Abstract
Introduction:
Many scoring models have been proposed for evaluating level of consciousness in trauma patients. The aim of this study is to compare Glasgow coma scale (GCS) and Full Outline of UnResponsiveness (FOUR) score in predicting the mortality of trauma patients.
Methods:
In this diagnostic accuracy study trauma patients hospitalized in intensive care unit (ICU) of 2 educational hospitals were evaluated. GCS and FOUR score of each patient were simultaneously calculated on admission as well as 6, 12 and 24 hours after that. The predictive values of the two scores and their area under the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve were compared.
Results:
90 patients were included in the present study (mean age 39.4±17.3; 74.4% male). Comparing the area under the ROC curve of GCS and FOUR score showed that these values were not different at any of the evaluated times: on admission (p=0.68), and 6 hours (p=0.13), 12 hours (p=0.18), and 24 hours (p=0.20) after that.
Conclusion:
The results of our study showed that, GCS and FOUR score have the same value in predicting the mortality of trauma patients. Both tools had high predictive power in predicting the outcome at the time of discharge.
Introduction:
In severe injuries, especially traumatic brain injuries, a considerable portion of the patients are hospitalized in intensive care unit (ICU). In recent years, the prevalence of injuries has significantly increased in developing countries. Based on the latest reports of world health organization, injury is the tenth cause of mortality in the world and third cause of death in Iran. This high prevalence leads to increased treatment costs, loss of society’s work force, greater burden of diseases and increase in the workload of treatment staff, especially nurses (1-3). By using appropriate tools for measuring the level of consciousness to evaluate the severity of the injury in head trauma patients, nurses will be able to prepare for taking critical measures for the injury in the shortest time and in the best possible way and reduce the disability and mortality of trauma patients (4-12).
Many scoring models have been proposed to evaluate level of consciousness in patients who are affected with traumatic brain injuries, the most famous of which is Glasgow coma scale. This scale has some limitations such as its low efficiency in intubated patients, its poor use in cases of language differences, and not being able to evaluate the reflexes of brainstem (13, 14). In intubated patients, the verbal part is practically non-measurable and therefore, it is possible that the reported level of consciousness in these patients is lower than its real level (15). Full Outline of Unresponsiveness (FOUR) score is another scale for evaluating level of consciousness, the accuracy and precision of which in critically ill patients has been evaluated in only a few studies (16, 17). Availability of a scoring system that in addition to accuracy, precision, and easy use, leads to facilitation of the nursing care of trauma patients is a necessity.
By providing an accurate picture of injury severity, such a system would be able to give a reflection of the outcome of the patient to the health care team. Contradicting results exist from comparing GCS and FOUR score in prediction of final outcomes. In a multi-center study, Wijdicks et al. showed that FOUR score and GCS do not differ in prediction of in-hospital mortality, although they suggested that FOUR score can be a better diagnostic tool for assessing brainstem reflexes and respiratory pattern (17). However, Jalali and Rezaei showed that FOUR score performs better than GCS in prediction of mortality (18). Presence of these contradictions shows the need for carrying out more studies. Therefore, the present study was done with the aim of comparing GCS and FOUR score in predicting the mortality of trauma patients.
Methods:
Study design and setting
The present prospective diagnostic accuracy study was designed with the aim of comparing the 2 systems of GCS and FOUR score in predicting the outcome of trauma patients hospitalized in ICU of 2 hospitals affiliated with Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. For this purpose, data of 90 patients were evaluated in the time interval between February and September 2017. This study was approved by the Ethics committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. Throughout the study, the researchers adhered to the principles indicated in the declaration of Helsinki. Before inclusion in the study, an informed consent was obtained from the patient or their relative.
Participants
Over 14 years old trauma patients hospitalized in ICU were studied using consecutive sampling. Patients with hearing and talking disabilities and with a history of sensorimotor disability were excluded from the study.
Data gathering
Demographic data (age, sex), trauma mechanism (pedestrian-car accident, motorcycle accident, falling, pedestrian-motorcycle accident, direct trauma, car rollover, and car-car accident), and length of stay in ICU were gathered. In addition, a checklist consisting of items used for calculating GCS (evaluation of eye, speech, and motor score) and FOUR score (evaluation of eye, motor, brainstem reflexes, and respiratory pattern score) was also used in this study.
Data were gathered by 2 trained ICU nurses who were completely familiar with data gathering tools. Before the initiation of the study, in order to approve inter-rater reliability of the 2 nurses in scoring of GCS and FOUR score, a primary study was performed in which both nurses evaluated both scores simultaneously for the same 15 patients. The agreement rate obtained was 91% (kappa=0.91).
Index test
In the present study, predictive values of GCS and FOUR score in prediction of in-hospital mortality of trauma patients were assessed. The details of scoring methods of the 2 mentioned scores have been reported in previous studies (19, 20). GCS and FOUR score of each patient were simultaneously calculated on admission as well as 6, 12 and 24 hours after that.
Reference test
Death or survival of the patient at the time of discharge from the hospital was used as the reference test. Patients were followed until their discharge from the hospital and their living status at the time of discharge was evaluated.
Statistical analysis
Area under the curves reported for GCS and FOUR score have been 0.78 and 0.84, respectively (21). Therefore, by considering 95% confidence interval (α=5%) and power of 90% (β=10%), sample size is calculated as about 90 patients.
Data were analyzed using STATA 14.0 statistical software. Descriptive analyses were presented as mean and standard deviation, or frequency and percentage, for quantitative and qualitative factors, respectively. To compare mean score of GCS and FOUR score in dead and alive patients at the evaluated times, two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc was applied.
In addition, the predictive values of GCS and FOUR score were evaluated in predicting the outcome of patients via drawing receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Fitness of the model was evaluated using Hosmer-lemeshow test and in the end, the mentioned values were compared between the 2 models. In this study, p<0.05 was considered as level of significance.
Results
Demographic and clinical data
In this study, data of 90 trauma patients hospitalized in ICU were evaluated. Mean and standard deviation of patients’ age was 39.4±17.3 years (74.4% male). The most important mechanisms of trauma were motorcycle (35.6%) and car (24.4%) accidents, and falling from a height more than 3 meters (13.3%). 13.3% of the patients had hypertension, 4.4% had diabetes, 3.3% had neurologic deficiencies, 2.2% had cardiovascular diseases, and 3.3% had other underlying diseases. Outcome of hospitalization in ICU was death in 21 cases (23.3%) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Demographic and baseline characteristics of the studied patients
| Baseline Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 23(25.6) |
| Male | 67(74.4) |
| Trauma mechanism | |
| Motorcycle accident | 32 (35.6) |
| Car accident | 22 (24.4) |
| Falling | 20 (22.2) |
| Pedestrian | 10 (10.1) |
| Other | 6 (6.7) |
| Vital signs on admission | |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 115.4±6.27 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 72.5±3.16 |
| Heart rate (beat per min) | 94.6±0.26 |
| Respiratory rate (beat per min) | 18.2±9.6 |
| Temperature (degree of Celsius) | 36.9±0.3 |
| Oxygen saturation (%) | 92.2±9.9 |
| Length of stay in ICU (days) | 7.4±5.9 |
Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation or number (%).
The trend of changes in GCS and FOUR score during 24 hours based on death or survival of the patients is presented in table 2. Based on these findings mean GCS (df: 1, 87; F=6.58; p=0.01) and FOUR score (df: 1, 88; F=46.64; p<0.001) were lower in those who died compared to those who survived.
Table 2.
Mean GCS and Full Outline of UnResponsiveness (FOUR) score at different times with 95% confidence interval (CI)
|
Survived
|
Non survived
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | |
| GCS | ||||
| On admission | 11.3 | 10.6 – 12.1 | 5.5 | 4.0 – 7.1 |
| After 6 hours | 11.7 | 11.0 – 12.5 | 5.1 | 3.9 – 6.3 |
| After 12 hours | 11.8 | 11.1 – 12.5 | 5.6 | 4.9 – 6.3 |
| After 24 hours | 11.6 | 10.8 – 12.3 | 4.0 | 3.3 – 4.6 |
| FOUR score | ||||
| On admission | 12.7 | 11.8 – 13.6 | 4.1 | 1.8 – 6.3 |
| After 6 hours | 13.0 | 12.1 – 13.9 | 2.7 | 1.2 – 4.2 |
| After 12 hours | 13.9 | 13.1 – 14.7 | 3.4 | 2.0 – 4.8 |
| After 24 hours | 13.6 | 12.7 – 14.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 – 0.3 |
GCS and FOUR score in predicting mortality
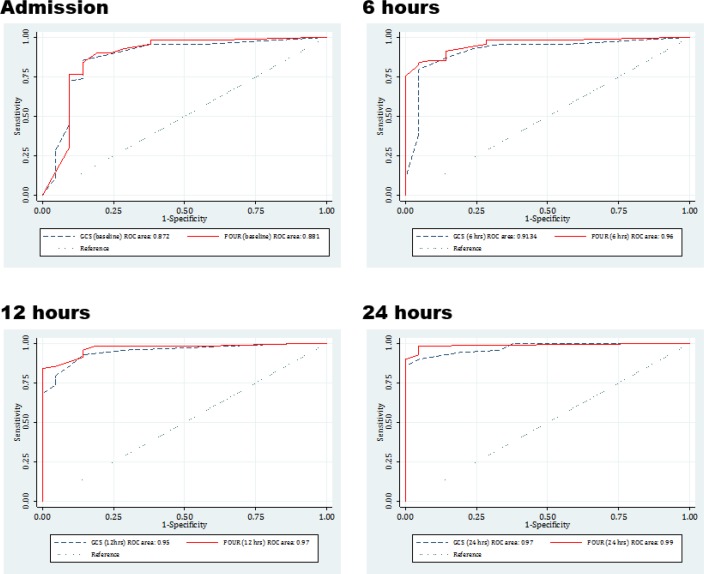
Area under the ROC curve calculated for GCS on admission and 6, 12, and 24 hours after that were 0.87 (95% CI: 0.77 to 0.98), 0.91 (95% CI: 0.84 to 0.99), 0.95 (95% CI: 0.90 to 0.99) and 0.97 (95% CI: 0.95 to 1.0), respectively. These values were calculated as 0.88 (95% CI: 0.77 to 0.99), 0.96 (95% CI: 0.92 to 1.0), 0.97 (95% CI: 0.92 to 1.0) and 0.99 (95% CI: 0.97 to 1.0), respectively for FOUR score. Comparison of area under the ROC curve of GCS and FOUR score showed that this value was not different between the 2 systems in any of the evaluated times of on admission (p=0.68), 6 hours (p=0.13), 12 hours (p=0.18), and 24 hours (p=0.20) after that (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Area under the ROC curve of Glasgow coma scale (GCS) and Full Outline of UnResponsiveness (FOUR) score for predicting the mortality of trauma patients at different times.
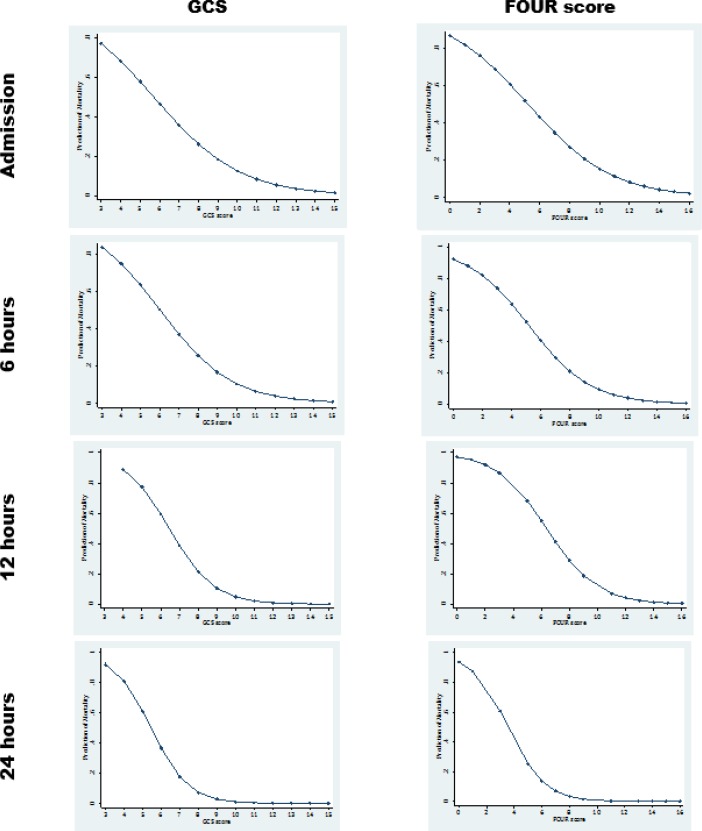
The correlation between predicted in-hospital mortality and the 2 scales (GCS and FOUR score) was also similar (Figure 2). Findings resulting from multivariate logistic regression showed that with a decrease in scores of GCS and FOUR score, the probability of mortality increases in trauma patients. Range of predicted mortality was similar in both GCS and FOUR score models (Table 3).
Figure 2.
The correlation of Glasgow coma scale (GCS) and Full Outline of UnResponsiveness (FOUR) score with in-hospital mortality of trauma patients at different times.
Table 3.
Multiple logistic regression analysis for the values of GCS and FOUR score in predicting the morality of trauma patients with 95% confidence interval (CI)
| Variable | Odds ratio | 95% CI | P* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glasgow coma scale | |||
| At admission | 0.72 | 0.53 to 0.98 | 0.04 |
| 6 hours | 0.57 | 0.38 to 0.86 | 0.007 |
| 12 hours | 0.28 | 0.10 to 0.76 | 0.01 |
| 24 hours | 0.21 | 0.06 to 0.75 | 0.02 |
| FOUR score | |||
| At admission | 0.79 | 0.62 to 0.99 | 0.049 |
| 6 hours | 0.55 | 0.36 to 0.83 | 0.004 |
| 12 hours | 0.43 | 0.22 to 0.84 | 0.01 |
| 24 hours | 0.05 | 0.02 to 0.08 | <0.0001 |
, Adjusted for age, systolic blood pressure, oxygen saturation, need for intubation and need for sedation.
Discussion
Based on the findings of our study, area under the ROC curve of both GCS and FOUR score on admission and 6, 12, and 24 hours after that were not different and both scales had the same predictive values in identifying the outcome at the time of discharge. In line with our study, the results of the study by Sahin et al. (2015) in evaluation of 105 patients also showed that GCS and FOUR score have similar value in prediction of patient mortality and can be used interchangeably (22). The results of a study by Atahar et al. (2017) also showed that GCS and FOUR score have the same predictive value in prediction of in-hospital mortality and mortality within 3 months of discharge among children (23). The findings of Gujjar et al. study showed that FOUR score is a better scale compared to GCS for evaluation of changes in level of consciousness in medical wards (24). One of the reasons for the dissimilarity of the results of this study with ours might be their different research environment. The research environment in our study was trauma ICU department. In line with our findings, the study by Temiz et al. (2016) also showed that FOUR score has the same prediction value as GCS in evaluating the level of consciousness and follow-up of patient’s status in neurosurgery ICU (25). In contrast to these findings, the results of the study by Nair et al. (2017) showed that there is a statistically significant difference between FOUR score and GCS in estimating the severity of injury in head traumas. They reported that FOUR score is a better index for evaluating the level of consciousness in patients with head trauma (26). The results of Wolf et al. study (2011) showed that GCS is one of the proper indices in prediction of mortality in emergency medical admission (27).
In this study we evaluated GCS and FOUR score in 4 points of time: on admission, and 6 hours, 12 hours, and 24 hours after admission. The results showed that the mean and standard deviation of both of these scales were different between those who died and those who survived in the 4 evaluated points of time. In line with these findings were the results of a study by Gujjar et al. (2013) that evaluated GCS and FOUR score during the initial 3 days of patients’ hospitalization and showed that there is no significant difference regarding mean value of these scales on the second and third day between dead and survived patients but there is a significant difference between these mean values on the first day (24).
Limitation
This study also had limitations including its small sample size and being performed in 2 trauma centers. Using a larger sample size and designing a multicenter study might provide more valuable and reliable results.
Conclusion:
The results of our study showed that, GCS and FOUR score have the same value in predicting the mortality of trauma patients. Both tools had high predictive power in predicting the outcome at the time of discharge.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all of participants during the different stages of this study.
Funding
This study was one part of the MS dissertation of the first author, financially supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest has been declared by the authors.
Author contribution
Parisa Ghelichkhani, Maryam Esmaeili, and Khatereh Seylani designed the study. Parisa Ghelichkhani participated in data gathering. Mostafa Hosseini analyzed data. Parisa Ghelichkhani and Maryam Esmaeili wrote the first draft and others critically revised it.
References
- 1.Saadat S, Yousefifard M, Asady H, Jafari AM, Fayaz M, Hosseini M. The most important causes of death in Iranian population; a Retrospective Cohort Study. Emergency. 2015;3(1):16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Forouzanfar MH, Sepanlou SG, Shahraz S, BESc PN, Pourmalek F, Lozano R, et al. Evaluating causes of death and morbidity in Iran, global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors study 2010. Archives of Iranian medicine. 2014;17(5):304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.de Souza Nogueira L, de Alencar Domingues C, Poggetti RS, de Sousa RMC. Nursing workload in intensive care unit trauma patients: analysis of associated factors. PloS one. 2014;9(11):e112125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Knaus WA, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Zimmerman JE, Bergner M, Bastos PG, et al. The APACHE III prognostic system Risk prediction of hospital mortality for critically ill hospitalized adults. Chest Journal. 1991;100(6):1619–36. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.6.1619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Breslow MJ, Badawi O. Severity scoring in the critically ill: part 1—interpretation and accuracy of outcome prediction scoring systems. CHEST Journal. 2012;141(1):245–52. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-0330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nakhjavan-Shahraki B, Yousefifard M, Faridaalaee G, Shahsavari K, Oraii A, Hajighanbari MJ, et al. Performance of physiology scoring systems in prediction of in-hospital mortality of traumatic children: A prospective observational study. Journal of clinical orthopaedics and trauma. 2017;8:S43–S8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2017.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ahmadi S, Yousefifard M. Accuracy of Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network Rules in Prediction of Clinically Important Head Injuries; A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Pediatrics. 2017;5(12):6285–300. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Safari S, Yousefifard M, Baikpour M, Rahimi-Movaghar V, Abiri S, Falaki M, et al. Validation of thoracic injury rule out criteria as a decision instrument for screening of chest radiography in blunt thoracic trauma. Journal of clinical orthopaedics and trauma. 2016;7(2):95–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2016.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nakhjavan-Shahraki B, Baikpour M, Yousefifard M, Nikseresht ZS, Abiri S, Mirzay Razaz J, et al. Rapid Acute Physiology Score versus Rapid Emergency Medicine Score in Trauma Outcome Prediction; a Comparative Study. Emergency (Tehran, Iran) 2017;5(1):e30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nakhjavan-Shahraki B, Yousefifard M, Hajighanbari MJ, Karimi P, Baikpour M, Mirzay Razaz J, et al. Worthing Physiological Score vs Revised Trauma Score in Outcome Prediction of Trauma patients; a Comparative Study. Emergency (Tehran, Iran) 2017;5(1):e31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nakhjavan-Shahraki B, Yousefifard M, Hajighanbari MJ, Oraii A, Safari S, Hosseini M. Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) prediction rules in identifying high risk children with mild traumatic brain injury. European journal of trauma and emergency surgery : official publication of the European Trauma Society. 2017;43(6):755–62. doi: 10.1007/s00068-017-0811-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nakhjavan-Shahraki B, Yousefifard M, Oraii A, Sarveazad A, Hajighanbari MJ, Safari S, et al. Prediction of clinically important traumatic brain injury in pediatric minor head trauma; proposing pediatric traumatic brain injury (PTBI) prognostic rule. International journal of pediatrics. 2017;5(1):4127–35. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gill M, Martens K, Lynch EL, Salih A, Green SM. Interrater reliability of 3 simplified neurologic scales applied to adults presenting to the emergency department with altered levels of consciousness. Annals of emergency medicine. 2007;49(4):403–7. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.03.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Balestreri M, Czosnyka M, Chatfield D, Steiner L, Schmidt E, Smielewski P, et al. Predictive value of Glasgow Coma Scale after brain trauma: change in trend over the past ten years. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 2004;75(1):161–2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Staff T, Eken T, Wik L, Røislien J, Søvik S. Physiologic, demographic and mechanistic factors predicting New Injury Severity Score (NISS) in motor vehicle accident victims. Injury. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2012.11.010. [In press] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dong PV, Cremer OL. Limitations of the use of the Glasgow Coma Scale in intensive care patients with non-neurological primary disease: a search for alternatives. Critical Care. 2011;15(Suppl 1):P506–P. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wijdicks EF, Bamlet WR, Maramattom BV, Manno EM, McClelland RL. Validation of a new coma scale: the FOUR score. Annals of neurology. 2005;58(4):585–93. doi: 10.1002/ana.20611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jalali R, Rezaei M. A comparison of the Glasgow Coma Scale score with full outline of unresponsiveness scale to predict patients’ traumatic brain injury outcomes in intensive care units. Critical care research and practice. 2014;2014:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2014/289803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stead LG, Wijdicks EF, Bhagra A, Kashyap R, Bellolio MF, Nash DL, et al. Validation of a new coma scale, the FOUR score, in the emergency department. Neurocritical care. 2009;10(1):50–4. doi: 10.1007/s12028-008-9145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baratloo A, Shokravi M, Safari S, Awat KA. Predictive value of Glasgow Coma Score and Full Outline of Unresponsiveness score on the outcome of multiple trauma patients. Archives of Iranian medicine. 2016;19(3):215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fischer M, Rüegg S, Czaplinski A, Strohmeier M, Lehmann A, Tschan F, et al. Research Inter-rater reliability of the Full Outline of UnResponsiveness score and the Glasgow Coma Scale in critically ill patients: a prospective observational study. Critical Care. 2010;(14):R64. doi: 10.1186/cc8963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Şahin AS, Şahin M, Öztürk NK, Kızılateş E, Karslı B. Comparision Of GCS And FOUR Scores Used In The Evaluation Of Neurological Status In Intensive Care Units. Journal of Contemporary Medicine. 2015;5(3):167–72. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jamal A, Sankhyan N, Jayashree M, Singhi S, Singhi P. Full Outline of Unresponsiveness score and the Glasgow Coma Scale in prediction of pediatric coma. World Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2017;8(1):55–60. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2017.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gujjar AR, Jacob PC, Nandhagopal R, Ganguly SS, Obaidy A, Al-Asmi AR. Full Outline of UnResponsiveness score and Glasgow Coma Scale in medical patients with altered sensorium: interrater reliability and relation to outcome. Journal of critical care. 2013;28(3):316.e1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Temiz NC, Kose G, Tehli O, Acikel C, Hatipoglu S. A comparison between the effectiveness of full outline of unresponsiveness and glasgow coma score at neurosurgical intensive care unit patients. Turkish Neurosurgery. 2016 doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.19504-16.0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nair SS, Surendran A, Prabhakar RB, Chisthi MM. Comparison between FOUR score and GCS in assessing patients with traumatic head injury: a tertiary centre study. International Surgery Journal. 2017;4(2):656. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wolf CA, Wijdicks EF, Bamlet WR, McClelland RL, editors. Further validation of the FOUR score coma scale by intensive care nurses. Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Elsevier; 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]