Abstract
Background
Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer worldwide and the second leading cause of cancer mortality. Chronic liver disease caused by viral infection, alcohol abuse, or other factors can lead to cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is the most important clinical risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) whereby the normal hepatic architecture is replaced by fibrous septa and a spectrum of nodules ranging from benign regenerative nodules to HCC, each one of them with different imaging features.
Conclusions
Furthermore, advanced techniques including the quantification of hepatic and intralesional fat and iron, magnetic resonance elastography, radiomics, radiogenomics, and positron emission tomography (PET)-MRI are highly promising for the extraction of new imaging biomarkers that reflect the tumor microenvironment and, in the future, may add decision-making value in the management of patients with HCC.
Key words: hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatic nodule, liver, cirrhosis, magnetic, resonance imaging
Introduction
Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer worldwide and the second leading cause of cancer mortality.1, 2, In the United States, approximately 42220 new cases of liver cancer will be diagnosed and 30200 deaths will occur in 2018.3 The incidence in men is three times higher than in women. Over a third of liver cancer consists of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In recent years, five-year survival rates of HCC have considerably improved due to earlier detection and curative therapies.4 However, the incidence is still rising in women while it has reached a plateau in men since 2010.3
The two most common risk factors of HCC are chronic infection from hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus and alcohol abuse.3 Other important risk factors include consumption of aflatoxin (toxin produced by a fungus that can infects grains, soybeans and peanuts) which occurs mainly in less developed countries and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease which occurs mainly in Western countries.2 Figure 1 demonstrates the geographical distribution of the main risk factors for HCC worldwide.
FIGURE 1.
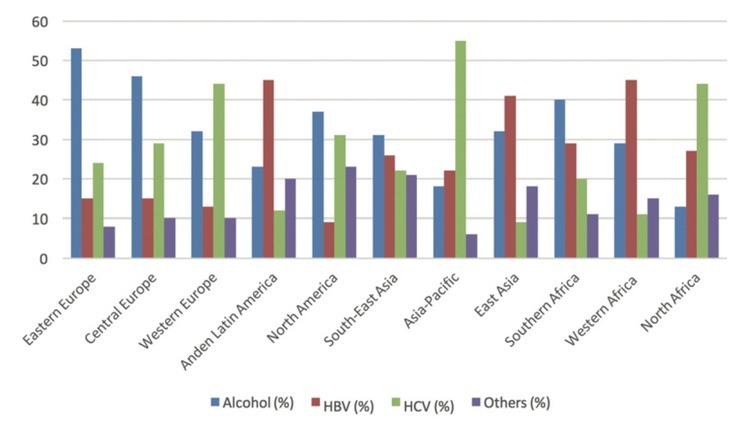
Geographical distribution of main risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide.
Chronic liver disease caused by viral infection, alcohol abuse, or other factors can lead to cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is the most important clinical risk factor for HCC whereby the normal hepatic architecture is replaced by fibrous septa and a spectrum of nodules ranging from benign regenerative nodules to HCC.5 The cirrhotic liver gives way to HCC via hepatocarcinogenesis, an anaplastic complex process characterized by stepwise accumulation of epigenetic and genetic alterations at the molecular and cellular level6, 7, and changes in the hepatic architecture seen at the histologic level. While initially hepatocarcinogenesis involves the replacement of normal hepatic architecture with regenerative nodules, this subsequently progresses to replacement with dysplastic nodules and then HCC. HCC itself progresses from well-differentiated to poorly differentiated HCC.6
The liver has a dual blood supply, i.e., the hepatic portal vein and the hepatic artery. In the normal liver, approximately 75% of the liver is supplied by the hepatic portal vein. However, during hepatocarcinogenesis, neoangiogenesis decreases the portal blood supply and increases the arterial supply relative to the degree of malignancy within the nodules. This allows lesions to be detected on imaging. Emerging evidence also suggests that in hepatocarcinogenesis, the expression levels of organic anionic transporting polypeptides (OATP), a bile salt transporter protein on hepatocytes membranes, diminishes even before neoangiogenesis, which may have implications for earlier radiological detection of lesions using hepatobiliary agents (Figure 2).7
FIGURE 2.
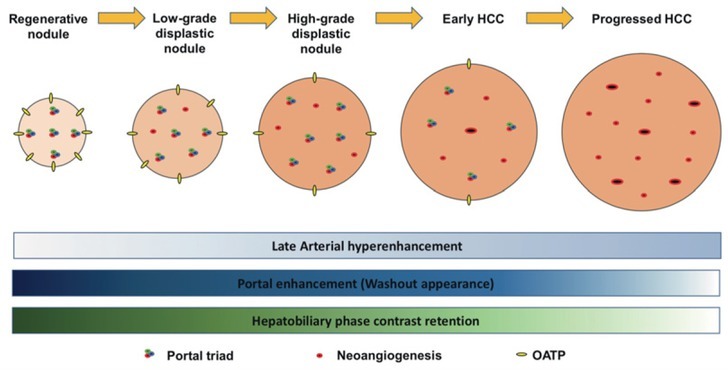
Graphic demonstrating hepatocarcinogenesis from regenerative nodules to progressed hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), emphasizing the proportion of portal triad, neoangiogenesis, and organic anionic transporting polypeptides, and, consequently, the pattern of enhancement on late arterial, portal, and hepatobiliary phases.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has rapidly evolved as a superior imaging technique in the oncologic field in the past few decades, having undergone improvements in its acquisition time and imaging quality. Multiple studies have demonstrated that MRI has excellent sensitivity and specificity for the detection and characterization of HCC compared with computed tomography (CT) and ultrasound.8, 9, 10, 11, However, mainly because of its high cost and limited availability especially in underdeveloped countries which bear a disproportionately high risk of HCC, its large-scale use for HCC screening is still restricted. Table 1 summarizes the main indications of MRI for HCC as recommended by the European Association (EASL) and American Association for the Study od Liver Diseases (AASLD) guidelines. 9, 10, 11, 12,
TABLE 1.
Main indications of MRI for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
| Main indications of MRI for HCC evaluation |
|---|
| Nodules larger than 1.0 cm identified on ultrasound |
| For patients on the orthotopic liver transplantation waiting list |
| When the imaging features of the nodule on CT are not elucidative |
| History of allergy to iodinated contrast agent used on CT scans |
| After locoregional therapy |
MRI protocol
Standardized MRI protocols for HCC surveillance must be developed to allow clinicians and technologists to perform repeatable and reproducible high-quality examinations.11 The minimum magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla (T) provides acceptable temporal, spatial, and contrast resolution that enable adequate assessment of hepatic lesions.12
The following sequences are essential for the diagnosis of HCC: T2-weighted imaging (WI); unenhanced T1WI opposed and in-phase; and multiphase T1WI (pre-contrast, late arterial, portal venous, and delayed or transitional phases). Slice thickness should be 5 mm or less for dynamic series and 8 mm or less for other imaging.13, 14,
Other sequences have been proposed to improve the detection of HCC, especially in cases of well-differentiated HCC or HCC post-treatment. These include diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) with apparent diffusion coefficient mapping, subtraction imaging, multi-planar acquisition, and hepatobiliary phase.14, 15, Table 2 summarizes these MRI sequences.
TABLE 2.
MRI sequences and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) features that can be assessed in each sequence
| MRI sequences | HCC imaging features |
|---|---|
| T2WI | Usually hyperintense |
| T1WI opposed and in-phase | Intralesional microscopic fat (lower signal on opposed-phase) or iron (lower signal on in-phase) |
| T1WI with fat saturation pre-contrast | Demonstrates the presence of macroscopic fat and blood products After locoregional therapies, hyperintensity indicates coagulative necrosis |
| Dynamic late arterial phase | Hyperenhancement |
| Dynamic portal venous phase | Washout and capsule appearance |
| Dynamic delayed phase | Washout and capsule appearance |
| Diffusion weighted imaging | Restricted diffusion (helps to identify small lesions) |
| Subtraction imaging | Characterizes contrast enhancement in spontaneously hyperintense nodules on T1WI pre-contrast (especially important for lesions with blood products and after locoregional treatment) |
| Multi-planar acquisition | Helps to differentiate HCC from mass-like lesions or extra-hepatic lesions |
| Hepatobiliary phase | Generally hypointense |
T1W1 = T1 weighted image; T2WI = T2 weighted image
DWI improves the characterization of liver nodules without requiring contrast media injection.15, 16, 17, Currently, DWI is used to increase the sensitivity of other sequences for the detection and characterization of HCC. Studies investigating the utility of DWI have demonstrated promising results for assessing prognosis, predicting response, distinguishing tumor from treatment effect, and monitoring response to therapy in patients with HCC.18, 19, 20, 21, 22,
Contrast media agents
Dynamic contrast-enhanced sequences are routinely performed with gadolinium-based extracellular contrast agents (ECA) or hepatobiliary contrast agents (HBA). They allow the diagnosis of HCC by exploiting the physiologic changes in blood flow that accompany hepatocarcinogenesis. Following administration of the contrast agent, the dual vascular supply of the liver is opacified in the following sequential order: the hepatic arteries, the portal veins, and finally the hepatic veins.7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
Typically, contrast agents are administered at rates of 2 mL/sec followed by saline infusion. The dose is usually based on body weight (ranging from 0.025 to 0.1 mmol gadolinium per kg) as well as on the agent and other factors.7
ECAs include gadoterate meglumine (Gd-DOTA) and gadopentate dimeglumine (Gd-DTPA) which are excreted primarily through glomerular filtration. The pattern of contrast enhancement can be studied in dynamic T1WI in the following phases: late arterial, portal venous, and delayed phases. HBAs include gadoxetate disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA) and gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA) which are excreted through glomerular filtration but are also taken up by hepatocytes and excreted into the biliary system. As such, HBAs provide additional information regarding the presence of hepatocytes with OATP, which decrease in hepatocarcinogenesis.23 With HBA administration, the pattern of contrast enhancement can be studied in the late arterial, portal venous, transitional, and hepatobiliary phases.
Recently, in Europe, the use of intravenous linear agents such as gadodiamide and intravenous gadopentate dimeglumine have been suspended or restricted in response to the retention of gadolinium in the brain and in other tissues as reported in a scientific review. 24 However, there is still no evidence that this deposition causes any harm to patients. Hepatobiliary linear contrast agents continue to be available as their properties allow the recognition of poorly vascularized hepatic lesions which cannot be studied with other agents. The macrocyclic agents (gadobutrol, gadoteric acid, and gadoteridol) have a lower propensity to release gadolinium than linear agents and can continue to be used in their current indications.24
Advanced techniques
Quantification of fat and iron
Liver biopsy is the gold standard for quantifying iron and fat in the liver. However, this method is invasive and susceptible to sampling variability. MRI is a non-invasive, alternative method to quantify iron and fat within the liver. There are several sequences that can be used to quantify iron and fat within the liver. Regarding iron, the following techniques can be employed: signal intensity ratio techniques based on T2WI or T2*WI, quantitative relaxometry (based mainly on T2WI but also on T1WI), and MR susceptometry.25, 26, In regards to fat, post-processing of T1WI in- and opposed-phase provides quantification from a scale of 0–50% while the proton density fat fraction allows quantification of a full fat fraction from 0–100%.27 Iron and fat content may contribute to differential diagnosis and may be a potential prognostic biomarker of HCC.28 However, the evidence is still limited and this method is not used in the daily practice.
Magnetic resonance elastography
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) is an imaging modality used to stage liver fibrosis.29, 30, Recent studies have demonstrated the use of MRE for the evaluation of HCC with promising results for the prediction of tumor grade31 and assessment of treatment response.32 Well/moderately differentiated tumors demonstrated increased stiffness compared to poorly differentiated ones and there was a correlation between the percentage of tumor necrosis and tumor stiffness, particularly in HCCs treated with radioembolization.31 However, the evidence is still limited and MRE is not yet routinely implemented.
Imaging features on MRI
Regenerative nodules
Regenerative nodules correspond to an area of parenchyma surrounded by fibrosis. These nodules are usually similar to background liver parenchyma but some may exhibit a fine area of peripheral late-phase enhancement corresponding to fibrosis. Regenerative nodules may present accumulation of iron which results in low signal intensity on T1-and T2-weighted imaging.6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32,
Dysplastic nodules
Dysplastic nodules contain atypical cells but without malignancy on histological analysis. The radiological pattern of dysplastic nodules is variable and can be similar to regenerative nodules (in those with low-grade dysplasia) or well-differentiated HCC (in those with high-grade dysplasia).33, 34, 35, These lesions often present as iso- or hypointense on T2-weighted imaging and are frequently hypovascular. Occasionally, a mildly elevated signal intensity may occur within a low signal-intensity nodule on T2-weighted imaging. This represents foci of HCC (the foci of high signal intensity) within a dysplastic nodule (the area with low signal intensity). The foci of HCC may also enhance in the arterial phase.35
HCC
HCC has a wide spectrum of radiological characteristics depending on its size and degree of histological differentiation. HCC can be classified as early or progressed HCC.
Early HCC often measures less than 2.0 cm and sometimes appears similar to high-grade dysplastic nodules on imaging. Histologically, it differs from dysplastic nodules because of stromal invasion. Radiologically, it has higher T2WI signal intensity, hypo- or iso- vascularization in the arterial phase, and washout appearance in the delayed phase.7 Mild restricted diffusion has improved the sensitivity for HCC detection, mostly for small HCC, especially well-differentiated HCC with atypical postcontrast imaging patterns.36
Progressed HCCs are malignant lesions with the ability to invade vascular planes and metastasize. The radiological pattern is variable, but frequently a mosaic pattern is exhibited due to nodular areas’ being interspersed by areas of hemorrhage, arteriovenous shunting, fibrosis, and necrosis. The main findings are: high signal intensity on T2-weighted imaging (Figures 3–Figures 4), hyperenhancement on arterial phase (Figures 3–Figures 7), washout appearance on delayed phase (Figures 3–5), and nodules that are surrounded by a capsule / pseudocapsule (more evident in the delayed phase) (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
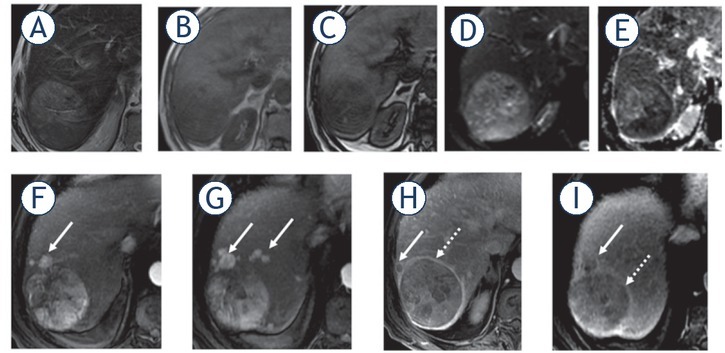
53-year-old man with cirrhosis due to hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic nodule in segment VII with high signal intensity on T2 weighted image (T2WI) (A); with fat content (B, C) demonstrated by reduction of signal intensity on T1 weighted image (T1WI) opposite phase (C) when compared with T1WI in-phase (B); restriction on diffusion (D, E) characterized by high signal on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) (D) and low signal on the apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) map (E). On dynamic phases (F-I), the nodule showed arterial hypervascular enhancement in the late arterial phase (F); mosaic architecture (F-I); washout appearance in the portal venous (H) and delayed (I) phases; and capsule (dashed arrows) (H-I) and satellites nodules (arrows) with the same pattern of enhancement (F-I).
FIGURE 4.
63-year-old man with chronic hepatitis C and HCC with tumor invasion within the portal vein. Main and right portal veins demonstrate dilation (arrows), high signal intensity on T2 weighted image (T2WI) (A), restriction on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) (B,C).
FIGURE 7.
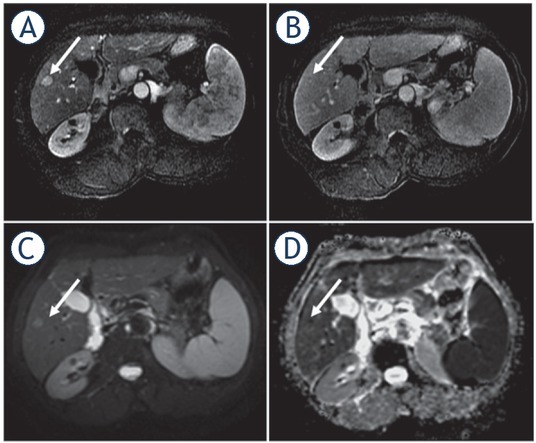
59-year-old woman with cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis B and small HCC. Small nodule (arrows) in segment V with arterial phase hyperenhancement (A), without washout appearance (B), and with diffusion restriction (C, D). The patient underwent percutaneous biopsy with the diagnosis of well-differentiated HCC.
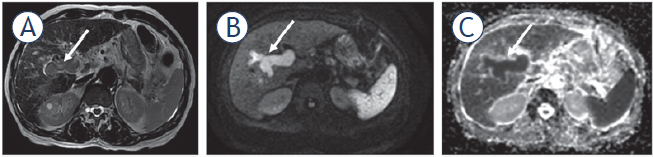
FIGURE 5.
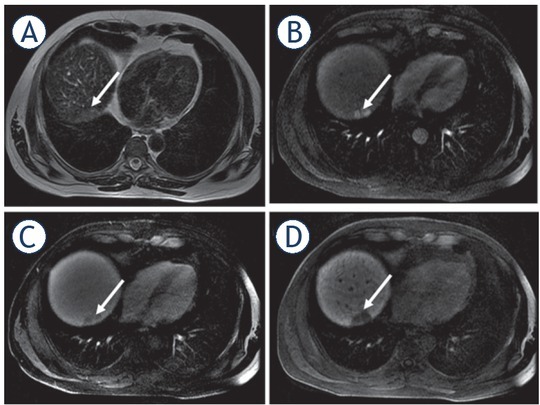
49-year-old woman with cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis C had a new hepatic nodule detected on screening ultrasound which was confirmed as HCC on MRI with hepatobiliary contrast agent. Hepatic nodule in segment VII (arrows) with high signal intensity on T2 weighted image (T2WI) (A), hyperenhancement in the late arterial phase (B), washout appearance (C), and hypointense appearance in the hepatobiliary phase.
HCC may also be classified according to its growth patterns / macroscopic appearance into: single nodular type, well-defined, encapsulated with better prognosis; or multifocal type (multiple nodules in several hepatic segments), with a diffuse pattern, usually extensive, heterogeneous, with variable enhancement, usually better detected in the delayed phase (hypoenhancement), and often associated with vascular invasion (Figures 4).35, 36, 37, Table 3 summarizes the main imaging features of HCC.
TABLE 3.
Main imaging features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
| Imaging features | Description |
|---|---|
| Arterial hyperenhancement | Increased enhancement in the arterial phase. Reflects tumor neoangiogenesis. |
| Washout appearance | Hypoenhancement of the lesion compared with background liver tissue. Secondary to HCC extracellular reduced volume, rapid venous drainage and reduced intranodular portal venous supply. |
| Capsule appearance | Observed in approximately 80% of HCCs, detected on delayed phase, secondary to the lack of portal supply to malignant nodules. Corresponds to a pseudocapsule consisting of compressed adjacent liver parenchyma with occasional nonspecific inflammatory cells on histology. |
| Portal vein tumoral thrombosis | HCC invades and grows within the lumen. The vein appears dilated and with the same pattern of enhancement observed in the nodule. |
| T2 hyperintensity | The elevated signal intensity on T2WI can be useful to differentiate HCC from dysplastic nodules. |
| Restricted diffusion | Mildly elevated signal relative to the surrounding liver parenchyma on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and low signal intensity on apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) map. |
| Corona enhancement | Enhancement of the peritumoral parenchyma after enhancement of the tumor itself, because of the passage of contrast through the draining sinusoids and portal venules into the surrounding sinusoids. |
| Intralesional fat | Loss of signal on the opposed-phase T1WI compared with the in-phase images. |
| Lesion iron sparing | Siderotic nodule is likely to be a dysplastic nodule. Development of an iron-free around the nodule suggests HCC foci. |
| Mosaic architecture | Nodular areas interspersed by areas of fibrosis, hemorrhage, arteriovenous shunting and necrosis. Characteristic of progressed HCCs. |
| Nodule-in-nodule architecture | Mildly elevated signal intensity on T2WI within nodule with low signal intensity, representing the focus of HCC within the low density dysplastic nodule, that may also enhance in the arterial phase. |
| Transitional phase hypointensity | Hypointensity compared with background liver following administration of a hepatobiliary contrast agent (2–5 minutes after contrast media administration). |
| Hepatobiliary phase hypointensity | Hypointensity compared with background liver following administration of a hepatobiliary contrast agent (20 minutes after). |
T1W1 = T1 weighted image; T2WI = T2 weighted image
Atypical HCC
A minority of HCC presents atypical imaging features and awareness of these is important for early diagnosis and improving patient outcomes. Most of these cases are challenging and biopsy may be needed for confirmatory diagnosis.
Atypical enhancement patterns
Hypervascular nodules without washout appearance: Well-differentiated and small HCC lesions may show atypical patterns of enhancement with lack of or poor arterial phase enhancement and persistent enhancement in the venous and delayed phases (Figures 7).38, 39, Differential diagnoses are benign hypervascular lesions (e.g., hemangioma, focal nodular hyperplasia, and adenomas) and hypervascular metastasis.
Hypovascular nodules: Only about 10% of HCC are hypovascular38 and the diagnosis can be challenging. However, in a patient with high risk to develop HCC, hypovascular nodules are suspicious.
Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma
Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma is a rare aggressive form of HCC characterized by poorly defined margins and atypical enhancement patterns (mild heterogeneous enhancement, most commonly hypovascular). Frequently, there is involvement of the portal and hepatic veins with thrombosis (Figures 8).38
FIGURE 8.
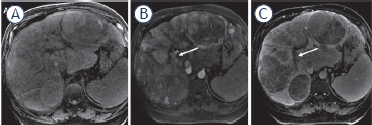
69-year-old man with cirrhosis due to alcohol with diffuse infiltrative HCC (A). Diffuse hepatic mass with areas of hypervascular arterial phase (B) and washout appearance (C), with tumoral thrombus within the right portal vein (arrows).
Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver
Twenty percent of HCCs may occur in a non-cirrhotic liver. The radiological appearance of such HCCs is larger, well-demarcated, solitary lesions with large areas of necrosis; they are usually diagnosed at a later stage.4 0
Differential diagnosis
Although arterial hyperenhancement is considered the most consistent feature of HCC, it is also present in other non-malignant lesions especially small non-malignant ones, which contributes to the high incidence of false positives.
Vascular disorders
Transient arterial enhancement due to focal obstruction of a distal parenchymal portal vein or nontumorous arterioportal shunts, for example, is often seen in the cirrhotic liver. Usually, these vascular disorders are peripheral, wedge-shaped lesions, isointense to surrounding parenchyma on pre-contrast images and do not present restricted diffusion or displace internal vasculature.36, 37, 38,
Focal confluent hepatic fibrosis
Observed in end-stage liver disease, focal confluent hepatic fibrosis can be mass-like and mistaken for HCC once it presents similar low signal intensity relative to the liver on T1WI and hyperintensity on T2WI. However, unlike HCC, it is usually associated with atrophy and capsular retraction of the affected segment, as well as delayed contrast enhancement. 36, 37, 38,
Hemangiomas, focal nodular hyperplasia, and hepatic adenomas
Other benign lesions such as hemangiomas, focal nodular hyperplasia, and hepatic adenomas are rare in the cirrhotic liver, probably because of the process of cirrhosis, and they can be difficult to distinguish from HCC. 36, 37, 38,
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma usually shows rim enhancement with progressive and concentric filling of contrast material in the later phases, which would be an atypical pattern of enhancement for HCC (Figure 9). Other features more commonly associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma than HCC are intrahepatic biliary duct dilation distal to the tumor and associated capsular retraction. Association with tumoral thrombosis is rare and when narrowing or obstruction of the portal vein occurs, the latter are usually due to external compression .18
FIGURE 9.
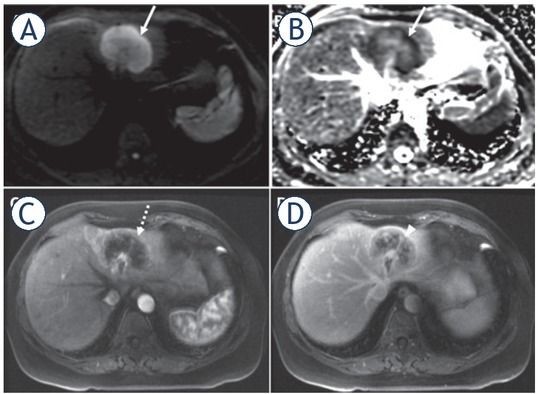
65-year-old woman without liver disease with surgically-proven intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma confirmed. Nodule in the left hepatic lobe with peripheral restricted diffusion (arrows) (A, B), rim of arterial hyperenhancement (dashed arrow), and peripheral washout appearance (arrowhead).
Hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CC) is a rare variant of primary hepatic cancer that is clinically and pathologically distinct from pure HCC. Imaging features are variable depending on the predominant histologic component, and although they overlap more frequently with those of cholangiocarcinoma, they can also mimic HCC.18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, cHCC-CC may appear hypointense on T1WI and iso to hyperintense on T2WI with or without central hypointense focus, which represents a central cholangiocarcinoma or fibrotic component.19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, On dynamic imaging, early ring enhancement with centripetal progression or heterogeneous early enhancement with partial washout are possible presentations.41 On MR imaging with a hepatocellular agent, irregular shape, strong peripheral enhancement, and absence of target sign favor cHCC-CC, particularly the HCC predominant type.42
Hypervascular metastases
Hypervascular metastases may also be a diagnostic challenge and typically arise from primary neuroendocrine tumors (pancreatic islet cell tumor, carcinoid tumor, and pheochromocytoma), renal cell carcinoma, thyroid carcinoma, choriocarcinoma, and melanoma.43 They are generally irregular with indistinct margins and hyperintense on T2WI with a central cystic or necrotic component and with a variable sign on T1WI, depending on the presence of blood, melanin, and other substances that present high signal on this sequence. On dynamic imaging, they show perilesional rim enhancement and irregular washout on delayed images.44
MRI after locoregional therapy of HCC
Surgical resection or transplantation is the standard treatment of HCC. However, most patients are not eligible for resection and the waiting list for liver transplantation is long. Locoregional therapies can be performed as curative treatment, mainly in small HCC, or as a bridge before transplantation. The goal of locoregional therapy is to achieve tumor necrosis. Overall, treated tumors appear with no internal enhancement on postcontrast phases and viable tumors may have areas of arterial phase hyperenhancement with or without washout appearance (Figures 6).44, 45, Table 4 shows the main systems used to assess tumor response after locoregional treatment.
FIGURE 6.
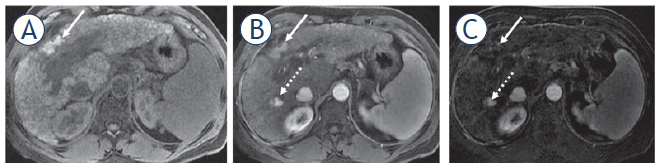
62-year-old man with cirrhosis due to alcohol with a history of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of a nodule in segment IV. On pre-contrast T1 weighted image (T1WI) with fat suppression (A) there is high signal intensity within the treated area (arrows) that was maintained in the arterial phase (B); however, on subtraction no enhancement is detected (C), which is compatible with no viable tumor. New HCC appeared during the follow-up in the segment VI (dashed arrow) with a true arterial hyperenhancement.
TABLE 4.
Main classifications used to assess tumor response after locoregional treatment
| Criteria | System | Response | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | WHO | CR | Disappearance of all TL |
| PR | ≥ 50% decrease in CP of TL | ||
| SD | < 50% decrease to ≤25% increase in CP of TL | ||
| PD | > 25% increase from maximum response of TL | ||
| RECIST | CR | Disappearance of all TL | |
| PR | ≥ 30% decrease in MD of TL | ||
| SD | < 30% decrease to ≤20% increase in MD of TL | ||
| PD | > 20% increase from maximum response of TL | ||
| Necrosis | mRECIST | CR | Disappearance of any intratumoral enhancement in all TL |
| PR | ≥ 30% decrease in SMD of enhancing tissue in TL | ||
| SD | < 30% decrease to ≤20% in SMD of enhancing tissue in TL | ||
| PD | > 20% increase in amount of enhancing tissue in TL | ||
| EASLmeas | CR | Disappearance of any intratumoral enhancement in all TL | |
| and | PR | ≥ 50% decrease in amount of enhancing tissue in TL | |
| EASLest | SD | < 50% decrease in amount of enhancing tissue in TL | |
| PD | > 25% increase in amount of enhancing tissue in TL and/or new enhancement in previously treated lesions | ||
| LI-RADS | Nonviable | No suspicious lesion enhancement | |
| Equivocal | Atypical enhancement not meeting criteria to viable tumor | ||
| Viable | Nodular, mass-like, or thick irregular tissue in or along the treated lesion with any of the following: arterial phase hyperenhancement or washout appearance or enhanced similar to pretreatment 100% of tumor necrosis or reduction | ||
| RECICL | TE4 a | Necrotized area larger than the tumor (enough ablative margin) | |
| b | Necrotized area similar in size to the tumor (insufficient ablative margin) | ||
| TE3 | 50–100% of tumor necrosis or reduction | ||
| TE2 | Other effect than TE3 and TE1 | ||
| TE1 | Tumor enlargement of > 25% regardless of necrosis |
CR = complete response, CP = cross-product, EASL = European Association for the Study of Liver, LI-RADS = Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System, MD = maximum diameter, PD = progressive disease, PR = partial response, RECIST = Response Evaluation Criteria for Solid Tumors, mRECIST = modified RECIST, RECICL = Response Evaluation Criteria in Cancer of the Liver, SD = stable disease, SMD = sum of maximum diameters, TE = treatment effect, TL = target lesion(s), WHO = World Health Organization
Diagnostic performance
The imaging diagnosis of HCC using only the features on dynamic MRI is highly specific. The overall MRI sensitivity for detection of HCC is 81%, against 68% using CT.46 The dynamic contrast enhanced arterial phase is the most sensitive and specific sequence (>95%).47
MRI is especially sensitive for the detection of lesions larger than 2 cm. On the other hand, for the detection of small tumors, although MRI still outperforms CT, the sensitivity remains disappointing.48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, This can be explained by the high frequency of atypical enhancement patterns these small lesions present.52 Regarding contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), it is not recommended as a first-line imaging technique, but improvements have been made in the differential diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma and some studies have shown it to be more specific than CT and MRI for nodules between 10 and 20 mm.12 Table 5 summarizes and compares the sensitivity of MRI, CT, and CEUS for the detection of HCC according to tumor size.51
TABLE 5.
MRI and CT estimated sensitivity for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
| MRI | CT | CEUS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 82% | 77% | 73% |
| Tumor size ≥ 2 cm | 96% | 94% | 94% |
| Tumor size < 2 cm | 66% | 63% | 77% |
CEUS = contrast-enhanced ultrasound
As an attempt to improve the performance of MRI among small HCC, the combined use of DWI with conventional dynamic MRI54 as well as the use of contrast agents other than gadolinium-based contrast media have been proposed.55 The combination of super-paramagnetic iron oxide particles with gadolinium-based contrast media have been shown to increase the sensitivity for the detection of HCC measuring 1–2 cm to 92%.56
After local therapies, MRI has also shown to be specific but not sensitive for the detection of small foci of recurrent or residual tumor.57, 58, In this context, DWI has shown promising results for evaluating response to treatment.
Future directions
Radiomics
Advances in technology have allowed for quantitative features to be extracted from imaging scans, adding value to clinical decision-making. In oncology, quantitative radiomics features may allow for the assessment of tumor characteristics including cellularity, perfusion, and oxygenation that can help in characterizing tumors characterization, assessing treatment response, and predicting treatment response. Considering that MRI involves different sequences with several physical mechanisms, the use of MRI in radiomics is promising.59
Radiogenomics
Both quantitative and qualitative data extracted from imaging scans can also be correlated with genetic profiles. It has been demonstrated that imaging phenotypes reflect underlying genomics59 and can guide the treatment of those patients, which is important in the new era of personalized medicine.
Positron emission tomography (PET)-MRI
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)-MRI combines high contrast and anatomical resolution from MRI with wide metabolic properties from PET. This technique is promising considering several new radiotracers. PET-MRI could be especially beneficial for evaluating tumor characteristics.60, 61, 62,
While conventional imaging modalities (MRI and CT) are preferable for detecting HCC, PET can offer additional information about functional or metabolic characteristics of the tumor. Several radiotracers have been used to achieve this objective, including 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) to estimate glucose consumption and choline labelled with either 11C (Cho) or 18F (FCho) to reflect cell-membrane metabolism and tumor proliferation.63, 64, 65,
18F-FDG is the most widely used radiotracer in oncology and has great sensitivity for detecting metastases from most cancers. FDG uptake correlates with the degree of HCC differentiation, with a higher avidity for poorly differentiated HCC.66 On the other hand, choline shows strong avidity for HCC, especially in well and moderately-differentiated tumors.68 Some studies showed that a dual-tracer PET using FDG and choline has the best performance to detect HCC66, 67, 68, as these tracers complement each other in the detection of HCC based on its histological differentiation. This combination may also be a prognostic indicator, with worst outcomes associated with FDG-PET captation.68
Perfusion MRI
Perfusion MRI is a function imaging technique that can provide quantitative data regarding tumor microvasculature. Several studies demonstrated that perfusion MRI can assess tumor response after locoregional therapies, such as transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation.69, 70, Perfusion MRI can detect vasculature changes of HCC before and after therapy. It is a promising tool in the diagnosis of HCC, as it can be used to target lesions for therapy, to evaluate the efficacy of the treatments and to evaluate recurrence.69, 70, 71
Conclusions
In summary, MRI is an essential imaging modality in the diagnostic arsenal of HCC and is especially indicated for the evaluation of small lesions, unclear lesions on CT, and lesions after locoregional therapies. Considering the multiple sequences included on MRI, there is a huge potential to extract several imaging biomarkers that reflect the tumor microenvironment and which, in the future, may add decision-making value in the management of patients with HCC.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Joanne Chin for her editorial support on this manuscript.
This research was funded in part through the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA008748. The work by Romina Grazia Giancipoli was partially supported by a scholarship awarded by ISSNAF Imaging Science Chapter.
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
References
- 1.Ferenci P, Fried M, Labrecque D, Bruix J, Sherman M, Omata M. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a global perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:239–45. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181d46ef2. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;2015;65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tang A, Hallouch O, Chernyak V, Kamaya A, Sirlin CB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: target population for surveillance and diagnosis. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2018;43:13–25. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krinsky GA, Lee VS. MR imaging of cirrhotic nodules. Abdom Imaging. 2000;25:471–82. doi: 10.1007/s002610000015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nishida N, Goel A. Genetic and epigenetic signatures in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Curr Genomics. 2011;12:130–7. doi: 10.2174/138920211795564359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Choi JY, Lee JM, Sirlin CB. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: part I. Development, growth, and spread: key pathologic and imaging aspects. Radiology. 2014;272:635–54. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14132361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Crissien AM, Frenette C. Current management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY) 2014;10:153–61. PMCID: PMC4014047. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.European Association For The Study Of The Liver, European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:908–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Elsayes KM, Hooker JC, Agrons MM, Kielar AZ, Tang A, Fowler KJ. Version of LI-RADS for CT and MR imaging: an update. Radiographics. 2017;2017;37:1994–2017. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017170098. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Arif-Tiwari H, Kalb B, Chundru S, Sharma P, Costello J, Guessner RW. MRI of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update of current practices. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014;20:209–21. doi: 10.5152/dir.2014.13370. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, Sirlin CB, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2018;67:358–80. doi: 10.1002/hep.29086. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wald C, Russo MW, Heimbach JK, Hussain HK, Pomfret EA, Bruix J. New OPTN/UNOS policy for liver transplant allocation: standardization of liver imaging, diagnosis, classification, and reporting of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2013;266:376–82. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12121698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kambadakone AR, Fung A, Gupta RT. LI-RADS technical requirements for CT, MRI, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2018;43:56–74. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1345-7. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Le Moigne F, Durieux M, Bancel B, Boublay N, Boussel L, Ducerf C. Impact of diffusion-weighted MR imaging on the characterization of small hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30:656–65. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.01.002. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mannelli L, Nougaret S, Vargas HA, Do RK. Advances in diffusion-weighted imaging. Radiol Clin North Am. 2015;53:569–81. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2015.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mannelli L, Bhargava P, Osman SF, Raz E, Moshiri M, Laffi G. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: a comprehensive review. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2013;42:77–83. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2012.07.001. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Horvat N, Nikolovski I, Long N, Gerst S, Zheng J, Pak LM. Imaging features of hepatocellular carcinoma compared to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and combined tumor on MRI using liver imaging and data system (LI-RADS) version. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2014;2018;43:169–78. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1261-x. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mannelli L, Kim S, Hajdu CH, Babb JS, Taouli B. Serial diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: prediction and assessment of response to transarterial chemoembolization. Preliminary experience. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:577–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chegai F, Merolla S, Greco L, Nezzo M, Mannelli L, Orlacchio A. Re: Baseline and early MR apparent diffusion coefficient quantification as a predictor of response of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma to doxorubicin drug-eluting bead chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27:1456–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gluskin JS, Chegai F, Monti S, Squillaci E, Mannelli L. Hepatocellular carcinoma and diffusion-weighted MRI: detection and evaluation of treatment response. J Cancer. 2016;7:1565–70. doi: 10.7150/jca.14582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Park MS, Kim S, Patel J, Hajdu CH, Do RK, Mannelli L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with diffusion-weighted versus contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in pretransplant patients. Hepatology. 2012;56:140–8. doi: 10.1002/hep.25681. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Agostini A, Kircher MF, Do R, Borgheresi A, Monti S, Giovagnoni A. Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver (including biliary contrast agents) part 1: technical considerations and contrast materials. Semin Roentgenol. 2016;51:308–16. doi: 10.1053/j.ro.2016.05.015. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ramalho J, Ramalho M. Gadolinium deposition and chronic toxicity. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2017;25:765–78. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2017.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hernando D, Levin YS, Sirlin CB, Reeder SB. Quantification of liver iron with MRI: state of the art and remaining challenges. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;40:1003–21. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Agostini A, Kircher MF, Do RK, Borgheresi A, Monti S, Giovagnoni A. Magnetic resonanance imaging of the liver (including biliary contrast agents) part 2: protocols for liver magnetic resonanance imaging and characterization of common focal liver lesions. Semin Roentgenol. 2016;51:317–33. doi: 10.1053/j.ro.2016.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu D, Song B, Huang ZX, Wu B, Tang HH. [The iron content of hepatocellular carcinoma associated nodules: study of histopathology and MR imaging] Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;47:376–81. [Chinese] PMID: 27468484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Siripongsakun S, Lee JK, Raman SS, Tong MJ, Sayre J, Lu DS. MRI detection of intratumoral fat in hepatocellular carcinoma: potential biomarker for a more favorable prognosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199:1018–25. doi: 10.2214/AJR.12.8632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Singh S, Venkatesh SK, Loomba R, Wang Z, Sirlin C, Chen J. Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a diagnostic accuracy systematic review and individual participant data pooled analysis. Eur Radiol. 2016;26:1431–40. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3949-z. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Thompson SM, Wang J, Chandan VS, Glaser KJ, Roberts LR, Ehman RL. MR elastography of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation of tumor stiffness with histopathology features-preliminary findings. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;37:41–5. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2016.11.005. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gordic S, Ayache JB, Kennedy P, Besa C, Wagner M, Bane O. Value of tumor stiffness measured with MR elastography for assessment of response of hepatocellular carcinoma to locoregional therapy. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017;42:1685–94. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1066-y. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hanna RF, Aguirre DA, Kased N, Emery SC, Peterson MR, Sirlin CB. Cirrhosis-associated hepatocellular nodules: correlation of histopathologic and MR imaging features. Radiographics. 2008;28:747–69. doi: 10.1148/rg.283055108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Efremidis SC, Hytiroglou P. The multistep process of hepatocarcinogenesis in cirrhosis with imaging correlation. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:753–64. doi: 10.1007/s00330-001-1142-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Efremidis SC, Hytiroglou P, Matsui O. Enhancement patterns and signal-intensity characteristics of small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: pathologic basis and diagnostic challenges. Eur Radiol. 2007;17:2969–82. doi: 10.1007/s00330-007-0705-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jeong YY, Yim NY, Kang HK. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver with helical CT and MRI: imaging spectrum and pitfalls of cirrhosis-related nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:1024–32. doi: 10.2214/AJR.04.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sadek AG, Mitchell DG, Siegelman ES, Outwater EK, Matteucci T, Hann HW. Early hepatocellular carcinoma that develops within macroregenerative nodules: growth rate depicted at serial MR imaging. Radiology. 1995 doi: 10.1148/radiology.195.3.7754006. 195753-6. doi. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Willatt JM, Hussain HK, Adusumilli S, Marrero JA. MR Imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: challenges and controversies. Radiology. 2008;247:311–30. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2472061331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Roumanis PS, Bhargava P, Kimia Aubin G, Choi JI, Demirjian AN, Thayer DA. Atypical magnetic resonance imaging findings in hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2015;44:237–45. doi: 10.1067/j.cpra-diol.2014.03.002. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mannelli L, Hoang MV, Sabath AP, Linnau KF. An unusual oral mass. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:e14–5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Trevisani F, Frigerio M, Santi V, Grignaschi A, Bernardi M. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver: a reappraisal. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42:341–7. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Potretzke TA, Tan BR, Doyle MB, Brunt EM, Heiken JP, Fowler KJ. Imaging features of biphenotypic primary liver carcinoma (hepatocholangiocarcinoma) and the potential to mimic hepatocellular carcinoma: LI-RADS analysis of CT and MRI features in 61 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207:25–31. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Maximin S, Ganeshan DM, Shanbhogue AK, Dighe MK, Yeh MM, Kolokythas O. Current update on combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma. Eur J Radiol Open. 2014;1:40–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2014.07.001. et al. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mannelli L, Monti S, Grieco V, Matesan M. Hepatic lesions in a cirrhotic liver: primary or metastases? J Nucl Med Technol. 2017;45:50–2. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.116.183228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Khosa F, Khan AN, Eisenberg RL. Hypervascular liver lesions on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:W204–20. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.5382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ayuso C, Rimola J, Garcia-Criado A. Imaging of HCC. Abdom Imaging. 2012;37:215–30. doi: 10.1007/s00261-011-9794-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mannelli L, Kim S, Hajdu CH, Babb JS, Clark TW, Taouli B. Assessment of tumor necrosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after chemoembolization: diffusion-weighted and contrast-enhanced MRI with histopathologic correlation of the explanted liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193:1044–52. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Colli A, Fraquelli M, Casazza G, Massironi S, Colucci A, Conte D. Accuracy of ultrasonography, spiral CT, magnetic resonance, and alpha-fetoprotein in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:513–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00467.x. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Becker-Weidman DJ, Kalb B, Sharma P, Kitajima HD, Lurie CR, Chen Z. Hepatocellular carcinoma lesion characterization: single-institution clinical performance review of multiphase gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging-comparison to prior same-center results after MR systems improvements. Radiology. 2011;261:824–33. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11110157. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Krinsky GA, Lee VS, Theise ND, Weinreb JC, Morgan GR, Diflo T. Transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis: sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging. Liver Transpl. 2002;8:1156–64. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2002.35670. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Burrel M, Llovet JM, Ayuso C, Iglesias C, Sala M, Miquel R. MRI angiography is superior to helical CT for detection of HCC prior to liver transplantation: an explant correlation. Hepatology. 2003;38:1034–42. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50409. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lee YJ, Lee JM, Lee JS, Lee HY, Park BH, Kim YH. Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnostic performance of multidetector CT and MR imaging-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology. 2015;275:97–109. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14140690. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Forner A, Vilana R, Ayuso C, Bianchi L, Solé M, Ayuso JR. Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis: Prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;47:97–104. doi: 10.1002/hep.21966. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chou R, Cuevas C, Fu R, Devine B, Wasson N, Ginsburg A. Imaging techniques for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:697–711. doi: 10.7326/M14-2509. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Xu PJ, Yan FH, Wang JH, Shan Y, Ji Y, Chen CZ. Contribution of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic liver. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010;34:506–12. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e3181da3671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kierans AS, Kang SK, Rosenkrantz AB. The diagnostic performance of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging for detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma measuring up to 2 cm: a meta-analysis. Radiology. 2016;278:82–94. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ward J, Guthrie JA, Scott DJ, Atchley J, Wilson D, Davies MH. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: double-contrast MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology. 2000;216:154–62. doi: 10.1148/radiology.216.1.r00jl24154. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lu DS, Yu NC, Raman SS, Limanond P, Lassman C, Murray K. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment success as defined by histologic examination of the explanted liver. Radiology. 2005;234:954–60. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2343040153. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M, Vallisa D, Quaretti P, Rocca A.. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:914–21. doi: 10.1007/s003300000659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kuo MD, Gollub J, Sirlin CB, Ooi C, Chen X. Radiogenomic analysis to identify imaging phenotypes associated with drug response gene expression programs in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18:821–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2007.04.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jadvar H, Colletti PM. Competitive advantage of PET/MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83:84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.05.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kong E, Chun KA, Cho IH. Quantitative assessment of simultaneous F-18 FDG PET/MRI in patients with various types of hepatic tumors: correlation between glucose metabolism and apparent diffusion coefficient. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0180184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sun L, Wu H, Guan YS. Positron emission tomography/computer tomography: challenge to conventional imaging modalities in evaluating primary and metastatic liver malignancies. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:2775–83. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Talbot JN, Gutman F, Fartoux L, Grange JD, Ganne N, Kerrou K. PET/CT in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma using [(18)F]fluorocholine: preliminary comparison with [(18)F]FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:1285–9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-006-0164-9. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mertens K, Slaets D, Lambert B, Acou M, De Vos F, Goethals I.. PET with (18)F-labelled choline-based tracers for tumour imaging: a review of the literature. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:2188–93. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1496-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yang SH, Suh KS, Lee HW. The role of (18)F-FDG-PET imaging for the selection of liver transplantation candidates among hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Liver Transpl. 2006;12:1655–60. doi: 10.1002/lt.20861. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bertagna F, Bertoli M, Bosio G, Biasiotto G, Sadeghi R, Giubbini R. Diagnostic role of radiolabelled choline PET or PET/CT in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 2014;8:493–500. doi: 10.1007/s12072-014-9566-0. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ho CL, Chen S, Yeung DW, Cheng TK. Dual-tracer PET/CT imaging in evaluation of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:902–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.106.036673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Castilla-Lièvre MA, Franco D, Gervais P, Kuhnast B, Agostini H, Marthey L. Diagnostic value of combining 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:852–9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-015-3241-0. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Shao GL, Zheng JP, Guo LW, Chen YT, Zeng H, Yao Z. Evaluation of efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma using magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion imaging: A prospective study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e5518. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Chen X, Xiao E, Shu D, Yang C, Liang B, He Z. Evaluating the therapeutic effect of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization by magnetic resonance perfusion imaging. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;26:109–13. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328363716e. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bayle M, Clerc-Urmès I, Ayav A, Bronowicki JP, Petit I, Orry X. Computed tomographic perfusion with 160-mm coverage: comparative analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma treated by two transarterial chemoembolization courses relative to magnetic resonance imaging findings. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2018 doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1714-x. et al. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


