ABSTRACT
DDX39B, a DExD RNA helicase, is known to be involved in various cellular processes such as mRNA export, splicing and translation. Previous studies showed that the overexpression of DDX39B promotes the global translation but inhibits the mRNA export in a dominant negative manner. This presents a conundrum as to how DDX39B overexpression would increase the global translation if it inhibits the nuclear export of mRNAs. We resolve this by showing that DDX39B affects the levels of pre-ribosomal RNA by regulating its stability as well as synthesis. Furthermore, DDX39B promotes proliferation and colony forming potential of cells and its levels are significantly elevated in diverse cancer types. Thus, increase in DDX39B enhances global translation and cell proliferation through upregulation of pre-ribosomal RNA. This highlights a possible mechanism by which dysregulation of DDX39B expression could lead to oncogenesis.
KEYWORDS: RNA helicase, pre-ribosomal RNA, translation, clonogenic capacity, cancers
Introduction
The DExD RNA helicases are known to regulate different steps of RNA metabolism and various cellular processes [1,2]. DDX39B is one of the well-studied members of DExD RNA helicases and plays an important role in pre-mRNA splicing and nuclear export of mRNAs [3]. Specifically, DDX39B affects splicing by facilitating the unwinding of U4/U6 snRNA duplex and is required for the association of U2 snRNP to the pre-mRNA [4,5]. DDX39B facilitates the nuclear export of mRNAs by recruiting the mRNA export factors, Aly and UIF to the mRNAs [3,6–8]. Both Aly and DDX39B associate with THO complex and participates in the export of bulk mRNAs [9,10]. DDX39B plays a central role in the assembly of TREX mRNA export complex by mediating the ATP-dependent interaction of CIP29, Aly, PDIP3 and ZC11A with the THO complex [11–13]. The ATPase activity of DDX39B is essential for its splicing functions [4] and the export of mRNAs [14]. Aly and Chtop, a component of TREX complex, stimulate the helicase activity of DDX39B, while DDX39B recruits the Aly and Chtop to mRNAs [15].
Interestingly, both the knock-down and overexpression of DDX39B leads to the nuclear retention of poly (A) containing mRNAs indicating that the mRNA export activity of DDX39B is dosage-sensitive [7]. Investigations in different cell types such as HeLa and HEK293 cells by others [6] and us [16] (Figure S1) yield similar results, implying this phenomenon could be cell-type independent. On the contrary, overexpression of DDX39B has been shown to increase the global translation [17]. This presents a conundrum as to how would overexpression of DDX39B increase global translation if it inhibits mRNA export. In this study, we aimed to resolve this contradiction by elucidating other functional role(s) of DDX39B to mechanistically explain the molecular and phenotypic effects of DDX39B-level perturbation. We find that DDX39B is involved in the regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA levels and global translation. DDX39B promotes the proliferation and colony forming capacity of cells and is upregulated in different cancer types indicating that it could have a potential role in cancer manifestation.
Results
DDX39B regulates the pre-ribosomal RNA levels
To elucidate how overexpression of DDX39B can enhance global translation, even though it inhibits mRNA export, we mined the literature to find clues for other possible roles of DDX39B in RNA metabolism. We found that DDX39B, along with few other members of DExD family, has been implicated in pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis in a lentiviral based high-throughput RNAi screen [18]. This prompted us to study the mechanistic roles of DDX39B in the maintenance of pre-ribosomal RNA levels. To investigate this, we depleted or overexpressed DDX39B in HEK293 cells by transfecting siRNA (siDDX39B-1) or pEGFP-DDX39B construct respectively and quantified the levels of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA by using quantitative RT-PCR. We confirmed the knockdown of DDX39B by qRT-PCR and immunoblotting (Figure 1(A–B)). On the other hand, overexpression of GFP-DDX39B resulted in a ~2.7 fold increase in protein abundance compared to the endogenous levels (Figure 1(C)). The qRT-PCR analysis of pre-ribosomal RNA revealed that siRNA mediated depletion of DDX39B reduced the levels of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA by 30% suggesting that DDX39B is required for maintaining the steady-state levels of pre-ribosomal RNA (Upper panel of Figure 1(D)). Importantly, we observed similar effects when transfected with another unrelated siRNA (siDDX39B-2) targeting a completely different region of DDX39B (Figure 1(A–B) and (D)-upper panel), implying that our observations are not confounded by siRNA-mediated off-target effects. Consistent with our findings with gene-silencing, we observed that the overexpression of DDX39B increased the pre-ribosomal 47S RNA levels by 3.4 folds (Lower panel of Figure 1(D)). These findings suggest that DDX39B positively regulates the pre-ribosomal RNA levels.
Figure 1.
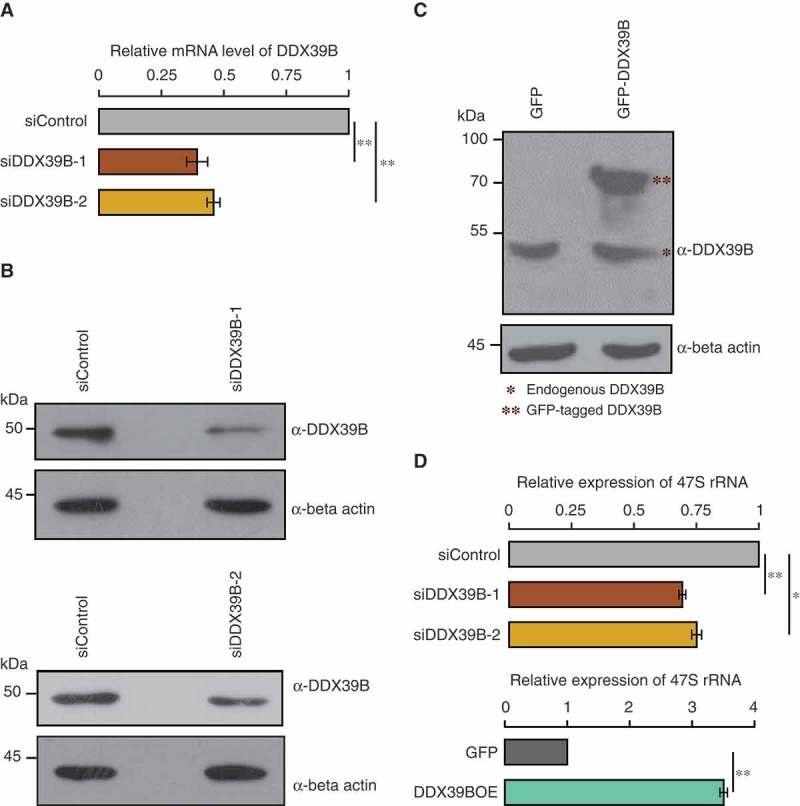
DDX39B regulates the levels of pre-ribosomal RNA.
(A) Efficiency of siRNA mediated knockdown of DDX39B by qRT-PCR. HEK293 cells were treated with control siRNA or DDX39B siRNA-1 (siDDX39B-1) or DDX39B siRNA-2 (siDDX39B-2) and transcript levels of DDX39B were quantified using qRT-PCR. DDX39B transcripts levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are presented relative to the control sample. Data are represented as mean of three independent experiments, with error bars representing standard deviation. Statistical significance was assessed by two tailed t-Test: paired two samples for means. ** represents P-value <0.01. (B) DDX39B protein levels in HEK293 cells treated with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 (Upper panel) or siDDX39B-2 (Lower panel) were analysed using western blotting. The immunoblotting was performed with whole cell extracts using DDX39B antibody or beta actin antibody. (C) Comparison of over-expressed DDX39B with endogenous DDX39B. HEK293 cells were transfected with pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct and the DDX39B levels were analysed using western blotting. The western blotting was performed with whole cell extracts using DDX39B antibody or beta actin antibody. (D) DDX39B maintains the steady state levels of pre-ribosomal RNA. DDX39B levels were perturbed in HEK293 cells by transfecting with siDDX39B-1 or siDDX39B-2 or pEGFP-DDX39B and pre-ribosomal 47S rRNA levels were quantified by qRT-PCR. The 47S rRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are presented relative to the control sample. Data are represented as mean of three independent experiments, with error bars representing standard deviations. Statistical significance was assessed by two tailed t-Test: paired two samples for means. * represents P-value <0.05 and ** P-value <0.01.
DDX39B regulates the stability and transcription of pre-ribosomal RNA
DDX39B might regulate the steady-state levels of pre-ribosomal RNA in three possible ways. DDX39B can affect pre-ribosomal RNA (i) stability, (ii) synthesis or (iii) both. We investigated the stability of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA in the DDX39B perturbed cells by using actinomycin D pulse chase assay. We found that the knock down of DDX39B highly reduced the stability of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA, while the overexpression of DDX39B did not alter 47S rRNA stability significantly (Figure 2(A)). This suggests that DDX39B is necessary to stabilize 47S rRNA and that the endogenous levels of DDX39B might be sufficient to saturate this effect.
Figure 2.
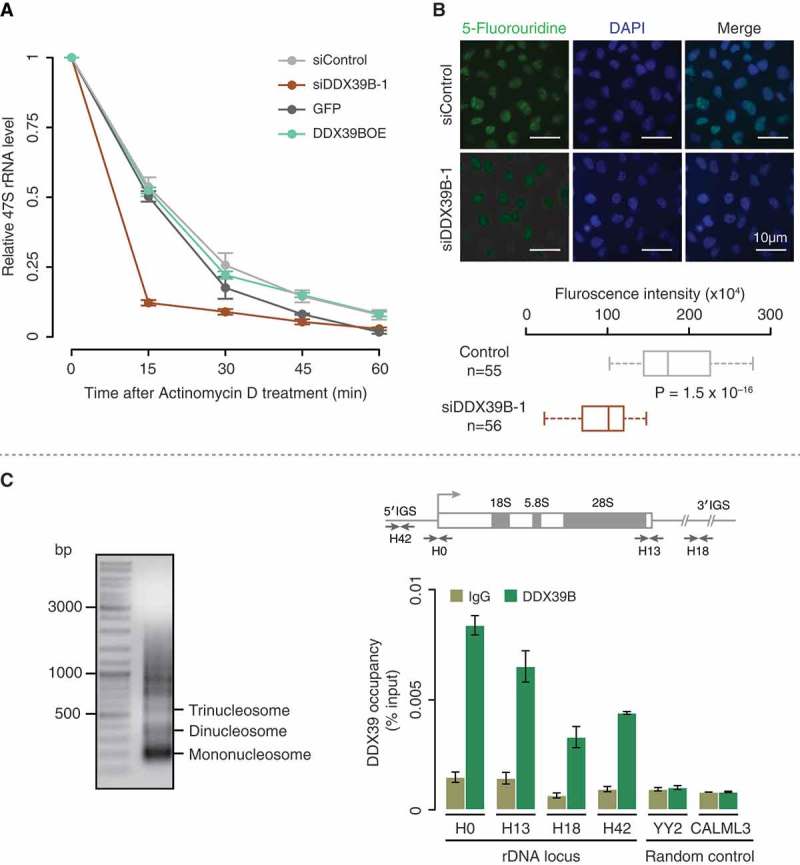
DDX39B regulates the stability and transcription of pre-ribosomal RNA.
(A) DDX39B perturbation affects the stability of pre-ribosomal RNA. HEK293 cells were transfected with control or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B. After 48 hours of transfection, the cells were harvested at the indicated time points after the addition of actinomycin D. The levels of 47S rRNA were then quantified by qRT-PCR. The 47S rRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are presented relative to the 0 min time point sample. Data are represented as mean of three independent experiments. The error bars represent standard deviations. (B) DDX39B is required for efficient synthesis of pre-ribosomal rRNA. The control or DDX39B knock down HeLa cells were pulse labelled with 5-fluorouridine (5-FUrd) and immunostained with BrdU antibody (left panel). DNA was stained with DAPI (middle panel). The right panel shows the merge of fluorescent images. The graph at the bottom of the panel represents the quantification of fluorescence signals in 55 cells of each group. The quantification of fluorescence signals was done by using ImageJ software. Statistical significance was assessed using nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test. P-Values are depicted. (C) DDX39B is recruited to the promoter and regulatory regions of rDNA. The chromatin was prepared from HEK293 cells and fragmented (upper panel gel image). Immunoprecipitation was performed using rabbit IgG antibody or DDX39B antibody. The immunoprecipitated DNA was investigated for the enrichment of promoter and regulatory regions of rDNA and two random control regions (YY2 and CALML3) by using qRT-PCR. The primer binding locations in the rDNA locus are indicated in the schema (above the graph). Data are shown relative to input and the values represent the mean of three independent experiments, with the error bars depicting standard deviations.
To investigate a possible role of DDX39B on the transcription of pre-ribosomal RNA, we performed 5-Fluorouridine (FUrd) incorporation assay in DDX39B perturbed HEK293 cells. We observed a strong reduction of FUrd staining in the DAPI excluded nucleolar regions of DDX39B depleted cells while the control cells displayed a prominent staining in these regions (Figure 2(B)). Since pre-ribosomal RNA transcripts are the major fraction of RNA in the nucleolar regions [19,20], this observation suggests that DDX39B is required for the synthesis of pre-ribosomal RNA. Interestingly, overexpression of DDX39B increased the pre-ribosomal 47S RNA level by 3.4 folds (Figure 1(D)), without any significant effects on the stability of 47S rRNA (Figure 2(A)). This suggests that overexpression of DDX39B might increase pre-ribosomal 47S RNA levels, predominantly by affecting its synthesis.
Since DDX39B is involved in the synthesis of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA, we investigated the binding of DDX39B to the promoter (H0: −51 to +32 bp) and other regulatory regions of rDNA locus (H42: −924 to −1042 bp; H13: +12,855 to +12,970 bp; H18: +18,155 to +18,280 bp) [21,22] by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). We observed that DDX39B was recruited to all the tested regulatory regions of rDNA, with the occupancy being highest at the promoter (H0; Figure 2(C)). The lack of enrichment in DDX39B-binding compared to the IgG control at two random control regions (within the transcription factor YY2 and Calmodulin-like protein 3; CALML3), indicates the specificity of DDX39B recruitment to the rDNA locus (Figure 2(C)). This suggests that DDX39B binds to the promoter and regulatory regions of rDNA either directly or indirectly as a co-activator and regulates the transcription of pre-ribosomal RNA. Taken together, these findings establish that DDX39B regulates the stability and synthesis of pre-ribosomal RNA.
DDX39B positively regulates the global translation
Since DDX39B regulates the stability and transcription of pre-ribosomal RNA, we investigated the role of DDX39B on global translation by using puromycin incorporation assay. For this, we perturbed the DDX39B levels in HEK293 cells, followed by a transient treatment with puromycin. We then quantified the puromycin labelled nascent polypeptides by using immunoblotting. The complete lack of puromycin signal in the cells pre-treated with cycloheximide confirmed the specificity of the assay. We observed a strong reduction in the global translation of DDX39B depleted cells while the overexpression of DDX39B enhanced the translation (Figure 3(A)). This corroborates with the previous reports that showed that over-expression of DDX39B enhances translation in HeLa cells and cardiomyocytes using tritiated leucine incorporation assay [17]. Collectively, these findings suggest that the DDX39B-mediated positive regulation of global translation is cell-type independent.
Figure 3.
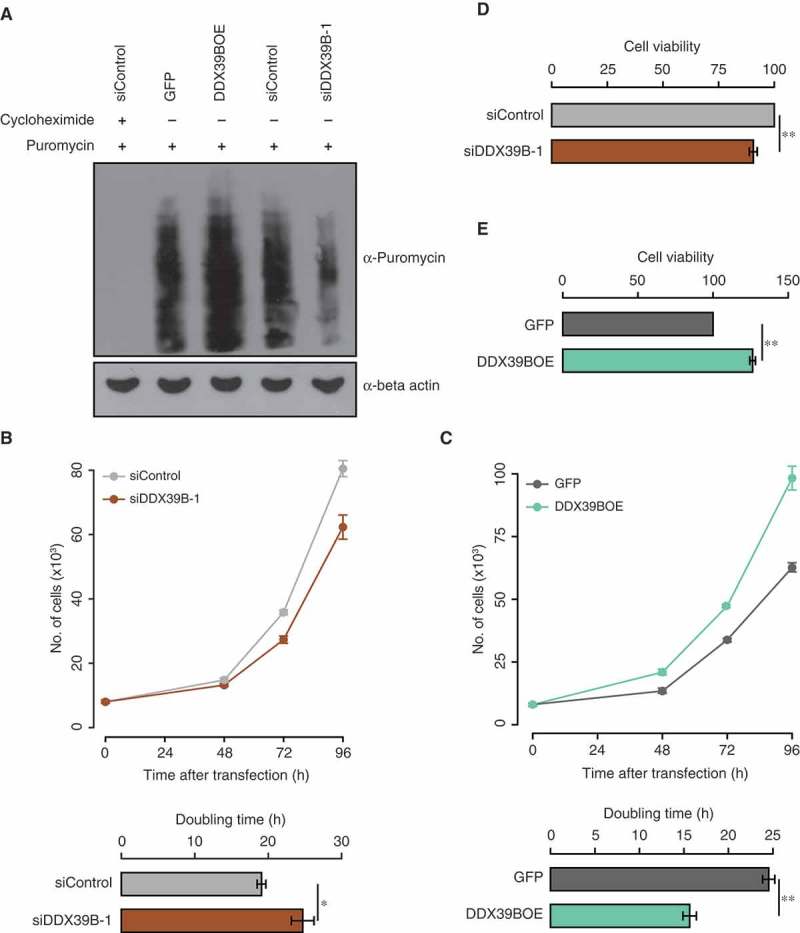
DDX39B positively regulates translation and cell proliferation.
(A) Perturbation of DDX39B levels affects the translation. HEK293 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct and treated with puromycin. Nascent polypeptides in these samples were analysed by immunoblotting using puromycin antibody or beta actin antibody. The first lane represents cell lysate prepared from the cells, which were pre-treated with cycloheximide. These experiments were done in replicates and representative image is provided here. (B and C) DDX39B regulates cell proliferation. HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct. After 48, 72 and 96 hours of transfection, the cells were stained with tryphan blue and the viable cells were counted (Upper panel). From these cell numbers, the doubling times were calculated (Lower panel). The values in the graph represent the mean of triplicates and the error bars represent standard deviations. Statistical significance was assessed by two tailed t-Test: paired two samples for means. * represents P-value <0.05 and ** P-value <0.01. (D and E) MTT assay was performed in HeLa cells after 72 hours transfection with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct. Data are represented as mean of three independent experiments, with the error bars representing standard deviations. Statistical significance was assessed by two tailed t-Test: paired two samples for means. ** represents P-value <0.01.
DDX39B regulates cell proliferation and is elevated in diverse cancers
Since DDX39B is involved in the regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA levels and translation, we studied the role of DDX39B on cell growth and proliferation. For this, we depleted or overexpressed DDX39B in HeLa cells by transfecting siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-DDX39B construct respectively and studied the cell proliferation by cell counting, MTT assay and colony forming assay. We found that the knockdown of DDX39B decreased the cell proliferation as reflected by the increase in doubling time (Figure 3(B)). Strikingly, the overexpression of DDX39B increased cell proliferation (Figure 3(C)). We made similar observations using MTT assay upon perturbation of DDX39B levels in HeLa cells (Figure 3(D–E)). Based on the findings presented here, we posit that the increase in cell proliferation, upon over-expression of DDX39B is mediated by the concomitant increase in the pre-ribosomal RNA levels and global translation (Figures 1(D) and 3(A)).
Since DDX39B regulates cell proliferation, we next examined the effect of DDX39B perturbation on the colony forming potential of the HeLa cells. We found that the overexpression of DDX39B increased the colony forming ability of HeLa cells (Figure 4(A)), with magnitude of increase comparable to that reported previously [23]. However, the effect of reduction in the levels of DDX39B on cell proliferation is not known. We observed a strong reduction in colony forming capacity of HeLa cells upon knockdown of DDX39B (Figure 4(B)). Based on these findings, we speculated that elevated levels of DDX39B could contribute to oncogenesis. To test this, we investigated the pan cancer differential gene-expression data from BioXpress database [24]. We found that DDX39B was upregulated in 75% (12 in 16) of cancers regardless of cancer types (Figure 4(C)). Taken together, these data confirm that the DDX39B is required for the proper cell growth and proliferation. Importantly, the dysregulation of DDX39B increases the proliferation and tumorigenic capacity of the cells.
Figure 4.
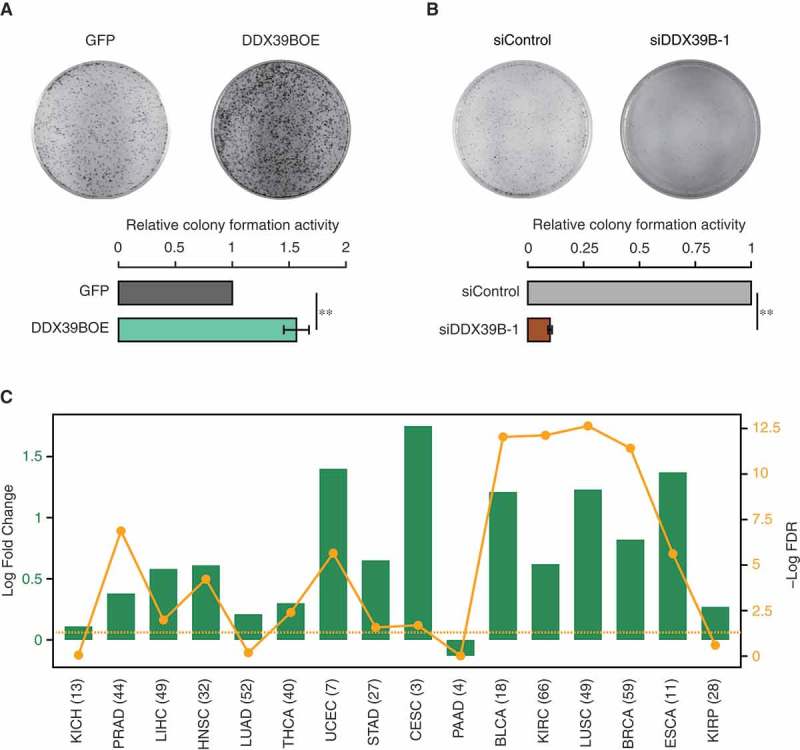
DDX39B promotes cellular clonogenicity and is elevated in diverse cancers.
HeLa cells were transfected with (A) pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct or (B) control siRNA or siDDX39B-1. Colony forming capacity was measured by staining the colonies with crystal violet, 10 days after transfection. Experiments were performed in triplicates and representative images are provided here. Colony numbers were counted using ImageJ software and the values in the graph represent the mean of triplicates and the error bars represent the standard deviations. Statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed t-test. ** indicates P-value <0.01. (C) DDX39B is significantly upregulated in diverse cancers. Differential expression of DDX39B in different cancer types is shown as log2 fold changes (represented by green bars), with each cancer type abbreviated in the X-axis. The yellow line shows the distribution of – Log10 FDR values (False Discovery Rates; P-values corrected for multiple testing for each cancer type by Benjamini-Hochberg method), with the dots representing the value for the corresponding cancer type. The horizontal dotted line represents the FDR cut-off of 0.05, indicating statistical significance. The numbers given in the parenthesis provide the number of patients for which the expression data for each cancer type was available. KICH; kidney chromophobe, PRAD; prostate adenocarcinoma, LIHC; liver hepatocellular carcinoma, HNSC; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, LUAD; lung adenocarcinoma, THCA; thyroid carcinoma, UCEC; uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma, STAD; stomach adenocarcinoma, CESC; cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma, PAAD; pancreatic adenocarcinoma, BLCA; bladder urothelial carcinoma, KIRC; kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, LUSC; lung squamous cell carcinoma, BRCA; breast invasive carcinoma, ESCA; esophageal carcinoma, KIRP; kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma.
Both DDX39B and DDX49 are required for efficient regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA
Recently, we showed that DDX49 affects the pre-ribosomal 47S RNA levels [16] and here we find that DDX39B has a similar function. Since both DDX39B and DDX49 displayed overlapping roles in regulating pre-ribosomal RNA levels, we investigated the functional relationship between these two RNA helicases. To address this, we performed complementation assays by overexpressing DDX49 or DDX39B in the cells depleted of DDX39B or DDX49 respectively. We then measured the levels of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA by using qRT-PCR. As expected, depletion of DDX39B and DDX49 showed a significant reduction in the pre-ribosomal 47S RNA levels (Figure 5(A)). We found that the overexpression of DDX39B in DDX49-depleted cells and that of DDX49 in DDX39B-depleted cells partially rescued the levels of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA. However, this rescue was significantly lower compared to that of siControl (Figure 5(A)). A partial rescue could indicate that these two RNA helicases might not be partners in the same functional complex. To test the possibility of DDX39B-DDX49 interaction, we performed a GST pull down assay. We could not detect any interaction between DDX39B and DDX49 in the conditions tested here (Figure 5(B)). Therefore, (i) while DDX39B and DDX49 could partly compensate for each other, they might be involved in different steps/complexes of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA regulation and (ii) both these proteins are necessary for effective regulation of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA levels.
Figure 5.
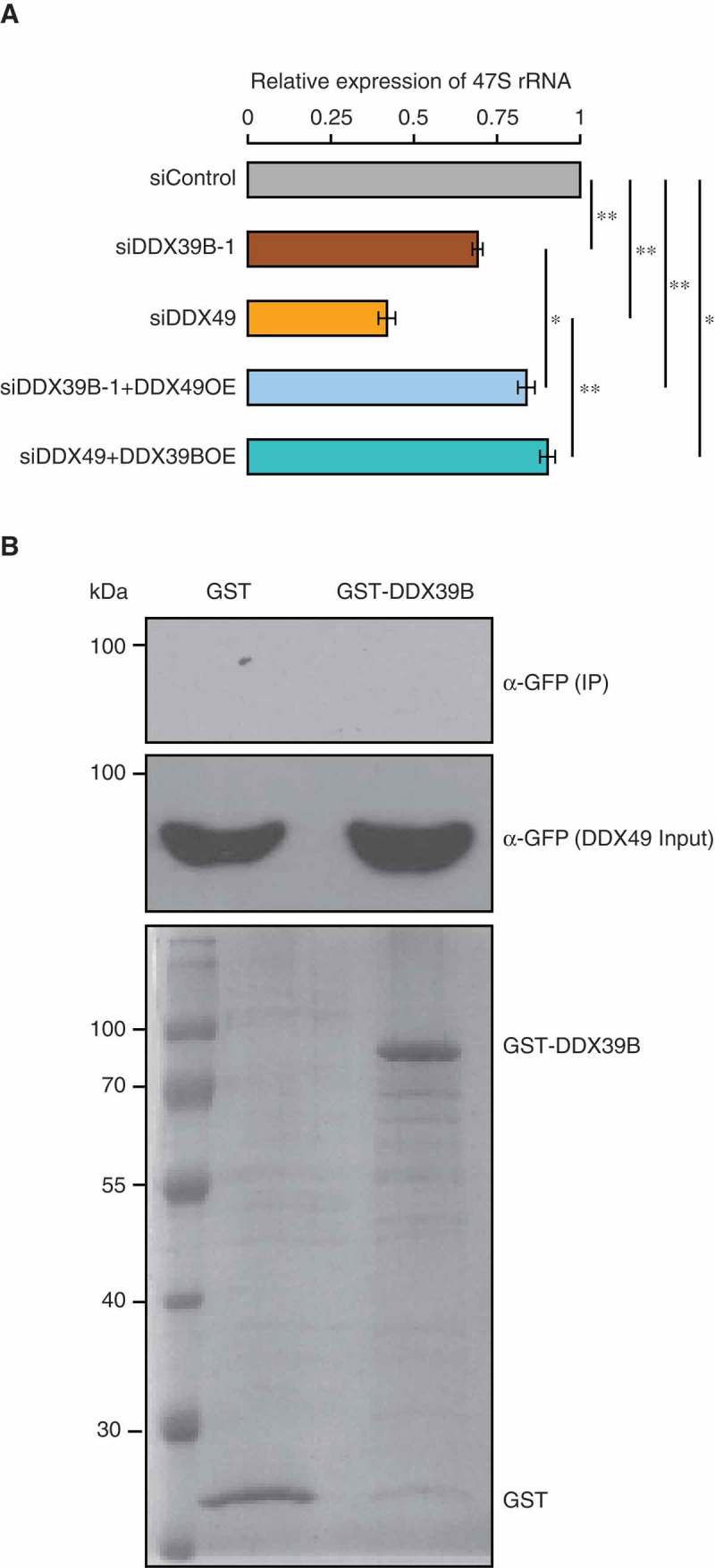
DDX39B partly compensates the function of DDX49 and vice versa.
(A) Functional compensation of DDX39B by DDX49 and vice versa. HEK293 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or DDX49 siRNA or combination DDX49 siRNA and pEGFP-DDX39B or combination siDDX39B-1 and pEGFP-DDX49 and the 47S rRNA levels were quantified using qRT-PCR. The 47S rRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are presented relative to the control sample. Data are represented as mean of three independent experiments, with error bars representing standard deviations. The 47S rRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are presented relative to the control sample. Data are represented as mean of three independent experiments, with error bars representing standard deviations. Statistical significance was assessed by two tailed t-Test: paired two samples for means. * represents P-value <0.05 and ** P-value <0.01.(B) DDX39B does not interact with DDX49. The possibility of DDX39B-DDX49 interaction was investigated by GST pulldown assay. The GST-tagged DDX39B or the GST protein were coupled to the glutathione sepharose and the beads were incubated with the cell lysates prepared from the cells, which were overexpressing of GFP-tagged DDX49 protein. The beads were washed with wash buffer and the bound fractions were probed with anti-GFP antibody (Upper blot). About 1% of the whole cell lysates used in the pull-down assay, were probed with anti-GFP antibody (Middle blot) and 5% of the GST or GST-tagged DDX39B proteins, which were used in pull down assay were separated in SDS-PAGE and stained with coomassie blue dye (Lower blot).
Discussion
Previous studies have documented that the overexpression of DDX39B (i) inhibits DDX39B-mediated mRNA export, and (ii) increases the translation [17,23]. These observations are contradictory as mRNA export from nucleus to cytoplasm is essential for the efficient translation. This raises a fundamental question, as to how do elevated levels of DDX39B enhance translation, when it inhibits mRNA export. In this study, we show that DDX39B is involved in the maintenance of pre-ribosomal RNA levels by regulating its stability and transcription. Since, translational output is a function of ribosome numbers, which in turn is regulated by the rRNA levels, perturbation of DDX39B levels would be expected to have a strong impact on translation. Indeed, overexpression of DDX39B increases global translation and hence the cell proliferation. Only a few members of DExD RNA helicases have been studied extensively for their role in regulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis and processing (Table 1). Our findings presented here on the regulation of pre-ribosomal levels, adds DDX39B to this list.
Table 1.
DExD family members involved in the regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA.
| DExD protein | Regulatory role | References |
|---|---|---|
| DDX5 | Pre-rRNA processing | [28] |
| DDX17 | Pre-rRNA processing | [28] |
| DDX21 | Pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis and processing | [29–31] |
| DHX33 | Pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis | [18] |
| DDX39B | Pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis and stability | This study |
| DDX47 | Pre-rRNA processing | [32] |
| DDX49 | Pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis and stability | [16] |
| DDX51 | Pre-rRNA processing | [33] |
Recently, we reported that DDX49 regulates the steady state levels of pre-ribosomal 47S RNA [16]. Here, we show that both DDX49 and DDX39B are essential for efficient regulation of 47S rRNA in the cell. While both DDX49 and DDX39B affect rDNA transcription, there is a considerable difference in the magnitude of their effects. Depletion of DDX49 has a more severe effect on the regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA levels compared to that of DDX39B (~65% versus 30% reduction). This is consistent with the chromatin immunoprecipitation data as well, where we observe at least a 2-fold increased occupancy of DDX49 at the rDNA loci H0 and H13 compared to DDX39B. It is noteworthy that the ChIPed factor may not directly bind to the DNA [25] but ‘piggy-back’ on other factor(s) that bind to a specific DNA locus. Based on the occupancy profiles obtained through ChIP, it is tempting to speculate that DDX49 might directly bind to the rDNA locus and/or play a more prominent co-activator role for RNA PolI driven rRNA transcription. On the other hand, DDX39B might not directly bind to the rDNA locus, but act as a weak coactivator for RNA PolI driven transcription. Further studies are required to unravel the relationships between different DExD RNA helicases in regulating ribosomal RNA levels.
Interestingly, DDX39B shows a dosage-dependent effect on its functions. While the elevation of DDX39B levels inhibits the nuclear export of mRNAs by sequestering the mRNA export factor Aly [7], it highly enhances the pre-ribosomal RNA levels. Therefore, up-regulation of DDX39B leading to two opposing functions simultaneously, could determine which transcripts get selectively translated. DDX39B is known to affect bulk mRNA export and therefore, up-regulation under specific conditions might serve as a mechanism to arrest mRNA export and facilitate rapid and increased translation of transcripts already present in the cytoplasm. Such a yin-yang regulation of DDX39B functions might have important implications, especially in host-pathogen interactions and disease-contexts. For instance, DDX39B has been shown to play an important role in the replication of Influenza virus by interacting with nucleoprotein [26,27]. Similarly, DDX39B levels are upregulated in diverse cancer types, suggesting that dysregulation of DDX39B could have oncogenic potential, through their effect on rRNA synthesis and enhanced translation and inhibition of mRNA export. In light of the findings presented here, further extensive studies are required to delineate mechanistically how such opposing regulatory roles of DDX39B might be exploited for preferential translation of viral mRNAs or facilitate translation of genes involved in oncogenesis.
Materials and methods
Cloning
The full length human DDX39B (NM_004640.6) was PCR amplified from cDNA prepared from HEK293 cells and cloned in pEGFP-C1 vector (Clontech) using the restriction sites BamHI and XhoI (DDX39B) to generate pEGFP-DDX39B construct. The generation of pEGFP-DDX49 and pGEX-DDX39B constructs was described previously [16].
Cell culture and transfection
HEK293 and HeLa cells were grown in DMEM media containing 10% FBS at 37 °C in 5% CO2 condition. pEGFP-C1, pEGFP-DDX39B and pEGFP-DDX49 constructs were transfected by the standard calcium phosphate precipitation method. The siControl (5ʹ AUC CGC GCG AUA GUA CGU A 3ʹ), siDDX39B-1 (5ʹ GUG CUA CCU UGA GCA AAG A 3ʹ), siDDX39B-2 (5ʹ GGA UCG CUU UGA GGU CAA U 3ʹ) and siDDX49 (5ʹ GAG AGU GUG AGA UCA AAC U 3ʹ) were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Quantitative real time PCR and immunoblotting to investigate the knock-down efficiency
Quantitative real time PCR was performed as described previously [16]. Briefly, HEK293 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or siDDX39B-2 or siDDX49. After 48 hours of transfection, total RNA was isolated and reverse transcribed using random hexamers. qRT-PCR analysis of DDX39B or DDX49 transcripts was performed using Fast start essential DNA green master mix (Roche). Data were obtained from three independent biological repeats and ∆∆Ct method was used to assess for differences in DDX39B or DDX49 in control siRNA vs corresponding siRNA treatment. DDX39B and DDX49 expression was normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and presented relative to the control siRNA sample (Figure 1 and Figure S2). The primers used for these investigations are presented in Table S1. Anti-DDX39B antibody (Abcam, ab181061) was used for immunoblotting to detect DDX39B.
Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of pre-ribosomal 47S rRNA
The HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated siRNA or plasmid construct or combination of siRNA and plasmid construct. The qRT-PCR experiments were performed to quantify 47S pre-ribosomal RNA levels after 48 h of transfection as described above. The primers used in these qRT-PCR experiments are provided in Table S1.
Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA export
The HEK293 cells were transfected with pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct. After 60 hours of transfection, cytoplasmic and total RNAs were isolated and qRT-PCR analysis of EGR1, GAPDH and YY2 transcripts was performed as described previously [16]. The cytoplasmic extract, which was used for RNA isolation, was also subjected to western blotting using beta actin antibody (Sigma, A2228) or histone 3 antibody (Abcam, ab1791) to investigate purity of the prepared cytoplasmic extract (Figure S1).
Actinomycin D pulse chase assay to measure the stability of 47S pre-ribosomal RNA
The actinomycin D pulse chase assay was performed as described previously [16]. DDX39B levels were perturbed in HEK293 cells by transfecting with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct. Actinomycin D was added to the cells at the concentration of 5 µg/ml after 48 h of transfection and the cells were collected at different time points (0, 5, 15, 30, 45 and 60 min). The 47S pre-ribosomal RNA levels in these samples were quantified by using qRT-PCR.
5-fluorouridine pulse chase assay
5-Fluorouridine pulse chase assay was performed to study the effect of DDX39B perturbation on the transcription of pre-ribosomal RNA. DDX39B levels were depleted in HeLa cells by transfecting with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1. The cells were treated with 2 mM of 5-fluorouridine (FUrd) for 20 min after 48 hours of transfection and processed for fluorescence microscopy as described previously [16]. The images were captured using 63X oil immersion objective of fluorescence microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ti). The fluorescence signals were quantified by using ImageJ software.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments were performed to investigate the association of DDX39B with promoter and regulatory regions of rDNA gene and two random control regions (within the transcription factor YY2 and Calmodulin-like protein 3; CALML3). The chromatin was prepared from the HEK293 cells and immunoprecipitation was performed as described earlier [16]. For immunoprecipitation, 15 µg of rabbit IgG (CST, #2729) or DDX39B antibody (Abcam, ab181061) and 15 µg of chromatin was used. The qRT-PCR analysis was performed using Fast start essential DNA green master mix (Roche) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. The primers used for this analysis are listed in Table S1.
Puromycin incorporation assay to measure the translation
DDX39B levels were perturbed in HEK293 cells by transfecting with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct. The cells were treated with puromycin at the concentration of 10 µg/ml for 15 min after 48 h of transfection. After the puromycin treatment, the cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting using puromycin antibody (Merck, MABE343) or beta-actin antibody (Sigma, A2228) as described previously [16]. For the negative control, cells were treated with cycloheximide (100 µg/ml) prior to the addition of puromycin.
Cell proliferation assay, MTT assay and clonogenic assay
The HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or siDDX39B-1 or pEGFP-C1 vector or pEGFP-DDX39B construct. After 48 h of transfection, the cells were processed for cell proliferation assay, MTT assay and clonogenic assay. These assays were performed as described previously [16].
Gene-expression data in cancers
Differential gene-expression data, for DDX39B obtained by RNA sequencing in different cancer types was retrieved from BioXpress database [24]. BioXpress provides statistical significance estimates corrected for multiple testing (False Discovery Rates, FDR) using Benjamini-Hochberg method. We disregarded cancer types with less than 3 patients.
GST pulldown assay
GST-tagged DDX39B recombinant protein was overexpressed and affinity purified as described previously [16]. About 20 µg of GST or the GST-tagged DDX39B recombinant proteins were coupled with 25 µl of Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast flow resin (GE Healthcare) in the interaction buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH: 7.5, 150 mM KCl, 0.2 mM DTT, 1 mM EDTA and 10% glycerol). The protein-coupled beads were blocked at 4°C for 2 hours with blocking buffer (Interaction buffer containing 5% BSA). Subsequently, the beads were incubated with the cell lysates prepared from the cells transfected with pEGFP-DDX49. After the incubation, the beads were washed thrice with wash buffer (10 mM Tris, pH: 7.5, 300 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA and 0.5% NP-40) and boiled with 2X LAP for 5 minutes for elution. The bound fraction was loaded in 12% SDS-PAGE and the resolved proteins were transferred to PVDF membrane and probed with anti-GFP antibody (Clontech).
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Innovative Young Biotechnologist Award, Department of Biotechnology, Government of India [BT/03/IYBA/2010 to A.D.]; Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India (Junior and Senior Research Fellowships to S.A. and B.C.); University Grants Commission, Government of India (BSR-Junior and Senior Research Fellowships to A.M.); Medical Research Council, UK (P.L.C, S.C.).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge DST - FIST and UGC-Special Assistant Programme (SAP) - funded instrumentation facilities of Department of Biotechnology and the Central Instrumentation Facility, Pondicherry University.
Author contributions
S.A. and A.D. designed the study. S.A., B.C., A.M. and P.L.C performed experiments or associated analysis. S.C. performed the bioinformatics analyses. All authors were involved in interpreting the results. S.A., S.C. and A.D. wrote the manuscript. All authors read the manuscript and provided inputs. A.D. conceived, initiated and supervised the study.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Supplementary material
Supplemental data for this article can be accessed here.
References
- [1].Linder P, Jankowsky E.. From unwinding to clamping - the DEAD box RNA helicase family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:505–516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Bleichert F, Baserga SJ. The long unwinding road of RNA helicases. Mol Cell. 2007;27:339–352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Shen H. UAP56- a key player with surprisingly diverse roles in pre-mRNA splicing and nuclear export. BMB Rep. 2009;42:185–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Shen H, Zheng X, Shen J, et al. Distinct activities of the DExD/H-box splicing factor hUAP56 facilitate stepwise assembly of the spliceosome. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1796–1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Fleckner J, Zhang M, Valcarcel J, et al. U2AF65 recruits a novel human DEAD box protein required for the U2 snRNP-branchpoint interaction. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1864–1872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Hautbergue GM, Hung ML, Walsh MJ, et al. UIF, a New mRNA export adaptor that works together with REF/ALY, requires FACT for recruitment to mRNA. Curr Biol CB. 2009;19:1918–1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Luo ML, Zhou Z, Magni K, et al. Pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA export linked by direct interactions between UAP56 and Aly. Nature. 2001;413:644–647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Jensen TH, Boulay J, Rosbash M, et al. The DECD box putative ATPase Sub2p is an early mRNA export factor. Curr Biol CB. 2001;11:1711–1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Li Y, Wang X, Zhang X, et al. Human hHpr1/p84/Thoc1 regulates transcriptional elongation and physically links RNA polymerase II and RNA processing factors. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:4023–4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Strasser K, Masuda S, Mason P, et al. TREX is a conserved complex coupling transcription with messenger RNA export. Nature. 2002;417:304–308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Folco EG, Lee CS, Dufu K, et al. The proteins PDIP3 and ZC11A associate with the human TREX complex in an ATP-dependent manner and function in mRNA export. PloS One. 2012;7:e43804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Dufu K, Livingstone MJ, Seebacher J, et al. ATP is required for interactions between UAP56 and two conserved mRNA export proteins, Aly and CIP29, to assemble the TREX complex. Genes Dev. 2010;24:2043–2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Sugiura T, Sakurai K, Nagano Y. Intracellular characterization of DDX39, a novel growth-associated RNA helicase. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:782–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Kota KP, Wagner SR, Huerta E, et al. Binding of ATP to UAP56 is necessary for mRNA export. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:1526–1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Chang CT, Hautbergue GM, Walsh MJ, et al. Chtop is a component of the dynamic TREX mRNA export complex. EMBO J. 2013;32:473–486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Awasthi S, Verma M, Mahesh A, et al. DDX49 is an RNA helicase that affects translation by regulating mRNA export and the levels of pre-ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:6304–6317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Sahni A, Wang N, Alexis JD. UAP56 is an important regulator of protein synthesis and growth in cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393:106–110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Zhang Y, Forys JT, Miceli AP, et al. Identification of DHX33 as a mediator of rRNA synthesis and cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:4676–4691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Zhao Z, Dammert MA, Hoppe S, et al. Heat shock represses rRNA synthesis by inactivation of TIF-IA and lncRNA-dependent changes in nucleosome positioning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:8144–8152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Hein N, Hannan KM, George AJ, et al. The nucleolus: an emerging target for cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19:643–654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Voit R, Seiler J, Grummt I. Cooperative action of Cdk1/cyclin B and SIRT1 is required for mitotic repression of rRNA synthesis. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].O’Sullivan AC, Sullivan GJ, McStay B. UBF binding in vivo is not restricted to regulatory sequences within the vertebrate ribosomal DNA repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:657–668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Sugiura T, Nagano Y, Noguchi Y. DDX39, upregulated in lung squamous cell cancer, displays RNA helicase activities and promotes cancer cell growth. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6:957–964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Wan Q, Dingerdissen H, Fan Y, et al. BioXpress: an integrated RNA-seq-derived gene expression database for pan-cancer analysis. Database. 2015;2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Bailey TL, Machanick P. Inferring direct DNA binding from ChIP-seq. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Momose F, Basler CF, O’Neill RE, et al. Cellular splicing factor RAF-2p48/NPI-5/BAT1/UAP56 interacts with the influenza virus nucleoprotein and enhances viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 2001;75:1899–1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Wisskirchen C, Ludersdorfer TH, Muller DA, et al. The cellular RNA helicase UAP56 is required for prevention of double-stranded RNA formation during influenza A virus infection. J Virol. 2011;85:8646–8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Jalal C, Uhlmann-Schiffler H, Stahl H. Redundant role of DEAD box proteins p68 (Ddx5) and p72/p82 (Ddx17) in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:3590–3601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Calo E, Flynn RA, Martin L, et al. RNA helicase DDX21 coordinates transcription and ribosomal RNA processing. Nature. 2015;518:249–253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Zhang Y, Baysac KC, Yee LF, et al. Elevated DDX21 regulates c-Jun activity and rRNA processing in human breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res BCR. 2014;16:449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Henning D, So RB, Jin R, et al. Silencing of RNA helicase II/Gualpha inhibits mammalian ribosomal RNA production. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:52307–52314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Sekiguchi T, Hayano T, Yanagida M, et al. NOP132 is required for proper nucleolus localization of DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX47. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:4593–4608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Srivastava L, Lapik YR, Wang M, et al. Mammalian DEAD box protein Ddx51 acts in 3ʹ end maturation of 28S rRNA by promoting the release of U8 snoRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:2947–2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


