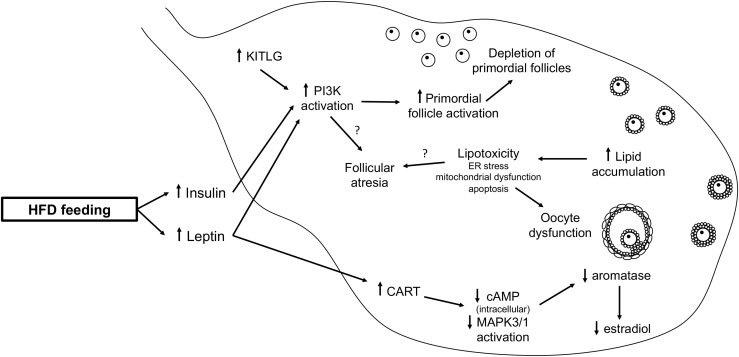
Figure 2.
HFD-induced ovarian dysfunction. In the ovary, elevated leptin signaling increases CART, which decreases intracellular cAMP levels and MAPK3/1 activation, leading to decreased aromatase and estradiol production. Elevated levels of leptin, insulin, and KITLG increase PI3K activation, which leads to increased primordial follicle activation, resulting in the depletion of the ovarian reserve. Increased lipid accumulation in the ovary leads to lipotoxicity. Both increased PI3K signaling and lipotoxicity may contribute to increased follicle atresia. These alterations in ovarian function contribute to the reproductive dysfunction. cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CART, cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript; MAPK3/1, mitogen-activated protein kinase 3/1.