Abstract
Estrogen has diverse effects on cardiovascular function, including regulation of the contractile response to vasoactive substances such as serotonin. The serotonin system recently emerged as an important player in the regulation of vascular tone in humans. However, hyperreactivity to serotonin appears to be a critical factor for the pathophysiology of hypertension. In this study, we examined the modulatory mechanisms of estrogen in serotonin-induced vasoconstriction by using a combinatory approach of isometric tension measurements, molecular biology, and patch-clamp techniques. 17β-Estradiol (E2) elicited a significant and concentration-dependent relaxation of serotonin-induced contraction in deendothelialized aortic strips isolated from male rats. E2 triggered a relaxation of serotonin-induced contraction even in the presence of tamoxifen, an estrogen receptor antagonist, suggesting that E2-induced changes are not mediated by estrogen receptor. Patch-clamp studies in rat arterial myocytes showed that E2 prevented Kv channel inhibition induced by serotonin. Serotonin increased Src activation in arterial smooth muscle required for contraction, which was significantly inhibited by E2. The estrogen receptor-independent inhibition of Src by E2 was confirmed in HEK293T cells that do not express estrogen receptor. Taken together, these results suggest that estrogen exerts vasodilatory effects on serotonin-precontracted arteries via Src, implying a critical role for estrogen in the prevention of vascular hyperreactivity to serotonin.
Vascular disease: estrogen suppresses artery-constricting effect of serotonin
Estrogen helps lower blood pressure by blocking a key signaling protein that the neurotransmitter serotonin normally activates to promote the constriction of blood vessels. A team from South Korea led by Hana Cho from Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, and Young Min Bae from Konkuk University School of Medicine, Chungju, showed that estradiol, a type of estrogen steroid hormone, spurred a relaxation of serotonin-induced constriction in rat artery tissue, but the effect was not mediated through the estrogen receptor. Instead, the researchers showed in rat tissue and human cells that an enzyme called Src was essential: serotonin increased Src activity in the muscle cells that contract during arterial narrowing, while estradiol inhibited Src function. The findings could help inform future therapies for vascular diseases.
Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the major cause of death in developed countries. However, there are sex-specific clinical characteristics, some of which may be dependent on levels of the sex hormone estrogen1. Observational studies have demonstrated that both the incidence of CVD and the resultant morbidity and mortality are much lower in premenopausal women compared to age-matched men, and this sex advantage for women becomes far less or disappears with increased age and reduced estrogen levels after menopause2–5. Observational studies have also shown that postmenopausal women who receive hormone replacement therapy (HRT) have a lower rate of CVD and cardiac death than those not receiving HRT6,7. However, two randomized prospective primary or secondary prevention trials, the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI)8 and the Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study (HERS I and II)9,10, showed that HRT may actually increase the risk and events of CVD in postmenopausal women. The reasons for this paradoxical characterization of HRT as both beneficial and detrimental remain unclear. Many potential factors may contribute to the adverse outcomes, namely, age, preexisting CVD and/or risk, when HRT was initiated, the type of HRT given (conjugated equine estrogen with progestin), dosage, and the thromboembolic properties of estrogen and progestin7,11–14. Overall, the use of HRT has become one of the most controversial topics related to women’s health, making it all the more urgent to clarify whether estrogens prevent or promote CVD, as well as the mechanism(s) involved.
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) is a neurotransmitter with potent vasoconstriction properties that regulates a variety of processes in the nervous and cardiovascular systems15. Blood 5-HT levels can be changed by nutrition, drugs, and malfunction of the 5-HT transporter16,17 and tend to increase after menopause18. We and others reported that vasoconstriction by 5-HT in arteries arises via the activation of 5-HT 2A receptor (5-HT2AR) and the consequent decrease of Kv channel activity19–23. 5-HT2A antagonists may have clinical potential for the treatment of a broad range of CVDs, including vasospastic angina, ischemic heart disease, reperfusion injury and hindlimb ischemia24. Importantly, several lines of evidence from studies of the vasculature suggest that hyperreactivity (or enhanced vasoconstriction) to 5-HT is a hallmark of vascular damage16. This is observed experimentally as a lower threshold for 5-HT to cause contraction, an increased potency of 5-HT, and/or an increased efficacy of 5-HT compared with a normotensive control. One of the best-studied changes in the vascular response to 5-HT has been in vessels from humans and animals with high blood pressure (hypertension). Under hypertensive conditions, hyperreactivity has been observed in a number of different vascular beds and differently sized vessels25–30. In this study, we hypothesized a potential link between estrogen and the 5-HT pathway in the control of vasoconstriction.
The present study demonstrates that estrogen (estradiol, E2) suppressed 5-HT-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction in a dose-dependent manner. E2 produced a relaxation of 5-HT-induced contractions even in the presence of tamoxifen, an estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist, suggesting that E2-induced changes are not mediated by ER. 5-HT increased Src activation in arterial smooth muscle required for contraction, which was significantly inhibited by E2. ER-independent inhibition of Src by E2 was confirmed in HEK293T cells, which do not express ER. Taken together, our findings suggest that E2 relieves 5-HT-mediated vascular contraction via Src inhibition, providing an underlying mechanism for the estrogen regulation of vascular hyperreactivity to 5-HT and hypertension.
Materials and methods
Animals and tissue preparation
All experiments were conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines for the care and use of animals. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Konkuk University approved this study. Mesenteric arterial rings and aortic rings were prepared as previously described19,20. The carotid arteries of male Sprague-Dawley rats (10 to 11 weeks old) were cut to exsanguinate the rats under deep ketamine-xylazine anesthesia or after exposure to 100% carbon dioxide. Branches of the superior mesenteric arteries and thoracic aorta were promptly isolated and placed in physiological saline solution (PSS) containing 136.9 mM NaCl, 5.4 mM KCl, 1.5 mM CaCl2, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 23.8 mM NaHCO3, 1.2 mM NaH2PO4, 0.01 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and 5.5 mM glucose. The arteries were carefully cleaned of fat and connective tissues under a stereomicroscope and prepared as rings (3.5 mm in length) for tension measurements. The endothelium was mechanically removed with a fine stainless steel wire. Endothelial removal was confirmed by the absence of relaxation induced by acetylcholine (10 μM) after norepinephrine- (NE; 1–10 μM) or 5-HT (1–10 μM)-induced contraction.
Organ chamber isometric contraction measurements
The isometric tension of arterial rings was measured as previously described19,20. The arterial rings were mounted vertically onto two L-shaped stainless steel wires in a 3-mL tissue chamber. One wire was attached to a micromanipulator and the other to an isometric force transducer (FT03; Grass, West Warwick, RI, USA). Changes in isometric force were digitally acquired at 1 Hz with a PowerLab data acquisition system (ADInstruments, Colorado Springs, CO, USA). Resting tension was set to 2 g by the micromanipulator. After equilibration for 60 min under resting tension in a tissue chamber filled with PSS, the rings were sequentially exposed to 70 mM KCl PSS (10 min) and PSS (15 min) thrice for stabilization. High KCl (70 mM) PSS was prepared by replacing NaCl with equimolar KCl in PSS. The bathing solutions were thermostatically controlled at 37 °C and continuously saturated with a mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2 to achieve a pH of 7.4.
Cell culture
HEK293T cells were cultured in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 in Dulbecco Modified Eagle’s Medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with penicillin and streptomycin.
Electrophysiology
Whole-cell KV currents were recorded under the nystatin-perforated patch-clamp configuration at room temperature (22–23 °C). Micropipettes fabricated from glass capillary tubing (PG10165-4; World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, FL, USA) with a double-stage vertical puller (PC-10; Narishige, Tokyo, Japan) had a tip resistance of 2–3 MΩ when filled with the pipette solution. Whole-cell currents were amplified with an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), digitized with Digidata 1440 A (Molecular Devices) at 5 kHz, and low-pass filtered with a four-pole Bessel filter at 1 kHz. The generation of voltage commands and acquisition of data were controlled with pClamp 10.1 software (Molecular Devices) running on an IBM-compatible Pentium computer.
Solutions and drugs
Bicarbonate-buffered PSS with 1.5 mM CaCl2 was used as the bath solution for the organ chamber isometric contraction measurement experiments. The bicarbonate-buffered PSS contained 136.9 mM NaCl, 5.4 mM KCl, 1.5 mM CaCl2, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 23.8 mM NaHCO3, and 0.01 mM EDTA with a mixture of 95% O2 in 5% CO2 to achieve a pH of 7.4. High K+ solution contained 70 mM KCl, 72.3 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM CaCl2, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 23.8 mM NaHCO3, and 0.01 mM EDTA with a mixture of 95% O2 in 5% CO2 to achieve a pH of 7.4. For KV current recording, normal Tyrode’s solution was used as the bathing solution in the patch-clamp. Normal Tyrode’s solution contained 143 mM NaCl, 5.4 mM KCl, 0.33 mM NaH2PO4, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulphonic acid (HEPES), and 11 mM glucose and was adjusted to a pH of 7.4 with NaOH. The pipette solution contained 135 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES, 0.05 mM ethyleneglycol-bis (2-aminoethyl)-N,N,N′,N′,-tetraacetic acid, and 200 μg/mL nystatin and was adjusted to a pH of 7.2 with KOH.
Cell lysis and Western blotting
For aortic tissue disruption, isolated tissues were frozen with liquid nitrogen, followed by grinding with a mortar and pestle. Next, the cells were lysed with RIPA buffer (AbFRONTIER, Korea) containing 10 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4 and complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). For HEK293T cell lysis, lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Triton X-100, 10 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4 and complete protease inhibitor cocktail) was utilized. After separating by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), the protein lysates were transferred to a PVDF membrane (Immobilon-P; Merk Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) and blotted with the indicated primary antibody. The membrane was then incubated with a secondary antibody conjugated with horse radish peroxidase and reacted with enhanced chemiluminescence substrate (WestSave-Gold; AbFRONTIER) for detection. The primary antibodies used in this study are as follows: phospho-Src (2101 S, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), Src (2108 S, Cell Signaling Technology) and β-tubulin (T5293, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Band intensity was quantified by using ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Drugs
All chemicals and drugs were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich unless otherwise stated. Genistein (Cat. No. 1110) was purchased from Tocris Bioscience (Woongbee MeDiTech, Seoul, Korea).
Statistical analysis
Origin 8.0 software (Microcal Software, Inc., Northampton, MA, USA) was used for data analysis. The results are presented as the mean ± standard error or the mean ± standard deviation. Paired or independent Student’s t-tests were used to test for significance where appropriate. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
E2 attenuated 5-HT-induced vasoconstriction
We used isometric organ chamber mechanics to examine whether E2 regulates 5-HT–mediated vascular smooth muscle contraction. Under control conditions, 5-HT treatment evoked a concentration-dependent constriction in deendothelialized aortic strips isolated from male rats (Fig. 1a). In contrast, 5-HT-induced vasoconstriction was markedly suppressed when 10 μM E2 was applied (Fig. 1b). E2 inhibited 5-HT-induced vasoconstriction in a concentration-dependent manner (Figs. 1c, d). Taken together, these results suggest that E2 relaxes the 5-HT-precontracted artery in a dose-dependent manner.
Fig. 1. Effects of E2 on 5-HT-induced arterial contraction.
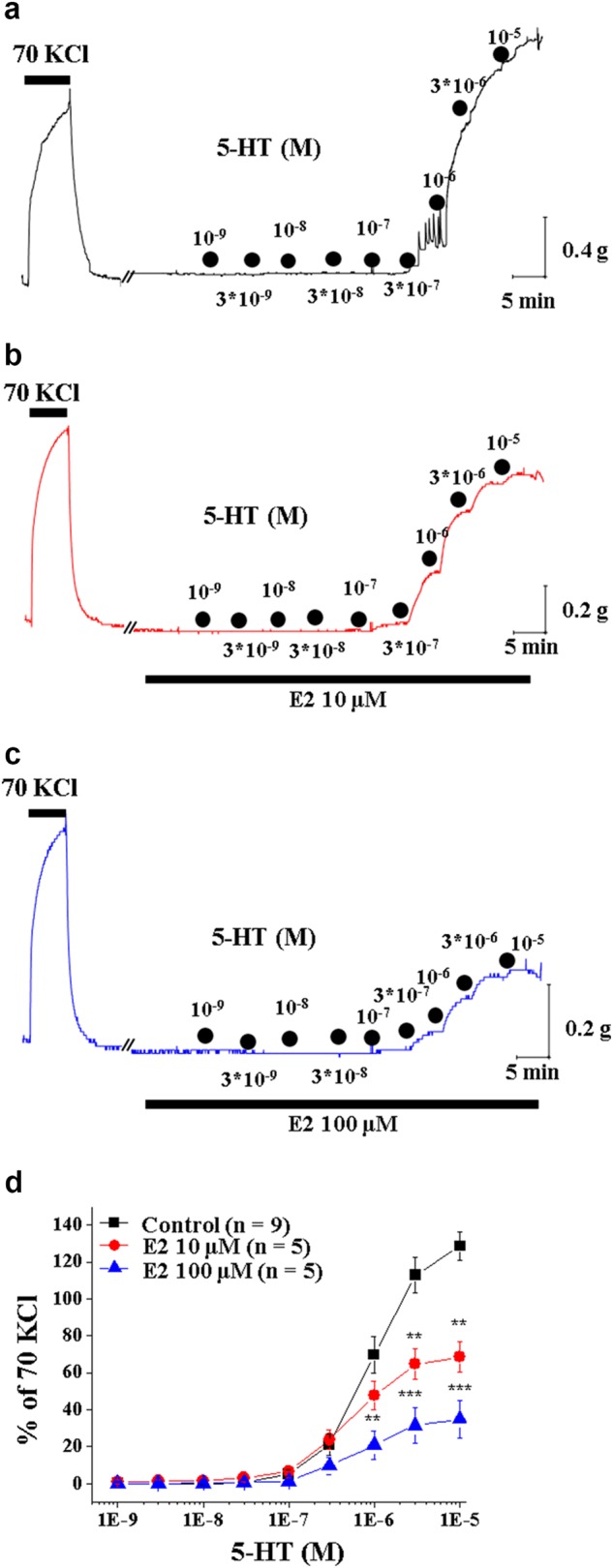
a A representative tracing of the concentration-dependent response (CRC) of arterial contraction by cumulative application of 5-HT under control conditions. b A representative tracing of the CRC of arterial contraction by cumulative application of 5-HT in the presence of 10 μM E2. c A representative tracing of the CRC of arterial contraction by cumulative application of 5-HT in the presence of 100 μM E2. d Summary of the CRC of 5-HT-induced arterial contraction in the absence and presence of 10 μM and 100 μM E2. The number in parenthesis (n) indicates the number of animals examined. **p < 0.01 vs control. ***p < 0.001 vs control
Estrogen action on 5-HT-mediated vasoconstriction is mediated by an ER-independent mechanism
Both ER subtypes, classical ER (ERα) and the newly identified ER subtype (ERβ), are expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells31. Thus, we determined whether an ER blocker, tamoxifen, reverses E2-induced relaxation of the 5-HT-precontracted artery. Tamoxifen is a nonselective ER blocker32. Surprisingly, pretreatment with 10 μM tamoxifen did not affect relaxation of the 5-HT-precontracted artery by E2 treatment at a concentration of 10 μM (Figs. 2a, b and d). The addition of tamoxifen to vascular rings in the absence of E2 did not alter 5-HT effects (Figs. 2c, d). These data indicate that the E2-elicited inhibition of 5-HT-mediated contraction in vascular smooth muscles is independent of the ER-mediated pathway.
Fig. 2. Effects of tamoxifen on the attenuation of 5-HT-induced arterial contraction by E2.
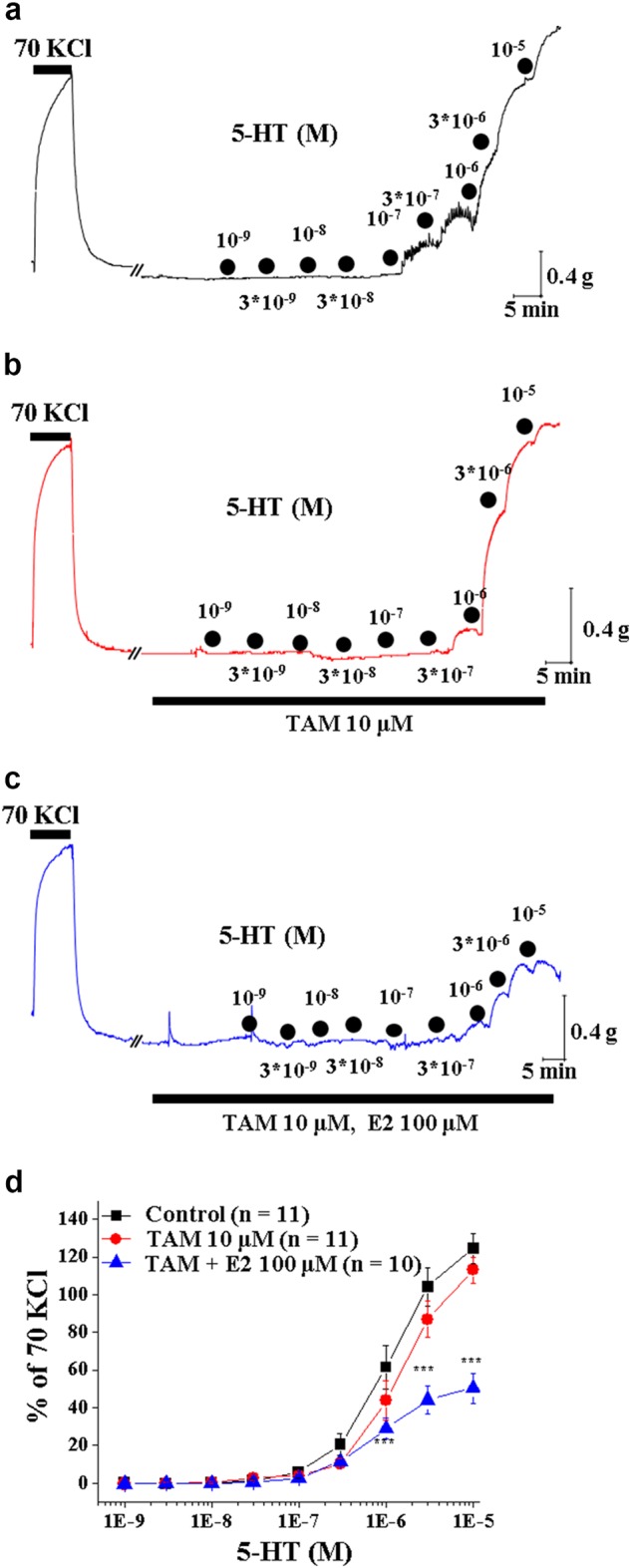
a A representative tracing of the CRC of arterial contraction by cumulative application of 5-HT under control conditions. b A representative tracing of the CRC of arterial contraction by cumulative application of 5-HT in the presence of tamoxifen (10 μM). c A representative tracing of the CRC of arterial contraction by cumulative application of 5-HT in the presence of tamoxifen (TAM, 10 μM) and E2 (100 μM). d Summary of the CRC of 5-HT-induced arterial contraction in the absence and presence of tamoxifen (10 μM) or tamoxifen (10 μM) plus E2 (100 μM). The number in parenthesis (n) indicates the number of animals examined. ***p < 0.001 vs control
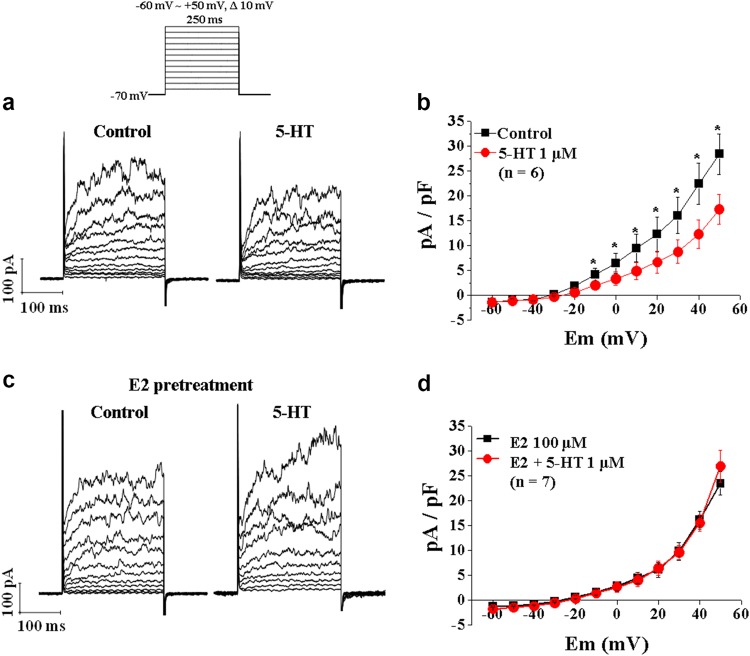
E2 blocked 5-HT-induced Kv channel inhibition in rat aortic smooth muscle cells
5-HT exerted vasoconstriction effects by inhibiting Kv channel activity in vascular smooth muscle cells19. Thus, we examined whether E2 regulates Kv channel activity in 5-HT-treated vascular smooth muscle cells. We examined the effect of E2 on 5-HT-induced Kv current inhibition in vascular smooth muscle cells isolated from rat aortas. We recorded Kv currents using the nystatin-perforated patch-clamp technique with depolarizing voltage steps as described previously19 (Fig. 3). Under control conditions without E2 treatment, 5-HT treatment (1 μM) reduced outward Kv currents (current density at + 50 mV before and after 5-HT: 28.4 ± 4 and 17.3 ± 2.9 pA/pF, respectively; paired t-test; n = 6, p < 0.05) (Figs. 3a, b). In contrast, treatment with E2 blocked the 5-HT-induced inhibition of the Kv current (current density at + 50 mV before and after 5-HT: 23.5 ± 2.3 and 26.9 ± 3.2, respectively; paired t-test; n = 7, p < 0.05) (Figs. 3c, d). These data suggest that E2 relieves 5-HT-induced Kv channel inhibition, an essential step for 5-HT-mediated vasoconstriction.
Fig. 3. Effects of E2 on the 5-HT-induced inhibition of Kv currents in arterial myocytes.
a Representative tracings of outward K+ currents in the absence and presence of 5-HT (1 μM). The shapes of voltage step pulses are included as a figure inset. b Summary of the current-voltage (I-V) relationships of the outward K+ currents in the absence and presence of 5-HT (1 μM). c Representative tracings of outward K+ currents in the absence and presence of 5-HT (1 μM) after pretreatment with E2 (100 μM). d Summary of the I-V relationships of outward K+ currents in the absence and presence of 5-HT (1 μM) after pretreatment with E2 (100 μM). The number in parenthesis (n) indicates the number of cells examined. *p < 0.05 vs control
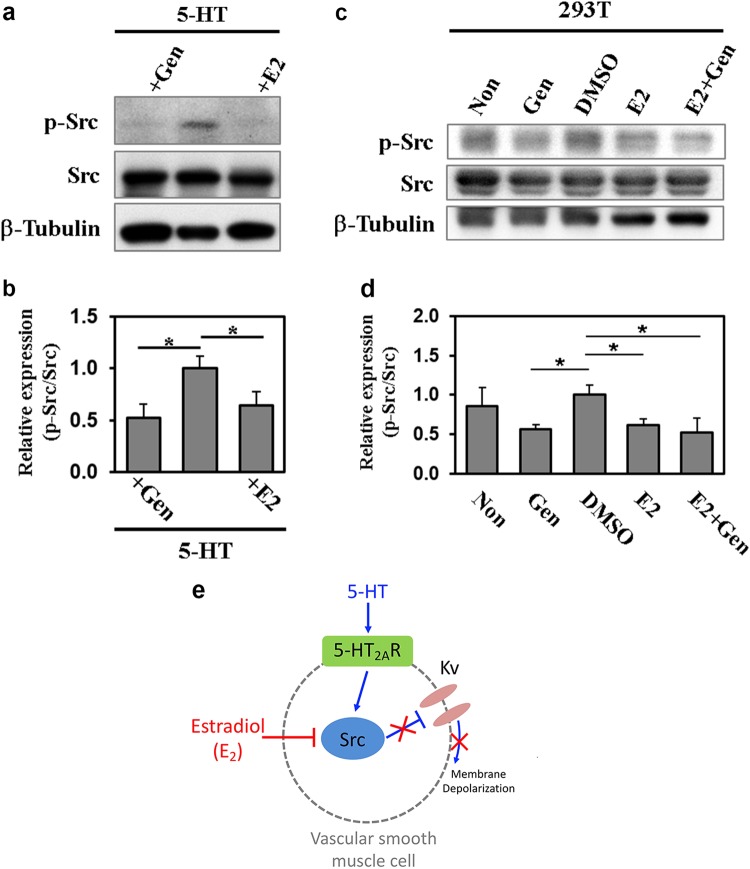
E2 attenuated 5-HT-induced Src activation in rat aortic smooth muscle
Given that 5-HT exerted its inhibitory effects on Kv channels via Src in vascular smooth muscle cells19, our data suggest that the relieving effect of E2 on Kv channels may involve Src suppression with a consequent prevention of arterial contraction by 5-HT. To investigate whether Src activation is altered by E2 treatment, we measured the level of an active phosphorylated form of Src (p-Src) in endothelium-denuded aortas treated with 5-HT in combination with vehicle or E2. 5-HT markedly elevated the level of p-Src protein and the increase was significantly blunted by E2 treatment (Fig. 4a). The inhibitory effect of E2 on Src phosphorylation was equivocal to that induced by a general tyrosine kinase inhibitor, genistein (Fig. 4b). We also studied the effect of E2 on Src phosphorylation in HEK293T cells that are devoid of ER (Figs. 4c, d). Similar to vascular smooth muscle, treatment with E2 or genistein in HEK293T cells also reduced the level of p-Src protein. The extent of Src inhibition by E2 was indistinguishable from that induced by genistein. Moreover, the combined treatment of E2 and genistein had no additional effects on p-Src compared with treatment with either compound alone. These data suggest that E2 inhibits 5-HT-induced Src activation independently of ER. Based on these data, we propose a working hypothesis that E2 suppresses Src activation induced by 5-HT in vascular smooth muscle, preventing membrane depolarization and exerting a vasodilatory effect (Fig. 4e).
Fig. 4. E2 inhibited Src activation in 5-HT-stimulated rat aortic smooth muscle and in HEK293T cells.
a Aortic tissues from 10-week-old rats treated with 5-HT in combination with vehicle, genistein (Gen) or E2 were subjected to Western blotting for phospho-Src (p-Src) or Src. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. b The relative band intensity shown in panel a was quantified with the use of ImageJ software. The value of pSrc was normalized to that of Src, and the value of 5-HT-treated cells was set to 1.0. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05. c Protein lysates from HEK293T cells that were non- or mock-treated (DMSO) or treated with 100 μM genistein (Gen), 100 μM E2, or Gen plus E2 for 10 min after 24-h starvation were analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody against p-Src or Src. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. d The relative band intensity shown in panel c was quantified with ImageJ software. The value of pSrc was normalized to that of Src, and the value of DMSO-treated cells was set to 1.0. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05. e A working model summarizing the regulatory mechanism of serotonin-induced vasoconstriction by estradiol
Discussion
In the current study, we showed that E2 inhibited the 5-HT-evoked contraction of vascular smooth muscles. Furthermore, we identified the underlying mechanism of this regulation. Estrogen blocked 5-HT-induced Kv channel modulation in vascular smooth muscle cells through Src inhibition independently of ERs. Our data imply that estrogen critically impacts the suppression of 5-HT-mediated vascular contraction by Src inhibition, offering an attractive mechanism as a target for hyperreactivity to 5-HT. Many reports have elucidated that estrogen acts on ER-dependent activation of the eNOS signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells33. However, the identity of estrogen-mediated signaling pathways leading to endothelium-independent vasodilation has been elusive34,35. In contrast to the ER-dependent nature of endothelial cell signaling, the effects of estrogen in smooth muscle cells may be independent of ER35, but the underlying mechanism is not yet clear.
Our current study suggests that suppression of the 5-HT-induced vasoconstriction response by E2 is mediated through Src inhibition independently of ER based on the following observations. (1) The suppression of 5-HT-mediated arterial contraction by E2 was not blocked by an inhibitor of ER, tamoxifen. (2) E2 blocked 5-HT-induced Kv channel inhibition in arterial smooth muscle cells. In the rat aorta and mesenteric arteries, activation of the 5-HT receptor 5-HT2AR is followed by Src phosphorylation and consequent Kv inhibition19,21. (3) The increase in Src phosphorylation in aortic smooth muscles by 5-HT was inhibited by E2. In addition, Src phosphorylation in HEK293T cells that do not express ER was also inhibited by E2 with a similar potency to that induced by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, genistein. Because Kv inhibition is a downstream effector step of Src in 5-HT-mediated vasoconstriction, it is tempting to speculate that decreased Src phosphorylation by E2 may relieve the 5-HT-induced Kv channel inhibition that ultimately elicits vasoconstriction.
The regulatory mechanisms of cardiovascular effects by estrogen are diverse. Estrogen can act both systemically on circulating factors (e.g., cholesterol, cytokines, coagulation/fibrinolytic factors)36 and directly on blood vessel endothelial cells37. Some estrogen effects occur rapidly, whereas others require prolonged estrogen exposure. At physiologically relevant concentrations of estrogen, both the rapid and long-term cardiovascular effects of estrogen are regulated by ER-mediated pathways37–40. To date, two ERs have been described, ERα and ERβ41–43. Although their physiological relevance in the vasculature is incompletely understood, ERα and ERβ are expressed in endothelial cells and in vascular smooth muscle cells44–50. ERα triggers a signaling cascade that results in the release of cardioprotective nitric oxide in endothelial cells33. Similar to endothelial cells, ERα contributes to the estrogen-mediated inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, preventing vascular diseases, especially atherosclerosis33. However, a recent study employing ERα, β (double) knockout mice revealed a receptor-independent mechanism. These mice were still responsive to the E2–mediated inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation upon vascular injury36. Our data further support that estrogen exerts a protective effect on vascular diseases through ER-independent mechanisms in vascular smooth muscle cells. Although the mechanism by which E2 inhibited the phosphorylation of Src independent of ERs remains unclear, it is interesting that the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein and E2 are structurally similar. In addition to being a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, genistein is also a member of the isoflavone family and acts as a phytoestrogen in mammals51. A systematic future study on how isoflavones and estrogen inhibit protein tyrosine kinase would be worthwhile.
In conclusion, our data suggest that E2 attenuates 5-HT-induced vasoconstriction in an ER-independent manner, likely by Src inhibition. Considering that 5-HT hyperreactivity represents a risk factor for vascular diseases, this E2-mediated vasodilatory mechanism through Src inhibition is an attractive target for the intervention of vascular diseases. This pathway can also provide valuable information for the design and interpretation of HRT.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HI17C1438 to HC) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grants funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (2016R1A5A2945889 to HC, 2016R1A2B4014795 to YMB, and 2017R1A6A3A01009196 to JGK).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Jae Gon Kim, Young-Eun Leem
Contributor Information
Young Min Bae, Phone: +82-2-2030-7823, Email: ymbae30@kku.ac.kr.
Hana Cho, Phone: +82-31-299-6104, Email: hanacho@skku.edu.
References
- 1.Sasaki H, et al. PDE5 inhibitor efficacy is estrogen dependent in female heart disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2014;124:2464–2471. doi: 10.1172/JCI70731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bittner V. Menopause, age, and cardiovascular risk: a complex relationship. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009;54:2374–2375. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Coylewright M, Reckelhoff JF, Ouyang P. Menopause and hypertension: an age-old debate. Hypertension. 2008;51:952–959. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.105742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kim ES, Menon V. Status of women in cardiovascular clinical trials. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009;29:279–283. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.179796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reckelhoff JF, Maric C. Sex and gender differences in cardiovascular-renal physiology and pathophysiology. Steroids. 2010;75:745–746. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grodstein F, et al. A prospective, observational study of postmenopausal hormone therapy and primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000;133:933–941. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-133-12-200012190-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rosano GM, Vitale C, Fini M. Cardiovascular aspects of menopausal hormone replacement therapy. Climacteric. 2009;12(Suppl 1):41–46. doi: 10.1080/13697130903012306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Manson JE, et al. Estrogen plus progestin and the risk of coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;349:523–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hulley S, et al. Randomized trial of estrogen plus progestin for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women. Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study (HERS) Research Group. JAMA. 1998;280:605–613. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.7.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hulley S, et al. Noncardiovascular disease outcomes during 6.8 years of hormone therapy: Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study follow-up (HERS II) JAMA. 2002;288:58–66. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hodis HN. Assessing benefits and risks of hormone therapy in 2008: new evidence, especially with regard to the heart. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2008;75(Suppl 4):S3–S12. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.75.Suppl_4.S3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schnatz PF. Hormonal therapy: does it increase or decrease cardiovascular risk? Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2006;61:673–681. doi: 10.1097/01.ogx.0000238674.98471.bb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Haines CJ, Farrell E. Menopause management: a cardiovascular risk-based approach. Climacteric. 2010;13:328–339. doi: 10.3109/13697130903450154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Harman SM. Estrogen replacement in menopausal women: recent and current prospective studies, the WHI and the KEEPS. Gend. Med. 2006;3:254–269. doi: 10.1016/S1550-8579(06)80214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Watts SW. 5-HT in systemic hypertension: foe, friend or fantasy? Clin. Sci. 2005;108:399–412. doi: 10.1042/CS20040364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Watts SW, Morrison SF, Davis RP, Barman SM. Serotonin and blood pressure regulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012;64:359–388. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brenner B, et al. Plasma serotonin levels and the platelet serotonin transporter. J. Neurochem. 2007;102:206–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Haliloglu B, et al. Serotonin dilemma in postmenopausal women: is it low or high? Maturitas. 2008;60:148–152. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2008.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sung DJ, et al. Serotonin contracts the rat mesenteric artery by inhibiting 4-aminopyridine-sensitive Kv channels via the 5-HT2A receptor and Src tyrosine kinase. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013;45:e67. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lin H, et al. Enhancement of 5-HT2A receptor function and blockade of Kv1.5 by MK801 and ketamine: implications for PCP derivative-induced disease models. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018;50:47. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0073-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lu R, et al. c-Src tyrosine kinase, a critical component for 5-HT2A receptor-mediated contraction in rat aorta. J. Physiol. 2008;586:3855–3869. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.153593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bae YM, et al. Serotonin depolarizes the membrane potential in rat mesenteric artery myocytes by decreasing voltage-gated K+currents. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006;347:468–476. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cogolludo A, et al. Serotonin inhibits voltage-gated K+currents in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: role of 5-HT2A receptors, caveolin-1, and KV1.5 channel internalization. Circ. Res. 2006;98:931–938. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000216858.04599.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Doggrell SA. The role of 5-HT on the cardiovascular and renal systems and the clinical potential of 5-HT modulation. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2003;12:805–823. doi: 10.1517/13543784.12.5.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cummings SA, Groszmann RJ, Kaumann AJ. Hypersensitivity of mesenteric veins to 5-hydroxytryptamine- and ketanserin-induced reduction of portal pressure in portal hypertensive rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1986;89:501–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Thompson LP, Webb RC. Vascular responsiveness to serotonin metabolites in mineralocorticoid hypertension. Hypertension. 1987;9:277–281. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.9.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Huzoor A, Chen NY, Fossen DV, Wallace D. Increased vascular contractile sensitivity to serotonin in spontaneously hypertensive rats is linked with increased turnover of phosphoinositide. Life. Sci. 1989;45:577–583. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dohi Y, Luscher TF. Endothelin in hypertensive resistance arteries. Intraluminal Extra. Dysfunct. Hypertens. 1991;18:543–549. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.4.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Webb RC, Schreur KD, Papadopoulos SM. Oscillatory contractions in vertebral arteries from hypertensive subjects. Clin. Physiol. 1992;12:69–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097X.1992.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Moreno L, Martinez-Cuesta MA, Pique JM, Bosch J, Esplugues JV. Anatomical differences in responsiveness to vasoconstrictors in the mesenteric veins from normal and portal hypertensive rats. Naunyn Schmiede. Arch. Pharmacol. 1996;354:474–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00168439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Holm A, Nilsson BO. Identification and characterization of new mechanisms in vascular oestrogen signalling. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013;113:287–293. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Watanabe T, et al. Estrogen receptor beta mediates the inhibitory effect of estradiol on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003;59:734–744. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6363(03)00496-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Menazza S, Murphy E. The expanding complexity of estrogen receptor signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2016;118:994–1007. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.305376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sudhir K, et al. Mechanisms of estrogen-induced vasodilation: in vivo studies in canine coronary conductance and resistance arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1995;26:807–814. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Teoh H, Quan A, Leung SW, Man RY. Differential effects of 17beta-estradiol and testosterone on the contractile responses of porcine coronary arteries. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000;129:1301–1308. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Karas RH, et al. Effects of estrogen on the vascular injury response in estrogen receptor alpha, beta (double) knockout mice. Circ. Res. 2001;89:534–539. doi: 10.1161/hh1801.097239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mendelsohn ME. Nongenomic, ER-mediated activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase: how does it work? What does it mean? Circ. Res. 2000;87:956–960. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.87.11.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chen Z, et al. Estrogen receptor alpha mediates the nongenomic activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by estrogen. J. Clin. Invest. 1999;103:401–406. doi: 10.1172/JCI5347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Haynes MP, et al. Membrane estrogen receptor engagement activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase via the PI3-kinase-Akt pathway in human endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 2000;87:677–682. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.87.8.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Simoncini T, et al. Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 2000;407:538–541. doi: 10.1038/35035131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gustafsson JA. Estrogen receptor beta--getting in on the action? Nat. Med. 1997;3:493–494. doi: 10.1038/nm0597-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Katzenellenbogen BS, Korach KS. A new actor in the estrogen receptor drama--enter ER-beta. Endocrinology. 1997;138:861–862. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.3.5080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gustafsson JA. Estrogen receptor beta--a new dimension in estrogen mechanism of action. J. Endocrinol. 1999;163:379–383. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1630379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Iafrati MD, et al. Estrogen inhibits the vascular injury response in estrogen receptor alpha-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 1997;3:545–548. doi: 10.1038/nm0597-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Karas RH, Patterson BL, Mendelsohn ME. Human vascular smooth muscle cells contain functional estrogen receptor. Circulation. 1994;89:1943–1950. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.89.5.1943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim-Schulze S, et al. Expression of an estrogen receptor by human coronary artery and umbilical vein endothelial cells. Circulation. 1996;94:1402–1407. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.94.6.1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lindner V, et al. Increased expression of estrogen receptor-beta mRNA in male blood vessels after vascular injury. Circ. Res. 1998;83:224–229. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.83.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Venkov CD, Rankin AB, Vaughan DE. Identification of authentic estrogen receptor in cultured endothelial cells. A potential mechanism for steroid hormone regulation of endothelial function. Circulation. 1996;94:727–733. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.94.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Losordo DW, Kearney M, Kim EA, Jekanowski J, Isner JM. Variable expression of the estrogen receptor in normal and atherosclerotic coronary arteries of premenopausal women. Circulation. 1994;89:1501–1510. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.89.4.1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Register TC, Adams MR. Coronary artery and cultured aortic smooth muscle cells express mRNA for both the classical estrogen receptor and the newly described estrogen receptor beta. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998;64:187–191. doi: 10.1016/S0960-0760(97)00155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Berdanier CD, Dwyer JT, Feldman EB. Handbook of Nutrition and Food. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2007. Plant foods and phytochemicals in human health. [Google Scholar]