Abstract
Pepper (Capsicum annuum) is an economically important vegetable and heat stress can severely impair pepper growth, development, and productivity. The molecular mechanisms underlying pepper thermotolerance are therefore important to understand but remain elusive. In the present study, we characterized the function of CaHSL1, encoding a HAESA-LIKE (HSL) receptor-like protein kinase (RLK), during the response of pepper to high temperature and high humidity (HTHH). CaHSL1 exhibits the typical structural features of an arginine-aspartate RLK. Transient overexpression of CaHSL1 in the mesophyll cells of Nicotiana benthamiana showed that CaHSL1 localizes throughout the cell, including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and the nucleus. CaHSL1 was significantly upregulated by HTHH or the exogenous application of abscisic acid but not by R. solanacearum inoculation. However, CaHSL1 was downregulated by exogenously applied salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate, or ethephon. Silencing of CaHSL1 by virus-induced gene silencing significantly was reduced tolerance to HTHH and downregulated transcript levels of an associated gene CaHSP24. In contrast, transient overexpression of CaHSL1 enhanced the transcript abundance of CaHSP24 and increased tolerance to HTHH, as manifested by enhanced optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of photosystem II in the dark (Fv/Fm) and actual photochemical efficiency of photosystem II in the light. In addition, CaWRKY40 targeted the promoter of CaHSL1 and induced transcription during HTHH but not in response to R. solanacearum. All of these results suggest that CaHSL1 is directly modulated at the transcriptional level by CaWRKY40 and functions as a positive regulator in the response of pepper to HTHH.
Keywords: Capsicum annuum, CaHSL1, CaWRKY40, thermotolerance, positive regulator
Introduction
Heat stress is an important abiotic stress, causing cellular damage including misfolding and aggregation of proteins, membrane damage, disruption of microtubule organization and accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Rao et al., 2010; Mayer, 2012), eventually leading to arrested plant growth and development. To cope with heat stress, plants have evolved defense mechanisms including basal thermotolerance induced by a gradual increase to the normally lethal temperature and acquired thermotolerance induced by a short acclimation period at moderately high temperatures or other non-lethal stress prior to heatstress (Larkindale et al., 2005). During basal and acquired thermotolerance, genes encoding heat shock proteins (HSPs) are transcriptionally regulated by transcription factors including heat shock factors (HSFs) to protect plants against stress by re-establishing normal protein conformation and, thus, cellular homeostasis (Wang W. et al., 2004; Kotak et al., 2007; Mittler et al., 2012; Waters, 2013).
To respond effectively to heat stress, it is crucial for plants to sense the heat stress, which will translate the signals into the appropriate HSRs. Plants employ a set of sensors that perceive heat stress; these sensors include a plasma-membrane channel that initiates an inward calcium flux, a histone sensor in the nucleus, 2 unfolded protein sensors in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the cytosol (Mittler et al., 2012), phytochrome B (Jung et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2017) and an ER-localized bZIP28 (Srivastava et al., 2014). The perception of heat stress by these sensors initiates complicated downstream signaling networks involving Ca2+ signaling (Delk et al., 2005; Saidi et al., 2011; Jia et al., 2014), phytohormones including salicylic acid (SA) (Clarke et al., 2004, 2009), jasmonic acid (JA) (Clarke et al., 2009), ethylene (ET) (Larkindale and Huang, 2004) and abscisic acid (ABA) (Larkindale and Huang, 2004; Halter et al., 2014), ROS such as hydrogen peroxide (Dat et al., 1998; Saidi et al., 2011), nitric oxide (Zhao et al., 2010; Wang L. et al., 2014), and the MAPK cascade (Zhai et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2018). These signaling pathways amplify signals and transduce them to the nucleus where many defense-related genes are transcriptionally modulated, leading to appropriate thermotolerance. This is regulated by various transcription factors (TFs) such as HSFs (Liu et al., 2013; Xue et al., 2015), SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (Chao et al., 2017), WRKY (Dang et al., 2013), and NAC family members (Guan et al., 2014). These TFs are recruited and regulated by complicated signaling networks. The dissection of these signaling networks is an important approach to elucidating the mechanism underlying plant thermotolerance. However, the components of the signaling network during HSR have not been fully identified or characterized.
Phosphorylation that is mediated by protein kinases is an important regulatory mechanism in cellular signal transduction. Plant RLKs contain a cytoplasmic serine/threonine protein kinase domain, a single membrane-spanning segment and a large extracytoplasmic domain that can be divided into the S-domain class, leucine-rich repeat (LRR) class and a class that has epidermal growth factor-like repeats (Walker, 1994). Receptor-like kinases in plants are encoded by a big gene family, including at least 610 members in Arabidopsis thaliana and 1132 in rice (Oryza sativa) (Shiu et al., 2004). Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs) constitute the largest RLK subfamily with at least 223 members in Arabidopsis (Gou et al., 2010). They are characterized by 1-32 copies of leucine-rich repeats in their extracellular domains (Shiu and Bleecker, 2001a,b; Lehti-Shiu et al., 2009), and can be grouped into 13 subfamilies (LRR I to XIII) (Shiu and Bleecker, 2001a). Based on the presence or absence of an arginine aspartate (RD) motif in the kinase domains, they can be classified as RD-or non-RD LRR-RLKs (Wu et al., 2015). Many non-RD LRR-RLKs such as LRK10, FLS2 (Gómez-Gómez and Boller, 2002; Göhre et al., 2008), and Xa21 (da Silva et al., 2004) do not autophosphorylate the activation loop and act as potential pathogen/microbe-associated molecular pattern recognition receptors (Dardick and Ronald, 2006). RD-LRR RLKs such as SIRK, SYMRK, BAK1/SERK3, SCM, RKF1, PSK, Bri1/Systemin, WAKL, and ERECTA have been implicated in a broad spectrum of biological processes including plant growth, development, environmental stress response and plant immunity (Godiard et al., 2003; Dardick and Ronald, 2006; Sánchez-Rodríguez et al., 2009). In addition, two Arabidopsis RLKs, HAESA (HAE) and HAESA-like 2 (HSL2) play roles in the regulation of floral organ abscission (Cho et al., 2008; Stenvik et al., 2008; Patharkar and Walker, 2015; Baer et al., 2016). However, the results described above were largely drawn from a small numbers of RLKs in the model plants rice and Arabidopsis. The roles of RLKs in other non-model plants, particularly in thermotolerance, remain to be investigated.
Pepper is one of the most important vegetables worldwide. Exposure to frequent heat stress can cause damage to pepper plants, resulting in arrested growth, development and productivity. In particular, frequent concurrent exposure to high temperature and high humidity (HTHH) might leave pepper plants more susceptible to pathogens by direct damage, or by causing serious diseases via attenuating pepper immunity on the one hand and promoting the development of associated soil-borne pathogens on the other hand. Ralstonia solanacearum (R. solanacearum) is a typical soil-borne pathogen in pepper field, and it causes pepper bacterial wilt, one of the most important pepper diseases in worldwide. Our previous studies have revealed that CaWRKY6, CaWRKY40, CabZIP63, and CaCDPK15 act as positive regulators in the response of pepper to HTHH, with CaWRKY40 directly regulated by CaWRKY6 and CabZIP63, and indirectly regulated by CaCDPK15, forming positive feedback loops (Wang et al., 2013; Cai et al., 2015; Shen et al., 2016a,b). In the present study, with an approach of gain- and loss-of-function assay by transient overexpression and virus induced gene silencing, respectively, we provided evidence that CaHSL1 (HAESA-LIKE1 of Capsicum annuum), encoding an RD RLK, acts directly as a positive regulator in the thermotolerance of pepper under HTHH and is transcriptionally regulated by CaWRKY40, our result might benefit the elucidation of molecular mechanism underlying pepper thermotolerance.
Materials and Methods
Pepper and Tobacco Plant Cultivation and Heat Stress or Exogenous Hormone Treatments
Pepper plants (variety CM334) and Nicotiana benthamiana plants were cultivated using the method described in our previous study (Cheng et al., 2017). R. solanacearum strain FJC100301 (Dang et al., 2013) was cultured using a previously described method (Cheng et al., 2017). The bacterial cell solution used for inoculation was diluted to 108 cfu mL−1 (OD600 = 0.8). For root inoculation, pepper and tobacco plants at the 8-leaf stage were irrigated with 1 mL of the resulting R. solanacearum suspension. For leaf inoculation, the third leaves from the top of the pepper or tobacco plants at the 8-leaf stage were infiltrated with 10 μL of the R. solanacearum suspension using a syringe without a needle, and the mock-treated control was inoculated with 10 mM MgCl2.
For the assay of the transcript levels of CaHSL1, the leaves of pepper plants at the 4-leaf stage were sprayed with 1 mM of SA (in 10% distilled ethanol), 100 μM of MeJA (in 10% distilled ethanol), 100 μM of ETH (in sterile double-distilled H2O [ddH2O]) or 200 μM of ABA (in sterile double-distilled H2O). The mock treatment was performed by spraying with a corresponding solvent or sterile ddH2O.
For HTHH, the TRV::CaHSL1 and TRV::00 and wild pepper plants were exposed to heat stress at 42°C or other temperatures as indicated under 90% humidity in darkness to exclude the effect of dehydration, and then were either harvested at indicated time points to isolate total RNA for assay of transcriptional levels of CaHSL1, or monitored for heat-stress damage.
Vector Construction
All the vectors used in the present study were constructed using Gateway cloning technology (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States). The full length ORF of CaHSL1, CaWRKY40 or (with or without the termination codon) were cloned to the entry vector pDONR207 by BP reaction, then to various destination vectors including pEarleyGate201, pEarleyGate103 (containing a GFP protein tag for subcellular localization) or pEarleyGate202 [containing a FLAG protein tag for chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis] by LR reaction using a gateway cloning technique (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States). To construct the vector for VIGS to avoid possible off targeting, two specific fragments of CaHSL1 were employed, one is 360 bps in length from the ORF and the other is 300 bps in length from the 3′ UTR of CaHSL1, to construct the vector for CaWRKY40 silencing, a fragment of 300 bps in length from the 3′UTR of CaWRKY40 were used. The sequence specificities of all of these fragments were further confirmed by searching with BLAST against genome sequence in database of CM3341 and Zunla-12, which were cloned individually into the entry vector pDONR207, and then cloned into the PYL279 destination vector by BP and LR reaction.
Virus Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) of CaHSL1 in Pepper Plants
For VIGS of CaHSL1 in pepper plants, two specific fragments of 200–500 bps in length in the ORF or 3′ UTR were used to construct the VIGS vectors TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2, respectively, which were transformed into agrobacterium strain GV3101 cells. GV3101 cells containing PYL192 (TRV1) and TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 or TRV::00 (as a negative control) were resuspended in the induction medium at 1:1 ratio (OD600 = 0.6) used in the VIGS following the method in our previous study (Dang et al., 2013), and were co-infiltrated into cotyledons of 2-week-old pepper plants.
Transient Expression of CaHSL1 or CaWRKY40 in Pepper Leaves
For transient expression analysis, GV3101 cells containing the 35S::CaHSL1-HA or 35S::CaWRKY40-HA, 35S::HA construct were grown overnight and resuspended in the induction medium (10 mM MES, 10 mM MgCl2, 200 μM acetosyringone, pH 5.6) to OD600 = 0.8, 10 μL of which was infiltrated into the leaves of pepper plants at the 8-leaf stage using a syringe without a needle. The injected leaves were monitored for phenotyping or collected at the indicated time points for further assays, including trypan blue and diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining or total RNA isolation.
Subcellular Localization
GV3101 cells containing different vectors were grown overnight and then resuspended in the induction medium to OD600 = 0.8 for further use. To assay subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in epidermic cells of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-YFP (35S::YFP) were infiltrated into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves using a syringe without a needle, the inoculated leaves were harvested and the YFP signals in the in epidermic cells were observed using a Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope (TCS SP8, Leica, Solms, Germany) with an excitation wavelength of 513 and a 527 nm band-pass emission filter. For assay subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in pepper protoplasts, GF3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-GFP and GV3101 cells containing 35S:CBL1n-CFP were mixed at a 1:1 ratio, the mixed cells were infiltrated into pepper leaves, which were harvested at 48 hpi and protoplasts were isolated following the method of Yoo et al. (2007), with a slight adjustment that 1.25% cellulase plus 0.3% macerozyme was employed. In order to burst the protoplasts, distilled water was added to the protoplasts suspension, GFP signals were monitored during protoplast rupture under Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and a 530 nm band-pass emission filter, while CFP signals were observed with a 434 and 477 nm band-pass emission filter.
To confirm the results of subcellular localization of CaHSL1 by detection of GFP, cytoplasmic protein and nuclear protein were isolated with specific kits from the pepper leaves transiently overexpressing CaHSL1-Flag, respectively. These protein extracts were incubated with anti-FLAG agarose (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) at 4°C overnight. Beads were collected and washed with Tris-buffered saline and Tween 20 (0.05%). The eluted protein was examined by immunoblotting with the help of anti-FLAG-peroxidase antibodies (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom).
Imaging-PAM
As high Fv/Fm (Marias et al., 2017) and actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light (ΦPS II) (Yan et al., 2008) were used as indicator of thermostability of plants, a MINI-version of the Imaging-PAM (Heinz Walz GmbH, Effeltrich, Germany) was used to image these two chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of CaHSL1 silenced or CaHSL1 transient overexpressing pepper leaves. The pepper plants were darkly adapted for 15 min and then directly put into the instrument for testing according to Schreiber et al. (1986) and Li et al. (2008).
Histochemical Staining
Leaf staining with trypan blue and DAB was done according to a previously described method (Choi et al., 2012; Dang et al., 2013; Cai et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015).
Immunoblotting
Total protein extracts were incubated with anti-GFP or anti-FLAG agarose (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) at 4°C overnight. Beads were collected and washed with Tris-buffered saline and Tween 20 (0.05%). The eluted protein was examined by immunoblotting with the help of anti-GFP-peroxidase or anti-FLAG-peroxidase antibodies (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom).
ChIP Analysis
ChIP analysis was performed following a previously described protocol (Ifnan et al., 2018). CaWRKY40-HA was transiently overexpressed in pepper leaves. The leaves were collected at 24 hpi and crosslinked with 1% of formaldehyde. The chromatin was isolated and sheared into fragments of 300–500 bp length, and the DNA-protein complexes were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibodies. The samples were de-crosslinked, and DNA was purified and employed as a template for PCR using specific primer pairs of the fragment containing W-box or fragment without W-box within the promoter of CaHSL1 by semi-quantitative PCR using gene-specific primers (Supplementary Table S1).
Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
The qRT-PCR was used to detect the relative transcript levels of selected genes with specific primer pairs (Supplementary Table S1). A BIO-RAD Real-time PCR system (Foster City, CA, United States) and SYBR Premix Ex Taq II system (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) were used. Total RNA preparation and real-time RT-PCR were carried out as described in previous studies (Dang et al., 2013; Cai et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015). Five biological replicates of each treatment were performed. Data were analyzed by the Livak method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001) and expressed as a normalized relative expression level (2−ΔΔCT) of the respective genes. The relative transcript level of each sample was normalized to CaActin (GQ339766) and 18S ribosomal RNA (EF564281).
Results
Cloning and Sequence Analysis of a Putative Receptor-Like Protein Kinase That Responds to Heat Stress
Since RLKs have seldom been characterized in the plant response to heat stress, we focused on a putative RLK in the present study because promoter scanning of genome sequence data3 with4 showed that its promoter region contains a putative heat-stress responsive heat shock element (HSE) and one W-box (Supplementary Figure S1C). The corresponding cDNA fragment containing a full-length open reading frame (ORF) was cloned by RT-PCR with a specific primer pair using the cDNA library derived from heat-stress challenged plants of the pepper line CM334 as a template. The amplified DNA fragment contained an ORF of 3096 bp, encoding a protein of 1031 amino acids.
The amino-acid sequence deduced by a SMART-analysis (Schultz et al., 2000) contains 5 LRR motifs, one transmembrane region and one Serine/Threonine protein kinase domain with the conserved G-T/S-XX-Y/F-X-APE motif (Krupa et al., 2004) that shared 100, 85, 65, 59, 47, and 41% sequence similarity to that in Solanum tuberosum, Solanum lycopersicum, Nicotiana tabacum, Erythranthe guttata, Tarenaya hassleriana, Oryza sativa, and Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. As the corresponding protein in the majority of these plant species (including Solanum tuberosum, Solanum lycopersicum, and Nicotiana tabacum) was designated as HSL1 (HAESA-LIKE1), we named this gene CaHSL1 (Supplementary Figures S1A,B). In addition, the Serine/Threonine protein kinase domain in CaHSL1 contains a conserved active-site signature motif (HRDVKSSNILLD) (Dardick et al., 2012), indicating that CaHSL1 belongs to the RD RLK group.
The Subcellular Localization of CaHSL1
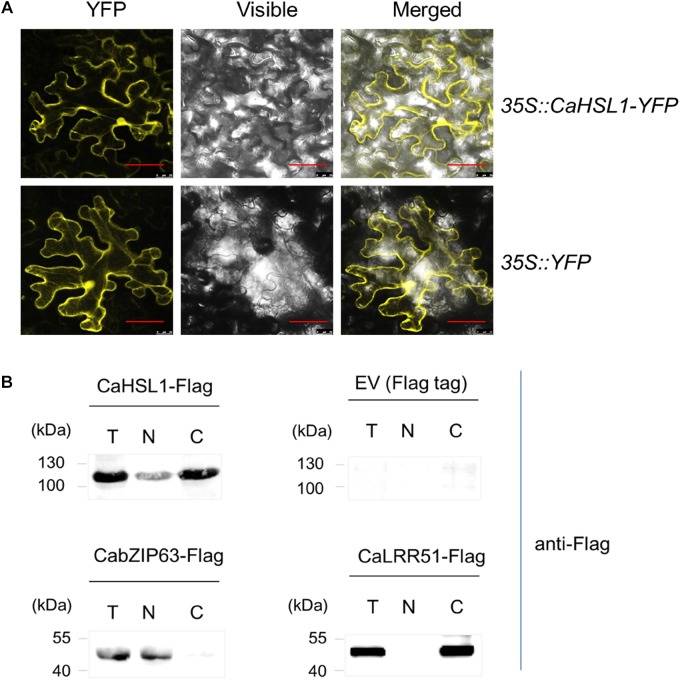
To determine the subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in epidermic cells of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, CaHSL1-YFP was transiently overexpressed in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, the YFP signals were observed in epidermic cells of Nicotiana benthamiana at 48 hpi, the result showed that YFP signals exhibited in the epidermic cells including plasma membrane, cytoplasm and the nuclei (Figure 1A). In parallel, the subcellular localization of CaHSL1 was assayed in pepper protoplast by transient overexpression of CaHSL1-GFP and we get similar result to that in epidermic cells of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, and CaHSL1-GFP targeted to the plasma membrane similar to the fused CBL1n-CFP (as an additional control targeting to the plasma membrane) (Oliver et al., 2008) (Supplementary Figure S2A), indicating that CaHSL1 might localizes to the plasma membrane. To further determine whether CaHSL1 localize to plasma membrane, the subcellular localization of CaHSL1 was monitored at different time points in cracked pepper protoplasts by addition of 10 μL distilled water to 20 μL of CaHSL1-GFP or GFP overexpressing protoplasts suspension. The result showed that the GFP signals in CaHSL1-GFP overexpressing protoplasts were originally observed in a circular distribution in cell periphery (0 s), from 1.29 to 2.58 s, a considerable part of GFP signal in plasma membrane diminished, from 3.87 to 10.32 s, irregularly distributed GFP signal and spherical highly concentrated GFP signal, which might be invisible due to occlusion of cell membrane before 3.87 s, were observable. In the case of GFP overexpressing protoplasts, GFP signal was observed in the whole cells from 0 to 1.29 s, and GFP signal disappeared where the cell ruptured from 2.58 to 10.32 s and no spherical highly concentrated GFP signal was observed, indicating that GFP alone does not target to cell but that it is a soluble protein (Supplementary Figure S2B). A total of 5 protoplasts of CaHSL1-GFP or GFP overexpressing were monitored, and in all of them the GFP dynamic was identical. All these results indicate that CaHSL1 might localize to plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nuclei.
FIGURE 1.
The subcellular localization of CaHSL1. (A) CaHSL1 was localized to the plasma membrane and nucleus when transiently overexpressed in leaves of N. benthamiana that were infiltrated with GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-YFP using 35S::YFP as control. The Agrobacterium-infiltrated N. benthamina leaves were harvested at 48 hpi, and counterstained by DAPI. Images were taken by confocal microscopy. Control (35S::YFP) showed signal throughout the cell. Bars = 50 μm. (B) The detection of CaHSL1 in the nucleus and cytoplasm by immunoblotting with total (T), nuclear (N), and cytoplasmic (C) proteins isolated from CaHSL1-FLAG or FLAG transiently overexpressing N. benthamina leaves using antibodies to FLAG. α-FLAG, FLAG antibodies.
To confirm this result, fused CaHSL1-FLAG was transiently overexpressed by infiltrating N. benthamiana leaves with GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-FLAG using 35S::CabZIP63-FLAG and 35S::CaLRR51-FLAG as controls. The leaves were harvested at 24 hpi for nuclear and cytoplasmic protein isolation; the isolated proteins were also subjected to immunoblotting analysis using antibodies of FLAG. The results showed that the nuclear protein CabZIP63-FLAG, a protein targeted exclusively to the nucleus in our previous study (Shen et al., 2016b) and used as a control for nuclear targeting, was exclusively present in the nuclear protein fraction, whereas CaLRR51-FLAG [used as cytoplasmic targeting control which exclusively localizes to the plasma membrane by our previous study (Cheng et al., 2017)] was present only in the cytoplasmic protein fraction. The CaHSL1 protein was present in both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions (Figure 1B). All these data suggest that CaHSL1 localize to plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nuclei, which is consistent to the presence of a TM and a NLS in the deduced amino acid sequence of CaHSL1.
Transcript Levels of CaHSL1 in Pepper Plants Upon Exposure to Heat Stress, R. solanacearum Inoculation, and Exogenous Applications of Phytohormones
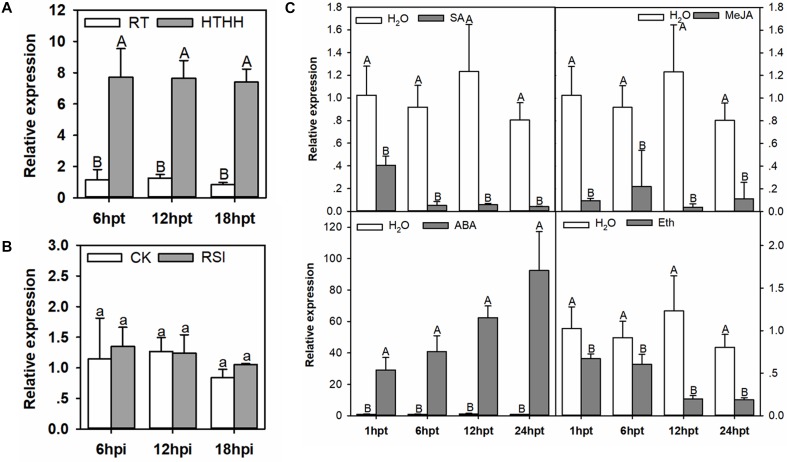
The presence of HSE and W-box in the promoter of CaHSL1 implies its possible involvement in the response of the pepper plant to heat stress and pathogen infection, as WRKY proteins, which bind to W-boxes in promoters of their target genes, have been largely implicated in plant immunity (Eulgem et al., 2000; Zhang and Wang, 2005; Eulgem, 2006; Rushton et al., 2010) or heat stress responses (Li et al., 2009, 2010, 2011; Dang et al., 2013; Cai et al., 2015; He et al., 2016). To test this hypothesis, we used qRT-PCR to assay the transcript levels of CaHSL1 in pepper plants challenged with R. solanacearum or heat stress under high humidity (42°C, 90% humidity, high humidity treatment is used to eliminate the effects of dehydration on plants during high temperature) compared to the in control plants. The transcript levels of CaHSL1 were significantly higher in pepper plants challenged with HTHH for 6, 12, and 18 hpt (hours post-treatment), than in the plants kept at room temperature and high humidity, while transcript level of CaHSL1 in pepper plants inoculated with R. solanacearum exhibited no significant difference from those in mock-treated plants (Figures 2A,B).
FIGURE 2.
The qRT-PCR of CaHSL1 transcript levels in pepper plants exposed to RSI, HTHH, and exogenous applications of SA, MeJA, ETH and ABA. (A) CaHSL1 transcript levels at different time points in pepper leaves after HTHH (39°C, 90% humidity). (B) CaHSL1 transcript levels measured at different time points in pepper leaves inoculated with the R. solanacearum strain FJC100301. (C) (top-left panel) transcript levels of CaHSL1 in pepper plants treated with 1 mM SA at different time points; (top-right panel) transcript levels of CaHSL1 in pepper plants treated with 100 μm MeJA at different time points; (bottom-left panel) transcript levels of CaHSL1 in pepper plants treated with 100 μm ABA at different time points. (bottom-right panel) transcript levels of CaHSL1 in pepper plants treated with 100 μm ETH at different time points. The transcript levels of CaHSL1 in RSI, HTHH and SA, MeJA, ABA and ETH in pepper leaves were compared with those in mock-treated control plants, which were set to a relative expression level of “1.” Error bars indicate standard error. Data show the mean ± SD obtained from four independent experiments. Different upper-case letters indicate significant differences among means (P < 0.01), as calculated with Fisher’s protected-LSD-test. High temperature and high humidity treatment, HTHH; hpi, hours post infiltration; hpt, hours post treatment.
Phytohormones, such as SA, jasmonic acid (JA), ABA, and ET serve as important signaling molecules in the plant responses to pathogen or heat stress (Clarke et al., 2009; Huang et al., 2016; Suzuki et al., 2016; Verma et al., 2016). To test if the signaling pathways mediated by these molecules are involved in the regulation of CaHSL1 expression, the transcript abundance of CaHSL1 in pepper plants treated with SA, MeJA, ABA or ETH was measured against that in control plants. The results showed that transcript levels of CaHSL1 were significantly down-regulated by exogenous applications of SA, MeJA, or ETH from 1 to 24 hpt but dramatically upregulated by exogenous ABA from 1 to 24 hpt (Figure 2C). These results suggest that CaHSL1 might play a role in the response to heat stress.
Our data indicate that CaHSL1 might participate in the response to heat stress but not to R. solanacearum inoculation in pepper.
Silencing of CaHSL1 Decreased Basal and Acquired Thermotolerance Under High Humidity in Pepper Plants but Did Not Alter Response to R. solanacearum
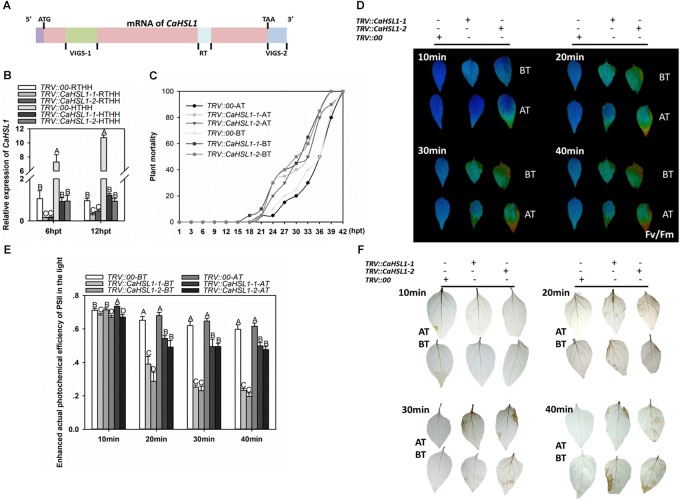
With these CaHSL1 silenced pepper plants, the effect of CaHSL1 silencing on basal and acquired thermotolerance was determined (Figures 3A,B). To test the role of CaHSL1 in pepper acquired thermotolerance, the plants were pretreated with 37°C under 90% humidity for 5 h, recovered for 24 h and then exposed to HTHH (42°C under 90% humidity), the mortality of HTHH challenged plants was calculated after 1–42 h of HTHH treatment, Fv/Fm (the optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII in the dark), an indicator of plant tolerance to heat stress (Yan et al., 2008; Wang Y. et al., 2014) and actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light (ΦPSII), an indicator of thermostability of the photosynthetic apparatus (Yan et al., 2008), were detected immediately after the HTHH treatment. The results showed that the TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2 plants exhibited higher mortality from 1 to 42 hpt (Figure 3C), lower Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color in detach leaves or whole plants (Figure 3D and Supplementary Figure S3A) as well as lower ΦPSII in detach leaves or whole plants compared to that in the mock treated TRV::00 plants (Figure 3E and Supplementary Figure S3B). To test if CaHSL1 also play a role in pepper basal thermotolerance, pepper plants were HTHH and the mortality, Fv/Fm and ΦPSII of plants were measured as did in acquired thermotolerance assay, the result showed that CaHSL1 silenced plants exhibited higher mortality, lower Fv/Fm and ΦPSII after HTHH treatment in CaHSL1 plants or their detached leaves compared to that in the mock treated wild type plants (Figures 3C–E and Supplementary Figure S2B). In addition, accumulation of H2O2, a typical ROS that causes peroxidative damage to plant tissues (RoyChoudhury et al., 2007; Chen et al., 2013), was measured in HTHH challenged plant leaves by staining with 3, 3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB), the results showed that, compared to the mock treated TRV::00 plants, darker DAB staining was detected in TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2 plants after 10–40 min of HTHH treatment with or without 37°C pretreatment (Figure 3F). This result indicate that higher level of H2O2 accumulation and therefore probable heavier peroxidative damage might be caused by HTHH in TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2 plants than in mock treated TRV::00 plants. All these data suggest that silencing of CaHSL1 significantly impaired pepper basal and acquired thermotolerance.
FIGURE 3.
The effect of CaHSL1 silencing by VIGS on response of pepper to HTHH. (A) Distribution of two specific fragments (VIGS-1 and VIGS-2) employed to construct the vectors (TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2) for CaHSL1 silencing in pepper plants. (B) The transcript levels of CaHSL1 in HTHH (42°C, 90% humidity) or RTHH (28°C, 90% humidity) treated TRV::CaHSL1-1 and CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 pepper plants by qRT-PCR, the transcript levels of CaHSL1 in HTHH challenged TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 pepper plants were compared with those in mock-treated TRV::00 plants, which were set to a relative expression level of “1.” (C) The plant mortality of TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV:00 pepper plants challenged with HTHH (42°C, 90% humidity) pretreated with or without 37°C, a total of 50 plants of each genotypes were monitored from 1 to 42 hpt. (D) Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images in HTHH challenged detached leaves of TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 plants pretreated with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C, which were detected immediately after HTHH treatment for 10–40 min. (E) ΦPSII in HTHH treated detached leaves of TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 plants pretreated with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C, which was detected immediately after HTHH treatment for 10, 20, 30, and 40 min. (F) The DAB staining of detached leaves of HTHH treated TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 plants pretreated with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C after the treatment of HTHH for 10 to 40 min. In (B,C,E), Error bars indicate standard error, data show the mean ± SD obtained from four replicates. Different upper-case letters indicate significant differences among means (P < 0.01), as calculated with Fisher’s protected-LSD-test. hpt, hours post treatment. AT: acquired thermotolerance. BT: basal thermotolerance. Fv/Fm: the optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII in the dark; ΦPSII: the actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light.
To further confirm the role of CaHSL1 in pepper thermotolerance, the transcription of genes including CaHSP24 (Guo et al., 2015a), CaHSP24.2 (Guo et al., 2015a), CaHSP70 (Guo et al., 2016), and CaHsfA2 (Guo et al., 2015b) that act as positive regulators in pepper thermotolerance by previous studies was assayed by qRT-PCR, the results showed that HTHH-challenged TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2 pepper plants with or without pretreatment with 37°C exhibited lower levels of CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 and CaHsfA2 transcript abundance at 6 and 12 hpt (Supplementary Figure S3C). All of these data supported that result that CaHSL1 act as a positive regulator in pepper basal and acquired thermotolerance.
When the pepper plants were challenged with the R. solanacearum strain FJC100301, no significant difference in phenotype between TRV::CaHSL1-1 and TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 plants at 7 and 15 dpi was observed (data not shown), suggesting that the silencing of CaHSL1 did not alter the response of pepper plants to R. solanacearum inoculation.
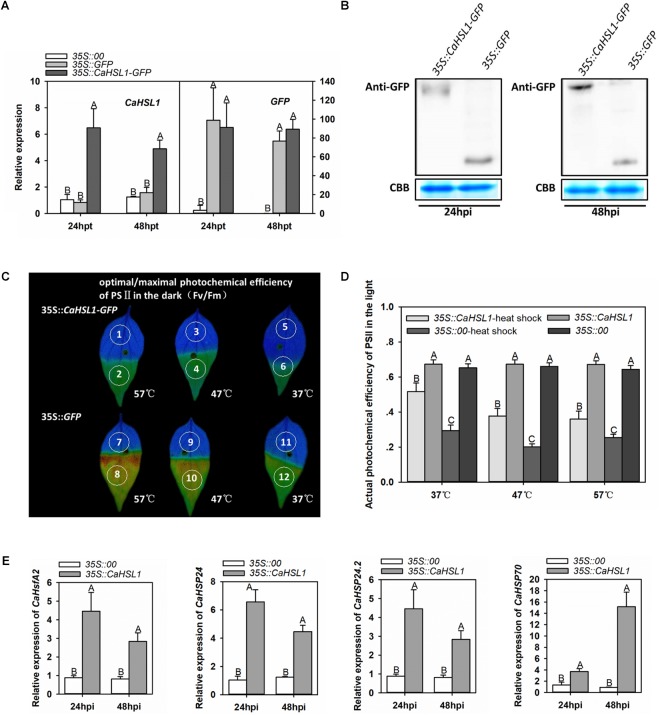
Transient Overexpression of CaHSL1 Induced Tolerance to Heat Stress and Upregulation of CaHSP24 in Pepper Plants
To confirm that CaHSL1 acts as a positive regulator during pepper’s heat stress response, the function of CaHSL1 in thermotolerance was further tested by transient overexpression in pepper leaves via infiltrating pepper leaves with Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 cells carrying 35S::CaHSL1-GFP (using 35S::GFP as control). The success of CaHSL1-GFP transient overexpression was confirmed by qRT-PCR at transcriptional level (Figure 4A), and at posttranslational level by immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP 24 and 48 hpi (Figure 4B). The lower half blades of CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing and the control pepper leaves were inserted into water of 57, 47, and 37°C for 1 min, and Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images were measured after 15 min of darker adaptation, the result showed that the upper half blades of mock treated control pepper leaves exhibited a much brown color than that of the CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves, although there was no difference in the lower half blades which was kept in the room temperature (Figure 4C), indicating a higher Fv/Fm in CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves. In addition, the CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves also exhibited higher ΦPSII than that of control plants upon the heat shock treatment for 1 min (Figure 4D). Furthermore, much higher levels of CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 and CaHsfA2 transcript were detected in CaHSL1 transiently overexpressing pepper leaves than that in control leaves (Figure 4E). These results collectively suggest that the transient overexpression of CaHSL1 enhanced thermotolerance probably through modulating the thermotolerance associated genes.
FIGURE 4.
Transient overexpression of CaHSL1 induced tolerance to HTHH and upregulation of thermotolerance associated genes in pepper plants. (A) The transcript levels of CaHSL1 in CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves by qRT-PCR. (B) The detection of transient expression of CaHSL1-GFP by immunoblotting using the protein isolated from pepper leaves infiltrated with GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-GFP with antibodies to GFP. (C) Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images in CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves challenged with HTHH compared to that in the mock treated control pepper leaves, the lower half leaf blades (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11) were kept in room temperature, while the upper half leaf blades 2 and 8, 4 and 10, 6 and 12 were inserted into water of 57, 47, and 37°C for 1 min, respectively, the pseudo color images were detected immediately after heat stress treatment. (D)ΦPSII in CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves and the control plants challenged with (AT) or without (BT) HTHH, which were detected immediately after heat stress treatment by Imaging-PAM. (E) The transcript levels in CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 and CaHsfA2 in CaHSL1-GFP transiently overexpressing pepper leaves compared to the control plants. In (A,E), the transcript levels of CaHSL1, CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 or CaHsfA2 in transiently CaHSL1 overexpressing pepper leaves at different time points were compared to those in the mock treated control plants, which were set to a relative expression level of “1.” In (A,D,E), error bars indicate standard error, data show the mean ± SD obtained from four replicates. Different upper-case letters indicate significant differences among means (P < 0.01), as calculated with Fisher’s protected-LSD-test. AT, acquired thermotolerance. BT, basal thermotolerance. hpi, hours post infiltration. hpt, hours post treatment. Fv/Fm, the optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII in the dark; ΦPSII, the actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light.
CaWRKY40 Bind to the Promoter Region of CaHSL1 Containing the W-box in Pepper Plants
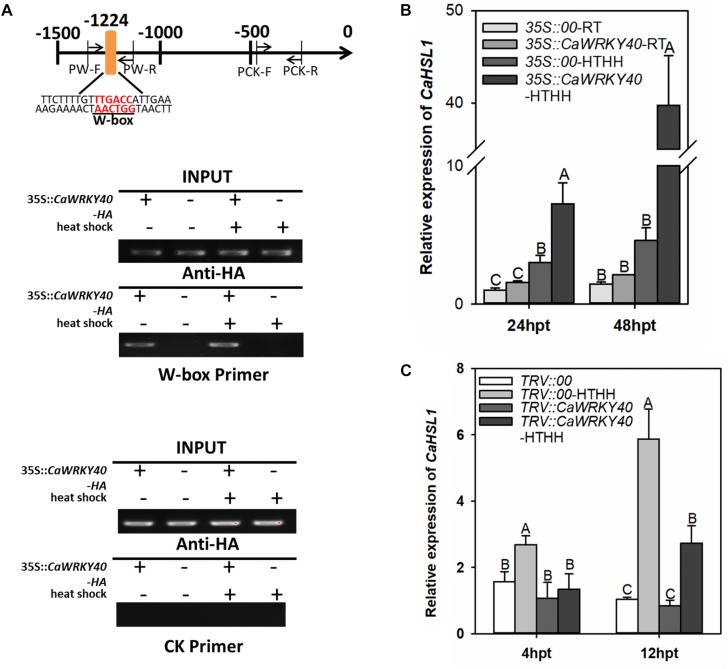
Our previous study showed that CaWRKY40 acts as a positive regulator of the response of pepper to HTHH by binding to its target genes via a typical W-box in their promoters (Dang et al., 2013). Since only one W-box is present in the promoter of CaHSL1, it is possible that CaHSL1 might be transcriptionally regulated by CaWRKY40 during the response of pepper to HTHH. We tested this possibility by ChIP-PCR using plants transiently overexpressing CaWRKY40-GFP. The enrichment of CaWRKY40 was found in the promoter of CaHSL1 by PCR with DNA fragments precipitated from CaWRKY40-GFP overexpressing pepper leaves with antibodies of GFP as template using specific primer pair of the W-box containing fragment of CaHSL1 promoter, whereas no binding signal was detected in the promoter fragment of CaHSL1 that lacks a W-box (Figure 5A), indicating that CaWRKY40 binds to the promoter of CaHSL1, probably in a W-box-dependent manner.
FIGURE 5.
CaHSL1 was directly regulated by CaWRKY40 at the transcriptional level. (A) ChIP assay showed that the W-boxes in the promoter of CaHSL1 are bound by CaWRKY40. CaWRKY40-HA was transiently overexpressed in pepper leaves, the leaves were collected at 24 hpi and the DNA-protein complexes were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibodies. The immunoprecipitated DNA was employed as template for PCR using primer pairs specific to the fragment containing the W-boxes or without the W-box within the CaHSL1 promoter. PW, specific primer pair for the fragment containing W-boxes within the promoter of CaHSL1; PCK, specific primer pair of the W-box free fragment within the promoter of CaHSL1. (B) Effect of transient overexpression of CaWRKY40 on transcript levels of CaHSL1 in pepper plants with or without HTHH challenge by qRT-PCR; (C) Effect of CaWRKY40 silencing by VIGS in pepper leaves with or without HTHH challenge on transcription of CaHSL1 by qRT-PCR. In (B,C), CaHSL1 transcript levels in CaWRKY40 transient overexpressing or CaWRKY40-silenced pepper plants were compared with those in mock-treated control plants, which were set to a relative expression level of “1.” Data show the mean ± SD from four biological replicates; error bars indicate standard error. Different upper-case letters on the bars indicate significant differences between means (p < 0.01), as determined by Fisher’s protected LSD test.
Transcription of CaHSL1 Was Enhanced by Transient Overexpression of CaWRKY40 but Downregulated by Silencing of CaWRKY40
The direct binding of CaWRKY40 to the promoter of CaHSL1 implies that CaHSL1 might be transcriptionally regulated by CaWRKY40. To test this speculation, the effects of transient overexpression or silencing of CaWRKY40 by VIGS were assayed (with or without HTHH) in pepper plants on transcription of CaHSL1. The transcript levels of CaHSL1 were significantly enhanced in pepper leaves transiently overexpressing CaWRKY40 compared to that in control plants (35S::00), regardless of HTHH challenge (Figure 5B). The silencing of CaWRKY40 by VIGS was performed using a highly specific fragment within the 3′ UTR of CaWRKY40, the transcript level in HTHH treated TRV::CaWRKY40 pepper plants was only 10–20% of that in the TRV::00 plants, while no difference in the transcription of CaWRKY40b, a WRKY genes with the highest sequence similarity to CaWRKY40 (Ifnan et al., 2018), was found between TRV::CaWRKY40 and TRV::00 plants was found by qRT-PCR (data not shown). The transcription abundance of CaHSL1 was measured by qRT-PCR in HTHH challenged TRV::CaWRKY40 and TRV::00 plants, the result showed that transcript levels of CaHSL1 were significantly lower in TRV::CaWRKY40 than that in TRV::00 plants at the two tested time points (Figure 5C). These results suggested that CaHSL1 is directly and positively regulated by CaWRKY40 in pepper plants exposed to HTHH.
Discussion
Although pepper is an important vegetable that suffers from heat stress, the molecular mechanism underlying pepper thermotolerance remains elusive. Our previous studies have shown that CaWRKY40 acts as a positive regulator in the response of pepper to HTHH or RSI (Dang et al., 2013; Cai et al., 2015; Shen et al., 2016a,b; Qiu et al., 2018). The present study builds on these data by demonstrating that CaHSL1, encoding an RD RLK, is target by CaWRKY40 and the CaHSL1 protein acts as a positive regulator in pepper basal and acquired thermotolerance under high humidity; however, CaHSL1 differs from CaWRKY40 in its role during the response of pepper to RSI.
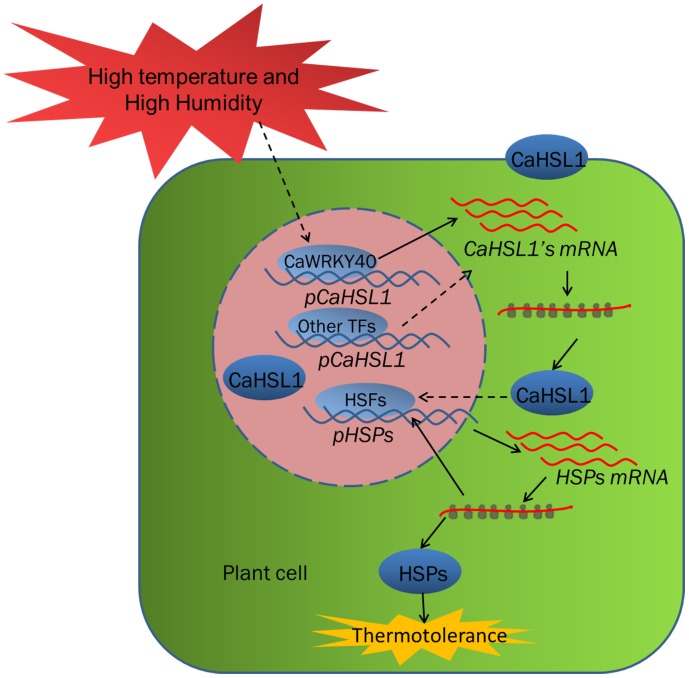
The deduced amino-acid sequence of CaHSL1 shares domain-structure similarity with RLKs and high sequence similarity with putative HSLs from other plant species; it also contains a conserved arginine-aspartic acid motif in its S_TKc domain, thus suggesting that CaHSL1 belongs to the RD RLKs in pepper. CaHSL1 exhibited transcriptional upregulation in pepper plants exposed to HTHH, CaHSL1 silenced pepper plants by VIGS showed decreased both basal and acquired thermotolerance and optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII in the dark (Fv/Fm), and downregulation of the thermotolerance-associated gene CaHSP24 (Heckathorn et al., 1996; Pivovarova et al., 2005). In contrast, transient overexpression of CaHSL1 significantly enhanced the transcriptions of CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 and CaHsfA2 and significantly increased Fv/Fm as well as actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light, another indicator of thermal stability (Yan et al., 2008; Wang Y. et al., 2014) in pepper plants. These data collectively suggest a role for CaHSL1 as a positive regulator in pepper basal and acquired thermotolerance under high humidity. Similarly, previous studies have found that some regulatory proteins in HSR signaling, for example, AtHsfA3, Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH) (Zhao et al., 2017), ATPase6 (ALA6) (Niu et al., 2017) HsfA2 (Ogawa et al., 2007) in Arabidopsis and LlHsfA3A in lily (Lilium longiflorum) (Wu et al., 2018), FaHsfA2c in Festuca arundinacea (Wang et al., 2017) act as positive regulator in both basal and acquired thermotolerance, while LlHsfA3B (Wu et al., 2018) in lily acts as positive regulator only in acquired thermotolerance, salicylic acid dependent signaling (Clarke et al., 2004) promotes only basal thermotolerance, indicating that basal and acquired thermotolerance might be modulated by different signaling pathways with extensive crosstalks between them. Noticeably, our data showed that CaHSP24 and CaHSP24.2 that might localize to chloroplast (Heckathorn et al., 1996) were dramatically downregulated by silencing of CaHSL1, coupled with significant decrease in Fv/Fm, whereas the transient overexpression of CaHSL1 significantly enhanced transcription of CaHSP24 and CaHSP24.2 as well as enhanced Fv/Fm, it can be speculated that as an indicator of plant thermotolerance, the stability of photochemical efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) might be contributed by multiple HSPs including CaHSP24 and CaHSP24.2, as Fv/Fm differed in timing and amplitudes with CaHSP24 and CaHSP24.2 during response CaHSL1 silenced pepper plant to heat stress. CaHSL1 might act as upstream components in HSR signaling and circuits the transcription of HSPs via various TFs including HSFs, as transcription of CaHsfA2 was found to be modulated by CaHSL1 in the present study (Figure 6). However, the precise details how these HSPs are regulated by CaHSL1 and how they contribute to the stability of photochemical efficiency of PSII remain to be elucidated.
FIGURE 6.
The relationship of the factors including CaHSL1 and CaWRKY40 under HTHH conditions. Upon the challenge of HTHH, CaWRKY40 or other transcription factors such as HSFs are transcriptionally upregulated in some way, which in turn activate the transcription of CaHSL1. The upregulated CaHSL1 might positively modulate basal and acquired thermotolerance by activating the downstream signaling cascades. Solid line indicates direct effect, dotted lines indicate indirect or speculative relationships. HSFs, heat shock factors; HSPs, Heat shock proteins; HTHH, high temperature and high humidity.
Abscisic acid functions as a key messenger in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, including heat stress (Wang K. et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2016) and shows synergistic or antagonistic interactions with factors involved in immune responses (Moeder et al., 2010; Montillet and Hirt, 2013; Xu et al., 2013). The present study showed that CaHSL1 was dramatically upregulated by exogenous ABA, further supporting the idea that CaHSL1 acts as a positive regulator in the response of pepper to heat stress. Similarly, the RD RLK ERECTA act as a positive regulator in plant thermotolerance, as shown by gain- and loss-function analyses in Arabidopsis, rice and tomato (Shen et al., 2015). Another RLK, OsGIRL1, acts as a negative regulator in the response of Arabidopsis to heat stress (Park et al., 2014). Unlike ERECTA, which acts as positive regulator in plant immunity (ten Hove et al., 2011; Jordá et al., 2016), it appears that CaHSL1 does not play a role in pepper immunity, as the silencing of CaHSL1 did not affect pepper responses to RSI. Not only was the expression of CaHSL1 unaffected by RSI, it was downregulated by SA, MeJA or ETH, which activate the expression of immunity-associated genes and play important roles in the regulation of plant immunity (Dang et al., 2013, 2014; Cai et al., 2015; Shen et al., 2016a,b; Hussain et al., 2018; Ifnan et al., 2018; Qiu et al., 2018). We speculate that during infection by R. solanacearum, the transcription of CaHSL1 and therefore the heat shock response mediated by CaHSL1 is blocked, which might benefit the recruitment of other resources to plant immunity. Furthermore, as heat-stress sensors targeting plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, cytosol, and nucleus have been found (Mittler et al., 2012; Srivastava et al., 2014; Song et al., 2017), thus it puts forward the possibility that the whole-cell targeting of CaHSL1 might be required for signal transduction after perception of heat stress by the abovementioned sensors. However, the mechanisms for the initiation of CaHSL1-mediated HSR and the connection of CaHSL1 to these sensors remain to be elucidated.
Since thermotolerance consumes resources and energy, plants generally induce responses that minimize consumption of cellular resources. Genome-wide assays indicate that plants undergo massive reprogramming upon challenge by heat stress (Castandet et al., 2016; González-Schain et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2016; Gao et al., 2017); the transcriptional regulation of thermotolerance-associated genes by various transcription factors might play crucial roles in this process. CaWRKY40, which is transcriptionally modulated by CaWRKY6 (Cai et al., 2015) and CabZIP63 (Shen, et al., 2016a), acts as a positive regulator in the response of pepper to HTHH or RSI (Dang et al., 2013) by regulating different target genes (Cai et al., 2015; Shen et al., 2016a,b; Hussain et al., 2018; Ifnan et al., 2018; Qiu et al., 2018). Our data showed that the promoter of CaHSL1 was bound by CaWRKY40; correspondingly, transcription of CaHSL1 was positively regulated by CaWRKY40 during the response of pepper to heat stress but not to RSI, despite upregulation of CaWRKY40 by RSI (Dang et al., 2013). Notably, the silencing of CaWRKY40 in pepper plants did not abolish the upregulation of CaHSL1 by HTHH, and a HSE is present in the promoter of CaHSL1, it can be speculated that the transcription of CaHSL1 might also be modulated by unidentified HSFs, since HSFs have been suggested to participate in modulation of the expression of HSPs and other HS-induced transcripts during HSR by binding HSE in the promoters of their target genes (Kotak et al., 2007; Fragkostefanakis et al., 2015). It can also be speculated that the binding of CaHSL1 promoter and transcriptional activation of CaHSL1 by CaWRKY40 are modulated by unknown regulators specifically activated by heat stress but not by RSI, since the targeting and transcriptional activities of WRKY TFs have been found to be modulated by other regulators in protein-protein interactions (Chi et al., 2013). Further identification of these regulators might provide insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying thermotolerance mediated by CaHSL1. This non-linear relationship between different components of signaling pathways might provide plants with a powerful means to fine-tune their responses to be different environmental cues.
Conclusion
Our data in the present study indicate that CaHSL1 is transcriptionally upregulated by HTHH, leading to enhanced thermotolerance under high humidity. In addition, it was found that CaHSL1 is transcriptionally regulated by CaWRKY40 directly during the response of pepper to HTHH. CaHSL1 might be used as potential target for the genetic improvement of pepper thermotolerance.
Author Contributions
DG, FY, XX, YS, SY, and WC performed the experiments and analyzed the results. DG, FY, XX, and SH designed the experiments. SH wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mark D. Curtis for kindly providing the Gateway destination vectors, Bernd Weisshaar for pBT10-GUS, and Dr. S.P. Dinesh-Kumar (Yale University) for the pTRV1 and pTRV2 vectors. We also thank Dr. Zonghua Wang (Key Laboratory of Bio-pesticide and Chemistry Biology, Ministry of Education, Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University, China) for providing the Co-IP plasmids (pEarleyGate201).
Funding. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572136, 31601761, and 31501767).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2018.01802/full#supplementary-material
The sequence analysis of CaHSL1 and cis-elements within the promoter of CaHSL1. (A) Schematic diagram of CaLRR-RLK1 protein domain architecture and multiple-sequence-alignment (MSA) of the amino-acid sequence of CaHSL1 with its homologues from other plant species; CaHSL1 shared 99, 75, 73, 72, 57, 61, 54, 49, and 48% sequence similarity to the sequences of HSL1s from Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chinense and Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum tuberosum, Nicotiana tabacum, Sesamum indicum, Coffea canephora, Glycine max, Brassica napus, and Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. Different colors indicate different percentages of similarity between CaHSL1 and HSL1s of the other species (i.e., black, red and green shades represent 100%, 75–100%, and 50–75% similarity, respectively). NLS: nuclear localization signal (Read bar in Supplementary Figure S1A); LRR, Leucine-rich repeats; TM, transmembrane region; S_TKc, Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain. (B) Phylogenetic relationship between CaHSL1 and HSL1s of the above mentioned plants species. (A,B) were assayed using online SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?NORMAL=1) and DNAMAN5 (Lynnon Biosoft, United States). (C) Distribution of stress responsiveness related cis-elements in the promoter of CaHSL1 by PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/), the “A” in the translational start codon ATG was set to +1. GARE, gibberellin-responsive element; W-box, TTGACC/T bound by WRKY TFs; HSE, cis-acting element involved in heat stress responsiveness; CGTCA, cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA-responsiveness; AuxRR, auxin-responsive region; LTR, low temperature-response element; TCA, cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness.
Subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in protoplasts of pepper. (A) Subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in protoplasts of pepper, GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-GFP (35S::GFP) and 35S:CBL1n-CFP were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and co-infiltrated into pepper leaves, which were harvested for protoplasts isolation, and the GFP signals were observed immediately. Bars = 50 μm. (B) Dynamics of the GFP fluorescence in protoplasts suspended in a hypotonic medium. Protoplasts were isolated from pepper leaves infiltrated with GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-GFP or 35S::GFP, 10 μL of distilled water was added to a 20 μL of acquired protoplasts to rupture the protoplasts, and GFP signals were monitored using laser confocal at different time points after the addition of distilled water.
Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and transcription of thermotolerance associated genes in CaHSL1 silenced pepper plants upon the challenge of HTHH. (A) Phenotype and Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images in detached leaves of TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 plants challenged with 42°C, 90% humidity pretreated with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C, the Phenotype and Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images were measured at 1, 3, 12, and 24 hpt. (B) ΦPSII in HTHH challenged CaHSL1 silenced pepper plants with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C compared to that in the mock treated wild type plants, which was detected 1, 3, 12, and 24 hpt. (C) The transcript levels of CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 and CaHsfA2 in HTHH challenged TRV::CaHSL1-1,TRV::CaHSL1-1 pepper plants with (AT) or without (BT) pretreatment of 37°C compared with those in mock-treated TRV::00 plants, which were set to a relative expression level of “1.” In (B,C), error bars indicate standard error, data show the mean ± SD obtained from four replicates. Different upper-case letters indicate significant differences among means (P < 0.01), as calculated with Fisher’s protected-LSD-test. AT, acquired thermotolerance. BT, basal thermotolerance. HTHH, High temperature and high humidity treatment. hpt, hours post treatment. Fv/Fm, the optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII in the dark. ΦPSII, the actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light.
The primers used in PCR assay in the present study.
References
- Baer J., Taylor I., Walker J. C. (2016). Disrupting ER-associated protein degradation suppresses the abscission defect of a weak hae hsl2 mutant in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 67 5473–5484. 10.1093/jxb/erw313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Yang S., Yan Y., Xiao Z., Cheng J., Wu J., et al. (2015). CaWRKY6 transcriptionally activates CaWRKY40, regulates Ralstonia solanacearum resistance, and confers high-temperature and high-humidity tolerance in pepper. J. Exp. Bot. 66 3163–3174. 10.1093/jxb/erv125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castandet B., Hotto A. M., Strickler S. R., Stern D. B. (2016). ChloroSeq, an optimized chloroplast RNA-Seq bioinformatic pipeline, reveals remodeling of the organellar transcriptome under heat stress. G3 6 2817–2827. 10.1534/g3.116.030783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao L. M., Liu Y. Q., Chen D. Y., Xue X. Y., Mao Y. B., Chen X. Y. (2017). Arabidopsis transcription factors SPL1 and SPL12 confer plant thermotolerance at reproductive stage. Mol. Plant 10 735–748. 10.1016/j.molp.2017.03.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Liu A. R., Zhang S. J., Li C., Chang R., Liu D. L., et al. (2013). Overexpression of mitochondrial uncoupling protein conferred resistance to heat stress and Botrytis cinerea infection in tomato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 73 245–253. 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng W., Xiao Z. L., Cai H. Y., Wang C. Q., Hu Y., Xiao Y. P., et al. (2017). A novel leucine-rich repeat protein, CaLRR51, acts as a positive regulator in the response of pepper to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 18 1089–1100. 10.1111/mpp.12462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi Y. J., Yang Y., Zhou Y., Zhou J., Fan B. F., Yu J. Q., et al. (2013). Protein-protein interactions in the regulation of WRKY transcription factors. Mol. Plant 6 287–300. 10.1093/mp/sst026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S. K., Larue C. T., Chevalier D., Wang H. C., Jinn T. L., Zhang S. Q., et al. (2008). Regulation of floral organ abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 15629–15634. 10.1073/pnas.0805539105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. S., Hwang I. S., Hwang B. K. (2012). Requirement of the cytosolic interaction between PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEIN10 and LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT PROTEIN1 for cell death and defense signaling in pepper. Plant Cell 24 1675–1690. 10.1105/tpc.112.095869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. M., Cristescu S. M., Miersch O., Harren F. J. M., Wasternack C., Mur L. A. J. (2009). Jasmonates act with salicylic acid to confer basal thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 182 175–187. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02735.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. M., Mur L. A., Wood J. E., Scott I. M. (2004). Salicylic acid dependent signaling promotes basal thermotolerance but is not essential for acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 38 432–447. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02054.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva F. G., Shen Y. W., Dardick C., Burdman S., Yadav R. C., de Leon A. L., et al. (2004). Bacterial genes involved in type I secretion and sulfation are required to elicit the rice Xa21-mediated innate immune response. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 17 593–601. 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang F. F., Wang Y. N., She J. J., Lei Y. F., Liu Z. Q., Eulgem T., et al. (2014). Overexpression of CaWRKY27, a subgroup IIe WRKY transcription factor of Capsicum annuum, positively regulates tobacco resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Physiol. Plant. 150 397–411. 10.1111/ppl.12093 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang F. F., Wang Y. N., Yu L., Eulgem T., Lai Y., Liu Z. Q., et al. (2013). CaWRKY40, a WRKY protein of pepper, plays an important role in the regulation of tolerance to heat stress and resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Plant Cell Environ. 36 757–774. 10.1111/pce.12011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardick C., Ronald P. (2006). Plant and animal pathogen recognition receptors signal through non-RD kinases. PLoS Pathog. 2:e2. 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardick C., Schwessinger B., Ronald P. (2012). Non-arginine-aspartate (non-RD) kinases are associated with innate immune receptors that recognize conserved microbial signatures. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15 358–366. 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dat J. F., Lopez-Delgado H., Foyer C. H., Scott I. M. (1998). Parallel changes in H2O2 and catalase during thermotolerance induced by salicylic acid or heat acclimation in mustard seedlings. Plant Physiol. 116 1351–1357. 10.1104/pp.116.4.1351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delk N. A., Johnson K. A., Chowdhury N. I., Braam J. (2005). CML24, regulated in expression by diverse stimuli, encodes a potential Ca2+ sensor that functions in responses to abscisic acid, daylength, and ion stress. Plant Physiol. 139 240–253. 10.1104/pp.105.062612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulgem T. (2006). Dissecting the WRKY web of plant defense regulators. PLoS Pathog. 2:e126. 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020126 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulgem T., Rushton P. J., Robatzek S., Somssich I. E. (2000). The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 5 199–206. 10.1016/S1360-1385(00)01600-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fragkostefanakis S., Roth S., Schleiff E., Scharf K. D. (2015). Prospects of engineering thermotolerance in crops through modulation of heat stress transcription factor and heat shock protein networks. Plant Cell Environ. 38 1881–1895. 10.1111/pce.12396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao L. L., Ma Y. Z., Wang P., Wang S. A., Yang R. T., Wang Q., et al. (2017). Transcriptome profiling of Clematis apiifolia: insights into heat-stress responses. DNA Cell Biol. 36 938–946. 10.1089/dna.2017.3850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiard L., Sauviac L., Torii K. U., Grenon O., Mangin B., Grimsley N. H., et al. (2003). ERECTA, an LRR receptor-like kinase protein controlling development pleiotropically affects resistance to bacterial wilt. Plant J. 36 353–365. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01877.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göhre V., Spallek T., Häweker H., Mersmann S., Mentzel T., Boller T., et al. (2008). Plant pattern-recognition receptor FLS2 is directed for degradation by the bacterial ubiquitin ligase AvrPtoB. Curr. Biol. 18 1824–1832. 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Gómez L., Boller T. (2002). Flagellin perception: a paradigm for innate immunity. Trends Plant Sci. 7 251–256. 10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02261-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Schain N., Dreni L., Lawas L. M. F., Galbiati M., Colombo L., Heuer S., et al. (2016). Genome-wide transcriptome analysis during anthesis reveals new insights into the molecular basis of heat stress responses in tolerant and sensitive rice varieties. Plant Cell Physiol. 57 57–68. 10.1093/pcp/pcv174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gou X. P., He K., Yang H., Yuan T., Lin H. H., Clouse S. D., et al. (2010). Genome-wide cloning and sequence analysis of leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics 11:19. 10.1186/1471-2164-11-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Q. M., Yue X. L., Zeng H. T., Zhu J. H. (2014). The protein phosphatase RCF2 and its interacting partner NAC019 are critical for heat stress-responsive gene regulation and thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26 438–453. 10.1105/tpc.113.118927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo M., Liu J. H., Lu J. P., Zhai Y. F., Wang H., Gong Z. H., et al. (2015a). Genome-wide analysis of the CaHsp20 gene family in pepper: comprehensive sequence and expression profile analysis under heat stress. Front. Plant Sci. 6:806. 10.3389/fpls.2015.00806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo M., Lu J. P., Zhai Y. F., Chai W. G., Gong Z. H., Lu M. H. (2015b). Genome-wide analysis, expression profile of heat shock factor gene family (CaHsfs) and characterisation of CaHsfA2 in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 15:151. 10.1186/s12870-015-0512-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo M., Liu J. H., Ma X., Zhai Y. F., Gong Z. H., Lu M. H. (2016). Genome-wide analysis of the Hsp70 family genes in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) and functional identification of CaHsp70-2 involvement in heat stress. Plant Sci. 252 246–256. 10.3389/fpls.2015.00806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter T., Imkampe J., Mazzotta S., Wierzba M., Postel S., Bücherl C., et al. (2014). The leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase BIR2 is a negative regulator of BAK1 in plant immunity. Curr. Biol. 24 134–143. 10.1016/j.cub.2013.11.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He G. H., Xu J. Y., Wang Y. X., Liu J. M., Li P. S., Chen M., et al. (2016). Drought-responsive WRKY transcription factor genes TaWRKY1 and TaWRKY33 from wheat confer drought and/or heat resistance in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 16:116. 10.1186/s12870-016-0806-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckathorn S. A., Poeller G. J., Coleman J. S., Hallberg R. L. (1996). Nitrogen availability alters patterns of accumulation of heat stress-induced proteins in plants. Oecologia 105 413–418. 10.1007/BF00328745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. C., Niu C. Y., Yang C. R., Jinn T. L. (2016). The heat stress factor HSFA6b connects ABA signaling and ABA-mediated heat responses. Plant Physiol. 172 1182–1199. 10.1104/pp.16.00860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain A., Li X., Weng Y. H., Liu Z. Q., Ashraf M. F., Noman A., et al. (2018). CaWRKY22 acts as a positive regulator in pepper response to Ralstonia solanacearum by constituting networks with CaWRKY6, CaWRKY27, CaWRKY40, and CaWRKY58. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19:E1426. 10.3390/ijms19051426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ifnan K. M., Zhang Y. W., Liu Z. Q., Hu J., Liu C. L., Yang S., et al. (2018). CaWRKY40b in pepper acts as a negative regulator in response to Ralstonia solanacearum by directly modulating defense genes including CaWRKY40. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19:E1403. 10.3390/ijms19051403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia L. X., Chu H. Y., Wu D., Feng M., Zhao L. Q. (2014). Role of calmodulin in thermotolerance. Plant Signal. Behav. 9:e28887 10.4161/psb.28887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordá L., Sopeña-Torres S., Escudero V., Nuñez-Corcuera B., Delgado-Cerezo M., Torii K. U., et al. (2016). ERECTA and BAK1 receptor like kinases interact to regulate immune responses in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 7:897. 10.3389/fpls.2016.00897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. H., Domijan M., Klose C., Biswas S., Ezer D., Gao M. J., et al. (2016). Phytochromes function as thermosensors in Arabidopsis. Science 354 886–889. 10.1126/science.aaf6005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotak S., Larkindale J., Lee U., von K. P., Vierling E., Scharf K. D. (2007). Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10 310–316. 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupa A., Preethi G., Srinivasan N. (2004). Structural modes of stabilization of permissive phosphorylation sites in protein kinases: distinct strategies in Ser/Thr and Tyr kinases. J. Mol. Biol. 339 1025–1039. 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.04.043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkindale J., Hall J. D., Knight M. R., Vierling E. (2005). Heat stress phenotypes of Arabidopsis mutants implicate multiple signaling pathways in the acquisition of thermotolerance. Plant Physiol. 138 882–897. 10.1104/pp.105.062257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkindale J., Huang B. (2004). Thermotolerance and antioxidant systems in Agrostis stolonifera: involvement of salicylic acid, abscisic acid, calcium, hydrogen peroxide, and ethylene. J. Plant Physiol. 161 405–413. 10.1078/0176-1617-01239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehti-Shiu M. D., Zou C., Hanada K., Shiu S. H. (2009). Evolutionary history and stress regulation of plant receptor-like kinase/pelle genes. Plant Physiol. 150 12–26. 10.1104/pp.108.134353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. M., Liu B. B., Wu Y., Zou Z. R. (2008). Interactive effects of drought stresses and elevated CO2 concentration on photochemistry efficiency of cucumber seedlings. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 50 1307–1317. 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00686.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. J., Fu Q. T., Chen L. G., Huang W. D., Yu D. Q. (2011). Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY25, WRKY26, and WRKY33 coordinate induction of plant thermotolerance. Planta 233 1237–1252. 10.1007/s00425-011-1375-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. J., Fu Q. T., Huang W. D., Yu D. Q. (2009). Functional analysis of an Arabidopsis transcription factor WRKY25 in heat stress. Plant Cell Rep. 28 683–693. 10.1007/s00299-008-0666-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. J., Zhou X., Chen L. G., Huang W. D., Yu D. Q. (2010). Functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY39 in heat stress. Mol. Cells 29 475–483. 10.1007/s10059-010-0059-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. J., Du F. F., Li N. W., Chang Y. J., Yao D. R. (2016). Gene expression profile in the long-living lotus: insights into the heat stress response mechanism. PLoS One 11:e0152540. 10.1371/journal.pone.0152540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. F., Zhang C. X., Chen J., Guo L. H., Li X. L., Li W. P., et al. (2013). Arabidopsis heat shock factor HsfA1a directly senses heat stress, pH changes, and hydrogen peroxide via the engagement of redox state. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 64 92–98. 10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.12.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Zhang S. M., Sun N., Liu H. Y., Zhao Y. H., Liang Y. L., et al. (2015). Functional diversity of jasmonates in rice. Rice 8:42. 10.1186/s12284-015-0042-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J., Schmittgen T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25 402–408. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marias D. E., Meinzer F. C., Woodruff D. R., McCulloh K. A. (2017). Thermotolerance and heat stress responses of Douglas-fir and ponderosa pine seedling populations from contrasting climates. Tree Physiol. 37 301–315. 10.1093/treephys/tpw117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. P. (2012). The unfolding story of a redox chaperone. Cell 148 843–844. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittler R., Finka A., Goloubinoff P. (2012). How do plants feel the heat? Trends Biochem. Sci. 37 118–125. 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.11.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeder W., Ung H., Mosher S., Yoshioka K. (2010). SA-ABA antagonism in defense responses. Plant Signal. Behav. 5 1231–1233. 10.4161/psb.5.10.12836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montillet J., Hirt H. (2013). New checkpoints in stomatal defense. Trends Plant Sci. 18 295–297. 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu Y., Qian D., Liu B., Ma J., Wan D., Wang X., et al. (2017). ALA6, a P4-type ATPase, is involved in heat stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 8:1732. 10.3389/fpls.2017.01732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa D., Yamaguchi K., Nishiuchi T. (2007). High-level overexpression of the Arabidopsis HsfA2 gene confers not only increased themotolerance but also salt/osmotic stress tolerance and enhanced callus growth. J. Exp. Bot. 58 3373–3383. 10.1093/jxb/erm184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver B., Nadav S., Stefanie S., Shaul Y., Jörg K. (2008). Dual fatty Acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20 1346–1362. 10.1105/tpc.108.058123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S., Moon J. C., Park Y. C., Kim J. H., Kim D. S., Jang C. S. (2014). Molecular dissection of the response of a rice leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK) gene to abiotic stresses. J. Plant Physiol. 171 1645–1653. 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patharkar O. R., Walker J. C. (2015). Floral organ abscission is regulated by a positive feedback loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112 2906–2911. 10.1073/pnas.1423595112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pivovarova A. V., Mikhailova V. V., Chernik I. S., Chebotareva N. A., Levitsky D. I., Gusev N. B. (2005). Effects of small heat shock proteins on the thermal denaturation and aggregation of F-actin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 331 1548–1553. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu A. L., Lei Y. F., Yang S., Wu J., Li J. Z., Bao B. J., et al. (2018). CaC3H14 encoding a tandem CCCH zinc finger protein is directly targeted by CaWRKY40 and positively regulates the response of pepper to inoculation by Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 19 2221–2235. 10.1111/mpp.12694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao J. L. U. M., Reddy P. S., Mishra R. N., Gupta D., Sahal D., Tuteja N., et al. (2010). Thermo and pH stable ATP-independent chaperone activity of heat-inducible Hsp70 from Pennisetum glaucum. Plant Signal. Behav. 5 110–121. 10.4161/psb.5.2.10547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RoyChoudhury A., Roy C., Sengupta D. N. (2007). Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing the heterologous lea gene Rab16A from rice during high salt and water deficit display enhanced tolerance to salinity stress. Plant Cell Rep. 26 1839–1859. 10.1007/s00299-007-0371-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton P. J., Somssich I. E., Ringler P., Shen Q. J. (2010). WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 15 247–258. 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saidi Y., Finka A., Goloubinoff P. (2011). Heat perception and signalling in plants: a tortuous path to thermotolerance. New Phytol. 190 556–565. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03571.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez C., Estévez J. M., Llorente F., Hernández-Blanco C., Jordá L., Pagán I., et al. (2009). The ERECTA receptor-like kinase regulates cell wall-mediated resistance to pathogens in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 22 953–963. 10.1094/MPMI-22-8-0953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber U., Schliwa U., Bilger W. (1986). Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer. Photosynth. Res. 10 51–62. 10.1007/BF00024185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Copley R. R., Doerks T., Ponting C. P., Bork P. (2000). SMART: a web-based tool for the study of genetically mobile domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 28 231–234. 10.1093/nar/28.1.231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen H., Zhong X. B., Zhao F. F., Wang Y. M., Yan B. X., Li Q., et al. (2015). Overexpression of receptor-like kinase ERECTA improves thermotolerance in rice and tomato. Nat. Biotechnol. 33 996–1003. 10.1038/nbt.3321 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Liu Z. Q., Yang S., Yang T., Liang J. Q., Wen J. Y., et al. (2016a). Pepper CabZIP63 acts as a positive regulator during Ralstonia solanacearum or high temperature-high humidity challenge in a positive feedback loop with CaWRKY40. J. Exp. Bot. 67 2439–2451. 10.1093/jxb/erw069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Yang S., Yang T., Liang J. Q., Cheng W., Wen J. Y., et al. (2016b). CaCDPK15 positively regulates pepper responses to Ralstonia solanacearum inoculation and forms a positive-feedback loop with CaWRKY40 to amplify defense signaling. Sci. Rep. 6:22439. 10.1038/srep22439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu S. H., Bleecker A. B. (2001a). Plant receptor-like kinase gene family: diversity, function, and signaling. Sci STKE 2001:re22. 10.1126/stke.2001.113.re22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu S. H., Bleecker A. B. (2001b). Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 10763–10768. 10.1073/pnas.181141598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu S. H., Karlowski W. M., Pan R. S., Tzeng Y. H., Mayer K. F. X., Li W. H. (2004). Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 16 1220–1234. 10.1105/tpc.020834 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J. Y., Liu Q. J., Hu B. R., Wu W. J. (2017). Photoreceptor PhyB involved in Arabidopsis temperature perception and heat-tolerance formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:E1194. 10.3390/ijms18061194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava R., Deng Y., Howell S. H. (2014). Stress sensing in plants by an ER stress sensor/transducer, bZIP28. Front. Plant Sci. 5:59. 10.3389/fpls.2014.00059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenvik G., Tandstad N. M., Guo Y. F., Shi C. L., Kristiansen W., Holmgren A., et al. (2008). The EPIP peptide of INFLORESCENCE DEFICIENT IN ABSCISSION is sufficient to induce abscission in Arabidopsis through the receptor-like kinases HAESA and HAESA-LIKE2. Plant Cell 20 1805–1817. 10.1105/tpc.108.059139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Bassil E., Hamilton J. S., Inupakutika M. A., Zandalinas S. I., Tripathy D., et al. (2016). ABA is required for plant acclimation to a combination of salt and heat stress. PLoS One 11:e0147625. 10.1371/journal.pone.0147625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Hove C. A., de Jong M., Lapin D., Andel A., Sanchez-Perez G. F., Tarutani Y., et al. (2011). Trans-repression of gene activity upstream of T-DNA tagged RLK902 links Arabidopsis root growth inhibition and downy mildew resistance. PLoS One 6:e19028. 10.1371/journal.pone.0019028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma V., Ravindran P., Kumar P. P. (2016). Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 16:86. 10.1186/s12870-016-0771-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C. (1994). Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 26 1599–1609. 10.1007/BF00016492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Zhang X. Z., Goatley M., Ervin E. (2014). Heat shock proteins in relation to heat stress tolerance of creeping bentgrass at different N levels. PLoS One 9:e102914. 10.1371/journal.pone.0102914 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Guo Y. J., Jia L. X., Chu H. Y., Zhou S., Chen K. M., et al. (2014). Hydrogen peroxide acts upstream of nitric oxide in the heat shock pathway in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Physiol. 164 2184–2196. 10.1104/pp.113.229369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. H., Mei Y., Xu L., Zhu X. W., Wang Y., Guo J., et al. (2018). Genome-wide characterization of differentially expressed genes provides insights into regulatory network of heat stress response in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Funct. Integr. Genomics. 18 225–239. 10.1007/s10142-017-0587-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Vinocur B., Shoseyov O., Altman A. (2004). Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. Trends Plant Sci. 9 244–252. 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.03.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Huang W., Liu J., Yang Z., Huang B. (2017). Molecular regulation and physiological functions of a novel FaHsfA2c cloned from tall fescue conferring plant tolerance to heat stress. Plant Biotechnol. J. 15 237–248. 10.1111/pbi.12609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Chang H. P., Hu S., Lu X. T., Yuan C. Y., Zhang C., et al. (2014). Plastid casein kinase 2 knockout reduces abscisic acid (ABA) sensitivity, thermotolerance, and expression of ABA- and heat-stress-responsive nuclear genes. J. Exp. Bot. 65 4159–4175. 10.1093/jxb/eru190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Dang F., Liu Z., Wang X., Eulgem T., Lai Y., et al. (2013). CaWRKY58, encoding a group I WRKY transcription factor of Capsicum annuum, negatively regulates resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 14 131–144. 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00836.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters E. R. (2013). The evolution, function, structure, and expression of the plant sHSPs. J. Exp. Bot. 64 391–403. 10.1093/jxb/ers355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. Z., Wu Y. J., Gao Y., Li M. Z., Yin H. J., Lv M. H., et al. (2015). Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase 5 in the ecotype Landsberg erecta of Arabidopsis is a functional RD LRR-RLK in regulating brassinosteroid signaling and cell death control. Front. Plant Sci. 6:852. 10.3389/fpls.2015.00852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Liang J., Wang C., Zhao X., Zhong X., Cao X., et al. (2018). Overexpression of lily HsfA3s in Arabidopsis confers increased thermotolerance and salt sensitivity via alterations in proline catabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 69 2005–2021. 10.1093/jxb/ery035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Audenaert K., Hofte M., De Vleesschauwer D. (2013). Abscisic acid promotes susceptibility to the rice leaf blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae by suppressing salicylic acid-mediated defenses. PLoS One 8:e67413. 10.1371/journal.pone.0067413 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue G. P., Drenth J., McIntyre C. L. (2015). TaHsfA6f is a transcriptional activator that regulates a suite of heat stress protection genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) including previously unknown Hsf targets. J. Exp. Bot. 66 1025–1039. 10.1093/jxb/eru462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan K., Chen N., Qu Y. Y., Dong X. C., Meng Q. W., Zhao S. J. (2008). Overexpression of sweet pepper glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gene enhanced thermotolerance of photosynthetic apparatus in transgenic tobacco. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 50 613–621. 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00652.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo S. D., Cho Y. H., Sheen J. (2007). Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2 1565–1572. 10.1038/nprot.2007.199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai N., Jia H. H., Liu D. D., Liu S. C., Ma M. L., Guo X. Q., et al. (2017). GhMAP3K65, a cotton Raf-Like MAP3K gene, enhances susceptibility to pathogen infection and heat stress by negatively modulating growth and development in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:E2462. 10.3390/ijms18112462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Liu B., Li M., Feng D., Jin H., Wang P., et al. (2015). The bHLH transcription factor bHLH104 interacts with IAA-LEUCINE RESISTANT3 and modulates iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27 787–805. 10.1105/tpc.114.132704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. J., Wang L. J. (2005). The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 5:1. 10.1186/1471-2148-5-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Missihoun T. D., Bartels D. (2017). The role of Arabidopsis aldehyde dehydrogenase genes in response to high temperature and stress combinations. J. Exp. Bot. 68 4295–4308. 10.1093/jxb/erx194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. Q., Xuan Y., Zhou S., Wang L., Jiang H. J. (2010). Role of nitric oxide in thermotolerance. Plant Signal. Behav. 5 1423–1424. 10.4161/psb.5.11.13292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The sequence analysis of CaHSL1 and cis-elements within the promoter of CaHSL1. (A) Schematic diagram of CaLRR-RLK1 protein domain architecture and multiple-sequence-alignment (MSA) of the amino-acid sequence of CaHSL1 with its homologues from other plant species; CaHSL1 shared 99, 75, 73, 72, 57, 61, 54, 49, and 48% sequence similarity to the sequences of HSL1s from Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chinense and Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum tuberosum, Nicotiana tabacum, Sesamum indicum, Coffea canephora, Glycine max, Brassica napus, and Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. Different colors indicate different percentages of similarity between CaHSL1 and HSL1s of the other species (i.e., black, red and green shades represent 100%, 75–100%, and 50–75% similarity, respectively). NLS: nuclear localization signal (Read bar in Supplementary Figure S1A); LRR, Leucine-rich repeats; TM, transmembrane region; S_TKc, Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain. (B) Phylogenetic relationship between CaHSL1 and HSL1s of the above mentioned plants species. (A,B) were assayed using online SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?NORMAL=1) and DNAMAN5 (Lynnon Biosoft, United States). (C) Distribution of stress responsiveness related cis-elements in the promoter of CaHSL1 by PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/), the “A” in the translational start codon ATG was set to +1. GARE, gibberellin-responsive element; W-box, TTGACC/T bound by WRKY TFs; HSE, cis-acting element involved in heat stress responsiveness; CGTCA, cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA-responsiveness; AuxRR, auxin-responsive region; LTR, low temperature-response element; TCA, cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness.
Subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in protoplasts of pepper. (A) Subcellular localization of CaHSL1 in protoplasts of pepper, GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-GFP (35S::GFP) and 35S:CBL1n-CFP were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and co-infiltrated into pepper leaves, which were harvested for protoplasts isolation, and the GFP signals were observed immediately. Bars = 50 μm. (B) Dynamics of the GFP fluorescence in protoplasts suspended in a hypotonic medium. Protoplasts were isolated from pepper leaves infiltrated with GV3101 cells containing 35S::CaHSL1-GFP or 35S::GFP, 10 μL of distilled water was added to a 20 μL of acquired protoplasts to rupture the protoplasts, and GFP signals were monitored using laser confocal at different time points after the addition of distilled water.
Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and transcription of thermotolerance associated genes in CaHSL1 silenced pepper plants upon the challenge of HTHH. (A) Phenotype and Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images in detached leaves of TRV::CaHSL1-1, TRV::CaHSL1-2 and TRV::00 plants challenged with 42°C, 90% humidity pretreated with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C, the Phenotype and Fv/Fm shown in pseudo color images were measured at 1, 3, 12, and 24 hpt. (B) ΦPSII in HTHH challenged CaHSL1 silenced pepper plants with (AT) or without (BT) 37°C compared to that in the mock treated wild type plants, which was detected 1, 3, 12, and 24 hpt. (C) The transcript levels of CaHSP24, CaHSP24.2, CaHSP70 and CaHsfA2 in HTHH challenged TRV::CaHSL1-1,TRV::CaHSL1-1 pepper plants with (AT) or without (BT) pretreatment of 37°C compared with those in mock-treated TRV::00 plants, which were set to a relative expression level of “1.” In (B,C), error bars indicate standard error, data show the mean ± SD obtained from four replicates. Different upper-case letters indicate significant differences among means (P < 0.01), as calculated with Fisher’s protected-LSD-test. AT, acquired thermotolerance. BT, basal thermotolerance. HTHH, High temperature and high humidity treatment. hpt, hours post treatment. Fv/Fm, the optimal/maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII in the dark. ΦPSII, the actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light.
The primers used in PCR assay in the present study.