Abstract
Background
Weaning post-cardiac surgery patients from mechanical ventilation (MV) poses a big challenge to these patients. Optimized left ventricular-arterial coupling (VAC) may be crucial for reducing the MV duration of these patients. However, there is no research exploring the relationship between VAC and the duration of MV. We performed this study to investigate the relationship between left ventricular-arterial coupling (VAC) and prolonged mechanical ventilation (MV) in severe post-cardiac surgery patients.
Methods
This was a single-center retrospective study of 56 severe post-cardiac surgery patients from January 2015 to December 2017 at the Department of Critical Care Medicine of Peking Union Medical College Hospital. Patients were divided into two groups according to the duration of MV (PMV group: prolonged mechanical ventilation group, MV > 6 days; Non-PMV group: non-prolonged mechanical ventilation group, MV ≤ 6 days). Hemodynamics and tissue perfusion data were collected or calculated at admission (T0) and 48 h after admission (T1) to the ICU.
Results
In terms of hemodynamic and tissue perfusion data, there were no differences between the two groups at admission (T0). Compared with the non-prolonged MV group after 48 h in the ICU (T1), the prolonged MV group had significantly higher values for heart rate (108 ± 13 vs 97 ± 12, P = 0.018), lactate (2.42 ± 1.24 vs.1.46 ± 0.58, P < 0.001), and Ea/Ees (5.93 ± 1.81 vs. 4.05 ± 1.20, P < 0.001). Increased Ea/Ees (odds ratio, 7.305; 95% CI, 1.181–45.168; P = 0.032) and lactate at T1 (odds ratio, 17.796; 95% CI, 1.377–229.988; P = 0.027) were independently associated with prolonged MV. There was a significant relationship between Ea/EesT1 and the duration of MV (r = 0.512, P < 0.01). The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUC) of the left VAC for predicting prolonged MV was 0.801, and the cutoff value for Ea/Ees was 5.12, with 65.0% sensitivity and 90.0% specificity.
Conclusions
Left ventricular-arterial coupling was associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation in severe post-cardiac surgery patients. The assessment and optimization of left VAC might be helpful in reducing duration of MV in these patients.
Keywords: Ventricular-arterial coupling, Severe cardiogenic shock, Post-cardiac surgery, Prolonged mechanical ventilation, Cardiac work efficiency cardiac reserve
Background
Prolonged mechanical ventilation (PMV) is required by 2.4–9.9% of post-cardiac surgery patients and is associated with increased medical resource use and mortality [1–4]. Cardiac function has been identified as an important factor during weaning from mechanical ventilation (MV). MV has several advantages effects on hemodynamics in post-cardiac surgery patients with poor cardiac function, including reducing venous return with low cardiac preload and decreasing the afterload of the left ventricle (LV) [5]. In contrast, weaning from MV with increased left ventricular preload and afterload may pose a considerable challenge for these patients [5, 6].
Several investigators have found that low cardiac output (CO) was associated with PMV in post-cardiac surgery patients [7, 8]. However, in some research, patients with normal CO value might also be difficult to wean [9]. Some more superior indicators need to be explored to assess the possibility of PMV.
The LV pumps blood to the arterial vessel, which is the output of energy [10]. Importantly, weaning from a mechanical ventilator challenges the heart, and the heart should generate more stroke work (SW) in response to the challenge. Cardiac work efficiency is the ratio of SW to total mechanical energy [11]. The higher efficiency is, the more SW a heart can produce with a given total energy. Therefore, cardiac work efficiency might play an important role in the weaning process.
As we all know, left ventricular-arterial coupling (VAC) was used to assess cardiac work efficiency [12]. There are two parameters in VAC: Ea and Ees. Ea is the arterial end-systolic elastance, the slope of blue dotted line, which reflects afterload, and Ees is the left ventricular end-systolic elastance, the slope of black dotted line, which represents contractility (Fig. 1). VAC, the ratio of Ea to Ees, can appropriately reflect the proportion between area A and area B (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
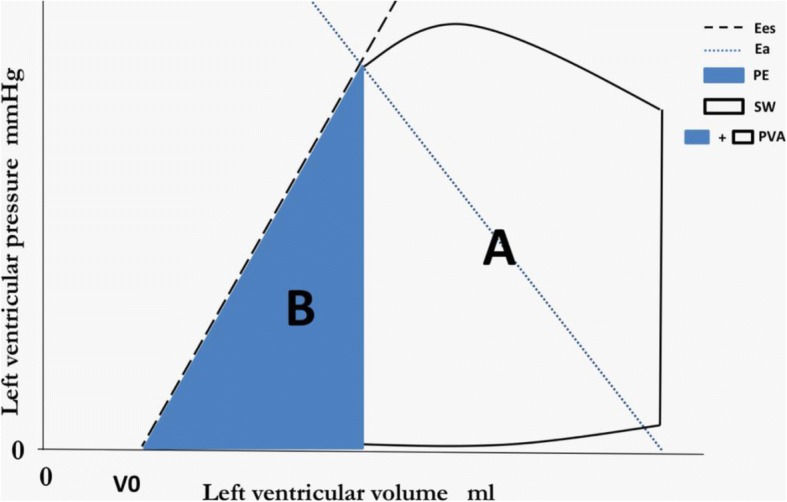
Analysis of ventricular-arterial coupling in the pressure-volume plane. A pressure-volume loop is shown along with the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (black dashed line). The unfilled “A” area represents stroke work; the blue “B” area represents potential energy. EES is the slope of the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship. EA (blue dashed line) is plotted on top of the pressure-volume loop. V0 is the volume-axis intercept of the end-systolic pressure- volume relationship, representing the LV volume at zero intracavitary pressure. The pressure-volume area (PVA) is the sum of potential energy and stroke (i.e., external) work. The PVA represents the total mechanical energy generated by LV contraction until the end of systole
For a given beat, the pressure–volume area (PVA, SW plus potential energy, Fig. 1) stands for the total mechanical energy and correlates strongly with myocardial oxygen consumption (MVO2) [13, 14]. The ratio of SW to PVA, which can be estimated by proportion of area B to area A, is representative of cardiac work efficiency. As we have discussed above, VAC can reflect the proportion of area A to area B, so it is understandable that VAC can be a surrogate for cardiac work efficiency [12, 15]. A heart with a high Ea/Ees usually presents an increased proportion of the PVA corresponding to potential energy rather than stroke work, denoting an unfavorable energy efficiency state [11]. In contrast, a more efficient heart with a lower Ea/Ees can consume less energy to attain suitable SW and thus has a greater SW reserve. Thus, VAC can reflect efficiency as well as SW reserve. When the VAC is appropriate, the heart have more power potential to face the challenge of weaning. Here, we hypothesized that left VAC is associated with the duration of MV.
To the best of our knowledge, the predictive value of VAC for PMV has not been investigated in severe post-cardiac surgery patients. Therefore, we performed this study to investigate whether left VAC can predict PMV in this patient population.
Methods
Patients
We performed a retrospective single-center study of severe cardiac patients who were admitted to the ICU after cardiac surgery with continuous PiCCO monitors (Pulsio Cath PV 2015 L20: Pulsion Medical Systems: Munich, Germany) for unstable hemodynamics from January 2015 to December 2017 at the Department of Critical Care Medicine of Peking Union Medical College Hospital. These patients had a preoperative class III or IV New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification. The exclusion criteria include 1. Discharged within 48 h; 2. Discharged against medical advice or died in the first 6 days; 3. Acquired pneumonia or serious cerebrovascular accidents in the first 6 days of ICU admission.
Data collection
A standardized weaning protocol has been applied for all included patients. We divided patients into two groups according to the duration of MV (PMV group: prolonged MV group, defined as MV > 6 days; non-PMV group: non-prolonged MV group, defined as MV ≤6 days). Medical records were reviewed to obtain information about gender, age, concomitant diseases, types of surgery, the 1st day SOFA, the duration of extracorporeal circulation (ECC), vasopressor and inotrope treatment, and the duration of MV and ICU stay. We also collected hemodynamics and tissue perfusion data at two time points (T0: admission; T1: 48 h after admission; both time points were approximate, within +/− 3 h) from the Critical Care Monitor System of the Department of Critical Care Medicine at Peking Union Medical College Hospital, which recorded real-time clinical data from bedside equipment. This system is maintained by Donghua software cooperation through DtHealth system. We also collected the PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) data on the first and second day in the ICU.
Study definitions
Severe post-cardiac surgery patients defined as after conventional treatments, patients still have the following problems: a. lactate clearance less than 30% in the first 24 h;b. high dose of norepinephrine, more than 1μg/kg/min; c. undefined shock type, requiring more accurate monitoring techniques, like PiCCO.
PMV group: prolonged MV group, defined as MV > 6 days; non-PMV group: non-prolonged MV group, defined as MV ≤6 days.
End-systolic aortic pressure can be estimated as 0.9 times the peak brachial systolic pressure. In this study, we calculated Ea as 0.9*SBP divided by SV (stroke volume), which can be expressed as Ea = 0.9 SBP/SV.
The simplified formula for calculating Ees was Ees = SBP/(GEDV/4-SV). Technically, Ees = ESP/(ESV-V0). ESP is LV end-systolic pressure and ESV is LV end-systolic volume. V0 represents a purely theoretical LV volume at zero intracavitary pressure [16]. We considered ESP as 0.9*SBP [16] and left out V0. Global end-diastolic volume (GEDV) divided by 4 was used as the left ventricular end-diastolic volume.
Statistical analysis
A descriptive analysis was performed. Continuous variables are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, and categorical variables are expressed as absolute values and percentages. For continuous variables, the data were analyzed using Student’s t-test, the Mann-Whitney U test or the Kruskal-Wallis test depending on data distribution and the number of variables. Categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher’s test.
Variables were introduced into a multivariable binary logistic regression model if they were significantly associated with prolonged MV in the univariate analysis (p value < 0.2). General demographics were also used in the model. Discrimination of values was performed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. All comparisons were two-tailed, and P < 0.05 was required to exclude the null hypothesis. The statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 20.0 (Armonk, NY: IBM Corp).
Results
During the study period, a total of 101 severe post-cardiac surgery patients were admitted to our department, and 45 were excluded for various reasons: 13 were discharged within 48 h; 10 were discharged against medical advice or died in the first 6 days; and 19 acquired pneumonia and 3 had serious cerebrovascular accidents in the first 6 days after cardiac surgery in the ICU. Therefore, 56 patients were enrolled in this study. The flow diagram for patient enrollment is shown in Fig. 2. There were 26 patients in the PMV group and 30 patients in the non-PMV group.
Fig. 2.
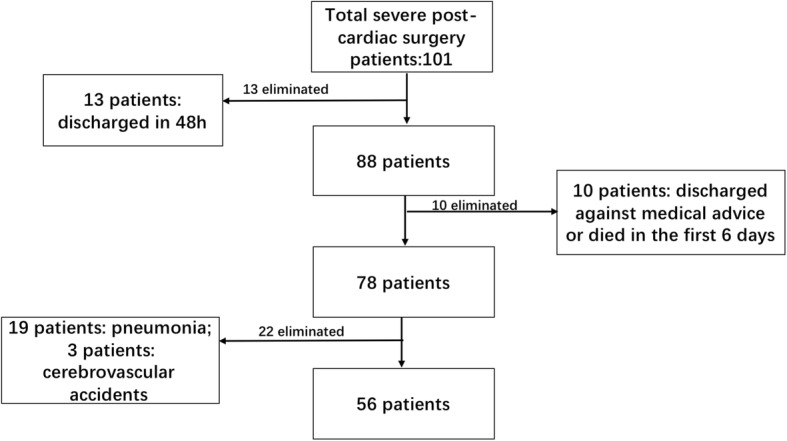
Flow diagram showing the enrollment of patients
Demographics and clinical characteristics
There were no significant differences in gender, age, types of surgery (CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting), pericardiectomy, valve surgery, ventricular septal defect repair, atrial neoplasm resection, aorta replacement) or concomitant diseases (hypertension, diabetes, CAC, CKD, CHF) between the two groups. The PMV group had a significantly higher SOFA score than the non-PMV group (PMV group vs non-PMV group: 12.56 ± 2.71 vs 11.09 ± 2.01, P = 0.003). No significant differences were found in the use of inotropes between the two groups during the three periods. The demographics and clinical characteristics of all the patients are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
The demographics and clinical characteristics of all the patients
| Characteristics | Groups | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-prolonged MV (n = 30) | Prolonged MV (n = 26) | ||
| Gender Males n (%) | 23 (76.67%) | 22 (84.62%) | 0.455 |
| Age (years) | 49.90 ± 16.60 | 54.27 ± 16.52 | 0.329 |
| SOFA | 11.09 ± 2.01 | 12.56 ± 2.71 | 0.003 |
| MV (hours) | 97.33 ± 26.97 | 280.50 ± 141.65 | < 0.001 |
| ICU LOS (days) | 8.13 ± 4.14 | 15.73 ± 7.02 | <0.001 |
| Types of surgery | |||
| CABG n (%) | 6 (20.00%) | 5 (19.23%) | 0.942 |
| Pericardiectomy n (%) | 10 (33.33%) | 13 (50.00%) | 0.206 |
| Valve surgery n (%) | 13 (43.33%) | 9 (34.62%) | 0.505 |
| Ventricular septal defect repair n (%) | 0 (00.00%) | 1 (3.85%) | 0.464 |
| Atrial neoplasms resection n (%) | 2 (6.67%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0.282 |
| Replacement of aorta n (%) | 1 (3.33%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1.000 |
| ECC duration (min) | 116.21 ± 98.56 | 82.56 ± 79.50 | 0.200 |
| Concomitant diseases | |||
| Hypertension n (%) | 11 (36.67%) | 6 (23.08%) | 0.270 |
| Diabetes n (%) | 7 (23.33%) | 3 (11.54%) | 0.310 |
| CAC n (%) | 8 (26.67%) | 5 (19.23%) | 0.511 |
| CKD n (%) | 4 (13.33%) | 1 (3.85%) | 0.358 |
| CHF n (%) | 8 (26.67%) | 9 (34.62%) | 0.519 |
| Post-surgery drugs | |||
| Vasopressors | |||
| 0-24 h n (%) | 28 (93.33%) | 26 (100%) | 0.494 |
| 24-48 h n (%) | 25 (83.33%) | 26 (100%) | 0.055 |
| > 48 h n (%) | 24 (80.00%) | 26 (100%) | < 0.001 |
| Intropes | |||
| 0-24 h n (%) | 28 (93.33%) | 25 (96.15%) | 1.000 |
| 24-48 h n (%) | 28 (93.33%) | 25 (96.15%) | 1.000 |
| > 48 h n (%) | 19 (63.33%) | 20 (76.92%) | 0.384 |
MV mechanical ventilation, SOFA sequential organ failure assessment, LOS length of stay, CABG coronary artery bypass grafting, ECC extracorporeal circulation, CAC coronary atherosclerotic cardiopathy, CKD chronic kidney disease, CHF chronic heart failure
Relationship between hemodynamic parameters and the duration of MV
There were no differences in HRT0 (heart rate), SBPT0 (systolic blood pressure), CVPT0 (central venous pressure), P/FT0 (PaO2/FiO2), lactateT0, CIT0 (cardiac index), SVIT0 (stroke volume index), SVRIT0 (systemic vascular resistance index), Ea,T0, Ees,T0 or Ea/Ees,T0 between the two groups (Table 2). Compared to the non-PMV group, the PMV group had significantly higher values for HRT1 (P = 0.018), lactateT1 (P < 0.001), and Ea/Ees,T1 (4.05 ± 1.20 VS 5.93 ± 1.81, P < 0.001) and lower values for Ees,T1 (P = 0.022), SVIT1 (P = 0.049), SBPT1 (P = 0.014).
Table 2.
Comparison of hemodynamic parameters and tissue perfusion between the two groups
| Variables | Times | Non-prolonged MV | n | Prolonged MV | n | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR bpm | T0 | 103 ± 15 | 30 | 110 ± 17 | 26 | 0.113 |
| T1 | 97 ± 13 | 30 | 108 ± 13 | 26 | 0.018 | |
| SBP mmHg | T0 | 129 ± 17 | 30 | 129 ± 15 | 26 | 0.938 |
| T1 | 131 ± 17 | 30 | 118 ± 22 | 26 | 0.014 | |
| CVP mmHg | T0 | 10.03 ± 2.80 | 30 | 11.08 ± 3.72 | 26 | 0.237 |
| T1 | 10.59 ± 2.15 | 29 | 9.35 ± 2.55 | 26 | 0.055 | |
| P/F mmHg | T0 | 355.00 ± 172.43 | 30 | 291.65 ± 91.29 | 23 | 0.092 |
| T1 | 293.90 ± 93.65 | 29 | 280.48 ± 120.81 | 25 | 0.648 | |
| T °C | T0 | 36.03 ± 0.79 | 30 | 35.87 ± 0.66 | 26 | 0.406 |
| T1 | 36.78 ± 0.61 | 30 | 36.63 ± 0.72 | 26 | 0.319 | |
| Lac mmol/L | T0 | 5.56 ± 3.80 | 30 | 5.66 ± 3.99 | 23 | 0.928 |
| T1 | 1.46 ± 0.58 | 29 | 2.42 ± 1.24 | 25 | < 0.001 | |
| CI L/min/m2 | T0 | 2.89 ± 0.81 | 18 | 2.90 ± 0.87 | 17 | 0.988 |
| T1 | 2.82 ± 0.63 | 21 | 2.59 ± 0.80 | 21 | 0.318 | |
| SVI ml/m2 | T0 | 27.12 ± 7.75 | 18 | 26.24 ± 8.04 | 17 | 0.887 |
| T1 | 29.52 ± 10.84 | 21 | 23.58 ± 6.75 | 21 | 0.049 | |
| SVRI dyn.sec.cm−5.m2 | T0 | 2399.06 ± 1146.16 | 17 | 2255.71 ± 883.40 | 17 | 0.615 |
| T1 | 2260.71 ± 668.84 | 24 | 2309.76 ± 555.38 | 23 | 0.980 | |
| Ea mmHg/ml | T0 | 2.62 ± 1.07 | 18 | 2.86 ± 1.38 | 17 | 0.566 |
| T1 | 2.57 ± 1.22 | 21 | 2.93 ± 0.91 | 21 | 0.279 | |
| Ees mmHg/ml | T0 | 0.570 ± 0.175 | 18 | 0.523 ± 0.109 | 17 | 0.346 |
| T1 | 0.578 ± 0.179 | 21 | 0.461 ± 0.136 | 21 | 0.022 | |
| Ea/Ees | T0 | 4.39 ± 1.90 | 18 | 4.89 ± 1.80 | 17 | 0.423 |
| T1 | 4.05 ± 1.20 | 21 | 5.93 ± 1.81 | 21 | < 0.001 |
MV mechanical ventilation, HR heart rate, SBP systolic blood pressure, CVP central venous pressure, P/F PaO2/FiO2, T temperature, Lac lactate, CI cardiac output index, SVI stroke volume index, SVRI Systemic vascular resistance index, Ea arterial end-systolic elastance, Ees left ventricular end-systolic elastance, Ea/Ees ventricular arterial coupling, T0 at admission, T1 48 h after admission
There was a significant correlation between Ea/Ees,T1and the duration of MV (Fig. 3); the correlation coefficient was 0.512 (Ea/Ees,T1,P < 0.01). There were no correlations between SVIT1 or CIT1 and the duration of MV.
Fig. 3.
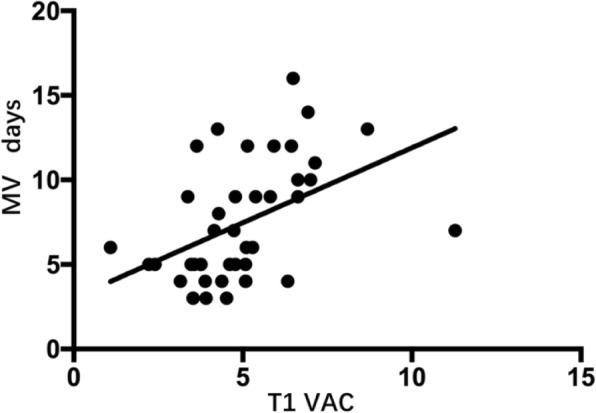
The relationship between Ea/Ees at T1 and the duration of MV. r2 = 0.262
Multivariable binary logistic regression
The multivariable logistic regression analysis of the data at T1 demonstrated that SBPT1 (OR 0.921; 95% CI 0.853–0.994, P < 0.05), Ea/Ees,T1 (OR 6.840; 95% CI 1.031–45.359, P < 0.05) and lactateT1 (OR 15.269; 95% CI 1.231–189.427, P < 0.05) were independent predictors of PMV in severe post-cardiac surgery patients (Table 3).
Table 3.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis for possible risk factors of prolonged mechanical ventilation
| Variable | B | SE | Wald | P | OR | 95% CI for OR Lower Upper |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariate | |||||||
| Age years | 0.040 | 0.050 | 0.625 | 0.429 | 1.040 | 0.943 | 1.148 |
| SOFA | 0.012 | 0.361 | 0.001 | 0.974 | 1.012 | 0.498 | 2.055 |
| T1 SBP mmHg | −0.083 | 0.039 | 4.495 | 0.034 | 0.921 | 0.853 | 0.994 |
| T1 HR bpm | 0.103 | 0.085 | 1.459 | 0.227 | 1.108 | 0.938 | 1.310 |
| T1 CVP mmHg | −0.300 | 0.278 | 1.164 | 0.281 | 0.741 | 0.430 | 1.277 |
| T1 CI L/min/m2 | −1.771 | 1.788 | 0.982 | 0.322 | 0.170 | 0.005 | 5.657 |
| T1 SVI ml/m2 | 0.196 | 0.183 | 1.150 | 0.284 | 1.216 | 0.850 | 1.739 |
| T1 Ea/Ees | 1.923 | 0.966 | 3.965 | 0.046 | 6.840 | 1.031 | 45.395 |
| T1 Lac mmol/L | 2.726 | 1.285 | 4.501 | 0.034 | 15.269 | 1.231 | 189.427 |
HR heart rate, SBP systolic blood pressure, CVP central venous pressure, CI cardiac output index, SVI stroke volume index, Ea/Ees ventricular arterial coupling, Lac lactate, T0 at admission, T1 48 h after admission
Predictive value of three variables in prolonged mechanical ventilation
ROC curves were drawn to compare the predictive values of three different variables for PMV (Fig. 4). The AUC demonstrated that the predictive values of SOFA, Ea/Ees,T1 and lactateT1 were 0.766 (95% CI:0.680–0.952), 0.801 (95% CI:0.664–0.938), 0.816 (95% CI:0.680–0.952), respectively (Table 4). The cutoff values for SOFA (1st day in the ICU), Ea/Ees,T1 and lactateT1 were 12.5 (sensitivity: 70%; specificity: 80%), 5.12 (sensitivity: 65%; specificity: 90%) and 1.60 (sensitivity: 75%; specificity: 85%), respectively, based on the maximum Youden index.
Fig. 4.
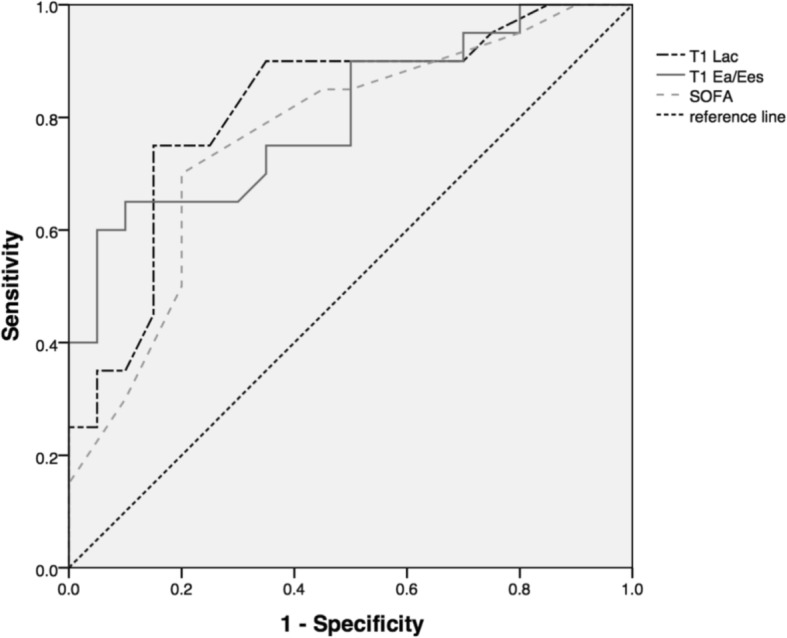
The ROC curves of lactateT1, Ea/Ees,T1 and SOFA for prolonged MV in post-cardiac surgery patients
Table 4.
The results of ROC analysis for LacT1, Ea/Ees,T1 and SOFA
| Variables | ROC area | 95%CI | Cutoff value | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lac (mmol/L) | 0.816* | 0.680–0.952 | 1.60 | 75% | 85% |
| Ea/Ees | 0.801* | 0.664–0.938 | 5.12 | 65% | 90% |
| SOFA | 0.766* | 0.616–0.916 | 12.5 | 70% | 80% |
Lac lactate, Ea/Ees ventricular arterial coupling, SOFA sequential organ failure assessment
*P < 0.05
Discussion
The main findings of this study are as follows: (a) VAC is associated with the duration of MV, and a worse VAC indicates a longer duration of MV; (b) VAC is an independent risk factor for PMV. A cut-off value of VAC > 5.12 predicts PMV with 65% sensitivity and 90% specificity.
Prolonged MV is associated with many complications [17, 18], such as ventilator-associated pneumonia, ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction, increased use of medical resources, etc. [3, 17]. Clinicians aim to reduce the duration of MV as quickly as possible. However, for severe post-cardiac surgery patients, early weaning is much more difficult. Low CO or impaired contractility has always been considered a risk factor for PMV [8] . However, patients who have a normal CO before weaning can still be difficult to wean [9, 19]. Hence, CO might not be adequate for predicting PMV. We also found that in severe post-cardiac surgery patients, the cardiac index was not associated with the duration of MV and could not predict PMV.
The role of left VAC in prolonged MV
When weaning begins, the cardiac preload and afterload of the LV increase dramatically, which requires the LV to increase its SW. If a patient’s heart has a greater SW reserve before weaning, which indicates better VAC, it will be much easier to achieve adequate SW and wean the patient earlier. In several previous studies, SW before weaning was considered a predictive factor for PMV [7]. Actually, a heart can maintain adequate SW by sacrificing its reserve. Under this circumstance, CO or SV may be not altered, but the VAC will be changed. Therefore, it is the SW reserve and not the absolute SW that is important for early weaning. Our study confirmed this with the finding of no correlations between CI or SVI and the duration of MV in severe post-cardiac surgery patients.
Several studies [20, 21] have recommended VAC reserve as a significant tool for assessing cardiovascular function and prognosis. Tonino [20] et al. found that the change in VAC during stress echocardiography can be used as to predict adverse events in patients with negative stress echocardiography. In their study, they defined the change as the VAC reserve (VAC reserve = VACbefore-VACafter), which can reflect the cardiac compensatory function capability. Kensuke [21] et al. also proved that a good VAC reserve was an important determinant of cardiovascular outcome for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. In the present study, we found that an increased Ea/Ees,T1 (OR 6.840; 95% CI 1.031–45.359, P < 0.05) was a risk factor for prolonged MV. Hence, the assessment and optimization of the left VAC might be helpful during ventilator weaning in severe post-cardiac surgery patients. Further studies are required to validate VAC-directed weaning from ventilation.
Optimizing VAC during weaning
Vasodilators and inotropes are always used in severe post-cardiac surgery patients to assist in weaning from MV, which also optimizes VAC. Vasodilators, which decrease Ea by reducing the afterload, and inotropes, which augment Ees by strengthening contractility [22], are two important therapies that can improve VAC, which is crucial for ensuring a short duration of MV. Several studies have shown that vasodilators and inotropes can facilitate the weaning process [9, 23]. Routsi [9] et al. used a nitroglycerin infusion to control systolic blood pressure, and it greatly improved the weaning process of difficult-to-wean patients. Despite concerns about inotrope use, the researchers verified that levosimendan and dobutamine can facilitate weaning in difficult-to-wean COPD patients [24]. Moreover, fluid management also be favorable for VAC. Teboul [5] et al. suggested fluid removal as a reasonable option to help difficult-to-wean patients. Removing excessive fluid can reduce left ventricular end-diastolic pressure [25], which can increase coronary perfusion pressure and ameliorate myocardial perfusion [26].
Several limitations should be acknowledged. First, leaving V0 out of the calculation formula and using GEDV/4 as LVEDV might be an arbitrary decision. However, we had several reasons for making this decision: (a) we considered the heart as a whole, because PMV is not only a problem of poor left ventricular function but also a thing of right ventricle [27]. It might be more proper to combine right and left ventricle together, so we used GEDV/4, which can take both cardiac chambers into consideration, to address this problem. (b) the value of GEDV as a reflection of the preload of the LV has been confirmed in many studies [28], and (c) GEF, calculated by 4SV/GEDV, has a good correlation with LVEF, calculated by SV/LVEDV [29]. Most importantly, in 2015, our department had done a research about sepsis and this “revised VAC” previously, and confirmed its significance in managing sepsis. Further studies are required to validate these choices; however, to some extent, they were reasonable. Second, this was a single-center study with a small sample size. Further investigations with large sample sizes need to be completed to confirm our results. Third, VAC is influenced by many factors: gender, age, concomitant diseases, etiologies, etc. [30–32]. We analyzed these possible variables and found no differences between the two groups. In addition, there were no differences in VAC at admission. We believe that the significance of the differences in VAC was not caused by these irrelevant factors. Fourth, in this study, we aimed to determine what we should do before weaning and tried to recognize patients at risk for prolonged MV patients early in their stay; consequently, we chose the first 48 h as our study period [33, 34]. Fifth, existing research leaves no doubt that VAC is a measure of cardiac work efficiency. Considering our thorough descriptions of VAC and its role in prolonged MV, there is adequate support for our views and conclusions. Further studies must be performed to confirm our perspectives in practice.
Conclusion
Compared to CO, VAC is better in predicting PMV in severe post-cardiac surgery patients, and it’s also an independent risk factor for PMV, which means poorer VAC indicates higher possibility of PMV. The assessment and optimization of left VAC might be helpful when weaning severe post-cardiac surgery patients from MV.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by a Union youth educator project from Peking Union Medical College [No. 2016zlgc0713].
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during the current study are not publicly available due the regulation of data management of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CABG
Coronary artery bypass grafting
- CAC
Coronary atherosclerotic cardiopathy
- CHF
Chronic heart failure
- CI
Cardiac output index
- CKD
Chronic kidney disease
- CO
Cardiac output
- COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CVP
Central venous pressure
- Ea
Arterial end-systolic elastance
- Ea/Ees
Ventricular arterial coupling
- ECC
Extracorporeal circulation
- Ees
Left ventricular end-systolic elastance
- GEDV
Global end-diastolic volume
- GEDVI
Global end-diastolic volume index
- HR
Heart rate
- Lac
Lactate
- LV
Left ventricle
- MV
Mechanical ventilation
- MVO2
Myocardial oxygen consumption
- P/F
PaO2/FiO2
- PMV
Prolonged mechanical ventilation
- PVA
Pressure–volume area
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic
- SBP
Systolic blood pressure
- SBT
Spontaneous breathing test
- SOFA
Sequential organ failure assessment
- SV
Stroke volume
- SVI
Stroke volume index
- SVRI
Systemic vascular resistance index
- SW
Stroke work
- VAC
Ventricular-arterial coupling
Authors’ contributions
YL conceived and designed the study, interpreted data and helped draft the manuscript. XW participated in the study conception and design, recruited patients, collected data, performed the statistical analysis, interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. HH, NC, HW, XR, XZ participated in technically support and contributed in the critical review of the manuscript. WL, RZ participated in data collection. GS assisted us in performing the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Institutional Research and Ethics Committee of the Peking Union Medical College Hospital approved this study for human subjects. Because this retrospective study only collected clinical data, the Institutional Research and Ethics Committee waived the need to obtain consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Xu Wang, Email: sunshinewx@126.com.
Yun Long, Phone: + 86-010-69152318, Email: ly_wxicu@163.com.
Huaiwu He, Email: tjmuhhw@163.com.
Guangliang Shan, Email: guangliang_shan@hotmail.com.
Rui Zhang, Email: 359466965@qq.com.
Na Cui, Email: nanagirl@sina.com.
Hao Wang, Email: newwanghao@hotmail.com.
Xiang Zhou, Email: zx_pumc@163.com.
Xi Rui, Email: xi2000congli@sina.com.
Wanglin Liu, Email: 814047267@qq.com.
References
- 1.LoCicero J, 3rd, McCann B, Massad M, Joob AW. Prolonged ventilatory support after open-heart surgery. Crit Care Med. 1992;20(7):990–992. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199207000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Knapik P, Ciesla D, Borowik D, Czempik P, Knapik T. Prolonged ventilation post cardiac surgery--tips and pitfalls of the prediction game. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;6:158. doi: 10.1186/1749-8090-6-158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rajakaruna C, Rogers CA, Angelini GD, Ascione R. Risk factors for and economic implications of prolonged ventilation after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130(5):1270–1277. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.06.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vagheggini G, Vlad EP, Mazzoleni S, Bortolotti U, Guarracino F, Ambrosino N. Outcomes for difficult-to-wean subjects after cardiac surgery. Respir Care. 2015;60(1):56–62. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dres M, Teboul JL, Monnet X. Weaning the cardiac patient from mechanical ventilation. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014;20(5):493–498. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Teboul JL. Weaning-induced cardiac dysfunction: where are we today? Intensive Care Med. 2014;40(8):1069–1079. doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rady MY, Ryan T. Perioperative predictors of extubation failure and the effect on clinical outcome after cardiac surgery. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(2):340–347. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199902000-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Siddiqui MM, Paras I, Jalal A. Risk factors of prolonged mechanical ventilation following open heart surgery: what has changed over the last decade? Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2012;2(3):192–199. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-3652.2012.06.05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Routsi C, Stanopoulos I, Zakynthinos E, Politis P, Papas V, Zervakis D, Zakynthinos S. Nitroglycerin can facilitate weaning of difficult-to-wean chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: a prospective interventional non-randomized study. Crit Care. 2010;14(6):R204. doi: 10.1186/cc9326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sunagawa K, Sagawa K, Maughan WL. Ventricular interaction with the loading system. Ann Biomed Eng. 1984;12(2):163–189. doi: 10.1007/BF02584229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sweitzer N, Chirinos JA. Ventricular–arterial coupling in chronic heart failure. Cardiac Failure Rev. 2017;03(01):12. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2017:4:2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shigemi K, Fuke S, Une D, Saku K, Shimizu S, Kawada T, Shishido T, Sunagawa K, Sugimachi M. Physiological insights of recent clinical diagnostic and therapeutic technologies for cardiovascular diseases. J Physiol Sci. 2017;67(6):655–672. doi: 10.1007/s12576-017-0554-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Suga H. Total mechanical energy of a ventricle model and cardiac oxygen consumption. Am J Phys. 1979;236(3):H498–H505. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.3.H498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Walley KR. Left ventricular function: time-varying elastance and left ventricular aortic coupling. Crit Care. 2016;20:270. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1439-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Burkhoff D, Sagawa K. Ventricular efficiency predicted by an analytical model. Am J Phys. 1986;250(6 Pt 2):R1021–R1027. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.6.R1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Antonini-Canterin F, Poli S, Vriz O, Pavan D, Bello VD, Nicolosi GL. The ventricular-arterial coupling: from basic pathophysiology to clinical application in the echocardiography laboratory. J Cardiovasc Echogr. 2013;23(4):91–95. doi: 10.4103/2211-4122.127408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Loss SH, de Oliveira RP, Maccari JG, Savi A, Boniatti MM, Hetzel MP, Dallegrave DM, Balzano Pde C, Oliveira ES, Hoher JA, et al. The reality of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: a multicenter study. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):26–35. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20150006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Busl KM, Ouyang B, Boland TA, Pollandt S, Temes RE. Prolonged mechanical ventilation is associated with pulmonary complications, increased length of stay, and unfavorable discharge destination among patients with subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2015;27(1):31–36. doi: 10.1097/ANA.0000000000000085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lemaire F, Teboul JL, Cinotti L, Giotto G, Abrouk F, Steg G, Macquin-Mavier I, Zapol WM. Acute left ventricular dysfunction during unsuccessful weaning from mechanical ventilation. Anesthesiology. 1988;69(2):171–179. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198808000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bombardini T, Costantino MF, Sicari R, Ciampi Q, Pratali L, Picano E. End-systolic elastance and ventricular-arterial coupling reserve predict cardiac events in patients with negative stress echocardiography. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:235194. doi: 10.1155/2013/235194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matsumoto K, Tanaka H, Ooka J, Motoji Y, Sawa T, Mochizuki Y, Ryo K, Tatsumi K, Hirata K-i. Significant prognostic impact of improvement in ventriculo-arterial coupling induced by dobutamine stress on cardiovascular outcome for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;17(11):1296–1304. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guarracino F, Cariello C, Danella A, Doroni L, Lapolla F, Stefani M, Baldassarri R, Vullo C. Effect of levosimendan on ventriculo-arterial coupling in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007;51(9):1217–1224. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Binkley PF, Van Fossen DB, Nunziata E, Unverferth DV, Leier CV. Influence of positive inotropic therapy on pulsatile hydraulic load and ventricular-vascular coupling in congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(5):1127–1135. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90253-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ouanes-Besbes L, Ouanes I, Dachraoui F, Dimassi S, Mebazaa A, Abroug F. Weaning difficult-to-wean chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: a pilot study comparing initial hemodynamic effects of levosimendan and dobutamine. J Crit Care. 2011;26(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2010.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Burggraf GW, Parker JO. Effects of dextran infusion on left ventricular volume and pressure in man. Catheter Cardiovasc Diagn. 1978;4(4):383–390. doi: 10.1002/ccd.1810040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Arnold G, Kosche F, Miessner E, Neitzert A, Lochner W. The importance of the perfusion pressure in the coronary arteries for the contractility and the oxygen consumption of the heart. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;299(4):339–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00602910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Papaioannou VE, Stakos DA, Dragoumanis CK, Pneumatikos IA. Relation of tricuspid annular displacement and tissue Doppler imaging velocities with duration of weaning in mechanically ventilated patients with acute pulmonary edema. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2010;10:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-10-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hofer CK, Furrer L, Matter-Ensner S, Maloigne M, Klaghofer R, Genoni M, Zollinger A. Volumetric preload measurement by thermodilution: a comparison with transoesophageal echocardiography. Br J Anaesth. 2005;94(6):748–755. doi: 10.1093/bja/aei123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Monnet X, Teboul JL. Transpulmonary thermodilution: advantages and limits. Crit Care. 2017;21(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1739-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chantler PD, Lakatta EG. Arterial-ventricular coupling with aging and disease. Front Physiol. 2012;3:90. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Faconti L, Bruno RM, Ghiadoni L, Taddei S, Virdis A. Ventricular and vascular stiffening in aging and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2015;11(2):100–109. doi: 10.2174/1573402111666150529131208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Coutinho T, Borlaug BA, Pellikka PA, Turner ST, Kullo IJ. Sex differences in arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial interactions. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.08.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gray R, Maddahi J, Berman D, Raymond M, Waxman A, Ganz W, Matloff J, Swan HJ. Scintigraphic and hemodynamic demonstration of transient left ventricular dysfunction immediately after uncomplicated coronary artery bypass grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1979;77(4):504–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Breisblatt WM, Stein KL, Wolfe CJ, Follansbee WP, Capozzi J, Armitage JM, Hardesty RL. Acute myocardial dysfunction and recovery: a common occurrence after coronary bypass surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(6):1261–1269. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(10)80011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are not publicly available due the regulation of data management of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


