Abstract
A single cheating mutant can lead to the invasion and eventual eradication of cooperation from a population. Consequently, cheat invasion is often considered equal to extinction in empirical and theoretical studies of cooperator-cheat dynamics. But does cheat invasion necessarily equate extinction in nature? By following the social dynamics of iron metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa during cystic fibrosis lung infection, we observed that individuals evolved to replace cooperation with a ‘private’ behaviour. Phenotypic assays showed that cooperative iron acquisition frequently was upregulated early in infection, which, however, increased the risk of cheat invasion. With whole-genome sequencing we showed that if, and only if, cooperative iron acquisition is lost from the population, a private system was upregulated. The benefit of upregulation depended on iron availability. These findings highlight the importance of social dynamics of natural populations and emphasizes the potential impact of past social interaction on the evolution of private traits.
Research organism: Other
Introduction
Identifying mechanisms responsible for the maintenance of cooperation is a major achievement of evolutionary biology (Axelrod and Hamilton, 1981; Hamilton, 1963). We can predict in which conditions cooperation will thrive, and where it might pay to exploit cooperative neighbours. Evidence of tension between cooperative and cheating strategies are all around us in nature – for example, in the co-evolution between flowers and their pollinators (Jandér and Herre, 2010), the policing and counter-policing behaviours of social insects (Foster and Ratnieks, 2000) – and in human society (Mathew and Boyd, 2011; Rand et al., 2011). Cases where these dynamics have resulted in the loss of cooperation are much less well understood, primarily because long-term consequences of cheat invasions are unobserved and unreported (Sachs and Simms, 2006). This is for the obvious reason that it is inherently difficult to detect a history of something that no longer exists. And also because it is generally the case that once cheating has gone to fixation, it is almost impossible for cooperation to re-invade (Axelrod and Hamilton, 1981). This is where most studies of social dynamics end.
Individuals are nevertheless under selection to survive the loss of cooperation. Consider a population where cheating has gone to fixation. If cooperation fulfilled an important function, this population may now be at risk of extinction (Fiegna and Velicer, 2003). To escape this fate, selection may favour individuals that can restore function by employing a ‘privatisation’ strategy – replacement of a mechanism that was once performed cooperatively as a group, with a selfish one that only benefits the actor (Bel, 2006). As such, we use the term privatisation as it is normally understood in common language to describe a switch in strategy from one that helps a whole group to achieve a goal to one where a goal is achieved by the actor alone. This differs from its use for describing the acquisition of property for future benefit by a group or an individual (Strassmann and Queller, 2014), the retention of public goods for individual use (Asfahl and Schuster, 2017), and for when public goods only are useable to a part of a community (Niehus et al., 2017). Privatisation could be a common occurrence in nature that has nevertheless been overlooked because there is no reason, a priori, to interpret private function as a result of past social interaction. It may also have been missed for the practical reason that we are required to track behaviour over many generations post-cheat invasion in a natural population. We overcome these difficulties by studying the evolutionary dynamics of a cooperative trait for more than an estimated 1.3 million generations (Supplementary file 1A), in a population of bacterial cells. We report the first observation (to our knowledge) of a natural population responding to cheat invasion by adopting a privatisation strategy and, therefore, avoiding the possibility of extinction.
Our study population is comprised of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria causing lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). CF is a genetic disease that causes the build-up of dehydrated mucus in lungs and sinuses, which P. aeruginosa infects (Folkesson et al., 2012). The host actively withholds iron to limit infection, and, as a counter-measure, P. aeruginosa employ a range of different iron acquisition strategies (Poole and McKay, 2003). The primary mechanism relies on secretion of the siderophore pyoverdine (Haas et al., 1991; Konings et al., 2013). This has been demonstrated to be a cooperative trait, where iron-bound pyoverdine molecules are available for uptake not only by the producer, but also by neighbouring cells (Buckling et al., 2007; West and Buckling, 2003). P. aeruginosa also make a secondary siderophore, pyochelin, which is cheaper to produce but has a lower affinity for iron (Dumas et al., 2013). In contrast, the Pseudomonas heme uptake system (phu) is private, as the iron-rich compound heme is taken up directly without the secretion of exploitable exoproducts (Table 1). Additional mechanisms of uptake include the private ferrous iron transport system (feo; Table 1 [Cartron et al., 2006]), and the heme assimilation system (has). The has system produces a hemophore that can bind to heme, or hemoglobin that contains heme. In the closely related system of Serratia marcescens it is conditionally cooperative, as uptake is direct without the hemophore at high concentrations (Ghigo et al., 1997; Létoffé et al., 2004).
Table 1. Main iron uptake systems of P. aeruginosa.
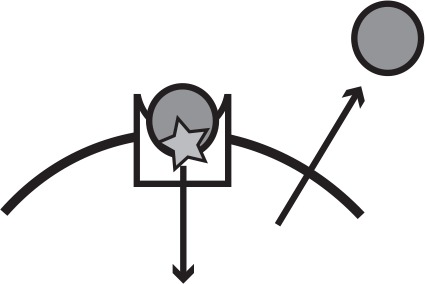
The pyoverdine and pyochelin systems produce siderophores which can steal Fe3+from host carriers. The conditionally cooperative has system produces a hemophore that can bind to heme, or hemoglobin that contains heme. The phu and feo systems are private. All systems have a specific receptor and uptake feeds back to increase system expression. The illustration shows a receptor in the cell membrane taking up an iron source (star). In a cooperative system a secreted public good (circle) binds the target and is taken up by the receptor, whereas a private system takes up the iron source directly.
| System | Mechanism | Social status | Target | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyoverdine | Public good; siderophore and specific receptor | Cooperative | Fe3+, host-bound |
 |
| Pyochelin | Public good; siderophore and specific receptor | Cooperative | Fe3+, host-bound |
|
| has | Public good; hemophore and specific receptor | Conditionally cooperative or private | Heme, hemoglobin | |
| phu | Specific receptor | Private | Heme, hemoglobin | 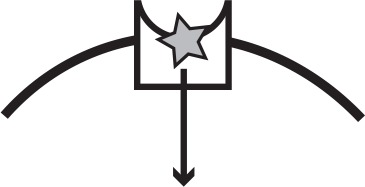 |
| feo | Specific receptor | Private | Fe2+ |
P. aeruginosa iron metabolism evolves during long term infection. Pyoverdine production has repeatedly been found to be lost during CF infection (Andersen et al., 2015; Jeukens et al., 2014; Konings et al., 2013; Martin et al., 2011), and the phu system has been observed to be upregulated late in infection (Marvig et al., 2014; Nguyen et al., 2014). A major challenge is to identify the selective pressures experienced in situ that cause such changes. Host adaptation, to accommodate for example antibiotic pressure and resource limitations, is frequently predicted to be the primary force in pathogen evolution (Lieberman et al., 2011; Young et al., 2012). Experimentally recreating host conditions in vitro is challenging, given the complex interplay between spatial structure, host immunity and nutrient availability (Clevers, 2016), which we are only beginning to be able to measure (Koo et al., 2011). Clinical measurements may differ from experimental in vivo and in vitro findings (Cornforth et al., 2018), and studies using ‘simple’ experimental conditions do not always give comparable results to those that use more complex, and potentially more clinically relevant conditions (Harrison et al., 2017). In contrast, longitudinal sampling of patients to track in situ evolution provides an opportunity to infer selection without making a priori assumptions about the experienced environment. Evolutionary theory lets us make testable predictions to distinguish the effect of host adaptations and social interactions. With this approach we have shown that cheating is a major selective force in the loss of cooperative iron acquisition in the CF lung (Andersen et al., 2015).
Here, we identified changes in iron uptake strategies from genome sequences and correlated these with the social environment (the P. aeruginosa clonal lineage infecting a host), and duration of infection. Specifically, we test two hypotheses: first, we ask whether an increase in cooperation facilitates the breakdown of cooperation in a natural population, and second, can cells survive the loss of cooperation by switching to a private, and, therefore, unexploitable mechanism for acquiring iron. Two collections of P. aeruginosa samples were used, covering 551 whole genome sequenced isolates from 64 Danish patients, of 55 clone types (Andersen et al., 2015; Markussen et al., 2014; Marvig et al., 2013; Marvig et al., 2015; Rau et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2011); allowing for the identification of patterns of convergent evolution. While the P. aeruginosa populations within patients are remarkably uniform at the clone type level, colonizers diversify during infection (Mowat et al., 2011; Winstanley et al., 2016), and lineages may occupy distinct niches at late stages (Jorth et al., 2015). The isolate collection has been shown to represent the genetic diversity well, with multiple genotypes co-occurring within individual patient samples (Sommer et al., 2016). A key step in our analysis is to categorise isolates with respect to their social environment, for example, presence vs absence of cooperators (pyoverdine producers). This is necessary for testing our hypothesis that iron acquisition strategy is influenced by the social environment. The likelihood that we do not capture all co-infecting strains in our sample, for example leading to mis-classification of isolates as belonging to an environment without pyoverdine, will homogenise the sample groups and hence obscure any differences. Sampling errors of this kind will, therefore, hinder our ability to detect an effect (Type I error).
Materials and methods
Isolate collections
Two collections of whole genome sequenced P. aeruginosa isolates were used, as described previously (Andersen et al., 2015). The transmissible clonetypes DK1 (46 isolates) and DK2 (54 isolates) were sampled from 28 CF patients between 1972 and 2012 (Jelsbak et al., 2007; Markussen et al., 2014; Marvig et al., 2013; Rau et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2011). Six previously unanalysed DK1 isolates were included (from patients P55M3, P24M2 and P30M0, Supplementary file 1B). Further, 451 isolates of 54 clonetypes from 36 young CF patients were used (the ‘children’s collection’ (Andersen et al., 2015; Marvig et al., 2015), of which 10 were of the DK1 clone type). At each sampling time, 1–8 colonies were cultured from patient sputum, and stored at −80° C (Johansen et al., 2012; Sommer et al., 2016). The sampling regimen for each patient is described in Supplementary file 1B, and Appendix 1—figures 1 and 2. The two collections complement each other as one covers a long time period, with relatively few samples from each patient and of both early and late infection stages, whilst the other covers the first 10 years of infection by environmental clone types, with more extensive sampling within patients. In the children’s collection there is limited transmission between patients, but some clone types infect multiple patients, and some patients are infected by multiple clone types either at the same time or in succession (Marvig et al., 2015). All but two patients, however, harbour only one dominant clone type at a time and the social environment is thus made up of clonal lineages sharing the same ancestor. The analysis of increased pyoverdine production was only performed on the children’s collection, as described below.
The phylogeny of the 54 DK2 isolates has previously been reported by Marvig et al. (2013), and this was adapted for this study to phylogenetically map the order of mutations in regions of interest. To allow a similar analysis for the DK1 clone type, we used Snippy (Seeman, 2015) to identify SNPs in each of the 56 DK1 isolates relative to the PAO1 reference genome (RefSeq assembly accession GCF_000006765.1) and compared the SNPs of all the DK1 isolates to identify those that differed between the isolates. The SNPs were further filtered to only retain SNPs at positions covered by at least 10 reads in all isolates and exclude those where all isolates show more than 80% non-reference reads at the given position. Based on 4,639 SNPs within 2,614,892 sites, a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was computed with RAxML version 8.2.11 (Stamatakis, 2014), with default settings using a general time reversible model of nucleotide substitution (option -m GTRCAT). The tree was rooted with the PAO1 reference genome.
The length of infection of each clone type in each patient was calculated. Clone types sampled only once from an individual patient were excluded (23 isolates of 22 clone types). For the transmissible clone types DK1 and DK2 the total length of infection across patients was used (39 and 36 years, respectively). This is a very conservative estimate of length of infection, as evolution occurs independently in different patients. To calculate the number of generations, a doubling time of 74 min was used for clonal lineages infecting for less than 6 years, 83 min for 6–24 years and 109 min for >24 years based on the measurements of Yang et al. (2011).
Changes in pyoverdine production during infection
We tested if the appearance of pyoverdine non-producers is correlated with preceding upregulation. Measurement of pyoverdine production was carried out by fluorescence readings at 400/460 nm excitation/emission with a 475 nm cut-off following growth in iron-limited media (Andersen et al., 2015; Kümmerli et al., 2009). For each clonal lineage the baseline pyoverdine production was determined as that of the first isolate(s) of a clone type from a patient, and the production of all subsequent isolates of this clone type was compared to this. An isolate was classified as an over-producer if its production was >30% higher than that of the first. This cut-off was chosen as ~95% of the isolates had a lower standard deviation between replicates. The data is available from Dryad (doi:10.5061/dryad.6963pj3). The analysis was performed on longitudinally sampled clone types from the children’s collection only, as the DK1 and DK2 isolates were not sampled frequently within patients. Only non-producers evolved from a clonal lineage that produced pyoverdine at the beginning of the infection period were included. Therefore clone types DK1 (10 isolates, P36F2), DK11 (two isolates, P51M5), DK40 (two isolates, P73M4) and DK53 (10 isolates, P36F2) were excluded from the analysis, as they were ‘chronic’ clone types with no pyoverdine producers sampled from the young patients (Appendix 1—figure 1; Andersen et al., 2015). As there were only three samples from P51M5, this whole patient was excluded from the analyses. In lineages with both over- and non-producers, over-producers were sampled before non-producers in all but three cases. In two cases there was <5 months between sampling, and we scored non-producers as occurring at the same time as overproducers. In one case the non-producer was sampled 2.95 years prior to the over-producer and scored as having occurred in the absence of an over-producer. The subsequent sampling of the over-producer, and an additional non-producer that shared the genotype with the first non-producer, was not included in the analyses (Appendix 1—figure 1, P53M4). In two clone types two independent transitions to non-producers were observed (non-producing isolates harboured different pyoverdine mutations) and these were included as independent events (P44F5 and P14M4). We focus here on within-clone type dynamics, as temporal overlap of longitudinally sampled clone types only occurred in two patients (Appendix 1—figure 1; Andersen et al., 2015).
We categorized each clone type in individual patients as harbouring over-producers or not. If an over-producer was present, the length of time from that sampling to a non-producer was observed, or till the last sample was collected from the patient, was noted. Clone types without non-producers were classified as right-censored. The same was done for patients without over-producers. In total, 45 clonal lineages were followed covering 404 isolates of 33 clonetypes from 35 patients (Appendix 1—figure 1; some clone types occur in multiple patients, and some patients are infected by multiple clone types [Marvig et al., 2015]). The timing of sampling of non-producers was analysed with the ‘survival’ package in R, which takes into account the sampling extent of a clonal lineage, that is both the timing and frequency of events (R Core Team, 2013; Therneau, 2015).
Identification of mutations in the pyoverdine, pyochelin, phu, has and feo systems
Mutations in the pyoverdine (pvdQ-pvdI +pvdS pvdG+pvcA ptxR+fpvB), the pyochelin (ampP-pchA), the phu (prrF1-phuR), the has (PA3404-hasI) and the feo systems (PA4357-feoA) were identified previously from Illumina GAIIx or HiSeq2000 reads (Andersen et al., 2015; Markussen et al., 2014; Marvig et al., 2013; Marvig et al., 2015; Rau et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2011) (Supplementary file 1C-D). Mutations of iron systems in the six new DK1 isolates were identified as described previously (Andersen et al., 2015), by mapping reads against a DK1 draft genome (Markussen et al., 2014). Mapping of reads revealed low sequencing depth of the hasD (required for hemophore secretion) and hasS (the has anti-sigma factor) genes, likely due to repetitive regions. These were unsuccessfully attempted amplified by PCR. Mutations were categorized as synonymous (syn) or non-synonymous (ns) SNPs, insertions or deletions (indels), or intergenic. We tested for a bias in which genes in each operon were mutated with [Poisson test, P(X ≥ changes observed)~Poisson distribution (pois) (X; changes expected) < 0.05].
We identified the order of mutation across the different iron uptake systems, with a system classified as mutated by the presence of ns SNPs or indels in any gene in the system. For pyoverdine, the presence of mutations was compared to the actual measurements of production; the two measures are highly consistent (Andersen et al., 2015) but when incongruent the phenotype was used. For the phu region intergenic phuS//phuR mutations predicted to cause receptor upregulation were included, and when occurring without other phu mutations these were recorded separately. Transitions were identified within clonal lineages, that is if an isolate for example had a pyoverdine mutation and measured loss of production, and a subsequent isolate had the same pyoverdine mutation in addition to a pyochelin mutation, this was considered a transition from wild-type (WT) to loss of pyoverdine, to loss of pyochelin. If for example a phu and pyochelin mutation was observed for the first time in the same isolate the exact order could not be inferred. In the transmissible clone type DK2 pyoverdine production was detected to have been lost in an isolate from 1973 and the mutation and phenotype was found in all later isolates. Subsequently, independent clonal lineages for example accumulate phu mutations. In the analyses this was counted as one loss of pyoverdine, and then multiple independent phu mutations. We calculated the expected order of mutation, equally weighted by the size and number of mutations of the different systems. We tested, as described above, whether this was different from the observed, using only cases where there was a clear order of mutations. The social environment, that is the genotypes of co-occurring isolates, was not considered in this analysis.
For the phu system, we located mutations in the phuR receptor gene to functional regions (the N-terminal-domain, periplasmic turns, transmembrane strands or extracellular loops) using a predicted structure of the receptor (http://bioinformatics.biol.uoa.gr//PRED-TMBB [Bagos et al., 2004]). For each domain in the receptor we calculated the expected number of non-synonymous amino acid changes, as the proportion the domain comprises of the entire protein times the observed number of changes. Whether the observed changes in each domain differed significantly from the expected was calculated as described above.
Transitions between public and private iron uptake
To test if the appearance of intergenic phuS//phuR mutations that cause upregulation of the phu system was correlated with overall loss of pyoverdine production in the social environment we categorized each independent acquisition of these mutations as having occurred in the presence or absence of measured pyoverdine production, by the focal isolate and co-occurring isolates. In the absence of pyoverdine production the time between loss of production and occurrence of mutations was estimated. The analysis was performed on longitudinally sampled clonal lineages from both collections of isolates, that is lineages with at least two isolates with or without pyoverdine production. Further, three cases where the loss of pyoverdine production and phuS//phuR mutations were observed in the same isolate were also included. Clonal lineages that did not acquire phuS//phuR mutations were classified as right-censored. For DK1 and DK2 we used monophyletic clades with and without mutations as independent clonal lineages (Blue lines in Appendix 1—figure 3 and 4). Branches with single isolates were not included unless they showed loss of pyoverdine from the social environment or phuS//phuR mutations (inclusion of these did not significantly affect the result of the test). We included isolates of DK53 where no WT pyoverdine producer was sampled, but phuS//phuR mutations were inferred by comparison to PAO1 (Supplementary file 1C).
The phuS//phuR mutations only occurred in isolates that had lost pyoverdine production (Appendix 1—figure 3 and 4). In three instances these, however, co-occurred in the patient with isolates that produced pyoverdine (Appendix 1—figure 5 and 6). The producers and non-producers with phu upregulation are unlikely to have interacted at the time when the iron system mutations occurred in two of these. In patient P30M0, infected with clone type DK1, the cooperating isolates were sampled from the patient’s sinuses only, while the non-producers with phu upregulation came from lung samples. In patient P28F1, two lineages of clone type DK1 co-occurred. One had been transmitted from another patient, where pyoverdine production was lost, and phu likely upregulated, prior to transmission and establishment of a co-infection. In patient P82M3 a pyoverdine producer and an isolate with a phuS//phuR mutation, both of clone type DK32, were found in the same lung sample. The latter harbours the most common phuS//phuR mutation (G 146 upstream//35 upstream A, Supplementary file 1C), which is located outside the phuR promoter (Marvig et al., 2014). It is the only isolate to have this phuS//phuR mutation in isolation, all others with it have an additional SNP, and the effect of it is unknown (but see below).
The timing of sampling of mutants was analysed with the ‘survival’ package in R (Therneau, 2015). We are likely to over-estimate the length of time to mutation, as patients chronically infected with the transmissible DK1 and DK2 clone types were infrequently sampled (Markussen et al., 2014; Marvig et al., 2013). In these cases, with several years between longitudinal samples, a mutation may only be detected years after occurring.
Uptake of heme following phuS//phuR mutations
We tested if the presence of phuS//phuR mutations gives a growth advantage in iron-limited media supplemented with heme at different concentrations, using an isogenic pair of DK2 isolates only differing in the presence of a 1 bp phuS//phuR deletion (Marvig et al., 2014). Three biological replicates of each isolate were cultured in liquid LB media for 24–48 hr, so that all cultures reached an OD600 above 0.1. Cultures were subsequently standardised to a starting OD600 of 0.001, in iron-limited CAA media following Kümmerli et al. (2009), without heme or supplemented with 1, 2.5, 5 or 10 μM heme as an iron source (BioXtra porcine hemin ≥97.0%, Sigma-Aldrich). Of each culture 200 μL were inoculated in 96 well plates. Plates were sealed with a breathable membrane to avoid evaporation and incubated in a plate reader measuring OD600 every 30 min for 48 hr. Growth curves were plotted in Excel and the average maximum OD600 of the three replicates calculated. The difference in max OD600 between the isolates with and without the phuS//phuR mutation at the various heme concentrations was analysed in R with a Two-Way ANOVA test with post hoc comparisons with Tukey HSD (R Core Team, 2013).
We also compared growth of pairs of clinical isolates with phuS//phuR mutations matched to their closest genetically related isolate without mutations. The phuS//phuR mutations occurred in three different clone types without additional phu mutations (DK1, DK2 and DK32, highlighted in yellow in Supplementary file 1C). Six isolates with mutations were matched with four closest relatives without, because DK2 in two instances had independent phuS//phuR mutations in two closely related isolates. The WT isolate for these pairs was used to make the isogenic pair described above, and the mutation of one of these clinical isolates moved to this background (P0M30-1979 and P173-2005; Appendix 1—figure 7; Marvig et al., 2014). One additional DK2 isolate with a mutation was lost from the collection, and only available as sequence reads (P80F1; Appendix 1—figure 4 and Supplementary file 1C). Growth was measured as described above with 2.5 or 5 μM heme as an iron source, and differences in max OD600 within a pair were compared with a t-test in R (R Core Team, 2013).
Results and discussion
More cooperative populations are more vulnerable to exploitation
The environmental clones that infect CF patients produce pyoverdine (Andersen et al., 2015) but what happens as they transition to life in a host? We compared pyoverdine production between isolates sampled at different time points of infection in iron-limited media, in which cells must produce pyoverdine to avoid iron starvation. In some clonal lineages of P. aeruginosa, defined as longitudinally sampled isolates of the same clone type that share a recent ancestor, pyoverdine production was maintained for >30 years of CF infection: in the 12 clonal lineages of the transmissible clone type DK1 that were followed for >30 years there were five independent losses of pyoverdine production but three clonal lineages maintained production (Andersen et al., 2015); Appendix 1—figure 3, and below). Limited diffusion of secreted pyoverdine, as is likely in viscous CF sputum, impairs the ability of potential cheats to exploit and may contribute to stabilize cooperation in these lineages (Julou et al., 2013; Kummerli et al., 2009); although there may be significant exchange between spatially distinct microcolonies (Weigert and Kümmerli, 2017).
When analysing the isolates from 35 frequently sampled young patients of 33 clone types (some clone types infect multiple patients and some patients harbour multiple clone types), we found that pyoverdine production increased in 36% of clonal lineages within the first two years of infection. Overall, these ‘super-cooperator’ isolates, which had >30% higher production than isolates initiating infection, were detected in 25 of 45 independent clonal lineages (55%; Figure 1), and on average sampled 1.89 ± 1.79 st. dev. years into the infection. This suggests that upregulation is initially favoured, likely by iron limitation or inter-species competition. In CF patients, P. aeruginosa frequently co-infects with Staphylococcus aureus (Folkesson et al., 2012), and co-culture in vitro causes an upregulation of pyoverdine production (Harrison et al., 2008). When in co-infection, iron sequestering can have the additional benefit of making it unavailable for S. aureus or other competitors (Leinweber et al., 2018; Niehus et al., 2017). Increased production could also be part of a general acute infection phenotype, as either a pleiotropic side-effect or a beneficial trait (Coggan and Wolfgang, 2012). For six out of the 25 lineages with super-cooperators we identified candidate mutations in global regulatory and quorum sensing genes that likely cause increased production of pyoverdine as well as other virulence factors, such as pyochelin, pyocyanin and alginate (Supplementary file 1E). For the remainder, super-cooperators produced pyoverdine at a consistently higher rate than their ancestors but the genetic basis of upregulation was unclear.
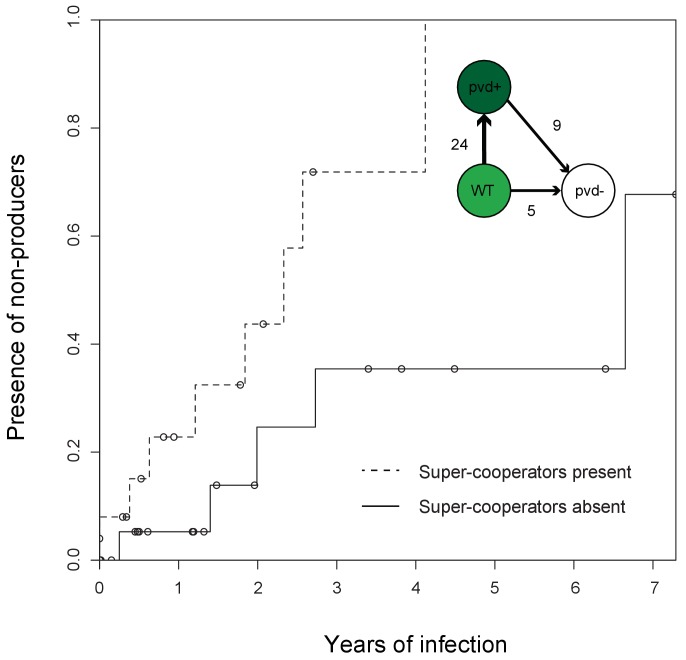
Figure 1. Super-cooperators precede the sampling of non-producers.
Inverse Kaplan-Meier graph showing that pyoverdine non-producers are found more often in the presence of super-cooperators (dotted line, n = 25 representing 24 clonal lineages in patients, one of which had two independent losses of pyoverdine production), compared to when super-cooperators are absent (solid line, n = 22, representing 21 clonal lineages in patients, one of which had two independent losses). Circles indicate when sampling of clonal lineages stopped, without the observation of lost pyoverdine production. Insert shows that a transition from wild-type (WT) production to super-cooperation (pvd+) was observed in 24 clonal lineages, followed by nine independent occurrences of non-producers. Non-producers evolved in the absence of super-cooperators five times. In total, 33 clone types infecting 35 patients were followed.
Despite the potential benefits of pyoverdine production, the presence of super-cooperators appears to weaken long-term stability of cooperation in the lung. In 12 out of the 35 patients, we previously observed the appearance of mutants that have lost the ability to synthesise pyoverdine (Andersen et al., 2015), sampled on average 3.06 ± 2.29 st. dev. years into infection. Here, we found that the likelihood of these non-producers arising was significantly higher in the presence of super-cooperators [Survival analysis, χ2 (2, N = 47) = 5.7; p < 0.05; Figure 1]. Non-producers were present in four out of 21 clonal lineages without (19%, on average 2.60 ± 2.45 st. dev years into infection) and in eight out of 24 lineages (disregarding one where the non-producer was sampled prior to the super-cooperator) with super-cooperators (33%, on average 3.32 ± 3.32 st. dev years into infection and 1.45 ± 1.39 st. dev. years after sampling of a super-cooperator). There was no significant difference between the time of sampling of non-producers between lineages with or without super-cooperators (Welch Two Sample t-test, t = −0.54, df = 8.01, p = 0.61). From the data set it is not clear whether cheats evolve from super-cooperators or directly from isolates with WT pyoverdine production, as the genetic basis of over-production is unknown.
Why is upregulation of pyoverdine production associated with the subsequent loss of this trait? Non-producers appear to be favoured as a result of exploiting the pyoverdine production of neighbouring cells – a strategy referred to as cheating (Ghoul et al., 2014a). We have previously shown that non-producers in the lung acquire mutations in a pattern consistent with a cheating strategy, as opposed to one expected from redundancy, in that they retained the pyoverdine receptor only if producers were present (Andersen et al., 2015). In other words, non-producers lose the capacity to contribute but retain the ability to benefit from pyoverdine, as long as it is being supplied by cooperative neighbours. The relative fitness of cheats is predicted by theory to be greater when there are higher levels of cooperation in a population, because their competitors are bearing a higher cost (Ross-Gillespie et al., 2007). This prediction has been shown to hold in empirical tests (Ghoul et al., 2014b; Harrison et al., 2008; Jiricny et al., 2010). Hence, super-cooperators are predicted to be especially vulnerable to exploitation and invasion of cheats. While isolates with a WT level of pyoverdine production may also benefit from the presence of super-cooperators, the larger production cost differential between non-producers and super-cooperators gives non-producers a greater advantage than WT producers. The pattern of upregulation, followed by loss, is likely to be applicable to the evolution of other exoproducts during infection.
Evolution of iron acquisition systems in the lung – the sequence of events
How do the changes in cooperative pyoverdine production relate to the overall iron metabolism of the cells? Comparison of the accumulation of mutations across five different iron uptake systems (Table 1) and measurement of pyoverdine production showed that the appearance of pyoverdine non-producers is the first change in iron metabolism observed in most clonal lineages, in both isolate collections. Loss-of-function of the cooperative pyoverdine system occurred earliest in 16 out of 25 clonal lineages where the phenotypic measurements and sequence analysis provided a clear order of systems affected (Figure 2; Supplementary file 1F). These were observed to occur on average 3.06 years after the first sampling of the clone type in the young patients (n = 11 clonal lineages in nine patients), and between 1–39 years after infection for the more rarely sampled transmissible clone types (n = 5 clonal lineages in five patients). When weighed by the high mutation rate of the system, reflecting a strong selection pressure, and its large size, this is not unexpected [Poisson test, P(X ≥ 16) ∼ pois (X; 14.69) > 0.05), Figure 2; Supplementary file 1D].
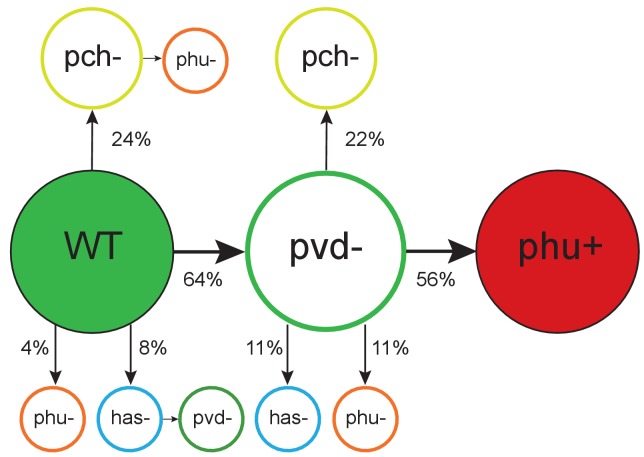
Figure 2. Order of mutations across iron acquisition systems.
Wild type-like (WT) isolates colonize patients, and subsequent loss of cooperative pyoverdine production (pvd-) is the most common change in iron metabolism (n = 25), compared to mutations expected to affect the pyochelin, phu and has systems negatively (pch-, phu-, has-). Loss of pyoverdine production in clonal lineages is followed by intergenic phuS//phuR mutations, predicted to upregulate the private phu system, significantly more often than expected by chance (phu+, n = 9). Colour indicates iron uptake system (green = pyoverdine, yellow = pyochelin, dark red = intergenic phuS//phuR, orange = phu (either a mix of phuS//phuR and other phu mutations, or only ns SNPs), blue = has). The occurrence of has mutations may be underestimated due to low sequencing depth of two genes. The figure shows only transitions where there was a clear order in which systems were affected, see Supplementary file 1F for all transitions.
Mutation of the cooperative pyochelin system first was found not to differ from that expected given a random distribution of mutations [Poisson test, P(X ≥ 6) ∼ pois (X; 5.14) > 0.05), Figure 2; Supplementary file 1D]. The conditionally private or cooperative has heme uptake system was found to acquire few mutations during infection. It remains to be tested if this is because maintenance of the system is favoured by selection, or if selection for loss is relatively weak. The private feo system is rarely mutated (Supplementary file 1D) and has been suggested to be of increased importance as conditions turn microanaerobic during infection (Hunter et al., 2013).
Across both isolate collections we observed pyoverdine cheats appear 14 times without going to fixation within the patient during the sampling period, but further recorded eight cases where no producers were sampled a year prior to, or after emergence a non-producer, and two clonal lineages from where no producers are sampled at any point. This is the potential extinction scenario of cheat invasion. However, because we have continued to sample after this event, we can observe how the population responds to this potentially catastrophic situation. One of these events for example occurred in the transmitted clone type DK2 that was subsequently sampled from 16 patients over 35 years. And because cheat invasion is not inevitable, we can compare dynamics in lungs with and without availability of pyoverdine.
Cheat invasion is associated with a subsequent switch to private iron uptake mechanism
After cooperation was lost from a clonal lineage, and only if it was lost, we observed that iron uptake was privatised (Figure 3). This was achieved by upregulation of the private phu system. The phu system targets the iron-rich heme molecule, which is taken up directly through a membrane-bound receptor PhuR (Table 1; Ochsner et al., 2000). Increased expression of the phu system results from intergenic mutations between the phuS gene encoding a heme traffic protein, and the receptor gene phuR (phuS//phuR mutations; Marvig et al., 2014). In the isolate collections, a total of 29 SNPs and two indels accumulate in the phuS//phuR region. Eight of these mutations in the phuR promoter have been found to cause a significant upregulation of promoter activity, and one of these has further been shown, in an isogenic pair, to provide a growth benefit to the carrier when heme is available as an iron source (Marvig et al., 2014); see also below). These specific mutations were found to arise significantly more frequently than expected by chance following the loss of pyoverdine production [Poisson test, P(X ≥ 5) ∼ pois (X; 0.39) < 0.01); Figure 2]. In three patients, non-producing isolates with phuS//phuR mutations were sampled at the same time as pyoverdine producers, however in two of these the producer and non-producers were unlikely to interact, and in the third the phuS//phuR mutation occurred outside the phu promoter region with unknown effects on heme uptake (but see Appendix 1—figure 7). We thus conclude that phu upregulation takes place when pyoverdine production is lost from the social environment. Many of the isolates with phuS//phuR mutations also harboured pyoverdine receptor mutations that eliminate the possibility to cheat (6 out of 7 in DK1, 7 out of 7 in DK2, 1 out of 2 in DK53, 0 out of 1 in DK32; Appendix 1—figure 3–6; Andersen et al., 2015). Knock-out of the pyoverdine receptor is, however, not expected to be a selective force in phu upregulation. Rather, the data suggest that both occur because pyoverdine is no longer available in the environment, selecting for privatisation of iron uptake and elimination of the costly receptor (Andersen et al., 2015).
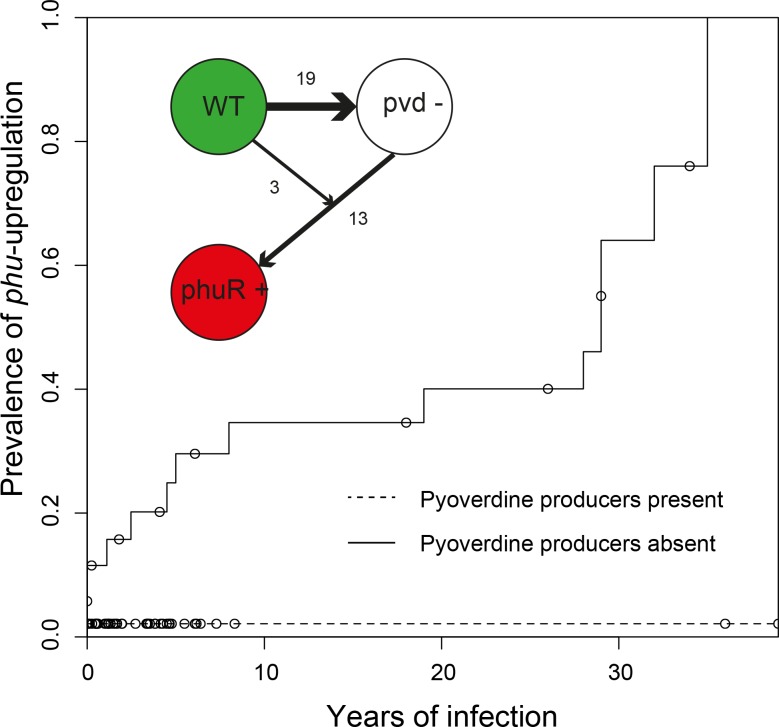
Figure 3. Loss of cooperation precedes privatisation of iron uptake.
Inverse Kaplan-Meier graph showing that phuS//phuR mutations are observed 15 times when pyoverdine is absent from the social environment (solid line, n = 26), and only once when pyoverdine is available in the social environment (dashed line, n = 47, see text). The mutations are only found in clonal lineages that do not produce pyoverdine. Circles indicate when sampling of clonal lineages stopped, without the observation of phuS//phuR mutations. Insert shows that a transition from wild-type pyoverdine production (WT) to no production (pvd-) was observed 22 times in clonal lineages, while phuS//phuR mutations occurred 16 times independently (phu+), 13 of which were after loss of pyoverdine production from the environment. The order could not be inferred in three cases, in one of which the isolate co-occurred with pyoverdine producers.
Social interactions are unlikely to be the only selection pressure influencing dynamics in iron acquisition strategies. Changes in iron uptake strategy might more readily be expected to reflect changes in the lung environment as the availability of iron in different forms increases with disease progression (Hunter et al., 2013). And while iron is found to be equally available in its oxidized ferric (Fe3+) and reduced ferrous forms (Fe2+) in early infection, there is a skew towards the reduced form later, which the feo system targets (Hunter et al., 2013). Heme and hemoglobin are also present in the sputum (Ghio et al., 2013), and availability has been speculated to increase as the lung tissue degrades (Marvig et al., 2014), as evidenced by increased coughing up of blood, termed hemoptysis, with age (Thompson et al., 2015). As such, pyoverdine may be most efficient early in infection, and phu only advantageous later as lung tissue degrades and/or alternative sources of iron become more or less abundant. However, the patterns we observe are not consistent with this explanation. If pyoverdine production is maintained, the phuS//phuR genotype remains unaltered from colonization, even after more than 30 years of infection (Figure 3). The phuS//phuR mutations, responsible for upregulating the private phu system, are only observed in non-producers, and in 15 out of 16 cases after the loss of cooperation in the population [Survival analysis, χ2 (2, N = 73) = 11.7; p < 0.01; Figures 3 and 4], occurring between 0 to 35 years after the loss of pyoverdine production. Upregulation of private iron uptake can, therefore, be predicted from the social environment, not duration of infection and associated changes in the lung environment.
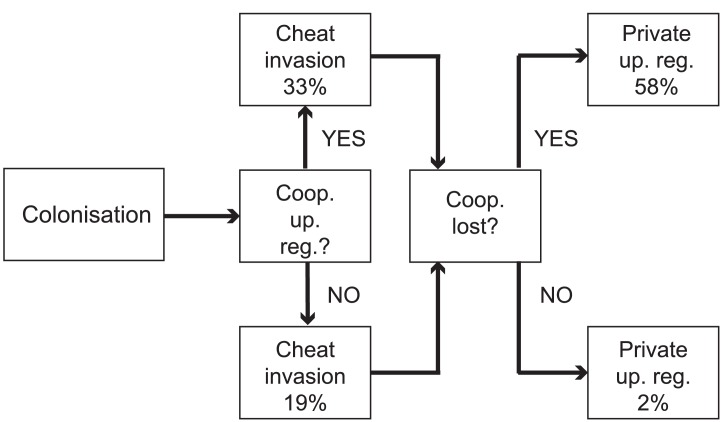
Figure 4. Evolutionary trajectories of iron metabolism in the CF airways.
Following infection (n = 45 clonal lineages of 33 clone types), pyoverdine production is frequently upregulated (n = 25). Cheaters are significantly more likely to invade following upregulation. Following loss of pyoverdine production in the social environment (n = 26 non-producing clonal lineages of 6 clone types, from eight independent losses of production and two clonal lineages from which no pyoverdine producers were sampled), the phu system is frequently upregulated by intergenic phuS//phuR mutations (15 times), while this very rarely occurs (one time) when pyoverdine is produced in the social environment (n = 47 producing clonal lineages of 32 clone types).
Why is private heme uptake only upregulated if cooperation is lost?
The fact that we only observe upregulation of the phu system if pyoverdine production has been lost suggests that privatisation is not universally beneficial but may instead represent a final recourse when other mechanisms are no longer functioning. P. aeruginosa iron uptake is finely controlled by feedback loops, in response to environmental iron concentrations and need (Vasil and Ochsner, 1999). As iron is toxic at high concentrations (Anzaldi and Skaar, 2010; Touati, 2000), an indiscriminate upregulation of one system could be a significant disadvantage in environments where iron concentrations fluctuate. We, therefore, tested whether the growth benefits of phu upregulation (by phuS//phuR mutations) were dependent on iron availability, in the form of heme which the phu system targets. We examined the growth difference between a clinical isolate that had lost pyoverdine production, and an isolate, isogenic but for a clinical phuS//phuR mutation that cause an upregulation of the heme receptor gene phuR (Marvig et al., 2014). The experiment was performed in iron-limited media supplemented with heme at biologically relevant concentrations, which ranged from <1 μM typical of healthy individuals, across 2.5 μM, 5 μM to 10 μM typical of CF patients (Ghio et al., 2013).
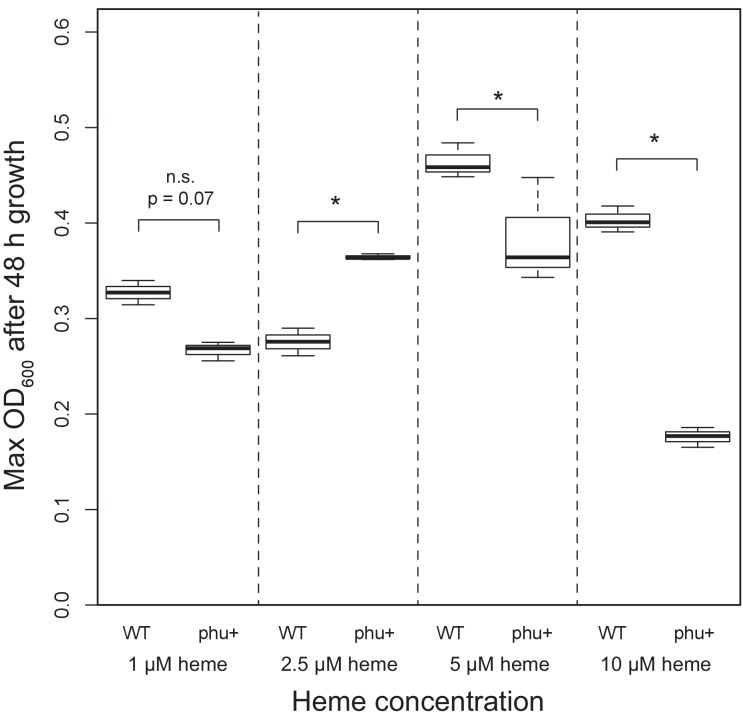
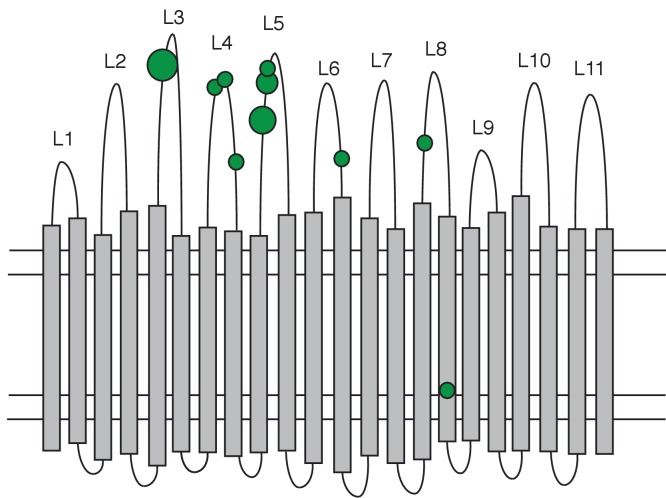
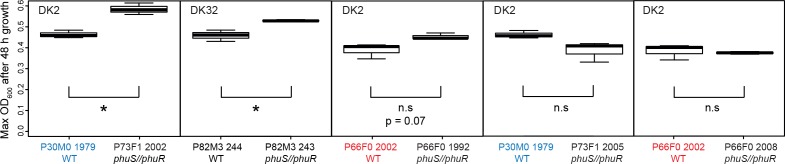
Consistent with our hypothesis, we find that phu upregulation is only beneficial at a narrow range of intermediate heme concentrations. There was a significant growth difference between the isolates and heme concentrations, and an interaction effect (Two-Way ANOVA; Interaction term: Isolate*Heme: F = 48.11, df = 3, p < 0.01; Figure 5; Supplementary file 1G). At 2.5 μM heme the isolate with an upregulated phu system achieved a higher density (Tukey HSD, padj <0.01, Figure 5), consistent with previous findings (Marvig et al., 2014). In contrast, at 5 and 10 μM the isolate without upregulation had an advantage (padj <0.05, Figure 5). No growth was observed in the absence of heme, and at 1 μM there was no significant difference in growth between the isolates but a trend for the WT to do better (padj = 0.073). This suggests that phuS//phuR mutations lead to increased heme uptake that is beneficial at low external concentrations (>1 and<5 μM heme) but detrimental at high concentrations (>5 μM heme). Analyses of pairs of clinical isolates with and without phuS//phuR mutations gave less clear results, but showed a similar pattern of a benefit of phuS//phuR mutations at low concentrations of added heme (Appendix 1—figure 7). If iron availability increases during infection, an initially beneficial upregulation of heme uptake would turn toxic. In the phu system we found a significant bias towards mutations of the phu receptor gene phuR (Poisson test, P(X ≥ 24) ∼ pois (X; 10.69) < 0.05; Supplementary file 1D). These were not randomly distributed but primarily found in the extracellular loops of the phu receptor, that initiate the uptake of heme (Noinaj et al., 2010; Smith et al., 2015) [Poisson test, P(X ≥ 15)~pois (X; 7.28) < 0.05; Figure 6]. If there is selection to reduce iron concentration within cells, these may, therefore, represent compensatory mutations.
Figure 5. Effect of phu upregulation depends on the heme concentration.
An isogenic pair of isolates differing only in a 1 bp phuS//phuR deletion was grown in iron-limited media supplemented with heme at 1–10 μM. The clinical isolate without the mutation, that does not produce pyoverdine (WT), had a significant higher maximum OD600 after 48 hr growth at 5 and 10 μM, whereas the mutant (phu+) grew best at 2.5 μM. There was no significant difference at 1 μM. Boxplots show median value, and the interquartile range ±25%. The * marks a significant difference at p < 0.05.
Figure 6. Distribution of non-synonymous mutations in the PhuR heme receptor.
The figure shows the β-barrel structure spanning the cell membrane (horizontal lines) with transmembrane strands (grey bars), extracellular loops (labelled L1-L11) and periplasmic turns (bottom loops). Green circles indicate the location of non-synonymous SNPs, the smallest circles denoting one mutation and the largest four. Mutations were significantly biased towards the extracellular loops.
Conclusions
Bacterial cells will be under selection to adapt to the host environment, including antibiotic pressure (Lieberman et al., 2011). The observations we report here, however, demonstrate the errors of interpretation that can arise from assuming that bacterial cells are driven entirely by the evolutionary imperative to survive in the host. As in all other organisms, fitness is also determined by the ability to compete with members of the same species, and these two evolutionary drivers – host adaptation and competition – do not always coincide. Our results show that the initial upregulation of cooperation, selected by either the environmental conditions, competition or as a pleiotropic side-effect, facilitates cheating. The subsequent privatisation of iron uptake is a response to the loss of cooperation, not simply an adaptation to iron availability in the host as previously suggested (Marvig et al., 2014), and as we show this carries its own costs. The effect of the social environment on iron acquisition mechanism remains statistically detectable despite the noise from variation in patient age, sex, infection and treatment. In a clinical system like this, failure to appreciate these factors can lead to misinterpretation of how bacterial cells are influenced by the host environment and, therefore, impair necessary understanding for the development of intervention strategies (Leggett et al., 2014).
Evolutionary theory clearly predicts that any adaptation involving cooperation can be vulnerable to exploitation, irrespective of its benefits (Axelrod and Hamilton, 1981). But this is often overlooked when it is difficult to characterize the selective environment, as for example, inside a human host. By longitudinal sampling of bacterial populations, we were able to observe the consequences of cheat invasion for an essential trait and show that switching to a private strategy can provide bacterial cells with an evolutionary alternative. This observation highlights the importance of considering potential constraints imposed by social interactions: if a private trait is expressed it may not be the most efficient in a given environment, but simply the final recourse in a population with a history of exploitation.
Acknowledgements
We thank Stuart West, Lars Jelsbak and Rolf Kümmerli for comments on the manuscript. Trine Markussen and Lars Jelsbak provided analysed sequences of additional DK1 isolates, and S M Hossein Khademi provided valuable discussion of the phu mutations. This work was supported by grants from Villum Fonden (grant 95-300-13894) and Lundbeckfonden (grant R108-2012-10094) to SBA, the European Research Council (grant SESE) to ASG, and Rigshospitalet (grant R88-A3537), Novo Nordisk Fonden (grant NNF12OC1015920) and Lundbeckfonden (grant R167-2013-15229) to HKJ.
Appendix 1
The sampling regimen behind the two isolate collections.
We used two collections of P. aeruginosa isolates to study iron metabolism during CF infection. For the ‘children’s’ collection the young patients have been sampled frequently, for up to 10 years, and that the majority are infected with unique environmental clone types. When P. aeruginosa was found to transmit between CF patients (Cheng et al., 1996; Jelsbak et al., 2007), care was taken to avoid that younger patients become infected with adapted clone types in the clinic. In the collections we use this is clear as the children’s collection encompass 54 clone types while the collection of isolates from adults contain only two, highly transmissible, clone types. This collection covers >30 years. To give an overview of the sampling regimen we present first an overview of isolates sampled from the individual patients (Appendix 1—figures 1 and 2). To further illustrate how the DK1 and DK2 evolve and transmit between patients we present phylogenies of the two transmissible clone types with the primary changes in iron metabolism in the pyoverdine and phu systems highlighted (Appendix 1—figures 3 and 4).
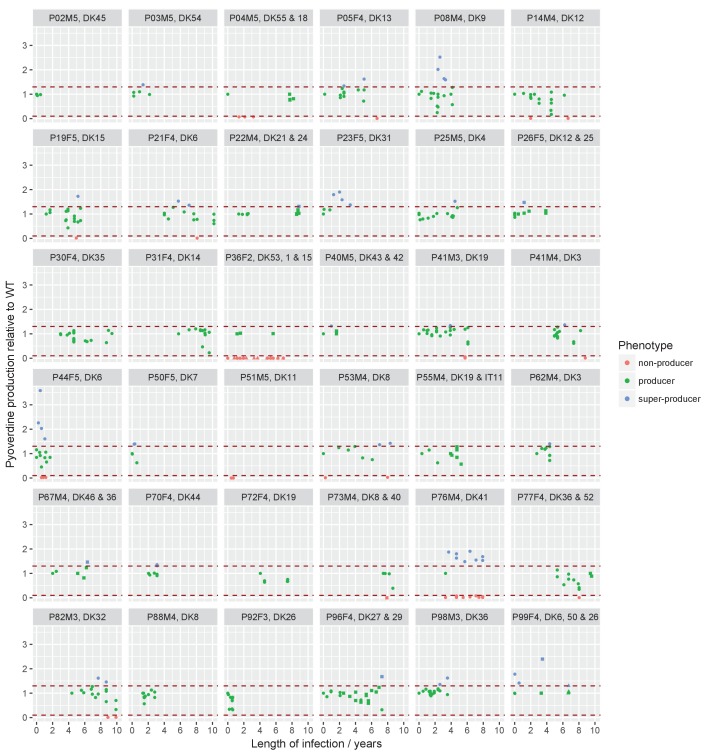
Appendix 1—figure 1. Sampling regimen and standardised pyoverdine production of longitudinally sampled clonal lineages (>1 isolate) from the children’s collection.
Plots show the sampling time of isolates from individual patients denoted by the patient code and clone type. When more than one clone type was sampled they are ordered so that the first listed corresponds to the dot symbol, followed by the square and triangle. The y-axis shows pyoverdine production standardized by production of the first sampled isolate(s). Isolates with a production of 10–129% of the WT are green, non-producers with a production at <10% of the WT are red, and super-cooperators with a production >130% of the WT are blue. Dashed red lines mark these cut-off points. Four clonal lineages of a ‘chronic’ phenotype with no pyoverdine producers sampled were excluded from the analysis on super-cooperators (DK1 and DK53 in P36F2, DK40 in P73M4, and DK11 in P51M5). When sampling is shown to start later than year 0 (as e.g. for P67M4) there was a sample collected earlier from the patient that either was not sequenced or of a clone type only sampled once. Created with ggplot2 in R (R Core Team, 2013; Wickham, 2016).
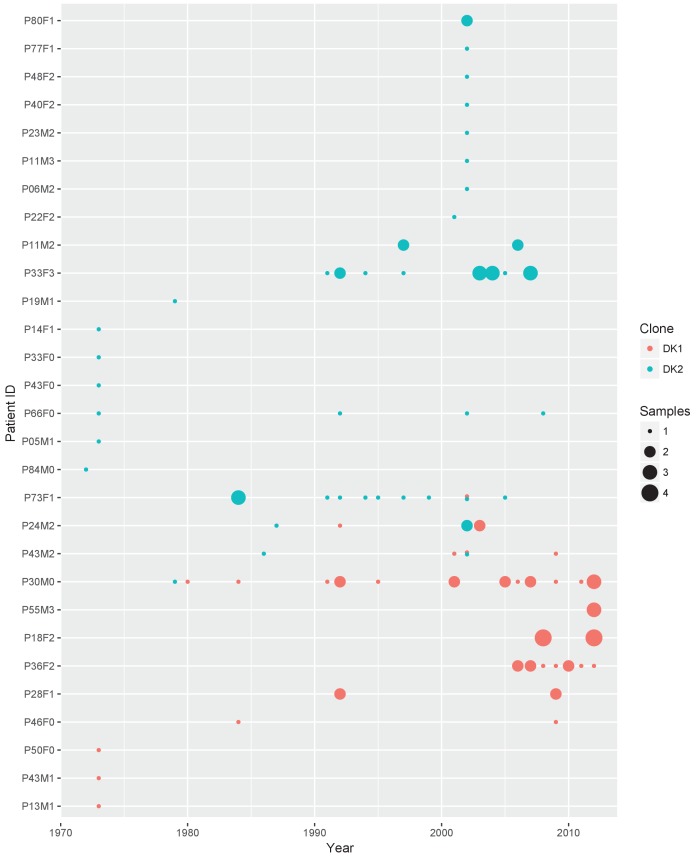
Appendix 1—figure 2. Sampling regimen for the transmissible clone types DK1 and DK2.
On the x-axis is sampling year and on the y-axis the patient ID. Red dots show DK1 and blue DK2. Dot size reflects the number of samples collected in a given year (1-4). Note that patient P36F2 from the children’s collection is included here as this patient harboured DK1 in addition to two other clone types (see also Appendix 1—figures 1 and 6). Created with ggplot2 in R (R Core Team, 2013; Wickham, 2016).
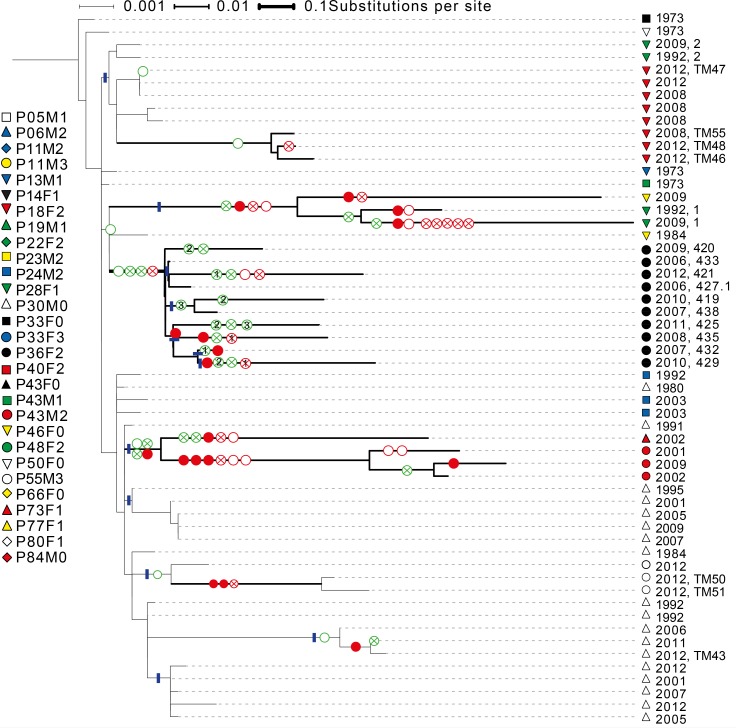
Appendix 1—figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of DK1 samples.
Tree was generated as described in Methods. Patient ID is denoted by shape and sampling year is listed. When multiple samples were collected from the same patient the same year, they are labelled corresponding to labels used in Supplementary file 1C. Scale depends on branch thickness; the thickest branch is only used for samples from P36F2. A green empty circle shows the loss of pyoverdine production measured phenotypically. A green circle with a cross shows the occurrence of a non-synonymous mutation in the pyoverdine receptor gene fpvA or the receptor sigma-factor gene fpvI. A full red circle shows phuS//phuR mutations, a red circle with a cross non-synonymous mutations in the phu receptor gene phuR and an empty red circle additional non-synonymous phu mutations. Additional mutations in the pyoverdine, pyochelin, has and feo systems are not shown. Blue lines mark monophyletic clades used in the analysis on phu upregulation. For isolates from P36F2, one phuR mutation, and three in fpvA were found in multiple isolates on polyphyletic branches (marked with 1, 2 and 3). These are likely not independent, and were not treated as such. Differences in pyoverdine mutations between isolates from P36F2 and P46F0 and P28F1 suggest two independent losses of production..
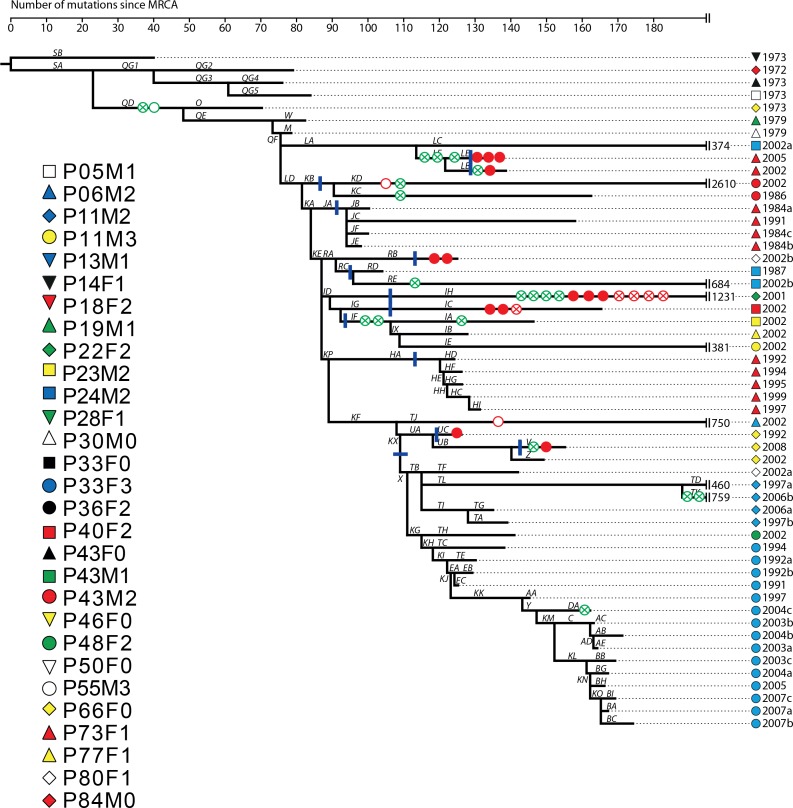
Appendix 1—figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of DK2 samples, adapted from (Marvig et al., 2013).
Pheno- and genotypes highlighted as in Appendix 1—figure 3.
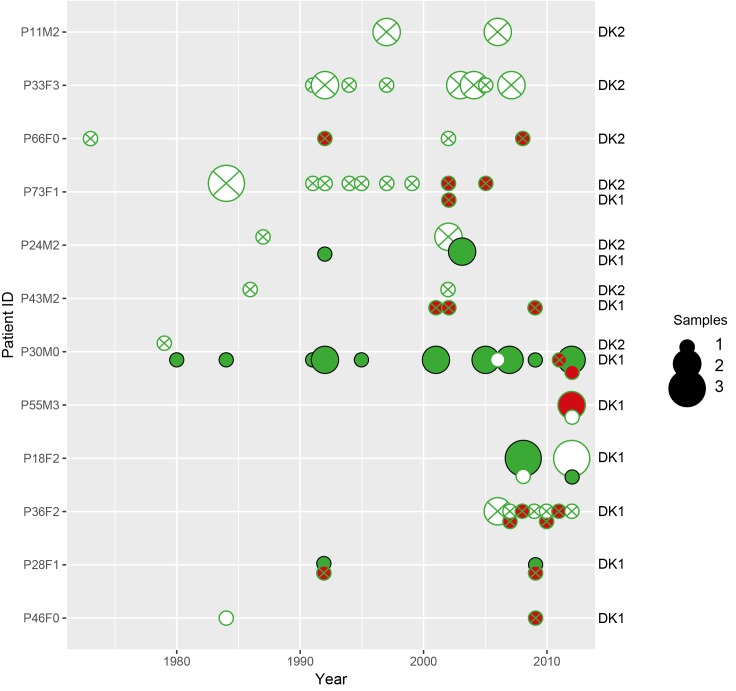
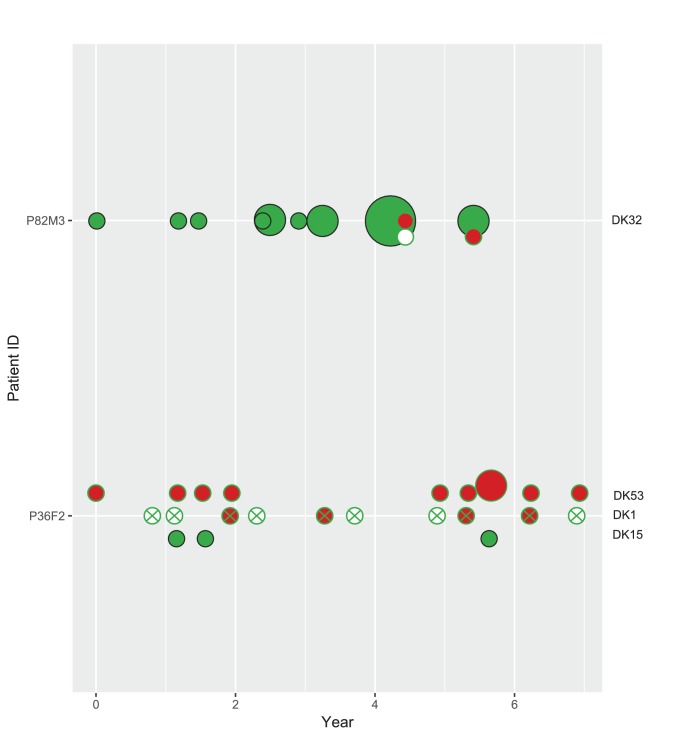
To clarify the within-patient dynamics and social environment we provide an overview of the phenotypes of isolates for the 11 patients with DK1 and DK2 that were sampled longitudinally (Appendix 1—figure 5). There are two patients (P28F1 and P30F0) where DK1 isolates that have lost pyoverdine production and have phu upregulated are sampled concurrently with WT pyoverdine producers. In P30F0 the isolates with phu upregulation were isolated from the sinuses, and the rest from the lungs, and these have therefore inhabited different niches. In P28F1, the pyoverdine and phu mutations occurred in another patient (likely P46F0, Appendix 1—figure 3) and were transmitted to patient P28F1 where another DK1 lineage also established. In three patients DK1 and DK2 overlapped in time (P24M2, P43M2 and P73F1, Appendix 1—figure 5). Could the two clone types have interacted, in regards to iron uptake, in these three patients? Patient P73F1 was first found to be colonized by DK2 in 1984, which had already lost pyoverdine production and uptake ability in 1973 (Appendix 1—figure 4). In the last two isolates there were two independent upregulations of the phu system (Appendix 1-fig. 4 and 5). A DK1 isolate was sampled in 2002 that also had pyoverdine production and uptake knocked-out, and carried phuS//phuR mutations for phu upregulation. From the DK1 phylogeny (Appendix 1—figure 3) it is unclear whether these mutations in DK1 occurred in patient P73F1 and were transmitted to patient P43M2 or vice versa. Given the simultaneous upregulation of phu in DK2 in P73F1 we speculate that they may have occurred in this patient. In patient P24M2 a WT-like DK1 clonal lineage is sampled over a timespan of nine years co-occurring with the non-cooperative and non-cheating DK2. The young patient P82M3 was infected by clone type DK32, and three of the late isolates had lost pyoverdine production (Appendix 1—figure 6). Two of these, co-occurring with pyoverdine producers, had a phuS//phuR mutation outside of the phuR promoter, as discussed in the main text. Patient P36F2 was first infected by DK53 and DK1, neither of which produced pyoverdine and DK53 further had phuS//phuR mutations. A WT- like pyoverdine producer, DK15, was later sampled (Appendix 1—figures 1 and 6).
Appendix 1—figure 5. Phenotypes of longitudinally sampled DK1 and DK2 lineages.
Size of circle denotes the number of samples (1-3). WT-like isolates that produce pyoverdine are shown as a full green circle, non-producers in white with a green stroke, pyoverdine receptor mutations with a green cross and phu-upregulation by phuS//phuR mutations is shown with red. Created with ggplot2 in R (R Core Team, 2013; Wickham, 2016).
Appendix 1—figure 6. Phenotypes of co-occurring clone types in two patients from the children’s collection.
Phenotypes as in Appendix 1—figure 5. Size of circle denotes the number of samples (1, 2 and 4). On the x-axis years since colonization. Note that patient P36F2 is shown in both Appendix 1—figures 5 and 6.
Growth effect of phuS//phuR mutations in clinical isolates.
We tested if the phuS//phuR mutations are beneficial in the clinical isolates, using six isolates of three different clone types that had acquired a variety of phuS//phuR mutations, and no additional phu mutations (Supplementary file 1C, marked in yellow). We compared fitness of the mutants with their closest genetically related isolate without phuS//phuR mutations. The isolates in a pair were, however, separated by numerous other mutations as they were sampled up to 26 years apart. The pairs were grown in iron-limited media with 2.5 and 5 μM heme added. Three mutants with intergenic SNPs had significantly higher (P73F1; 26% higher; t = −6.33, df = 3.48, p > 0.01 and P83M2; 16% higher, t = −4.48, df = 2.15, p < 0.05; isolates sampled 0 and 23 years apart) or a non-significant tendency towards a higher maximum OD600 in 5 μM heme compared to their closest relative (P66F0; 17% higher, t = −2.85, df = 2.67, p = 0.07; isolates sampled 10 years apart; Appendix 1—figure 7). A mutant with a three bp insertion, and an isolate with a one base pair deletion in phuS//phuR in addition to a SNP, showed no significant difference in growth compared to their closest relative (17% higher, t = −1.78, df = 2.95, p = 0.18; 16% lower, t = - 0.55, df = 2.56, p = 0.10; isolates sampled 3 and 26 years apart; Appendix 1—figure 7). These two isolates have, however, previously been shown to have respectively 25 and 116 fold increased expression of the phu receptor compared to the wild type (Marvig et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2011), and transfer of the one base pair deletion to its ancestor confirms that it infers growth benefits in heme media (Marvig et al., 2014; Figure 5). This suggest that other mutations across the genome affect the phenotype we are interested in, which is not unexpected given that we are comparing isolates sampled years apart, and the complex genome of P. aeruginosa where almost 10% of the genes are predicted to be regulatory (Stover et al., 2000). There were no significant growth differences with 2.5 μM heme added. Both isolates of the sixth pair, with a SNP, grew very slowly in rich LB media, and not at all in iron-limited media with or without heme. It is not clear why the beneficial effect of heme in these isolates is seen at a higher concentration compared to the isogenic pair (5 μM vs 2.5 μM, Figure 5).
Appendix 1—figure 7. Growth of pairs of clinical isolates with and without phuS//phuR mutations. .
Isolates were grown in iron-limited media with 5 μM heme added. Pairs where the same WT isolate is used because of two independent acquisitions of phuS//phuR mutations are highlighted in red and blue. Boxplots show median value of three biological replicates, and the interquartile range ±25%. * marks a significant difference. Plotted in R (R Core Team, 2013; Wickham, 2016).
Funding Statement
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Contributor Information
Sandra Breum Andersen, Email: sandrabreumandersen@gmail.com.
Ashleigh S Griffin, Email: ashleigh.griffin@zoo.ox.ac.uk.
Ian T Baldwin, Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology, Germany.
Funding Information
This paper was supported by the following grants:
Villum Fonden 95-300-13894 to Sandra Breum Andersen.
Lundbeckfonden r108-a10094 to Sandra Breum Andersen.
Danmarks Grundforskningsfond 126 to Rasmus L Marvig.
Rigshospitalet R88-A3537 to Helle Krogh Johansen.
Novo Nordisk NNF12OC1015920 to Helle Krogh Johansen.
Lundbeckfonden R167-2013-15229 to Helle Krogh Johansen.
H2020 European Research Council SESE to Ashleigh S Griffin.
Additional information
Competing interests
No competing interests declared.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Validation, Investigation, Visualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Project administration, Writing—review and editing.
Investigation, Methodology, Writing—review and editing.
Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing.
Investigation.
Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing.
Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing.
Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Project administration, Writing—review and editing.
Ethics
Human subjects: The CF isolates used for sequencing were obtained from the Department of Clinical Microbiology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, where they had been isolated from CF patients treated at the Copenhagen CF clinic. The use of isolates was approved by the local ethics committee at the Capital Region of Denmark Region Hovedstaden: registration number H-1-2013-032. All patients have given informed consent. In patients under 18 years of age, informed consent was obtained from their parents. All patient isolates were anonymized prior to any experimental use or analysis.
Additional files
(A) Calculation of estimated generation times of infecting clone types. For each, the patient ID, clone type, length of infection in years and minutes, estimated doubling time and calculated number of generations is given. A doubling time of 74 min was used for clonal lineages infecting for less than 6 years, 83 min for 6–24 years and 109 min for >24 years based on the measurements of Yang et al. (2011). This is, to our knowledge, the best available for CF conditions. (B) Overview of patients and isolates. For each patient is given the ID, the number of samples, the year of first sample, the extent of sampling in years, whether pyoverdine non-producers were sampled, the number of clone types sampled, and the clone type name(s). (C) List of mutations in genes associated with iron metabolism. For each isolate, the patient ID, clone type and mutations are listed. A //denotes an intergenic mutation. The isolate names refer to previous descriptions (Andersen et al., 2015; Markussen et al., 2014; Marvig et al., 2015). The six DK1 isolates that were not included in the previous analysis of pyoverdine mutations had one ns SNP in pvdL (A5702G) and one in pvdP (C1508T, patient P55M3, isolate TM50 and TM51). The six isolates used in the phenotypic assay of phuS//phuR mutations are highlighted in yellow. (D) Summary of the mutations found in five different iron uptake systems in P. aeruginosa. The size of the respective systems is given in kb, and mutations are listed as non-synonymous (ns) SNPs, synonymous (syn) SNPs, insertions and deletions (indels) and intergenic (IG). The overall mutations, and ns SNPS and indels, per kb are listed. The phu operon experienced the highest mutation rate, dominated by intergenic mutations. Two genes in the has operon were poorly sequenced in the majority of isolates, and this is taken into account in the size and mutations listed in parentheses. (E) Mutations identified in pyoverdine over-producers that may contribute to this phenotype. For each mutation, the patient ID, clone type and gene is listed, as well as a reference to previous work showing a link between the gene and pyoverdine production (Frangipani et al., 2014; Ochsner et al., 2002; Stintzi et al., 1998; Visaggio et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2004). (F) Transitions between iron uptake systems characterized as the order in which mutations accumulate. When a clear order of mutations could be established the observed and expected number of transitions, given a Poisson distribution, is stated and whether the difference between them is statistically significant. (G) Results of Tukey HSD post hoc comparison of a Two-Way ANOVA analysing the difference in Max OD600 between an isogenic pair of isolates differing in a phuS//phuR mutation at four different heme concentrations.
Data availability
Pyoverdine reads are available on Dryad at DOI: https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.6963pj3, and were used to identify isolates with increased pyoverdine production, as presented in Appendix 1-Fig. 1 and Fig. 1. Sequencing data is previously published and available from GenBank. The mutation lists for the isolates from the Children's collection from Marvig et al., 2015, can be downloaded from https://www.nature.com/articles/ng.3148#supplementary-information. The mutation list for the transmissible clone type DK1 from Markussen et al., 2014, can be downloaded from https://mbio.asm.org/content/mbio/5/5/e01592-14/DC1/embed/inline-supplementary-material-1.pdf. The mutation lists for the transmissible clone type DK2 from Marvig et al., 2013, can be downloaded from https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003741.s009 and https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003741.s010. Datasets S03 and S04 from Andersen et al, 2015, with lists of mutations in the pyoverdine system, are downloadable from http://www.pnas.org/content/112/34/10756/tab-figures-data#fig-data-tables. The raw reads and mutation lists were used to identify mutations in five iron uptake systems, as presented in Supplementary Table 1C and D. Table S03 from Yang et al., 2011, is downloadable from http://www.pnas.org/content/108/18/7481/tab-figures-data, and was used to estimate the number of generations that Pseudomonas aeruginosa was followed for in cystic fibrosis patients.
The following dataset was generated:
Andersen SB, Ghoul M, Marvig RL, Lee Z, Molin S, Johansen HK, Griffin A. 2018. Data from: Privatisation rescues essential function following loss of cooperation. Dryad Digital Repository.
The following previously published datasets were used:
Marvig RL, Sommer LM, Molin S, Johansen HK. 2015. Convergent evolution and adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa within patients with cystic fibrosis. Sequence Read Archive. ERP004853
Rau MH, Marvig RL, Ehrlich GD, Molin S, Jelsbak L. 2010. Deletion and acquisition of genomic content duringearly stage adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toa human host environment. Nucleotide. CP003149.1
Andersen SB, Marvig RL, Molin S, Johansen HK, Griffin AS. 2015. Long-term social dynamics drive loss of function in pathogenic bacteria. BioProject. PRJEB8028
Marvig RL, Johansen HK, Molin S, Jelsbak L. 2013. Genome analysis of a transmissible lineage of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals pathoadaptive mutations and distinct evolutionary paths of hypermutators. Sequence Read Archive. ERP002277
Rau MH, Marvig RL, Ehrlich GD, Molin S, Jelsbak L. 2010. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PADK2_CF510, whole genome shotgun sequencing project. Nucleotide. AJHI00000000
References
- Andersen SB, Marvig RL, Molin S, Krogh Johansen H, Griffin AS. Long-term social dynamics drive loss of function in pathogenic bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2015;112:10756–10761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508324112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzaldi LL, Skaar EP. Overcoming the heme paradox: heme toxicity and tolerance in bacterial pathogens. Infection and Immunity. 2010;78:4977–4989. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00613-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asfahl KL, Schuster M. Social interactions in bacterial cell-cell signaling. FEMS Microbiology Reviews. 2017;41:92–107. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod R, Hamilton WD. The evolution of cooperation. Science. 1981;211:1390–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.7466396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagos PG, Liakopoulos TD, Spyropoulos IC, Hamodrakas SJ. PRED-TMBB: a web server for predicting the topology of beta-barrel outer membrane proteins. Nucleic Acids Research. 2004;32:W400–W404. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bel G. Retrospectives: The coining of “privatization” and Germany's National Socialist Party. Journal of Economic Perspectives. 2006;20:187–194. doi: 10.1257/jep.20.3.187. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Buckling A, Harrison F, Vos M, Brockhurst MA, Gardner A, West SA, Griffin A. Siderophore-mediated cooperation and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2007;62:135–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartron ML, Maddocks S, Gillingham P, Craven CJ, Andrews SC. Feo-transport of ferrous iron into bacteria. BioMetals. 2006;19:143–157. doi: 10.1007/s10534-006-0003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K, Smyth RL, Govan JRW, Doherty C, Winstanley C, Denning N, Heaf DP, van Saene H, Hart CA. Spread of β-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis clinic. The Lancet. 1996;348:639–642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)05169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell. 2016;165:1586–1597. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggan KA, Wolfgang MC. Global regulatory pathways and cross-talk control Pseudomonas aeruginosa environmental lifestyle and virulence phenotype. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2012;14:47–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornforth DM, Dees JL, Ibberson CB, Huse HK, Mathiesen IH, Kirketerp-Møller K, Wolcott RD, Rumbaugh KP, Bjarnsholt T, Whiteley M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptome during human infection. PNAS. 2018;115:E5125–E5134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717525115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas Z, Ross-Gillespie A, Kummerli R. Switching between apparently redundant iron-uptake mechanisms benefits bacteria in changeable environments. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2013;280:20131055. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiegna F, Velicer GJ. Competitive fates of bacterial social parasites: persistence and self-induced extinction of Myxococcus xanthus cheaters. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2003;270:1527–1534. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2003.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkesson A, Jelsbak L, Yang L, Johansen HK, Ciofu O, Høiby N, Molin S. Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the cystic fibrosis airway: an evolutionary perspective. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2012;10:841–851. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster KR, Ratnieks FL. Facultative worker policing in a wasp. Nature. 2000;407:692–693. doi: 10.1038/35037665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangipani E, Visaggio D, Heeb S, Kaever V, Cámara M, Visca P, Imperi F. The Gac/Rsm and cyclic-di-GMP signalling networks coordinately regulate iron uptake in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environmental Microbiology. 2014;16:676–688. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghigo JM, Létoffé S, Wandersman C. A new type of hemophore-dependent heme acquisition system of. Journal of Bacteriology. 1997;179:3572–3579. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.11.3572-3579.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghio AJ, Roggli VL, Soukup JM, Richards JH, Randell SH, Muhlebach MS. Iron accumulates in the lavage and explanted lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis. 2013;12:390–398. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2012.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoul M, Griffin AS, West SA. Toward an evolutionary definition of cheating. Evolution. 2014a;68:318–331. doi: 10.1111/evo.12266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoul M, West SA, Diggle SP, Griffin AS. An experimental test of whether cheating is context dependent. Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 2014b;27:551–556. doi: 10.1111/jeb.12319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas B, Kraut J, Marks J, Zanker SC, Castignetti D. Siderophore presence in sputa of cystic fibrosis patients. Infection and Immunity. 1991;59:3997–4000. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3997-4000.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton WD. The evolution of altruistic behavior. The American Naturalist. 1963;97:354–356. doi: 10.1086/497114. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison F, Paul J, Massey RC, Buckling A. Interspecific competition and siderophore-mediated cooperation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The ISME Journal. 2008;2:49–55. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2007.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison F, McNally A, da Silva AC, Heeb S, Diggle SP. Optimised chronic infection models demonstrate that siderophore 'cheating' in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is context specific. The ISME Journal. 2017;11:2492–2509. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter RC, Asfour F, Dingemans J, Osuna BL, Samad T, Malfroot A, Cornelis P, Newman DK. Ferrous iron is a significant component of bioavailable iron in cystic fibrosis airways. mBio. 2013;4:e00557. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00557-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandér KC, Herre EA. Host sanctions and pollinator cheating in the fig tree-fig wasp mutualism. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2010;277:1481–1488. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsbak L, Johansen HK, Frost AL, Thøgersen R, Thomsen LE, Ciofu O, Yang L, Haagensen JA, Høiby N, Molin S. Molecular epidemiology and dynamics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations in lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. Infection and Immunity. 2007;75:2214–2224. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01282-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeukens J, Boyle B, Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Ouellet MM, Aaron SD, Charette SJ, Fothergill JL, Tucker NP, Winstanley C, Levesque RC. Comparative genomics of isolates of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemic strain associated with chronic lung infections of cystic fibrosis patients. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e87611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiricny N, Diggle SP, West SA, Evans BA, Ballantyne G, Ross-Gillespie A, Griffin AS. Fitness correlates with the extent of cheating in a bacterium. Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 2010;23:738–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2010.01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen HK, Aanaes K, Pressler T, Nielsen KG, Fisker J, Skov M, Høiby N, von Buchwald C. Colonisation and infection of the paranasal sinuses in cystic fibrosis patients is accompanied by a reduced PMN response. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis. 2012;11:525–531. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2012.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorth P, Staudinger BJ, Wu X, Hisert KB, Hayden H, Garudathri J, Harding CL, Radey MC, Rezayat A, Bautista G, Berrington WR, Goddard AF, Zheng C, Angermeyer A, Brittnacher MJ, Kitzman J, Shendure J, Fligner CL, Mittler J, Aitken ML, Manoil C, Bruce JE, Yahr TL, Singh PK. Regional isolation drives bacterial diversification within cystic fibrosis lungs. Cell Host & Microbe. 2015;18:307–319. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julou T, Mora T, Guillon L, Croquette V, Schalk IJ, Bensimon D, Desprat N. Cell-cell contacts confine public goods diffusion inside Pseudomonas aeruginosa clonal microcolonies. PNAS. 2013;110:12577–12582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301428110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings AF, Martin LW, Sharples KJ, Roddam LF, Latham R, Reid DW, Lamont IL. Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses multiple pathways to acquire iron during chronic infection in cystic fibrosis lungs. Infection and Immunity. 2013;81:2697–2704. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00418-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H, Huh MS, Ryu JH, Lee D-E, Sun I-C, Choi K, Kim K, Kwon IC. Nanoprobes for biomedical imaging in living systems. Nano Today. 2011;6:204–220. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2011.02.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kummerli R, Griffin AS, West SA, Buckling A, Harrison F. Viscous medium promotes cooperation in the pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2009;276:3531–3538. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.0861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kümmerli R, Jiricny N, Clarke LS, West SA, Griffin AS. Phenotypic plasticity of a cooperative behaviour in bacteria. Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 2009;22:589–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett HC, Brown SP, Reece SE. War and peace: social interactions in infections. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2014;369:20130365. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinweber A, Weigert M, Kümmerli R. The bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa senses and gradually responds to interspecific competition for iron. Evolution. 2018;72:1515–1528. doi: 10.1111/evo.13491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S, Delepelaire P, Wandersman C. Free and hemophore-bound heme acquisitions through the outer membrane receptor HasR have different requirements for the TonB-ExbB-ExbD complex. Journal of Bacteriology. 2004;186:4067–4074. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.13.4067-4074.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman TD, Michel JB, Aingaran M, Potter-Bynoe G, Roux D, Davis MR, Skurnik D, Leiby N, LiPuma JJ, Goldberg JB, McAdam AJ, Priebe GP, Kishony R. Parallel bacterial evolution within multiple patients identifies candidate pathogenicity genes. Nature Genetics. 2011;43:1275–1280. doi: 10.1038/ng.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markussen T, Marvig RL, Gómez-Lozano M, Aanæs K, Burleigh AE, Høiby N, Johansen HK, Molin S, Jelsbak L. Environmental heterogeneity drives within-host diversification and evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio. 2014;5:e01592-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01592-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin LW, Reid DW, Sharples KJ, Lamont IL. Pseudomonas siderophores in the sputum of patients with cystic fibrosis. BioMetals. 2011;24:1059–1067. doi: 10.1007/s10534-011-9464-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvig RL, Johansen HK, Molin S, Jelsbak L. Genome analysis of a transmissible lineage of pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals pathoadaptive mutations and distinct evolutionary paths of hypermutators. PLoS Genetics. 2013;9:e1003741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvig RL, Damkiær S, Khademi SM, Markussen TM, Molin S, Jelsbak L. Within-host evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals adaptation toward iron acquisition from hemoglobin. mBio. 2014;5:e00966. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00966-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvig RL, Sommer LM, Molin S, Johansen HK. Convergent evolution and adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa within patients with cystic fibrosis. Nature Genetics. 2015;47:57–64. doi: 10.1038/ng.3148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew S, Boyd R. Punishment sustains large-scale cooperation in prestate warfare. PNAS. 2011;108:11375–11380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105604108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat E, Paterson S, Fothergill JL, Wright EA, Ledson MJ, Walshaw MJ, Brockhurst MA, Winstanley C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa population diversity and turnover in cystic fibrosis chronic infections. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2011;183:1674–1679. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201009-1430OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen AT, O'Neill MJ, Watts AM, Robson CL, Lamont IL, Wilks A, Oglesby-Sherrouse AG. Adaptation of iron homeostasis pathways by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdine mutant in the cystic fibrosis lung. Journal of Bacteriology. 2014;196:2265–2276. doi: 10.1128/JB.01491-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehus R, Picot A, Oliveira NM, Mitri S, Foster KR. The evolution of siderophore production as a competitive trait. Evolution. 2017;71:1443–1455. doi: 10.1111/evo.13230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noinaj N, Guillier M, Barnard TJ, Buchanan SK. TonB-dependent transporters: regulation, structure, and function. Annual Review of Microbiology. 2010;64:43–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner UA, Johnson Z, Vasil ML. Genetics and regulation of two distinct haem-uptake systems, phu and has, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology. 2000;146:185–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-1-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner UA, Wilderman PJ, Vasil AI, Vasil ML. GeneChip expression analysis of the iron starvation response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of novel pyoverdine biosynthesis genes. Molecular Microbiology. 2002;45:1277–1287. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K, McKay GA. Iron acquisition and its control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: many roads lead to Rome. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2003;8:d661–d686. doi: 10.2741/1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2013 https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing
- Rand DG, Arbesman S, Christakis NA. Dynamic social networks promote cooperation in experiments with humans. PNAS. 2011;108:19193–19198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1108243108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau MH, Marvig RL, Ehrlich GD, Molin S, Jelsbak L. Deletion and acquisition of genomic content during early stage adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to a human host environment. Environmental Microbiology. 2012;14:2200–2211. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross-Gillespie A, Gardner A, West SA, Griffin AS. Frequency dependence and cooperation: theory and a test with bacteria. The American Naturalist. 2007;170:331–342. doi: 10.1086/519860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs JL, Simms EL. Pathways to mutualism breakdown. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2006;21:585–592. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2006.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman T. Snippy: Rapid haploid variant calling and core genome alignment. Snippy. 2015 https://github.com/tseemann/snippy
- Smith AD, Modi AR, Sun S, Dawson JH, Wilks A. Spectroscopic determination of distinct heme ligands in outer-membrane receptors PhuR and HasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochemistry. 2015;54:2601–2612. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer LM, Marvig RL, Luján A, Koza A, Pressler T, Molin S, Johansen HK. Is genotyping of single isolates sufficient for population structure analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis airways? BMC Genomics. 2016;17:589. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2873-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzi A, Evans K, Meyer JM, Poole K. Quorum-sensing and siderophore biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: lasR/lasI mutants exhibit reduced pyoverdine biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 1998;166:341–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman FSL, Hufnagle WO, Kowalik DJ, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Larbig K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GK-S, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Reizer J, Saier MH, Hancock REW, Lory S, Olson MV. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature. 2000;406:959–964. doi: 10.1038/35023079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassmann JE, Queller DC. Privatization and property in biology. Animal Behaviour. 2014;92:305–311. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2014.02.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Therneau T. A package for Survival Analysis in S. 2015 https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/survival/index.html
- Thompson V, Mayer-Hamblett N, Kloster M, Bilton D, Flume PA. Risk of hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis clinical trials: A retrospective cohort study. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis. 2015;14:632–638. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. Iron and oxidative stress in bacteria. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2000;373:1–6. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil ML, Ochsner UA. The response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to iron: genetics, biochemistry and virulence. Molecular Microbiology. 1999;34:399–413. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visaggio D, Pasqua M, Bonchi C, Kaever V, Visca P, Imperi F. Cell aggregation promotes pyoverdine-dependent iron uptake and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2015;6:902. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M, Kümmerli R. The physical boundaries of public goods cooperation between surface-attached bacterial cells. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2017;284:20170631. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2017.0631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West SA, Buckling A. Cooperation, virulence and siderophore production in bacterial parasites. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2003;270:37–44. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham H. ggplot 2: Elagant graphics for data analysis. 2016 doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-98141-3. [DOI]
- Winstanley C, O'Brien S, Brockhurst MA. Pseudomonas aeruginosa evolutionary adaptation and diversification in cystic fibrosis chronic lung infections. Trends in Microbiology. 2016;24:327–337. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W, Badrane H, Arora S, Baker HV, Jin S. MucA-mediated coordination of type III secretion and alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology. 2004;186:7575–7585. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.22.7575-7585.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L, Jelsbak L, Marvig RL, Damkiær S, Workman CT, Rau MH, Hansen SK, Folkesson A, Johansen HK, Ciofu O, Høiby N, Sommer MO, Molin S. Evolutionary dynamics of bacteria in a human host environment. PNAS. 2011;108:7481–7486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018249108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young BC, Golubchik T, Batty EM, Fung R, Larner-Svensson H, Votintseva AA, Miller RR, Godwin H, Knox K, Everitt RG, Iqbal Z, Rimmer AJ, Cule M, Ip CL, Didelot X, Harding RM, Donnelly P, Peto TE, Crook DW, Bowden R, Wilson DJ. Evolutionary dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus during progression from carriage to disease. PNAS. 2012;109:4550–4555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113219109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]