Abstract
Gastrointestinal cancers (GICs) are a huge threat to human health, which mainly include esophageal, gastric, and colorectal cancers. The purpose of this study was to clarify the prognostic value of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in GICs. A total of 111 articles were included, and 13103 patients (3123 with esophageal cancer, 4972 with gastric cancer, and 5008 with colorectal cancer) were enrolled in this study. The pooled hazard ratio (HR) values and corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of overall survival (OS) related to different lncRNA expressions in esophageal, gastric, colorectal, and gastrointestinal cancer patients were 1.92 (1.70–2.16), 1.96 (1.77–2.16), 2.10 (1.87–2.36), and 2.00 (1.87–2.13), respectively. We have identified 74 lncRNAs which were associated closely with poor prognosis of GIC patients, including 58 significantly upregulated lncRNA expression and 16 significantly downregulated lncRNA expression. In addition, 47 of the included studies revealed relative mechanisms and 12 of them investigated the correlation between lncRNAs and microRNAs. Taken together, this meta-analysis supports that specific lncRNAs are significantly related to the prognosis of GIC patients and may serve as novel markers for predicting the prognosis of GIC patients. Furthermore, lncRNAs may have a promising contribution to lncRNA-based targeted therapy and clinical decision-making in the future.
1. Introduction
Gastrointestinal cancers (GICs) are one of the most common causes of cancer-related deaths with a high mortality worldwide, which mainly include esophageal, gastric, and colorectal cancers (EC, GC, and CRC). In addition to aging and expansion of world population, cancer-causing behaviors play a key role in the increasing largely global burden of GIC, such as smoking and changes in dietary patterns [1]. There are many therapy strategies applicable to GIC patients, such as surgery, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy [2], and GIC patients at early stage could be curable by receiving suitable treatment with a 90% five-year overall survival, However, five-year overall survivals are still poor for patients with advanced stages [3, 4]. Consequently, early diagnosis and selection of high-risk individuals with poor prognosis are important in the recovery of patients. However, effective methods to evaluate prognosis of GIC patients are still lacking nowadays. Currently, mounting reports have reported that noncoding RNA could be used to predict the prognosis of GIC patients, For example, microRNAs are potentially eligible for predicting the survival of GIC patients [5]. Many studies indicated that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) could competitively suppress microRNAs by acting as molecular sponges recently [6]. Besides, aberrant expression of specific lncRNAs as molecular biomarkers was associated closely with prognosis of GIC patients and involved in targeted therapy, which might promote the development of novel prevention strategies and advanced therapies [7–12].
lncRNA is a long (more than 200 nucleotides) class of noncoding RNA that is often expressed in a disease-, tissue-, or stage-specific manner [13]. According to recent estimate, more than 28000 distinct lncRNAs are encoded by human genome and they regulate gene expression by means of different mechanisms, including chromatin modification, transcription, and posttranscriptional processing, which are becoming attractive therapeutic targets of cancers [14, 15]. Such upregulated lncRNA HOXA11-AS expression promotes tumor proliferation and invasion by scaffolding the chromatin modification factors PRC2, LSD1, and DNMT1 [16]. lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 recruits and bounds to LSD1 to epigenetically repress downstream gene p21, thereby promoting proliferation [17], and lncRNA GHET1 promotes gastric carcinoma cell proliferation by increasing c-Myc mRNA stability [18]. Furthermore, lncRNA plays crucial roles in the diverse biological processes such as development, differentiation, and carcinogenesis [19]. In addition, lncRNA may induce resistance of an anticancer drug. For example, upregulated lncRNA MALAT1 induces chemoresistance of CRC cells [20].
Recently, mounting evidences have indicated that various lncRNAs can function as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes and the dysregulation of lncRNA expression as molecular biomarkers presented promising huge prognostic values in GIC patients [21–26]. However, the ability of evaluating relationship between multiple lncRNA expression and prognosis of GIC patients was limited due to monocentric, small samples and various experimental methods and criteria from different research departments. Therefore, the purpose of the study was to elaborate the relationship between multiple lncRNA expression and prognosis of GIC patients so that further understanding of prognostic values of lncRNAs might promote lncRNA-based target therapeutic development and make a clinical decision that is suitable for the individual quickly.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
To obtain the relevant studies for this meta-analysis, two authors (Weibiao Kang and Qiang Zheng) searched a wide range of database (PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase) independently up to August 27, 2018. Search terms are as follows: “LncRNA”, “Long non-coding RNAs”, “lncRNAs”, “lncRNA”, “Long ncRNA”, “LincRNAs”, “LINC RNA”, “Long ncRNAs”, “cancer”, “tumor”, “malignancy”, “carcinoma”, “neoplasia”, “neoplasm”, “gastrointestine”, “gastroenteric”, “colon”, “colorectal”, “rectum”, “intestinal”, “gastric”, “esophageal”, “esophagus”, “follow up studies”, “prognosis”, “prediction”, “survival”, “hazard ratio”, “incidence”, and “mortality”, which were combined with AND/OR.
2.2. Selection Criteria
All eligible studies were assessed and extracted data by the same two investigators independently based on the selection criteria. Inclusion criteria are the following: (1) patients who were diagnosed as having gastrointestinal cancer by pathologists and did not receive any preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy before obtaining samples; (2) predicting prognosis of full stage (I–IV) patients on the basis of the expression levels of lncRNAs; (3) the expression levels of lncRNAs were divided into high and low levels; (4) we could obtain overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), hazard ratio (HR), and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) directly from full text or extract survival data from Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Exclusion criteria are the following: (1) reviews, letters, case reports, statements, and not clinical related studies were excluded; (2) besides non-English and nonhuman studies, articles lack of data were also excluded; (3) studies focused on lncRNA variants or relationship between lncRNA expression and prognosis in different histological types of GIC. We resolved disagreements by discussing with the third investigator (Changjun Yu) and got consensus finally.
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
The two authors (Weibiao Kang and Qiang Zheng) extracted data independently and got consensus finally. The characteristics collected of individual articles were as follows: author, year of publication, nation of population enrolled, number of patients, HR and 95% CI (OS/DFS), cut-off value, method, sample type, and follow-up. We assessed the quality of each study by using the guidelines for meta-analysis of observation studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) [27].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted by Review Manager 5.2 (provided by Cochrane collaboration). P < 0.01 was considered statistically significant. The heterogeneity among studies was calculated by Q and I2 tests. P > 0.10 in combination with I2 < 50% indicated low heterogeneity; fixed-effect models should be used. Otherwise, random-effect model would be used finally. For some studies from which we could not extract HR and corresponding 95% CI (OS/DFS) directly, Engauge Digitizer 4.1 software was applied to obtain the necessary points and the relevant data from Kaplan-Meier survival curves, then HR and corresponding 95% CI were calculated by published methods proposed by Tierney et al. [28]. Additionally, forest plots of the pooled HR values and funnel plots used to analyse qualitatively publication bias were presented. Furthermore, we also applied sensitivity analysis for this meta-analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Study Identification and Characteristics
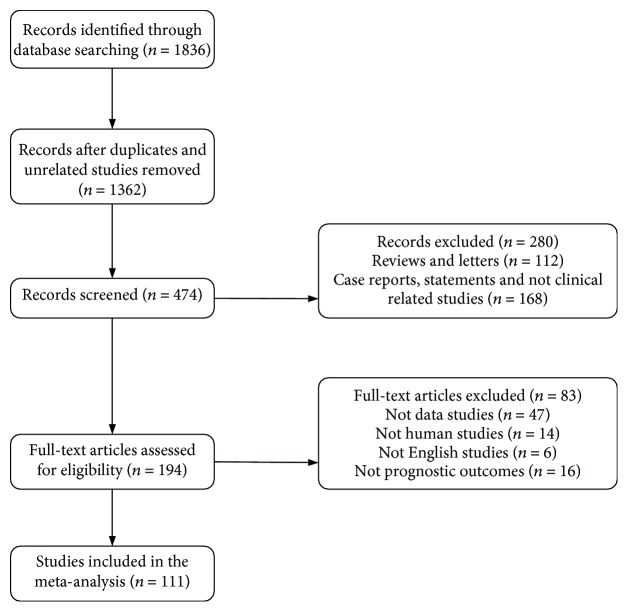
According to the selection criteria, a total of 111 articles (21 EC, 47 GC, and 44 CRC; one study involved GC and CRC) involving 13103 patients (3123 with EC, 4972 with GC, and 5008 with CRC) were identified and included in the meta-analysis; specific steps were showed in Figure 1 [10–13, 15–26, 29–123]. Most of the studies taken into account refer to Asian population, especially china. Cut-off values of high or low lncRNA expression were mostly median or mean. Detection methods of lncRNA expression were mainly RT-PCR (reverse transcription PCR) or ISH (in situ hybridization). Sample types were almost from tissues. As for clinical outcome indicators, 74 studies [10–13, 16, 18–23, 25, 26, 29, 31–33, 36, 38, 40, 41, 43–47, 50, 51, 53–58, 61, 63, 64, 66–68, 71–74, 77, 78, 83, 85, 86, 88, 89, 91, 92, 96–102, 105–107, 109–112, 115–119, 121, 122] included overall survival (OS), 8 studies [17, 24, 30, 34, 79, 95, 114, 123] included disease-free survival (DFS), and another 29 studies [15, 35, 37, 39, 42, 48, 49, 52, 59, 60, 62, 65, 69, 70, 75, 76, 80–82, 84, 87, 90, 93, 94, 103, 104, 108, 113, 120] included both OS and DFS. We have identified 74 lncRNAs which were associated closely with poor prognosis of GIC patients, including 58 significantly upregulated lncRNA expression and 16 significantly downregulated lncRNA expression (Tables 1 and 2). Moreover, 47 of the included studies revealed relative mechanisms, and 12 of them investigated the correlation between lncRNAs and microRNAs (Table 3).
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram.
Table 1.
Characteristics of studies and lncRNA expression related to OS in GIC patients.
| References | lncRNAs (n = 105) | Year | Nations | Number (n = 12178) | OS | Cut-off value | Detection methods | Sample types | Follow-up | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | |||||||||
| Sun et al. [13] | RNAGAS5↓ | 2014 | China | 89 GC | 2.43∗ | 1.29–4.59 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <40 |
| Li et al. [29] | SNHG20↑ | 2016 | China | 107 CRC | 2.97∗ | 1.51–5.82 | YI | RT-PCR | Tissue | <40 |
| Kong et al. [15]! | PVT1↑ | 2015 | China | 80 GC | 2.09∗ | 1.07–4.10 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <40 |
| Qi et al. [31] | AGAP2-AS1↑ | 2017 | China | 50 GC | 2.67# | 1.45–4.93 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 6–36# |
| Chen et al. [32] | XIST↑ | 2016 | China | 106 GC | 3.11 | 1.67–3.78 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <120 |
| Ye et al. [33] | lnc-GNAT1-1↓ | 2016 | China | 68 CRC | 2.16∗ | 1.01–4.63 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <20 |
| Saito et al. [21] | ATB↑ | 2015 | Japan | 183 GC | 3.50∗ | 1.73–7.44 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 0.192–134.4 |
| Yuan et al. [35]! | PVT1↑ | 2016 | China | 111 GC | 2.28∗ | 1.05–4.93 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Ye et al. [36] | CLMAT3↑ | 2015 | China | 90 CRC | 2.05∗ | 1.10–3.82 | Dichotomize | RT-PCR | Tissue | <45 |
| Zheng et al. [37]! | UCA1↑ | 2015 | China | 112 GC | 2.35∗ | 1.22–4.52 | Dichotomize | RT-PCR | Tissue | <92 |
| Chen et al. [38] | NEAT1↑ | 2015 | China | 96 EC | 1.92∗ | 1.40–6.49 | YI | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Wang et al. [39]! | CCAT2↑ | 2016 | China | 108 GC | 2.11∗ | 1.44–3.20 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Zhao et al. [22] | HOTAIR↑ | 2015 | China | 168 GC | 1.47∗ | 1.04–2.06 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Zhang et al. [40] | Sox2ot↑ | 2016 | China | 132 GC | 2.05∗ | 1.28–3.30 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <96 |
| Chen et al. [41] | HIF1A-AS2↑ | 2015 | China | 83 GC | 1.72∗ | 1.00–2.96 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Li et al. [10] | HOTAIR↑ | 2013 | China | 100 EC | 1.91 | 1.06–4.00 | 125-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Yue et al. [42]! | FER1L4↓ | 2015 | China | 70 CC | 3.99∗ | 1.67–9.01 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| He et al. [43] | CCAT1↑ | 2014 | China | 48 CC | 2.09# | 1.42–3.06 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 24–37# |
| Yin et al. [44] | MEG3↓ | 2015 | China | 62 CRC | 0.13∗ | 0.02–0.99 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Nie et al. [45] | MIR31HG↓ | 2016 | China | 48 CC | 2.35# | 1.15–4.79 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 3–36# |
| Park et al. [46] | BM742401↓ | 2013 | Korea | 113 GC | 1.03∗ | 0.57–1.88 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Liu et al. [23] | CRNDE-h↑ | 2016 | China | 148 CRC | 2.39∗ | 1.30–4.39 | Median | RT-PCR | Serum | 1–65 |
| Li et al. [47] | PANDAR↑ | 2017 | China | 102 CRC | 3.08∗ | 0.84–7.89 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Chen et al. [48]! | H19↑ | 2016 | China | 128 GC | 1.96∗ | 0.97–3.97 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Zou et al. [49]! | Sox2ot↑ | 2016 | China | 155 GC | 3.24∗ | 1.24–6.43 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Jiang et al. [50] | TUG1↑ | 2016 | China | 218 EC | 1.40∗ | 1.01–1.95 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | 12–72 |
| Svoboda et al. [51] | HOTAIR↑ | 2014 | Czech | 84 CRC | 5.9 | 1.34–26.1 | Median | RT-PCR | Blood | 12–54 |
| Wang et al. [52]! | OTUB1-isoform 2↑ | 2016 | China | 156 GC | 1.54 | 1.04–2.27 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Guo et al. [53] | FTX↑ | 2015 | China | 187 CRC | 2.37 | 1.42–2.74 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Pan et al. [54] | FOXCUT↑ | 2014 | China | 82 EC | 2.13# | 1.38–3.29 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–72 |
| Zhou et al. [55] | LET↓ | 2014 | China | 93 GC | 2.28 | 1.30–5.18 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Hu et al. [56] | linc-UBC1↑ | 2015 | China | 85 GC | 3.56# | 1.71–7.39 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <100 |
| Wang et al. [57] | CCAT2↑ | 2015 | China | 86 GC | 2.41 | 1.19–5.42 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Ren et al. [58] | HOTTIP↑ | 2015 | China | 156 CRC | 2.15 | 1.31–3.42 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 33–65 |
| Liu et al. [59]! | DANCR↑ | 2015 | China | 104 CRC | 2.13∗ | 1.16–7.06 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Wang et al. [60]! | ZEB1-AS1↑ | 2015 | China | 87 EC | 2.37 | 1.28–6.12 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <61 |
| Li et al. [61] | BANCR↑ | 2015 | China | 184 GC | 1.51∗ | 1.03–2.23 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 5–93 |
| Ma [62]! | PANDAR↑ | 2016 | China | 100 GC | 3.68 | 1.13–12.06 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | 2–36 |
| Huang et al. [63] | MALAT1↑ | 2016 | China | 132 EC | 6.64 | 2.95–14.95 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Ni et al. [64] | UCA1↑ | 2015 | China | 54 CRC | 3.11# | 0.59–16.39 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 9–51# |
| Wu et al. [25] | uc002yug.2↑ | 2014 | China | 684 EC | 2.61 | 1.50–3.78 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <140 |
| Sun et al. [16] | HOXA11-AS↑ | 2016 | China | 85 GC | 2.85# | 1.65–4.91 | Median | ISH | Tissue | 9–36 |
| Peng et al. [65]! | NEAT1↑ | 2016 | China | 56 CRC | 1.70# | 1.04–2.80 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Jiao et al. [66] | UCA1↑ | 2016 | China | 66 EC | 2.24# | 1.17–4.29 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 5–30# |
| Liu and Shangguan [67] | CARLo-5↑ | 2017 | China | 240 GC | 2.41∗ | 1.13–5.94 | 0.041 | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Ma et al. [11] | CCAL↑ | 2016 | China | 252 CRC | 2.25∗ | 1.35–3.74 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <100 |
| Yang et al. [18] | GHET1↑ | 2014 | China | 42 GC | 1.90# | 0.53–6.85 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 7–40# |
| Wu et al. [68] | HOTAIR↑ | 2014 | China | 120 CC | 3.92 | 1.23–12.50 | 5-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 10–72 |
| Zhou et al. [69]! | ROR↑ | 2016 | China | 60 CC | 7.22∗ | 2.43–17.43 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Yang et al. [70]! | Loc554202↓ | 2016 | China | 178 CRC | 2.45 | 1.34–7.74 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Lü et al. [71] | BC032469↑ | 2016 | China | 58 GC | 2.78# | 0.95–8.09 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <23 |
| Su et al. [72] | BLACAT1↑ | 2017 | China | 48 CRC | 1.50∗ | 1.32–1.70 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Hu et al. [12] | GAPLINC↑ | 2014 | China | 90 GC | 1.54∗ | 1.22–1.94 | Median | ISH | Tissue | <80 |
| Fu et al. [73] | NEAT1↑ | 2016 | China | 140 GC | 1.61 | 1.03–2.53 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <96 |
| Yao et al. [26] | RP11-766N7.4↓ | 2017 | China | 50 EC | 2.14# | 1.10–4.15 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 32–60# |
| Xie et al. [74] | SPRY4-IT1↑ | 2014 | China | 92 EC | 2.05 | 1.04–4.03 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 3–60 |
| Peng [75]! | SPRY4-IT1↑ | 2015 | China | 175 GC | 0.82∗ | 0.31–1.57 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Nie et al. [76]! | ZFAS1↑ | 2016 | China | 54 GC | 2.08# | 1.11–3.93 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 3–36# |
| Ohtsuka et al. [77] | H19↑ | 2016 | USA | 117 CC | 1.28∗ | 1.08–1.50 | 0.64 | RT-PCR | Tissue | <90 |
| Li et al. [20] | MALAT1↑ | 2017 | China | 68 CRC | 2.17# | 1.32–3.55 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–51# |
| Zhou et al. [78] | AFAP1-AS1↑ | 2016 | China | 162 EC | 1.89∗ | 1.22–2.92 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 6–72 |
| Sun et al. [80]! | RP11-119F7.4↓ | 2015 | China | 96 GC | 1.20# | 0.84–1.71 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <100 |
| Zhang et al. [81]! | ANRIL↑ | 2014 | China | 120 GC | 1.74∗ | 1.04–2.93 | 3-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Li et al. [82]! | NEAT1↑ | 2015 | China | 239 CRC | 1.70∗ | 1.18–2.45 | 2-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Chen et al. [83] | LINC00152↑ | 2016 | China | 97 GC | 1.66∗ | 1.01-2.73 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Chen et al. [19] | FEZF1-AS1↑ | 2016 | China | 153 CRC | 2.40∗ | 1.07–5.41 | NR | ISH | Tissue | <100 |
| Han et al. [84]! | H19↑ | 2016 | China | 83 CRC | 1.43∗ | 1.24–1.79 | 3-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Yang et al. [85] | GAPLINC↑ | 2016 | China | 180 CRC | 2.21∗ | 1.38–3.57 | NR | ISH | Tissue | <100 |
| Jin et al. [86] | HULC↑ | 2016 | China | 54 GC | 1.92# | 1.00–3.67 | 2-fold | RT-PCR | Serum | 11–32# |
| Cao et al. [87]! | BC200↑ | 2016 | China | 70 EC | 2.24∗ | 1.12–4.49 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Cao et al. [88] | SPRY4-IT1↑ | 2016 | China | 84 CRC | 3.21∗ | 1.55–6.67 | 2.87-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 3–36 |
| Gao et al. [89] | linc-UBC1↑ | 2017 | China | 96 CRC | 2.43∗ | 1.09–5.42 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Wang et al. [90]! | AFAP1-AS1↑ | 2016 | China | 52 CRC | 2.36 | 1.11–5.01 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Ge et al. [91] | PCAT-1↑ | 2013 | China | 108 CRC | 3.12 | 1.36–7.19 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <100 |
| Deng et al. [92] | 91H↑ | 2014 | China | 72 CRC | 3.66 | 1.66–8.10 | 2.86-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 2–36 |
| Sun et al. [93]! | AK098081↑ | 2016 | China | 84 CRC | 1.90∗ | 1.39–2.58 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–118# |
| Xu et al. [94]! | FENDRR↓ | 2014 | China | 158 GC | 1.76 | 1.04–3.12 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Bian et al. [96] | UCA1↑ | 2016 | China | 90 CRC | 2.40∗ | 1.04-5.50 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <100 |
| Zuo et al. [97] | UCA1↑ | 2017 | China | 37 GC | 2.92∗ | 1.07–7.96 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <40 |
| Lu et al. [98] | PANDAR↑ | 2017 | China | 124 CRC | 3.53∗ | 1.41–4.45 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Lv et al. [99] | MEG3↓ | 2016 | China | 96 EC | 2.12 | 1.05–4.27 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <120 |
| Xu et al. [100] | TUSC7↓ | 2017 | China | 63 CRC | 2.92 | 1.03–8.33 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <120 |
| Ma et al. [101] | DUXAP8↑ | 2016 | China | 72 GC | 2.37# | 1.39–4.05 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 5–36# |
| Fei et al. [103]! | LINC00982↓ | 2016 | China | 106 GC | 2.87∗ | 1.34–6.17 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Chen et al. [104]! | SNHG15↑ | 2016 | China | 106 GC | 2.93∗ | 1.30–6.58 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Tan et al. [105] | SPRY4-IT1↑ | 2017 | China | 106 CRC | 2.34∗ | 1.14–4.83 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Wang and Xing [106] | ZFAS1↑ | 2016 | China | 159 CRC | 1.88∗ | 1.01–3.53 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <101 |
| Yao et al. [107] | MALAT-1↑ | 2016 | China | 137 EC | 1.27# | 0.90–1.80 | 0.5-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 3–36# |
| Liu et al. [108]! | BANCR↑ | 2016 | China | 142 EC | 0.95∗ | 0.21–0.95 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–60# |
| Chen et al. [109] | HOTAIR↑ | 2013 | China | 78 EC | 2.40∗ | 1.35–4.28 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | 2–60 |
| Hu et al. [102]a | Linc00152↑ | 2016 | China | 205 EC | 1.89 | 1.22–2.58 | Upper 95% CI in control group | RT-PCR | Plasma | <60 |
| POU3F3↑ | 1.82 | 1.17–2.51 | ||||||||
| CFLAR↑ | 1.68 | 1.08–2.32 | ||||||||
| Yu et al. [110] | u50535↑ | 2018 | China | 98CRC | 4.01∗ | 1.06–15.14 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Jiang et al. [111] | CRNDE↑ | 2017 | China | 251CRC | 1.69∗ | 1.05–2.74 | NR | ISH | Tissue | 1–117 |
| Cui et al. [112] | HEIH↑ | 2018 | China | 84CRC | 1.46∗ | 1.02–2.08 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Wu et al. [113]! | GHRLOS↓ | 2017 | China | 366CRC | 1.96∗ | 1.34–2.86 | 1/2-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 5–85 |
| Li et al. [115] | ZEB1-AS1↑ | 2017 | China | 24GC | 2.36∗ | 1.41–3.96 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 72 |
| Huang et al. [116] | LINC00673↑ | 2017 | China | 73GC | 2.38∗ | 1.12–5.06 | 2-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <20 |
| Li et al. [117] | PVT1↑ | 2017 | China | 104ESCC | 2.75∗ | 1.35–5.59 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Shi et al. [118] | ZFAS1↑ | 2017 | China | 246ESCC | 1.59∗ | 1.07–2.36 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 114 |
| Wu et al. [119] | XIST↑ | 2017 | China | 127ESCC | 2.4∗ | 1.44–4.01 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Ba et al. [120] | LINC00673↑ | 2017 | China | 79GC | 2.56∗ | 1.01–4.54 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Zhu et al. [121] | SNHG1↑ | 2017 | China | 108CRC | 3.17∗ | 1.55–6.21 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Yang et al. [122] | LINC01133↓ | 2018 | China | 149ESCC | 2.18∗ | 1.23–3.85 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
aOne study involved lncRNA Linc00152, lncRNA POU3F3, and lncRNA CFLAR. ∗ indicates adjusted HR; # indicates calculated HR of OS and follow-up time; ! indicates studies included OS and DFS; ↑ or ↓ indicates upregulated or downregulated with poor prognosis. OS: overall survival; DFS: disease-free survival; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; EC: esophageal cancer; GC: gastric cancer; CRC: colorectal cancer; GIC: gastrointestinal cancer; NR: no report; YI: Youden index; RT-PCR: reverse transcription PCR; ISH: in situ hybridization.
Table 2.
Characteristics of studies and lncRNAs expression related to DFS in GIC patients.
| References | lncRNAs (n = 37) | Year | Nations | Number (n = 4360) | DFS | Cut-off value | Detection methods | Sample types | Follow-up | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | |||||||||
| Kong et al. [15]! | PVT1↑ | 2015 | China | 80GC | 2.22∗ | 1.13–4.44 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <40 |
| Liu et al. [17] | FEZF1-AS1↑ | 2017 | China | 82GC | 1.52# | 0.88–2.63 | 2-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–43# |
| Fan et al. [30] | LINC00261↓ | 2016 | China | 138GC | 1.81∗ | 1.06–3.10 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Xu et al. [34] | PVT1↑ | 2017 | China | 190GC | 1.75 | 1.25–2.56 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–85 |
| Yuan et al. [35]! | PVT1↑ | 2016 | China | 111GC | 2.21∗ | 1.11–4.40 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Zheng et al. [37]! | UCA1↑ | 2015 | China | 112GC | 2.55∗ | 1.33–4.97 | Dichotomize | RT-PCR | Tissue | <92 |
| Wang et al. [39]! | CCAT2↑ | 2016 | China | 108GC | 2.31∗ | 1.55–3.42 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Yue et al. [42]! | FER1L4↓ | 2015 | China | 70CC | 4.51∗ | 1.99–9.02 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Chen et al. [48]! | H19↑ | 2016 | China | 128GC | 1.29∗ | 1.00-1.65 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Zou et al. [49]! | Sox2ot↑ | 2016 | China | 155GC | 3.84∗ | 1.87–7.33 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Wang et al. [24] | NR_034119↓ | 2016 | China | 107CRC | 1.93∗ | 1.04–3.61 | NR | RT-PCR | Serum | 11–74 |
| Wang et al. [52]! | OTUB1-isoform 2↑ | 2016 | China | 156GC | 1.50∗ | 1.02–2.20 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Liu et al. [59]! | DANCR↑ | 2015 | China | 104CRC | 2.40∗ | 1.39–7.28 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Wang et al. [60]! | ZEB1-AS1↑ | 2015 | China | 87EC | 2.7 | 1.38–8.35 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <61 |
| Ma et al. [62]! | PANDAR↑ | 2016 | China | 100GC | 2.36 | 1.15–4.83 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | 2–36 |
| Peng et al. [65]! | NEAT1↑ | 2016 | China | 56CRC | 2.39# | 1.37–4.19 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Zhou et al. [69]! | ROR↑ | 2016 | China | 60CC | 5.64∗ | 1.92–16.58 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <80 |
| Yang et al. [70]! | Loc554202↓ | 2016 | China | 178CRC | 2.75 | 1.55–7.93 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <70 |
| Peng et al. [75]! | SPRY4-IT1↑ | 2015 | China | 175GC | 1.74∗ | 1.32–2.48 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Nie et al. [76]! | ZFAS1↑ | 2016 | China | 54GC | 1.83# | 1.07–3.15 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 3–36# |
| Xu et al. [79]a | LSINCT5↑ | 2014 | China | 71GC | 1.08∗ | 1.29–3.56 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <72 |
| 74CRC | 1.30∗ | 1.11–3.84 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | <72 | ||||
| Sun et al. [80]! | RP11-119F7.4↓ | 2015 | China | 96GC | 1.16# | 0.81–1.65 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <100 |
| Zhang et al. [81]! | ANRIL↑ | 2014 | China | 120GC | 1.72∗ | 1.04–2.84 | 3-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Li et al. [82]! | NEAT1↑ | 2015 | China | 239CRC | 1.80∗ | 1.27–2.55 | 2-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Han et al. [84]! | H19↑ | 2016 | China | 83CRC | 1.52∗ | 1.30–1.90 | 3-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Cao et al. [87]! | BC200↑ | 2016 | China | 70EC | 2.17∗ | 1.12–4.19 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Wang et al. [90]! | AFAP1-AS1↑ | 2016 | China | 52CRC | 2.12 | 1.03-4.35 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Sun et al. [93]! | AK098081↑ | 2016 | China | 84CRC | 1.40# | 0.86–2.28 | Mean | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–118# |
| Xu et al. [94]! | FENDRR↓ | 2014 | China | 158GC | 1.8 | 1.11–2.91 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Shang et al. [95] | UCA1↑ | 2016 | China | 77GC | 2.54 | 1.09–5.92 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <60 |
| Fei et al. [103]! | LINC00982↓ | 2016 | China | 106GC | 2.40∗ | 1.19--4.81 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Chen et al. [104]! | SNHG15↑ | 2016 | China | 106GC | 2.40∗ | 1.38–4.18 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
| Liu et al. [108]! | BANCR↑ | 2016 | China | 142EC | 3.42# | 2.29–5.10 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 1–60# |
| Wu et al. [113]! | GHRLOS↓ | 2017 | China | 366CRC | 2.02∗ | 1.42–2.88 | 1/2-fold | RT-PCR | Tissue | 5–85 |
| Yu et al. [114] | linc00261↓ | 2017 | China | 80GC | 2.57∗ | 1.39–4.20 | NR | RT-PCR | Tissue | <30 |
| Ba et al. [120] | LINC00673↑ | 2017 | China | 79GC | 2.94∗ | 1.23–4.21 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | <50 |
| Xu et al. [123] | FOXD2-AS1↑ | 2018 | China | 106GC | 1.75∗ | 1.04–2.97 | Median | RT-PCR | Tissue | 20–48 |
aOne study involved GC and CRC. ∗ indicates adjusted HR; # indicates calculated HR of DFS and follow-up time; ! indicates studies included OS and DFS; ↑ or ↓ indicates upregulated or downregulated with poor prognosis. OS: overall survival; DFS: disease-free survival; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; EC: esophageal cancer; GC: gastric cancer; CRC: colorectal cancer; GIC: gastrointestinal cancer; NR: no report; RT-PCR: reverse transcription PCR.
Table 3.
lncRNAs and relevant targets in gastrointestinal cancer.
| lncRNAs (n = 37) | Poor prognosis | Role | Relevant targets | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNHG20↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | Cyclin A1, p21 | Proliferation/invasion/migration | [29] |
| PVT1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, p15, p16, FOXM1 | Proliferation/metastasis | [15, 34] |
| FEZF1-AS1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | LSD1, P21, FEZF1 | Proliferation/invasion/migration | [17, 19] |
| AGAP2-AS1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | LSD1, EZH2, P21, E-cadherin | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [31] |
| XIST↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | miR-101, EZH2 | Proliferation/migration/invasion/growth/metastasis | [32] |
| ATB↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | miR-200s, ZEB1, ZEB2 | Invasion/EMT | [21] |
| UCA1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | Ets-2, Sox4, miR-204, miR-204-5p, TGFβ1 | Migration/invasion/proliferation/apoptosis/chemoresistance/EMT | [64, 66, 96, 97] |
| NEAT1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | Akt, vimentin, N-cadherin, Zo-1, E-cadherin | Proliferation/apoptosis/EMT/migration/invasion | [65, 73] |
| CCAT2↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, E-cadherin, LATS2 | Progression | [39] |
| CCAT1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | c-Myc | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [43] |
| PANDAR↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | N-cadherin, vimentin, β-catenin, Snail, Twist, E-cadherin | EMT/growth/migration/invasion/apoptosis | [98] |
| H19↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | E-cadherin, Rb-E2F, CDK8, β-catenin, eIF4A3 | Migration/invasion/proliferation | [48, 77, 84] |
| FOXCUT↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | FOXC1 (mRNA) | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [54] |
| MALAT1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, miR-218 | Chemoresistance/EMT | [20] |
| uc002yug.2↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | RUNX1 | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [25] |
| HOXA11-AS↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, LSD1, miR-1297 | Growth/migration/invasion/apoptosis | [16] |
| CCAL↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | AP-2α | Progression/multidrug resistance | [11] |
| GHET1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | c-Myc (mRNA) | Proliferation | [18] |
| ROR↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | miR-145 | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [69] |
| BC032469↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | miR-1207-5p | Proliferation | [71] |
| BLACAT1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, p15 | Proliferation | [72] |
| GAPLINC↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | miR211-3p, CD44, PSF, NONO, SNAI2 | Invasion | [12, 85] |
| SPRY4-IT1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | Cyclin D1, MMP2, MMP9, E-cadherin, vimentin | Proliferation/migration/invasion/EMT/metastasis | [75, 88] |
| ZFAS1↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, LSD1, CoREST, KLF2, NKD2 | Proliferation | [76] |
| ANRIL↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | PRC2, miR-99a, miR-449a | Proliferation | [81] |
| LINC00152↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, p15, p21 | Proliferation | [83] |
| DUXAP8↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | EZH2, SUZ12, PLEKHO1 | Proliferation/migration | [101] |
| SNHG15↑ | Upregulated | Oncogene | MMP2, MMP9 | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [104] |
| GAS5↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | E2F1, P21 | Proliferation | [13] |
| lnc-GNAT1-1↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | RKIP-NF-κB-Snail | Proliferation/migration/invasion/metastasis | [33] |
| FER1L4↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | miR-106a-5p | Proliferation/migration/invasion | [42] |
| MEG3↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | p53 | Proliferation/apoptosis | [99] |
| MIR31HG↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | E2F1, P21 | Proliferation | [45] |
| RP11-766N7.4↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | Vimentin, N-cadherin, E-cadherin | Migration/invasion/EMT | [26] |
| FENDRR↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | FN1, MMP2, MMP9 | Migration/invasion | [94] |
| TUSC7↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | miR-211-3p | Proliferation | [100] |
| LINC00982↓ | Downregulated | Suppressor | P15, P16 | Proliferation | [103] |
3.2. Meta-Analysis Findings
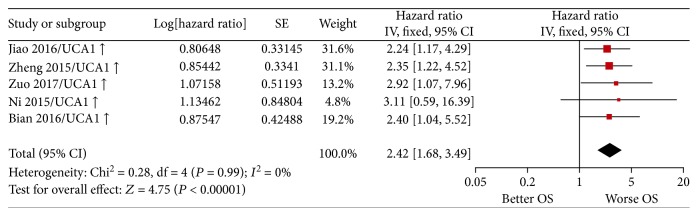
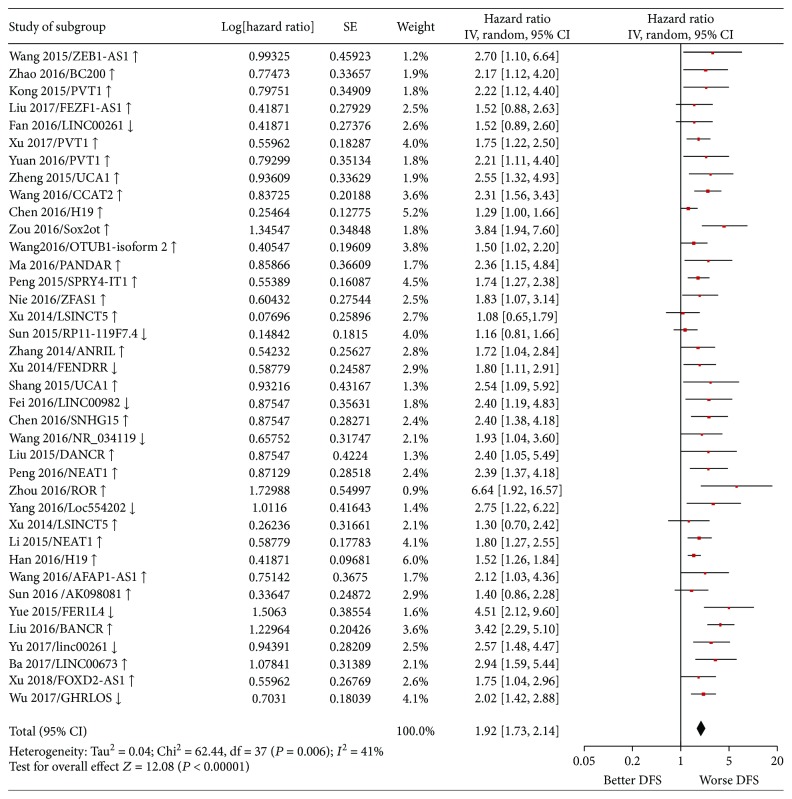
Random-effect and fixed-effect models were applied to evaluate the pooled hazard ratio (HR) and its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) of OS or DFS based on the heterogeneity level. The pooled HR value (95% CI) of OS which correlated with the expression of lncRNA-UCA1 [37, 64, 66, 96, 97] was 2.42 (1.68–3.49) with low heterogeneity (P = 0.99, I2 = 0%) and statistically significant (P < 0.00001) (Figure 2). For all included studies, the pooled HR values (95% CI) of OS related to different lncRNA expressions in EC, GC, and CRC patients were 1.92 (1.70–2.16), 1.96 (1.77–2.16), and 2.10 (1.87–2.36), respectively. And the pooled HR value (95% CI) of OS related to different lncRNA expressions was 2.00 (1.87–2.13) in GIC with moderate heterogeneity (P = 0.0001, I2 = 37%) and statistically significant (P < 0.00001) (Figure 3). Besides, the pooled HR value (95% CI) of DFS related to different lncRNA expressions was 1.92 (1.73–2.14) in GIC patients with moderate heterogeneity (P = 0.006, I2 = 41%) and statistically significant (P < 0.00001) (Figure 4). Furthermore, funnel plots of included studies related to lncRNA-UCA1, OS, and DFS in GIC patients were presented in Figures 5, 6, and 7, respectively. These figures are approximately symmetrical, and we can think that there is no obvious publication bias.
Figure 2.
Forest plot showing the pooled HR and corresponding 95% CI of OS related to the expression level of lncRNA UCA1 in gastrointestinal cancer patients. HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; OS: overall survival.
Figure 3.
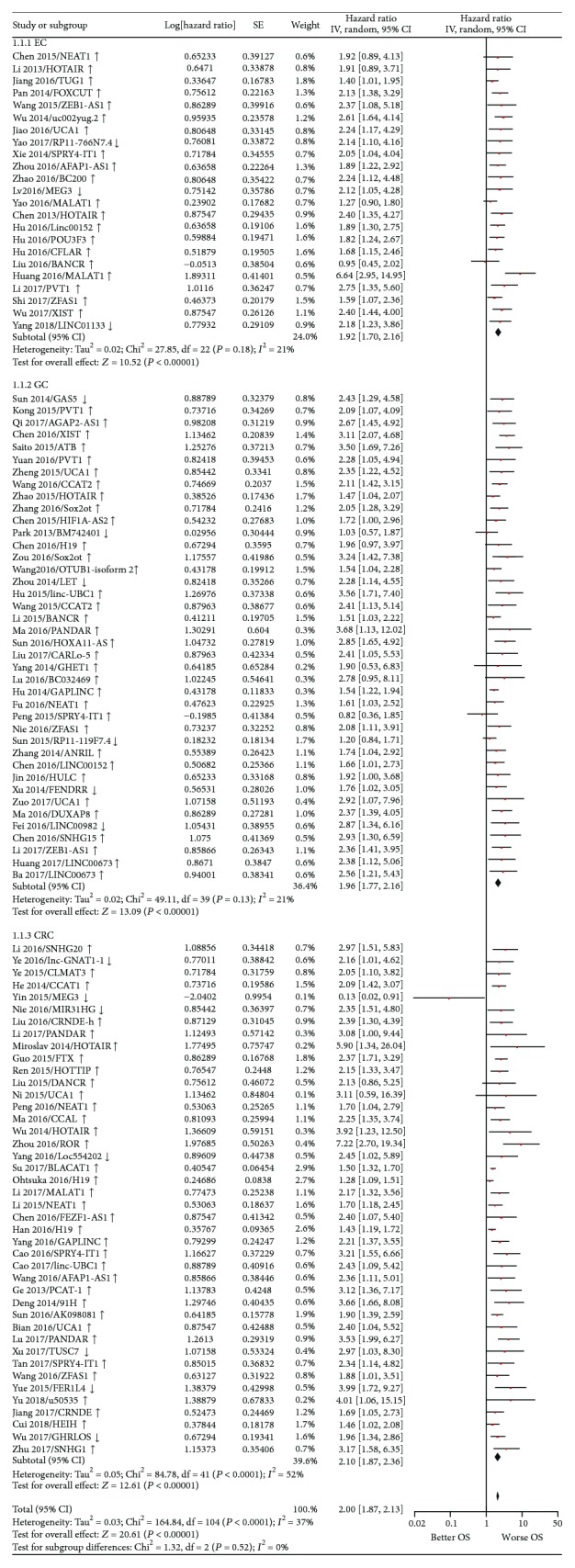
Forest plot showing the pooled HR (95% CI) of OS related to the expression level of different lncRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer patients. (1.1.1) Specific lncRNA expression in EC (esophageal cancer); (1.1.2) specific lncRNA expression in GC (gastric cancer); (1.1.3) specific lncRNA expression in CRC (colorectal cancer). HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; OS: overall survival.
Figure 4.
Forest plot showing the pooled HR (95% CI) of DFS related to the expression level of different lncRNAs in GIC patients. HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; DFS: disease-free survival; GIC: gastrointestinal cancer.
Figure 5.
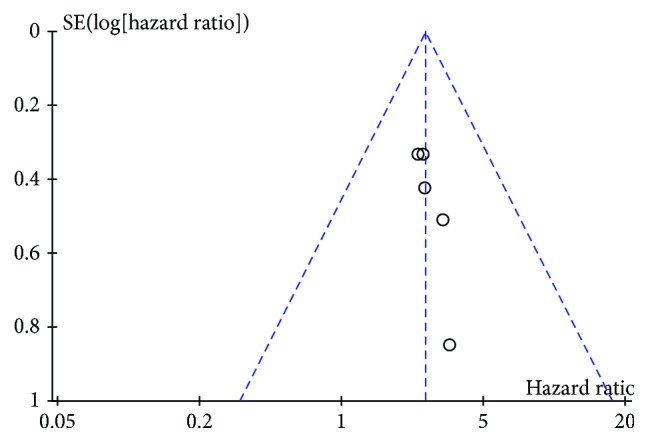
Funnel plot of included studies: highly expressed lncRNA UCA1 related to overall survival in gastrointestinal cancer patients.
Figure 6.

Funnel plot of included studies: aberrantly expressed lncRNAs related to overall survival in gastrointestinal cancer patients. EC: esophageal cancer; GC: gastric cancer; CRC: colorectal cancer.
Figure 7.
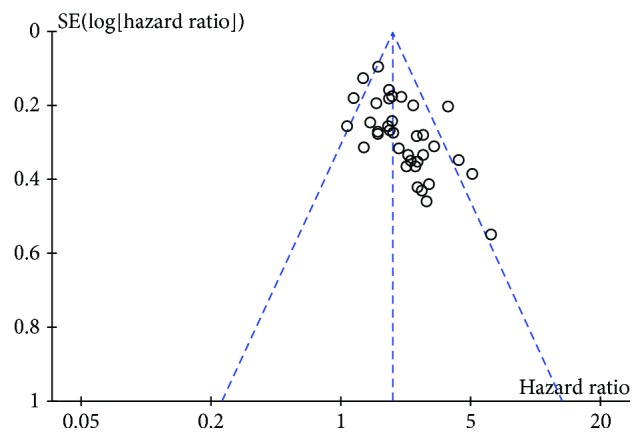
Funnel plot of included studies: aberrantly expressed lncRNAs related to disease-free survival in gastrointestinal cancer patients.
4. Discussion
GIC is still a huge threat to human health in spite of ongoing emergence of new anticancer drugs because of chemotherapy resistance and metastasis inducing poor prognosis. In the last decade, more and more studies focused on the clinical roles of lncRNAs and many reports indicated that lncRNA can be a molecular biomarker in gastrointestinal cancer patients for predicting prognosis. However, the prognostic value of lncRNAs that need to be clarified, verified, and summarized was limited by various research centers and small samples.
The purpose of this study was to elucidate the relationship between multiple lncRNA expressions and prognosis of GIC patients. Through big data meta-analysis, we provided evidence to illustrate the prognostic value of aberrantly expressed lncRNAs in GIC patients. The results from this meta-analysis showed that the pooled HR values (95% CI) of OS and DFS related to different lncRNA expressions in GIC patients were 2.00 (1.87–2.13) and 1.92 (1.73–2.14), respectively, which implied that aberrantly expressed lncRNAs may serve as cancer biomarkers in GIC patients. By detecting expression levels of specific lncRNAs in tissue or other body fluids, we cannot only make appropriate clinical decisions based on different prognoses but also monitor the therapeutic efficacy of GIC patients receiving different treatments. In addition, lncRNAs may be used to screen patients at high risk at the early stage based on abnormal expression. Moreover, elevated lncRNA-UCA1 expression promoted tumor cell migration, invasion, EMT, proliferation, and chemoresistance and inhibited its apoptosis by different target genes, which was associated with poor prognosis. For example, Jiao et al. [66] reported that lncRNA-UCA1 as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) of Sox4 enhanced tumor cell proliferation by targeting miR-204 and Sox4 and Bian et al. [96] demonstrated that lncRNA-UCA1 promoted tumor cell proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance by functioning as a ceRNA of miR-204-5p. The pooled HR value (95% CI) of OS which correlated with the expression of lncRNA-UCA1 was 2.42 (1.68–3.49) with low heterogeneity (P = 0.99, I2 = 0%) and statistically significant (P < 0.00001). Therefore, lncRNA-UCA1 as a molecular biomarker can be applied in predicting the prognosis of GIC patients. Generally, predicting prognosis of patients and exploring mechanisms of lncRNAs play pivotal roles in clinical decision-making and development of novel targeted gene therapies. Therefore, we summarized the researches involved in mechanisms of lncRNAs; we found that 37 lncRNAs had explicit targets and 11 lncRNAs as ceRNAs regulated cancer progression by sponging corresponding microRNAs. These studies demonstrated that the potential relationship between lncRNAs and microRNAs plays a key role in tumor pathogenesis and promoted carcinogenic study and development of gene therapy. Many studies focusing on the same lncRNA revealed different targets, and the underlying correlation between lncRNAs and microRNAs was still unclear. In the future, we should focus on the interrelationship between lncRNA and microRNA or other types of RNA, in achieving targeted treatment by simultaneous intervention of multiple types of RNA.
Several limitations should not be ignored. First, most of included patients were from East Asia, especially China, which makes our conclusions may just be suitable for Chinese patients. Second, the cut-off values and detection methods in evaluating different lncRNA expressions were various in different included studies, which may lead to heterogeneity between studies. Third, language bias was also one of the limitations, because we only enrolled English papers in the meta-analysis. Fourth, the majority of authors were generally more inclined to report positive results so that the pooled effect values calculated might overestimated the predictive significance of lncRNAs in prognosis of GIC patients; the publication bias have reached a consensus. Fifth, we calculated the HR estimates from the Kaplan-Meier survival curves because of some studies from which we could not extract HR and 95% CI directly. Sixth, the confounding factors in some included studies without the adjusted HR values would lead to high heterogeneity.
In summary, this meta-analysis supports the fact that specific lncRNAs are significantly related to the prognosis of GIC patients and may serve as novel markers for predicting the prognosis in GIC patients. In addition, lncRNAs may have a promising contribution to lncRNA-based targeted therapy and clinical decision-making in the future.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all authors of the included studies. This work was supported by the Natural Science Research Projects at Higher Institutions in Anhui Province (KJ2018ZD017).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Authors' Contributions
Weibiao Kang and Qiang Zheng contributed equally.
References
- 1.Jemal A., Bray F., Center M. M., Ferlay J., Ward E., Forman D. Global Cancer statistics. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2014 (ver. 4) Gastric Cancer. 2017;20(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/s10120-016-0622-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Suzuki H., Gotoda T., Sasako M., Saito D. Detection of early gastric cancer: misunderstanding the role of mass screening. Gastric Cancer. 2006;9(4):315–319. doi: 10.1007/s10120-006-0399-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McFarland E. G., Levin B., Lieberman D. A., et al. Revised colorectal screening guidelines: joint effort of the American Cancer Society, U.S. Multisociety Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and American College of Radiology. Radiology. 2008;248(3):717–720. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2483080842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zheng Q., Chen C., Guan H., Kang W., Yu C. Prognostic role of microRNAs in human gastrointestinal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(28):46611–46623. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cesana M., Cacchiarelli D., Legnini I., et al. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 2011;147(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wahlestedt C. Targeting long non-coding RNA to therapeutically upregulate gene expression. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2013;12(6):433–446. doi: 10.1038/nrd4018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhou X., Yin C., Dang Y., Ye F., Zhang G. Identification of the long non-coding RNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(1, article 11516) doi: 10.1038/srep11516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Qi P., Du X. The long non-coding RNAs, a new cancer diagnostic and therapeutic gold mine. Modern Pathology. 2013;26(2):155–165. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li X., Wu Z., Mei Q., et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a driver of malignancy, predicts negative prognosis and exhibits oncogenic activity in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. British Journal of Cancer. 2013;109(8):2266–2278. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ma Y., Yang Y., Wang F., et al. Long non-coding RNA CCAL regulates colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway via suppression of activator protein 2Α. Gut. 2016;65(9):1494–1504. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hu Y., Wang J., Qian J., et al. Long noncoding RNA GAPLINC regulates CD44-dependent cell invasiveness and associates with poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Research. 2014;74(23):6890–6902. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun M., Jin F. Y., Xia R., et al. Decreased expression of long noncoding RNA GAS5 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1) doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huarte M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nature Medicine. 2015;21(11):1253–1261. doi: 10.1038/nm.3981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kong R., Zhang E. B., Yin D. D., et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes cell proliferation through epigenetically regulating P 15 and P 16. Molecular Cancer. 2015;14(1):p. 82. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0355-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sun M., Nie F., Wang Y., et al. LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by scaffolding the chromatin modification factors PRC2, LSD1, and DNMT1. Cancer Research. 2016;76(21):6299–6310. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu Y., Xia R., Lu K., et al. LincRNAFEZF1-AS1 represses P 21 expression to promote gastric cancer proliferation through LSD1-mediated H3K4me2 demethylation. Molecular Cancer. 2017;16(1):p. 39. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0588-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang F., Xue X., Zheng L., et al. Long non-coding RNA GHET1 promotes gastric carcinoma cell proliferation by increasing c-Myc mRNA stability. The FEBS Journal. 2014;281(3):802–813. doi: 10.1111/febs.12625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen N., Guo D., Xu Q., et al. Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 facilitates cell proliferation and migration in colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(10):11271–11283. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li P., Zhang X., Wang H., et al. MALAT1 is associated with poor response to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients and promotes chemoresistance through EZH2. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2017;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Saito T., Kurashige J., Nambara S., et al. A long non-coding RNA activated by transforming growth factor-β is an independent prognostic marker of gastric cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2015;22(S3):915–922. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4554-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhao W., Dong S., Duan B., et al. HOTAIR is a predictive and prognostic biomarker for patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma receiving fluorouracil and platinum combination chemotherapy. American Journal of Translational Research. 2015;7(7):1295–1302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu T., Zhang X., Gao S., et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a novel serum-based biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(51):85551–85563. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang R., du L., Yang X., et al. Identification of long noncoding RNAs as potential novel diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology. 2016;142(11):2291–2301. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wu H., Zheng J., Deng J., et al. LincRNA-uc002yug.2 involves in alternative splicing of RUNX1 and serves as a predictor for esophageal cancer and prognosis. Oncogene. 2015;34(36):4723–4734. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yao G.-L., Pan C.-F., Xu H., et al. Long noncoding RNA RP11-766N7.4 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2017;88:778–785. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stroup D. F., Berlin J. A., Morton S. C., et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2000;283(15):2008–2012. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tierney J. F., Stewart L. A., Ghersi D., Burdett S., Sydes M. R. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007;8(1) doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-8-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li C., Zhou L., He J., Fang X. Q., Zhu S. W., Xiong M. M. Increased long noncoding RNA SNHG20 predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16(1):p. 655. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2719-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fan Y., Wang Y. F., Su H. F., et al. Decreased expression of the long noncoding RNA LINC00261 indicate poor prognosis in gastric cancer and suppress gastric cancer metastasis by affecting the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2016;9(1):p. 57. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0288-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 31.Qi F., Liu X., Wu H., et al. Long noncoding AGAP2-AS1 is activated by SP1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2017;10(1):p. 48. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0420-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen D., Ju H. Q., Lu Y. X., et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates gastric cancer progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-101 to modulate EZH2 expression. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2016;35(1):p. 142. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0420-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ye C., Shen Z., Wang B., et al. A novel long non-coding RNA lnc-GNAT1-1 is low expressed in colorectal cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor through regulating RKIP-NF-κB-snail circuit. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2016;35(1):p. 187. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0467-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xu M., Wang Y., Weng W., et al. A positive feedback loop of lncRNA-PVT1 and FOXM1 facilitates gastric cancer growth and invasion. Clinical Cancer Research. 2017;23(8):2071–2080. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yuan C. L., Li H., Zhu L., Liu Z., Zhou J., Shu Y. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNA PVT1 and its diagnostic and prognostic significance in patients with gastric cancer. Neoplasma. 2016;63(3):442–449. doi: 10.4149/314_150825N45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ye L., Ren L., Qiu J. J., et al. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in colorectal cancer with liver metastasis. Tumor Biology. 2015;36(11):8747–8754. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3627-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zheng Q., Wu F., Dai W. Y., et al. Aberrant expression of UCA1 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Clinical and Translational Oncology. 2015;17(8):640–646. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chen X., Kong J., Ma Z., Gao S., Feng X. Up regulation of the long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell progression and correlates with poor prognosis. American Journal of Cancer Research. 2015;5(9):2808–2815. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang Y. J., Liu J. Z., Lv P., Dang Y., Gao J. Y., Wang Y. Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes gastric cancer proliferation and invasion by regulating the E-cadherin and LATS2. American Journal of Cancer Research. 2016;6(11):2651–2660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhang Y., Yang R., Lian J., Xu H. LncRNA sox2ot overexpression serves as a poor prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer. American Journal of Translational Research. 2016;8(11):5035–5043. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen W., Huang M. D., Kong R., et al. Antisense long noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 is upregulated in gastric cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2015;60(6):1655–1662. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yue B., Sun B., Liu C., et al. Long non-coding RNA Fer-1-like protein 4 suppresses oncogenesis and exhibits prognostic value by associating with miR-106a-5p in colon cancer. Cancer Science. 2015;106(10):1323–1332. doi: 10.1111/cas.12759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.He X., Tan X., Wang X., et al. C-Myc-activated long noncoding RNA CCAT1 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Tumor Biology. 2014;35(12):12181–12188. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yin D., Liu Z. J., Zhang E., Kong R., Zhang Z. H., Guo R. H. Decreased expression of long noncoding RNA MEG3 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Tumor Biology. 2015;36(6):4851–4859. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nie F., Ma S., Xie M., Liu Y. W., de W., Liu X. H. Decreased long noncoding RNA MIR31HG is correlated with poor prognosis and contributes to cell proliferation in gastric cancer. Tumor Biology. 2016;37(6):7693–7701. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4644-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Park S.-M., Park S.-J., Kim H.-J., et al. A known expressed sequence tag, BM742401, is a potent lincRNA inhibiting cancer metastasis. Experimental & Molecular Medicine. 2013;45(7) doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li X., Wang F., Sun Y., Fan Q., Cui G. Expression of long non-coding RNA PANDAR and its prognostic value in colorectal cancer patients. The International Journal of Biological Markers. 2017;32(2):218–223. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chen J. S., Wang Y. F., Zhang X. Q., et al. H19 serves as a diagnostic biomarker and up-regulation of H19 expression contributes to poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Neoplasma. 2016;63(2):223–230. doi: 10.4149/207_150821N454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zou J. H., Li C. Y., Bao J., Zheng G. Q. High expression of long noncoding RNA Sox2ot is associated with the aggressive progression and poor outcome of gastric cancer. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2016;20(21):4482–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jiang L., Wang W., Li G., et al. High TUG1 expression is associated with chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology. 2016;78(2):333–339. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3066-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Svoboda M., Slyskova J., Schneiderova M., et al. HOTAIR long non-coding RNA is a negative prognostic factor not only in primary tumors, but also in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(7):1510–1515. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang Y., Zhang Q. Y., Weng W. W., et al. Upregulation of the non-coding RNA OTUB1-isoform 2 contributes to gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion and predicts poor gastric cancer prognosis. International Journal of Biological Sciences. 2016;12(5):545–557. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.13540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Guo X. B., Hua Z., Li C., et al. Biological significance of long non-coding RNA FTX expression in human colorectal cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2015;8(9):15591–15600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pan F., Yao J., Chen Y., et al. A novel long non-coding RNA FOXCUT and mRNA FOXC1 pair promote progression and predict poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2014;7(6):2838–2849. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhou B., Jing X. Y., Wu J. Q., Xi H. F., Lu G. J. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA LET is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2014;7(12):8893–8898. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hu Y., Pan J., Wang Y., Li L., Huang Y. Long noncoding RNA linc-UBC1 is negative prognostic factor and exhibits tumor pro-oncogenic activity in gastric cancer. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology. 2015;8(1):594–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang C. Y., Hua L., Yao K. H., Chen J. T., Zhang J. J., Hu J. H. Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 is up-regulated in gastric cancer and associated with poor prognosis. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2015;8(1):779–785. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ren Y. K., Xiao Y., Wan X. B., et al. Association of long non-coding RNA HOTTIP with progression and prognosis in colorectal cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2015;8(9):11458–11463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Liu Y., Zhang M., Liang L., Li J., Chen Y. X. Over-expression of lncRNA DANCR is associated with advanced tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2015;8(9):11480–11484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wang Y. L., Bai Y., Yao W. J., Guo L., Wang Z. M. Expression of long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its correlation with tumor progression and patient survival. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2015;8(9):11871–11876. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li L., Zhang L., Zhang Y., Zhou F. Increased expression of LncRNA BANCR is associated with clinical progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2015;72:109–112. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ma P., Xu T., Huang M., Shu Y. Increased expression of LncRNA PANDAR predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2016;78:172–176. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Huang C., Yu Z., Yang H., Lin Y. Increased MALAT1 expression predicts poor prognosis in esophageal cancer patients. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2016;83:8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ni B., Yu X., Guo X., et al. Increased urothelial cancer associated 1 is associated with tumor proliferation and metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. International Journal of Oncology. 2015;47(4):1329–1338. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Peng W., Wang Z., Fan H. LncRNA NEAT1 impacts cell proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer via regulation of Akt signaling. Pathology & Oncology Research. 2017;23(3):651–656. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Jiao C., Song Z., Chen J., et al. lncRNA-UCA1 enhances cell proliferation through functioning as a ceRNA of sox4 in esophageal cancer. Oncology Reports. 2016;36(5):2960–2966. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Liu J. N., Shangguan Y. M. Long non-coding RNA CARLo-5 upregulation associates with poor prognosis in patients suffering gastric cancer. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2017;21(3):530–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wu Z., Wang X. L., Tang H. M., et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a powerful predictor of metastasis and poor prognosis and is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer. Oncology Reports. 2014;32(1):395–402. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zhou P., Sun L., Liu D., Liu C., Sun L. Long non-coding RNA lincRNA-ROR promotes the progression of colon cancer and holds prognostic value by associating with miR-145. Pathology Oncology Research. 2016;22(4):733–740. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yang L., Wei H., Xiao H. J. Long non-coding RNA Loc 554202 expression as a prognostic factor in patients with colorectal cancer. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2016;20(20):4243–4247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lü M.-H., Tang B., Zeng S., et al. Long noncoding RNA BC032469, a novel competing endogenous RNA, upregulates hTERT expression by sponging miR-1207-5p and promotes proliferation in gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35(27):3524–3534. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Su J., Zhang E., Han L., et al. Long noncoding RNA BLACAT1 indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and affects cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of P 15. Cell Death & Disease. 2017;8(3):p. e2665. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Fu J., Kong Y., Sun X. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 is an unfavorable prognostic factor and regulates migration and invasion in gastric cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology. 2016;142(7):1571–1579. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Xie H.-W., Wu Q.-Q., Zhu B., et al. Long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and associated with poor prognosis. Tumor Biology. 2014;35(8):7743–7754. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2013-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Peng W., Wu G., Fan H., Wu J., Feng J. Long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 predicts poor patient prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis in gastric cancer. Tumor Biology. 2015;36(9):6751–6758. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nie F., Yu X., Huang M., et al. Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes gastric cancer cells proliferation by epigenetically repressing KLF2 and NKD2 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8(24):38227–38238. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ohtsuka M., Ling H., Ivan C., et al. H19 noncoding RNA, an independent prognostic factor, regulates essential Rb-E2F and CDK8-β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer. eBioMedicine. 2016;13:113–124. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Zhou X.-L., Wang W.-W., Zhu W.-G., et al. High expression of long non-coding RNAAFAP1-AS1predicts chemoradioresistance and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Molecular Carcinogenesis. 2016;55(12):2095–2105. doi: 10.1002/mc.22454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Xu M.-D., Qi P., Weng W.-W., et al. Long non-coding RNA LSINCT5 predicts negative prognosis and exhibits oncogenic activity in gastric cancer. Medicine. 2014;93(28, article e303) doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Sun J., Song Y., Chen X., et al. Novel long non-coding RNA RP11-119F7.4 as a potential biomarker for the development and progression of gastric cancer. Oncology Letters. 2015;10(1):115–120. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhang E., Kong R., Yin D. D., et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes tumor growth by epigenetically silencing of miR-99a/miR-449a. Oncotarget. 2014;5(8):2276–2292. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Li Y., Li Y., Chen W., et al. NEAT expression is associated with tumor recurrence and unfavorable prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(29):27641–27650. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Chen W., Huang M. D., Sun D. P., et al. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00152 promotes tumor cell cycle progression by binding to EZH2 and repressing P 15 and P 21 in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(9):9773–9787. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Han D., Gao X., Wang M., et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and promotes tumor growth by recruiting and binding to eIF4A3. Oncotarget. 2016;7(16):22159–22173. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Yang P., Chen T., Xu Z., Zhu H., Wang J., He Z. Long noncoding RNA GAPLINC promotes invasion in colorectal cancer by targeting SNAI2 through binding with PSF and NONO. Oncotarget. 2016;7(27):42183–42194. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Jin C., Shi W., Wang F., et al. Long non-coding RNA HULC as a novel serum biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction of gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(32):51763–51772. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Cao X.-G., Zhao R., Zhu C., et al. BC200 LncRNA a potential predictive marker of poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. OncoTargets and Therapy. 2016;9:2221–2226. doi: 10.2147/ott.s99401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Cao D., Ding Q., Yu W., Gao M., Wang Y. Long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 promotes malignant development of colorectal cancer by targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets and Therapy. 2016;9:5417–5425. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S111794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Gao X., Wen J., Gao P., Zhang G., Zhang G. Overexpression of the long non-coding RNA, linc-UBC1, is associated with poor prognosis and facilitates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in colorectal cancer. OncoTargets and Therapy. 2017;10:1017–1026. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S129343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wang F., Ni H., Sun F., Li M., Chen L. Overexpression of lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 correlates with poor prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2016;81:152–159. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ge X., Chen Y., Liao X., et al. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA PCAT-1 is a novel biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Medical Oncology. 2013;30(2):p. 588. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0588-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Deng Q., He B., Gao T., et al. Up-regulation of 91H promotes tumor metastasis and predicts poor prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(7, article e103022) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sun X., Hu Y., Zhang L., et al. Mining, validation, and clinical significance of colorectal cancer (CRC)-associated lncRNAs. PLoS One. 2016;11(10, article e0164590) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Xu T., Huang M. D., Xia R., et al. Decreased expression of the long non-coding RNA FENDRR is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer and FENDRR regulates gastric cancer cell metastasis by affecting fibronectin 1 expression. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2014;7(1):p. 63. doi: 10.1186/s13045-014-0063-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Shang C., Guo Y., Zhang J., Huang B. Silence of long noncoding RNA UCA1 inhibits malignant proliferation and chemotherapy resistance to adriamycin in gastric cancer. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology. 2016;77(5):1061–1067. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bian Z., Jin L., Zhang J., et al. LncRNA—UCA1 enhances cell proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-204-5p. Scientific Reports. 2016;6(1) doi: 10.1038/srep23892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Zuo Z. K., Gong Y., Chen X. H., et al. TGFβ1-induced LncRNA UCA1 upregulation promotes gastric cancer invasion and migration. DNA and Cell Biology. 2017;36(2):159–167. doi: 10.1089/dna.2016.3553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lu M., Liu Z., Li B., Wang G., Li D., Zhu Y. The high expression of long non-coding RNA PANDAR indicates a poor prognosis for colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis by EMT pathway. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology. 2017;143(1):71–81. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2252-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lv D., Sun R., Yu Q., Zhang X. The long non-coding RNA maternally expressed gene 3 activates P 53 and is downregulated in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Tumour Biology. 2016;37(12):16259–16267. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5426-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Xu J., Zhang R., Zhao J. The novel long noncoding RNA TUSC7 inhibits proliferation by sponging MiR-211 in colorectal cancer. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2017;41(2):635–644. doi: 10.1159/000457938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ma H. W., Xie M., Sun M., et al. The pseudogene derived long noncoding RNA DUXAP8 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via epigenetically silencing PLEKHO1 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8(32):52211–52224. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hu H.-b., Jie H.-Y., Zheng X.-X. Three circulating LncRNA predict early progress of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2016;40(1-2):117–125. doi: 10.1159/000452529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Fei Z. H., Yu X. J., Zhou M., Su H. F., Zheng Z., Xie C. Y. Upregulated expression of long non-coding RNA LINC00982 regulates cell proliferation and its clinical relevance in patients with gastric cancer. Tumour Biology. 2016;37(2):1983–1993. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3979-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Chen S., Yin J. F., Lin B. C., et al. Upregulated expression of long noncoding RNA SNHG15 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through regulates MMP2/MMP9 in patients with GC. Tumor Biology. 2016;37(5):6801–6812. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Tan W., Song Z. Z., Xu Q., et al. Up-regulated expression of SPRY4-IT1 predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Medical Science Monitor. 2017;23:309–314. doi: 10.12659/MSM.898369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wang W., Xing C. Upregulation of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 predicts poor prognosis and prompts invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Pathology - Research and Practice. 2016;212(8):690–695. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2016.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Yao W., Bai Y., Li Y., et al. Upregulation of MALAT-1 and its association with survival rate and the effect on cell cycle and migration in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biology. 2016;37(4):4305–4312. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Liu Z., Yang T., Xu Z., Cao X. Upregulation of the long non-coding RNA BANCR correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2016;82:406–412. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Chen F. J., Sun M., Li S. Q., et al. Upregulation of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and poor prognosis. Molecular Carcinogenesis. 2013;52(11):908–915. doi: 10.1002/mc.21944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Yu X., Yuan Z., Yang Z., et al. The novel long noncoding RNA U50535 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by regulating CCL20. Cell Death & Disease. 2018;9(7):p. 751. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0771-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Jiang H., Wang Y., Ai M., et al. Long noncoding RNA CRNDE stabilized by hnRNPUL2 accelerates cell proliferation and migration in colorectal carcinoma via activating Ras/MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Death and Disease. 2017;8(6, article e2862) doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Cui C., Zhai D., Cai L., Duan Q., Xie L., Yu J. Long noncoding RNA HEIH promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis via counteracting miR-939–mediated transcriptional repression of Bcl-xL. Cancer Research and Treatment. 2018;50(3):992–1008. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Wu S., Liu J., Wang X., Li M., Chen Z., Tang Y. Aberrant expression of the long non-coding RNAGHRLOS and its prognostic significance in patients with colorectal cancer. Journal of Cancer. 2017;8(19):4040–4047. doi: 10.7150/jca.21304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Yu Y., Li L., Zheng Z., Chen S., Chen E., Hu Y. Long non-coding RNA linc00261 suppresses gastric cancer progression via promoting Slug degradation. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2017;21(5):955–967. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Li Y., Wen X., Wang L., et al. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 predicts unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer. Surgical Oncology. 2017;26(4):527–534. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2017.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Huang M., Hou J., Wang Y., et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00673 is activated by SP1 and exerts oncogenic properties by interacting with LSD1 and EZH2 in gastric cancer. Molecular Therapy. 2017;25(4):1014–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.01.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 117.Li P.-D., Hu J.-L., Ma C., et al. Upregulation of the long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-203 and LASP1. Oncotarget. 2017;8(21):34164–34176. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Shi H., Liu Z., Pei D., Jiang Y., Zhu H., Chen B. Development and validation of nomogram based on lncRNA ZFAS1 for predicting survival in lymph node-negative esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8(35):59048–59057. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Wu X., Dinglin X., Wang X., et al. Long noncoding RNA XIST promotes malignancies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of miR-101/EZH2. Oncotarget. 2017;8(44):76015–76028. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Ba M. C., Long H., Cui S. Z., et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00673 epigenetically suppresses KLF4 by interacting with EZH2 and DNMT1 in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(56):95542–95553. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Zhu Y., Li B., Liu Z., et al. Up-regulation of lncRNA SNHG1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(67):111715–111727. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Yang X.-Z., He Q.-J., Cheng T.-T., et al. Predictive value of LINC01133 for unfavorable prognosis was impacted by alcohol in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2018;48(1):251–262. doi: 10.1159/000491724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Xu T., Wang W. Y., Ma P., et al. Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes carcinogenesis by epigenetically silencing EphB3 through EZH2 and LSD1, and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2018;37(36):5020–5036. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]