋯Cg1x | 0.83 (3) | 2.85 (3) | 3.442 (3) | 130 (2) | |
| C5—H5⋯O41v | 0.93 | 2.40 | 3.314 (3) | 166 | |
| C12—H12⋯O41v | 0.93 | 2.44 | 3.354 (3) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, 1 + y, z; (ii) x,  − y, −
− y, − + z; (iii)
+ z; (iii)  − x,
− x,  + y, z; (iv) 1 − x, −
+ y, z; (iv) 1 − x, − + y,
+ y,  − z; (v) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (vi) −x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (vii)
− z; (v) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (vi) −x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (vii)  + x,
+ x,  − y,
− y,  + z; (viii) −
+ z; (viii) − + x,
+ x,  − y, −
− y, − + z; (ix) 1 − x, 1 − y, −z; (x) −1 + x, y, −1 + z.
+ z; (ix) 1 − x, 1 − y, −z; (x) −1 + x, y, −1 + z.
In each of (I) and (II), the planes of the aryl and pyrazole rings make much larger dihedral angles than these planes do in (II) and (IV) (Table 1 ▸). This may be associated with the cooperative effect in (III) and (IV) of the C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving atoms C5 and C12 as donors (Table 2 ▸), whereas no such cooperation is found in the structures of (I) and (II).
Supramolecular features
The supramolecular assembly of compound (I) to form a three-dimensional framework structure depends upon four types of hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸), and the framework formation can readily be analysed in terms of one-dimensional sub-structures (Ferguson et al., 1998a
▸,b
▸; Gregson et al., 2000 ▸). A combination of O—H⋯O and O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, the latter rather weak, links molecules related by translation into a C(6)C(7)[ (5)] (Etter, 1990 ▸; Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸) chain of rings running parallel to the [010] direction (Fig. 6 ▸). In the second sub-structure, molecules related by the c-glide plane at y = 0.25 are linked by a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond to form a simple C(10) chain running parallel to the [001] direction, and the combination of these two chain motifs generates an almost planar sheet lying parallel to (100) in the domain
(5)] (Etter, 1990 ▸; Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸) chain of rings running parallel to the [010] direction (Fig. 6 ▸). In the second sub-structure, molecules related by the c-glide plane at y = 0.25 are linked by a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond to form a simple C(10) chain running parallel to the [001] direction, and the combination of these two chain motifs generates an almost planar sheet lying parallel to (100) in the domain  < x <
< x <  (Fig. 6 ▸). Finally, two weak C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds link this sheet to the adjacent sheets in the domains 0 < x <
(Fig. 6 ▸). Finally, two weak C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds link this sheet to the adjacent sheets in the domains 0 < x <  and
and  < x <
< x <  , and in this way all of the (100) sheets are linked to form a three-dimensional framework structure.
, and in this way all of the (100) sheets are linked to form a three-dimensional framework structure.
Figure 6.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (I) showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded sheet parallel to (100). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms but not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted.
By contrast, the supramolecular assembly in the ester (II) is extremely simple, with inversion-related pairs of molecules linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸) to form a centrosymmetric  (10) dimer (Fig. 7 ▸). A similar, but more complex centrosymmetric dimer is formed by the ester (III), where the same
(10) dimer (Fig. 7 ▸). A similar, but more complex centrosymmetric dimer is formed by the ester (III), where the same  (10) motif as found in (II) is present, along with two flanking
(10) motif as found in (II) is present, along with two flanking  (7) rings within an outer
(7) rings within an outer  (16) ring (Fig. 8 ▸). In neither (II) nor (III) are there any direction-specific interactions between adjacent dimers.
(16) ring (Fig. 8 ▸). In neither (II) nor (III) are there any direction-specific interactions between adjacent dimers.
Figure 7.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (II) showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded  (10) dimer. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms not involved in the motif shown have been omitted. The atoms marked with an asterisk (*) are at the symmetry position (1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z).
(10) dimer. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms not involved in the motif shown have been omitted. The atoms marked with an asterisk (*) are at the symmetry position (1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z).
Figure 8.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (III) showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded dimer containing  (7),
(7),  (10) and
(10) and  (16) ring motifs. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the minor disorder component and the H atoms not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted. The atoms marked with an asterisk (*) are at the symmetry position (−x, 1 − y, 1 − z).
(16) ring motifs. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the minor disorder component and the H atoms not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted. The atoms marked with an asterisk (*) are at the symmetry position (−x, 1 − y, 1 − z).
The supramolecular assembly in the hydrazide (IV) is the most complex of those reported here. A three-dimensional framework structure is built from four types of hydrogen bonds: N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N, N—H⋯π(arene) and C—H⋯O (Table 2 ▸). As for (I), the assembly is readily analysed in terms of simpler substructures. The hydrogen bond involving atom H42A links an inversion-related pair of molecules into an  (10) dimer centred at (
(10) dimer centred at ( ,
,  , 0), and this finite, zero-dimensional sub-structure can be regarded as the basic building block of the overall structure, which can then be analysed in terms of the ways in which these dimers are linked together. The hydrogen bonds involving the atoms H31 and H32B directly link the reference dimer centred at (
, 0), and this finite, zero-dimensional sub-structure can be regarded as the basic building block of the overall structure, which can then be analysed in terms of the ways in which these dimers are linked together. The hydrogen bonds involving the atoms H31 and H32B directly link the reference dimer centred at ( ,
,  , 0) to four similar dimers, centred at (0, 0, −
, 0) to four similar dimers, centred at (0, 0, − ), (0, 1, −
), (0, 1, − ), (1, 0,
), (1, 0,  ) and (1, 1,
) and (1, 1,  ), so forming a sheet lying parallel to (10
), so forming a sheet lying parallel to (10 ) (Fig. 9 ▸), which is reinforced by the N—H⋯π hydrogen bond (Table 2 ▸). The final sub-structure in the assembly of (IV) is one-dimensional: two C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the basic
) (Fig. 9 ▸), which is reinforced by the N—H⋯π hydrogen bond (Table 2 ▸). The final sub-structure in the assembly of (IV) is one-dimensional: two C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the basic  (10) dimers into a chain of rings running parallel to the [001] direction. Within this chain, two types of centrosymmetric
(10) dimers into a chain of rings running parallel to the [001] direction. Within this chain, two types of centrosymmetric  (10) ring can be identified, one containing N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and the other containing C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, along with
(10) ring can be identified, one containing N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and the other containing C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, along with  (7) rings (Fig. 10 ▸).
(7) rings (Fig. 10 ▸).
Figure 9.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (IV) showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded sheet lying parallel to (10 ) and built from N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and N—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms have been omitted.
) and built from N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and N—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms have been omitted.
Figure 10.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (IV) showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded chain of rings parallel to [001] and built from N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are shown as broken lines and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms but not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted.
Database survey
It is of interest to compare briefly the structures of compounds (I)–(IV) reported here with those of some related compounds. In dimethyl 1-(3-chloro-4-methyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate, which differs from (III) only in the presence of the additional 3-chloro substituent, there are again two C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds in the structure, involving exactly the same pair of C—H bonds as in (III), but here the molecules are linked into a C(5)C(8)[ (7)] chain of rings, rather than into cyclic dimers (Thamotharan et al., 2003 ▸). The esters dimethyl 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (Li et al., 2014 ▸) and dimethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (Alizadeh et al., 2010 ▸), which carry an additional substituent in the pyrazole ring, are isostructural, and the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form simple chains.
(7)] chain of rings, rather than into cyclic dimers (Thamotharan et al., 2003 ▸). The esters dimethyl 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (Li et al., 2014 ▸) and dimethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (Alizadeh et al., 2010 ▸), which carry an additional substituent in the pyrazole ring, are isostructural, and the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form simple chains.
The structures of several esters derived from 1-substituted-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylic acids have been reported, including dimethyl 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate (Xiao & Zhao, 2009 ▸), dimethyl 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate (Yao et al., 2009 ▸) and dimethyl 1-cyanomethyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate (Qu, 2009 ▸). There are no significant intermolecular interactions in either of the benzyl derivatives, but the inversion-related pairs of molecules of the 1-cyanomethyl compound are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form centrosymmetric  (10) dimers.
(10) dimers.
In each of 1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid (Tang et al., 2007 ▸) and 1-cyclohexyl-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (Fun et al., 2011 ▸), inversion-related pairs of molecules are linked by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form centrosymmetric  (8) dimers. For the simpler analogue 3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid, the structure was described (Zhang et al., 2007 ▸) as consisting of chains built from O—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, which were then linked into sheets by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. However, scrutiny of the atomic coordinates shows that the structure contains no C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, and that the combination of one O—H⋯O hydrogen bond and one N—H⋯N hydrogen bond generates sheets lying parallel to (100) and containing alternating
(8) dimers. For the simpler analogue 3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid, the structure was described (Zhang et al., 2007 ▸) as consisting of chains built from O—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, which were then linked into sheets by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. However, scrutiny of the atomic coordinates shows that the structure contains no C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, and that the combination of one O—H⋯O hydrogen bond and one N—H⋯N hydrogen bond generates sheets lying parallel to (100) and containing alternating  (8) and
(8) and  (28) rings (Fig. 11 ▸).
(28) rings (Fig. 11 ▸).
Figure 11.
Part of the crystal structure of 3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid showing the formation of a sheet of  (8) and
(8) and  (28) rings lying parallel to (100): hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The original atomic coordinates (Zhang et al., 2007 ▸) have been used and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms have all been omitted.
(28) rings lying parallel to (100): hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The original atomic coordinates (Zhang et al., 2007 ▸) have been used and, for the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms have all been omitted.
Finally, we note that structures have been reported for each of the precursor sydnones employed here (Fig. 5 ▸), for X = H (Hope, 1978 ▸), X = Me (Wang et al., 1984 ▸) and X = MeO (Fun et al., 2010 ▸) although, when X = H, there are no atomic coordinates deposited in the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The precursor sydnones (A) (Fig. 5 ▸) were prepared from the corresponding anilines (Greco et al., 1962 ▸; Wang et al., 1984 ▸; Fun et al., 2010 ▸). For the synthesis of the esters (II) and (III), a mixture of the sydnone of type (A) having X = H for (II) or X = CH3 for (III), (1 mmol) and dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (1 mmol) in dry p-xylene (10 ml) was heated under reflux for 1 h. The mixtures were then cooled to ambient temperature, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the resulting solid products were recrystallized from ethanol. (II): yield 95%, m.p. 373 K. IR (ATR, cm−1) 1712 (C=O), 1582 (C=N). NMR (CDCl3) δ(1H) 3.81 (s, 3H, O—CH3), 4.08 (s, 3H, O—CH3), 7.31 (m, 1H, H14), 7.40 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, H13 & H15), 7.81 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, H12 & H16), 9.28 (s, 1H, H5). Analysis found C 60.2, H 4.7, N 10.8%, C13H12N2O4 requires C 60.0, H 4.6, N 10.8%. (III): yield 93%, m.p. 371 K. IR (ATR, cm−1) 1732 (C=O), 1532 (C=N). NMR (CDCl3) δ(1H) 2.21 (s, 3H, C—CH3), 3.82 (s, 3H, O—CH3), 4.10 (s, 3H, O—CH3), 7.48 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H, H13 & H15), 7.88 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H, H12 & H16), 8.94 (s, 1H, H5). Analysis found C 61.4, H 5.2, N 10.4%, C14H14N2O4 requires C 61.3, H 5.1, N 10.2%.
For the synthesis of the acid (I), the ester (II) (1 mmol) and solid sodium hydroxide (2 mmol) were dissolved in a water–ethanol mixture (water:ethanol 80:20 v/v, 50 ml). This mixture was heated under reflux for 2h, cooled to ambient temperature and then acidified to pH 2 using dilute aqueous hydrochloric acid. The resulting solid product was collected by filtration, washed with water and then recrystallized from ethanol. (I): yield 71%, m.p. 508–509 K. IR (ATR, cm−1) 3427 (O—H), 1717 (C=O), 1542 (C=N). NMR (CDCl3) δ(1H) 7.41 (m, 1H, H14), 7.53 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H, H13 & H15), 7.93 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H, H12 & H16), ?.10 (s, 1H, H5). LC–MS m/z 230.9. Analysis found C 57.1, H 3.6, N 12.2%, C11H8N2O4 requires C 56.9, H 3.5, N 12.1%. For the synthesis of the hydrazide (IV), the intermediate ester (B) (Fig. 5 ▸) was prepared in exactly the same fashion of the esters (II) and (III), yield 90%, m.p. 458 K. A mixture of ester (B) (1 mmol) and hydrazine hydrate (99% aqueous solution, 10 mmol) in ethanol (10 ml) was heated under reflux for 2 h. The mixture was cooled to ambient temperature and the resulting solid product was collected by filtration and then recrystallized from ethanol. (IV): yield 75%, m.p. 502 K. IR (ATR, cm−1) 3354 (N—H), 3308 (N—H), 1650 (C=O), 1562 (C=N). NMR (DMSO-d 6) δ(1H) 3.67 (br, 6H, N-H), 3.82 (s, 3H, O-CH3), 6.98 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H, H13 & H15), 7.69 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H, H12 & H16), 8.91 (s, 1H, H5). LC-MS m/z 290.3. Analysis found C 49.5, H 4.8, N 28.8%, C12H14N6O3 requires C 49.6, H 4.9, N 29.0%. Crystals of compounds (I)–(IV) suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction were selected directly from the purified samples.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. One low-angle reflection, (001) in compound (III), which had been attenuated by the beam stop was removed from the data set. All H atoms were located in difference maps. The H atoms bonded to C atoms were subsequently treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized position with C—H distances 0.93 Å (aryl and pyrazole) or 0.96 Å (CH3) and with U iso(H) = kU eq(C), where k = 1.5 for the methyl groups, which were permitted to rotate but not to tilt, and 1.2 for all other H atoms bonded to C atoms. For the H atoms bonded to O or N atoms, the atomic coordinates were refined with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O) or 1.2U eq(N), leading to the O—H and N—H distances shown in Table 2 ▸. It was apparent that one of the ester substituents in compound (III) was disordered over two sets of atomic sites. For the minor disorder component, the bonded distances and the 1,2 non-bonded distances were restrained to be the same as the corresponding distances in the major disorder component, subject to s.u. values of 0.005 and 0.01 Å, respectively. In addition, the anisotropic displacement parameters for the corresponding pairs of atoms in the two disorder components were constrained to be the same, and the two disordered carboxylate fragments were constrained to be planar. Subject to these conditions, the occupancies of the two sets of sites refined to 0.71 (2) and 0.29 (2).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | C11H8N2O4 | C13H12N2O4 | C14H14N2O4 | C12H14N6O3 |
| M r | 232.19 | 260.25 | 274.27 | 290.29 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P b c a | Monoclinic, P21/n | Triclinic, P

|
Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 296 | 296 | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 13.164 (2), 7.4692 (9), 21.173 (3) | 5.9000 (4), 14.5273 (12), 14.8726 (12) | 7.6546 (5), 8.0959 (5), 11.3065 (6) | 7.6030 (6), 22.6605 (19), 7.6751 (7) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 98.867 (3), 90 | 78.988 (3), 85.527 (3), 87.548 (4) | 90, 102.284 (3), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 2081.8 (6) | 1259.51 (17) | 685.40 (7) | 1292.05 (19) |
| Z | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.16 × 0.14 × 0.11 | 0.17 × 0.14 × 0.13 | 0.16 × 0.15 × 0.12 | 0.14 × 0.13 × 0.11 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.931, 0.987 | 0.960, 0.987 | 0.955, 0.988 | 0.929, 0.988 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 31526, 2218, 1304 | 21653, 2704, 1624 | 12818, 2526, 1777 | 20456, 2521, 1722 |
| R int | 0.063 | 0.046 | 0.030 | 0.053 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.634 | 0.635 | 0.605 | 0.618 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.045, 0.122, 1.03 | 0.042, 0.129, 1.04 | 0.044, 0.128, 1.05 | 0.046, 0.108, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 2218 | 2704 | 2526 | 2521 |
| No. of parameters | 161 | 175 | 196 | 210 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.16 | 0.19, −0.18 | 0.24, −0.24 | 0.20, −0.21 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III, IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIIsup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IVsup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
BK thanks Mangalore University for research facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Crystal data
| C11H8N2O4 | Dx = 1.482 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 232.19 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 2218 reflections |
| a = 13.164 (2) Å | θ = 2.5–26.8° |
| b = 7.4692 (9) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| c = 21.173 (3) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 2081.8 (6) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.16 × 0.14 × 0.11 mm |
| F(000) = 960 |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2218 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 1304 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.063 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.8°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | h = −16→16 |
| Tmin = 0.931, Tmax = 0.987 | k = −9→9 |
| 31526 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.043P)2 + 0.9866P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.03 | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2218 reflections | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| 161 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0015 (3) |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.37444 (14) | 0.5732 (2) | 0.38946 (7) | 0.0382 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.37411 (13) | 0.4662 (2) | 0.44062 (7) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.37378 (16) | 0.5767 (2) | 0.48951 (9) | 0.0318 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.37462 (16) | 0.7576 (2) | 0.46953 (10) | 0.0341 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.37519 (17) | 0.7475 (3) | 0.40517 (10) | 0.0416 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.3760 | 0.8437 | 0.3773 | 0.050* | |
| C11 | 0.37392 (17) | 0.4958 (3) | 0.32759 (9) | 0.0415 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.3296 (2) | 0.5877 (4) | 0.27889 (11) | 0.0572 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.2988 | 0.6978 | 0.2863 | 0.069* | |
| C13 | 0.3311 (2) | 0.5164 (4) | 0.21895 (11) | 0.0691 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.3017 | 0.5787 | 0.1856 | 0.083* | |
| C14 | 0.3756 (2) | 0.3540 (5) | 0.20857 (13) | 0.0718 (9) | |
| H14 | 0.3771 | 0.3063 | 0.1680 | 0.086* | |
| C15 | 0.4181 (2) | 0.2612 (4) | 0.25766 (13) | 0.0665 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.4474 | 0.1499 | 0.2503 | 0.080* | |
| C16 | 0.41776 (19) | 0.3311 (3) | 0.31810 (12) | 0.0548 (7) | |
| H16 | 0.4465 | 0.2682 | 0.3515 | 0.066* | |
| C31 | 0.37166 (17) | 0.4926 (3) | 0.55265 (9) | 0.0377 (5) | |
| O31 | 0.37408 (14) | 0.33081 (19) | 0.55896 (7) | 0.0540 (5) | |
| O32 | 0.36707 (14) | 0.5958 (2) | 0.60230 (7) | 0.0524 (5) | |
| H32 | 0.3671 (19) | 0.724 (4) | 0.5880 (13) | 0.079* | |
| C41 | 0.37522 (17) | 0.9202 (3) | 0.50785 (11) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| O41 | 0.37173 (14) | 0.91999 (19) | 0.56526 (8) | 0.0578 (5) | |
| O42 | 0.37916 (14) | 1.06752 (19) | 0.47441 (8) | 0.0528 (5) | |
| H42 | 0.375 (2) | 1.164 (4) | 0.4979 (13) | 0.079* |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0500 (11) | 0.0337 (9) | 0.0309 (9) | 0.0033 (9) | −0.0029 (8) | −0.0027 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0296 (9) | 0.0301 (9) | 0.0015 (8) | −0.0021 (9) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0375 (11) | 0.0287 (9) | 0.0293 (10) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0010 (9) | −0.0059 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0404 (12) | 0.0279 (10) | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0011 (10) | 0.0015 (11) | −0.0031 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0562 (14) | 0.0302 (11) | 0.0383 (12) | 0.0037 (10) | −0.0012 (12) | 0.0011 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0487 (14) | 0.0483 (12) | 0.0276 (11) | −0.0013 (12) | −0.0019 (10) | −0.0099 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0711 (18) | 0.0649 (16) | 0.0356 (13) | 0.0016 (14) | −0.0049 (12) | −0.0026 (12) |
| C13 | 0.083 (2) | 0.092 (2) | 0.0323 (14) | −0.0064 (18) | −0.0068 (13) | −0.0047 (14) |
| C14 | 0.074 (2) | 0.107 (2) | 0.0348 (14) | −0.0165 (19) | 0.0040 (15) | −0.0250 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0658 (18) | 0.0745 (18) | 0.0591 (18) | 0.0048 (16) | 0.0012 (15) | −0.0330 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0606 (16) | 0.0594 (16) | 0.0445 (14) | 0.0108 (13) | −0.0067 (13) | −0.0193 (12) |
| C31 | 0.0493 (13) | 0.0329 (11) | 0.0309 (11) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0021 (11) | −0.0031 (9) |
| O31 | 0.0923 (13) | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0392 (9) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0035 (9) | 0.0028 (7) |
| O32 | 0.0871 (13) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0296 (8) | −0.0052 (9) | 0.0042 (8) | −0.0071 (7) |
| C41 | 0.0431 (13) | 0.0297 (11) | 0.0507 (14) | −0.0011 (10) | 0.0061 (11) | −0.0054 (10) |
| O41 | 0.0945 (14) | 0.0358 (9) | 0.0432 (10) | −0.0070 (9) | 0.0135 (9) | −0.0126 (7) |
| O42 | 0.0783 (13) | 0.0255 (8) | 0.0547 (11) | 0.0011 (8) | 0.0056 (9) | −0.0049 (7) |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C5 | 1.344 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.365 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.346 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C11 | 1.432 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.369 (4) |
| N2—C3 | 1.324 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.416 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.382 (3) |
| C3—C31 | 1.477 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.365 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C41 | 1.461 (3) | C31—O31 | 1.216 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C31—O32 | 1.305 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.369 (3) | O32—H32 | 1.00 (3) |
| C11—C16 | 1.374 (3) | C41—O41 | 1.216 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.377 (3) | C41—O42 | 1.309 (2) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | O42—H42 | 0.88 (3) |
| C5—N1—N2 | 112.07 (16) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C5—N1—C11 | 128.16 (18) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| N2—N1—C11 | 119.77 (17) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.2 (2) |
| C3—N2—N1 | 105.03 (15) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 111.17 (17) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| N2—C3—C31 | 116.28 (16) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.7 (3) |
| C4—C3—C31 | 132.55 (17) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 104.21 (16) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—C41 | 126.91 (18) | C11—C16—C15 | 118.4 (2) |
| C3—C4—C41 | 128.87 (19) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.8 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 107.50 (18) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.8 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 126.2 | O31—C31—O32 | 119.95 (19) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 126.2 | O31—C31—C3 | 121.43 (18) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 121.2 (2) | O32—C31—C3 | 118.62 (17) |
| C12—C11—N1 | 119.2 (2) | C31—O32—H32 | 108.6 (15) |
| C16—C11—N1 | 119.6 (2) | O41—C41—O42 | 122.89 (19) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.6 (3) | O41—C41—C4 | 123.62 (19) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.2 | O42—C41—C4 | 113.48 (19) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.2 | C41—O42—H42 | 112.5 (18) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 119.9 (3) | ||
| C5—N1—N2—C3 | 0.5 (2) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.6 (4) |
| C11—N1—N2—C3 | −179.43 (19) | N1—C11—C12—C13 | 178.4 (2) |
| N1—N2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.6 (4) |
| N1—N2—C3—C31 | 179.03 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.6 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.9 (4) |
| C31—C3—C4—C5 | −179.2 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.3 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4—C41 | −179.6 (2) | N1—C11—C16—C15 | −178.7 (2) |
| C31—C3—C4—C41 | 1.1 (4) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.1 (4) |
| N2—N1—C5—C4 | −0.4 (3) | N2—C3—C31—O31 | 2.7 (3) |
| C11—N1—C5—C4 | 179.5 (2) | C4—C3—C31—O31 | −178.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 0.2 (3) | N2—C3—C31—O32 | −177.2 (2) |
| C41—C4—C5—N1 | 179.9 (2) | C4—C3—C31—O32 | 2.1 (4) |
| C5—N1—C11—C12 | −29.3 (4) | C5—C4—C41—O41 | 177.8 (2) |
| N2—N1—C11—C12 | 150.6 (2) | C3—C4—C41—O41 | −2.5 (4) |
| C5—N1—C11—C16 | 150.6 (2) | C5—C4—C41—O42 | −1.7 (3) |
| N2—N1—C11—C16 | −29.4 (3) | C3—C4—C41—O42 | 178.0 (2) |
1-Phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (I) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O32—H32···O41 | 1.00 (3) | 1.54 (3) | 2.546 (2) | 178 (2) |
| O42—H42···O31i | 0.88 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.660 (2) | 168 (3) |
| O42—H42···N2i | 0.88 (3) | 2.56 (3) | 3.063 (2) | 117 (2) |
| C14—H14···O31ii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.456 (3) | 177 |
| C12—H12···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.86 | 3.685 (3) | 148 |
| C15—H15···Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.92 | 3.755 (3) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, z; (iv) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Crystal data
| C13H12N2O4 | F(000) = 544 |
| Mr = 260.25 | Dx = 1.372 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.9000 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2704 reflections |
| b = 14.5273 (12) Å | θ = 2.8–26.8° |
| c = 14.8726 (12) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 98.867 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1259.51 (17) Å3 | Block, orange |
| Z = 4 | 0.17 × 0.14 × 0.13 mm |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2704 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 1624 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.046 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.8°, θmin = 2.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | h = −6→7 |
| Tmin = 0.960, Tmax = 0.987 | k = −18→18 |
| 21653 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0511P)2 + 0.3996P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.129 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.04 | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2704 reflections | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 175 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.014 (2) |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.5660 (3) | 0.34915 (11) | 0.69867 (11) | 0.0412 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.4302 (3) | 0.27659 (11) | 0.71300 (11) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.2695 (3) | 0.27445 (13) | 0.64031 (13) | 0.0410 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.3003 (3) | 0.34570 (14) | 0.57864 (13) | 0.0416 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.4919 (3) | 0.39140 (14) | 0.61917 (13) | 0.0438 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.5587 | 0.4424 | 0.5959 | 0.053* | |
| C11 | 0.7563 (3) | 0.37397 (13) | 0.76566 (13) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.9342 (3) | 0.42372 (15) | 0.73977 (15) | 0.0490 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.9325 | 0.4396 | 0.6791 | 0.059* | |
| C13 | 1.1146 (4) | 0.44954 (17) | 0.80489 (17) | 0.0617 (6) | |
| H13 | 1.2344 | 0.4838 | 0.7880 | 0.074* | |
| C14 | 1.1201 (4) | 0.42556 (18) | 0.89396 (18) | 0.0683 (7) | |
| H14 | 1.2442 | 0.4423 | 0.9373 | 0.082* | |
| C15 | 0.9413 (4) | 0.3766 (2) | 0.91897 (17) | 0.0738 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.9443 | 0.3608 | 0.9797 | 0.089* | |
| C16 | 0.7567 (4) | 0.35049 (16) | 0.85540 (15) | 0.0588 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.6353 | 0.3177 | 0.8728 | 0.071* | |
| C31 | 0.0986 (4) | 0.19862 (14) | 0.62958 (15) | 0.0461 (5) | |
| O31 | 0.0528 (3) | 0.15354 (14) | 0.56252 (12) | 0.0900 (7) | |
| O32 | 0.0058 (3) | 0.18661 (10) | 0.70371 (10) | 0.0596 (4) | |
| C32 | −0.1630 (4) | 0.11423 (17) | 0.70126 (19) | 0.0701 (7) | |
| H32A | −0.2925 | 0.1283 | 0.6559 | 0.105* | |
| H32B | −0.2120 | 0.1094 | 0.7597 | 0.105* | |
| H32C | −0.0966 | 0.0569 | 0.6866 | 0.105* | |
| C41 | 0.1559 (3) | 0.37509 (14) | 0.49430 (14) | 0.0453 (5) | |
| O41 | 0.2172 (3) | 0.42800 (13) | 0.44075 (11) | 0.0740 (5) | |
| O42 | −0.0501 (2) | 0.33820 (12) | 0.48518 (10) | 0.0614 (5) | |
| C42 | −0.2056 (4) | 0.3587 (2) | 0.40269 (17) | 0.0704 (7) | |
| H42A | −0.2395 | 0.4233 | 0.4004 | 0.106* | |
| H42B | −0.3449 | 0.3244 | 0.4020 | 0.106* | |
| H42C | −0.1355 | 0.3419 | 0.3509 | 0.106* |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0431 (9) | 0.0388 (9) | 0.0406 (10) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0039 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0470 (9) | 0.0380 (9) | 0.0449 (10) | −0.0039 (7) | 0.0027 (8) | 0.0052 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0437 (11) | 0.0410 (11) | 0.0379 (11) | −0.0009 (9) | 0.0049 (9) | −0.0003 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0430 (11) | 0.0382 (11) | 0.0000 (9) | 0.0055 (9) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0407 (11) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0065 (9) | 0.0057 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0408 (10) | 0.0389 (11) | 0.0425 (12) | 0.0041 (9) | −0.0002 (9) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0407 (11) | 0.0571 (13) | 0.0493 (12) | 0.0034 (10) | 0.0069 (10) | −0.0016 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0429 (12) | 0.0712 (16) | 0.0695 (17) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0043 (12) | −0.0028 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0550 (14) | 0.0788 (18) | 0.0641 (17) | −0.0031 (13) | −0.0130 (12) | −0.0067 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0765 (17) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0477 (15) | −0.0081 (15) | −0.0110 (13) | 0.0077 (13) |
| C16 | 0.0609 (14) | 0.0625 (15) | 0.0500 (14) | −0.0100 (11) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0084 (11) |
| C31 | 0.0522 (12) | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0445 (12) | −0.0027 (9) | 0.0018 (10) | −0.0008 (9) |
| O31 | 0.1229 (16) | 0.0839 (13) | 0.0665 (12) | −0.0478 (12) | 0.0247 (11) | −0.0260 (10) |
| O32 | 0.0649 (10) | 0.0556 (9) | 0.0613 (10) | −0.0205 (8) | 0.0191 (8) | −0.0043 (8) |
| C32 | 0.0586 (14) | 0.0551 (15) | 0.100 (2) | −0.0169 (11) | 0.0222 (14) | 0.0029 (14) |
| C41 | 0.0473 (11) | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0398 (11) | −0.0036 (10) | 0.0057 (9) | 0.0000 (9) |
| O41 | 0.0718 (11) | 0.0869 (13) | 0.0584 (10) | −0.0226 (9) | −0.0054 (8) | 0.0310 (9) |
| O42 | 0.0476 (9) | 0.0812 (11) | 0.0519 (10) | −0.0100 (8) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0123 (8) |
| C42 | 0.0536 (14) | 0.0910 (19) | 0.0593 (16) | 0.0017 (13) | −0.0144 (12) | 0.0035 (13) |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C5 | 1.344 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| N1—N2 | 1.360 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.381 (3) |
| N1—C11 | 1.428 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C3 | 1.324 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.413 (3) | C31—O31 | 1.189 (2) |
| C3—C31 | 1.485 (3) | C31—O32 | 1.316 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.368 (3) | O32—C32 | 1.445 (3) |
| C4—C41 | 1.467 (3) | C32—H32A | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C32—H32B | 0.9600 |
| C11—C16 | 1.377 (3) | C32—H32C | 0.9600 |
| C11—C12 | 1.377 (3) | C41—O41 | 1.202 (2) |
| C12—C13 | 1.376 (3) | C41—O42 | 1.316 (2) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | O42—C42 | 1.445 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.365 (3) | C42—H42A | 0.9600 |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | C42—H42B | 0.9600 |
| C14—C15 | 1.370 (4) | C42—H42C | 0.9600 |
| C5—N1—N2 | 111.86 (15) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C5—N1—C11 | 127.77 (16) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| N2—N1—C11 | 120.34 (15) | C11—C16—C15 | 118.6 (2) |
| C3—N2—N1 | 104.78 (15) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.7 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 111.42 (17) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.7 |
| N2—C3—C31 | 119.60 (17) | O31—C31—O32 | 124.04 (19) |
| C4—C3—C31 | 128.80 (18) | O31—C31—C3 | 124.1 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 104.46 (17) | O32—C31—C3 | 111.82 (17) |
| C5—C4—C41 | 124.54 (18) | C31—O32—C32 | 116.71 (18) |
| C3—C4—C41 | 130.71 (18) | O32—C32—H32A | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 107.48 (17) | O32—C32—H32B | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 126.3 | H32A—C32—H32B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 126.3 | O32—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| C16—C11—C12 | 120.88 (19) | H32A—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| C16—C11—N1 | 119.82 (18) | H32B—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—N1 | 119.27 (18) | O41—C41—O42 | 124.03 (19) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.1 (2) | O41—C41—C4 | 123.92 (19) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.5 | O42—C41—C4 | 112.03 (17) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.5 | C41—O42—C42 | 117.33 (18) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.9 (2) | O42—C42—H42A | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.5 | O42—C42—H42B | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 | H42A—C42—H42B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 119.4 (2) | O42—C42—H42C | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 120.3 | H42A—C42—H42C | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 120.3 | H42B—C42—H42C | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.0 (2) | ||
| C5—N1—N2—C3 | 0.1 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.8 (3) |
| C11—N1—N2—C3 | 178.19 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.3 (4) |
| N1—N2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.6 (4) |
| N1—N2—C3—C31 | 175.56 (16) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.0 (3) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (2) | N1—C11—C16—C15 | −179.0 (2) |
| C31—C3—C4—C5 | −175.11 (19) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.5 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4—C41 | −173.87 (19) | N2—C3—C31—O31 | −130.0 (2) |
| C31—C3—C4—C41 | 11.0 (3) | C4—C3—C31—O31 | 44.8 (3) |
| N2—N1—C5—C4 | −0.1 (2) | N2—C3—C31—O32 | 49.3 (2) |
| C11—N1—C5—C4 | −177.99 (17) | C4—C3—C31—O32 | −135.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 0.0 (2) | O31—C31—O32—C32 | −0.6 (3) |
| C41—C4—C5—N1 | 174.43 (18) | C3—C31—O32—C32 | −179.80 (17) |
| C5—N1—C11—C16 | 153.3 (2) | C5—C4—C41—O41 | 18.7 (3) |
| N2—N1—C11—C16 | −24.4 (3) | C3—C4—C41—O41 | −168.5 (2) |
| C5—N1—C11—C12 | −24.7 (3) | C5—C4—C41—O42 | −160.01 (19) |
| N2—N1—C11—C12 | 157.57 (17) | C3—C4—C41—O42 | 12.8 (3) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.3 (3) | O41—C41—O42—C42 | 4.0 (3) |
| N1—C11—C12—C13 | 178.35 (18) | C4—C41—O42—C42 | −177.34 (18) |
Dimethyl 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (II) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5···O41i | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.331 (3) | 170 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Crystal data
| C14H14N2O4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 274.27 | F(000) = 288 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.329 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.6546 (5) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.0959 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 2526 reflections |
| c = 11.3065 (6) Å | θ = 2.6–25.5° |
| α = 78.988 (3)° | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 85.527 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| γ = 87.548 (4)° | Block, brown |
| V = 685.40 (7) Å3 | 0.16 × 0.15 × 0.12 mm |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2526 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 1777 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.955, Tmax = 0.988 | k = −9→9 |
| 12818 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0529P)2 + 0.2439P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.128 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 2526 reflections | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
| 196 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 7 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.024 (4) |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| N1 | 0.3938 (2) | 0.7228 (2) | 0.38159 (13) | 0.0446 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.4458 (2) | 0.7773 (2) | 0.26297 (14) | 0.0477 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.3163 (2) | 0.7413 (3) | 0.20267 (16) | 0.0426 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.1791 (2) | 0.6623 (2) | 0.28127 (16) | 0.0428 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.2362 (3) | 0.6525 (3) | 0.39480 (17) | 0.0464 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.1765 | 0.6057 | 0.4675 | 0.056* | |
| C11 | 0.5036 (3) | 0.7482 (3) | 0.47287 (17) | 0.0446 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.4529 (3) | 0.6979 (3) | 0.59269 (19) | 0.0634 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.3468 | 0.6450 | 0.6157 | 0.076* | |
| C13 | 0.5596 (3) | 0.7261 (3) | 0.6790 (2) | 0.0663 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.5240 | 0.6911 | 0.7602 | 0.080* | |
| C14 | 0.7168 (3) | 0.8041 (3) | 0.6491 (2) | 0.0567 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.7647 (3) | 0.8500 (4) | 0.5289 (2) | 0.0758 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.8717 | 0.9011 | 0.5059 | 0.091* | |
| C16 | 0.6612 (3) | 0.8238 (3) | 0.4403 (2) | 0.0686 (7) | |
| H16 | 0.6979 | 0.8572 | 0.3592 | 0.082* | |
| C141 | 0.8328 (4) | 0.8354 (3) | 0.7436 (2) | 0.0797 (8) | |
| H14A | 0.7677 | 0.8190 | 0.8208 | 0.119* | |
| H14B | 0.8726 | 0.9489 | 0.7233 | 0.119* | |
| H14C | 0.9319 | 0.7584 | 0.7470 | 0.119* | |
| C31A | 0.3342 (3) | 0.7907 (3) | 0.06874 (18) | 0.0505 (5) | 0.71 (2) |
| O31A | 0.4587 (11) | 0.7554 (17) | 0.0048 (5) | 0.093 (3) | 0.71 (2) |
| O32A | 0.2044 (10) | 0.8936 (9) | 0.0288 (6) | 0.0542 (14) | 0.71 (2) |
| C32A | 0.2113 (19) | 0.9575 (17) | −0.0998 (7) | 0.0653 (16) | 0.71 (2) |
| H32A | 0.2195 | 0.8650 | −0.1421 | 0.098* | 0.71 (2) |
| H32B | 0.3121 | 1.0261 | −0.1233 | 0.098* | 0.71 (2) |
| H32C | 0.1070 | 1.0239 | −0.1196 | 0.098* | 0.71 (2) |
| C31B | 0.3342 (3) | 0.7907 (3) | 0.06874 (18) | 0.0505 (5) | 0.29 (2) |
| O31B | 0.413 (2) | 0.6979 (19) | 0.0113 (14) | 0.093 (3) | 0.29 (2) |
| O32B | 0.233 (2) | 0.9199 (19) | 0.0250 (15) | 0.0542 (14) | 0.29 (2) |
| C32B | 0.234 (5) | 0.966 (4) | −0.1050 (17) | 0.0653 (16) | 0.29 (2) |
| H32D | 0.1476 | 0.9035 | −0.1334 | 0.098* | 0.29 (2) |
| H32E | 0.3479 | 0.9404 | −0.1404 | 0.098* | 0.29 (2) |
| H32F | 0.2080 | 1.0842 | −0.1275 | 0.098* | 0.29 (2) |
| C41 | 0.0150 (3) | 0.5929 (3) | 0.25809 (17) | 0.0456 (5) | |
| O41 | −0.0860 (2) | 0.5221 (2) | 0.33564 (14) | 0.0756 (6) | |
| O42 | −0.01086 (18) | 0.61505 (19) | 0.14123 (12) | 0.0550 (4) | |
| C42 | −0.1738 (3) | 0.5551 (3) | 0.1112 (2) | 0.0679 (7) | |
| H42A | −0.2701 | 0.6035 | 0.1538 | 0.102* | |
| H42B | −0.1748 | 0.4346 | 0.1339 | 0.102* | |
| H42C | −0.1847 | 0.5873 | 0.0258 | 0.102* |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0561 (11) | 0.0331 (8) | −0.0093 (8) | −0.0050 (7) | −0.0041 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0458 (10) | 0.0613 (11) | 0.0345 (9) | −0.0105 (8) | −0.0028 (7) | −0.0030 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0397 (11) | 0.0511 (12) | 0.0369 (10) | −0.0032 (9) | −0.0047 (8) | −0.0067 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0407 (10) | 0.0505 (12) | 0.0372 (10) | −0.0050 (9) | −0.0045 (8) | −0.0063 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0436 (11) | 0.0567 (13) | 0.0373 (10) | −0.0110 (10) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0036 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0449 (11) | 0.0505 (12) | 0.0390 (11) | −0.0044 (9) | −0.0084 (8) | −0.0073 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0539 (13) | 0.0937 (19) | 0.0424 (12) | −0.0174 (12) | −0.0051 (10) | −0.0085 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0673 (16) | 0.0924 (19) | 0.0403 (12) | −0.0055 (14) | −0.0108 (11) | −0.0117 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0644 (15) | 0.0543 (13) | 0.0555 (14) | 0.0014 (11) | −0.0219 (11) | −0.0142 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0671 (16) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0649 (16) | −0.0367 (14) | −0.0163 (12) | −0.0063 (14) |
| C16 | 0.0661 (15) | 0.0951 (19) | 0.0441 (12) | −0.0334 (14) | −0.0082 (11) | −0.0035 (12) |
| C141 | 0.092 (2) | 0.0787 (19) | 0.0782 (18) | 0.0009 (15) | −0.0441 (15) | −0.0260 (14) |
| C31A | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0727 (15) | 0.0380 (11) | −0.0064 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0093 (10) |
| O31A | 0.070 (3) | 0.159 (6) | 0.0434 (12) | 0.035 (4) | 0.0031 (17) | −0.010 (2) |
| O32A | 0.054 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0395 (9) | −0.008 (2) | 0.0009 (13) | 0.0060 (12) |
| C32A | 0.075 (4) | 0.0739 (19) | 0.0406 (14) | −0.017 (3) | −0.0089 (17) | 0.0103 (13) |
| C31B | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0727 (15) | 0.0380 (11) | −0.0064 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0093 (10) |
| O31B | 0.070 (3) | 0.159 (6) | 0.0434 (12) | 0.035 (4) | 0.0031 (17) | −0.010 (2) |
| O32B | 0.054 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0395 (9) | −0.008 (2) | 0.0009 (13) | 0.0060 (12) |
| C32B | 0.075 (4) | 0.0739 (19) | 0.0406 (14) | −0.017 (3) | −0.0089 (17) | 0.0103 (13) |
| C41 | 0.0421 (11) | 0.0557 (13) | 0.0387 (11) | −0.0047 (10) | −0.0025 (9) | −0.0077 (9) |
| O41 | 0.0581 (10) | 0.1211 (15) | 0.0449 (9) | −0.0394 (10) | 0.0017 (7) | −0.0031 (9) |
| O42 | 0.0519 (9) | 0.0729 (10) | 0.0403 (8) | −0.0177 (7) | −0.0088 (6) | −0.0048 (7) |
| C42 | 0.0550 (14) | 0.0942 (19) | 0.0590 (14) | −0.0187 (13) | −0.0173 (11) | −0.0169 (13) |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C5 | 1.341 (2) | C141—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N1—N2 | 1.363 (2) | C141—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C11 | 1.430 (2) | C141—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C3 | 1.319 (2) | C31A—O31A | 1.209 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.413 (3) | C31A—O32A | 1.319 (3) |
| C3—C31A | 1.487 (3) | O32A—C32A | 1.446 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (3) | C32A—H32A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C41 | 1.459 (3) | C32A—H32B | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C32A—H32C | 0.9600 |
| C11—C12 | 1.368 (3) | O32B—C32B | 1.445 (5) |
| C11—C16 | 1.369 (3) | C32B—H32D | 0.9600 |
| C12—C13 | 1.378 (3) | C32B—H32E | 0.9600 |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | C32B—H32F | 0.9600 |
| C13—C14 | 1.372 (3) | C41—O41 | 1.198 (2) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | C41—O42 | 1.328 (2) |
| C14—C15 | 1.363 (3) | O42—C42 | 1.445 (2) |
| C14—C141 | 1.505 (3) | C42—H42A | 0.9600 |
| C15—C16 | 1.377 (3) | C42—H42B | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9300 | C42—H42C | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16 | 0.9300 | ||
| C5—N1—N2 | 111.67 (15) | C14—C141—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—C11 | 128.79 (16) | H14A—C141—H14B | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—C11 | 119.52 (15) | C14—C141—H14C | 109.5 |
| C3—N2—N1 | 105.05 (15) | H14A—C141—H14C | 109.5 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 111.50 (16) | H14B—C141—H14C | 109.5 |
| N2—C3—C31A | 117.41 (17) | O31A—C31A—O32A | 123.5 (3) |
| C4—C3—C31A | 131.07 (17) | O31A—C31A—C3 | 125.0 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 104.27 (16) | O32A—C31A—C3 | 111.1 (3) |
| C5—C4—C41 | 123.78 (17) | C31A—O32A—C32A | 116.5 (3) |
| C3—C4—C41 | 131.86 (17) | O32A—C32A—H32A | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 107.50 (17) | O32A—C32A—H32B | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 126.2 | H32A—C32A—H32B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 126.2 | O32A—C32A—H32C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 119.48 (19) | H32A—C32A—H32C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—N1 | 120.75 (18) | H32B—C32A—H32C | 109.5 |
| C16—C11—N1 | 119.77 (18) | O32B—C32B—H32D | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.7 (2) | O32B—C32B—H32E | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.1 | H32D—C32B—H32E | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.1 | O32B—C32B—H32F | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 122.1 (2) | H32D—C32B—H32F | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.0 | H32E—C32B—H32F | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.0 | O41—C41—O42 | 123.08 (18) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 116.7 (2) | O41—C41—C4 | 123.97 (18) |
| C15—C14—C141 | 121.4 (2) | O42—C41—C4 | 112.95 (17) |
| C13—C14—C141 | 121.9 (2) | C41—O42—C42 | 116.23 (16) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 122.7 (2) | O42—C42—H42A | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 118.6 | O42—C42—H42B | 109.5 |
| C16—C15—H15 | 118.6 | H42A—C42—H42B | 109.5 |
| C11—C16—C15 | 119.3 (2) | O42—C42—H42C | 109.5 |
| C11—C16—H16 | 120.4 | H42A—C42—H42C | 109.5 |
| C15—C16—H16 | 120.4 | H42B—C42—H42C | 109.5 |
| C14—C141—H14A | 109.5 | ||
| C5—N1—N2—C3 | 0.7 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.3 (4) |
| C11—N1—N2—C3 | −177.91 (17) | C12—C13—C14—C141 | 179.7 (2) |
| N1—N2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 1.3 (4) |
| N1—N2—C3—C31A | 178.57 (18) | C141—C14—C15—C16 | −179.7 (3) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.3 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.9 (4) |
| C31A—C3—C4—C5 | −178.9 (2) | N1—C11—C16—C15 | 179.1 (2) |
| N2—C3—C4—C41 | −176.7 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.2 (4) |
| C31A—C3—C4—C41 | 4.7 (4) | N2—C3—C31A—O31A | 52.4 (9) |
| N2—N1—C5—C4 | −0.9 (2) | C4—C3—C31A—O31A | −129.1 (9) |
| C11—N1—C5—C4 | 177.57 (18) | N2—C3—C31A—O32A | −121.0 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 0.7 (2) | C4—C3—C31A—O32A | 57.5 (6) |
| C41—C4—C5—N1 | 177.50 (18) | O31A—C31A—O32A—C32A | 3.6 (10) |
| C5—N1—C11—C12 | 0.3 (3) | C3—C31A—O32A—C32A | 177.1 (8) |
| N2—N1—C11—C12 | 178.6 (2) | C5—C4—C41—O41 | 0.6 (3) |
| C5—N1—C11—C16 | −179.7 (2) | C3—C4—C41—O41 | 176.5 (2) |
| N2—N1—C11—C16 | −1.4 (3) | C5—C4—C41—O42 | −178.86 (19) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.9 (4) | C3—C4—C41—O42 | −3.0 (3) |
| N1—C11—C12—C13 | −179.0 (2) | O41—C41—O42—C42 | 2.7 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.2 (4) | C4—C41—O42—C42 | −177.82 (18) |
Dimethyl 1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarboxylate (III) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5···O41i | 0.93 | 2.33 | 3.249 (3) | 168 |
| C12—H12···O41i | 0.93 | 2.43 | 3.352 (3) | 173 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Crystal data
| C12H14N6O3 | F(000) = 608 |
| Mr = 290.29 | Dx = 1.492 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.6030 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 2521 reflections |
| b = 22.6605 (19) Å | θ = 2.9–26.1° |
| c = 7.6751 (7) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 102.284 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1292.05 (19) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.14 × 0.13 × 0.11 mm |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2521 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 1722 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.053 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.1°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.929, Tmax = 0.988 | k = −27→27 |
| 20456 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.027P)2 + 1.1086P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 2521 reflections | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 210 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0045 (9) |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.7660 (2) | 0.36969 (8) | 0.6437 (2) | 0.0283 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.7948 (2) | 0.32224 (8) | 0.5473 (2) | 0.0314 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.7018 (3) | 0.33229 (9) | 0.3822 (3) | 0.0275 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.6115 (3) | 0.38765 (9) | 0.3717 (3) | 0.0280 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.6564 (3) | 0.40941 (10) | 0.5433 (3) | 0.0298 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.6181 | 0.4450 | 0.5828 | 0.036* | |
| C11 | 0.8572 (3) | 0.37355 (9) | 0.8268 (3) | 0.0276 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.8449 (3) | 0.42341 (10) | 0.9244 (3) | 0.0344 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.7747 | 0.4550 | 0.8727 | 0.041* | |
| C13 | 0.9380 (3) | 0.42666 (11) | 1.1013 (3) | 0.0365 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.9289 | 0.4603 | 1.1681 | 0.044* | |
| C14 | 1.0436 (3) | 0.38002 (10) | 1.1778 (3) | 0.0317 (5) | |
| C15 | 1.0555 (3) | 0.33004 (10) | 1.0777 (3) | 0.0368 (6) | |
| H15 | 1.1270 | 0.2986 | 1.1285 | 0.044* | |
| C16 | 0.9622 (3) | 0.32644 (10) | 0.9034 (3) | 0.0352 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.9696 | 0.2925 | 0.8372 | 0.042* | |
| O14 | 1.1404 (2) | 0.37883 (8) | 1.3504 (2) | 0.0444 (5) | |
| C141 | 1.1307 (4) | 0.42931 (12) | 1.4580 (3) | 0.0493 (7) | |
| H14A | 1.1762 | 0.4631 | 1.4063 | 0.074* | |
| H14B | 1.2016 | 0.4227 | 1.5757 | 0.074* | |
| H14C | 1.0077 | 0.4362 | 1.4647 | 0.074* | |
| C31 | 0.7103 (3) | 0.28637 (9) | 0.2463 (3) | 0.0295 (5) | |
| O31 | 0.6069 (2) | 0.28624 (7) | 0.0961 (2) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| N31 | 0.8329 (3) | 0.24513 (8) | 0.2954 (3) | 0.0356 (5) | |
| H31 | 0.911 (3) | 0.2477 (11) | 0.397 (3) | 0.043* | |
| N32 | 0.8637 (3) | 0.19995 (10) | 0.1787 (3) | 0.0520 (6) | |
| H32A | 0.782 (4) | 0.2047 (12) | 0.064 (4) | 0.062* | |
| H32B | 0.841 (4) | 0.1612 (13) | 0.232 (4) | 0.062* | |
| C41 | 0.5024 (3) | 0.42229 (10) | 0.2236 (3) | 0.0301 (5) | |
| O41 | 0.4610 (2) | 0.47395 (7) | 0.2471 (2) | 0.0456 (5) | |
| N41 | 0.4562 (3) | 0.39535 (9) | 0.0672 (2) | 0.0358 (5) | |
| H41 | 0.500 (3) | 0.3563 (12) | 0.058 (3) | 0.043* | |
| N42 | 0.3537 (3) | 0.42254 (10) | −0.0869 (3) | 0.0435 (6) | |
| H42A | 0.412 (4) | 0.4577 (13) | −0.110 (3) | 0.052* | |
| H42B | 0.262 (4) | 0.4361 (13) | −0.060 (4) | 0.052* |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0298 (10) | 0.0300 (10) | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0031 (8) | −0.0014 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0310 (10) | 0.0265 (11) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0006 (9) | −0.0032 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0260 (12) | 0.0287 (11) | 0.0264 (12) | −0.0016 (9) | 0.0022 (10) | 0.0004 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0274 (12) | 0.0288 (11) | 0.0266 (12) | −0.0023 (9) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0022 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0289 (12) | 0.0277 (11) | 0.0317 (13) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0040 (10) | 0.0021 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0265 (12) | 0.0319 (12) | 0.0238 (12) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0040 (10) | 0.0010 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0356 (14) | 0.0342 (13) | 0.0306 (13) | 0.0061 (11) | 0.0006 (11) | 0.0018 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0401 (14) | 0.0369 (13) | 0.0316 (14) | 0.0014 (11) | 0.0055 (11) | −0.0053 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0286 (13) | 0.0412 (13) | 0.0235 (12) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0010 (10) | 0.0028 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0371 (14) | 0.0356 (13) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0078 (11) | −0.0011 (11) | 0.0040 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0387 (14) | 0.0325 (12) | 0.0325 (13) | 0.0055 (11) | 0.0035 (11) | −0.0036 (10) |
| O14 | 0.0503 (11) | 0.0495 (11) | 0.0273 (9) | 0.0030 (9) | −0.0051 (8) | −0.0007 (8) |
| C141 | 0.0546 (18) | 0.0587 (18) | 0.0313 (14) | −0.0021 (14) | 0.0016 (13) | −0.0058 (13) |
| C31 | 0.0289 (13) | 0.0281 (12) | 0.0296 (13) | −0.0025 (10) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0001 (10) |
| O31 | 0.0433 (10) | 0.0387 (10) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0029 (8) | −0.0103 (8) | −0.0066 (7) |
| N31 | 0.0417 (12) | 0.0299 (10) | 0.0309 (11) | 0.0056 (9) | −0.0018 (9) | −0.0036 (9) |
| N32 | 0.0701 (17) | 0.0366 (13) | 0.0440 (14) | 0.0127 (12) | 0.0003 (12) | −0.0093 (11) |
| C41 | 0.0297 (12) | 0.0311 (12) | 0.0288 (13) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0050 (10) | 0.0024 (10) |
| O41 | 0.0640 (12) | 0.0331 (9) | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0141 (8) | 0.0030 (9) | 0.0014 (8) |
| N41 | 0.0391 (12) | 0.0367 (11) | 0.0274 (11) | 0.0063 (9) | −0.0022 (9) | 0.0022 (9) |
| N42 | 0.0436 (14) | 0.0509 (14) | 0.0314 (12) | 0.0039 (11) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0086 (10) |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—N2 | 1.349 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.351 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C11 | 1.431 (3) | O14—C141 | 1.422 (3) |
| N2—C3 | 1.333 (3) | C141—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.424 (3) | C141—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C31 | 1.485 (3) | C141—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) | C31—O31 | 1.249 (3) |
| C4—C41 | 1.482 (3) | C31—N31 | 1.317 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | N31—N32 | 1.412 (3) |
| C11—C12 | 1.369 (3) | N31—H31 | 0.87 (3) |
| C11—C16 | 1.387 (3) | N32—H32A | 0.97 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.394 (3) | N32—H32B | 1.00 (3) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | C41—O41 | 1.236 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.381 (3) | C41—N41 | 1.325 (3) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | N41—N42 | 1.412 (3) |
| C14—O14 | 1.371 (3) | N41—H41 | 0.95 (3) |
| C14—C15 | 1.382 (3) | N42—H42A | 0.95 (3) |
| C15—C16 | 1.377 (3) | N42—H42B | 0.83 (3) |
| N2—N1—C5 | 111.78 (17) | C15—C16—C11 | 119.8 (2) |
| N2—N1—C11 | 119.05 (17) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C5—N1—C11 | 129.07 (18) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C3—N2—N1 | 105.65 (17) | C14—O14—C141 | 117.50 (19) |
| N2—C3—C4 | 110.88 (19) | O14—C141—H14A | 109.5 |
| N2—C3—C31 | 117.06 (19) | O14—C141—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C31 | 132.06 (19) | H14A—C141—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 104.01 (18) | O14—C141—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C41 | 121.8 (2) | H14A—C141—H14C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C41 | 134.0 (2) | H14B—C141—H14C | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 107.67 (19) | O31—C31—N31 | 122.0 (2) |
| N1—C5—H5 | 126.2 | O31—C31—C3 | 122.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 126.2 | N31—C31—C3 | 115.47 (19) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 120.2 (2) | C31—N31—N32 | 122.4 (2) |
| C12—C11—N1 | 120.81 (19) | C31—N31—H31 | 120.9 (17) |
| C16—C11—N1 | 118.97 (19) | N32—N31—H31 | 116.0 (17) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.8 (2) | N31—N32—H32A | 109.5 (17) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.1 | N31—N32—H32B | 108.1 (16) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.1 | H32A—N32—H32B | 110 (2) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.2 (2) | O41—C41—N41 | 122.8 (2) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 | O41—C41—C4 | 120.6 (2) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 | N41—C41—C4 | 116.59 (19) |
| O14—C14—C13 | 124.7 (2) | C41—N41—N42 | 123.4 (2) |
| O14—C14—C15 | 115.8 (2) | C41—N41—H41 | 118.0 (15) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 119.5 (2) | N42—N41—H41 | 118.6 (15) |
| C16—C15—C14 | 120.5 (2) | N41—N42—H42A | 109.1 (16) |
| C16—C15—H15 | 119.7 | N41—N42—H42B | 107 (2) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 119.7 | H42A—N42—H42B | 101 (3) |
| C5—N1—N2—C3 | 0.2 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.3 (3) |
| C11—N1—N2—C3 | −176.56 (18) | O14—C14—C15—C16 | 179.4 (2) |
| N1—N2—C3—C4 | 0.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.4 (4) |
| N1—N2—C3—C31 | 179.81 (18) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.8 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.5 (3) |
| C31—C3—C4—C5 | 179.9 (2) | N1—C11—C16—C15 | 178.0 (2) |
| N2—C3—C4—C41 | 175.1 (2) | C13—C14—O14—C141 | 0.1 (3) |
| C31—C3—C4—C41 | −4.4 (4) | C15—C14—O14—C141 | −179.6 (2) |
| N2—N1—C5—C4 | −0.6 (2) | N2—C3—C31—O31 | 168.0 (2) |
| C11—N1—C5—C4 | 175.8 (2) | C4—C3—C31—O31 | −12.5 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 0.7 (2) | N2—C3—C31—N31 | −11.1 (3) |
| C41—C4—C5—N1 | −175.66 (19) | C4—C3—C31—N31 | 168.4 (2) |
| N2—N1—C11—C12 | 173.8 (2) | O31—C31—N31—N32 | 3.9 (4) |
| C5—N1—C11—C12 | −2.3 (3) | C3—C31—N31—N32 | −177.0 (2) |
| N2—N1—C11—C16 | −4.7 (3) | C5—C4—C41—O41 | 6.1 (3) |
| C5—N1—C11—C16 | 179.2 (2) | C3—C4—C41—O41 | −169.0 (2) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.2 (3) | C5—C4—C41—N41 | −175.2 (2) |
| N1—C11—C12—C13 | −178.6 (2) | C3—C4—C41—N41 | 9.8 (4) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.6 (4) | O41—C41—N41—N42 | −0.8 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—O14 | 180.0 (2) | C4—C41—N41—N42 | −179.5 (2) |
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3,4-dicarbohydrazide (IV) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N31—H31···O31i | 0.88 (2) | 2.04 (2) | 2.851 (3) | 153 (2) |
| N32—H32A···O14ii | 0.97 (3) | 2.58 (3) | 3.256 (3) | 127 (2) |
| N32—H32B···N42i | 1.00 (2) | 2.34 (3) | 3.317 (3) | 165 (2) |
| N41—H41···O31 | 0.95 (3) | 1.78 (3) | 2.714 (3) | 166 (2) |
| N42—H42A···O41iii | 0.95 (3) | 2.21 (3) | 3.120 (3) | 162 (2) |
| N42—H42B···Cg1iv | 0.83 (3) | 2.85 (3) | 3.442 (3) | 130 (2) |
| C5—H5···O41v | 0.93 | 2.40 | 3.314 (3) | 166 |
| C12—H12···O41v | 0.93 | 2.44 | 3.354 (3) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−3/2; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (iv) x−1, y, z−1; (v) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by University Grants Commission grants UGC-MANF-SRF Fellowship and UGC-BSR Faculty Fellowship.
References
- Alizadeh, A., Firuzyar, T. & Zhu, L.-G. (2010). Tetrahedron, 66, 9835–9839.
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–S19.
- Asma, Kalluraya, B., Manju, N., Adhikari, A. V., Chandra & Mahendra, M. (2018). Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem. 28, 335–345.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and XPREP. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Devi, N., Shankar, R. & Singh, V. (2018). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 373–390.
- Etter, M. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, G., Glidewell, C., Gregson, R. M. & Meehan, P. R. (1998a). Acta Cryst. B54, 129–138.
- Ferguson, G., Glidewell, C., Gregson, R. M. & Meehan, P. R. (1998b). Acta Cryst. B54, 139–150.
- Fun, H.-K., Goh, J. H., Nithinchandra & Kalluraya, B. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o3252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Quah, C. K., Chandrakantha, B., Isloor, A. M. & Shetty, P. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Girisha, K. S., Kalluraya, B., Narayana, V. & Padmashree (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 4640–4644. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Greco, C. V., Nyberg, W. H. & Cheng, C. C. (1962). J. Med. Chem. 5, 861–865. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gregson, R. M., Glidewell, C., Ferguson, G. & Lough, A. J. (2000). Acta Cryst. B56, 39–57. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hope, H. (1978). Acta Cryst. A34, S20.
- Huisgen, R., Grashey, R., Gotthardt, H. & Schmidt, R. (1962). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1, 48–49.
- Li, D. Y., Mao, Y. F., Chen, H. J., Chen, G. B. & Liu, P. N. (2014). Org. Lett. 16, 3476–3479. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Owen, J. E., Swanson, E. E. & Meyers, D. B. (1958). J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. (Sci. ed.), 47, 70–72. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-J., Lee, K., Park, S.-J., Ahn, B., Lee, J.-C., Cho, H. Y. & Lee, K.-I. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15, 3307–3312. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.-R. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Satheesha, R. N. & Kalluraya, B. (2007). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 46, 375–378.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008a). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008b). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z., Ding, X.-L., Dong, W.-L. & Zhao, B.-X. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3473.
- Thamotharan, S., Parthasarathi, V., Sanyal, R., Badami Bharati, V. & Linden, A. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o44–o45.
- Wang, Y., Lee, P. L. & Yeh, M.-H. (1984). Acta Cryst. C40, 1226–1228.
- Xiao, J. & Zhao, H. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yang, R., Xu, T., Fan, J., Zhang, Q., Ding, M., Huang, M., Deng, L., Lu, Y. & Guo, Y. (2018). Ind. Crops Prod. 117, 50–57.
- Yao, J.-Y., Xiao, J. & Zhao, H. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y., Liu, W., Tang, W. & Lai, Y.-B. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3764.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III, IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IIIsup8.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018015864/zl2741IVsup9.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report













