Abstract
STIM1 is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein with a key role in Ca2+ mobilization. Due to its ability to act as an ER-intraluminal Ca2+ sensor, it regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE), which is a Ca2+ influx pathway involved in a wide variety of signalling pathways in eukaryotic cells. Despite its important role in Ca2+ transport, current knowledge about the role of STIM1 in neurons is much more limited. Growing evidence supports a role for STIM1 and SOCE in the preservation of dendritic spines required for long-term potentiation and the formation of memory. In this regard, recent studies have demonstrated that the loss of STIM1, which impairs Ca2+ mobilization in neurons, risks cell viability and could be the cause of neurodegenerative diseases. The role of STIM1 in neurodegeneration and the molecular basis of cell death triggered by low levels of STIM1 are discussed in this review.
Keywords: Calcium, Neurodegeneration, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, STIM1, Voltage-operated Ca2+ channels
Core tip: STIM1 is an endoplasmic reticulum protein that regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry, which is a Ca2+ influx pathway involved in a wide variety of signalling pathways. Growing evidence supports a role for this protein, STIM1, in long-term potentiation and the formation of memory. In this regard, the loss of STIM1 observed in brain tissue from Alzheimer’s disease patients risks cell viability and could be the cause of neurodegenerative diseases. This is the reason for discussing the role of STIM1 in neurodegeneration in this review.
STIM1 AND CALCIUM MOBILIZATION
STIM1 (stromal interaction molecule 1) is a type I transmembrane protein located mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), with a significant pool of approximately 20% at the plasma membrane. Due to its Ca2+-sensitive EF-hand domain close to the N-terminus, STIM1 acts as an ER-intraluminal Ca2+ sensor[1,2]. This EF-hand domain shows an apparent dissociation constant for Ca2+ of 250 μmol/L[3]. The decrease of the ER-intraluminal Ca2+ concentration, with the subsequent dissociation of Ca2+ from the EF-hand domain, triggers the oligomerization and the conformational change of STIM1. These two events are critical for STIM1 activation.
The rapid decrease of the ER-intraluminal Ca2+ concentration is a common event in cells under diverse stimuli, such as the activation of growth factor receptors or the activation of G protein-coupled receptors. In both cases, phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to generate inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol. The generation of IP3 activates its receptor at the ER, with the subsequent release of Ca2+ through this channel/receptor and the rise of cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c). As mentioned above, the emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores (mainly the ER) activates STIM1, which is then able to bind and activate STIM1-dependent Ca2+ channels[4], such as ORAI1[5]. The activation of ORAI1 leads to the transient increase of Ca2+ influx and to the rise of [Ca2+]c, which is required for the refilling of the ER and for the sustainability of this system in successive stimulations. Thus, STIM1 protein and STIM1-dependent Ca2+ channels ensure Ca2+ mobilization and the stimulation of Ca2+-dependent signaling pathways by activating the “store-operated Ca2+ entry” (SOCE), i.e., the Ca2+ influx pathway activated by the decrease of the ER-intraluminal Ca2+ level.
The activation of plasma membrane Ca2+ channels by STIM1 is carried out in ER-plasma membrane contact sites (ER-PM junctions)[6], where STIM1 relocalizes in response to Ca2+ store depletion. When the ER-intraluminal Ca2+ concentration is high, STIM1 remains bound to the growing tip of microtubules and moves freely on the ER surface[7]. However, activated STIM1 becomes phosphorylated at three ERK1/2-target sites (Ser575, Ser608, and Ser621) and this phosphorylation is critical for enhancing the dissociation from microtubules[8,9]. Oligomers of active STIM1 are less mobile and phospho-STIM1 is found at the cell periphery[10], close to the plasma membrane, where it binds ORAI1. Because STIM1 and ORAI1 are ubiquitous, they are involved in a wide range of signaling pathways that regulate many cellular functions[11]. However, the number of studies about the role of STIM1 in neuronal tissue is much more limited.
STIM1 EXPRESSION AND FUNCTION IN NEURONAL CELLS
STIM1 is widely expressed in the brain according to databases such as Expression Atlas (from the European Bioinformatics Institute, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/gxa) or UniGene (from the National Center for Biotechnology Information, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/unigene). Indeed, it is well known that STIM1 becomes activated upon depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores in the brain in a similar fashion to that found in any other cell or tissue[12,13]. The role of STIM1 in neuronal function was initially suggested in Drosophila melanogaster neurons. Shortly after the description of STIM1 as the main regulator of SOCE, it was proved that STIM1 was required for normal flight and associated patterns of rhythmic firing of the flight motoneurons[14], and that SOCE regulates spatial and temporal Ca2+ mobilization in vertebrate photoreceptor cones, suggesting a role in the generation of excitatory signals across the retinal synapse[15].
A key finding was reported in 2010 by Ricardo Dolmetsch’s and Donald L. Gill’s labs. They found that STIM1 directly suppresses depolarization-induced opening of the voltage-operated Ca2+ channel (VOCC) CaV1.2[16,17]. What was striking was the fact that STIM1 binds to CaV1.2 through the same domain that activates ORAI1, the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ activation domain, and also triggers the internalization of the channel from the membrane. These findings provided the molecular explanation for the shared control of Ca2+ entry through ORAI1 and CaV1.2, making it possible for them to operate independently. In HEK293 cells, it was later reported that Homer proteins are required for the binding between STIM1 and CaV1.2 channels upon Ca2+ store-depletion conditions triggered by thapsigargin[18], an inhibitor of the ER-Ca2+ pump.
T-type VOCCs, such as CaV3.1, are also modulated by STIM1. This was first observed not in neurons but in cardiomyocytes, where it was reported that STIM1 co-precipitated with CaV1.3 channels, and that the knocking-down of STIM1 expression increased CaV1.3 surface expression and the current density of T-type VOCCs[19].
Given the abundance of STIM1 and STIM2 in neuronal tissues and their role in Ca2+ mobilization, it is not surprising to learn that they have a direct impact on cognitive functions. In mice with conditional deletion of Stim1 or Stim2 genes in the forebrain (conditional knock-outs or cKO), the analysis of spatial reference memory revealed a mild learning delay in Stim1 cKO mice, no effect in Stim2 cKO mice, and a deep impairment in spatial learning in the double cKO[20]. This striking effect was explained by the regulation of the phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit GluA1, the transcriptional regulator CREB and the CaV1.2 on protein kinase A-target sites, leading to the proposal that the upregulation of cAMP/PKA signaling impairs the development of spatial memory[20]. Kuznicki’s lab reported that STIM1 protein in neurons can control AMPA-induced Ca2+ entry, based on the inhibition of Ca2+ entry observed with AMPA receptors (AMPAR) inhibitors and the finding that STIM1 physically binds GluA1/GluA2 AMPAR[21].
On the other hand, in transgenic mice overexpressing STIM1 in neurons it was reported a reduction of long-term depression in hippocampal slices, as well as a decrease in anxiety-like behavior and an increase in contextual learning improvement[22]. All of this further confirms the role of STIM1 in the modulation of synaptic strength and memory formation.
Closely related to the above statement, the control of L-type VOCCs by STIM1 has functional consequences that were reported for dendritic spine structural plasticity. In hippocampal neurons, depolarization by the neurotransmitter glutamate activates postsynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and L-type VOCC-dependent Ca2+ influx, as well as the release of Ca2+ from the ER. The consequent activation of STIM1 inhibits VOCCs, an event that leads to the enlargement of ER content in spines, which is believed to help in the stabilization of mushroom spines that have become enlarged during long-term potentiation[23].
STIM1 IN NEURONAL CELL DEATH
There are some examples of the involvement of STIM1 and SOCE in neuronal injury. For instance, cell death due to diffuse axonal injury is preceded by an increase of STIM1 expression in neurons of the rat cerebral cortex after lateral head rotational injury[24]. In this regard, STIM1 expression was significantly increased in a traumatic brain injury model, and STIM1 knock-down inhibited apoptotic cell death after traumatic injury by decreasing the upregulation of mGluR1-dependent Ca2+ signaling[25]. However, Berna-Erro et al[26] demonstrated that STIM2, but not STIM1, was essential for ischemia-induced cytosolic Ca2+ accumulation in neurons using hypoxic conditions for culturing neurons from wild-type and Stim2-/- mice, hippocampal slice preparations, as well as in Stim2-/- mice subjected to focal cerebral ischemia.
Oxytosis, a type of cell death characterized by an increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and augmented Ca2+ influx, can be triggered in neurons in culture by depleting reduced glutathione content. Henke et al[27], reported that the Ca2+-influx pathway in this cell death could be mediated by ORAI1, the CRAC channel activated by STIM1. Similarly, in PC12 cells exposed to 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), an experimental model to trigger ROS-dependent cell death, the knockdown of STIM1 was able to attenuate apoptotic cell death by limiting the mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake induced by 6-OHDA. This resulted in the protection of PC12 cells against the oxidative stress generated by ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction[28]. On the other hand, the inhibition of SOCE or the knock-down of STIM1 limited ROS production and the activation of apoptosis in PC12 cells exposed to 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium or MPP+[29], the toxic metabolite of MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine), a well-known inducer of Parkinsonism. These studies revealed that oxidative stress induces an increase of [Ca2+]i mediated by the activation of SOCE. Indeed, STIM1 is a redox-sensitive protein, and it is known that Cys56 becomes S-glutathionylated during oxidative stress[30], a residue located near its luminal EF-hand domain. Hawkins et al[30], demonstrated that S-glutathionylation lowered the affinity of STIM1 for Ca2+, thereby activating STIM1 in a store-independent fashion. Similarly, ORAI1 is a redox sensor through the Cys195 located in the second extracellular loop. Although it was initially shown that the oxidation of this Cys residue inhibited Ca2+ current through this channel[31], other researchers found that exposure to H2O2 increased influx through ORAI1[32], suggesting that ROS has multiple redox-sensitive targets in the SOCE machinery.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is an early event in neurotoxicity triggered by massive Ca2+ influx, as observed during glutamate neurotoxicity[33]. Following acute increase in [Ca2+]i, Ca2+ uptake by mitochondria contributes to the protection against cell death. However, Ca2+ overload in mitochondria triggers the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), an event that led to cell death in different neuronal cell types[34,35]. It is accepted that the overproduction of ROS modulates the opening of the mPTP, but it has also been shown this opening at physiological levels of ROS. Recently, Agarwal et al[36], reported that astrocytes show transient cytosolic Ca2+ spikes generated by the Ca2+ release from mitochondria when the mPTP opens by a mechanism that involves ROS generated during the electron transfer in the respiratory systems. Electron transport rates are strongly dependent on the availability of NADH, and therefore dependent on the Krebs cycle status, which is tightly controlled by the mitochondrial [Ca2+]. Therefore, there is a strong correlation between dysregulation of Ca2+ entry through ORAI1, mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, ROS generation, mPTP opening and cell death.
STIM1 IN NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES
Alzheimer’s disease
Taking into consideration the information summarized above, it should not be surprising that the dysregulation of STIM1 could underlie the pathogenesis of some of the most frequent neurodegenerative diseases. In 1907 Alzheimer[37] described a disease in a 51-year-old woman with presenile dementia who displayed diffuse cortical atrophy, nerve cell loss, plaques, and tangles. Nowadays, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients are classified within 3 groups: Early-onset AD (up to 5% of all patients with AD), late-onset or sporadic AD (the most common form of the disease), and familial AD (FAD, less than 1% of AD patients). FAD is linked to known genes, such as the amyloid beta precursor protein gene (APP), the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE), presenilin1/2 genes (PSEN1, PSEN2), or the alpha-2-macroglobulin gene (A2M), and most early-onset AD patients are FAD patients. There is no significant pathological difference between sporadic AD and FAD, but symptoms progress more rapidly in FAD[38].
The major risk for sporadic AD is aging, which increases the difficulty of finding a suitable model animal that recapitulates all the hallmarks of the human disease in the absence of mutated genes as in FAD. However, there is a growing consensus regarding the hypothesis that Ca2+ dysregulation is in the pathogenesis of AD[39-42]. This hypothesis is supported by evidence that revealed how diverse Ca2+ mobilization systems are impaired in AD, including VOCCs, IP3 receptors, store-operated Ca2+ channels (SOCs), and mitochondrial Ca2+ transporters[43].
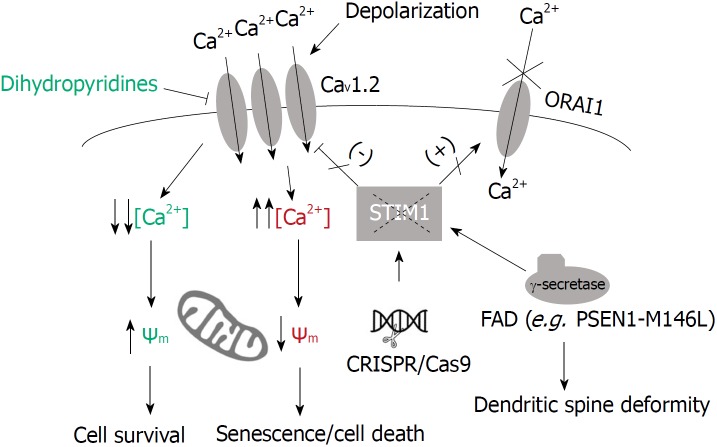
Regarding STIM1 and SOCE, it is known that SOCE is reduced and that STIM1 and ORAI1 expression are downregulated in long-term cultures of hippocampal neurons, an experimental approach intended to mimic in vivo neuronal aging[44]. Also, reduced expression of STIM2 was observed in hippocampal neurons from the presenilin-1 M146V knock-in mouse model of FAD. As it is assumed that STIM2 and the activation of the calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) mediates the stabilization of mushroom spines, this decrease in STIM2 levels could explain the loss of dendritic spines and the defects in the development of long-term potentiation LTP and memory development in AD patients[45]. In this regard, it is known that the gamma-secretase protein complex interacts with STIM1 in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, skin fibroblasts from FAD patients, and in mouse primary cortical neurons[46]. Tong et al[46], also reported that cultured hippocampal neurons expressing the mutant PSEN1 M146L, showed reduced dendritic spines, together with diminished SOCE. Because the wild-type phenotype was rescued by overexpressing STIM1, or by inhibiting gamma-secretase activity, they hypothesized that STIM1 could be a substrate for the gamma-secretase complex. Finally, they proved that the transmembrane domain of STIM1 shows a target domain for the proteolytic activity of the gamma-secretase complex and that the reduced SOCE in PSEN1-mutant neurons was due to the higher rates of STIM1 proteolysis. Although this proteolysis needs to be studied further to confirm cleavage sites on STIM1, this data fits well with the recent observation that there is a sharp decline of STIM1 protein levels in brain tissue from non-familial (sporadic) AD patients[47]. This is supporting evidence for a common hallmark in sporadic AD and FAD, i.e., reduced STIM1 could be severely affecting Ca2+ mobilization in neurons in both groups of patients. Thus, it is necessary to study the consequences of the reduced STIM1 expression in neurons in order to understand how neuronal cell physiology develops in the absence of STIM1 and to find possible targets for clinical interventions. An approach to studying the patho-physiological consequences of a limited level of STIM1 in neurons has been recently reported by our group[47]. In this report, we modified STIM1 gene locus using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing techniques, and we found that the differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells to neuronal-like cells was not impaired by the absence of STIM1. However, the loss of STIM1 triggered significant cell death due to the impairment of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I, and to reduced mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration. These two events led to high levels of senescence. STIM1-KO cells showed potentiation of Ca2+ entry through L-type VOCCs[47], further confirming earlier observations that demonstrated the inhibitory role of STIM1 on CaV1.2 channels[16,17]. Consequently, the knocking-down of CACNA1C gene transcripts (for CaV1.2 channel) rescued the wild-type phenotype, confirming that the upregulation of Ca2+ entry through CaV1.2 channels was deleterious in STIM1-deficient cells[47] (Figure 1). In this regard, higher Ca2+ entry through VOCCs had been recorded in CA1 pyramidal neurons from the hippocampus in aged rats[48], an effect that resulted in the down-regulation of short-term neuronal plasticity.
Figure 1.
Deficiency of STIM1 and neurodegeneration. Neurons expressing the mutant PSEN1 M146L showed higher rates of STIM1 proteolysis, reduced levels of STIM1, reduced store-operated Ca2+ entry and diminished dendritic spines[46]. Deficiency of STIM1 has been observed in non-familial (sporadic) Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients, and can be mimicked by genome edition of STIM1 locus in SH-SY5Y cells[47]. Because STIM1 is a negative regulator of CaV1.2 channels, this deficiency triggered the upregulation of Ca2+ entry through CaV1.2 channels which was responsible for the loss of inner mitochondrial membrane polarization, senescence, and cell death[47]. This higher rate of Ca2+ influx through CaV1.2 channels has also been monitored in 3xTgAD mice[51]. The long-term treatment with dihydropyridines, known blockers of CaV1.2, reduced sporadic dementia by 55% during aging[52], pointing out the decrease of STIM1 as a possible mechanism to explain neurodegeneration in sporadic and familial AD.
Accumulation of beta amyloid peptides (Aβ) begins earlier than most of the clinical symptoms associated with FAD. However, clinical interventions to prevent this accumulation have been inconclusive so far. Accumulation of Aβ directly affects Ca2+ mobilization, and the possibility that an increase of PKA-dependent phosphorylation of CaV1.2 channels could underlie the upregulation of Ca2+ influx through these channels has been discussed[49,50]. Therefore, an alternative clinical intervention is the blocking of excessive Ca2+ entry in neurons. Transgenic mice have been designed to accumulate Aβ and hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in CA1 pyramidal neurons, as an experimental approach to mimic some clinical features of FAD patients. Using these mice (known as 3xTgAD mice) it has been shown that Ca2+ current through L-type VOCCs became higher in these hippocampal neurons, supporting the possible role of VOCCs in neuronal degeneration in FAD patients[51]. In addition, the long-term treatment of subjects receiving active treatment with L-type VOCCs blockers (nitrendipine) reduced sporadic dementia by 55% during aging[52], suggesting that the enhanced Ca2+ entry through VOCCs could be in the pathogenesis of sporadic AD. Protection against the loss of working memory has also been monitored in rats treated with the VOCC blocker nimodipine, a treatment that reduced Ca2+ current through CaV1.3 in CA1 neurons[53]. Finally, isradipine, another dihydropyridine, attenuated Aβ accumulation toxicity by reducing CaV1.2 expression and Ca2+ influx in MC65 neuroblastoma cells[54]. Interestingly, isradipine also showed a neuroprotective effect in models of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and stroke[50,55].
Whereas a decline in STIM1 level is deleterious, in part due to the upregulation of VOCCs, high levels of STIM1 and SOCE might be protective, as suggested by the reduced Aβ secretion observed in cells expressing a constitutively activated STIM1 mutant (D76A)[56]. On the other hand, Aβ seems to affect STIM1-dependent Ca2+ entry because knocking-down APP transcripts delayed the binding of STIM1 to ORAI1 in response to store depletion[57], and SOCE was largely reduced in cultured astrocytes from APP-KO mice[58], confirming the crosstalk between SOCE and APP.
PD
A recent report showed that neurotoxins that trigger PD symptoms targeted TRPC1 expression and increased Ca2+ influx through CaV1.3 channels (L-type VOCC) which led to degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons[59]. Because of the key role of CaV1.3 in the regulation of basal single-spike firing in DA neurons[60], the reported inhibition of CaV1.3 by the STIM1-TRPC1 complex[59] could explain the disruption of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis in PD patients. Indeed, in mice treated with MPTP, the expression of CaV1.2 and CaV1.3 in the substantia nigra increased after 2 wk of treatment, and isradipine (L-type VOCC blocker) prevented this upregulation and the loss of DA neurons[61]. Similarly, nimodipine prevented cell death triggered by MPP+ in SH-SY5Y cell in culture and Parkinsonism in MPTP-treated mice[62]. Because dihydropyridines are not highly selective in discriminating between CaV1.2 and CaV1.3, Wang et al[61], reported a high-throughput screening that led to 1-(3-chlorophenethyl)-3-cyclopentylpyrimidine-2,4,6-(1H,3H,5H)-trione as the first potent and highly selective CaV1.3 antagonist with potential utility in clinical approaches. However, Ortner et al[63], reported later that this specific compound showed inhibitory activity of CaV1.3 only in a minority of cells.
On the other hand, antagonists of SOCE and depletion of STIM1 by siRNA increased cell viability, reduced intracellular ROS production as well as lipid peroxidation and prevented mitochondrial dysfunction in MPP+-treated PC12 cells[29], supporting the hypothesis that augmented Ca2+ entry through STIM1-activated channels mediates toxicity of MPP+. This result, however, is in conflict with the observation that treatment with this neurotoxin decreased TRPC1 expression, TRPC1 interaction with STIM1, and Ca2+ entry in SH-SY5Y cells[64], making further study necessary to discover the role of STIM1, SOCE, and VOCCs in the pathogenesis of PD.
CONCLUSION
Neurodegenerative diseases are devastating for the elderly population and no fully efficient therapies are available to treat some of them, particularly AD. However, a growing body of evidence supports a role for excessive Ca2+ entry through VOCCs in neurodegeneration. Recent reports proposed that the specific loss of STIM1 in neuronal tissue fully explains the observed Ca2+ homeostasis disruption in neurons during sporadic AD and FAD. In this regard, STIM1 deficiency triggered upregulation of Ca2+ entry through CaV1.2 in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells, which can be explained by the role of STIM1 in the inhibitory control of CaV1.2. This augmented Ca2+ influx led to the inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I activity, mitochondrial inner membrane depolarization, reduced mitochondrial free Ca2+ concentration, and to higher levels of senescence and cell death. All these effects were prevented by silencing CaV1.2 expression, emphasizing the upregulation of these channels as a major cause of neuronal cell death (Figure 1).
Footnotes
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Biochemistry and molecular biology
Country of origin: Spain
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Peer-review started: August 17, 2018
First decision: September 11, 2018
Article in press: October 23, 2018
P- Reviewer: Nesci S, Utkin YN S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Yin SY
Contributor Information
Carlos Pascual-Caro, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Life Sciences and Institute of Molecular Pathology Biomarkers, University of Extremadura, Badajoz 06006, Spain.
Noelia Espinosa-Bermejo, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Life Sciences and Institute of Molecular Pathology Biomarkers, University of Extremadura, Badajoz 06006, Spain.
Eulalia Pozo-Guisado, Department of Cell Biology, School of Medicine and Institute of Molecular Pathology Biomarkers, University of Extremadura, Badajoz 06006, Spain.
Francisco Javier Martin-Romero, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Life Sciences and Institute of Molecular Pathology Biomarkers, University of Extremadura, Badajoz 06006, Spain. fjmartin@unex.es.
References
- 1.Liou J, Kim ML, Heo WD, Jones JT, Myers JW, Ferrell JE Jr, Meyer T. STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggered Ca2+ influx. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1235–1241. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang SL, Yu Y, Roos J, Kozak JA, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH, Stauderman KA, Cahalan MD. STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature. 2005;437:902–905. doi: 10.1038/nature04147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stathopulos PB, Li GY, Plevin MJ, Ames JB, Ikura M. Stored Ca2+ depletion-induced oligomerization of stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) via the EF-SAM region: An initiation mechanism for capacitive Ca2+ entry. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35855–35862. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608247200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhou Y, Srinivasan P, Razavi S, Seymour S, Meraner P, Gudlur A, Stathopulos PB, Ikura M, Rao A, Hogan PG. Initial activation of STIM1, the regulator of store-operated calcium entry. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20:973–981. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Prakriya M, Feske S, Gwack Y, Srikanth S, Rao A, Hogan PG. Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel. Nature. 2006;443:230–233. doi: 10.1038/nature05122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ong HL, Liu X, Tsaneva-Atanasova K, Singh BB, Bandyopadhyay BC, Swaim WD, Russell JT, Hegde RS, Sherman A, Ambudkar IS. Relocalization of STIM1 for activation of store-operated Ca(2+) entry is determined by the depletion of subplasma membrane endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) store. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:12176–12185. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609435200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Grigoriev I, Gouveia SM, van der Vaart B, Demmers J, Smyth JT, Honnappa S, Splinter D, Steinmetz MO, Putney JW Jr, Hoogenraad CC, Akhmanova A. STIM1 is a MT-plus-end-tracking protein involved in remodeling of the ER. Curr Biol. 2008;18:177–182. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.12.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pozo-Guisado E, Casas-Rua V, Tomas-Martin P, Lopez-Guerrero AM, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Martin-Romero FJ. Phosphorylation of STIM1 at ERK1/2 target sites regulates interaction with the microtubule plus-end binding protein EB1. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:3170–3180. doi: 10.1242/jcs.125054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pozo-Guisado E, Martin-Romero FJ. The regulation of STIM1 by phosphorylation. Commun Integr Biol. 2013;6:e26283. doi: 10.4161/cib.26283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lopez-Guerrero AM, Tomas-Martin P, Pascual-Caro C, Macartney T, Rojas-Fernandez A, Ball G, Alessi DR, Pozo-Guisado E, Martin-Romero FJ. Regulation of membrane ruffling by polarized STIM1 and ORAI1 in cortactin-rich domains. Sci Rep. 2017;7:383. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00331-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Martin-Romero FJ, Pascual-Caro C, Espinosa-Bermejo N, Pozo-Guisado E. Buchholz JN, Editor. Intech Open: London; 2018. Regulation of calcium signaling by STIM1 and ORAI1, in Calcium and Signal Transduction. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Klejman ME, Gruszczynska-Biegala J, Skibinska-Kijek A, Wisniewska MB, Misztal K, Blazejczyk M, Bojarski L, Kuznicki J. Expression of STIM1 in brain and puncta-like co-localization of STIM1 and ORAI1 upon depletion of Ca(2+) store in neurons. Neurochem Int. 2009;54:49–55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Skibinska-Kijek A, Wisniewska MB, Gruszczynska-Biegala J, Methner A, Kuznicki J. Immunolocalization of STIM1 in the mouse brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2009;69:413–428. doi: 10.55782/ane-2009-1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Venkiteswaran G, Hasan G. Intracellular Ca2+ signaling and store-operated Ca2+ entry are required in Drosophila neurons for flight. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:10326–10331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902982106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Szikra T, Barabas P, Bartoletti TM, Huang W, Akopian A, Thoreson WB, Krizaj D. Calcium homeostasis and cone signaling are regulated by interactions between calcium stores and plasma membrane ion channels. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Park CY, Shcheglovitov A, Dolmetsch R. The CRAC channel activator STIM1 binds and inhibits L-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Science. 2010;330:101–105. doi: 10.1126/science.1191027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang Y, Deng X, Mancarella S, Hendron E, Eguchi S, Soboloff J, Tang XD, Gill DL. The calcium store sensor, STIM1, reciprocally controls Orai and CaV1.2 channels. Science. 2010;330:105–109. doi: 10.1126/science.1191086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dionisio N, Smani T, Woodard GE, Castellano A, Salido GM, Rosado JA. Homer proteins mediate the interaction between STIM1 and Cav1.2 channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1853:1145–1153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nguyen N, Biet M, Simard E, Béliveau E, Francoeur N, Guillemette G, Dumaine R, Grandbois M, Boulay G. STIM1 participates in the contractile rhythmicity of HL-1 cells by moderating T-type Ca(2+) channel activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1833:1294–1303. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Garcia-Alvarez G, Shetty MS, Lu B, Yap KA, Oh-Hora M, Sajikumar S, Bichler Z, Fivaz M. Impaired spatial memory and enhanced long-term potentiation in mice with forebrain-specific ablation of the Stim genes. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015;9:180. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gruszczynska-Biegala J, Sladowska M, Kuznicki J. AMPA Receptors Are Involved in Store-Operated Calcium Entry and Interact with STIM Proteins in Rat Primary Cortical Neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:251. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Majewski Ł, Maciąg F, Boguszewski PM, Wasilewska I, Wiera G, Wójtowicz T, Mozrzymas J, Kuznicki J. Overexpression of STIM1 in neurons in mouse brain improves contextual learning and impairs long-term depression. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017;1864:1071–1087. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dittmer PJ, Wild AR, Dell’Acqua ML, Sather WA. STIM1 Ca2+ Sensor Control of L-type Ca2+-Channel-Dependent Dendritic Spine Structural Plasticity and Nuclear Signaling. Cell Rep. 2017;19:321–334. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li Y, Song J, Liu X, Zhang M, An J, Sun P, Li D, Jin T, Wang J. High expression of STIM1 in the early stages of diffuse axonal injury. Brain Res. 2013;1495:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hou PF, Liu ZH, Li N, Cheng WJ, Guo SW. Knockdown of STIM1 improves neuronal survival after traumatic neuronal injury through regulating mGluR1-dependent Ca(2+) signaling in mouse cortical neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015;35:283–292. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0123-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Berna-Erro A, Braun A, Kraft R, Kleinschnitz C, Schuhmann MK, Stegner D, Wultsch T, Eilers J, Meuth SG, Stoll G, et al. STIM2 regulates capacitive Ca2+ entry in neurons and plays a key role in hypoxic neuronal cell death. Sci Signal. 2009;2:ra67. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Henke N, Albrecht P, Bouchachia I, Ryazantseva M, Knoll K, Lewerenz J, Kaznacheyeva E, Maher P, Methner A. The plasma membrane channel ORAI1 mediates detrimental calcium influx caused by endogenous oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e470. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li B, Xiao L, Wang ZY, Zheng PS. Knockdown of STIM1 inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress through attenuating calcium-dependent ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Free Radic Res. 2014;48:758–768. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.905687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li X, Chen W, Zhang L, Liu WB, Fei Z. Inhibition of store-operated calcium entry attenuates MPP(+)-induced oxidative stress via preservation of mitochondrial function in PC12 cells: involvement of Homer1a. PLoS One. 2013;8:e83638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hawkins BJ, Irrinki KM, Mallilankaraman K, Lien YC, Wang Y, Bhanumathy CD, Subbiah R, Ritchie MF, Soboloff J, Baba Y, et al. S-glutathionylation activates STIM1 and alters mitochondrial homeostasis. J Cell Biol. 2010;190:391–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201004152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bogeski I, Kummerow C, Al-Ansary D, Schwarz EC, Koehler R, Kozai D, Takahashi N, Peinelt C, Griesemer D, Bozem M, et al. Differential redox regulation of ORAI ion channels: a mechanism to tune cellular calcium signaling. Sci Signal. 2010;3:ra24. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Grupe M, Myers G, Penner R, Fleig A. Activation of store-operated I(CRAC) by hydrogen peroxide. Cell Calcium. 2010;48:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2010.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schinder AF, Olson EC, Spitzer NC, Montal M. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a primary event in glutamate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1996;16:6125–6133. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-19-06125.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Murchison D, Griffith WH. Mitochondria buffer non-toxic calcium loads and release calcium through the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and sodium/calcium exchanger in rat basal forebrain neurons. Brain Res. 2000;854:139–151. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Limke TL, Atchison WD. Acute exposure to methylmercury opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in rat cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;178:52–61. doi: 10.1006/taap.2001.9327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Agarwal A, Wu PH, Hughes EG, Fukaya M, Tischfield MA, Langseth AJ, Wirtz D, Bergles DE. Transient Opening of the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Induces Microdomain Calcium Transients in Astrocyte Processes. Neuron. 2018;93:587–605.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Alzheimer A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg Z Psychiat Med. 1907:146–148. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.LaFerla FM. Calcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:862–872. doi: 10.1038/nrn960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Berridge MJ. Calcium regulation of neural rhythms, memory and Alzheimer’s disease. J Physiol. 2014;592:281–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.257527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Raza M, Deshpande LS, Blair RE, Carter DS, Sombati S, DeLorenzo RJ. Aging is associated with elevated intracellular calcium levels and altered calcium homeostatic mechanisms in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2007;418:77–81. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Popugaeva E, Pchitskaya E, Bezprozvanny I. Dysregulation of neuronal calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease - A therapeutic opportunity? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483:998–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tong BC, Wu AJ, Li M, Cheung KH. Calcium signaling in Alzheimer’s disease and therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865:1745–1760. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Calvo-Rodríguez M, García-Durillo M, Villalobos C, Núñez L. In vitro aging promotes endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mitochondria Ca2+ cross talk and loss of store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) in rat hippocampal neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:2637–2649. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sun S, Zhang H, Liu J, Popugaeva E, Xu NJ, Feske S, White CL 3rd, Bezprozvanny I. Reduced synaptic STIM2 expression and impaired store-operated calcium entry cause destabilization of mature spines in mutant presenilin mice. Neuron. 2014;82:79–93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tong BC, Lee CS, Cheng WH, Lai KO, Foskett JK, Cheung KH. Familial Alzheimer’s disease-associated presenilin 1 mutants promote γ-secretase cleavage of STIM1 to impair store-operated Ca2+ entry. Sci Signal. 2016;9:ra89. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pascual-Caro C, Berrocal M, Lopez-Guerrero AM, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Pozo-Guisado E, Gutierrez-Merino C, Mata AM, Martin-Romero FJ. STIM1 deficiency is linked to Alzheimer’s disease and triggers cell death in SH-SY5Y cells by upregulation of L-type voltage-operated Ca2+ entry. J Mol Med (Berl) 2018;96:1061–1079. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1677-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Thibault O, Hadley R, Landfield PW. Elevated postsynaptic [Ca2+]i and L-type calcium channel activity in aged hippocampal neurons: relationship to impaired synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci. 2001;21:9744–9756. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-24-09744.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hall DD, Davare MA, Shi M, Allen ML, Weisenhaus M, McKnight GS, Hell JW. Critical role of cAMP-dependent protein kinase anchoring to the L-type calcium channel Cav1.2 via A-kinase anchor protein 150 in neurons. Biochemistry. 2007;46:1635–1646. doi: 10.1021/bi062217x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Anekonda TS, Quinn JF. Calcium channel blocking as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease: the case for isradipine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812:1584–1590. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.08.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang Y, Mattson MP. L-type Ca2+ currents at CA1 synapses, but not CA3 or dentate granule neuron synapses, are increased in 3xTgAD mice in an age-dependent manner. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35:88–95. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Forette F, Seux ML, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Babarskiene MR, Babeanu S, Bossini A, Fagard R, Gil-Extremera B, Laks T, et al. The prevention of dementia with antihypertensive treatment: new evidence from the Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) study. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:2046–2052. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.18.2046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Veng LM, Mesches MH, Browning MD. Age-related working memory impairment is correlated with increases in the L-type calcium channel protein alpha1D (Cav1.3) in area CA1 of the hippocampus and both are ameliorated by chronic nimodipine treatment. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003;110:193–202. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(02)00643-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Anekonda TS, Quinn JF, Harris C, Frahler K, Wadsworth TL, Woltjer RL. L-type voltage-gated calcium channel blockade with isradipine as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;41:62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lenhard SC, Strittmatter R, Price WJ, Chandra S, White RF, Barone FC. Brain MRI and neurological deficit measurements in focal stroke: rapid throughput validated with isradipine. Pharmacology. 2008;81:1–10. doi: 10.1159/000107661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zeiger W, Vetrivel KS, Buggia-Prévot V, Nguyen PD, Wagner SL, Villereal ML, Thinakaran G. Ca2+ influx through store-operated Ca2+ channels reduces Alzheimer disease β-amyloid peptide secretion. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:26955–26966. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gazda K, Kuznicki J, Wegierski T. Knockdown of amyloid precursor protein increases calcium levels in the endoplasmic reticulum. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14512. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15166-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Linde CI, Baryshnikov SG, Mazzocco-Spezzia A, Golovina VA. Dysregulation of Ca2+ signaling in astrocytes from mice lacking amyloid precursor protein. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;300:C1502–C1512. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00379.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sun Y, Zhang H, Selvaraj S, Sukumaran P, Lei S, Birnbaumer L, Singh BB. Inhibition of L-Type Ca2+ Channels by TRPC1-STIM1 Complex Is Essential for the Protection of Dopaminergic Neurons. J Neurosci. 2017;37:3364–3377. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3010-16.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Liu Y, Harding M, Pittman A, Dore J, Striessnig J, Rajadhyaksha A, Chen X. Cav1.2 and Cav1.3 L-type calcium channels regulate dopaminergic firing activity in the mouse ventral tegmental area. J Neurophysiol. 2014;112:1119–1130. doi: 10.1152/jn.00757.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wang QM, Xu YY, Liu S, Ma ZG. Isradipine attenuates MPTP-induced dopamine neuron degeneration by inhibiting up-regulation of L-type calcium channels and iron accumulation in the substantia nigra of mice. Oncotarget. 2017;8:47284–47295. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Singh A, Verma P, Balaji G, Samantaray S, Mohanakumar KP. Nimodipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker attenuates mitochondrial dysfunctions to protect against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinsonism in mice. Neurochem Int. 2016;99:221–232. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ortner NJ, Bock G, Vandael DH, Mauersberger R, Draheim HJ, Gust R, Carbone E, Tuluc P, Striessnig J. Pyrimidine-2,4,6-triones are a new class of voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channel activators. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3897. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Selvaraj S, Sun Y, Watt JA, Wang S, Lei S, Birnbaumer L, Singh BB. Neurotoxin-induced ER stress in mouse dopaminergic neurons involves downregulation of TRPC1 and inhibition of AKT/mTOR signaling. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1354–1367. doi: 10.1172/JCI61332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]