Abstract
Importance:
Hospitalizations of infants for bronchiolitis are common and costly. Despite the high incidence and resource burden of bronchiolitis, the mainstay of treatment remains supportive care, which frequently includes nasal suctioning.
Objective:
To examine the association between suctioning device type and suctioning lapses greater than 4 hours within the first 24 hours after hospital admission on length of stay (LOS) in infants with bronchiolitis.
Design:
Retrospective cohort study. Data were extracted from the electronic health record.
Setting:
Main hospital and satellite facility of a large quaternary care children’s hospital from January 10, 2010, through April 30, 2011.
Participants:
A total of 740 infants aged 2 to 12 months and hospitalized with bronchiolitis.
Main Outcome Measure:
Hospital LOS.
Results:
In the multivariable model adjusted for inverse weighting for propensity to receive deep suctioning, increased deep suction as a percentage of suction events was associated with increased LOS with a geometric mean of 1.75 days (95% CI, 1.56–1.95 days) in patients with no deep suction and 2.35 days (2.10–2.62 days) in patients with more than 60% deep suction. An increased number of suctioning lapses was also associated with increased LOS in a dose-dependent manner with a geometric mean of 1.62 days (95% CI, 1.43–1.83 days) in patients with no lapses and 2.64 days (2.30–3.04 days) in patients with 3 or 4 lapses.
Conclusions and Relevance:
For patients admitted with bronchiolitis, the use of deep suctioning in the first 24 hours after admission and lapses greater than 4 hours between suctioning events were associated with longer LOS.
HOSPITALIZATIONS OF IN-fants for bronchiolitis are common and costly.1–3 Despite the high incidence and resource burden of bronchiolitis, the mainstay of treatment remains supportive care, which frequently includes nasal suctioning.
The role of suctioning in the management of bronchiolitis is largely unstudied. Given that young infants prefer nasal breathing,4 the increased mucus production associated with bronchiolitis may inhibit breathingandleadtofeedingdifficulty.5Nasal suction has been suggested as an effective but temporary measure to diminish the work of breathing.6 Pharmacologic treatment of nasal obstruction with phenylephrine did not have a significant effect on clinical outcomes in bronchiolitis;however, the same study7noted a small clinical improvement in the total enrolled population that the authors attributed to nasal suctioning. Wehypothesizedthatrepeatednasopharyngealsuctioning,comparedwithnoninvasive nasal suctioning, may produce worse outcomes owing to local trauma caused by the invasive catheter. In addition, we hypothesized that because duration of relief of nasal obstruction by suctioning is time limited, frequent suctioning may improve clinical outcomes. In this retrospective cohort study, we examined the association between suctioning device type and lapses on length of stay (LOS) in infants with bronchiolitis.
METHODS
STUDY DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS
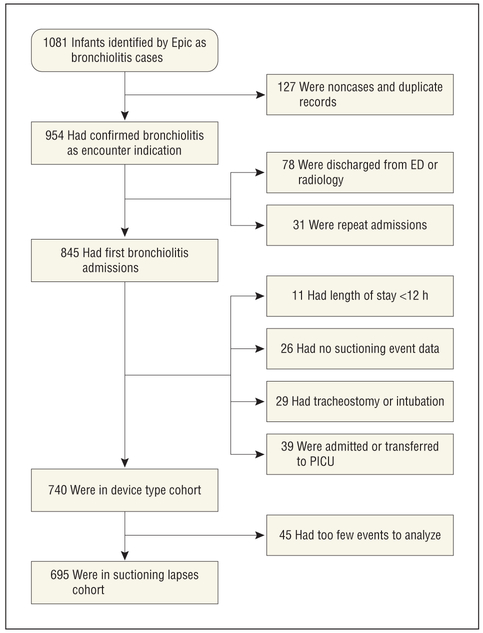
We performed a retrospective cohort study of infants hospitalized with bronchiolitis from January 10, 2010, through April 30, 2011, at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC), a large quaternary care center. All infants admitted during that period, which corresponded to 2 viral respiratory seasons, were eligible (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Study population of infants aged 2 to 12 months and hospitalized with bronchiolitis from January 10, 2010, through April 30, 2011. ED indicates emergency department; PICU, pediatric intensive care unit.
Eligible infants were aged 2 to 12 months and admitted to either the 410-bed main campus or the 12-bed satellite campus with a primary diagnosis of bronchiolitis. We excluded infants younger than 2 months owing to concerns that their increased risk of serious bacterial infection may prolong LOS for reasons unrelated to primary exposures. Patients were excluded if they had tracheostomies or if they were admitted to the intensive care unit, intubated, or had a stay less than 12 hours. Only the index admission was included for analysis for patients admitted twice during the study period.
DATA SOURCE
The identification of the cohort and extraction of the exposure and outcome variables were performed as a mediated query by staff supporting the CCHMC research data warehouse. The data were drawn from Clarity, the reporting database that stores information collected in the electronic health record Epic Systems. Data quality checks ensured proper application of inclusion criteria. Filters were applied to limit data to the specified nursing units. After data extraction identified cohort candidates, confirmation of bronchiolitis as the indication for admission and retrieval of the day of illness at presentation were performed by medical record review by 3 study investigators (G.M.M., M.W.P., and A.S.) on each chart. A sample of 37 medical records was selected for review by multiple reviewers to establish reliability of the day of illness measure, with an intra-class correlation coefficient of 0.96 (95% CI, 0.94–0.97).
EXPOSURE CLASSIFICATION
The 2 primary exposure variables of interest were suctioning device type and suctioning lapses. The CCHMC uses 2 mechanical suctioning methods, both of which use negative pressure from a vacuum system: insertion of a nasopharyngeal catheter (“deep” suction) or use of one of several types of nasal aspirators placed over the naris (“noninvasive” suction). Suctioning events by handheld bulb were not included for analysis. Mechanical suctioning events in which noninvasive suctioning was followed immediately by deep suctioning were classified as deep-suctioning events.
Device type exposure was defined as the percentage of mechanical suctioning events performed using deep suction. For example, if an infant was mechanically suctioned 5 times by deep suction and 3 times by noninvasive suction during the first 24 hours of admission, the percentage of deep-suctioning events would be 62.5%. The percentage was categorized in data quartiles giving 4 categories: none, 0 to 35%, greater than 35% to 60%, and greater than 60%, in part for ease of interpretation and to allow for nonlinear associations between the exposure and LOS.
A suctioning lapse was defined as 2 sequential mechanical suctioning events during the first 24 hours of admission separated by more than 4 hours. We limited assessment of the exposure variable to the first 24 hours of admission a priori to standardize the exposure window for infants with brief and longer hospitalizations and to define a window where suctioning would be reasonably indicated and less likely to be representative of variability in clinical status, which would confound the relationship between suctioning lapses and LOS. The 4-hour cutoff was used to reflect the most commonly ordered reassessment period and represented the 75th percentile of time elapsed between suctioning episodes for all suctioning events in the cohort. The number of suctioning lapses in the first 24 hours was treated as a categorical variable in our model, with 4 categories: none, 1, 2, and 3 or more for ease of interpretation and to allow for nonlinear associations between the exposure and LOS. Analyses including suctioning lapse were restricted to patients with at least 2 suctioning events.
OUTCOME MEASURE
The primary outcome was hospital LOS, calculated as time difference between arrival on the unit of admission and departure from the hospital.
COVARIATES
Data collected for analysis were age, sex, insurance status, co-morbid chronic or acute illnesses, admitting nursing unit, days of illness before admission, and potential severity of illness markers (average heart rate, average respiratory rate, temperature >38°C within first 24 hours, supplemental oxygen requirement in first 24 hours, and receipt of an intravenous fluid bolus ≥20 mL per kilogram body weight). For analysis, the admitting nursing unit was divided into 4 categories: academic unit A (a 24-bed infant/child unit at the base hospital with resident coverage), academic unit B (a 24-bed infant/child unit at the base hospital with resident coverage), satellite unit (a 12-bed inpatient unit at the satellite hospital with attending coverage), and other academic (any other unit at the base hospital). Data regarding administration of medical therapies within the first 24 hours, including β-agonists, racemic epinephrine, hypertonic saline, and systemic corticosteroids, were also collected. Comorbidities were identified by International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes and grouped anatomically or by disease state to account for possible pathophysiologic interference with bronchiolitis or suctioning as a treatment modality. Details of comorbidity groupings including ICD-9-CM codes and frequency are found in eTable 1 (http://www.jamapeds.com). Because our primary exposure variable of device type was the percentage of all suctioning events, the total number of suctioning events was included in each model such that children with the same total number of events were compared head to head regarding exposure variables.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Owing to the skewed nature of LOS data, these data were transformed using the natural logarithm. To address potential confounding by indication, propensity score regression adjustment was used to balance the 4 deep-suctioning groups (none, >0 to 35%, >35% to 60%, and >60%). Propensity scores were calculated using a generalized logistic model with the group greater than 60% specified as the reference group and were based on each of our 17 covariates. A propensity score weight was calculated as the inverse of the propensity score adjusted for the sample size in each deep-suctioning group. A propensity score–weighted generalized linear model was then used to assess association between LOS and the 2 independent variables (deep suctioning and suctioning lapses). Covariates were included in the propensity score–weighted model only if significant imbalances existed among exposure groups after propensity score weighting, which was assessed using linear regression, analysis of variance, and χ2 tests as appropriate.
Interaction between the 2 exposure variables was considered. The analyses were repeated after restricting the cohort to patients receiving supplemental oxygen and separately after excluding patients with comorbid conditions. Finally, an analysis stratified by hospital unit was performed. All multivariable models included the total number of suctioning events as a covariate. The reported statistical analyses did not account for potential clustering because of the small number of hospital units in the study.
The study was approved by the institutional review board at CCHMC with a waiver of informed consent.
RESULTS
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS
A total of 740 patients met inclusion and exclusion criteria for the device type cohort and 695 patients for the suctioning lapses cohort (Figure 1). In the device type cohort, patients had a mean (SD) age of 5.6 (2.7) months and 40.7% were female. More than half (65.6%) were insured by Medicaid, and 57.2% received β-agonist treatment, with most (60.5%) of these patients receiving a single dose and 20.6% receiving 2 doses (Table 1). Characteristics of the suctioning lapses cohort were similar (Table 2).
Table 1.
Descriptive Characteristics of the Device Type Cohorta
| Characteristic | Invasive Device Percentage, No. (%) | P Valueb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort (n = 740) |
None (n = 242) |
>0% to 35% (n = 171) |
>35% to 60% (n = 155) |
>60% (n = 172) |
||
| Female sex | 301 (40.7) | 97 (40.4) | 66 (38.6) | 60 (38.7) | 78 (45.3) | .54 |
| Age, mean (SD), mo | 5.6 (2.7) | 5.7 (2.7) | 5.5 (2.7) | 5.9 (2.9) | 5.3 (2.6) | .28 |
| Medicaid recipient | 488 (65.6) | 154 (63.6) | 113 (66.1) | 110 (71.0) | 111 (64.5) | .48 |
| Department | ||||||
| Academic unit B | 180 (24.3) | 58 (24.0) | 58 (33.9) | 41 (26.5) |  |
<.001 |
| Academic unit A | 339 (45.8) | 38 (15.7) | 76 (44.4) | 97 (62.6) | ||
| Satellite unit | 117 (15.8) | 95 (39.3) | 19 (11.1) | 2 (1.3) | ||
| Other academic | 104 (14.1) | 51 (21.1) | 18 (10.5) | 15 (9.7) | ||
| Ill before admission, d | ||||||
| <2 | 40 (5.4) | 12 (5.0) | 14 (8.2) | 7 (4.5) | 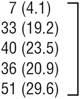 |
.74 |
| 2 to <3 | 165 (22.2) | 56 (23.1) | 38 (22.2) | 38 (24.5) | ||
| 3 to <4 | 150 (20.3) | 43 (17.8) | 32 (18.7) | 35 (22.6) | ||
| 4 to <5 | 130 (17.6) | 41 (16.9) | 28 (16.4) | 25 (16.2) | ||
| ≥5 | 229 (30.9) | 80 (33.1) | 51 (29.8) | 47 (30.3) | ||
| Intravenous fluid bolus | ||||||
| ≤20 mL/kg | 685 (92.6) | 229 (94.6) | 159 (92.9) | 140 (90.3) | .38 | |
| ≥20 mL/kg | 55 (7.4) | 13 (5.4) | 12 (7.0) | 15 (9.6) | ||
| Any O2 within first 24 h | 428 (57.8) | 122 (50.4) | 94 (54.9) | 96 (61.9) | 116 (67.4) | .004 |
| Temperature >38°C in first 24 h | 361 (48.8) | 115 (47.5) | 84 (49.1) | 82 (52.9) | 80 (46.5) | .67 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Asthma | 69 (9.3) | 23 (9.5) | 19 (11.1) | 15 (9.7) | 12 (7.0) | .62 |
| Bacterial pneumonia | 68 (9.2) | 20 (8.3) | 13 (7.6) | 12 (7.7) | 23 (13.4) | .19 |
| Congenital heart disease | 27 (3.6) | 7 (2.9) | 5 (2.9) | 3 (1.9) | 12 (7.0) | .09 |
| Nasal and sinus comorbidities | 23 (3.1) | 6 (2.5) | 7 (4.1) | 5 (3.2) | 5 (2.9) | .83 |
| Chronic lower respiratory disease | 7 (0.9) | 5 (2.1) | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) | 0 | .21 |
| Diseases of pharynx, larynx, and trachea | 29 (3.9) | 11 (4.5) | 6 (3.5) | 7 (4.5) | 5 (2.9) | .82 |
| Muscular dystrophy | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Medication usage | ||||||
| Hypertonic saline | 2 (0.3) | 0 | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) | 0 | |
| Racemic epinephrine | 73 (9.9) | 13(5.4) | 15(8.8) | 24 (15.5) | 21 (12.2) | .01 |
| Corticosteroids | 85 (11.4) | 26(10.7) | 25(14.9) | 19 (12.3) | 15 (8.7) | .37 |
| β-Agonists | 423 (57.2) | 130(53.7) | 103(60.2) | 98 (63.2) | 92 (53.4) | .16 |
Data are presented as number (percentage) unless otherwise indicated.
For difference between groups from analysis of variance, χ2 test, or Fisher exact test.
Table 2.
Descriptive Characteristics of the Suctioning Lapses Cohorta
| Characteristic | Suctioning Lapses, No. (%) | P Valueb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort (n = 695) |
None (n = 107) |
1 (n = 280) |
2 (n = 245) |
3 or 4 (n = 63) |
||
| Female sex | 282 (40.5) | 54 (50.5) | 104 (37.1) | 99 (40.4) | 25 (39.7) | .13 |
| Age, mean (SD), mo | 5.6 (2.7) | 5.3 (2.9) | 5.7 (2.6) | 5.6 (2.7) | 5.9 (2.9) | .53 |
| Medicaid recipient | 458 (65.9) | 81 (75.7) | 184 (67.5) | 153 (62.4) | 40 (63.4) | .11 |
| Department | ||||||
| Academic unit B | 162 (23.3) | 20 (18.7) | 70 (25.0) | 52 (21.2) |  |
.13 |
| Academic unit A | 326 (46.9) | 44 (41.1) | 127 (45.4) | 126 (51.4) | ||
| Satellite unit | 115 (16.5) | 26 (24.3) | 49 (17.5) | 32 (13.1) | ||
| Other academic | 92 (13.2) | 17 (15.9) | 34 (12.1) | 35 (14.3) | ||
| Ill before admission, d | ||||||
| <2 | 38 (5.4) | 7 (6.5) | 13 (4.6) | 15 (6.1) |  |
.80 |
| 2 to <3 | 153 (22.0) | 30 (28.0) | 61 (21.7) | 46 (18.8) | ||
| 3 to <4 | 142 (20.4) | 17 (15.9) | 59 (21.1) | 54 (22.1) | ||
| 4 to <5 | 125 (17.9) | 17 (15.9) | 56 (20.0) | 40 (16.3) | ||
| ≥5 | 214 (30.8) | 32 (29.9) | 81 (28.9) | 82 (33.5) | ||
| Intravenous fluid bolus | ||||||
| <20 mL/kg | 640 (92.1) | 94 (87.9) | 260 (92.8) | 226 (92.2) | .33 | |
| ≥20 mL/kg | 55 (7.9) | 13 (12.1) | 20 (7.1) | 19(7.8) | ||
| Any O2 in first 24 h | 409 (58.8) | 60 (56.1) | 154 (55.0) | 156 (63.7) | 39 (61.9) | .20 |
| Temperature >38°C in first 24 h | 343 (49.4) | 49 (45.8) | 133 (47.5) | 126 (51.4) | 35 (55.5) | .51 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Asthma | 68 (9.8) | 10 (9.3) | 30 (10.7) | 21 (8.6) | 7 (11.1) | .84 |
| Bacterial pneumonia | 65 (9.4) | 10 (9.3) | 23 (8.2) | 25 (10.2) | 7 (11.1) | .83 |
| Congenital heart disease | 24 (3.5) | 5 (4.6) | 6 (2.1) | 12 (4.9) | 1 (1.6) | .25 |
| Nasal and sinus comorbidities | 23 (3.3) | 2 (1.9) | 8 (2.9) | 10 (4.1) | 3 (4.8) | .60 |
| Chronic lower respiratory tract disease | 6 (0.8) | 1 (0.9) | 1 (0.4) | 4 (1.6) | 0 | .39 |
| Diseases of pharynx, larynx, and trachea | 25 (3.6) | 4 (3.7) | 8 (2.9) | 11 (4.5) | 2 (3.2) | .78 |
| Muscular dystrophy | 1 (0.1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.4) | 0 | |
| Medication usage | ||||||
| Hypertonic saline | 2 (0.1) | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | 0 | |
| Racemic epinephrine | 69 (9.9) | 10 (9.3) | 30 (10.7) | 25 (10.2) | 4 (6.3) | .81 |
| Corticosteroids | 80 (11.5) | 9 (8.4) | 28 (10.0) | 36 (14.7) | 7 (11.1) | .27 |
| β-Agonists | 401 (57.7) | 58 (54.2) | 175 (62.5) | 134 (54.7) | 34 (53.9) | .21 |
Data are presented as No. (%) unless otherwise indicated.
For difference between groups from analysis of variance, χ2 test, or Fisher exact test.
OUTCOMES
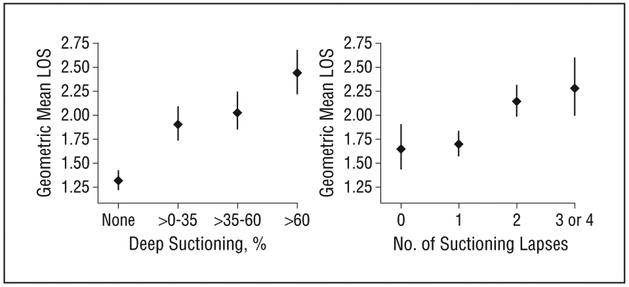
In the device type cohort, the unadjusted geometric mean LOS was 1.82 days (95% CI, 1.73–1.90). Of the 740 patients, 242 (32.7%) never received deep suctioning, 171(23.1%) had 0% to 35% deep suctioning, 155 (20.9%) had more than 35% to 60% deep suctioning, and 172(23.2%) had more than 60% deep suctioning. The un-adjusted geometric mean LOS was 1.32 days (95% CI,1.22–1.42 days) for patients with no deep-suctioning events, 1.91 days (1.74–2.09 days) for patients with 0 to 35% deep suctioning, 2.04 days (1.86–2.24 days) for patients with more than 35% to 60% deep suctioning, and2.44 days (2.22–2.68 days) for patients with more than 60% deep suctioning (P < .01) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Unadjusted length of stay (LOS) by exposure. Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
The suctioning frequency cohort had 695 patients after the exclusion of 45 patients who had 1 or 0 suctioning events and hence no opportunity to experience a suctioning lapse. The unadjusted geometric mean LOS of this cohort was 1.89 days (95% CI, 1.80–1.98 days). Among the cohort, 107 (15.4%) had no lapses, 280 (40.3%) had 1 lapse, 245 (35.3%) had 2, and 63 (9.1%) had 3 or more during the first 24 hours of admission, with a maximum number of recorded lapses of 4. The unadjusted geometric mean LOS was 1.65 days (95% CI, 1.44–1.90 days) in patients with no lapses, 1.70 days (1.58–1.83 days) in patients with 1 lapse, 2.14 days (1.99–2.31 days) in patients with 2 lapses, and 2.28 days (2.00–2.60 days) in patients with 3 or 4 lapses (P < .01) (Figure 2). The un-adjusted geometric mean LOS for the 45 patients excluded from the second cohort owing to fewer than 2 suctioning events was 1.01 (95% CI, 0.84–1.20).
For the multivariable analysis, both increased deep-suctioning frequency and suctioning lapses were significantly associated with an increased LOS in a dose-dependent manner (Table 3). There was no evidence of an interaction between the 2 exposures. These associations remained significant when the cohort was restricted to patients requiring oxygen or without comorbidities (eTables 2 and 3). In our analyses stratified by unit, consistent significant effects of suctioning lapses and device type were found on academic units A and B (Table 4). Similar trends in associations were observed in the satellite unit and other academic, but these did not reach statistical significance with the exception of suctioning lapses on the satellite unit.
Table 3.
Adjusted Geometric Mean Length of Stay
| Exposures | Coefficient (SE) | Length of Stay, d, Geometric Mean (95% CI)a |
P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invasive device percentage | |||
| None | −0.296 (0.059) |  |
<.001 |
| >0 to 35 | −0.205 (0.055) | ||
| >35 to 60 | −0.179 (0.058) | ||
| >60 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Suctioning lapses | |||
| 0 | −0.491 (0.080) |  |
<.001 |
| 1 | −0.432 (0.070) | ||
| 2 | −0.236 (0.070) | ||
| 3 or 4 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Covariates | |||
| Sex | |||
| Female | 0.001 (0.042) | .97 | |
| Male | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Age, mo | −0.020 (0.008) | … | .01 |
| Medicaid | |||
| Yes | 0.062 (0.043) | .15 | |
| No | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Department | |||
| Academic unit B | −0.068 (0.068) |  |
.02 |
| Academic unit A | −0.134 (0.062) | ||
| Satellite unit | −0.218 (0.076) | ||
| Other academic | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Ill before admission, d | |||
| <2 | 0.036 (0.087) |  |
.80 |
| 2 to <3 | −0.017 (0.054) | ||
| 3 to <4 | −0.053 (0.057) | ||
| 4 to <5 | −0.049 (0.065) | ||
| ≥5 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Intravenous fluid bolus | |||
| <20 mL/kg | −0.052 (0.075) | .49 | |
| ≥20 mL/kg | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Any O2 within first 24 h | |||
| Yes | 0.239 (0.043) | <.001 | |
| No | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Temperature >38°C in first 24 h | |||
| Yes | 0.040 (0.041) | .34 | |
| No | 1 [Reference] | ||
| β-Agonists, No. of doses | |||
| 0 | −0.083 (0.058) |  |
.01 |
| 1 | −0.168 (0.057) | ||
| ≥2 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Total No. of suctioning events | 0.076 (0.008) | <.001 |
Exponential of the estimated marginal means (least squares means). Geometric means with different superscript capital letters are statistically different at P < .05.
Table 4.
Adjusted Geometric Mean Length of Stay Stratified by Unit
| Unit | Coeflicient (SE) | Length of Stay, d, Geometric Mean (95% CI)a |
P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Academic B (n = 162) | |||
| Invasive device percentage | |||
| None | −0.378 (0.125) |  |
.002 |
| >0 to 35 | −0.068 (0.118) | ||
| >35 to 60 | 0.118 (0.126) | ||
| >60 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Suctioning lapses | |||
| 0 | −0.474 (0.179) |  |
.002 |
| 1 | −0.316 (0.144) | ||
| 2 | −0.033 (0.148) | ||
| 3 or 4 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Academic A (n = 326) | |||
| Invasive device percentage | |||
| None | −0.221 (0.092) |  |
.004 |
| >0 to 35 | −0.255 (0.079) | ||
| >35 to 60 | −0.236 (0.080) | ||
| >60 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Suctioning lapses | |||
| 0 | −0.421 (0.129) |  |
<.001 |
| 1 | −0.397 (0.111) | ||
| 2 | −0.186 (0.112) | ||
| 3 or 4 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Satellite (n = 115) | |||
| Invasive device percentage | |||
| None | −0.153 (0.105) | .15 | |
| Any | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Suctioning lapses | |||
| 0 | −0.347 (0.127) |  |
.03 |
| 1 | −0.172 (0.121) | ||
| 2, 3, or 4 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Other academic (n = 92) | |||
| Invasive device percentage | |||
| None | −0.363 (0.181) |  |
.10 |
| >0 to 35 | −0.405 (0.184) | ||
| >35 to 60 | −0.129 (0.186) | ||
| >60 | 1 [Reference] | ||
| Suctioning lapses | |||
| 0 | −0.353 (0.192) |  |
.19 |
| 1 | −0.144 (0.163) | ||
| 2, 3, or 4 | 1 [Reference] |
Exponential of the estimated marginal means (least squares means).
All models include the same covariates listed in Table 3.
COMMENT
Our study has 2 primary findings. First, we found a significant association between increased LOS and percentage use of deep suctioning during the first 24 hours of admission, with an average difference of 0.6 days between groups with low and high exposure. Second, we found that for infants hospitalized with bronchiolitis, lapses of more than 4 hours between suctioning events in the first 24 hours after admission were associated with statistically significant longer LOS. We believe the difference in geometric mean of up to 1.0 day between patients with no suctioning lapses and those with 3 or 4 lapses is clinically meaningful.
We propose that a mechanism for the association between the use of deep suctioning and increased LOS relative to noninvasive suctioning may be that deep suctioning causes edema and irritation of the upper airway. Alternatively, noninvasive suctioning could be more effective in mobilizing nasal secretions through the larger-caliber catheter, resulting in shorter LOS.
Our novel description of suctioning lapses as the exposure variable fits the proposed mechanistic benefit of suctioning in our hypothesis and provides a logical framework for further study and application to clinical care. Bronchiolitis is associated with edema, intermittent obstruction of the upper airways, and, on histologic examination, the presence of sloughed bronchiolar mucosal cellular debris in the smaller airways.8 Two potentially causal mechanisms support our identified association. One such mechanism is that maintaining the regularity of suctioning episodes maximizes air movement in the lower air way and thus increases mobilization of secretions, resulting in decreased recovery times. It is also possible that regular suctioning results in agitation of the patient, with resultant increased minute volume and secretion mobilization. Clinical research on suctioning in bronchiolitis is limited, but our findings complement those of Weisgerber et al,9 who found a significant association between deep suctioning early in hospitalization and LOS in bivariate analysis. We included medication exposures in our propensity score calculation despite a lack of evidence showing that they alter outcome because we believe they may be a proxy measure of severity of illness or a wheezing phenotype more similar to childhood asthma than acute bronchiolitis. Our rare use of hyper-tonic saline did not allow us to include this variable in any models. One medication exposure, β-agonists administered in the first 24 hours, was included in the model, although its relationship to LOS was complex, with in fants receiving 1 dose having a significantly shorter LOS than those who received 2 or more. We believe the longer LOS with multiple β-agonists is likely related to an asthma-like phenotype because inpatients at CCHMC with asthma are treated with a scheduled β-agonist weaning protocol, which carries with it expected discharge goals based on β-agonist administration frequency. The implementation of this additional discharge goal could subsequently prolong LOS. We included asthma and/or reactive airways disease diagnosis and β-agonists in the model to address and control for the challenges of diagnosing the etiology of wheezing in infants.
Our study has several limitations. Comorbid diagnoses were identified from discharge diagnoses generated in the course of clinical care and were subject to mis-classification bias. For several such diagnoses, it is difficult to predict their influence on LOS. We addressed this in 2 ways: first, by including the comorbidities to determine propensity score weights, and second, by doing a sub analysis that excluded comorbidities (eTable 3). In both cases, statistical significance of the exposure associations was unaffected. In addition, some comorbidities (eg, prematurity) were not reliably documented in our database.
Severity of illness classification in bronchiolitis remains challenging. We attempted to address this through the use of multiple prognostic markers, including underlying conditions,10,11 age,11–13 oxygen saturation,12 tachycardia, and dehydration,13 in our propensity score model. Age was not associated with LOS in bivariate analysis, but younger age was associated with increased LOS in the propensity-weighted model. The relationship between age, suctioning, and LOS is likely complex and is uncertain. As an outcome measure, LOS can be problematic. The bronchiolitis evidence-based care guideline and supporting physician order set14–16 that is widely used at our institution includes standardized discharge criteria, which somewhat mitigates this issue.
Confounding by indication could also have affected our results because our extensive covariates may not fully adjust for nurses’ and respiratory therapists’ tendency to use a more invasive intervention on an infant believed to be sicker, thus causing independent associations between deep suctioning and increased LOS. To our knowledge, there are no current practice standards regarding the use of suctioning, and this decision may have been based on individual nurse beliefs or unit culture. Confounding by indication for deep suctioning may be a source of systematic error, and our results should be interpreted with caution in this context. Adjustment for a propensity to receive deep suctioning attempts to account for this selection bias; however, bias may still exist if not fully captured in our set of covariates. A prospective study that randomizes suctioning device type or that has a specific device type protocol is needed to better address this bias. With suctioning lapses, however, confounding by indication would bias toward the null because nurses may suction infants perceived to be sicker more frequently. The true association between suctioning lapses and increased LOS may thus be larger than we report. Because these data were collected in the course of clinical care, we cannot comment on the validity or reliability of our exposure assessment; however, we would expect that any misclassification would be random and would not bias results. Finally, selection bias may have been introduced by selective assignment of patients with higher illness severity to nursing units more likely to use deep suctioning. Mitigating this were substantial overlap between nurses, the same group of hospital medicine faculty, and use of evidence-based care guidelines and order sets14–16 throughout each site. We addressed this limitation by including nursing unit in our regression analysis.
In summary, for patients admitted to the general pediatric wards with bronchiolitis, the use of deep suctioning in the first 24 hours after admission and lapses greater than 4 hours between suctioning events were associated with longer LOS. Because there is insufficient data to determine a causal relationship, we intend to continue to examine these associations as we incorporate these findings into clinical practice at our institution. Further investigation here and at other centers should include consideration of prospective designs with randomization or suctioning protocols to address confounding by indication for device type, as well as the use of validated respiratory scores to examine the effect of suctioning on more proximal outcomes.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Additional Contributions: We thank all our colleagues in the Division of Hospital Medicine for their support of our project; Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, for his mentor-ship, guidance, and critical review of the article; Jeffery M. Simmons, MD, MSc, and Joshua K. Schaffzin, MD, PhD, for their mentorship and guidance; and Keith Marsolo, PhD, for his assistance with data extraction.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported.
Online-Only Material: The 3 eTables are available at http://www.jamapeds.com.
REFERENCES
- 1.Shay DK, Holman RC, Newman RD, Liu LL, Stout JW, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980–1996. JAMA. 1999;282(15):1440–1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Leader S, Kohlhase K. Recent trends in severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) among US infants, 1997 to 2000. J Pediatr. 2003;143(5)(suppl):S127–S132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pelletier AJ, Mansbach JM, Camargo CA Jr. Direct medical costs of bronchiolitis hospitalizations in the United States. Pediatrics. 2006;118(6):2418–2423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bergeson PS, Shaw JC. Are infants really obligatory nasal breathers? Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2001;40(10):567–569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Panitch HB. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis: supportive care and therapies designed to overcome airway obstruction. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22 (2 suppl):S83–S88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Management of Bronchiolitis. Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics. 2006; 118(4):1774–1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ralston S, Roohi M. A randomized, controlled trial of nasal phenylephrine in infants hospitalized for bronchiolitis. J Pediatr. 2008;153(6):795–798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Allen TC. Pathology of small airways disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(5): 702–718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weisgerber MC, Lye PS, Li S-H, et al. Factors predicting prolonged hospital stay for infants with bronchiolitis. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(5):264–270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moler FW, Khan AS, Meliones JN, Custer JR, Palmisano J, Shope TC. Respiratory syncytial virus morbidity and mortality estimates in congenital heart disease patients: a recent experience. Crit Care Med. 1992;20(10):1406–1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McMillan JA, Tristram DA, Weiner LB, Higgins AP, Sandstrom C, Brandon R. Prediction of the duration of hospitalization in patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection: use of clinical parameters. Pediatrics. 1988;81(1):22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Green M, Brayer AF, Schenkman KA, Wald ER. Duration of hospitalization in previously well infants with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989;8(9):601–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Walsh P, Rothenberg SJ, O’Doherty S, Hoey H, Healy R. A validated clinical model to predict the need for admission and length of stay in children with acute bronchiolitis. Eur J Emerg Med. 2004;11(5):265–272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kotagal UR, Robbins JM, Kini NM, Schoettker PJ, Atherton HD, Kirschbaum MS. Impact of a bronchiolitis guideline: a multisite demonstration project. Chest. 2002; 121(6):1789–1797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Muething S, Schoettker PJ, Gerhardt WE, Atherton HD, Britto MT, Kotagal UR. Decreasing overuse of therapies in the treatment of bronchiolitis by incorporating evidence at the point of care. J Pediatr. 2004;144(6):703–710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bronchiolitis Guideline Team, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Evidence-based care guideline for management of bronchiolitis in infants 1 year of age or less with a first time episode. http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/service/j/anderson-center/evidence-based-care/recommendations/specialty-discipline/. Published 2010 Accessed January 26, 2013.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.